Abstract
Grey water has been identified as a potential source of water in a number of applications e.g., toilet flushing, laundering in first rinsing, floor cleaning, and irrigation. The major obstacle to the reuse of grey water relates to pathogens, nutrients, and organic matter found in grey water. Therefore, much effort has been put to treat grey water, in order to yield high-quality water deprived of bacteria and with an appropriate value in a wide range of quality parameters (Total Organic Carbon (TOC), nitrate, phosphate, ammonium, pH, and absorbance), similar to the values for tap water. The aim of this study was to treat the real grey water, and turn it into high-quality, safe water. For this purpose, the real grey water was treated by means of a sequential biological reactor (SBR) followed by ultrafiltration. Initially, grey water was treated in a laboratory SBR reactor with a capacity of 3 L, operated in a 24 h cycle. Then, SBR effluent was purified in a cross-flow ultrafiltration setup. Treatment efficiency in SBR and ultrafiltration was assessed using extended physicochemical and microbiological analyses (pH, conductivity, color, absorbance, Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD), Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD5), nitrate, phosphate, ammonium, total nitrogen, phenol index, nonionic and anionic surfactants, TOC, Escherichia coli, and enterococci). Additionally, ultrafiltration was evaluated in terms of fouling behavior for three polymer membranes with different MWCO (molecular weight cut-off). The values of quality parameters (pH, conductivity, COD, BOD5, TOC, N-NH4+, N-NO3−, Ntot, and P-PO43−) measured in SBR effluent did not exceed permissible values for wastewater discharged to soil and water. Ultrafiltration provided the high-quality water with very low values of COD (5.8–18.1 mg/L), TOC (0.47–2.19 mg/L), absorbanceUV254 (0.015–0.048 1/cm), color (10–29 mgPt/L) and concentration of nitrate (0.18–0.56 mg/L), phosphate (0.9–2.1 mg/L), ammonium (0.03–0.11 mg/L), and total nitrogen (3.3–4.7 mg/L) as well as lack of E. coli and enterococci. Membrane structural and surface properties did not affect the treatment efficiency, but did influence the fouling behavior.
1. Introduction
Water is emerging as one of the single most important resources of Planet Earth for the prosperity of the economy and human life. However, freshwater resources have been increasingly polluted and depleted globally. The constant increase in water usage and climate change—such as altered weather-patterns (including droughts or floods), deforestation, and increased pollution—are the main driving forces for the rising global scarcity of water. It is experienced especially by European countries, due to an improvement of living standards and economic development in recent years. Along with economic development, the total water use in Europe has been sharply increasing in the last decades [1]. Grey water recycling is the solution to the growing challenges associated with water shortages [2]. Quantitatively, grey water represents around 65% of the total volume of domestic sewage, making it the largest stream for water reuse [3]. Grey water contains nitrate, phosphate, organic matter, surfactants, pharmaceuticals, oils, and pathogens [4]. Therefore, the treatment of grey water before its reuse is necessary. Purified grey water could be reused for cleaning, car washing, concrete production, and irrigation [5,6]. The guidelines of the World Health Organization (WHO) point to four criteria for the reuse of grey water: hygiene, aesthetics, environmental tolerance, and economic feasibility. WHO recommends biological treatment and ultrafiltration in order to obtain high-quality water. However, the requirements that define “high water quality” are too sweeping and do not show the physical and chemical specifications. It is caused by a number of possible applications of reclaimed grey water that require various different quality standards. In 2006, WHO set microbiological criteria that reclaimed grey water should meet for its reuse for restricted and non-restricted agricultural irrigation. [7,8].
Numerous approaches, including low and high pressure-driven membrane techniques [9,10,11], coagulation [12,13], biological processes, and membrane bioreactors [3], have been proposed for the treatment of grey water. These technologies vary in both complexity and performance. For example, Li et al. recommended the employment of an aerobic treatment coupled with membrane filtration or an aerobic treatment with sand filtration, with disinfection as the last step for both systems [8]. Similarly, Ding et al. suggested applying a system that combines membrane filtration with biological treatment in a gravity-driven membrane filtration system. In this technique, the fouling layer attached to the membrane stabilizes a flux and improves the treatment effects due to the microbial activity of biofilm [14]. From these studies, it is clear that grey water requires both biological and physical treatment to meet non-potable reuse standards. Aerobic biological processes are effective to remove organics from grey water. Physical processes, particularly membrane filtration, are recommended for polishing effluents from the biological treatment step [9,15]. Ultrafiltration (UF) retains bacteria, suspension, colloids, natural organic matter, and partial micropollutants such as pharmaceuticals and personal care products. However, the efficiency of ultrafiltration in the removal of individual pollutants depends on membrane type and its properties such as molecular weight cut-off (MWCO). Membrane properties such as contact angle and zeta potential play an important role in the fouling behavior and hydraulic performance of the system [16]. Membrane fouling results in a permeability loss due to the increase in hydraulic resistances in the filtration system, especially in the case of porous polymer membranes. There are many studies reported in the literature that aimed at mitigating the fouling by selecting the most optimal operational parameters for ultrafiltration such as transmembrane pressure, velocity, temperature, or developing a cleaning method. [17,18,19]. On the other hand, they do not consider the effect of structure and surface properties of membrane i.e., MWCO and contact angle on fouling behavior. Another issue is that most of these studies were conducted for artificial grey water. While artificial grey water provides useful information for model development, it does not reflect real conditions, and the composition affects the process significantly.
