Abstract
Rainfall stations of a certain number and spatial distribution supply sampling records of rainfall processes in a river basin. Uncertainty may be introduced when the station records are spatially interpolated for the purpose of hydrological simulations. This study adopts a bootstrap method to quantitatively estimate the uncertainty of areal rainfall estimates and its effects on hydrological simulations. The observed rainfall records are first analyzed using clustering and correlation methods and possible average basin rainfall amounts are calculated with a bootstrap method using various combinations of rainfall station subsets. Then, the uncertainty of simulated runoff, which is propagated through a hydrological model from the spatial uncertainty of rainfall estimates, is analyzed with the bootstrapped rainfall inputs. By comparing the uncertainties of rainfall and runoff, the responses of the hydrological simulation to the rainfall spatial uncertainty are discussed. Analyses are primarily performed for three rainfall events in the upstream of the Qingjian River basin, a sub-basin of the middle Yellow River; moreover, one rainfall event in the Longxi River basin is selected for the analysis of the areal representation of rainfall stations. Using the Digital Yellow River Integrated Model, the results show that the uncertainty of rainfall estimates derived from rainfall station network has a direct influence on model simulation, which can be conducive to better understand of rainfall spatial characteristic. The proposed method can be a guide to quantify an approximate range of simulated error caused by the spatial uncertainty of rainfall input and the quantified relationship between rainfall input and simulation performance can provide useful information about rainfall station network management in river basins.
1. Introduction
Hydrological modelling has been widely used in numerous fields such as flood forecasting, water resource estimation, water project planning, groundwater level fluctuations, hydrological station planning, water quality monitoring and sediment load estimation [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10]. At present, a significant goal of existing research efforts in hydrological modelling is to improve the accuracy of runoff simulation and prediction. The accuracy improvement can be achieved by improving the structures of the hydrological models, the calibration of models, or the accuracy of the input data. Rainfall is regarded as the key driving input of hydrological models and it is impossible to produce accurate runoff predictions if forced with inaccurate rainfall data [11]. The impact of spatial and temporal error in predicting rainfall on predicted flow has been highlighted by many researchers [12,13,14,15]. Currently, rainfall data from rainfall stations are still indispensable because the station data are regarded to be relatively accurate and more reliable than the radar data at the point where a station locates [16,17]. Therefore, the spatial distribution of rainfall stations still plays an important role in the accuracy of basin rainfall estimates, as well as hydrological simulations.
Over the past several decades, many approaches have been developed to study the spatial variation of rainfall and numerous mathematical formulations have been proposed to identify the errors and uncertainties from rainfall measurements, including data-driven and analytical methods [18,19]. An important question is what spatial-temporal scales of rainfall measurement are required for estimating rainfall with an acceptable accuracy. For example, simple rules were proposed by Villarini et al. [20] to determine the number of rainfall stations required to estimate areal rainfall with a prescribed accuracy (e.g., more than 15 stations over an area of approximately 135 km2 in the Brue catchment in southwestern England were necessary to estimate the true areal rainfall at a three-hour scale with an error less than 20%). As the spatial variability of rainfall can cause large variations in simulated runoff, the propagation of error from rainfall to runoff has also been investigated in numerous previous studies. For example, Wilson et al. [21] indicated that the differences in simulated runoff could be quite significant when the rainfall inputs were changed based on different combinations of rainfall stations in the Fajardo basin, with an area of 68.6 km2 in Puerto Rico. Faurès et al. [22] proved that a single rainfall station with a uniform rainfall assumption could lead to large uncertainty in runoff estimation. Lopes [23] examined the effect of uncertainty in spatial estimates of rainfall on the prediction of runoff volume and the results showed that the density of the rainfall station network could greatly influence the catchment response predictions when rainfall stations were randomly excluded one by one from the analysis. Moulin et al. [15] quantified the effect of mean areal rainfall estimation errors on runoff simulation in three small- to medium-sized catchments with areas ranging from 60 to 3200 km2 and the results showed that the uncertainties on rainfall estimates had a strong influence on the rainfall-runoff modelling errors, especially in the case of smaller catchments. Casper et al. [24] investigated the influence of temporal and spatial variability in the rainfall on flood prediction by using ensembles of 100 rainfall realizations for several extreme events with several spatially distributed rainfall-runoff models and concluded that the differences in the model concepts led to different sensibilities against uncertainties in rainfall input. Some other studies compared the simulated runoff obtained through different rainfall estimation scenarios with rain gauge data or radar data and these different levels of rainfall spatial variability directly introduced the influence of simulation results [25,26,27]. Furthermore, a number of methods have been developed to demonstrate rainfall uncertainty using rainfall station measurements and to quantify its influence on hydrological simulation results. To demonstrate rainfall uncertainty, the most sophisticated method is a geostatistical approach, the conditional simulation, which is frequently applied to generate the spatial distribution of rainfall by constraining a stochastic dispersion field with the measurements at one, a subset or all of the rainfall stations. Vischel et al. [28] used this method to study the differences of simulated runoff using different simulated rainfall spatial patterns and concluded that for Hortonian runoffs, conditional simulation performs better than simply kriging station rainfall. Moreover, Renard et al. [29] used the Bayesian total error analysis methodology to decompose the total uncertainty of runoff predictions into the individual contributions of rainfall, runoff and model structural errors, where the uncertainty in the basin average rainfall was characterized using the geostatistical conditional simulation. Moreover, the spatial variation of rainfall has been proved to influence not only runoff but also erosion and sediment loads. Jaramillo et al. [30] measured sediment loadings from captured storms with a network of hydrologic and sediment monitoring instruments and concluded that the large storm events have remarkable impact on the sediment loadings.
The response of hydrological model parameters can be used to quantify the influence of rainfall uncertainty. Chaubey et al. [31] studied the variation of calibrated parameters solely due to the spatial variation of rainfall and a wide range of estimated parameter values was found when the rainfall measured at each station was used individually. To alleviate the influence of rainfall spatial uncertainty, Blume et al. [32] proposed an event-based runoff coefficient in combination with simple statistical models that could improve the understanding of the rainfall-runoff response of catchments with sparse data. Reichert and Mieleitner [33] proposed a time-dependent rainfall multiplier at the input side of a hydrological model, which was adjusted according to the goodness of fit of model results.
On the other hand, the influence of rainfall input on hydrological simulation can be investigated by quantifying model structural errors. The foundation of this method is the assumption that the model structure error represents model limitations and input uncertainty, then the effect of rainfall uncertainty can be explained with the changes in the model bias. For example, Del Giudice et al. [34] used a Bayesian framework to analyze five configurations of the EPA-SWMM (Environmental Protection Agency-Storm Water Management Model) with different distribution of reservoirs and conduits, as well as different numbers of parameters for sewer flow simulations and the results showed a progressive decrease of bias with increasing model parameterization, but with an upper bound of model performance caused by rainfall input.
All the above studies have been conducted to investigate the spatial variation of rainfall, as well as its effect on hydrological simulations. However, different river basins or different rainfall events may lead to different results of spatial rainfall variability and the effective representative area of rainfall stations could vary remarkably. The results of spatial rainfall variability in a certain case are usually not applicable to other river basins. Therefore, a straightforward methodology to estimate the influences of spatial rainfall variability, which can play an important role in understanding the accuracy improvement of hydrological simulation, is necessary.
To this end, first, the bootstrap method, which has the advantages of simplicity (i.e., no need to make any assumption of normality) and high-accuracy (i.e., asymptotically more accurate than the results obtained using sample variance and assumption of normality) [35,36,37], was introduced in this study to quantitatively analyze the spatial uncertainty of rainfall in river basins at different scales [38,39,40]. Second, by employing a distributed hydrological model on a high-performance computing (HPC) system, the uncertainty of simulated runoff was also analyzed using the bootstrap method. Finally, the response of the hydrological simulation to rainfall spatial uncertainty can be quantified with an exponential formula, indicating the relevant asymptotic line on rainfall station density. Moreover, the details of the mentioned methods along with references are listed in the Table 1.

Table 1.
Summary of the methods used in hydrological uncertainty estimation from the literatures.
This paper aims at estimating the influence of rainfall spatial uncertainty in hydrological simulations, focusing on the spatially distributed rainfall stations. For this purpose, several questions need to be emphasized, including (i) how to facilitate the uncertainty quantization with the bootstrap method, (ii) how to analyze the spatial rainfall uncertainty and (iii) how to understand the relationships between rainfall and simulated runoff. Following this Introduction, this paper has been divided into four further sections: Section 2 introduces the methodology, Section 3 describes the case study catchment and hydrological model, Section 4 presents the results of the uncertainty analysis of rainfall and simulated runoff, as well as related discussions and Section 5 draws several conclusions.
2. Methodology
2.1. Bootstrap Method
The bootstrap method is a resampling method that can refer to any test or metric that relies on random sampling with replacement to quantify uncertainty [41]. When the bootstrap method is used to estimate a sampling distribution, the procedure consists of three steps: sampling with replacement, calculating the bootstrap distribution and using the bootstrap distribution. Resamples from a sample represent what would be obtained if we took a number of samples from the population. Based on the resamples, the bootstrap distribution of a statistic represents the sampling distribution of the statistic. A great advantage of the bootstrap method is its simplicity, which can be a straightforward way to derive estimates of standard errors and confidence intervals for complex estimators of complex parameters of the distribution. Moreover, it is an appropriate way to control and check the stability of the results, which can be asymptotically more accurate than the standard intervals obtained using sample variance and assumptions of normality [42]. Compared to other linear resampling methods such as jackknife, the bootstrap method can be successfully used to estimate the non-smooth parameters and the variance of non-linear statistics [43]. It is worth noting that parametric methods are used when we know that the population is approximately normal, or we can approximately use a normal distribution after we invoke the central limit theorem. In contrast, when we do not know whether the population is normal, or the assumption of the normal distribution cannot be used for the population, we use non-parametric methods, for instance, in this study.
The bootstrap method has been widely applied in hydrological data analysis. Vogel and Shallcross [44] used the moving blocks bootstrap to resample the observed time series of stream flow to estimate the storage capacity of a reservoir with different reliability. In order to evaluate the correlation between evapotranspiration and forest biomass, Jaramillo et al. [45] performed a bootstrapping procedure to account for the sampling standard errors of the forest attribute data in the regression analysis. In addition, the bootstrap method can also be applied in time series prediction. For example, Lall and Sharma [46] proposed a nonparametric nearest neighbor bootstrapping algorithm to find historical nearest neighbors of a current feature vector, a short subset of a time series and to make predictions by resampling the successor of the current feature from the neighboring feature vectors’ successors. Moreover, Fortin et al. [47] introduced a non-parametric Bayesian simulation method, which is asymptotically equivalent to the bootstrap method. But this Bayesian method does not assume that the finite reference sample is equivalent to the whole population, which is assumed by the bootstrap method but not always guaranteed.
