Abstract
Epibiotic associations can result in co-introductions of non-indigenous species, which may affect ecosystems in several ways. In fouling communities of three estuaries in southern Brazil, a number of amphipods was found to harbour a dense coverage of epibionts. Three different species, the two globally widespread caprellids Caprella equilibra and Paracaprella pusilla, as well as the ischyrocerid Jassa valida, had been colonised by diatoms. Further scanning electron microscope analyses assigned these diatoms to 14 different species that had previously been reported from benthic habitats. This is one of the scarce records of diatoms attached to amphipods. The occurrence of the diatom Amphora helenensis represents the first report for Brazilian waters as well as the second record for the whole SW Atlantic Ocean. As some diatoms were associated with common fouling amphipods, a possible regional spread aided by these crustaceans seems likely. Possible effects of this amphipod-diatom association on the animals and their implications for the underlying ecosystems of this remain to be elucidated.
1. Introduction
Human-based transport mechanisms of non-indigenous species (NIS) are often investigated, but processes of co-introduction through associations like parasitism or epibiosis are still understudied [1,2]. These associations allow for simultaneous multiple introductions that can consequently affect ecosystems on several levels, and may further facilitate secondary invasions (i.e., invasion meltdown hypothesis) [3]. For example, the canopy-forming marine macroalga Sargassum muticum (Yendo) Fensholt, 1955, was probably introduced to North American and European shores with the Pacific oyster Magallana gigas (Thunberg, 1793) (formerly known as Crassostrea gigas), which was intentionally introduced for aquaculture purposes. Moreover, oyster trade is the presumed vector for the spread of different NIS around the world, including different macroalgae, ascidians, and even amphipods [4,5].
Marine ecosystems face an increased risk of the spread of NIS because even geographically distant locations are virtually connected through the oceans with intensive human shipping activities. Shipping facilitates the dispersal of species through hull fouling, ballast water, and other vessel components, e.g., [6,7]. Besides, ports meet most of the requirements for the successful introduction and establishment of NIS. Ports are subjected to continuous pressure of propagules in usually eutrophic environments and are modified by artificial structures where native species can lose their potential competitive advantage [8,9]. Hard substrates in ports are usually characterised by fouling communities consisting of r-strategists, filter feeders, and scavengers [10]. These communities are known to be comparably rich in NIS, which frequently outcompete native species in the colonisation of these substrates [11].
Amphipod crustaceans can dominate marine and estuarine fouling communities in terms of abundance [12,13]. Amphipod fouling assemblages are mainly characterised by either tubiculous or free-living suspension feeders, but different combinations of functional traits are also common including grazers, carnivores, and epibionts associated to other organisms [14]. Common tube constructors such as ischyrocerids (e.g., Jassa, Ericthonius), different corophiids (e.g., Monocorophium, Corophium, Apocorophium), aorids (e.g., Grandidierella, Microdeutopus), and photids (e.g., Photis, Gammaropsis) can dominate these communities along with crawling/clinging taxa such as caprellids (e.g., Caprella, Paracaprella), stenothoids (e.g., Stenothoe), and podocerids (e.g., Podocerus). Moreover, at least 55 species of Amphipoda are recognised as introduced or invasive in at least one marine region around the world, of which more than half are directly associated with biofouling [15]. Many species are recognised as neocosmopolitan (i.e., human-mediated cosmopolitan species; see [16]) as well as widespread in invaded regions [17,18,19,20]. Some amphipods are also known to bear different epibionts that, in some cases, would benefit from their basibiont movement without harming the host [21,22,23,24]. Accordingly, amphipods might be effective vectors for some organisms that are directly associated with them.
In a field experiment designed to study fouling communities related to ports, artificial plates of polyethene and rope (nylon rope wrapped around a squared iron frame) were deployed, at an average depth of 1.5 m, in three estuaries of southern Brazil: the Cananéia-Iguape estuarine complex, the Paranaguá estuarine complex, and the Guaratuba Bay. All investigations were carried out between June 2017 and June 2018. After three months, the plates were collected and separately preserved in 96% ethanol. At the site of the experimental set-up, additional samples of the fouling were scraped from buoys and preserved in ethanol for further comparison. All amphipod individuals were sorted and identified to species level. During this step, some amphipods displayed conspicuous levels of epibiosis and were separated for further examination with a scanning electron microscope (SEM). These specimens were mounted on aluminium stubs with a small piece of adhesive carbon tape, completely air-dried at room temperature, and kept in an air desiccator jar. The stubs were then sputter-coated with gold in a Baltec metallizer and observed in a JEOL JSM 6360-LV electron microscope at an acceleration voltage of 15 Kv and 7 mm working distance (Figure 1A). As no further frustule cleaning with chemicals could be applied, many diatom cells from different samples (i.e., amphipod specimens) were photographed, measured, and preliminary separated into morphotypes to ease identification. The definite identification was then determined by carefully comparing their frustule morphologies and dimensions.