The main novelty of this work shows that high-quality water can be obtained from grey water. For a need of this study, we established that high-quality water is water: (1) that fulfills criteria included in the Polish Regulation from the Minister of the Environment on the conditions to be met when discharging wastewater into water or soil and (2) with the basic quality parameters (smell, color, turbidity, TOC, ammonium, nitrate, chloride, conductivity, hardness, E. coli, and enterococci) like the standards for tap water. In order to gain this purpose, real grey water was treated using a sequential biological reactor (SBR) followed by ultrafiltration. Treatment efficiency was evaluated for SBR and ultrafiltration using extended physicochemical and microbiological analyses. Additionally, ultrafiltration was studied in terms of fouling behavior for three polymer membranes with different MWCO. In that context, the novelty of this work is also a determination of the effect of membrane type on the treatment of SBR effluent and fouling behavior.
2. Methodology
2.1. Grey Water Characteristic
Grey water was collected from a single-family household located in Silesia in Poland. This house is equipped with an installation to collect grey water from the shower, kitchen sink, and washing machine. The characteristic of the grey water is given in Table 1. Samples were taken directly from a storage tank and transported to the lab facilities, stored at 4 °C and analyzed within 48 h according to the methodology presented in Section 2.6.

Table 1.
Characteristic of grey water, as taken.
2.2. Biological Treatment in SBR
The SBR technology used provides for the dosing of wastewater in alternately used anaerobic reactor oxygen conditions. This guarantees a high degree of removal of carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus compounds. The operation of the reactor is simple, and during operation, modifications of individual separate phases of the technological cycles are possible. The biological process was carried out under laboratory conditions, using activated sludge taken from the municipal sewage treatment plant in Gliwice, Poland. The treatment of grey water was carried out in a laboratory SBR with a capacity of 3 L. During the treatment experiment, the excessive activated sludge was periodically removed from the SBR in order to keep its concentration at the level of 3.0 g/L. The solid retention time (SRT) was 20 days. The load of the sludge with the contaminants was equal to 0.1 g COD/gDMd and the concentration of oxygen was at the level of 3 mg/L. The system was operated as the sequential biological reactor in one cycle per day. The length of particular operation stages was as follows: filling and mixing phase for 2 h, aeration phase for 21 h, and sedimentation and SBR effluent removal for 1 h. The aeration system consisted of aquarium cubes placed on the bottom of the tank with connected aeration pumps of the Tetratec APS 300 type (Tetra, Melle, Germany). In order to thoroughly mix the contents of the chamber, it was mixed by means of a magnetic stirrer with the possibility of speed regulation in the range from 50 to 1000 revolutions/min. The chamber was filled and emptied using Heidolph peristaltic pumps (Heidolph, Schwabach, Germany). The electronic weekly programmer controlled the start and end of the relevant SBR work phase.
2.3. SBR Effluent Treatemnt by Ultrafilltration–Ultrafiltration Run
Ultrafiltration is especially dedicated to drinking water production because colloids, particulates, macromolecules, and pathogens are removed in this process. It is also a suitable process to purify effluent after biological treatment as this effluent contains bacteria, particles of organic matter, and suspended solids. Ultrafiltration was carried out in the lab, using a scale cross-flow configuration equipped with a plate-and-frame membrane module SEPA CF-NP (GE Osmonics, Minnetonka, MN, USA) as seen in Figure 1. Three ultrafiltration membranes were used in separate processes. Membrane properties are presented in Table 2. Before each experiment, the clean water flux was determined using ultrapure water. The process was operated at a constant pressure of 5 bar and a constant temperature of 22 ± 1 °C and a constant velocity of 1 m/s with continuous dosing of SBR effluent to the feed tank. Each filtration run consisted of three cycles including 60 min of filtration followed by forward flushing with ultrapure water during 60 s. The volume of permeate was monitored in order to determine the permeability from the following equation:
where: is permeability (L·m−2·h−1·bar−1) in short (LMHB), is permeate volume (L), is membrane surface area (m2), is permeate time collection (h), and is transmembrane pressure (bar).
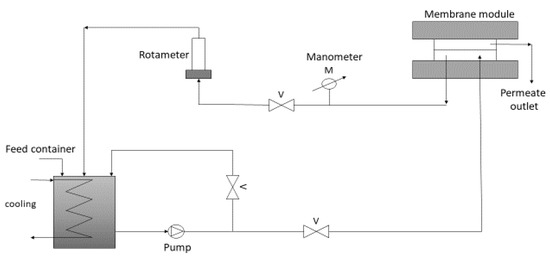
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of the cross-flow filtration set-up.