Different distributions of rainfall stations may lead to different areal rainfall estimation and runoff simulation. To keep a smaller range of result variation and to reduce the resample times, the bootstrap method in this paper is limited to the resampling of the presence of each rainfall station at its own location, without location permutation or random placement of the rainfall stations. Therefore, the uncertainty of spatial rainfall and its hydrological response to be quantified is primarily focused on the density of rainfall stations (noted as DS). A bootstrap method with location permutation or random placement can fully explore the spatial uncertainty of rainfall, but the influence of the DS is much more simple and practical to investigate.
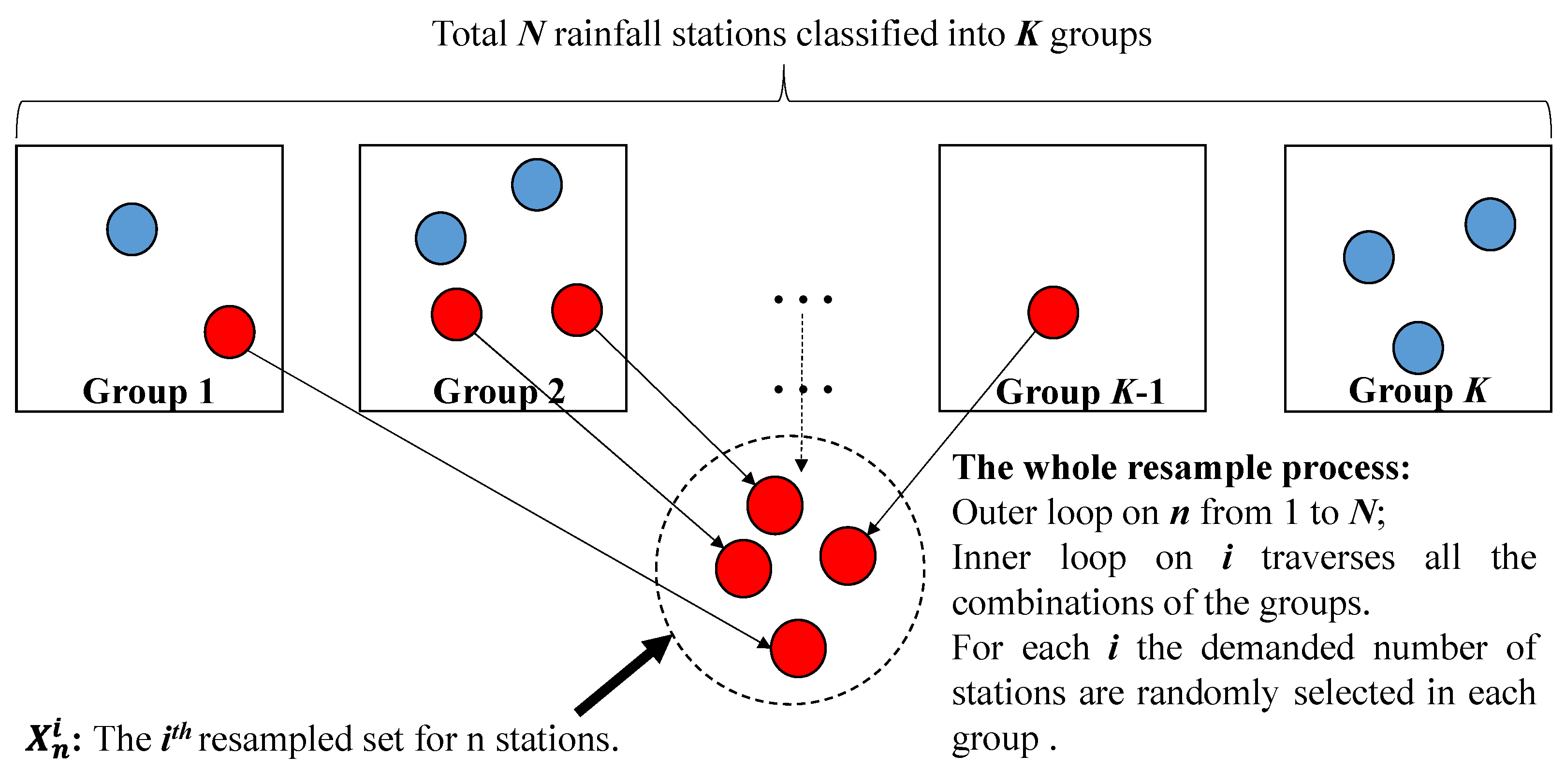
In this study, the Thiessen polygon method [48] is applied to calculate the average basin rainfall with resampled stations in a river basin. To make up the resampled station sets, two layers of loops are proposed as described in Figure 1. The outer loop is on the number of selected stations, while each inner loop resamples a possible combination of n stations from K groups. The inner loop traverses all the combinations of station groups, including the number of selected groups and the number of selected stations in each group, to form the n-station set. To reduce the repetition of simulations, for a certain combination, a certain number of stations in a certain group are randomly selected only once. By using the bootstrap method, rainfall station combinations will be obtained from the real rainfall station set with a resample number of n (Figure 1) and the total number of combinations is 2N. To improve the calculating efficiency for the bootstrap method, a python script is composed and executed (Appendix A).
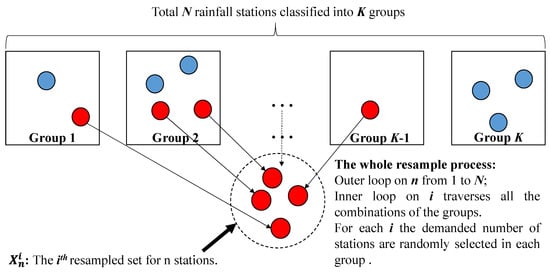
Figure 1.
Framework of the resample processes of the bootstrap method.
2.2. Framework Methodology
Firstly, rainfall events which can reveal different patterns of rainfall-runoff processes at different magnitudes in the designated river basins will be selected as the study cases (Table 2). The time steps of historical rainfall records are different among stations, varying from minutes to several hours. If the stations with high temporal resolution are selected by the bootstrap method, the simulation will benefit from the more detailed rainfall process and then perform better. Because this paper aims at the spatial uncertainty of rainfall, to avoid the influence of temporal resolution on simulation results, the measured rainfall data are firstly pre-treated to have a uniform time step. In this study, the time steps of all the rainfall data are adjusted to the same one, i.e., 2 h. For rainfall records with smaller time steps, an accumulation processing is conducted. For rainfall records with larger time steps, a linear downscaling approach in accordance with rainfall characteristics of a certain station is conducted to disaggregate the rainfall data to 2 h. It should be noted that this pre-treatment will affect the precision of hydrological model simulation, mainly because aggregating rainfall data with finer time steps into larger time steps may result in a negative impact of homogenizing short-duration and high-intensity rains, especially in this infiltration-excess dominated region.

Table 2.
Characteristic parameters of the three rainfall events for the upstream of the Qingjian River basin.
For each rainfall-runoff event, the rainfall stations in the river basin will be classified into groups. Rainfall processes with the similar time periods, duration and the time-to-peak can be grouped together [49]. Based on the total depths and processes of rainfall measurements, two steps are conducted in this paper using clustering and correlation methods. The first one is based on the total rainfall depth using the clustering method proposed by Park et al. [50]. The other step is the correlation statistics for the rainfall processes of every pair of stations.
Subsequently, reduced numbers of stations are obtained by resampling. Taking the classification of the stations into consideration, the bootstrap method is used to traverse most of the combinations of rainfall stations and to quantify the uncertainty of average basin rainfall. Then the influence of the DS on the uncertainty of the spatial rainfall can be analyzed using different reduced numbers of stations in the studied river basins.
Finally, after calibrating a hydrological model with all the rainfall stations and measured runoff depth and peak discharge at the river basin outlet, the impact of rainfall uncertainty on hydrological simulation can be assessed using the repeatedly simulated runoff with different rainfall inputs from bootstrapped rainfall, i.e., using different combinations of different reduced numbers of rainfall stations in the river basin.
2.3. Digital Yellow River Integrated Model
The Digital Yellow River Integrated Model (noted as DYRIM hereafter) is a physically-based, distributed-parameter and continuously-simulated hydrological model developed by Tsinghua University for hydrological and sediment simulations in river basins based on high-resolution digital drainage networks [51,52]. Former studies focused on the topic of hydrological simulation and soil erosion on the Loess Plateau using the DYRIM, as well as the parallelization of the DYRIM based on dynamic basin decomposition [53,54,55]. Moreover, the DYRIM has been widely employed to the simulations of streamflow, floods and sediment, which demonstrated its applicability with satisfactory results in the temporal scales ranging from daily to monthly in many river basins including the Yellow River basin [4,56,57,58,59].
The basic hillslope-channel unit of the model is river reach and its corresponding hillslopes. All the basic units of a river basin constitute a drainage network [60], which is generally extracted from digital elevation model (DEM) data [61], e.g., the 30-m-resolution Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER) Global DEM dataset [62,63] used in this paper. Runoff yield is simulated on each hillslope using a two-layer soil model to reflect both the infiltration-excess and storage-excess mechanisms, in fine time steps (e.g., 6 min). Infiltration-excess runoff on the hillslope surface, along with related processes, such as vegetation interception, evapotranspiration, ground water discharge and water redistribution between the two soil layers, constitute the fundamental hydrological processes simulated by this model. The flow routing is simulated over this drainage network using a diffusive wave method. The parameters of the DYRIM can be divided into physical parameters that are used to describe the properties of the land use and soil types and determined from field measurements and adjustable parameters that must be calibrated before model application [56]. Several representative adjustable parameters are listed in Table 3.

Table 3.
Key parameters of the model after calibration.
The actual physical meaning of the parameters and the effect on the simulation results are studied in detail in our previous work [55]. The topsoil initial moisture (θu,0) is the initial state of the topsoil layer and θd,0 represents that of the subsoil layer. The vertical conductivity of the topsoil layer, which is a non-linear function of Kzus (the vertical saturated conductivity of the topsoil layer) and θu(t) (the topsoil moisture, t is time). Kzus controls the surface infiltration rate and primarily influences the infiltration-excess runoff, as well as Ku-ds that controls the rate of water redistribution between the two soil layers. Khu and Khd control the lateral subsurface flow rate of the two soil layers, respectively. The two vertical saturated conductivities (Kzus and Ku-ds) are the key parameters to be calibrated before model application [51,56,58].
