Abstract
China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) needs little introduction; the infrastructure investment will reconfigure development in Central Asia. As its origin story and initial encounter, Central Asia offers a prismatic lens to delve into the vital impacts and significant changes wrought by the BRI. In the dryland region, the BRI impact on watersheds and agriculture is a critical challenge with direct implications for food security. Framed by diverse research sources, we utilized spatial datasets from the European Space Agency Climate Change Initiative and the World Bank to explore the intersection of food production, water and development. Investigation evaluates the possible trade-offs that Chinese infrastructure investment can have on the communities and environment of Central Asia. The findings identify more than 15,000 km of rail and 20,000 km of roads linked to the BRI crisscrossing the region in 2018. Whilst these transport corridors have improved connectivity, many of these rails and roads traverse important agricultural and water zones, creating undetermined risks and opportunities. Land use change was examined within a 10-km buffer around BRI roads and rails from 2008 to 2018. Railways increased by 23% during this time, yet irrigated and rainfed agriculture decreased whilst urban areas markedly expanded. Contextual research identifies how Chinese policies may encourage agribusiness investment for food exports as possible disruptions to national and regional food supply. However, to date Central Asia provides <1% of Chinese agricultural imports. In fact, Afghanistan is the region’s dominant export market, tripling agricultural imports >300% in this time. Similarly, five times more livestock are traded within the region than to China. Evaluating infrastructure change is essential to understand BRI impacts on environments and societies, with the food-water nexus a particular concern in Central Asia. Limited Chinese imports of Central Asian agriculture suggests the region’s food security will not be significantly altered by the Belt and Road Initiative.
1. Introduction
China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) needs little introduction; in 2019 alone the term was used in >18,000 academic publications (see Google Scholar). Designed as a USD 1 trillion program to build infrastructure, coordinate investment and policy and create connectivity between China and countries across the globe, the project has become President Xi Jinpeng’s key foreign policy initiative [1,2,3]. Initiated in 2013 in Astana (now Nur-Sultan), Kazakhstan, the program has the potential to reshape regional and international geopolitics. The BRI has been presented, theorized, investigated and parsed across disciplines, methods and perspectives [1]. Description and knowledge are coupled with a lack of program definition that encourages hope and speculation. Measured analysis is essential for understanding what the Belt and Road Initiative means for the host countries and partner nations it passes through and engages with. As its origin story and initial encounter, Central Asia offers a prismatic lens to examine the significant changes wrought by the BRI [2,3,4]. Across the steppes, one of the world’s largest drylands encompasses great climate variability, ancient cultures and glacier-fed rivers [5]. Once considered a Soviet breadbasket, today there are significant infrastructure implications for agriculture, watersheds and landscapes. This stresses the undefined environmental and social context of investment in the region where food security is critical [6]. Here, we investigate how the Belt and Road Initiative affects the food-water nexus in Central Asia through evaluating satellite imagery and data analysis in the remarkable region.
Central Asia was a key setting of the ancient Silk Road as routes meandered over the Tian Shan and Pamir Mountains and through renown oases towns like Samarakand, Osh, Bukhara and Merv [7]. These exotic trails and sites across Inner Asia were early forms of infrastructure based on dependable water sources and food supplies [8,9]. The notion of Middle or High Asia was extrapolated by the Soviet Union to mean the land between the Caspian Sea and the Tien Shan/Pamir mountains now represented by Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan and Uzbekistan (Figure 1a,b). In fact, an early mega-infrastructure thrust upon Central Asia was Krushchev’s optimistic, perhaps naïve, plan to conquer the steppe through the ‘Virgin Lands Campaign’ from 1954–1961 [10]. The concept of changing the region’s drylands into fields of grain resonates today, with communist-era challenges relevant to new BRI ideas of the region as a source for food exports to China [4,11]. Farming depends on adequate water for crops and transport to markets; thus, understanding investment and infrastructure from intensive cultivation to roads and railways is essential. As finite productive land is converted for food export by external agri-business [12,13], the vital question becomes how do changing dynamics affect water resources, communities and food supply across Central Asia.
Figure 1.
(a) Central Asian political map of countries (left) [14] and (b) environmental map (right) [15].
Since 2000, China has greatly expanded investment and engagement in Central Asia with a focus on energy, transport and consumer goods [16]. This has seen China become Central Asia’s key trading partner (25% of trade) to displace Russia’s (10%) traditional economic dominance in the region [17]. A twenty-fold increase in trade to >USD 200 billion annually (ibid), USD 18 billion in signed and claimed BRI projects and a role as the primary international lender has put China at the heart of regional economies. Here, countries present different versions of autocracy, with Turkmenistan and Tajikistan most restricted, followed by Uzbekistan and Kazakhstan: only Kyrgyzstan allows meaningful elections. As agrarian states during the Soviet era, agriculture continues to be a major employer, including >60% of labor in Tajikistan [6]. A lack of jobs, especially in farming and mining, has become a key trigger of massive labor out-migration to Russia [18]. Yet, BRI investment relies on Chinese workers [4,19], contributing to local dissatisfaction with the Chinese development approach and marked Sinophobia across the region [20,21].
An economically reasoned and efficient view of land dynamics sees Central Asia as a useful focus of Chinese agribusiness as an investment locus [12,22]. This offers two ready attractions—improving production methods and output and providing a new source of foodstuffs for the vast Chinese domestic market. The host-government welcome across the region encourages this thought and approach. The obverse is to question what the impacts will be on crop yield, water consumption and food availability for local populations. As Kraemer et al. [10] identify, in Kazakhstan the best and most suitable agricultural land is already extensively farmed; reintroducing previously-used marginal land will be of limited productivity. The contrasting directions point to core underlying issues: what does BRI mean for food security and water resources in Central Asian countries (Table 1)?

Table 1.
Social dynamics in Central Asia. Political insecurity—a positive number reflects higher state stability [23,24,25].