Table 2.
Properties of ultrafiltration membranes.
2.4. Membrane Fouling Characterization
In this study, hydraulic resistances were used to characterize the fouling behavior of ultrafiltration membranes treating SBR effluent. Hydraulic resistances of membrane and fouling layer were calculated using the resistance in the series model and Darcy’s law using the correlations as shown below [20].
where: k is hydraulic resistance, where subscripts m, f, irr, rev, and tot are related to membrane, fouling, hydraulically irreversible fouling, hydraulically reversible fouling, and total (m−1), respectively, J is the flux (m3·m−2·s−1), Δp is the transmembrane pressure (kg·s−2·m−1), and µ is the dynamic viscosity of water at given temperature (kg·m−1·s−1). Membrane resistance () was measured for the clean membrane with ultrapure water prior to feed water filtration. Hydraulically irreversible fouling was determined from the flux after forward flushing, while hydraulically reversible fouling was determined from the difference in fouling and irreversible resistances.
2.5. Membrane Characterization
Zeta potential of membranes was determined by the electrokinetic analyzer SurPASS ™ 3 (Anton Paar, Graz, Austria). Measurements of the contact angle were performed using the goniometer PG-1 (Fibro System AB, Hägersten, Sweden) and the sessile drop method was applied. By syringe on top, a drop of ultrapure water was put on the dried membrane surface. Through an enlarged projection of the water drop on the gauge, the value of the contact angle was measured. For every type of membrane, 10 samples were measured and the average value was calculated.
2.6. Quality Analysis and Microbiological Assessment
The treatment efficiency in SBR and ultrafiltration was evaluated by the monitoring of the typical quality parameters (color, turbidity, COD, BOD5, TOC, phenolic index, absorbance of UV254, nitrate (N-NO3−), phosphate (P-PO43−), ammonium (N-NH4+), total nitrogen (Ntot), conductivity, pH, and anionic and non-ionic surfactants). Color and turbidity measurements were performed with a UV-Vis Spectroquant® Pharo 300 (Merck, Kenilworth, NJ, USA). Phenolic index, COD, nitrate, phosphate, ammonium, total nitrogen, and anionic and non-ionic surfactant concentrations were determined spectrophotometrically with Merck test kits (codes of the Merck test kits are given in Table S1). The absorbance was measured at 254 nm, using a UV-visible light (UV-Vis) Cecil 1000 (Analytik Jena AG company, Jena, Germany). TOC was measured using a TOC-L series analyzer (Shimadzu, Kioto, Prefektura Kioto, Japan). pH and conductivity were monitored by multifunctional analyzer CX-461 (Elmetron, Zabrze, Poland). The BOD5 was determined by respirometric measurement using the OXI Top System WTW set (Xylem Analytics, Weilheim Germany). Microbiological analysis including E. coli and enterococci was conducted by an external accredited lab according to ISO methods PN-EN ISO 9308-1:2014-12/PN-EN ISO 9308-1/A1:2017; PN-EN ISO 7899-2:2004.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Grey Water Treatment in SBR
3.1.1. Reduction of COD, BOD5, and TOC
The biological sewage treatment aimed to reduce biodegradable organic matter and remove the biogenic substances i.e., nitrogen and phosphorus. In the preliminary stage, the activated sludge was taken from the municipal wastewater plant, then it was adapted to a new influent (grey water). The results discussed in Figure 2, Figure 3 and Figure 4 show the analysis of individual parameters after the adaptation process. Figure 2 shows the SBR system performance in relation to the concentration of organic compounds in purified grey water. Detailed results of physicochemical analyses are presented in Table S2 (in Supplementary file).
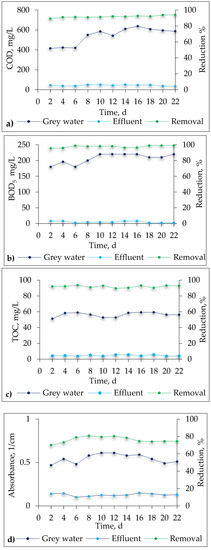
Figure 2.
The performance of the sequential biological reactor (SBR) system with respect to the changes in the concentration of the organic compounds.
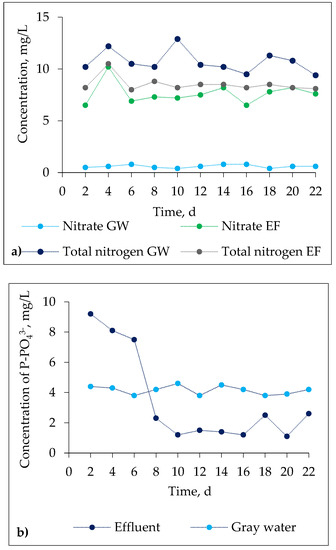
Figure 3.
The performance of the SBR system with respect to the changes in the concentration of the nutrients. GW—grey water, EF—effluent.