When the DYRIM is applied to a large river basin, high performance computing (HPC) technique is generally used. To implement the bootstrap method in this study, an HPC system with a large number of processor cores is used to guarantee the simulation efficiency and 8 processors are used for each model simulation. Therefore, the high-speed hydrological simulation of the DYRIM provides the support for repeated simulations in this study.
2.4. Calibration of the DYRIM
The calibration of model parameters is parallelized with a double-layer structure on an HPC system [55]. A dynamic sub-basin decomposition method [53] was developed to parallelize the hydrological simulation of the DYRIM, which contributes to the lower-layer parallelism. The MPI (Message Passing Interface) standard is adopted to realize the lower-layer parallelism, mainly because it is the dominant technique to develop parallel programs on distributed memory systems that most HPCs belong to. The job scheduling functions of an HPC system are used to manipulate simultaneous model executions with different parameter combinations in the same generation of an optimization algorithm, which contributes to the upper-layer parallelism.
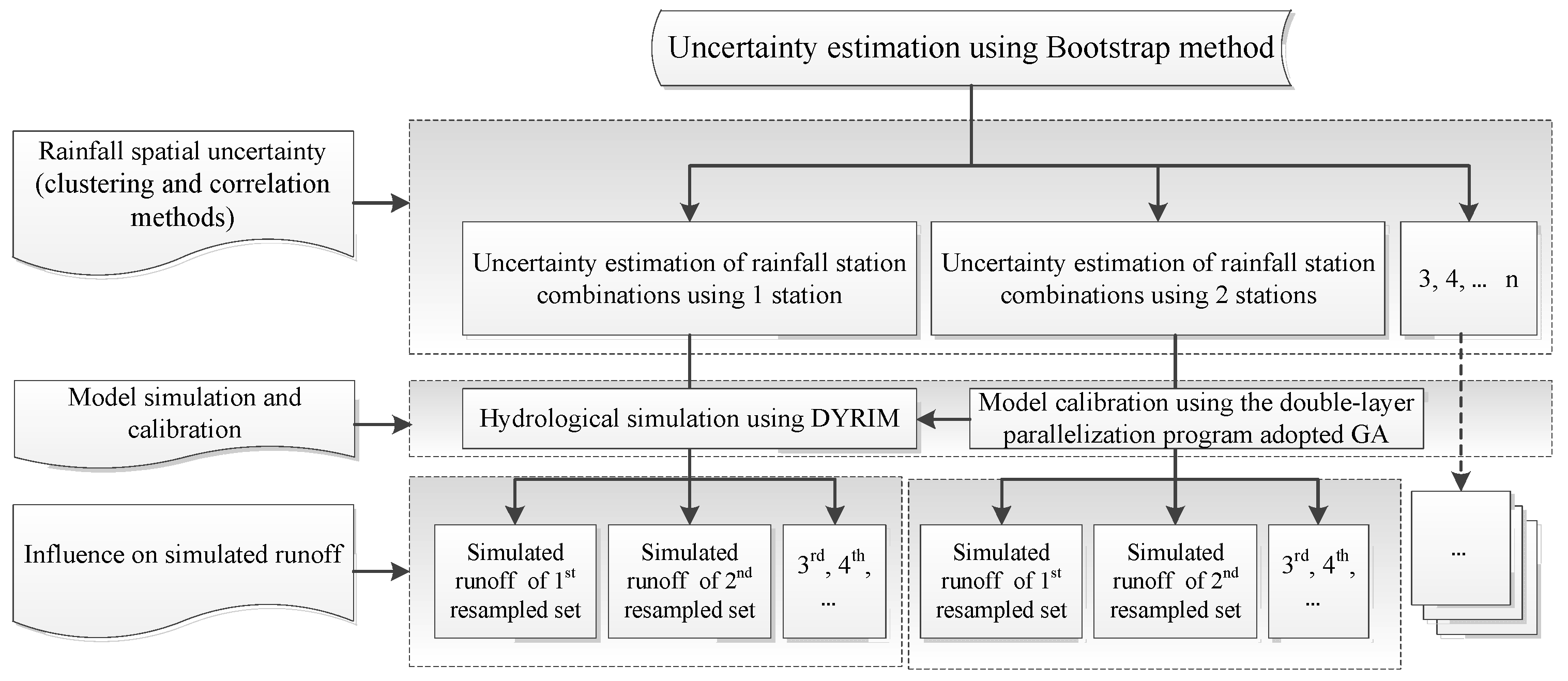
In this study, the genetic algorithm (GA), firstly proposed by Holland [64], is used for solving optimization problems since it is a heuristic technique. GA was widely used to search optimal model parameters because of its stability, natural parallelism and problem-independence. The GA implementation employed in this paper treats the parameters to be optimized as real numbers with simulated binary crossover and real-parameter mutation [65]. This technique promises the hydrological model parameters independent of the GA, which means these parameter combinations are input and output of the optimization programs. When the GA needs to evaluate the fitness of various model parameter combinations, the job scheduler of the HPC system is called to put a number of the DYRIM jobs with different parameter values into the job list of the HPC and to monitor the job list. When all of the jobs are completed, the model efficiency will be estimated using observed data to propose the fitness evaluation list. Generations of the GA will be run to explore more parameter combinations until the stop criterion is reached [55]. Because the fluctuation range of the NSE (Nash-Sutcliffe coefficient of efficiency) is needed to be explored in uncertainty estimation, so the maximum number of generations (e.g., 10 generations in this study) is set as the stop criterion. The flow chart of the uncertainty estimation using Bootstrap method is shown in Figure 2.
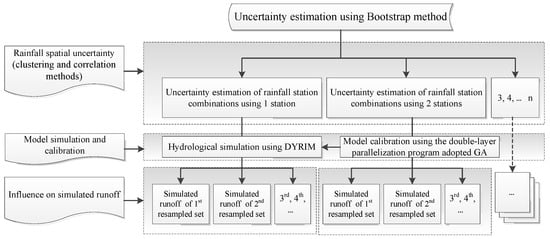
Figure 2.
The flow chart of the uncertainty estimation using Bootstrap method.
3. Application
3.1. Study Areas and the Rainfall Cases
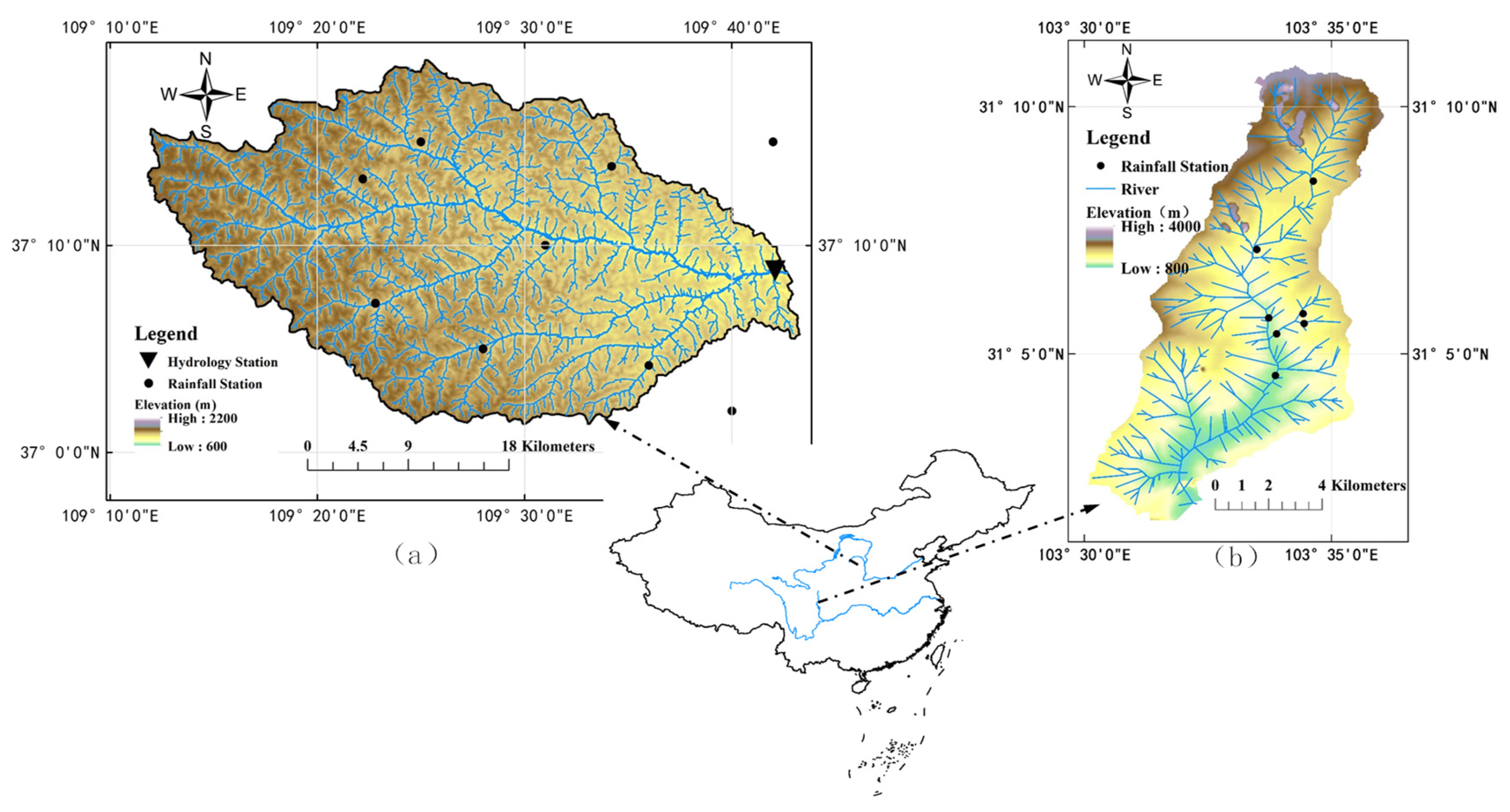
In order to compare the uncertainties of rainfall input in different densities of rainfall networks, two river basins are selected as study areas (Figure 3). The first one is the upstream of the Qingjian River basin (109°12′–109°44′ E, 37°01′–37°19′ N), a tributary of the Yellow River. The second one is the Longxi River basin located in Sichuan province (103°30′–103°36′ E, 31°01′–31°11′ N), a tributary of the Min River that flows into the Yangtze River. The digital drainage networks of these two river basins are also shown in Figure 3.