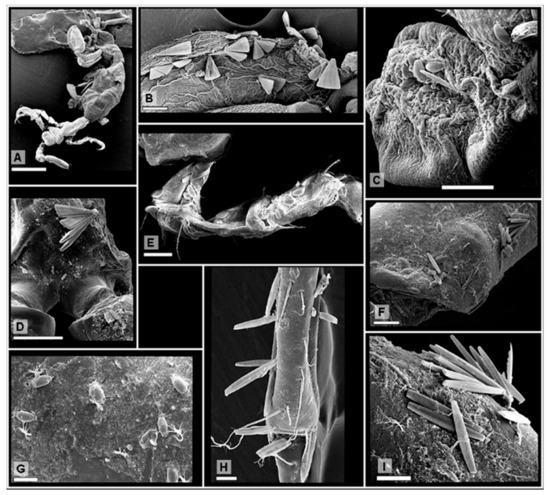
Figure 1.
Diatom distributions on amphipod body parts. (A) Female specimen of Caprella equilibra (scale: 500 μm); (B) Licmophora abbreviata on the dactyl of gnathopod 2 of C. equilibra (scale: 50 μm); (C) The diatoms Amphora and Tabularia on a gill of Paracaprella pusilla (scale: 50 μm); (D) Licmophora ehrenbergii on the head of P. pusilla (scale: 100 μm); (E) Amphora helenensis on the pereopod 5 of P. pusilla (scale: 50 μm); (F) The diatoms Halamphora and Tabularia on pereonite 5 of P. pusilla (scale: 50 μm); (G) Halamphora coffaeiformis on pereonite 4 of P. pusilla (scale: 20 μm); (H) Tabularia fasciculata on pereopod 5 of C. equilibra (scale: 20 μm); (I) Tabularia affinis on the head of P. pusilla (scale: 20 μm).
2. Results & Discussion
A total of 14 different diatom species belonging to seven families was identified (Table 1). Most of the taxa recorded fell into frustule size ranges reported in the literature, except for two species, which presented smaller valves than previously reported. Cocconeis dirupta Gregory, 1857 valves were shorter (length 16–12 μm, Table 1) than elsewhere (e.g., length 24–17 μm in [25]). The same deviation was found in Halamphora coffaeiformis (C. Agardh) Mereschkowsky, 1903, in which valves were 25–11 μm long, but usually ranging from 30 μm to 53 μm, even when our material is compared to another variety of this species, A. coffeaeformis var. aponina (Kützing) Archibald & Schoeman, 1984 (length 39–15 μm in [26]). The families Catenulaceae and Naviculaceae were the most species-rich with three species each. The diatoms found are typically benthic species, i.e., attached to substrates employing a variety of mucilage secretions. The most common structures were mucilaginous peduncles in Tabularia spp. and Licmophora spp. (Figure 1I and Figure 2B), along with mucilage pads as in Amphora helenensis M. H. Giffen, 1973, H. coffaeiformis, and Cocconeis spp. (Figure 1E,G and Figure 2I). Other species, such as Navicula spp., seemed to attach to amphipod individuals using mucilaginous secretions of the raphe (Figure 2L,O). Although no quantitative analysis was performed, some diatom taxa were dominant such as Tabularia affinis (Kützing) Snoeijs, 1992, Licmophora spp., H. coffaeiformis, and A. helenensis, comprising about 50% of the total diatom composition in the majority of analysed amphipod individuals. While some diatoms are known to be specialised epizoic on planktonic copepods [27], only a few studies have dealt with the growth of diatoms on benthic invertebrates. Usually diatoms of the genera Navicula, Amphora, and Cocconeis are known to occur on several species of cnidarians [28], sponges [29], and gastropods [30,31]. Despite some species being known to display specificity to some taxa, all the diatoms found here have been reported elsewhere from other substrates such as macroalgae and rocks [32,33], indicating that these species are rather opportunistic to grow on invertebrates. The fouling communities of the artificial plates inhabited by the amphipods were characterised by dense assemblages of hydrozoans (e.g., Clytia spp., Ectopleura crocea (Agassiz, 1862), Obelia spp., and Eudendrium carneum Clarke, 1882) and barnacles (e.g., Megabalanus coccopoma Darwin, 1854, Amphibalanus amphitrite (Darwin, 1854)), which are both recognised basibionts of either diatoms or amphipods, e.g., [34,35,36,37,38], which would make them the most probable vector of diatoms for the amphipods. Concomitantly, species inhabiting soft bottoms have been reported to host relatively few epibionts in comparison to hard-substrate species [39].