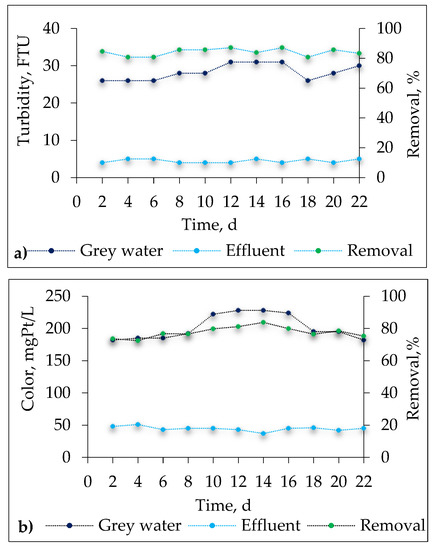
Figure 4.
The removal performance of the SBR system with respect to the changes in the color and the turbidity.
It was shown that the degree of pollution removal was high, and the values of the quality parameters in SBR effluent did not exceed the permissible values included in the currently in force in Poland, Regulation of the Minister of the Environment on the conditions to be met when discharging wastewater into water or soil [21]. Over the whole experimental period (22 days), the SBR system reduced COD by around 92%, from an average value of 543 mg/L (influent) to 44 mg/L (effluent) (Figure 2a). Fountoulakis et al. obtained a similar result in their studies [22]. More specifically, the removal of COD was approximately 87%. Such, a high removal was also obtained in studies on grey water purification in a membrane bioreactor operating in a flow-through system [3], where the COD reduction degree was 88%.
It was found that the easily biodegradable compounds expressed by BOD5 were removed in 99% of cases, and the average concentration in the effluent was 4 mg/L (Figure 2b). Similarly, a high reduction was recorded for TOC and absorbance, i.e., 91% and 76%, respectively (Figure 2c,d). Anionic and nonionic surfactants were reduced by 97% and 100%, respectively (as seen in Table S1 in the Supplementary File). In the study [22], the removal efficiency of the anionic surfactants was about 80% in the submerged membrane bioreactor. This is due to the fact that non-ionic and anionic surfactants are readily biodegradable under aerobic conditions [23,24,25].
3.1.2. Removal of Biogenic Compounds
As seen in Figure 3, the concentration of nutrients in SBR effluent was low and did not exceed permissible values laid out in the Polish regulations [21].
Raw grey water was characterized by a minimum content of ammonium and nitrate nitrogen at the level of 0.2 mg/L and 0.8 mg/L, respectively. After biological treatment with the SBR system, the concentration of nitrate and nitrogen increased to an average value of 7.6 mg/L. Differences in the nitrate concentrations in the influent and effluent indicate that a large part of nitrogen in grey water was organically bound [16]. The average value of total Kjeldahl nitrogen in the influent was 10.6 mg/L. The removal degree of total nitrogen was at the average level of 20% and the concentration in the effluent was 8 mg/L. It should be emphasized that despite the lack of total denitrification, the concentrations of individual forms of nitrogen in SBR effluent did not exceed the maximum permissible values given that are currently in force in Poland, (Regulations of the Minister of the Environment) on the conditions to be met when discharging wastewater into water or soil [21]. At the initial stage of the grey water purification process, there was a problem with phosphorus removal. Its value exceeded several times the permissible value. It can be explained by the variable physicochemical nature of the SBR influent. The effective dephosphatation takes place when the influent contains an easily biodegradable COD fraction and the COD/BOD5 ratio is 2 [26,27]. The second factor intensifying a release of phosphate under anaerobic conditions is the constant delivery of easily biodegradable organic compounds, e.g., volatile fatty acids and their salts. Their occurrence in grey water is likely to be changeable. Since grey water was collected in a holding tank over a longer time, it could undergo an acid fermentation during which volatile fatty acids may be formed. It was found that in the second week of the process, the degree of P-PO43− removal increased along with the increase of COD concentration of the inflowing grey water. In the following weeks of operation of the SBR reactor, the phosphate phosphorus concentration ranged from 1.1 to 2.6 mgP-PO43−/L. Despite the increase in efficiency of phosphorus removal, its permissible concentration specified in the Regulation of the Minister of the Environment [21] (Ptot = 2 mg/L) was still exceeded. In order to improve the effectiveness of phosphate removal, the cycle of operation of SBR should be modified by means of changes in the duration of aerobic–anaerobic phases [28].
3.1.3. Removal of Color and Turbidity
Figure 4 and Figure 5 show the treatment efficiency of the SBR system with respect to the changes in the color and the turbidity. From these results, it is clear that over the whole experiment, the efficiency of the SBR system in terms of color and turbidity was at a constant high level. During 22 days of continuous SBR system operation, the color of grey water decreased from an average value of 201 mgPt/L to 44 mgPt/L, which corresponds to an average removal of 78%. Meanwhile, the average grey water turbidity decreased from 28 FTU to 4 FTU corresponds to an average removal of 84%.

Figure 5.
Changes in the color and the turbidity of grey water under treatment with SBR followed by ultrafiltration.