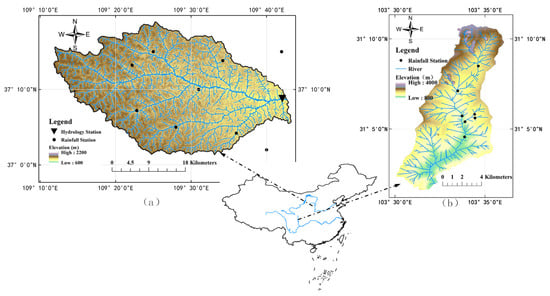
Figure 3.
The distribution of hydrological and rainfall stations in (a) the upstream of the Qingjian River basin and (b) the Longxi River basin.
The upstream of the Qingjian River has a drainage area of 930 km2 and the length of the main stream is 55.6 km. With a semi-arid warm temperate continental monsoon climate, the annual rainfall in this region is 486 mm and short-duration, high-intensity torrential rains that occur in the flood season (from July to September) account for 65% of the annual rainfall. The basin elevations vary from 930 m to 1562 m, with the obvious declining of terrain from northwest to southeast; and therefore, the spatial distribution of rainfall is also complex. The majority of the basin surface material is composed of highly erodible loess soil, covering 92% of the basin area. Consequently, runoff in this river basin, mainly in the form of infiltration-excess, can cause severe soil erosion that has been investigated in former study [51]. The total urban areas for resident, mining, industry and transportation cover 1.72% of the whole basin area, which indicates that the impervious areas have less impact on the runoff yield in this basin. The only hydrological station (i.e., Zichang) is located near the basin outlet and there are 11 rainfall stations located within or adjacent to this river basin, with an average controlling area of 84.5 km2 (see Figure 3). All of the rainfall and hydrological data used in this paper are provided by the Hydrographic Bureau of the Yellow River Conservancy Commission.
Three typical but different rainfall-runoff events after the year 2000 are manually chosen for the upstream of the Qingjian River basin (see Table 2). The three events are different from each other, not only in the order of magnitude of the measured peak discharges, but also in runoff coefficients. The 2002.7.3–7.7 rainfall event has the heaviest rainfall of 145 mm, leading to a flood with peak discharge of 4670 m3/s and a runoff coefficient as high as 0.600. The other two events have moderate rainfall, with similar basin average rainfall depths calculated from station measurements (34 mm and 28 mm). However, the two events have different peak discharges of 881 m3/s and 76 m3/s, respectively, as well as the runoff coefficients of 0.137 and 0.055. These two events are selected because their different rainfall-runoff responses are partially caused by the different spatial pattern of rainfall (Figure 4), though they cannot be easily simulated accurately using a same set of parameters.
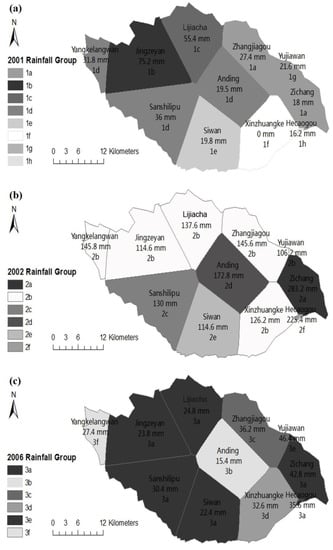
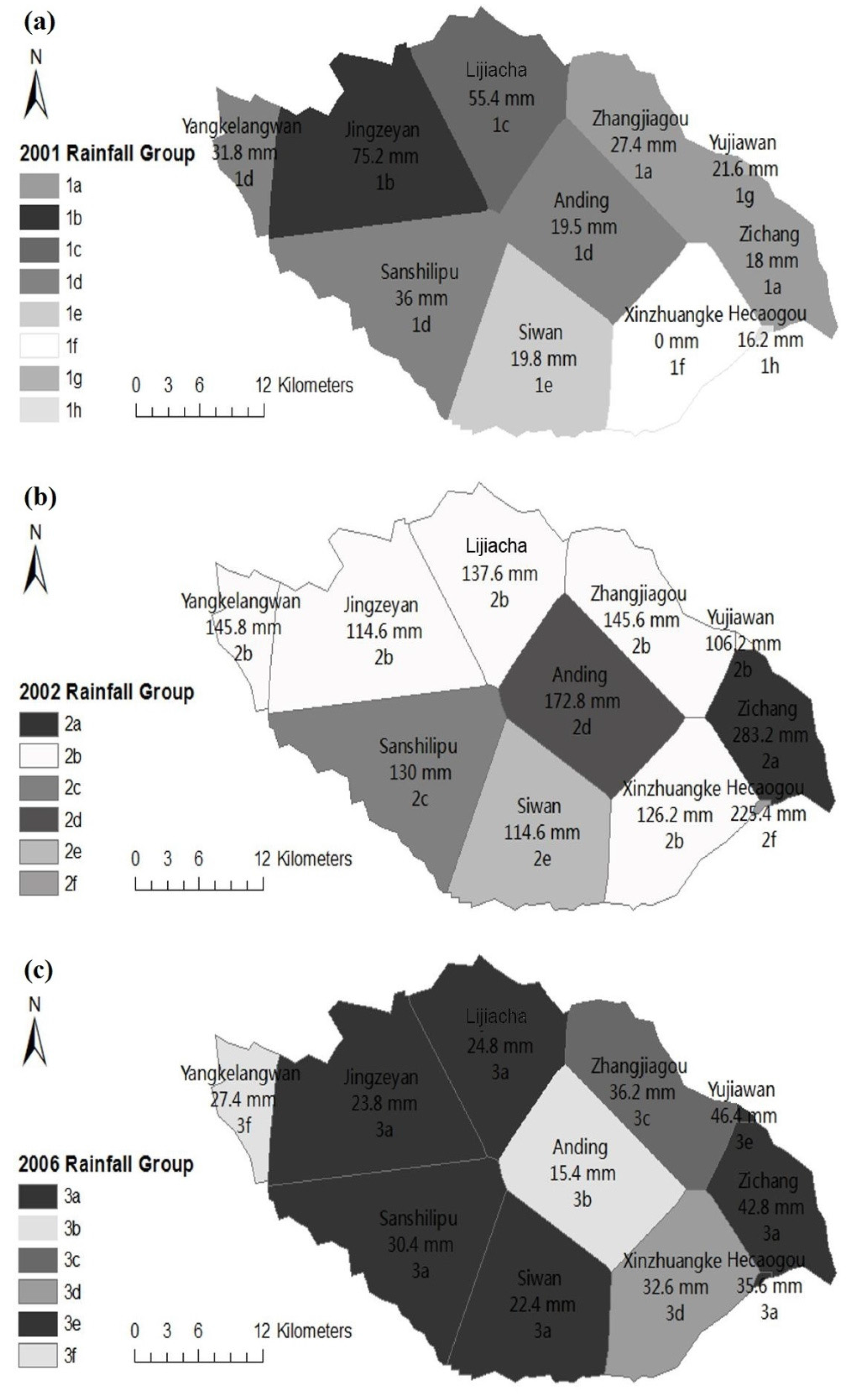
Figure 4.
Classification results of rainfall stations of three typical events in the upstream of the Qingjian River basin: (a) 2001, (b) 2002 and (c) 2006. Classification using clustering based on the total depths and correlation methods based on the processes of rainfall measurements are conducted.
In contrast, there are 7 rainfall stations located in the Longxi River basin (Figure 3), which has a drainage area of only 80 km2; and therefore, the average controlling area is only 11.4 km2 per station, much smaller than that of the upstream of the Qingjian River basin. One rainfall event, which occurred on 2012.7.11 in this river basin, is chosen for the analysis of the areal representation of rainfall stations, which has the heaviest rainfall of 52.5 mm, the lightest rainfall of 36.5 mm and the average basin rainfall of 47.1 mm.
3.2. Runoff Simulation
The DYRIM hydrological model is calibrated using the rainfall data from all the stations. There are two schemes of the model calibration. The first is to independently calibrate the model for each of the three rainfall-runoff events one by one. In such a scheme, three different sets of parameter combination will be obtained, which are the optimized parameters for the three events, respectively. In contrast, the second is to overall calibrate the model based on all the three events sharing a single set of parameter combination. Generally, more precise results would be obtained in the first scheme because it shows the potential performance of the model. However, to insulate the effect of rainfall spatial distribution from model parameters, at least in an average sense, the three events should be considered comprehensively in model calibration (i.e., the second scheme).
A set of key parameters [56] are calibrated according to the measured runoff process, runoff volume and the peak discharge at the basin outlet [3]. The precision of simulated runoff process is generally expressed by the NSE [66]:
where C is the simulated data, O is the measured data and the subscript i represents the sequential number of the simulated and measured data series. The NSE approaches 1.0 if the simulated values are quite close to the measured values. A positive NSE indicates that the means of the model predictions and measured values are still close, while a non-positive NSE indicates that the simulated values cannot be strong predictors of the measured sequence.
For runoff process, the time step of the simulated results is 6 min, consistent with that of the observed runoff during the main process; however, the time step is much larger in base flow periods. The NSEs are calculated according to the observed runoff data points, basically in the 6-min time step. But when the observed data points are sparse and do not exactly match the regular steps of the simulated results, the simulated discharge which is nearest to the actual observation time is selected for each observed data point. Finally, all the selected simulated data points constituted the data series with the observed data points to calculate the NSEs. It is worth noting that the purpose of using the high time step (i.e., 6 min) in this study is to emphasize the main runoff process, which led to certain side effects (e.g., a smaller NSE value than usual, despite the fact that base flow is generally stable and easier to fit).
