Abstract
The urban rainstorm can evolve into a serious emergency, generally characterized by high complexity, uncertainty, and time pressure. It is often difficult for individuals to find the optimal response strategy due to limited information and time constraints. Therefore, the classical decision-making method based on the “infinite rationality” assumption is sometimes challenging to reflect the reality. Based on the recognition-primed decision (RPD) model, a dynamic RPD (D-RPD) model is proposed in this paper. The D-RPD model assumes that decision-makers can gain experience in the escaping process, and the risk perception of rainstorm disasters can be regarded as a Markov process. The experience of recent attempts would contribute more in decision-making. We design the agent according to the D-RPD model, and employ a multi-agent system (MAS) to simulate individuals’ decisions in the context of a rainstorm. Our results show that experience helps individuals to perform better when they escape in the rainstorm. Recency acts as a one of the key elements in escaping decision making. We also find that filling the information gap between individuals and real-time disaster would help individuals to perform well, especially when individuals tend to avoid extreme decisions.
1. Introduction
Urban rainstorms are a type of major natural disaster and induce enormous loss [1]. The urban rainstorms may cause a seeper phenomenon noted as waterlogging too [2], which frequently happens in many big cities around the world, especially in the developing countries [3]. The 7/21 accident occurred in Beijing, China, on 21 July 2012, caused 79 deaths, and a great direct economic loss of 11.64 billion RMB [4]. In addition to direct damage, some indirect loss caused by the rainstorm is also huge. For instance, waterlogging and low visibility in the urban rainstorms will give rise to traffic problems and other derivative accidents [5]. Therefore, it is critical to study how to reduce the loss caused by urban rainstorms.
In recent years, many rainstorm disaster researchers have focused on scenario modeling and risk assessment [6]. Geographic information system (GIS) technology is widely applied to study the spatial distribution of rainstorm disasters, providing a basis for the establishment of shelters [2,3,7,8]. However, though waterlogging occurrence rules can be recognized, absent cognition and misunderstanding of information about rainstorm risk are common in real scenes [9]. The rainstorm disaster is a typical complex society system [10]. Given the complexity of human activities, agent-based modelling and simulation (ABMS) shows great advantages in urban emergencies [11]. Through ABMS, the disaster environment and human behaviors can be well captured [12]. In this way, emergency plans can be made in advance to prevent disaster and to reduce risk. ABMS on people’s behavior in the rainstorm is gradually developing [13,14], and mixed reality game system enables people to participate in the simulation of urban rainstorms [9]. ABMS has been applied widely in evacuation [9], risk assessment [15], and the spatial allocation of urban emergency shelters [16]. Although quite a few studies have simulated escape scenarios, these are based on entirely rational assumptions [13,14]. However, unconventional emergencies like escaping in the continuous heavy rainfall are characterized by complexity, uncertainty, and time pressure, which make it challenging for individuals to gain complete information and make entirely rational decisions [17]. People’s behavioral patterns and psychological characteristics are crucial in the multi-agent simulation [18]. The recognition-primed decision (RPD) model assumes that, in continually changing conditions, decisions are made in reaction to and on the basis of prior experience, and they mainly focus on situation recognition [19]. Human teams perform better with the help of RPD-enabled agent architecture in high time pressure situations [20]. People’s behavior in panic indicates that recognition of the situations is crucial [21]. Therefore, the RPD model can be employed in emergency events. The RPD model is an attempt to understand how experienced decision makers like firemen deal with complex real-world settings [19]. However, in continually changing conditions, people with no expert experience can also make decisions based on their experience. Thus, the RPD model can be applied to study an individual’s escape in the urban rainstorm.
There exist quite a few studies focused on the variations in the risk response attitudes of individuals during the rainstorm. However, relatively speaking, current studies focus on the macro-group instead of the emergence of micro-individual decision-making behavior. Considering that the micro individuals’ behavior pattern and risk attitudes towards rainstorms were mostly neglected in existing studies, in this paper, we improve the recognition-primed decision (RPD) theory and propose a dynamic recognition-primed decision (D-RPD) theory for personal risk decision making in a heavy rain environment. Based on D-RPD theory, we model agents that can update their strategies based on their experience gained in the process of the rainstorm. The objectives of this study are as follows: (1) Discovering individuals’ capability of risk perception. (2) Exploring the behavior pattern during the escape in the urban rainstorm. (3) Recognizing whether experience has an influence on individuals’ risk preferences during the rainstorm.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
To provide an illustrative flood risk analysis, we construct a typical community in Wuhan (N 29°58′–31°22′ and E 113°41′–115°05′), Hubei province in China (Figure 1). Wuhan is the biggest city in central China, covering an area of 8569 km2. It has a population of over 11 million. In the past few years, the average annual rainfall in Wuhan was approximately 1200 mm. Due to the summer monsoon, the rainfall is unevenly distributed throughout the year. Most of the annual precipitation falls from June to August. The flood in July 2016 had caused 14 deaths and caused a great direct economic loss of 4 billion RMB.
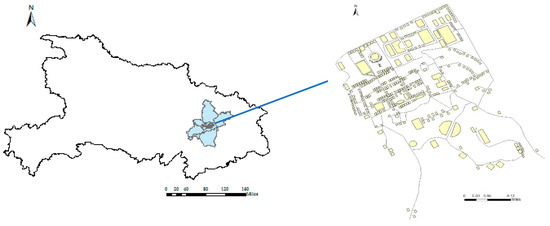
Figure 1.
A typical community in Wuhan, Hubei province, China.
Considering great similarities among regional plans in Wuhan, we have selected a typical community in this study. There are as well as loose dense gathering areas in the community. To fully capture every scenario, this selected community consists of both low- and high-density zones.