3.2. SBR Effluent Treatment by Ultrafiltration
The treatment efficiency of SBR effluent in an ultrafiltration unit with different membranes is presented in Figure 6 and Table S3 (Supplementary file). As expected, for ultrafiltration, removal of organics expressed by the color, absorbance, COD, and TOC was very high. More specifically, the color, absorbanceUV254, COD, and TOC were reduced maximally by 73%, 91%, 84%, and 91%, respectively. Slightly lower elimination was observed for inorganic quality parameters. Conductivity, nitrate, phosphate, ammonium, and total nitrogen were reduced by 61%, 64%, 79%, 85%, and 59%. It is important to emphasize that negative charge of membranes at pH 7–8 (as seen in Figure 8) played an important role in the reduction of conductivity, phosphate, and nitrate ions in SBR effluent. The literature describes that negatively charged ultrafiltration membranes reject phosphate ions by 87%, as an effect of electrostatic repulsion [29]. Another important influencing factor on the rejection of ions and organics in the ultrafiltration unit treating wastewater/surface water can be hydrophobic/hydrophilic interactions between organics and ions in feed water [30]. For example, Shang et al. reported that high phosphate removal was attributed to the adsorption of phosphate on biopolymers in effluent and removal with these biopolymers [31].
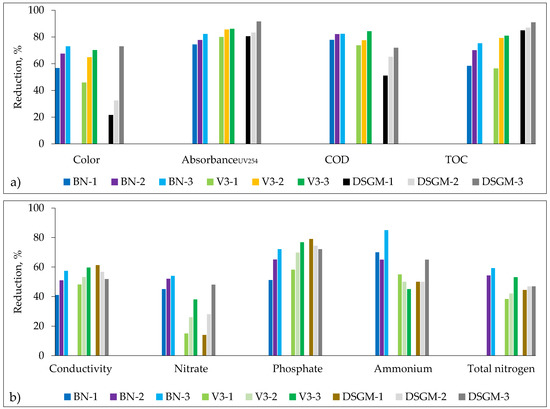
Figure 6.
Reduction values of organic (a) and inorganic (b) parameters during the ultrafiltration of SBR effluent. Each bar corresponds to the filtration cycle 1–3.
Surprisingly, membrane DSGM with the lower value of MWCO provided permeate quality values very similar to the values for BN and V3 membranes with higher MWCO. This brings an important finding that the treatment efficiency was more affected by operational conditions of cross-flow ultrafiltration than by membrane properties. When good mixing and turbulent flow along the membrane surface are guaranteed, as it is in cross-flow, other factors affecting permeability and selectivity are less important [32]. Feed nature could also play an important role. From the quality parameters of SBR effluent, we can assume that SBR effluent did not contain a significant portion of low molecular weight organics that needed to be removed. Another reason could be the fouling layer that supported the retention of pollutants by BN and V3 membranes. Jerman et al. found that the cake or gel layer acts as an additional membrane in ultrafiltration and improves retention by up to 40% [33].
It was also found that treatment efficiency increased within cycles 1–3 for all membranes (Figure 6). It can be related to the formation of the cake layer on the membrane surface of BN and V3. This corresponds well with the permeability loss observed for these membranes. Many authors suggest that the cake layer decreases membrane permeability by the reduction of effective pore size and improves the retention of organics and ions [34,35,36]. However, in the case of the DSGM membrane, there was no fouling so the cake layer was probably not created. The reason for increasing retention over time for DSGM can be related to the concentration effect of feed components within cycles 1–3. In the literature, the influence of the feed concentration on both ions and organics removal can be found [37,38]. Muthumareeswaran et al. have found that a change of the concentration of feed components in the multicomponent system affects their retention due to the ionic interaction between the feed components (Columbic interaction), molar volume, and interaction between ions and membrane surface charge [39].
Importantly, physical, chemical, and microbiological specifications (smell, color, turbidity, TOC, ammonium, nitrate, chloride, conductivity, hardness, E. coli, and enterococci) of the permeate correspond well with typical tap water values of basic quality parameters [40].
3.3. Microbiological Quality of Grey Water
Pathogens, such as Escherichia coli and Enterococci, have been identified in grey water (Table 3). The concentration of these bacteria was above 100 CFU per 100 mL. During the biological purification process in the SBR system, the presence of Escherichia coli did not change, while Enterococci decreased to an average of 3 CFU per 100 mL of sample. Then, ultrafiltration for each UF membranes resulted in the complete removal of the determined pathogens [41]. High pathogen removal from the E. coli group was also noted in the SMBR system from Khalid Bani-Melhem et al. [3].

Table 3.
Microbiological quality of grey water.