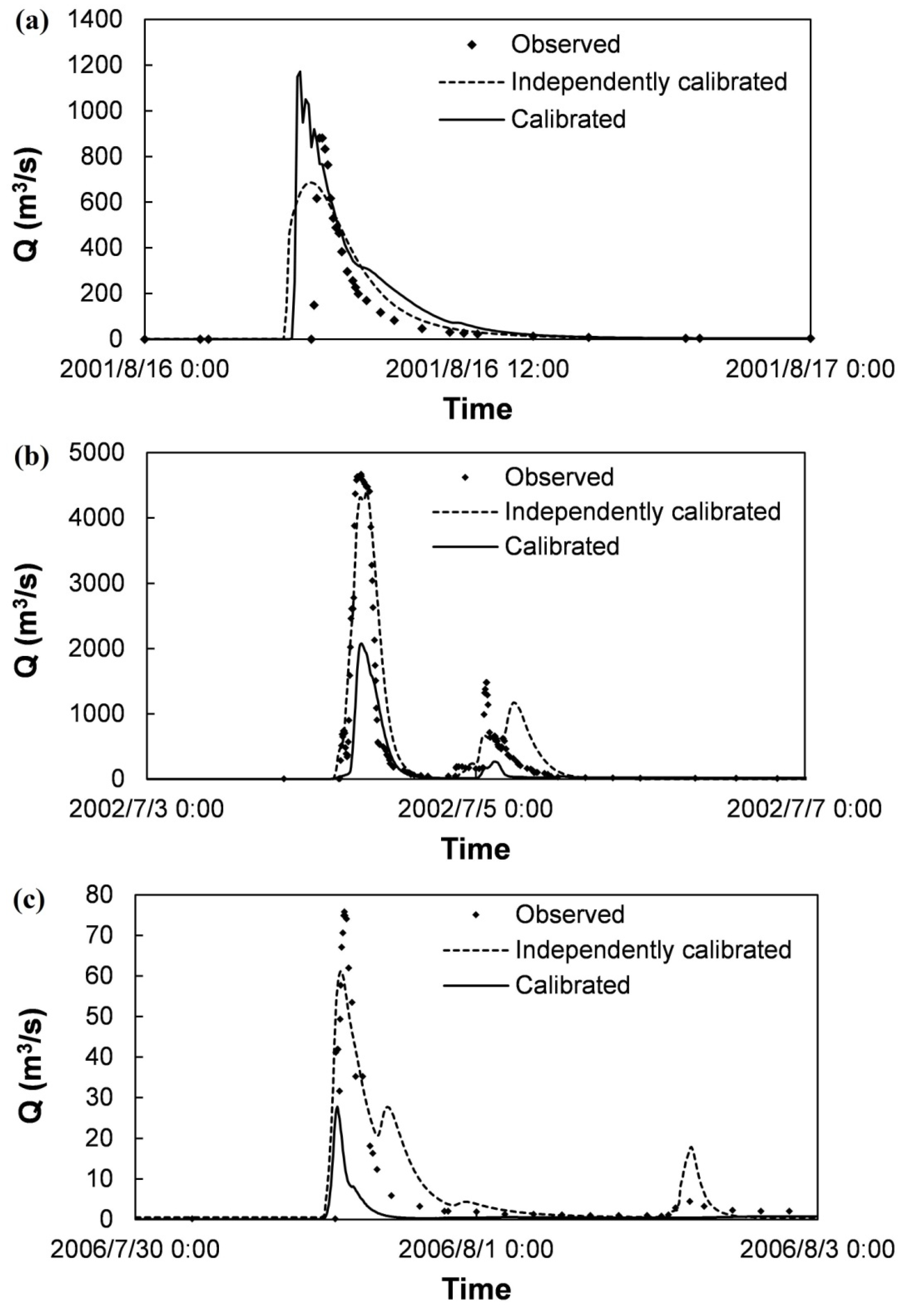
To demonstrate model performance in representing the rainfall-runoff events, the simulation results during calibration are shown in Table 2 and the simulated runoff processes are compared with observations in Figure 5. Optimized values of the key parameters are shown in Table 3. Because soil hydraulic conductivity parameters are the most sensitive to runoff simulation, only the topsoil vertical saturated conductivity Kzus is further optimized in independent calibration.
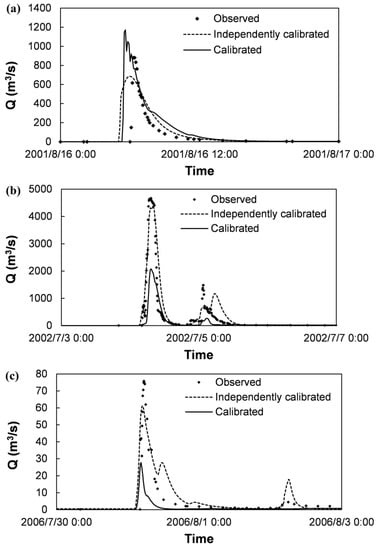
Figure 5.
Calibrated runoff processes compared with observations of the three events in the upstream of the Qingjian River basin: (a) 2001, (b) 2002 and (c) 2006.
It can be seen from the simulation results, the volume, peak discharge, peak time and fluctuation of the runoff processes are reproduced by the simulations. However, when all the events sharing a single set of parameter combination, the results could not match the observations well, especially in peak discharge. To balance the peak discharges among the three events, there must be one discharge overestimated and another underestimated. The main cause of the simulation errors would be the different spatial pattern of the rainfall events and the large time step of rainfall records. For the spatial pattern, using the simple Thiessen polygon method in this paper, the distribution can be represented better when real rainfall is more evenly distributed in the river basin; otherwise large errors are expected. For the time step, because each rainfall data point with a 2-h time step is uniformly assigned to its corresponding 20 simulation time steps of 6 min, the real peak intensity of rainfall is underestimated, resulting in non-realistic vertical infiltration parameters, as well as the early or delayed peak time. The influence degrees of spatial pattern and time step are different among the simulations of different events; as a result, a single set of parameter combination could not support all the events well.
In order to demonstrate the potential performance of the DYRIM, the topsoil vertical saturated conductivity Kzus is calibrated on the three events independently one by one. The results are shown in Table 2 and Figure 5. In Figure 5, the dash lines of the independently calibrated runoff processes can basically overlap the points of the observations, especially for the 2002 and 2006 rainfall events. With reference to the NSE of flow discharge, it is observed that the NSE values of these three rainfall-runoff events are all significantly improved, from 0.48, 0.43 and 0.05, to 0.61, 0.81 and 0.80, respectively. Such results proved that the DYRIM can represent these rainfall-runoff events in a sufficient way. It is worth noting that the impact of model calibration on results (i.e., the NSE value) is sometimes more significant than the influence of rainfall spatially uncertainty on results. Because the runoff of the 2006 rainfall event is much smaller than the other two events with the measured peak discharge of 76 m3/s, the NSE value changed more significantly when the model is independently calibrated.
The deficits of the simulation results are caused by multiple reasons. Except for the aforementioned low temporal resolution of rainfall and different orders of magnitude of the events, there must be some shortcomings in the model structure to meet all the difficulties in hydrological simulation in the middle Yellow River basin. More complex and sensitive hydrological processes occur in semi-arid region than in temperate and wet climates [67] and some aspects have not been considered in the DYRIM. For example, surface roughness and vegetation of a hillslope affect the residence time of water on its surface and finally influence the total amount of infiltration, which is not formulated in DYRIM mainly because of its steep slope assumption. Nevertheless, rainfall records with higher spatial and temporal resolutions are necessitated to better simulate such short-duration and high-intensity rainfall-runoff events.
3.3. Uncertainty Quantization of Basin Rainfall and Simulated Runoff
Uncertainty should not be ignored when only 11 rainfall stations are used to measure the basin rainfall and simulated runoff with the DYRIM in a 930 km2 area. Some previous studies, such as the study of Reichert and Mieleitner [33], have analyzed the input uncertainty of lumped conceptual nonlinear models by observing the variation of rainfall input multipliers for optimal results; however, by using the distributed hydrological models, such as the DYRIM in this study, the uncertainty quantization of rainfall input would be more complicated and difficult. In this study, we focus on the change of uncertainty corresponding to the number of rainfall stations. The uncertainty, noted as U(n), can be obtained by resampling n rainfall stations from the actual N stations. To make comparisons among different storm events and river basins, a non-dimensional uncertainty, noted as U’(n), is also defined in this paper. Normally, U’(n) should be calculated as U(n) dividing the true rainfall depth; however, because of the lack of the true rainfall depth, U’(n) can only be calculated as U’(n) = U(n)/R0, where R0 is the basin average rainfall using all the actual N stations. Moreover, it should be noted that the non-dimensional uncertainty U’(n) is only used to demonstrate the trend of uncertainty over each resampled number of rainfall stations n.
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Spatial Variation of Measured Rainfall
The classification results of rainfall stations for the three rainfall events are shown in Table 4 and Figure 4. The stations in the same group are shown in the same color. There are 8 groups of stations for the 2001 rainfall event and 6 groups for the 2002 and 2006 rainfall events.

Table 4.
Classification of rainfall stations for the three rainfall events.
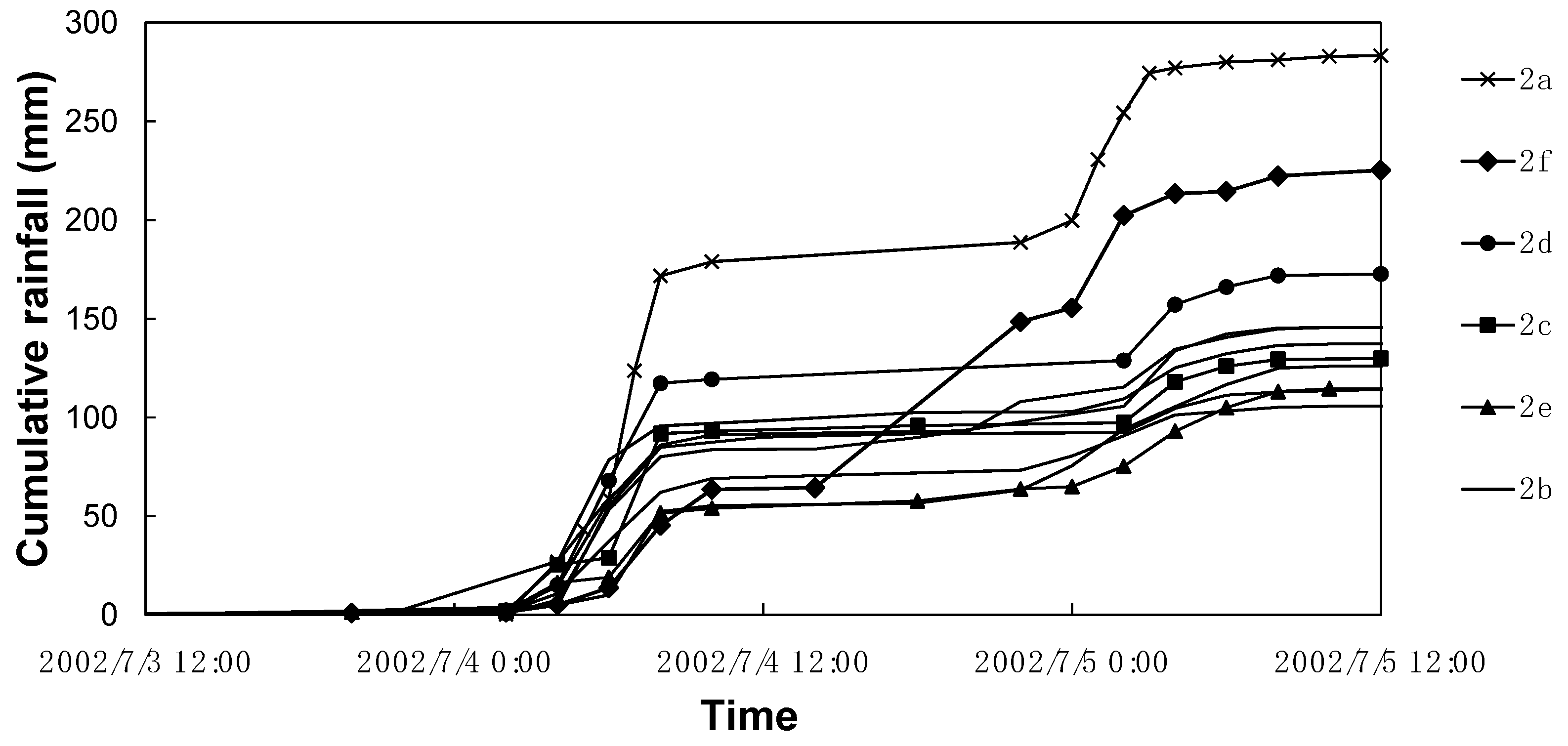
The 2002 rainfall event is taken as an example to interpret the classification results. This event was a heavy rain covering the whole basin and the measured data of 11 stations show statistically significant differences. It is observed that the stations are mainly included in group 2b. However, Zichang station (in group 2a) and Hecaogou station (in group 2f) have significant differences to the others. The total depth in Zichang station is much larger than those in the other stations and the cumulative rainfall during 7/4 12:00 to 7/5 0:00 of Hecaogou is different from those of the other stations (see Figure 6).