2.2. Framework of Multi-Agent Simulation
The traditional simulation model is limited to simple and low dependence problems [22], which is not suitable for our scenario. To solve this problem, we develop agent-based modeling and simulation (ABMS) to model systems comprised of autonomous, interacting agents.
The agent is defined as a physical or abstract entity and acts as a basic unit in multi-agent systems (MAS) [23]. The agent has properties as follows [24]:
{Attribute, State, Communication, Knowledge, Action, Environment}
Combining real and simulated data is a challenge for multi-agent simulation. In this study, we conduct artificial and real systems in parallel and apply adaptive control methods for the experiments [25]. Through the artificial societies-computational experiments-parallel execution (ACP) platform [26], we can interact with the real social system, and provide reliable support for the management and decision-making of real social scenes. Thus, we can realize the evolution of the situation, co-evolution, and closed-loop feedback.
The evacuation of individuals in the rainstorm is a complex, interacting social system [27]. The urban rainstorm escape simulation platform is demonstrated in Figure 2 [26]. The data of real system can be employed in the manual system. The results of simulation in manual system can help prevent risk in real system. Through management, control, observation and evaluation, data and model are exchanged between real and manual systems. In this paper, we get meteorological data from Hubei Meteorological Service and actual observations, and then turn it to the geographic information in the simulation.
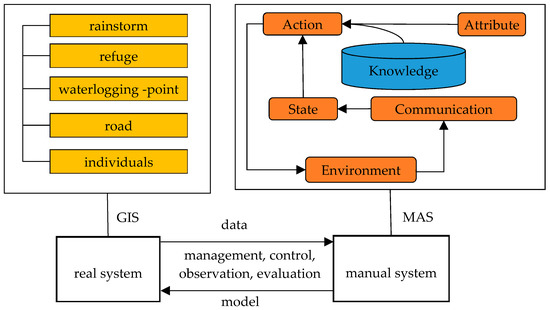
Figure 2.
Urban Rainstorm Escape Simulation Platform.
It is argued that the concept of risk can be regarded as expected loss, probability of an undesirable event, an event that endangers human value, and so on [28]. Risk preference reflects individuals’ attitudes towards risk [29]. When passing through waterlogging points, individuals may lose much energy because of trapping in the water, infecting with the virus and other events. In this paper, we refer risk as the probability of losing much energy in the waterlogging points. Risk preference reflects an individual’s tendency to implement risky or conservative strategies facing the potential loss caused by waterlogging points.
The risk of rainstorm is the result of multiple factors, such as elevation, density of the rainstorm, and slope [30]. According to the size of risk, we define a “risk environment” as an environment with all these factors. In low risk environment, individuals tend to lose less energy than that in a high risk environment. Evaluation methods with GIS techniques can be combined to provides reliable information about the rainstorm [31]. This paper mainly focuses on individuals’ behavior in the rainstorm, thus the risk is simplified in the simulation. As the simulation map comes from a small community, some factors like elevation to reflect the risk are ignored.
Expert knowledge (EK) and participant observation (PO) can be used to understand agents and their actions [11]. Detailed agent attribute data is from Hubei Meteorological Service, Civil Affairs Bureau of Wuhan, data analysis of rainstorms in Wuhan [32], and study of the mitigation behavior in floods [33].
This paper describes a simple scenario of an individual escape in the rainstorm. We employ ABMS to simulate an individual’s escape model in the rainstorm, and design the individual agent based on the D-RPD model. In the rainstorm, due to elevation, slope, and other factors, there will exist much accumulated water (we referred them waterlogging points in this paper). Here, ‘energy’ is one attribute of each human agent, representing essential resources and power for staying alive. Individuals may lose much energy when passing waterlogging points. To reach refuges in the rainstorm, individuals must keep their energy sufficient while passing by many waterlogging points. When wading directly, individuals will spend less time, but may lose more energy than wading cautiously. We use R to reflect the risk when individuals wade directly. After making some preparation, individuals will reduce risk, we use δ × R to reflect the risk of wading cautiously (0 < δ < 1). Individuals only have information about the intensity of the rain, but have little extra information about the waterlogging points like geographic information under water. Thus, individuals would struggle to judge whether it is safe to wade through the waterlogging point directly. After passing one waterlogging point, they will lose some energy and time, but gain some experience as to where to wade directly or cautiously.
2.3. Recognition-Primed Decision Model
Classical decision-making strategies generally describe a situation where decision-makers search for the optimal decision given sufficient information and perfect rationality [34]. The classical decision theory may not work well in real-world scenarios [17]. Different from classical decision theory, naturalistic decision making (NDM) mainly focuses on expert experience, and a satisfactory solution is acceptable [35]. Klein proposed the concept of NDM in 1989 to understand how people make decisions in real life rather than in artificial laboratory settings [36]. In complex situations, people act and react based on previous experience. Emergency responders tend to compare the current situation with previous ones and identify a plausible action. A “workable,” “timely,” and “cost-effective” decision is more acceptable in the real decision situation [19,37,38]. As Figure 3 shows, the process of situation matching, action implementing and strategy forming are integrated into a comprehensive recognition-primed decision model [19], in which typicality recognition and situation search could be performed simultaneously.