3.4. Membrane Permeability and Fouling Behavior in Ultrafiltration
Hydraulic performance of membranes was evaluated by permeability loss as a function of time. As seen in Figure 7, the permeability decreased gradually for BN and V3 membranes, while for DSGM, permeability was constant along the ultrafiltration. In other words, fouling was not observed for the DSGM membrane. This finding is very important in the context of membrane lifetime and reducing operational cost. Similarly, Acero et al. reported that UF membranes (with higher MWCO) revealed higher fouling than NF membranes (with lower MWCO) [42]. It can be explained by different surface properties of given membranes, such as hydrophilicity/hydrophobicity and surface charge (zeta potential curve and isoelectric point). The contact angle and isoelectric points of clean and fouled membranes are listed in Table 4. Zeta potential curves for clean and fouled membranes are presented in Figure 8. Owing to the lowest contact angle and strong negative surface charge, the DSGM membrane had the best antifouling properties. On the contrary, the surface of BN and V3 membranes was much more hydrophobic, and thus more prone to adsorb the feed components. Some authors reported a high importance of membrane hydrophilicity and negative charge for fouling mitigation in ultrafiltration [43,44,45] treating water or wastewater.
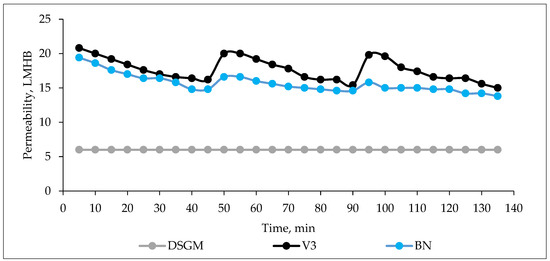
Figure 7.
Permeability loss as a function of time of UF for different types of membranes. Ultrafiltration with DSGM membrane was performed without forward flushing due to constant permeability.

Table 4.
Contact angle and isoelectric point for clean and fouled membranes.
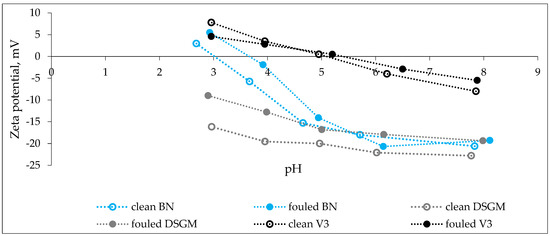
Figure 8.
Zeta potential vs pH for clean and fouled membranes.
In order to investigate this further, the hydraulically reversible and hydraulically irreversible resistances were calculated. As seen in Figure 9, the total fouling (sum of reversible and irreversible resistances) was higher for the V3 membrane. However, considering the proportion of reversible and irreversible resistances for these membranes, it is clear that fouling behavior for these membranes exhibited the opposite trend. More specifically, a significant proportion of the increase in resistance for the V3 membrane was hydraulically reversible, while hydraulically irreversible for the BN membrane. Reversibility/irreversibility of fouling depends on the surface properties of membranes. It is in good correspondence with changes of course of zeta potential curves and shift in isoelectric point for clean and fouled membranes. Membrane V3 with the lower negative charge was more sensitive to fouling overall than the BN membrane. However, for the BN membrane, we observed the higher shift in isoelectric point (from 3.01 to 3.55) than for V3 (from 5.1 to 5.25) indicating a persistent change in BN membrane properties caused by irreversible fouling.
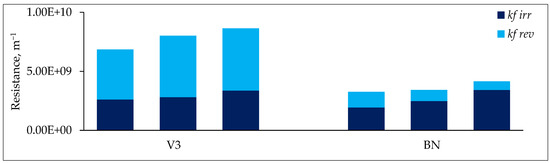
Figure 9.
Irreversible and reversible fouling resistances of ultrafiltration for all membranes. Each bar corresponds to the filtration cycle 1–3. kf irr and kf rev are irreversible and reversible resistances, respectively.
4. Conclusions
This study proved a great performance of SBR followed by ultrafiltration to obtain high-quality water for non-potable purposes from real grey water. Purified grey water fulfilled criteria for wastewater discharged into water or soil as well as physical, chemical, and microbiological requirements for tap water. It is a good starting point to find new reuse application of reclaimed grey water.
The following conclusions can be reached from the experimental results.
- The SBR system ensured the complete removal of nonionic surfactants and 97% removal of anionic surfactants from grey water.
- Removal of phosphate in SBR was, on average, 42%, but its concentration still exceeded acceptable values. It could probably be related to the variable concentration of raw grey water. It was stated that in order to improve the phosphorus reduction, in subsequent studies, the cycle of operation of SBR should be modified by means of changes in the duration of aerobic–anaerobic phases.
- In ultrafiltration treatment, there was an efficiency increase in filtration time due to the formation of a cake layer or concentration effect.
- Treatment efficiency in ultrafiltration was mainly influenced by the cross-flow filtration mode and nature of feed water.
- Membrane properties played an important role in fouling behavior, but did not greatly affect treatment efficiency.
- Membrane DSGM did not show fouling in permeate flux monitoring. It is a consequence of the initial properties of this membrane such as the lowest contact angle and the most negative zeta potential when compared with the BN and V3 membranes, for which fouling was observed.