1.1. BRI in Central Asia
China’s BRI relations with central governments are strong; benefits are seen to accrue to leadership and elites. More problematic are social perceptions and community engagement, as China’s outsized presence from mining and road building to agriculture, logistics and dry ports has escalated tension and distrust [20,21]. Though autocratic states, enforcement of licenses, contracts and laws requires some public cooperation and tolerance. This challenge is clearest in Kyrgyzstan where violent protest has become the most effective way for communities to express dissatisfaction with national leadership as well as Chinese investment and practices [18]. In February 2020, such protests led to the cancellation of the USD 275 million Ata-Bashi Chinese-Kyrgyz Logistics Center in Naryn Province as residents blockaded the highway from China [26]. The increasingly contested nature of the Belt and Road Initiative in the region reflects a widespread belief about the additional (non-economic) impacts the program engenders. This started with concerns about water pollution and environmental degradation at mines [27], the use of tens of thousands Chinese workers rather than legally required 90% local staff [4,19] and perceived takeover and control of agricultural land in Kazakhstan [20,28]. Public perception of limited benefits from Chinese investment leads to greater examination of the unstated realms and implications of BRI.
An important point in the BRI rubric is its intentional lack of definition, malleable interpretation and inscrutable nature [1]. In being akin to ‘all things to all people’, the program lacks salient details, neglects geographical facts and ignores social context, often to its own detriment [2]. This encourages rumor and breeds public distrust of companies, Chinese nationals and regional governments [21]. Whilst stressed, sinophobia (fear) is more accurately characterized as ‘misosiny’—the dislike, anger and animosity locals feel towards Chinese [20]. Billions of promised investment dollars mean little in rural steppe communities where basic development, jobs, education and foodstuffs are immediate concerns [3]. In this paper we ground research in the environment to examine BRI impacts through the lens of landscape and food productivity. This means recognition of geographical limitations in water and climate, acknowledging topography and environmental constraints. Here, the BRI is not a nebulous construct but a process that has potential to develop or disrupt Central Asian food supplies and social stability.
1.2. Central Asian Drylands
Across the Eurasian Steppe, vast drylands are defined by low precipitation and moisture levels and high potential evapo-transpiration (PET) rates. Measured by the Aridity Index, sparsely vegetated deserts, including the Karakum and Kyzylkum, cover 70 percent of the land. Continental arid and semi-arid climates feature hot, dry summers (to +40 °C in July and August), and severe cold winters (November to March), which can reach −35 °C, with a warmer belt in the south. Other ecological zones include mountain, forest, marsh and even aquatic ecosystems [29]. Precipitation of ~200 mm (more in mountains, to 70 mm in deserts [16]) and frequent droughts challenge cultivation with Central Asia experiencing greater warming than the global average [30,31]. Glaciers in the Tien Shan, Pamir and Hindu Kush Mountains along the east and northeast border with China are a vital part of Central Asia’s water cycle, sourcing 50,000 km of rivers and 15,000 km2 of lakes. The Amu Darya (2540 km) and Syr Darya (2256 km) serve as borders and thus have been the locus of transboundary conflict for centuries [32]. Since 1960, 27 percent of glacial mass and 18 percent of the area has been lost to rapid melting [33].
In recent years, infrastructure development, human activity and climate change have had an adverse impact on the environment of Central Asia [34]. The development of transregional road and rail networks, construction of hydroelectric dams and expansion of irrigated agriculture have contributed to unprecedented shifts in the region’s fragile ecosystems [35]. Wang et al. [36] found that transport infrastructure had a negative effect in East and Central Asia. Water resources have been dramatically reduced by dam construction and the diversion of water for irrigation projects [37]. This affects diverse plant and animal life, 167 IUCN Red List of Threatened Species and RAMSAR wetlands [38]. The marked changes to climate and water regimes directly affects farming productivity (Table 2) [39].

Table 2.
Physical characteristics of Central Asian states [23,24,25,39].
The complexity of the region’s physical geography presents a major challenge for infrastructure in the region, whether it is planned railways and pipelines over the Karakoram Pass (4700 m) in the Himalayas, sea routes through the arctic or farming Chinese and Asian deserts. Sternberg et al. [2] identify landscape obstacles in Central Asia from access routes (Torugart Pass, Kyrgysztan 3700 m; Khulab Pass, Tajikistan 4200 m) and high earthquake vulnerability to melting glaciers, limited water sources and marginal steppe environments.
Assessing BRI implementation in Central Asia explores the environmental and social dynamics that affect agricultural productivity. These center on physical forces—water resources, soil, climate and climate change and geography. Related factors then stress irrigation, productivity, nutrition, labor and transport. A third angle is alternate food supply in the region, predominantly through livestock raising in marginal drylands that maximizes a grazing animal’s ability to convert limited vegetation into calories for humans. This is culturally embedded such as in the traditional festival dish Beshparmak, a horse meat-centered delicacy. BRI investment plans envelop and may reconfigure food systems, yet food security in Central Asia is poor [30,40]. What is unclear with program implementation is the implication for domestic food supply and human well-being in host countries.
1.3. Food Security
National food security and self-sufficiency depend on several factors, including water, environment, policy, management, technology, economics and infrastructure. Here, Central Asia is a most-vulnerable region, placed with sub-Saharan Africa as having high vulnerability for malnourishment and food insecurity [41]. Risk factors encompass rural poverty, youth and women’s marginalization, nutritional availability, agricultural policies (i.e., favoring cotton over foodstuffs), elite rent-seeking, climate and environmental parameters. Tajikistan produces 31% of domestic food needs whilst Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan and Uzbekistan are at 50% [42]. Excepting Kazakhstan, poor quality wheat is often used as animal feed. Land degradation, soil contamination through agro-chemicals, reduced organic matter, pollutants and a 47% salination rate identify poor agricultural practices [5,10]. Topsoil erosion, desertification, dust and loss of biodiversity reduce crop yields [5,43]. State sovereignty, extensive over-intensive farming inherited from the Soviets, protectionism, debt, reduced farmer income and poorly applied policies and tariffs contribute to Central Asia being a food importer rather than a potential breadbasket.