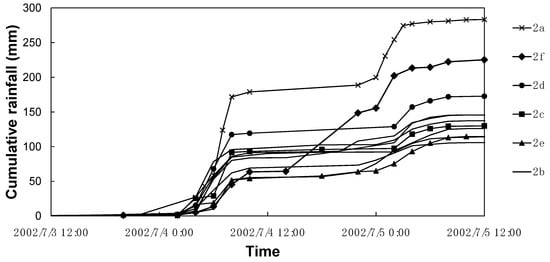
Figure 6.
Cumulative rainfall of each station in the 2002 rainfall event in the upstream of the Qingjian River basin.
The classification results of these rainfall stations show that, generally, in a rainfall event, some of the stations have the statistically uniform rainfall process and total depth. Moreover, the stations in the largest group are generally close to each other. For example, the stations in group 2b of the 2002 rainfall event are mainly located in the north of the basin, except for Xinzhuangke; the stations in group 3a of the 2006 rainfall event are mainly located in the west of the basin, except for Zichang.
The station that recorded the highest rainfall is regarded as the rainfall center. Total depth recorded in the rainfall center is generally 2–5 times greater than the average basin rainfall. Based on the analyses of the rainfall processes, the rainfall centers of the three rainfall events are Jingzeyan station in the 2001 rainfall event, Zichang station and Hecaogou station in the 2002 rainfall event and Zichang station in the 2006 rainfall event. That is, the rainfall center can only be captured with an approximately 100 km2 resolution at this rainfall station density. However, the coverage area of the rainfall center may be smaller than that scale. Therefore, the data recorded in the rainfall center will have an important influence on basin rainfall as well as runoff simulation.
4.2. Uncertainty of Basin Rainfall
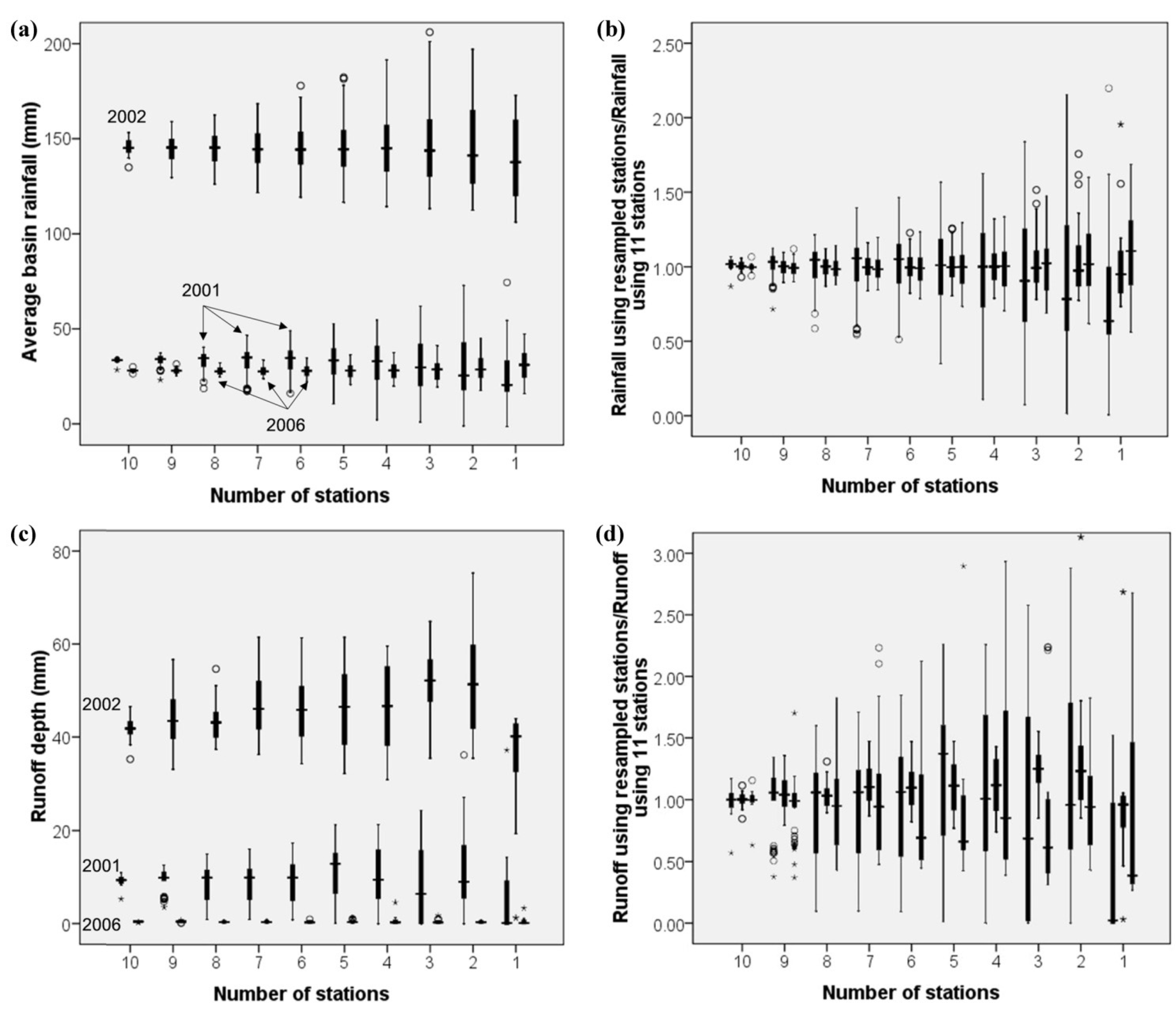
The uncertainty ranges are reflected by box plots. A box plot is a description of the data distribution, which denotes the five percentiles of the performance of quantitative variables, i.e., P2.5, P25, P50, P75 and P97.5. The P25–P75 range constitutes a box of the graphics and the P2.5–P25 and P75–P97.5 ranges constitute the two whiskers. Any data out of the whiskers should be plotted as an outlier with a dot or small circle. The U(n)–n and U’(n)–n results of the rainfall of the three rainfall-runoff events are shown in Figure 7a,b.
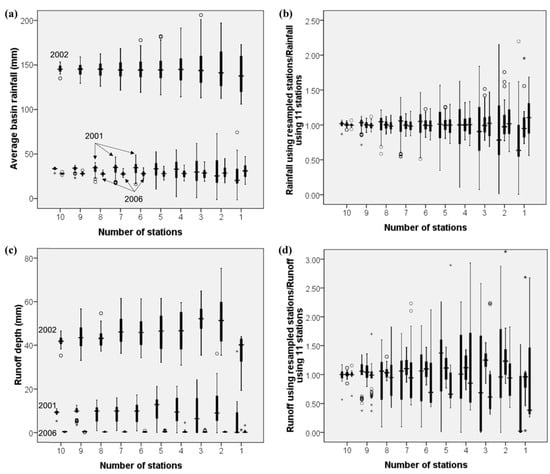
Figure 7.