Supplementary Materials
The following is available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4441/12/1/154/s1, Table S1: Codes of the Merck test kits, Table S2: Values of quality parameters and reduction degree for SBR system, Table S3: Values of quality parameters measured in SBR effluent and permeate samples.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization G.K. and A.M. methodology, G.K. and A.M.; investigation, G.K. and A.M.; writing—original draft preparation, G.K. and A.M., Writing—review and editing, G.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Polish Ministry of Science and Higher Education.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Use of Freshwater Resources. Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/data-and-maps/indicators/use-of-freshwater-resources-2/assessment-3 (accessed on 23 December 2019).
- Xin, D.; Saige, W.; Bin, C. The blue, green and grey water consumption for crop production in Heilongjiang. Energy Procedia 2019, 158, 3908–3914. [Google Scholar]
- Bani-Melhem, K.; Al-Qodah, Z.; Al-Shannag, M.; Qasaimeh, A.; Qtaishat, M.R.; Alkasrawi, M. On the performance of real grey water treatment using a submerged, Membrane bioreactor system. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 476, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Alcalá, I.; Pellicer-Martínez, F.; Fernández-López, C. Pharmaceutical grey water footprint: Accounting, influence of wastewater treatment plants and implications of the reuse. Water Res. 2018, 135, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galvis, A.; Zambrano, D.A.; Van der Steen, N.P.; Gijzen, H.J. Evaluation of pollution prevention options in the municipal water cycle. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 66, 599–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prajapati, B.; Jensen, M.B.; Jørgensen, N.O.G.; Petersen, N.B. Grey water treatment in stacked multi-layer reactors with passive aeration and particle trapping. Water Res. 2019, 161, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Guidelines for the Safe Use of Wastewater, Excreta and Greywater, Excreta and Greywater Use in Agriculture. 2006. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/78265/9241546824_eng.pdf;jsessionid=47807504FED628D9A9BB71654F04A9E7?sequence=1 (accessed on 23 December 2019).
- Li, F.; Wichmann, K.; Otterpohl, R. Review of the technological approaches for grey water treatment and reuses. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 3439–3449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boddu, M.V.; Paul, T.; Page, M.A.; Byl, C.; Ward, L.; Ruan, J. Gray water recycle: Effect of pretreatment technologies on low pressure reverse osmosis treatment, J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 4435–4443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manouchehri, M.; Kargari, A. Water recovery from laundry wastewater by the cross flow microfiltration process: A strategy for water recycling in residential buildings. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 168, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, A.; Liang, H.; Li, G.; Derlon, N.; Szivak, I.; Morgenroth, E.; Pronk, W. Impact of aeration shear stress on permeate flux and fouling layer properties in a low pressure membrane bioreactor for the treatment of grey water. Water Res. 2016, 510, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, M.J.; Takdastan, A.; Jorfi, S.; Neisi, A.; Farhadi, M.; Yari, A.R.; Dobaradaran, S.; Khaniabadi, Y.O. Electrocoagulation process to Chemical and Biological Oxygen Demand treatment from carwash grey water in Ahvaz megacity, Iran. Data Brief 2017, 11, 634–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bani- Melhem, K.; Smith, E. Grey water treatment by a continuous process of an electrocoagulation unit and a submerged membrane bioreactor system. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 198–199, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, A.; Liang, H.; Li, H.; Szivak, I.; Traber, J.; Pronk, W. A low energy gravity driven membrane bioreactor system for grey water treatment: Permeability and removal performance of organics. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 542, 408–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, J.; Oha, K.S.; Poh, P.E.; Chong, M.N. Prospects of hybrid rainwater-greywater decentralised system for water recycling and reuse: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 142, 3014–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamczak, M.; Kamińska, G.; Bohdziewicz, J. Application of waste polymers as basic material for ultrafiltration membranes preparation. Proceedings 2019, 16, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drews, A. Membrane fouling in membrane bioreactors—Characterisation, contradictions, cause and cures. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 363, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.; Jiang, W.; Song, Y.; Xia, S.; Hermanowicz, S. The characteristics of extracellular polymeric substances and soluble microbial products in moving bed biofilm reactor-membrane bioreactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 148, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, A.C.S.; Grossi, L.; Carvalho de Melo, R.A.; Macedo de Assis, T.; Ribeiro, V.M.; Santos Amaral, M.C.; de Souza Figueiredo, K.C. Carwash wastewater treatment by micro and ultrafiltration membranes: Effects of geometry, pore size, pressure difference and feed flow rate in transport properties. J. Water Process Eng. 2017, 17, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crittenden, J.C.; Trussell, R.R.; Hand, D.W.; Howe, K.J.; Tchobanoglous, J. Water Treatment: Principles and Design, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Dz.U.2014.poz.1800. Directive of the Minister of the Environment from 18th of November 2014. Available online: http://prawo.sejm.gov.pl/isap.nsf/download.xsp/WDU20140001800/O/D20141800.pdf (accessed on 3 January 2020).