In China, food insecurity is very different, driven by a dietary shift to higher caloric intake and increased meat consumption, growing incomes and a dramatic shift from cultivation in the fertile central and southern plains to the less productive arid north and west [44]. The combination of high demand, heavy soil contamination and low water resources per capita has driven the expansion of food sources. This has led to a six-fold increase in food imports between 2000–2015 with imports now accounting for >30 of China’s foodstuffs [44]. The dependency is focused on a few countries (Brazil, Argentina, USA), increasing vulnerability to changing trade policies, tariffs and climates. This suggests the efficacy of a Central Asian neighbor policy as BRI develops growing infrastructure links. Khorgos, on the Chinese–Kazakh border, claims to be the largest inland dry port in the world [13,45]. China views the country as a new source of wheat, sugar, meat and cooking oil, whilst the Kazakhs export beef, wheat, dairy and recently, soybeans [13]. Though traditionally a pastoral, animal-raising region, livestock exports have received limited attention. In moving domestic supply to external geographies, China is encouraging imports to address food security concerns [11]. The conflicting food scarcity scenarios between the regional suppliers and benefactor is striking.
Aminjonov et al. [16] identify 51 rail and road (USD 23.5 billion value) and 26 agriculture and food development (USD 1.45 billion value) BRI projects in Central Asia. In total, 90% of the Chinese road investments are considered strategic with two-thirds being bilateral projects. Protests and public relations fiascos from Chinese land purchase and rental schemes, notably in Kazakhstan, have shifted investment to finance, capital and infrastructure, such as agro-industrial chains, over property ownership [11]. In Kazakhstan, by far the largest producer in the region (80% of crop yield), there is limited suitable land for crop expansion [10]. Research suggests expanded livestock raising on marginal land is a more productive approach to increasing foodstuffs (ibid).
1.4. Water
Water exemplifies transboundary contestation with major rivers like the Amu and Syr Darya Rivers flowing through several countries. Withdrawal rates for agriculture, new dams, water quality, salinity, dust and the drying of the Aral Sea exemplify regional issues. In 1992, disputes between new nations led to the creation of the Interstate Commission for Water Coordination of Central Asia to minimize conflict [46]. This was joined by the Regional Environmental Centre for Central Asia (CAREC) in 2001 and similar agreements [47]. Downstream users—Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan and Turkmenistan—are hegemons, whilst the poorer upstream nations Kyrgyzstan and Tajikistan lack influence and have land-locked dependency on their neighbors (ibid). Dam building and hydropower development, such as the massive Rogon Dam in Tajikistan, may lead to a more balanced regional water regime. Within the water framework sit national policies, development plans, intrastate conflict and immense investment needs to modernize Soviet water infrastructure. China’s desire to access water resources and share transboundary rivers, such as the Ili in Kazakhstan [48], complicate water dynamics in Central Asia.
1.5. Climate
Central Asia is a ‘hotspot’ of climate change [6,31]. The key water sources in Central Asia are the Tien Shan and Pamir Mountains that form the eastern border with China. Mountains to 7000 m and their glaciers are the source of the Amu and Syr Darya Rivers (Oxus and Jaxartes of old); these glaciers have shrunk by 40% in recent decades [6]. Thus farmland radiates out from the ranges to the west with rapidly decreasing water availability in the dryland expanse [43]. The rivers supply hydropower and vast irrigation networks established as part of the Soviet Union’s ‘Virgin Land’ agricultural scheme. Favored cotton, with production dominated by Uzbekistan, has shown transboundary water competition to be a constant source of interstate conflict [42]. The Intergovernmental Panel on Clmate Change (IPCC) [30,49] highlights drought, degradation and demand, making water supply a challenge in the region. Recall the human-induced Aral Sea disaster, driven by over-extraction during the Soviet era, as the Amu and Syr Darya Rivers no longer reach the basin [50]. The specter of high water stress through increased irrigation and urbanization encounter temperature increases and precipitation decreases that impact water supply and distribution. Concurrently, glacial sources are melting [30,49] and, in the lowlands, potential evapotranspiration (PET) is greater than precipitation [5,43]. The implied longer growing season and warmer winters could be beneficial for agriculture and favor northerly Kazakhstan. The region is projected to experience greater aridity, particularly to the west. Change is matched by non-climatic (human driven) desertification, heatwaves and a negative impact on crop yields as Central Asia experiences global warming greater than the global mean [30,32].
1.6. Central Asian Scenario
Food production and supply encounters additional challenges and conflict in Central Asia that are often neglected or poorly understood (Table 3). Known but seldom spoken of is the great Kazakh famine of 1930–1933 when 1.5 to 2.5 million Kazakhs (>25% of the population) died of hunger during Stalin’s rule in a preventable disaster [51]. This affects national perceptions of food supply and farming and alerts communities to issues of external (foreign) investment and control, particularly in Kazakhstan. In this light, recent protests over Chinese farmland contracts in Kazakhstan and logistic centers and mining in Kyrgyzstan take on a nationalist perspective [18,26,29]. The Chinese internment of ethnic Kazakhs in Xinjiang detention centers and news reports that Kazakhstan had historically been part of China raise concern [52]. Public dissent, if framed as non-political and about food supply, jobs or land degradation, may evade government censors and crackdown. The Chinese role in agriculture can be perceived as affecting food sovereignty; resistance shows the publics having some ability to organize and counteract government-to-government contracts and licenses.

Table 3.
Food production and vulnerability in Central Asia [23,24,25].
Here, we examine the built infrastructure—roads and railways—that transect environments across the vast steppe landscape. The Central Asian ecosystem’s ‘wicked problem’, as Pueppke et al. [48] stress, is the complex and dynamic challenges the BRI presents with inherent ramifications and unexpected consequences to host nations. We focus on the water-food nexus to investigate what BRI means for food security in the region. Infrastructure does more than reconfigure land, it divides and demarcates watersheds, encloses cultivation and reimagines social spheres. Chatty [53] first investigated how roads and pipelines can separate pastoralists from their herds and grazing lands, livestock from water and communities from government. Conceptually, investment in improving agricultural productivity is positive; grounded reality may present a different picture. As Chinese billions flow with policy and investment into Central Asia we grapple with the BRI footprint on water and food.