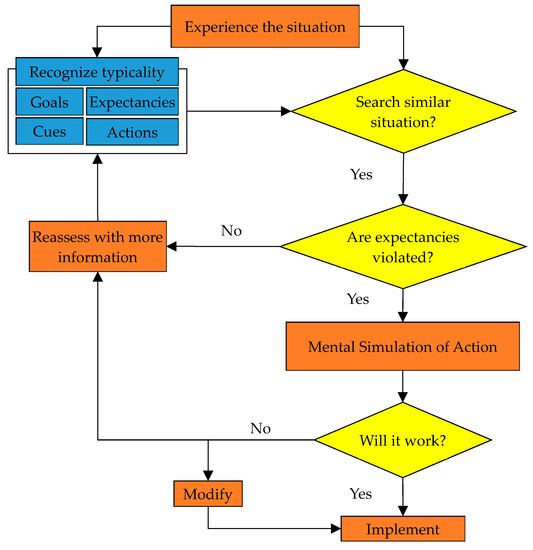
Figure 3.
Recognition-primed decision model.
The recognition-primed decision (RPD) model is the application of NDM theory. The focus of the RPD model is environmental condition identification and reproduction [37]. The RPD model can be divided into 2 phases: situation recognition and solution generation [39]. Klein proposed ideas in three scenarios: (1) recognize typicality and visible reaction, (2) recognize typicality and conscious evaluation, (3) situation reassessment and evaluation modification [19]. Although RPD theory has demonstrated unique advantages in the practice of quite a few fields, there still exist several controversies about it. The RPD model simplifies the situation and focuses little on rational decision, which is not universal in all situations. In other words, the conditions must be considered when employing the RPD model, which include experienced decision-makers, high-time pressure, limited cognitive resources, and so forth. In addition, few studies on the RPD model addresses dynamic decision problems, in which successive decisions are not independent and require an iterative “look-ahead” approach [40].
2.4. Dynamic Recognition-Primed Decision Model
The dynamic recognition-primed decision (D-RPD) model is motivated by the need for continuous decisions in a dynamic condition. In classical PRD model, decision makers are domain experts, and they make decisions based on all experiences. However, in the rainstorm, past experiences may not reflect the reality. The risk changes during the rainstorm process, and hence emergency decision making should also be carried out in stages [41]. Further, an individual’s risk perception changes in the disaster [4]. Apparently, an individual’s perceived risk of a rainstorm can be regarded as a Markov process [42]. That is, the perceived risk of the rainstorm at the next moment is only related to the first k states, and has nothing to do with the time before k + 1. Because of this, the individual only needs to consider the experience of the preceding k stages. The experience considered by the individual in the decision of tn time is presented in Figure 4:

Figure 4.
Markov property of individuals’ decision-making in the rainstorm.
In the actual urban rainstorm escape process, individuals will pass many waterlogging points. Since the risk of heavy rain is dynamic, not all the experience is valuable. In the actual situation, the experience within a period similar to the current environmental risk is the most helpful. However, the problem is the case that the assessment of risk is one of the individual’s goals, not the given information [9].
2.5. Model of Individuals’ Escape in the Urban Rainstorm Context
2.5.1. Agent Attributes
In the study of evacuees’ behaviors in a disaster situation using multi-agent simulation, initial locations and the number of agents can be decided depending on the aims [9,43,44]. To simplify the model, the following assumptions are proposed:
(1) The choice of the individual at the risk point does not include immediate detour.
(2) The waterlogging points are homogeneous, that is, all the waterlogging points have the same probability of risk and the loss caused by the risk. We set different risk environments for different groups of experiments. The probability of lose energy for individuals is influenced by the environment.
(3) There is only one refuge in the rainstorm area, and all individuals move there through an optimal path.
Unlike the simple accumulation of experience in the classical RPD model, the experience base in this model is dynamically updated. The agent attributes can be illustrated as follows:
Action set (AS): {direct wading (DW), cautious wading (CW)}. In actual urban rainstorms, there are usually three types of decisions when individuals pass through the waterlogging points: (1) bypassing the road (2) directly wading (3) observing the behavior of others or taking certain measures to reduce the risk. In this study, assuming that no one chooses to detour. Decision 2 is referred to as a direct wading strategy, and decision 3 is collectively referred to as a cautious wading strategy. We set a control parameter for cautious wading strategies. Supposing that the risk for direct wading is R, then the risk for cautious wading is δ × R, where 0 < δ < 1.
Energy loss (EL): A set with k elements, where the element Ee is displayed in Equation (1). EL represents the actual energy loss of wading each time, and E0 represents the energy loss when no risk breaks out. Set ER as the energy loss when the risk breaks out. Here, ER > E0
Time loss (TL): A set with k elements, where the element Te is presented in Equation (2). TL represents the actual time spent in wading each time, and T0 represents the time when an agent does not prepare the wading. Set Tp as the time when the individual makes some preparation for the wading. Here, Tp > T0.
Direct wading probability (DWP) reflects the individual’s risk preference, which is the function of P0, ST, and SE. P0 represents the initial risk preference, ST represents the direct wading support from TL, and SE represents the direct wading support from EL.
A value of 1 for Ee indicates that no risk has occurred this time, which will support direct wading. The number of elements equal to 1 in EL is ke. ke is an integer ranging from 0 to k. SE, as shown in Equation (3), represents the degree of direct wading support from EL, and its value is between −1 and 1. Here, k is positive integer, and keep constant in one specific experiment.
Similarly, when the value of Te is 1, it will support direct wading. The number of elements equal to 1 in TL is kt. kt is an integer between o and k. ST, as shown in Equation (4), represents the degree of direct wading support from TL, and its value is between −1 and 1.
The degree of support for wading directly can be divided in 2 parts: SE and ST, and α represents the weights between the two. Thus, the total degree of support, S, is shown in Equation (5).
where P, the probability of wading directly without preparation, is the sum of P0, and S, which is represented in Equation (6).
2.5.2. Agent Interaction Rule
In the first k times of wading, the agent only acts according to the initial preference. After the kth time, the agent makes decisions according to experience base and dynamically updates it. The process is demonstrated in Figure 5. TL and EL are updated after each wading, deleting the first element and adding a new element.