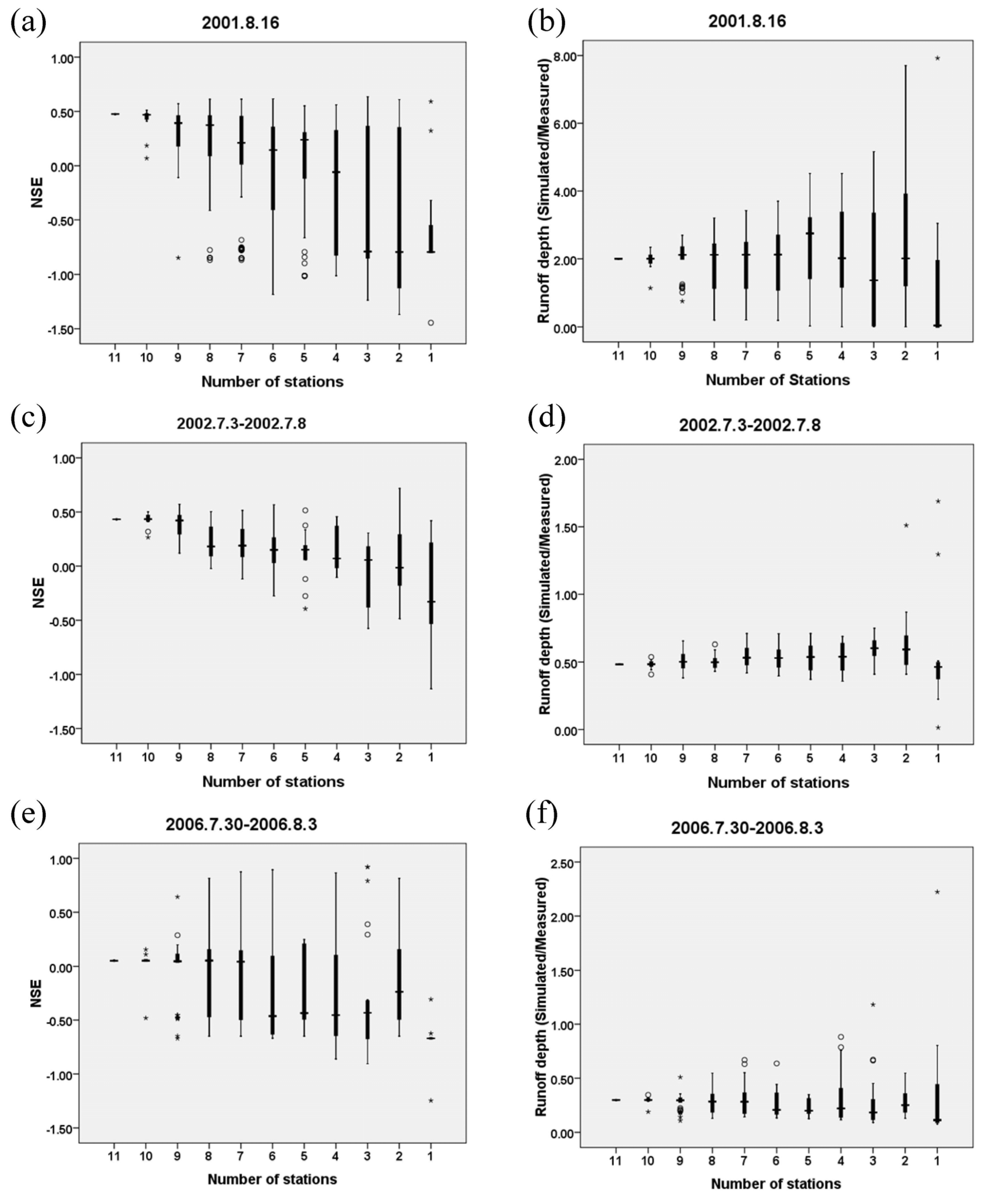
Uncertainty of the three rainfall-runoff events on different number of stations in the upstream of the Qingjian River basin: (a) Average basin rainfall, (b) Non-dimensional uncertainty of average basin rainfall, (c) Simulated runoff depth and (d) Non-dimensional uncertainty of simulated runoff depth. Note: every three boxes represent the results of 2001, 2002 and 2006 events from left to right.
For the 2001 and 2006 small rainfall events, the outliers of basin rainfall occur frequently as the n values are greater than 6 and the uncertainty ranges become much larger as the n values are less than 6. For the 2002 heavy rainfall event, the outliers of basin rainfall appear evenly and the uncertainty ranges are smaller than those of small rainfall events. This phenomenon can be caused by the smaller size of rainfall center for small rainfalls, i.e., the size of the small rainfall centers is much smaller than the area controlled by each rainfall station.
In addition, the non-dimensional uncertainty ranges (U’) of rainfall, which are calculated as the differences between the highest and lowest values of U’(n) in Figure 7b, are listed in Table 5. It is observed that the U’ values keep increasing along with the decrease of the number of stations and the ratios between the maximum and minimum U’ values are 11.0, 9.4 and 8.7 for the 2001, 2002 and 2006 rainfall events, respectively. This indicates that the impact of the number of stations on the uncertainty of basin rainfall is significant.

Table 5.
The non-dimensional uncertainty ranges (U’) of rainfall and simulated runoff depth.
4.3. Areal Representation of Rainfall Stations
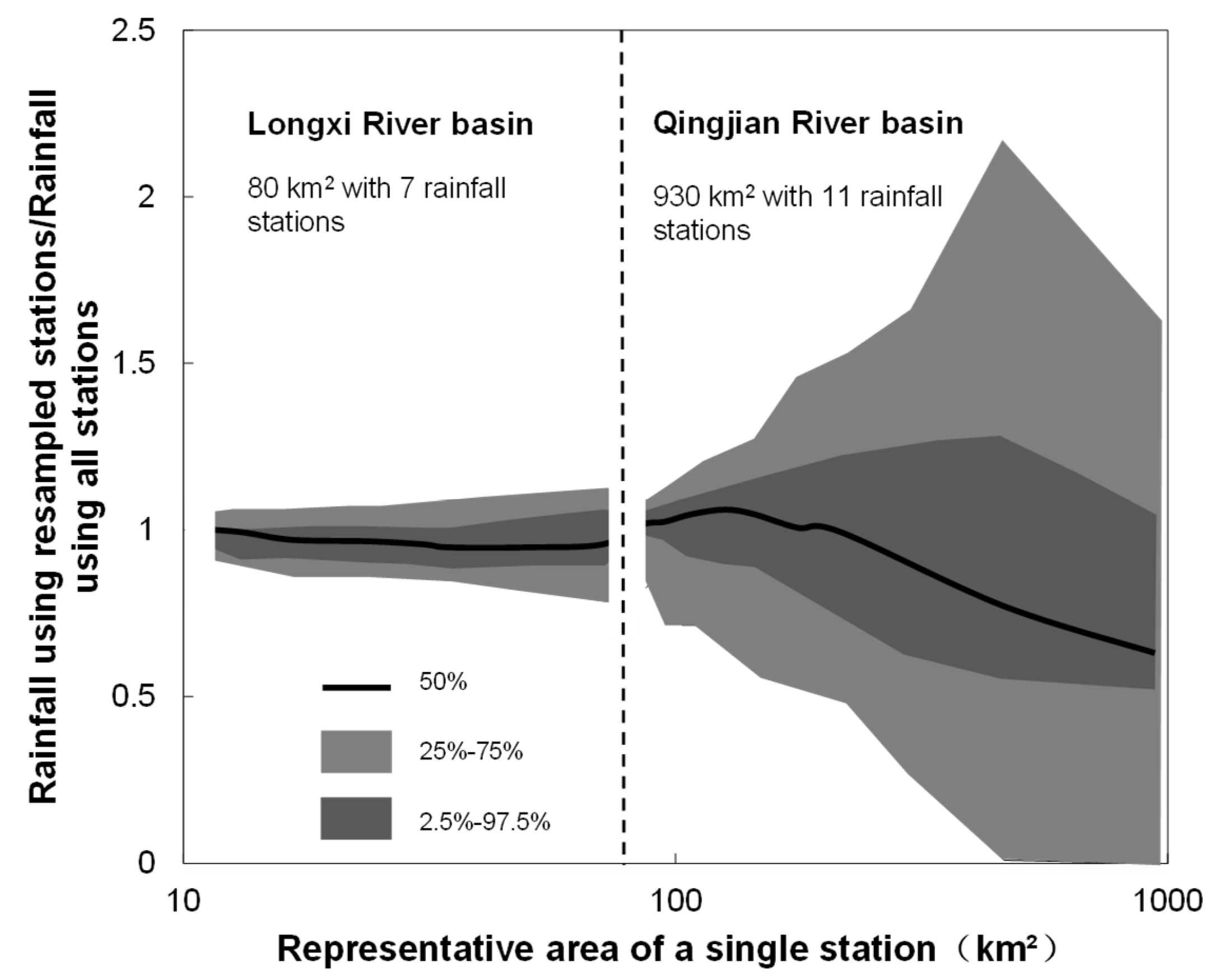
Based on the results of the upstream of the Qingjian River basin with the resampled rainfall stations, the range of the average basin rainfall shows wide fluctuation. What occurs if the coverage of rainfall stations in a basin is denser? The rainfall event with the average basin rainfall of 47.1 mm in the Longxi River basin with a denser rainfall station network and the 2001 rainfall event with the average basin rainfall of 34.2 mm in the upstream of the Qingjian River basin are compared (see Figure 8). The horizontal axis is the mean representative area of a single station that calculated from a certain number of the resampled stations (e.g., if 10 stations are selected for uncertainty estimation in the Qingjian river basin with 930 km2, the horizontal axis is 93).
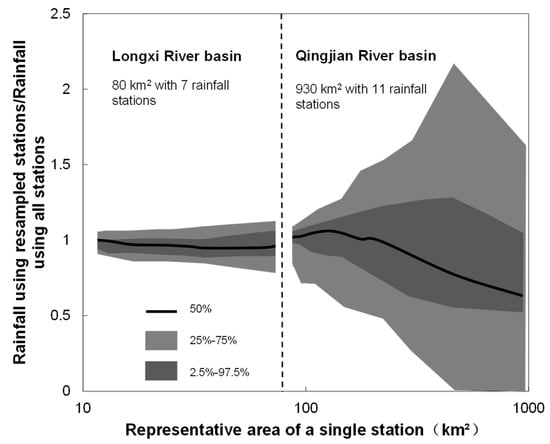
Figure 8.
The non-dimensional uncertainty range of the average basin rainfall over the representative area of a single station.
The results show that the fluctuation range of the average basin rainfall expands when the representative area of a single station increases. However, even if only one station exists in the Longxi river basin, the average basin rainfall fluctuates within a 25% range, but the fluctuation ranges of the upstream of the Qingjian river basin are 2–3 times wider. When the representative area of a single station decreases to less than 40 km2, the fluctuation range of the average basin rainfall has no evident changes. Thus, the fluctuation range of the average basin rainfall has a strong correlation with the station density in a river basin. With the increase of the station density, the uncertainty of the average basin rainfall decreases. However, in a real-world situation, the station density has an affordable threshold at which the uncertainty cannot be further decreased efficiently for certain applications and costs.
4.4. Uncertainty of Simulated Runoff
After calibrating the model with a single set of parameters, runoffs are repeatedly simulated using different numbers of resampled rainfall stations with different station combinations. Then the uncertainty of simulated runoffs is analyzed in regard of rainfall station density. From Figure 7c,d, it can be observed that the simulated runoffs using the resampled partial stations present a larger range of non-dimensional uncertainty than the average basin rainfall. The uncertainty of the rainfall input is amplified by the rainfall-runoff process, resulting in greater uncertainty of the simulated runoffs.