Table 1.
Morphometric data of the 14 epibiotic diatom species recorded on the amphipods, sampled in estuaries of South Brazil.
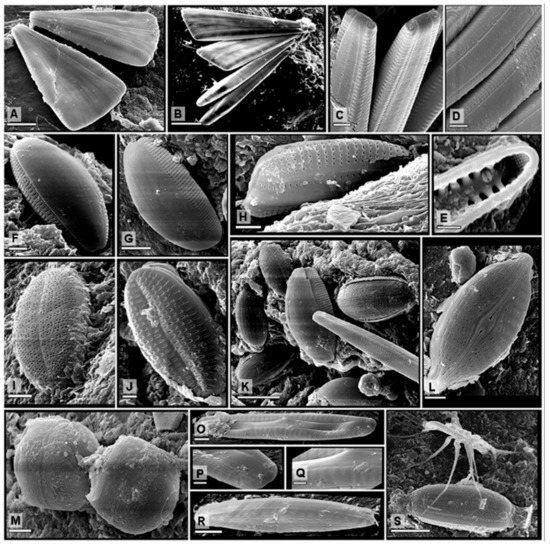

Figure 2.
Diatoms found on fouling amphipods in south Brazilian estuaries. (A) overall view of two frustules of Licmophora abbreviata (scale: 10 μm); (B) four cells attached by short mucilage stalks of Licmophora ehrenbergii (scale: 20 μm); (C,D) details of frustules showing the ocellulimbus at the apices of Tabularia affinis (scale: 2 μm) and (E) internal view of valve apex with rimoportula (scale: 1 μm); (F) lateral view of a frustule of Amphora pediculus (scale: 2 μm); (G) lateral view of a frustule of Amphora helenensis (scale: 5 μm); (H) Rhoicosphenia marina (scale: 2 μm); (I) Frustule attached by mucilage extruded through the raphe of Cocconeis dirupta (scale: 2 μm); (J) Frustule attached by mucilage extruded through the raphe of Cocconeis sp. 1 (scale: 1 μm); (K) Amphora, Halamphora, and Tabularia (scale: 10 μm) on a gill of Paracaprella pusilla; (L) Frustule in valve view, with a central raphe system of Navicula platyventris (scale: 2 μm); (M) Melosira moniliformis (scale: 5 μm); (O) Navicula sp.1 (scale: 2 μm) with (P,Q) two details of apical and central regions (scale: 1 μm); (R) Navicula sp. 2 (scale: 2 μm); (S) Frustule in girdle view of Halamphora coffaeiformis (scale: 5 μm) covered by a seta of P. pusilla.
Of the 15 analysed amphipod specimens, twelve individuals bore epibiotic diatoms (Table 2). The amphipod specimens belonged to only three species: the two globally distributed caprellids Caprella equilibra Say, 1818, and Paracaprella pusilla Mayer, 1890, and the ischyrocerid Jassa valida (Dana, 1853). On a single specimen of Ericthonius brasiliensis (Dana 1853), as well as on other specimens of J. valida and P. pusilla, non-identified apostomid ciliates were found, but no diatoms. The highest diversity of epibionts was found on a male specimen of P. pusilla with seven different diatom species on its cuticula (Table 2). Three diatom species were each found only once on caprellids: Melosira moniliformis C. Agardh, 1824, Rhoicosphenia marina (Kützing) M.Schmidt, 1889, and Tabularia fasciculata (C. Agardh) D. M. Williams & Round, 1986. Although males generally seemed to display higher epibiont diversity compared to females, only two female individuals were available for analysis. Possible sex-specific differences in epibiotic colonisation may relate to differences in the moulting cycle. However, due to the low replicate number, any assumptions must be regarded with caution. The diatoms were distributed over the whole body of the animals, but the appendages seemed to exhibit a higher coverage with epibionts than the rest of the body. This appears to be counterintuitive as antennas and pereopods are easily and frequently cleaned by the animals, suggesting that the amphipods might be unaffected by the diatoms as reported for epizoic ciliates on the amphipod Bathyporeia spp. [40]. This is in contrast to other crustaceans where epibionts have been shown to cause stress to the crustacean host individuals [41]. In addition, the possibility that the amphipods may even benefit from epibiotic diatoms as an additional food source cannot be ruled out as they are known to be omnivores and diatoms were frequently found in amphipod digestive tracts [42].