The immediate challenge is how to quantify a wide-ranging yet imprecise program (the BRI) to elucidate linkages between transport infrastructure and agricultural production. For this investigation, we used an inclusive approach, focusing on road and rail projects that loosely fall under the BRI rubric. This follows the pattern of China claiming related infrastructure, regardless of funder, as being under the infrastructure development umbrella. Work from Aminjonov et al. [16] provides parameters of BRI investment across Central Asia. Rail and road transport are valued at greater than USD 23 billion as of 2019. Table 4 highlights how Kazakhstan is the center of investment in the region.

Table 4.
Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) investment breakdown in Central Asia. All figures are multiplied by 1000 (×1000) [16].
2. Materials and Methods
Central Asia is part of the world’s largest grassland spanning 3,803,500 km2 across five predominantly agricultural countries—Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan and Uzbekistan. As home to ~70 million residents, there is low population density in the region. This stresses the importance of road and rail infrastructure to transport people and goods through rural landscapes. In the vast area, spatial data tools provide effective analysis of land cover.
2.1. Analysis of Land Cover Maps
To determine land cover change around BRI development, we utilized GIS to analyze land cover imagery within our specific study parameters. Imagery and features classes added to the GIS were reprojected to a regional Albers equal-area conic projection. Global land cover and transport data were clipped to our study area and 10-km buffer zones were created around each feature class. Within these zones, land cover change analysis between 2008 and 2018 was conducted using a post-classification comparison to reveal percent differences of our target indicators, including irrigated and rainfed agriculture, water features, and urban areas. The strengths and accuracy of the processing chain employed by CCI and C3S precluded a need for additional land cover classification. This approach presents some limitations as the accuracy of the change map is directly dependent on the accuracies of the parent maps. This may result in an over-estimated total change area, yet we believe this method to be most suitable to evaluate land cover change within our areas of interest.
2.2. Data Acquisition
We used a global BRI infrastructure database from the World Bank and 10-year (2008 and 2018) land cover data from the European Space Agency (ESA) Climate Change Initiative (CCI) and the Copernicus Climate Change Service (C3S). The BRI Database includes feature classes for transport data, roads, and inter urban transport, linked to BRI and are provided at the convenience of analysts researching BRI as of 2019 [54]. Landcover products from 2008 are based on the entire Medium Resolution Imaging Spectrometer (MERIS) Full and Reduced Resolution archive and Spot-Vegetation (SPOT-VGT) time series. Land cover products from 2018 rely on PROBA-Vegetation (PROBA-V) and Sentinel-3 OLCI (S3 OLCI) time series [55]. Both products were produced using the same processing chain and have a horizontal resolution of 300 m and spatial resolution of 0.002778°. Quality assessment of these land cover products consists of high temporal stability across years and robust and scientific validation, as defined by the Copernicus Global Land Service. Land surface classifications are defined using the United Nations Food and Agriculture 299 Organizations (UN FAO) Land Cover Classification System (LCCS). Detailed information regarding the methods for land cover classification can be found on the Copernicus Global Land Service website (https://land.copernicus.eu/global/products/lc) [55]. Additional geospatial data in this study includes administrative boundaries and secondary information about landcover classification types.
The most recent available satellite data were from 2018. Structuring the paper to analyze information from 2008 to 2018 coincides with China’s rapid expansion in agricultural production outside China. Since 2005, China has invested USD 43 billion in investment linked to the development of baseline infrastructure, e.g., roads, rails, seaports, and dry ports, to facilitate greater agriculture trade [13]. Using the World Bank integrated trade data set, we identify Central Asian agricultural and livestock exports from 2013 to 2018 to present a complete picture of food exports to China [56].
Whilst there are many ways to detect land cover change over time, land cover classification that relies on remotely sensed imagery is ideal to quantify change across large geographic areas with high temporal coverage. This approach, which has been used successfully to identify changes in a variety of terrestrial environments [57,58], including land-use specialization such as urbanization and agriculture intensification, is also particularly helpful to monitor and assess rural and remote areas, which are often inaccessible and difficult to obtain data using traditional methods. By understanding how land cover is changing along these BRI transport corridors, we are able to get a sense of what is unfolding across vast Central Asia.
3. Results
3.1. Extent of BRI Road and Rail Infrastructure in Central Asia
GIS investigation identified more than 15,000 km of rail and 20,000 km of roads linked to BRI crisscrossing Central Asia (Figure 2). Railway expansion increased significantly in Kazakhstan and Turkmenistan (the first and second largest recipients of BRI financing), creating transregional transport corridors that connect the far reaches of Central Asia. This spans from energy resources and cropland to Khorgos, the massive dry port and economic zone bordering China and Kazakhstan. Since 2008 the externally documented railway expansion [51,59], much of it in Kazakhstan, went for construction of the Khorgos-Aktau railway from the Chinese border to the Caspian Sea, the Beyney-Zhezkazgan railway and a second line to China at Altynkol, near Khorgos. These are vital links that now connect China with European hinterlands (Table 5). Rapid development of railways also occurred in Turkmenistan, which expanded its rail lines from 3095 km in 2008 to 7680 km in 2017, ultimately linking its agricultural areas, energy resources and urban centers with China.
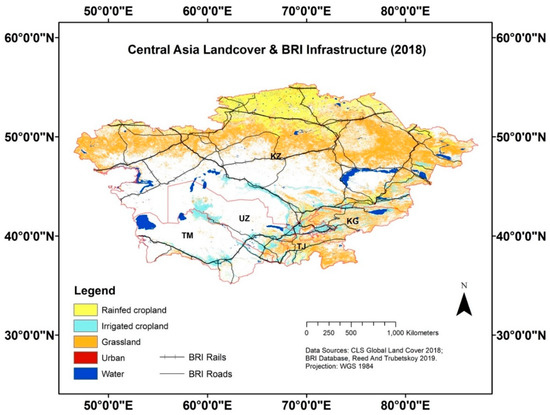
Figure 2.