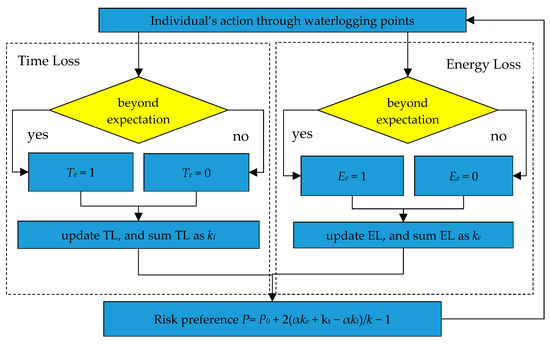
Figure 5.
Agent’s decision rule during the escaping in the rainstorm.
3. Result and Discussion
The simulation map is shown in Figure 6. The individuals represented by green circles walk along the road shown by lines. When traveling, individuals encounter a lot of waterlogging points represented by red forks, and lose some energy and time. Individuals try to adopt strategies to reduce the loss of energy to reach the refuge, which is the blue square on the map.
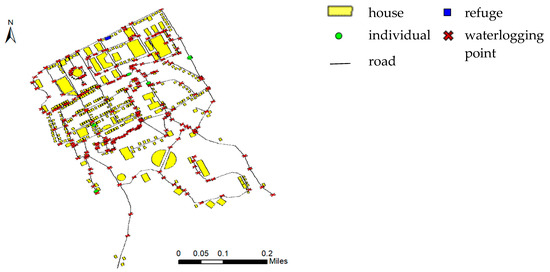
Figure 6.
Map of the simulated escape route in the urban rainstorm context.
Three sets of experiments are created based on the parameters k, δ, P. Each parameter has ten different values. In one test, all the parameters are constant and vary in different tests. Each test includes 50 agents.
3.1. Individual’s Perception of Risk
A rational individual should change decisions as the environment changes [45]. In the process of urban rainstorms, due to the high time pressure and information uncertainty, the risks at the waterlogging points is uncertain. In this case, the individual often judges the risk level of the waterlogging point through the experience of past waterlogging points. To explore the individual’s perception of risk in urban rainstorms, the variations in individual preferences in low-risk, medium risk and high-risk environments are studied through simulation. We set 3 types of agents: L-type (agents with low initial risk preference), M-type (agents with medium initial risk preference), and H-type (agents with high initial risk preference). Figure 7 reveals the individual’s initial preference and the average preference to reach the destination through multiple risk points in three types of environments. This describes how individuals continuously update their risk preferences through experience and gradually adapt to risk in the environment.
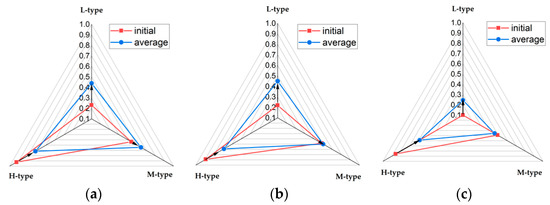
Figure 7.
Individuals’ risk preference in different contexts: (a) Low risk context; (b) Medium risk context; (c) High risk context (L-type: agents with low initial risk preference, M-type: agents with medium initial risk preference, H-type: agents with high initial risk preference).
In a low risk environment (Figure 7a), individuals with lower initial risk preferences constantly update their risk preference according to experience, and ultimately improve their risk preference to a large extent. Individuals with medium risk preference ultimately increase their risk preference to a small extent, while individuals with higher initial risk preferences moderately reduce risk preference to better adapt to actual risks in the environment. A low risk environment motivates people to take risks because the cost of risk (loss of energy) is small and the benefits (reducing time spent) are large. However, as can be observed in Figure 5, although the individual adopts a riskier strategy than the original, the overall risk preference remains at a lower level. In an emergency, the individual’s risk strategy is more conservative, though it may have adverse consequences [46].
In a moderate risk environment (Figure 7b), individuals with lower initial risk preference constantly update their risk preference according to experience, and finally improve their risk preference to a large extent. The individual with medium-risk preference almost fluctuated with his initial preference. Individuals with higher initial risk preferences reduce risk preferences to a great extent in order to better adapt to the actual risks in the environment. Since the probability of the risk occurring at the risk point is close to the likelihood of no risk occurring, it is challenging to decide the decision at the risk point.
For example, if the probability of a risk is 0.7, it may be better to adopt a cautious strategy; if the probability of a risk is 0.3, it may be better to adopt a direct strategy; if the probability of a risk is 0.5, then the two strategies are tough to judge advantages and disadvantages. Therefore, in a moderate risk environment, individual preferences tend to be arbitrary, that is, the probability of choosing a cautious strategy and a direct strategy is close. However, considering the time factor, the proportion of direct strategies should be higher.
In a high-risk environment (Figure 7c), individuals with lower initial risk preferences constantly update their risk preferences according to experience, and ultimately improve their risk preference. Individuals with a moderate risk preference reduce their risk preferences to a small extent. Individuals with higher initial risk preferences greatly reduce risk preference to avoid energy loss caused by wading without preparation. However, in the overall view, the individual’s risk preference is medium, which is contrary to the intuition that a cautious strategy should be adopted in a high-risk environment. This can be explained by the fact that the risk for taking a cautious strategy is still high, even in a high-risk environment, thus reducing time becomes the main goal. Therefore, under a high-risk environment and high time pressure, although individuals will present risk aversion from the overall trend, under the time pressure, a direct strategy will still be adopted sometimes.