Table 2.
Overview of amphipod and diatom species recorded for each analysed sample. Substrates: PP—polyethene plate; B—buoy; RP—rope plate.
Nevertheless, potential interactions of diatoms with their amphipod hosts (e.g., commensality) are completely unknown. Although it could be possible that high diatom densities on fragile body parts such as the gills or sensory appendages (Figure 1C,H) may lead to handicaps (e.g., interferences in gas exchange, reproduction, or sensorial activity) [43,44], the amphipods and the diatoms seemed to display a basibiont-epibiont association.
The biraphid diatom Amphora helenensis found in this work represents the first on record for Brazilian coasts. This species has been recorded repeatedly around the world outside of its type locality (South Africa). Recent records include the coastal waters of Australia and New Zealand [45], Europe (The Netherlands [46]), China (Yellow Sea [33]), and Mexico (Pacific Ocean [47]). We found A. helenensis in the Guaratuba Bay and in the Paranaguá estuarine complex. The latter site is well-studied and has been subject to extensive taxonomic diatom studies since 1960 (see [48]). This suggests that A. helenensis was introduced recently to South Brazil. However, it cannot be ruled out that this species had been overlooked or misidentified with other closely related species at other locations in the SW Atlantic, where it was recorded only once in Argentina [49]. Therefore, A. helenensis can be classified as cryptogenic.
The presence of diatoms on amphipods might not be a newly recorded association, although it was never further investigated and only briefly mentioned. Previous records on species of the genera Leucothoe and Caprella are documented, either in the descriptions of amphipods or unintentionally photographed (e.g., [50], see Figures 5 and 6 in [51]). As benthic amphipods can be associated with other sessile fauna (like in this case) or macroalgae [52], they are susceptible for colonisation by motile diatom species (e.g., Navicula spp.) or even sedentary species (e.g., Tabularia spp., Licmophora spp.) if these are abundant on the surface of the shared host. If the new basibiont is abundant (especially as part of a fouling community), this may result in a rapid spread of the diatom. In fact, regional boating is known to aid the spread of NIS among marinas and ports by allocating the whole communities on the ship hulls [53,54]. Diatoms may thus not only benefit from direct human-mediated transport, but also from the active movement of basibiont amphipods to new natural or artificial substrates as well as from nutrients provided by the host.
3. Conclusions
Our findings represent the first documented analysis of amphipod-associated epibiotic diatoms. In the current case, common benthic diatom species were found on the cuticle of three widespread amphipods, suggesting a rather opportunistic epibiosis due to the epifouling lifestyle of these crustaceans. Especially in fouling communities, amphipods can be potent vectors for epibiotic organisms such as diatoms and ciliates (e.g., [22]) aiding the spread of newly introduced epibionts to neighbouring habitats.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: A.D.; Data curation: A.D.; Funding acquisition: L.F.F. and M.A.H.; Investigation: A.D. and L.F.F.; Methodology: A.D. and L.F.F.; Project administration: A.D.; Resources: L.F.F., M.A.H. and J.B.; Supervision: M.A.H. and J.B.; Visualization: L.F.F. and A.D.; Writing–original draft: A.D. and L.F.F.; Writing–review & editing: A.D., L.F.F., J.B. and M.A.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
D.A. received a PhD grant by the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq) (process no. 365 141565/2017-9). This work was supported by CNPq-PROTAX Grant to F.L.F., Proj. 5621512010-9.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study is available in the current manuscript, raw data is available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The Centre of Electron Microscopy housed at the Federal University of Paraná state made the equipment available.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Consent for Publication
All the authors gave their consent to the publication of the manuscript.
Availability of Data and Material
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.