Roads and railways in Central Asia, 2018.

Table 5.
Length of rail lines in Central Asia, 2008–2018 [51,59].
3.2. Land Cover Change Around BRI Infrastructure
Within a 10-km infrastructure buffer zone, various degrees of land cover change are observed along Central Asia’s BRI transportation corridors (Table 6). We note that comparing 2008 to 2018 irrigated agriculture was unchanged or decreased along potential BRI roads and rails in Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan. Turkmenistan had a 1–2% increase. During that same time frame, rainfed agriculture, more common in Kazakhstan and Uzbekistan, also decreased in an area around BRI infrastructure.

Table 6.
Change in irrigated and rainfed agriculture, water resources and urbanization, 2008–2018.
Water areas decreased in Kazakhstan and Turkmenistan but remained generally stable in Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan and Uzbekistan. Urban centers connected by these transportation corridors experienced substantial expansion within our 10-year analytical window. Most significantly, Turkmenistan’s urban areas increased by 91 percent in cities connected by BRI roads and 76 percent in cities connected by rail. Tajikistan also saw rapid growth, with its urban areas around BRI roads and rails increasing by 52 percent and 57 percent, respectively. Urban areas in Uzbekistan expanded by 48 percent around BRI rails and 47 percent around BRI roads. In Kazakhstan, urban areas have grown by 32 percent connected by BRI roads and 33 percent by BRI rails. Kyrgyzstan had a 14% rate of urbanization. Interestingly, urbanization was higher in the total national area than in the buffers zones (except in Kazakhstan).
Results show that whilst there has been an expansion of road and rail infrastructure that may be labeled as BRI-related, there in not an observable increase in agricultural land use. Though much attention has been given to the notion of land grabs, an increase in cultivation is not discernible along transport corridors. Whilst in some cases agricultural development may be farther from transport, the idea of potential export suggests transport corridors as an essential component. More likely, any additional farming is not on a large scale or covering significant hectares to have a marked satellite image footprint.
The decrease in agricultural land in the two major producers, Kazakhstan and Uzbekistan, is striking and suggests farming continues to encounter physical and economic challenges. This includes noted climate, precipitation and evapotranspiration factors, poor soils, salinization and marginal land of limited productivity. State policies, crop selection, irrigation, fertilizers and technical levels may affect agricultural suitability. The lack of further surface water cover over ten years may affect the ability to irrigate the drylands; additional supply would be dependent on groundwater resources. Coupled with the decline in rural populations and rapid urbanization across the region, farm labor capacity is changing. The Chinese BRI approach—to bring in Chinese laborers—is a conflict flashpoint in communities.
Changes along a 10-km transport infrastructure buffer is mirrored at national levels. A slight overall decline in agriculture indicates that, starting from 2008, and including BRI’s launch in 2013 to 2018 there has been a reduction in land under cultivation. Though roads and railways have increased, there has not be a similar growth in farming. Whilst a direct connection between transport corridors and agriculture requires ground truthing, satellite assessment suggests little change has accompanied the Belt and Road Initiative. However, if there has been a redistribution of food grown in the region to China through exports this would be through socio-economic channels (food and commodity trading) and not captured in the GIS data.
Examination of agricultural exports from Central Asia highlights that China, receiving 8%, is not a dominant export destination. Table 7 stresses that (1) Afghanistan is the major export market, (2) Russia continues to import significantly more agricultural goods than China, and (3) that Central Asian agricultural exports have increased 26% over the 5 year period. China continues to export more foodstuffs to Central Asia (USD 477 m) than it imports (USD 284 m), with almost 2/3 of exports going to Kazakhstan. The growth and reallocation of exports, particularly to Afghanistan, suggests that the BRI has not had a disruptive impact on regional supply. An ancillary concern is that whilst food availability may have increased, the region remains food insecure as it continues to import food to meet domestic needs (see Section 1.3) [31].

Table 7.
Central Asian agricultural exports (in USD, multiply by 1000) *, 2013–2018 [56].
Whilst livestock is an integral component of food supply, it is difficult to assess grazing or production changes through satellite imagery. Here, we evaluated livestock numbers to discern possible BRI links. Between 2013–2018, livestock production, measured by livestock units [52,56], increased 20% in the region (Table 8). This upward trend was driven by a 26% rise in cattle in both Kazakhstan and Uzbekistan. During this time Central Asian livestock exports almost doubled, suggesting growing external markets (Table 9). Though exports to China tripled from a low base, this figure comprised about 5% of total livestock exports and was dwarfed by exports to Russia, Afghanistan and within the region. This suggests China is a potential growth market but that it has limited impact on food security in the region.

Table 8.
Livestock units produced in Central Asia, 2013–2018.

Table 9.
Central Asian livestock exports, 2013–2018 [56].
4. Discussion
Findings identified two striking trends from 2008–2018—that land under cultivation is stagnant and that water resources are decreasing in the largest agriculture producers (Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan) and static in Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan and Turkmenistan. These factors have significant implications for regional food production, stressing Central Asia’s already vulnerable food resources [31,40]. Furthermore, results question potential BRI plans for expanded agricultural investment and production for export. Rather than increasing cultivation and crop resources, the dramatic trend towards urbanization reflects significant resident out-migration and suggests a hollowing-out of the Central Asian countryside. The lack of jobs, investment and educational opportunity posits that marginal rural livelihoods are forgone for perceived better prospects away from the farming heartland. The takeaway is that agriculture faces multiple structural challenges as well as those encountered from new foreign investment. In fact, investigation does not find that BRI has significant impact on food security in Central Asia. Whilst the program generates much discussion, this relates to regional political perceptions and government perceptions of social stability rather than to food supply.