The risk of waterlogging points is set from 0 to 1 with 0.1 as interval, forming ten types of experiments. Figure 8 shows each average and standard deviation of the preferences of multiple agents in these ten types of experiments. Obviously, there exists a reverse association between environmental risks and individual risk preference. Although the values of standard deviation have slight fluctuation, they are all around 0.2. Furthermore, experimental calculation in large scale contains almost all possible situations, leading to a high credibility.
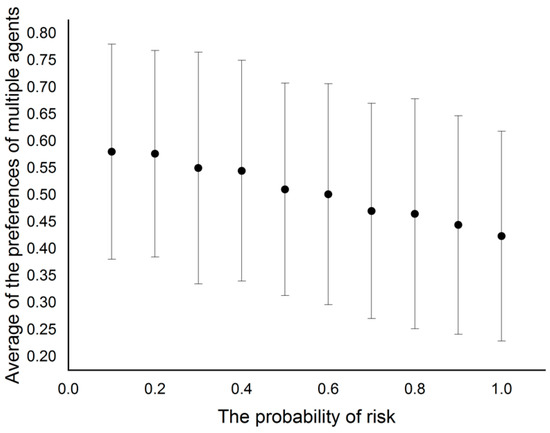
Figure 8.
Variation of individuals’ risk preference over the risk range.
Figure 9 shows energy variations with time in different risk environments. The energy is the average of all the agent’s energy. Energy is a linear function of time when the energy loss at the cumulative point is not considered. However, due to the risk of waterlogging points and the uncertainty of individual decision-making, the change in energy presents a curve fluctuation. It can be seen that energy consumption is no longer the same from the beginning due to different environmental risks. These three curves have no intersections other than the starting point, which means that individuals can evade certain risks through their own decisions, but since individuals cannot always make completely rational decisions, the energy loss values differ.
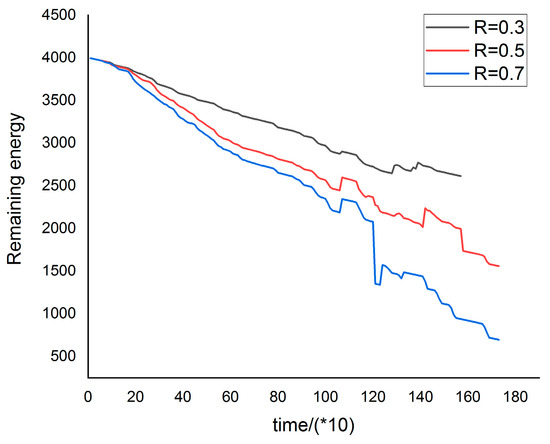
Figure 9.
Variation of energy over the period.
In the process of making multiple decisions, an individual’s experience affects their risk preference [4] and adapts to the actual risk of the environment. Specifically, after multiple wading experiences, individuals in low-risk situations will increase their risk preference, and individuals in high-risk situations will increase their risk preference. However, their risk preference tends to be “conservative” after multiple experiences regardless of the individual’s initial risk preference. For instance, even if the risk of the environment is extremely low, individuals will not adopt risky strategies all the time, but a small number of conservative strategies. For example, a heavy rain occurs, and waterlogging points are formed. Even though the risk of waterlogging points is quite low, a few people step into the deep waterlogging points at the water level and spend a certain amount of energy. Then, in the next few waterlogging points, the probability of adopting a cautious wading strategy will increase. However, classical decision theory tells us that environmental risks are exceedingly low. Even if encountering risk, individuals should continue to wade directly and reach the rescue point as soon as possible. The reason for the deviation is that the individual has limited information on the probability of future risks and can only choose to believe in past experience. Information during the rainstorm is vitally important, however, quite a few individuals will not be informed in advance [47]. In the process of urban rainstorms, the government should monitor the risk of the rainstorm in real-time and inform people of the risk by means of broadcasting, messages, screen display in public places. In a low-risk environment, tell the public not to panic, and take a direct strategy. If the government monitors potential risks in real time and discloses the relevant information to the public, individuals’ behavior to make decision is more compatible with the classical theory.
3.2. Influences of Individuals’ Experience Pool Size
Individuals decide their behavior according to their own experience. However, for two reasons, it is inappropriate for individuals to make decisions based on all previous experience in the rainstorm. First, the individual’s memory ability is limited [48], and it is impossible to retain all the memories about the risk point. Second, the variation of risk is a dynamic process, individuals’ perceived risk during the rainstorm has the Markov property, and the individual’s recent experience is more valuable [41]. Therefore, it is crucial to explore the influence of the size of the experience base on individuals. Figure 10 illustrates the relationship between the final remaining energy of the individuals and the size of the experience base. In one experiment, the size of k is the same, and we conducted different experiment to compare the remaining energy with various k. As the experience base increases, the individual’s residual energy begins to increase, and then decreases. That is, theoretically, there exists a moderate k value, making the remaining energy the largest. In this experiment, the value of k is 25. In reality, the value of k is affected by many factors, not all of which are 25.
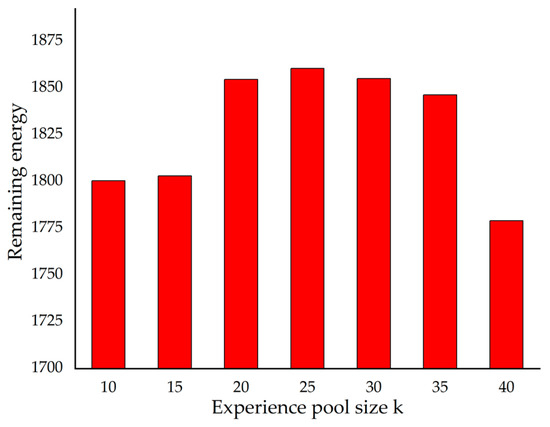
Figure 10.
The relation between energy remained and k.