References
- Goedknegt, M.A.; Feis, M.E.; Wegner, K.M.; Luttikhuizen, P.C.; Buschbaum, C.; Camphuysen, K.C.J.; van der Meer, J.; Thieltges, D.W. Parasites and marine invasions: Ecological and evolutionary perspectives. J. Sea Res. 2016, 113, 11–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhove, M.P.M.; Hablützel, P.I.; Pariselle, A.; Šimková, A.; Huyse, T.; Raeymaekers, J.A.M. Cichlids: A host of opportunities for evolutionary parasitology. Trends Parasitol. 2016, 32, 820–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, P.T.; O’Dowd, D.J.; Abbott, K.L.; Jeffery, M.; Retallick, K.; Mac Nally, R. Invasional meltdown: Invder–invder mutualism facilitates a secondary invasion. Ecology 2011, 92, 1758–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mineur, F.; Le Roux, A.; Maggs, C.A.; Verlaque, M. Positive feedback loop between introductions of non-native marine species and cultivation of oysters in Europe. Conserv. Biol. 2014, 28, 1667–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haydar, D.; Woflf, W.J. Predicting invasion patterns in coastal ecosystems: Relationship between vector strength and vector tempo. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2011, 431, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gollasch, S. The importance of ship hull fouling as a vector of species introductions into the North Sea. Biofouling 2002, 18, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seebens, H.; Schwartz, N.; Schupp, P.J.; Blasius, B. Predicting the spread of marine species introduced by global shipping. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 5646–5651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackburn, T.M.; Essl, F.; Evans, T.; Hulme, P.E.; Jeschke, J.M.; Kühn, I.; Kumschick, S.; Marková, Z.; Mrugała, A.; Nentwig, W.; et al. A unified classification of alien species based on the magnitude of their environmental impacts. PLoS Biol. 2014, 12, e1001850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byers, J.E. Impact of non-indigenous species on natives enhanced by anthropogenic alteration of selection regimes. Oikos 2002, 97, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer-Pinto, M.; Cole, V.J.; Johnston, E.L.; Bugnot, A.; Hurst, H.; Airoldi, L.; Glasby, T.M.; Dafforn, K.A. Functional and structural responses to marine urbanisation. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 014009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megina, C.; González-Duarte, M.M.; López-González, P.J. Benthic assemblages, biodiversity and invasiveness in marinas and commercial harbours: An investigation using a bioindicator group. Biofouling 2016, 32, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beermann, J. Spatial and seasonal population dynamics of sympatric Jassa species (Crustacea, Amphipoda). J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2014, 459, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, J.K.; Grizzle, R.E. Successional development of fouling communities on open ocean aquaculture fish cages in the western Gulf of Maine, USA. Aquaculture 2007, 262, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ros, M.; Navarro-Barranco, C.; González-Sánchez, M.; Ostalé-Valriberas, E.; Cervera-Currdao, L.; Guerra-García, J.M. Starting the stowaway pathway: The role of dispersal behavior in the invasion success of low-mobile marine species. Biol. Invasions 2020, 22, 2797–2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchini, A.; Cardeccia, A. Alien amphipods in a sea of troubles: Cryptogenic species, unresolved taxonomy and overlooked introductions. Mar. Biol. 2017, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darling, J.A.; Carlton, J.T. A framework for understanding marine cosmopolitanism in the anthropocene. Front. Mar. Sci. 2018, 5, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabezas, M.P.; Ros, M.; dos Santos, A.M.; Martínez-Laiz, G.; Xavier, R.; Montelli, L.; Hoffman, R.; Fersi, A.; Dauvin, J.C.; Guerra-García, J.M. Unravelling the origin and introduction pattern of the tropical species Paracaprella pusilla Mayer, 1890 (Crustacea, Amphipoda, Caprellidae) in temperate European waters: First molecular insights from a spatial and temporal perspective. NeoBiota 2019, 47, 43–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchini, A.; Ferrario, J.; Minchin, D. Marinas may act as hubs for the spread of the pseudo-indigenous bryozoan Amathia verticillata (Delle Chiaje, 1822) and its associates. Sci. Mar. 2015, 79, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beermann, J.; Hall-Mullen, A.K.; Havermans, C.; Coolen, J.W.P.; Crooijmans, R.P.M.A.; Dibbits, B.; Held, C.; Desiderato, A. Ancient globetrotters-Connectivity and putative native ranges of two cosmopolitan biofouling amphipods. PeerJ 2020, 8, e9613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Gonzalez, V.; Sanchez-Jerez, P. Fouling assemblages associated with off-coast aquaculture facilities: An overall assessment of the Mediterranean Sea. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2017, 18, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, T.; Fernandez-Leborans, G.; Senna, A.R. Ciliate epibionts on Melita petronioi Senna et al., 2012 (Crustacea: Amphipoda) from Brazil. Cah. Biol. Mar. 2013, 54, 393–404. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Leborans, G.; Fernandez-Gonzalez, V.; Sanchez-Jerez, P.; Roura, A. Epibiontic associations between apostomid ciliates Conidophrys spp. and amphipods associated with fish farms fouling in the western Mediterranean Sea. Helgol. Mar. Res. 2016, 70, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Carman, K.R.; Dobbs, F.C. Epibiotic microorganisms on copepods and other marine crustaceans. Microsc. Res. Tech. 1997, 37, 116–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krapp-Schickel, T.; Vdaer, W. What is, and what is not, Caprella acanthifera leach, 1814 (Amphipoda, Caprellidae)? Part 1: The acanthifera-group. J. Nat. Hist. 1998, 32, 949–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, L.F.; Brandini, F.P.; Gutseit, K.S.; Fonseca, A.; Pellizzari, F.M. Benthic diatoms growing on glass slides in the Paranaguá Bay, southern Brazil: Taxonomic structure and seasonal variation. INSULA 1999, 28, 53–100. [Google Scholar]
- Wachnicka, A.H.; Gaiser, E.E. Characterization of Amphora and Seminavis from South Florida, U.S.A. Diatom Res. 2007, 22, 387–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, L.F.; Calixto-Feres, M. Morphology and distribution of two epizoic diatoms (Bacillariophyta) in Brazil. Acta Bot. Bras. 2012, 26, 836–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romagnoli, T.; Bavestrello, G.; Cucchiari, E.M.; De Stefano, M.; Di Camillo, C.G.; Pennesi, C.; Puce, S.; Totti, C. Microalgal communities epibiontic on the marine hydroid Eudendrium racemosum in the Ligurian Sea during an annual cycle. Mar. Biol. 2007, 151, 537–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Totti, C.; Calcinai, B.; Cerrano, C.; Di Camillo, C.; Romagnoli, T.; Bavestrello, G. Diatom assemblages associated with Sphaerotylus antarcticus (Porifera: Demospongiae). J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2005, 85, 795–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillan, D.C.; Cdaée, G.C. Iron-encrusted diatoms and bacteria epibiotic on Hydrobia ulvae (Gastropoda: Prosobranchia). J. Sea Res. 2000, 43, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Alelio, D.; Cante, M.T.; Russo, G.F.; Totti, C.; De Stefano, M. Epizoic diatoms on gastropod shells. When substrate complexity selects for microcommunity complexity. In All Flesh is Grass: Plant-Animal Interrelationships; Cellular Origin, Life in Extreme Habitats and Astrobiology, 16; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 345–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snoeijs, P. Studies in the Tabularia fasciculata complex. Diatom Res. 1992, 7, 313–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witkowski, A.; Li, C.; Zgłobicka, I.; Yu, S.X.; Ashworth, M.; Dabek, P.; Qin, S.; Tang, C.; Krzywda, M.; Ruppel, M.; et al. Multigene assessment of biodiversity of diatom (Bacillariophyceae) assemblages from the littoral zone of the bohai and yellow seas in Yantai region of northeast China with some remarks on ubiquitous Taxa. J. Coast. Res. 2016, 74, 166–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bigelow, P.R.; Alexander, C.G. Diatoms on the cirri of tropical barnacles. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2000, 80, 737–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havermans, C.; De Broyer, C.; Mallefet, J.; Zintzen, V. Dispersal mechanisms in amphipods: A case study of Jassa herdmani (Crustacea, Amphipoda) in the North Sea. Mar. Biol. 2007, 153, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zintzen, V.; Norro, A.; Massin, C.; Mallefet, J. Temporal variation of Tubularia indivisa (Cnidaria, Tubulariidae) and associated epizoites on artificial habitat communities in the North Sea. Mar. Biol. 2008, 153, 405–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Totti, C.; Romagnoli, T.; De Stefano, M.; Camillo, D.C.G.; Bavestrello, G. The diversity of epizoic diatoms. In All Flesh Is Grass. Cellular Origin, Life in Extreme Habitats and Astrobiology; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 323–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conlan, K.E.; Desiderato, A.; Beermann, J. Jassa (Crustacea: Amphipoda): A new morphological and molecular assessment of the genus. Zootaxa 2021, 4939, 1–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, K. Epibionts on carapaces of some malacostrans from the gulf of Thailand. J. Crustac. Biol. 1996, 16, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijnhoven, S.; Zwiep, K.L.; Hummel, H. First description of epizoic ciliates (Sessilida Stein, 1933) on Bathyporeia Lindström, 1855 (Peracarida, Amphipoda) and infestation patterns in brackish and marine waters. Crustaceana 2018, 91, 133–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, Y.C.; De Stasio, B.T.; Ramcharan, C.W. Individual and population level consequences of an algal epibiont on Daphnia. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1993, 38, 592–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra-García, J.M.; Tierno de Figueroa, J.M.; Navarro-Barranco, C.; Ros, M.; Sánchez-Moyano, J.E.; Moreira, J. Dietary analysis of the marine Amphipoda (Crustacea: Peracarida) from the Iberian Peninsula. J. Sea Res. 2014, 85, 508–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtsuka, S.; Horiguchi, T.; Hanamura, Y.; Yamaguchi, A.; Shimomura, M.; Suzaki, T.; Ishiguro, K.; Hanaoka, H.; Yamdaa, K.; Ohtani, S. Symbiosis of planktonic copepods and mysids with epibionts and parasites in the North Pacific: Diversity and interactions. In New Frontiers in Crustacean Biology; Asakura, A., Ed.; Brill: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 1–14. ISBN 9789004174252. [Google Scholar]
- Gibson, R.A. Protoraphis atlantica sp. nov., a new marine epizoic diatom. Bacillaria 1979, 2, 109–126. [Google Scholar]
- Harper, M.A.; Cassie Cooper, V.; Chang, F.H.; Nelson, W.A.; Broday, P.A. Phylum Ochrophyta: Brown and golden-brown algae, diatoms, silicoflagellates, and kin. N. Z. Invent. Biodivers. 2012, 3, 114–163. [Google Scholar]
- Veen, A.; Hof, C.H.J.; Kouwets, F.A.C.; Berkhout, T. Rijkswaterstaat Waterdienst, Informatiehuis Water [Taxa Watermanagement the Netherlands (TWN)]. Available online: http://ipt.nlbif.nl/ipt/resource?r=checklist-twn (accessed on 1 March 2020).
- López-Fuerte, F.O.; Siqueiros-Beltrones, D.A.; Jakes-Cota, U.; Tripp-Valdéz, A. New records of marine diatoms for the American continent found on stone scorpionfish Scorpaena mystes. Open J. Mar. Sci. 2019, 9, 98–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Procopiak, L.; Fernandes, L.F.; Moreira-Filho, H. Diatomáceas (Bacillariophyta) marinhas e estuarinas do Paraná, Sul do Brasil: Lista de espécies com ênfase em espécies nocivas. Biota Neotrop. 2006, 6, bn02306032006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, G.S.; Espinosa, M.A.; Isla, F.I. Modern diatom assemblages in surface sediments from estuarine systems in the southeastern Buenos Aires Province, Argentina. J. Paleolimnol. 2006, 35, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serejo, C.S. The genus Leucothoe (Crustacea, Amphipoda, Leucothoidae) on the Brazilian coast. Beufortia 1998, 48, 105–135. [Google Scholar]
- Krapp, T.; Lang, C.; Libertini, A.; Melzer, R.R. Caprella scaura Templeton, 1836 sensu lato (Amphipoda: Caprellidae) in the Mediterranean. Org. Divers. Evol. 2006, 6, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Martínez-Laiz, G.; Ros, M.; Navarro-Barranco, C.; Guerra-García, J.M. Habitat selection of intertidal caprellid amphipods in a changing scenario. Behav. Process. 2018, 153, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrario, J.; Caronni, S.; Occhipinti-Ambrogi, A.; Marchini, A. Role of commercial harbours and recreational marinas in the spread of non-indigenous fouling species. Biofouling 2017, 33, 651–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zabin, C.J.; Ashton, G.V.; Brown, C.W.; Davidson, I.C.; Sytsma, M.D.; Ruiz, G.M. Small boats provide connectivity for nonindigenous marine species between a highly invaded international port and nearby coastal harbors. Manag. Biol. Invasions 2014, 5, 97–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).