The stark message is that Central Asian agriculture is of currently of limited importance to China. Regional exports comprise <0.003% of China’s agricultural imports (cereals, vegetables), an amount below Sudan or Peru [52,56]. The value of food products (produced consumables) from Iceland is greater than those from Central Asia (ibid). The prospect of Chinese investment generates much attention and anxiety across the region, yet from 2013 to 2018 agricultural exports were much greater to Afghanistan without complaint. The story with energy is similar—mineral imports from Kazakhstan to China ranks 17th, the only regional country in the top 50. In fuels, Turkmenistan is China’s 10th largest trading partner, Kazakhstan the 19th (ibid). Trade data makes clear that Central Asia is not a major agricultural partner of China. Thus, fears of investment in farming and its strategic implications are overstated, even pretentious, a product of political and social imaginaries centered on regional self-importance presented as self-survival. The question is less will China takeover food supplies but more can states produce adequate food for their populations, will elites favor Chinese financial interests over citizens and can China more effectively communicate its BRI ‘win-win’ approach in Central Asia.
A more salient question may be what is the impact of BRI on public perception, communities, social stability and governance in nations. Economics and environment currently favor Kazakhstan as the major investment recipient, dominant agricultural producer and most developed economy. Here, Chinese engagement has a successful history in energy resources and the cross-border volume of trade is large enough to attract attention and cooperation. Conversely, states such as Tajikistan and Kyrgyzstan are limited in size and opportunity and are thus less likely to receive major BRI investment. They effectively court second-tier investment, companies less likely to follow Chinese or international operational standards. The resulting unsatisfactory outcomes at community levels malign the BRI brand but are insignificant in China’s grander ambitions [60]. In essence, there are multiple BRIs and perspectives on impacts and benefits.
The prospect of BRI has become a dominant narrative across steppe nations steeped in awe and fear of the neighboring hegemon. Infrastructure is being built by a range of stakeholders, including China, the Asian Development Bank and governments. The economic clarity of BRI has exposed the shortcomings and corruption of presidents, potentates and dictators across the region [4]. In Kyrgyzstan, two former prime ministers and one ex-president are in prison and two ex-presidents in exile, a process that exemplifies the corrupt and disruptive investment politics in the region [18]. Through debt-driven investments, which are guaranteed by national governments, China has presented infrastructure packages that serve its own interests [4]. This includes addressing domestic over-capacity, exportation of Chinese jobs, new economic diplomacy and politicizing debt to China’s strategic advantage. That nations agree to terms exposes them to opprobrium and unrest from dissatisfied publics. Deflecting responsibility to the hegemon can be effective, but it is not a complete picture or explanation. Until states become effective representatives of their citizens, in public spheres, the BRI in Central Asia will be conflated with exploitive practices, elite rent-seeking and community disadvantage.
Our research found roads and railways had not expanded as greatly nor with as much impact as dominant parables suggest. Within the agglomerated transport data a marginal site impact was possible. The notion of major road and rail construction was not evident through GIS evaluation. Data identified that agricultural land evidenced minimal change, suggesting that infrastructure, BRI or otherwise, had a marginal impact on land under cultivation. Decreases in rainfed agriculture, particularly near roads, also suggests a role for climate parameters. Clearly documented was significant urbanization across the nations. Also noteworthy was a decrease in national water resources in the two largest agricultural producers, Kazakhstan (−5%) and Uzbekistan (−28%).
The promise of BRI is having difficulty outlasting the uncertain benefits to Central Asian citizens. Unintentionally it has effectively galvanized pre-existing sinophobia (or Gezgin’s ‘misosiny’ [20]), creating new avenues of complaint for dissatisfied publics. Roads and railways are conflated with perceived land grabs, exploitation and corruption. COVID-19 and related border closures and temporary isolation from China strikes a nationalist chord in the region [21]. Here, we find little BRI impact on food security, yet the Central Asian ‘streetocracy’ [61] will pass its own judgment, and not in China’s favor.
5. Conclusions
Research started with the grave, contemplative question of what the BRI means for food security in Central Asia. Investigation found this to be a ‘damp squib’, a minor issue sidelined by massive Chinese investment in energy, minerals and industry. When Central Asia comes behind Sudan in crop exports to China one can conclude agriculture is a minor factor in the regional Belt and Road Initiative. That farming captures public attention suggests an emotional response to Chinese investment and a weakness in host government public engagement. Much relevant data (World Bank, FAO, Aquastat) is freely available and would strengthen domestic understanding and engagement. This could include better public communication, improved government responsiveness, more focused complaints and drawing multiple stakeholders into the debate (communities, officials, nascent civil society, experts, international agencies) in available spheres in the autocratic region.