The value of k is neither as large as possible nor as small as possible. The reason is that as k increases, the individual’s preference at the current risk point is less sensitive to previous experience. Figure 11 indicates the fluctuations in individual risk preferences in four scenarios. The vertical axis is the first difference in risk preferences. And the horizontal axis represents the amounts of waterlogging points individuals have passed. We give 4 figures for different k in 4 groups of experiments. It can be clearly seen that, as k increases, the individual’s preference fluctuation between risk points decreases. Therefore, when k is small, the fluctuation of risk preference is too large, so that each time wading the waterlogging point, there is a considerable degree of randomness. When k is large, individuals are slow to update risk preferences, resulting in an inability to adapt to rapidly changing environments.

Figure 11.
Variation of preference’s first-order difference with wading experience.
In classical RPD theory, all the experience of the past can provide decision support [19]. However, in the heavy rain scenario, the individual’s experience is only related to several wading experience in current rainstorm. The experience of past rainstorms formed the initial preference of the individual in the rainstorm. Therefore, in the continuous decision-making process, the remaining energy is not positively correlated with the individual’s experience base size. Only experience that is similar to current environmental risks can provide favorable decision support for individuals.
For instance, an individual rushes to a refuge in heavy rain that continues to increase. If an individual assesses the risk of wading based on all previous wading experience, the risk of current wading is seriously underestimated. According to recent experience, the risk assessment will be more accurate. In the real situation, there is a certain judgment on the intensity of the rainstorm, by which the risk of wading the waterlogging points will be judged. However, complex problems, such as the intensity of heavy rain or the flow of water on the road, make it challenging to judge the risk of the waterlogging points by analysis, and it is more meaningful to refer to several experience with similar rainstorm intensity.
3.3. Influences of the Regulation Parameter on Individuals’ Behavior
By studying the individual decision-making and energy changes under different control parameters, it is likely to explore whether the individual’s decision-making behavior can perceive the size of the control parameters.
Figure 12 demonstrates the average proportion of individuals taking direct wading strategies under different regulation parameters. The result of linear regression fitting is also shown as the red line in Figure 12. It can be seen that as the regulation parameter increases, the proportion of individuals adopting direct wading strategies decreases. This may not be in line with our intuition, because an increase in regulation parameters means that the benefits of an indirect strategy are reduced. Thus, the proportion of indirect wading strategies should decrease. However, the increase of regulation parameters also implies the deterioration of the environment. That is, the illusion of individuals under time pressure: δ × R is regarded as the probability of occurrence of the risk, and the increase of regulation parameters means the probability of occurrence of risk becomes larger. As δ increases, the likelihood of the risk is increasing in people’s minds. Driven by this illusion, even if the actual effect of δ to reduce risk becomes smaller, the individual still adopts a cautious strategy. This reflects the bounded rationality of the individual: under high time pressure, it is arduous for an individual to explore the actual cause to the risk of taking a prudent strategy [49].
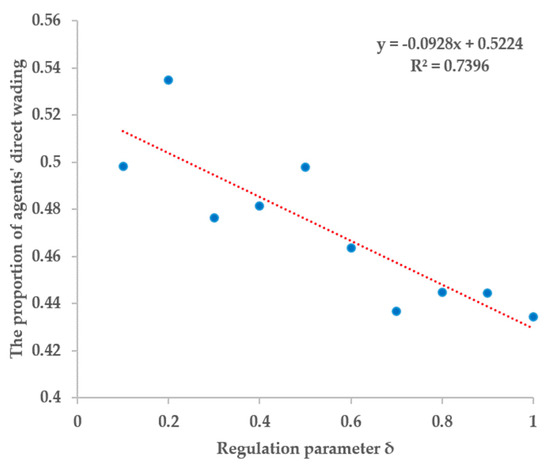
Figure 12.
Influences of δ on individuals’ behavior.
Figure 13 shows the energy’s variations under different control parameters. It can be seen that, as δ increases, the remaining energy decreases. The result of linear regression fitting is also shown as the red line in Figure 13. This seems inconsistent with our conclusions above: as δ increases, the proportion of individuals adopting direct wading strategies is decreasing, and the energy lost should also be reduced. However, it should be considered that as δ increases, although the proportion of individuals directly wading is reduced, the probability of the risk occurring is increasing. On the one hand, increasing the proportion of cautious strategies reduces risk. On the other hand, an increase in δ increases the risk of a prudent strategy. The combined effect of the two makes the final result represented in Figure 13. It can be concluded that, although the individual does not possess a clear understanding of the regulation parameters, the perception of the overall risk is correct.
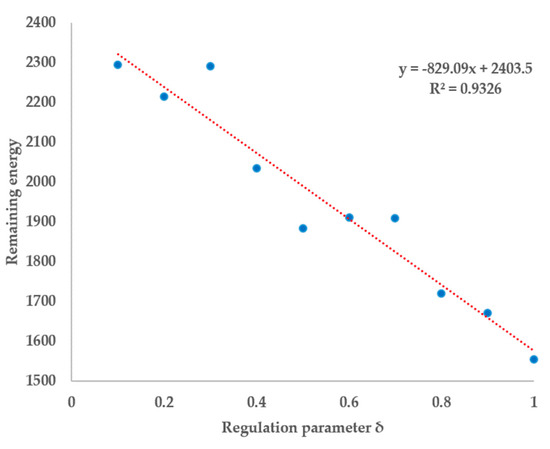
Figure 13.
Influences of δ on energy remained.