- Fountoulakis, M.S.; Markakis, N.; Petousi, I.; Manios, T. Single house on-site grey water treatment using a submerged membrane bioreactor for toilet flushing. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 551–552, 706–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guang-Guo, Y. Fate, behavior and effects of surfactants and their degradation products in the environment. Environ. Int. 2006, 32, 417–431. [Google Scholar]
- Ivanković, T.; Hrenović, J. Surfactants in the Environment. Arh. Hig. Rada Toksikol. 2010, 61, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, H.; Temmink, H.; Zeeman, G.; Buisman, C.J.N. Comparison of Three Systems for Biological Greywater Treatment. Water 2010, 2, 155–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Świerczynska, A.; Bohdziewicz, J. Determination of the most effective operating conditions of membrane bioreactor used to industrial wastewater treatment. Environ. Prot. Eng. 2015, 41, 41–51. [Google Scholar]
- Hocaoglua, S.M.; Atasoya, E.; Babana, A.; Orhonb, D. Modeling biodegradation characteristics of grey water in membrane bioreactor. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 429, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Świerczyńska, A.; Bohdziewicz, J.; Puszczało, E. Treatment of industrial wastewater in the sequential membrane bioreactor. Ecol. Chem. Eng. S 2016, 23, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Shang, R.; Verliefde, A.R.D.; Hu, J.; Zeng, Z.; Lu, J.; Kemperman, A.J.B.; Deng, H.; Nijmeijer, K.; Heijman, S.G.J.; Rietveld, L.C. Tight ceramic UF membrane as RO pre-treatment: The role of electrostatic interactions on phosphate rejection. Water Res. 2014, 48, 498–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peeva, P.D.; Million, N.; Ulbricht, M. Factors affecting the sieving behavior of anti-fouling thin-layer cross-linked hydrogel polyethersulfone composite ultrafiltration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 390–391, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, R.; Verliefde, A.R.D.; Hu, J.; Heijmann, S.G.J.; Rietveld, L.C. The impact of EfOM, NOM and cations on phosphate rejection by tight ceramic ultrafiltration. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 132, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broeckmann, A.; Busch, J.; Wintgens, T.; Marquardt, W. Modeling of pore blocking and cake layer formationin membrane filtration for wastewater treatment. Desalination 2006, 189, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jermann, D.; Pronk, W.; Boller, M.; Schafer, A.I. The role of NOM fouling for the retention of estradiol and ibuprofen during ultrafiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 329, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohdziewicz, J.; Kamińska, G.; Pawlyta, M.; Łukowiec, D. Comparison of effectiveness of advanced treatment of municipal wastewater by sorption and nanofiltration. Separate processes and integrated systems. Environ Prot. Eng. 2015, 41, 119–132. [Google Scholar]
- García-Martín, N.; Silva, V.; Carmona, F.J.; Palacio, L.; Hernández, A.; Prádanos, P. Pore size analysis from retention of neutral solutes through nanofiltration membranes. The contribution of concentration–polarization. Desalination 2014, 344, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, S.; Zhanf, M.; Yao, M.; Qiu, Z.; Hong, Y.; Lan, W.; Xia, H.; Jin, X. Membrane Fouling and Performance of Flat Ceramic Membranes in the Application of Drinking Water Purification. Water 2019, 11, 2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, F.C.; Shang, R.; Rietveld, L.C.; Heijman, S.J.G. Influence of pH, multivalent counter ions, and membrane fouling on phosphate retention during ceramic nanofiltration. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsuaga, J.M.; López-Muñoz, M.J.; Aguado, J.; Sotto, A. Temperature, pH and concentration effects on retention and transport of organic pollutants across thin-film composite nanofiltration membranes. Desalination 2008, 221, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthumareeswaran, M.R.; Agarwa, G.P. Feed concentration and pH effect on arsenate and phosphate rejection via polyacrylonitrile ultrafiltration membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 468, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acero, J.L.; Benitez, F.J.; Teva, F.; Leal, A.I. Retention of emerging micropollutants from UP water and a municipal secondary effluent by ultrafiltration and nanofiltration. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 163, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, R.; Opitz, R.; Grischek, T.; Otter, P. The AquaNES Project: Coupling Riverbank Filtration and Ultrafiltration in Drinking Water Treatment. Water 2019, 11, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Świerczyńska, A.; Bohdziewicz, J.; Kamińska, G.; Wojciechowski, K. Influence of the type of membrane-forming polymer on the membrane fouling. Environ. Prot. Eng. 2016, 42, 197–210. [Google Scholar]
- Ghiasi, S.; Behboudi, A.; Mohammadi, T.; Khanlari, S. Effect of surface charge and roughness on ultrafiltration membranes performance and polyelectrolyte nanofiltration layer assembly, Colloids and Surfaces A. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, P.; Modi, A.; Bellare, J. Enhanced flux and antifouling property on municipal wastewater of polyethersulfone hollow fiber membranes by embedding carboxylated multi-walled carbon nanotubes and a vitamin E derivative. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regulation of the Ministry of Health on the Quality of Water Intended for Human Consumption. Available online: https://www.igwp.org.pl/images/artykuly/prawo/Jako%C5%9B%C4%87-wody-przeznaczonej-do-spo%C5%BCycia-przez-ludzi.pdf (accessed on 23 December 2019).
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).