Food is a major concern; the region remains highly vulnerable to food scarcity. This is a national issue as the region is dependent on food imports, with China exporting 59% more food to the region than it imports (World Bank 2018). Thus, agriculture, like land, is located in situ; the problem is one of governance, policy, water, and community engagement. A clearer picture of BRI should be presented to the public in Central Asia by governments, companies and the international community. This may start with transparency in contracts, licenses, fees and taxes paid and direct community benefit. This could be matched by verifiable environmental and social impact assessments for infrastructure projects. Furthermore, borrowing from mining development, the positive concept of Social License to Operate in communities and nations can be applied to BRI and similar investments. Whilst China may bear responsibility for mining or energy mishaps in the region, agricultural challenges and food security are not driven by BRI investment or scheming. This is Central Asian state failure alone.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.S.; data curation, T.S., C.M. and B.H.; writing—original draft preparation, T.S.; writing—review and editing, T.S. and C.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grant Numbers (JP) 19H04362 (Risk assessment of the regional impact of the China “One-Belt-One-Road” (OBOR) project) and the UK’s Economic and Social Research Council and Global Challenges Research Fund (GCRF) Grant Ref: ES/S000798/1.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Tesse de Boer and Steven Pueppke for their inspiration. Kemel Toktomushev at the University of Central Asia–Kyrgyzstan and Aizhan Smailova at Al-Farabi Kazakh National University organised key events and discussions. Research is part of the ‘GOBI FRAMEWORK: Mediation model for sustainable infrastructure development’ project.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Jones, L.; Zeng, J. Understanding China’s ‘Belt and Road Initiative’: Beyond ‘grand strategy’ to a state transformation analysis. Third World Q. 2019, 40, 1415–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sternberg, T.; Ahearn, A.; McConnell, F. Central Asian ‘characteristics’ on China’s new Silk Road: The role of landscape and the politics of infrastructure. Land 2017, 6, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogilevskii, R. Kyrgyzstan and the Belt and Road Initiative; Working Paper #50; University of Central Asia: Bishkek, Kyrgyzstan, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Pantucci, R. China in Central Asia: The First Strand of the Silk Road Economic Belt. Asian Aff. 2019, 50, 202–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Qian, X.; Liu, T. Belt and road initiative and Chinese firms’ outward foreign direct investment. Emerg. Mark. Rev. 2019, 41, 100629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blondin, S. Environmental migrations in Central Asia: A multifaceted approach to the issue. Cent. Asian Surv. 2019, 38, 275–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frachetti, M.D.; Smith, C.E.; Traub, C.M.; Williams, T. Nomadic ecology shaped the highland geography of Asia’s Silk Roads. Nature 2017, 543, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polo, M.; Latham, R.E. The Travels of Marco Polo. Translated, with an Introduction, by Ronald Latham; Penguin Books: London, UK, 1958. [Google Scholar]
- Roerich, G. Trails to Inmost Asia: Five Years of Exploration with the Roerich Central Asian Expedition. J. R. Asiat. Soc. Great Br. Irel. 1932, 3, 713–717. [Google Scholar]
- Kraemer, R.; Prishchepov, A.V.; Müller, D.; Kuemmerle, T.; Radeloff, V.C.; Dara, A.; Terekhov, A.; Frühauf, M. Long-term agricultural land-cover change and potential for cropland expansion in the former Virgin Lands area of Kazakhstan. Environ. Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 054012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenderdine, T. Insurance plus futures: Agricultural commodity price reform in China. Asia Pac. Policy Stud. 2018, 5, 331–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erokhin, V.; Diao, L.; Du, P. Sustainability-Related Implications of Competitive Advantages in Agricultural Value Chains: Evidence from Central Asia—China Trade and Investment. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1117. [Google Scholar]
- GRAIN. Chinese Agribusiness Goes Global. 2019. Available online: Grain.org/en/article/6133-the-belt-and-road-initiative-chinese-agribusiness-going-global (accessed on 19 June 2020).
- Wikimedia Commons. Central Asia—Political Map. 2008. Available online: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/66/Central_Asia__political_map_2008.svg/1280px-Central_Asia_-_political_map_2008.svg.png (accessed on 1 July 2020).
- Kariyeva, J.; Van Leeuwen, W.J.D. Eironmental Drivers of NDVI-Based Vegetation Phenology in Central Asia. Remote Sens. 2011, 3, 203–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aminjonov, F.; Abylkasymova, A.; Aimée, A.; Eshchanov, B.; Moldokanov, D.; Overland, I.; Vakulchuk, R. BRI in Central Asia: Overview of Chinese Projects. Cent. Asia Reg. Data Rev 2019, 20, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Kokushkina, I.; Soloshcheva, M. The role of central Asia in the “One Belt—One Road” initiative. Iran Cauc. 2019, 23, 283–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sternberg, T. Conflict and contestation in Kyrgyz mining infrastructure. Extract. Ind. Soc. 2020, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Schild, L.; Ling, C.; Blackburn, J.; Stringhini, G.; Zhang, Y.; Zannettou, S. “Go eat a bat, chang!”: An early look on the emergence of sinophobic behavior on web communities in the face of Covid-19. arXiv 2020. arXiv:2004.04046. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.04046 (accessed on 12 May 2020).
- Gezgin, U. Russian and Central Asian Views on China’s Belt & Road Initiative. Çanakkale Onsekiz Mart Üniversitesi Uluslararası Sos. Bilimler Derg. 2020, 5, 135–148. [Google Scholar]
- Toktomushev, K. Coronavirus and Sinophobia: Fear along the Belt and Road. Chinafocus 2020. Available online: www.chinausfocus.com/energy-environment/coronavirus-and-sinophobia-fear-along-the-belt-and-road (accessed on 1 June 2020).
- Nurgozhayeva, R. Rule-Making, Rule-Taking or Rule-Rejecting under the Belt and Road Initiative: A Central Asian Perspective. 2020. Chin. J. Comp. Law 2020, 8, 250–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CIA Factbook. 2020. Available online: cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/kghtml (accessed on 19 July 2020).
- Food and Agriculture Organization. Aquastat. 2020. Available online: fao.org/aquastat/en/countries-and-basins/ (accessed on 19 July 2020).
- Food and Agriculture Data. Country Profiles. 2020. Available online: fao.org/faostat/en/#country/208 (accessed on 19 July 2020).
- Putz, C. Kyrgyz-Chinese Joint Venture Scrapped After Protests. Diplomat 2020. Available online: thediplomat.com/2020/02/kyrgyz-chinese-joint-venture-scrapped-after-protests/ (accessed on 22 April 2020).
- Horrocks-Taylor, J. Dirty Water, Muddied Politics: Hybridisation of Local and National Opposition to Kumtor Mine, Kyrgyzstan. Land 2018, 7, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakulchuk, R.; Øverland, I.; Aminjonov, F.; Abylkasymova, A.; Eshchanov, B.; Moldokanov, D. BRI in Central Asia: Agriculture and Food Projects. Central Asia Reg. Data Rev. 2019, 27, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, J.; Kulmatov, R. An Overview of Environmental Issues in Central Asia. In Environmental Problems of Central Asia and their Economic, Social and Security Impacts; Qi, J., Evered, K.T., Eds.; NATO Science for Peace and Security Series C: Environmental Security; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Climate Change and Land. 2019. Available online: ipcc.ch/2019/ (accessed on 19 July 2020).