4. Conclusions
During emergencies, individuals often make decisions based on previous experience. Especially in the process of continuous decision-making in urban rainstorm escape, decisions often depend only on recent experience. To better characterizes individuals’ continuous decision-making processes, we propose a D-RPD model for individuals’ decisions under the scenario of an urban rainstorm. The main conclusions of this study are as follows:
(1) Individuals’ experience can provide information about the risk, so individuals can perceive the size of risk. However, the information is insufficient and accurate in a dynamic risk environment. External information, e.g., government broadcast, will help individuals to perform better in the rainstorm.
(2) In the process of urban rainstorm disaster escape, individuals tend to choose “conservative” strategies. In other words, even the risk of waterlogging points is very low, individuals will choose some cautious decisions. Moreover, as the environment changes, individuals may find the changes after exploring some waterlogging points. This will cause extra loss due to the postponement of information.
(3) Individuals will enhance their abilities of risk perception according to their dynamic learning from past experience. However, based only on the previous experiences, they cannot find the best strategy to cope with the risk. In addition, individuals may have a slow response to dynamic risk. To solve this problem, a simulation environment can be developed based on actual decision-making scenarios to effectively train residents and improve decision-making skills.
Author Contributions
All the authors contributed to the research design, manuscript development, editing, and completion of the manuscript. conceptualization, Q.Y.; methodology, X.L. and X.S.; software, X.S. and J.W.; validation, Q.Y. and X.L.; formal analysis, X.L. and X.S.; resources, J.W.; data curation, X.S. and J.W.; writing—original draft preparation, Q.Y.; writing—review and editing, Q.Y.; visualization, X.S.; supervision, X.L., X.S. and J.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported in part by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 71603197) and “the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities” (WUT: 195203001).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Wei Zhou, Tianyu Wan for their helpful suggestions and technology support. Special thanks to the anonymous reviewers and the editors whose suggestions and comments have significantly improved the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Hegger, D.L.T.; Driessen, P.P.J.; Dieperink, C.; Wiering, M.; Raadgever, G.T.T.; van Rijswick, H.F.M.W. Assessing stability and dynamics in flood risk governance: An empirically illustrated research approach. Water Resour. Manag. 2014, 28, 4127–4142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y. Risk analysis of rainstorm waterlogging on residences in Shanghai based on scenario simulation. Nat. Hazards 2012, 62, 677–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, R.S. Rainstorm waterlogging risk assessment in central urban area of Shanghai based on multiple scenario simulation. Nat. Hazards 2014, 73, 1569–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Zhao, F.; Tan, L. Whether a large disaster could change public concern and risk perception: A case study of the 7/21 extraordinary rainstorm disaster in Beijing in 2012. Nat. Hazards 2015, 78, 555–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, B.; Huang, H.; Li, Y. Integrated simulation method for waterlogging and traffic congestion under urban rainstorms. Nat. Hazards 2016, 81, 23–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Yin, J.; Xu, S.; Wen, J. Community-based scenario modelling and disaster risk assessment of urban rainstorm waterlogging. J. Geogr. Sci. 2011, 21, 274–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.B. Rainstorm flash flood risk assessment using genetic programming: A case study of risk zoning in Beijing. Nat. Hazards 2016, 83, 485–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.; Sun, Y. Evaluation of resident evacuations in urban rainstorm waterlogging disasters based on scenario simulation: Daoli district (Harbin, China) as an example. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 9964–9980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiura, K. Masahiro Arakawa Evaluation of Behavior of Evacuees on a Floor in a Disaster Situation Using Multi-agent Simulation and Mixed Reality Game: Effectiveness of the Field of Vision and Priority of Referred Objects. Comput. Technol. Appl. 2016, 7, 227–235. [Google Scholar]
- Lomnitz, C.; Castaños, H. Unplanned and Unforeseen Effects of Instabilities in the Nature-Society System as Possible Causes of Earthquake Disasters. Nat. Hazards 1995, 11, 45–56. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, L.; Durnota, B.; Ding, Y.; Dai, H. An agent-based simulation system for evaluating gridding urban management strategies. Knowl. Based Syst. 2012, 26, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhan, F.B. Agent-based modelling and simulation of urban evacuation: Relative effectiveness of simultaneous and staged evacuation strategies. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 2008, 59, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uno, K.; Kashiyama, K. Development of Simulation System for the Disaster Evacuation Based on Multi-Agent Model Using GIS. Tsinghua Sci. Technol. 2008, 13, 348–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, T.; Tadokoro, S.; Ohta, M.; Ito, N. Agent Based Approach in Disaster Rescue Simulation-From Test-Bed of Multiagent System to Practical Application. In Robot Soccer World Cup; Springer: Berli/Heidelberg, Germany, 2002; pp. 102–111. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, W.Z.; Li, W.B.; Huang, Y.L.; Wang, W.X.; Xiao, D. Rainstorm flood building risk dynamic assessment conceptual model utilization agent based modeling. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Computer Science and Applications (CSA), Wuhan, China, 20–22 November 2015; pp. 191–195. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.; Zhang, C.; Wen, J.; Li, W.; Liu, R.; Xu, H. Integrating multi-agent evacuation simulation and multi-criteria evaluation for spatial allocation of urban emergency shelters. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2018, 32, 1884–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, D.; Beach, L.R.; Lipshitz, R. Why Classical Decision Theory is an Inappropriate Standard for Evaluating and Aiding Most Human Decision Making. Decis. Mak. Aviat. 2018, 85, 835–847. [Google Scholar]
- Abustan, M.S.; Rahman, N.A.; Gotoh, H.; Harada, E.; Talib, S.H.A. Numerical Simulation of Evacuation Process in Malaysia by Using Distinct-Element-Method Based Multi-Agent Model. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2016; Volume 136. [Google Scholar]
- Klein, G. Naturalistic Decision Making. Hum. Fact. J. Hum. Factors Ergon. Soc. 2008, 50, 456–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Sun, S.; McNeese, M.; Yen, J. Extending the recognition-primed decision model to support human-agent collaboration. In Proceedings of the Fourth International Joint Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems (ACM), New York, NY, USA, 25–29 July 2005; pp. 945–952. [Google Scholar]
- Patrix, J.; Mouaddib, A.-I.; Gatepaille, S. Detection of Primitive Collective Behaviours in a Crowd Panic Simulation Based on Multi-Agent Approach. Int. J. Swarm Intell. Res. 2012, 3, 50–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macal, C.M.; North, M.J. Tutorial on Agent-based Modeling and Simulation Agent-based Modeling and Simulation Initiative at Argonne National Laboratory View project Agent-Based Modeling and Simulation. In Proceedings of the Winter Simulation Conference, Orlando, FL, USA, 4 December 2005; p. 14. [Google Scholar]
- Linghu, B.; Chen, F.; Guo, X.; Li, W. A conceptual model for flood disaster risk assessment based on agent-based modeling. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Sciences and Applications, Wuhan, China, 14–15 December 2013; pp. 369–373. [Google Scholar]
- Macal, C.M.; North, M.J. Tutorial on agent-based modeling and simulation part 2: How to model with agents. In Proceedings of the 38th conference on Winter simulation. Winter Simulation Conference, Monterey, CA, USA, 3–6 December 2006; pp. 73–83. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.Y.; Zeng, D.; Carley, K.M.; Mao, W. Social computing: From social informatics to social intelligence. IEEE Intell. Syst. 2007, 22, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.Y.; Wang, X.; Li, L.; Li, L. Steps toward Parallel Intelligence. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sin. 2016, 3, 345–348. [Google Scholar]
- Dawson, R.J.; Peppe, R.; Wang, M. An agent-based model for risk-based flood incident management. Nat. Hazards 2011, 59, 167–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aven, T. The risk concept-historical and recent development trends. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2012, 99, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dave, D.; Saffer, H. Alcohol demand and risk preference. J. Econ. Psychol. 2008, 29, 810–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, R.; Barrett, D.; Gao, L.; Zhou, M.; Renzullo, L.; Emelyanova, I. A spatial assessment framework for evaluating flood risk under extreme climates. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 538, 512–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Chen, Y.; Wu, J.; Gao, L.; Barrett, D.; Xu, T.; Li, X.; Li, L.; Huang, C.; Yu, J. Integrating Entropy-Based Naïve Bayes and GIS for Spatial Evaluation of Flood Hazard. Risk Anal. 2017, 37, 756–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.Y.; Peng, T.; Zhang, H.Y.; Yao, W.L. Study of risk and early warning index of rainstorm waterlogging in Wuhan City. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2017, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haer, T.; Botzen, W.J.W.; de Moel, H.; Aerts, J.C.J.H. Integrating Household Risk Mitigation Behavior in Flood Risk Analysis: An Agent-Based Model Approach. Risk Anal. 2017, 37, 1977–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B. The Classical Model of Decision Making Has Been Accepted as not providing an Accurate Account of How People Typically Make Decisions. Int. J. Bus. Manag. 2009, 3, 151–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lipshitz, R.; Klein, G.; Orasanu, J.; Salas, E. Focus article: Taking stock of naturalistic decision making. J. Behav. Decis. Mak. 2001, 14, 331–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, G.A.; Calderwood, R.; Clinton-Cirocco, A. Rapid Decision Making on the Fire Ground. Proc. Hum. Factors Soc. Annu. Meet. 1986, 30, 576–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenberger, R. Decision Making in Action: Models and Methods, Klein, G.A., Orasanu, J., Calderwood, R., Zsambok, C.E. (eds). Norwood, NJ: Ablex, 1993, 480 pp. ISBN 0–89391–794–X (pb). J. Behav. Decis. Mak. 2007, 8, 218–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, G. A naturalistic decision making perspective on studying intuitive decision making. J. Appl. Res. Mem. Cogn. 2015, 4, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, K.G.; Klein, G.A.; Thunholm, P.; Schmitt, J.F.; Baxter, H.C. The Recognition-Primed Decision Model; Army Combined Arms Center: Fort Leavenworth, KS, USA, 2004; pp. 6–10. [Google Scholar]
- Martin-Clouaire, R. Modelling Operational Decision-Making in Agriculture. Agric. Sci. 2017, 08, 527–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Cai, J.; Guo, G.; Chen, C. An emergency decision-making method for urban rainstormwater-logging: A China study. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raudkivi, A.J.; Lawgun, N. Synthesis of urban rainfall. Water Resour. Res. 1970, 6, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Han, C.S.; Dauber, K.; Law, K.H. A multi-agent based framework for the simulation of human and social behaviors during emergency evacuations. AI Soc. 2007, 22, 113–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiura, K.; Arakawa, M.; Yokoi, N. Evaluation of the Behavior of Evacuees on Dynamic Floor Condition by Using Multi-agent Simulation. J. Electr. Eng. 2017, 5, 275–287. [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons, A. Becoming human. New fossils raise molecular questions. Science 2002, 295, 1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arend, I.; Botella, J.; Contreras, M.J.; Hernández, J.M.; Santacreu, J. A betting dice test to study the interactive style of risk-taking behavior. Psychol. Rec. 2003, 53, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papagiannaki, K.; Kotroni, V.; Lagouvardos, K.; Bezes, A. Perspectives on Atmospheric Sciences; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2017; pp. 217–223. [Google Scholar]
- Lilford, R.J.; Chilton, P.J. Does the internet limit or extend the human mind? Probably both. BMJ 2011, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, C. Learning to make decisions in dynamic environments: Effects of time constraints and cognitive abilities. Hum. Fact. 2004, 46, 449–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).