- Zou, S.; Jilili, A.; Duan, W.; Maeyer, P.; de Voorde, T. Human and natural impacts on the water resources in the Syr Darya River Basin, Central Asia. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, W.; Chen, Y.; Zou, S.; Nover, D. Managing the water-climate-food nexus for sustainable development in Turkmenistan. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 220, 212–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GFZ GeoForschungsZentrum Potsdam, Helmholtz Centre. Substantial glacier ice loss in Central Asia’s largest mountain range. ScienceDaily. 17 August 2015. Available online: www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2015/08/150817132329.htm (accessed on 2 August 2020).
- Reyer, C.; Otto, I.; Adams, S.; Albrecht, T.; Baarsch, F.; Cartsburg, M.; Coumou, D.; Eden, A.; Ludi, E.; Marcus, R.; et al. Climate change impacts in Central Asia and their implications for development. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2017, 17, 1639–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, W.; Zou, S.; Chen, Y.; Nover, D.; Fang, G.; Wang, Y. Sustainable water management for cross-border resources: The Balkhash Lake Basin of Central Asia, 1931–2015. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 263, 121614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Lim, M.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, L.; Lee, P. Railway and road infrastructure in the Belt and Road Initiative countries: Estimating the impact of transport infrastructure on economic growth. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2020, 134, 288–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, N.A.; Pueppke, S.G.; Uderbayev, T. The Current Status and Future of Central Asia’s Fish and Fisheries: Confronting a Wicked Problem. Water 2017, 9, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IUCN. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2020-2. 2020. Available online: www.iucnredlist.org (accessed on 9 July 2020).
- Sternberg, T. Moderating Climate Hazard Risk through Cooperation in Asian Drylands. Land 2018, 7, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Alhussam, M.; Abu Risha, O.; Memon, B. Analyzing the Relationship between Agricultural FDI and Food Security: Evidence from Belt and Road Countries. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baer-Nawrocka, A.; Sadowski, A. Food security and food self-sufficiency around the world: A typology of countries. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0213448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyrouse, S. Food Security in Central Asia: A Public Policy Challenge. PONARS Eurasia. 2013. Available online: ponarseurasia.org/memo/food-security-central-asia-public-policy-challenge (accessed on 12 July 2020).
- Hamidov, A.; Helming, K.; Balla, D. Impact of agricultural land use in Central Asia: A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2016, 36, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Ridoutt, B.; Thorp, K.R.; Wang, X.; Lan, K.; Liao, J.; Tao, X.; Wu, C.; Huang, J.; Chen, F.; et al. Water-scarcity footprints and water productivities indicate unsustainable wheat production in China. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 224, 105744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, A. Crossing Khorgos: Soft power, security, and suspect loyalties at the Sino-Kazakh boundary. Political Geogr. 2020, 76, 102070. [Google Scholar]
- Interstate Commission for Water Coordination of Central Asia. 2017. Available online: www.icwc-aral.uz/activity.htm (accessed on 19 June 2020).
- Zhupankhan, A.; Tussupova, K.; Berndtsson, R. Could changing power relationships lead to better water sharing in Central Asia? Water 2017, 9, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pueppke, S.G.; Zhang, Q.; Nurtazin, S.T. Irrigation in the Ili River basin of Central Asia: From ditches to dams and diversion. Water 2018, 10, 1650. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2014: Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014; pp. 1327–1370. [Google Scholar]
- Sternberg, T. Water megaprojects in deserts and drylands. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2016, 32, 301–320. [Google Scholar]
- Cameron, S. The Kazakh Famine of 1930–33: Current Research and New Directions. East/West J. Ukr. Stud. 2016, 3, 117–132. [Google Scholar]
- Reuters. Kazakhstan Summons Chinese Ambassador in Protest over Article. 2020. Available online: reuters.com/article/us-kazakhstan-china-idUSKCN21W1AH (accessed on 19 June 2020).
- Chatty, D. Petroleum exploitation and the displacement of pastoral nomadic households in Oman. Cent. Migr. Stud. Spec. Issues 1994, 11, 87–106. [Google Scholar]
- Reed, T.; Trubetskoy, A. Assessing the Value of Market Access from Belt and Road Projects; The World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2019. Available online: datacatalog.worldbank.org/dataset/bri-database-reed-and-trubetskoy-2019 (accessed on 21 July 2020).
- European Union, Copernicus Land Monitoring Service; European Environment Agency, European Union, Copernicus Land Monitoring Service, European Environment Agency (EEA). Land Cover Classification Gridded Maps from 1992 to Present Derived from Satellite Observations. 2018. Available online: cds.climate.copernicus.eu/cdsapp#!/dataset/satellite-land-cover?tab=overview (accessed on 20 July 2020).
- World Bank. World Integrated Trade Solution (by Country). 2018. Available online: wits.worldbank.org/CountryProfile/en/Country/CHN/Year/2018/TradeFlow/Import/Partner/by-country/Product/16-24_FoodProd (accessed on 1 August 2020).
- Nabil, M.; Zhang, M.; Bofana, J.; Wu, B.; Stein, A.; Dong, T.; Zeng, H.; Shang, J. Assessing factors impacting the spatial discrepancy of remote sensing based cropland products: A case study in Africa. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2020, 85, 102010. [Google Scholar]
- Buchhorn, M.; Lesiv, M.; Tsendbazar, N.-E.; Herold, M.; Bertels, L.; Smets, B. Copernicus Global Land Cover Layers—Collection 2. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1044. [Google Scholar]
- Knoema. Available online: https://knoema.com/atlas/Kazakhstan/Length-of-rail-lines (accessed on 13 August 2020).
- Tchoroev, A. Reclamation: Lack of awareness and post-mining mismanagement in Kyrgyzstan. In Mining Lifecycles in Central Asia and Mongolia; Routledge: Abingdon, UK, in press.
- Ludwig, J. The Kyrgyz Streetocracy and the Unraveling of the Belt and Road. Initiative. 2020. Available online: www.sageinternational.org.au/articles/fractured-zones/the-kyrgyzstreetocracy-and-the-unraveling-of-the-belt-and-road-initiative/ (accessed on 1 June 2020).
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).