Figure 9 illustrates the relationship of the NSE with the number of stations (n), as well as the ratio of runoff depth (Simulated/Measured). With the reduction of rainfall input information, the mean of the NSE decreases and its range expands. The average level of the simulated runoff volume fluctuates with no significant trend, but the expansion of the range is still notable. Meanwhile, as shown in Table 5, the non-dimensional uncertainty ranges (U’) of simulated runoff are 2 to 7 times wider than those of the corresponding average basin rainfall, for a certain number of stations. That is to say, the hydrological simulation is sensitive to the spatial uncertainty of rainfall and slight differences in rainfall input may lead to greater variance of simulated runoff. This amplification can probably be explained by the infiltration-excess rainfall-runoff mechanism as follows [51,57]. The fluctuations of total rainfall and excess rainfall (i.e., runoff) are similar; however, the depth of excess rainfall (i.e., runoff) is smaller than the depth of total rainfall. Therefore, the fluctuation rate of runoff expressed in percentage (i.e., the fluctuation of runoff/the depth of runoff) is larger than that of total rainfall (i.e., the fluctuation of total rainfall/the depth of total rainfall).
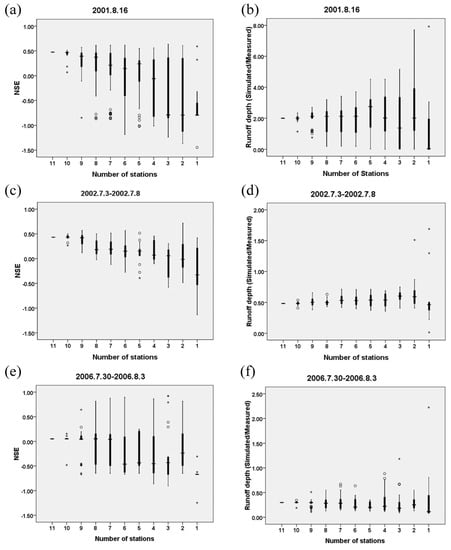
Figure 9.
Performance of simulated runoffs of the three cases using different numbers of resampled stations in the upstream of the Qingjian River basin: (a,c,e) NSE; (b,d,f) the ratio of simulated runoff depth over measured.
In addition, the effect of the rainfall center is analyzed. For the simulation of the 2001 rainfall event, the NSE (Figure 9a) reduces to 0.18 (using 10 stations) from 0.48 (using 11 stations), in the absence of Jingzeyan station with the highest rainfall depth of 75.2 mm (Figure 4a). For the 2002 rainfall event, the NSE (Figure 9c) reduces to 0.26 (using 10 stations) from 0.43 (using 11 stations), in the absence of Zichang station with the highest rainfall depth of 283.2 mm (Figure 4b). For the 2006 rainfall event, the rainfall center is mainly represented by Zichang station with the second highest rainfall depth of 42.8 mm because Yujiawan station (Figure 4c) with the highest rainfall depth (46.4 mm) only controls a very small area (0.13%). When Zichang station is absent, the NSE (Figure 9e) reduces to −0.48 (using 10 stations) from 0.05 (using 11 stations). As a result, it can be concluded that, with certain rainfall input combination, if the rainfall center is not captured and applied to the hydrological model, a large portion of the actual rainfall will be ignored in the rainfall-runoff simulation, resulting in significant deviation in simulated runoff. Even though some methods can produce high-intensity rainfall cells in a river basin, e.g., the geostatistical conditional approach used by Vischel et al. [28] and Renard et al. [29], the intensity and area of the rain centers are still difficult to simulate. Therefore, to obtain more confident simulation results, higher DS must be provided to capture more accurate range of the rainfall centers.
Furthermore, in the 2001 rainfall event, the NSE of the simulation result is 0.48 using all the 11 stations. However, the NSE increases to 0.51 in the absence of the Yangkelangwan station (rainfall depth = 31.8 mm) and reduces to 0.07 in the absence of the Sanshilipu station (rainfall depth = 36 mm). It can be concluded that even if the rainfall records of different stations are similar to each other (in the same group), their locations also have a great influence on the hydrological simulation.
4.5. Effect of Rainfall Station Density on Hydrological Simulations
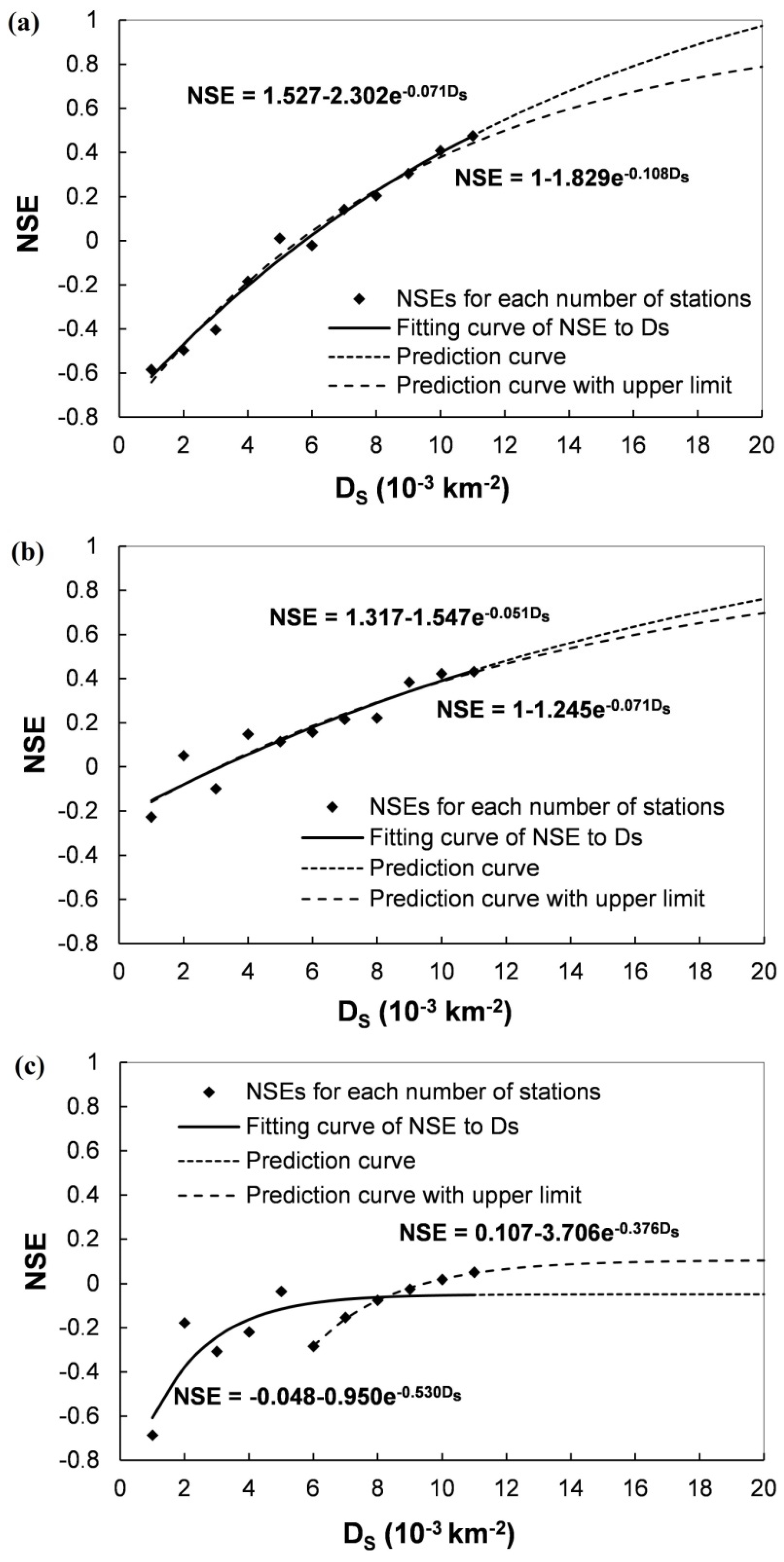
For the NSE of the simulated runoff with different number of rainfall stations (n) in Figure 9a,c,e, when n decreases, the NSE decreases because of the lack of rainfall information. To better quantify this relation, the mean NSE value for each n is correlated with the corresponding DS, i.e., the number of stations in each 1000 km2 area, as shown in Figure 10.
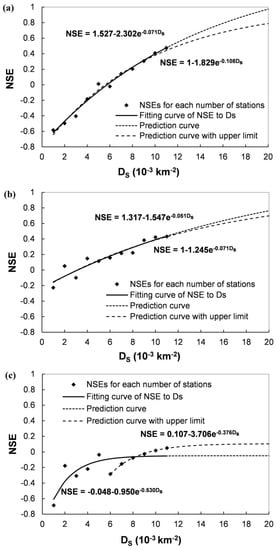
Figure 10.
Estimation of the effect of rainfall station density on hydrological simulation events in the upstream of the Qingjian River basin: (a) 2001, (b) 2002 and (c) 2006. The solid lines are the fitting curve between the NSE of simulated runoff and the rainfall station density and the dot dash lines are the prediction if the DS increase. And the dash lines are the predicted NSE values with the upper limit of 1.
An obvious relationship between the mean NSE of simulated runoff and the DS can be found in Figure 10 and this relationship can be fitted using an exponential curve (see the solid line). Furthermore, if the fit line is extrapolated to larger DS values (the dot dash line), the NSE will further increase, implying that the runoff simulation results will be improved. However, even if we can install as many rainfall stations as possible over the river basin, there is a limit of the NSE because of temporal uncertainty of rainfall, as well as the inherent uncertainty of the hydrological model and parameters. According to this trend, the exponential fitting curve is proposed as:
where a and b are the fitting parameters, NSEmax is the NSE value achieved when the DS approaching infinity. However, as the NSE value should be no more than 1, an upper limit of NSEmax (i.e., 1) is set when conducting the fitting process (the longer dash line in Figure 10).
In the first two cases, the NSE values are satisfactory and can reach 0.8 if the DS values are greater than 21 and 26 stations per 1000 km2, respectively. One general inference of this result is that the controlling area of about 40 km2 is appropriate for each rainfall station for hourly hydrological simulation in this region. This inference is in accordance with that the average basin rainfall estimation fluctuates within a 15% range when the representative area of each station is less than 40 km2. Several studies (e.g., [20]) also suggested higher spatial resolutions for rainfall measurement, but it is difficult to build and maintain a denser rainfall station network for the practical and financial reasons in many river basins.
In the third case, the NSE value is low, even if only higher DS values (6 to 11) are used for fitting. The spatially improvement of rainfall input cannot enhance the simulation performance of this case to the higher NSE value. After further examining the rainfall-runoff events, it is found that the runoff coefficient of the 2006 rainfall event (0.055) is remarkably lower than the former two events (0.137 and 0.600). As the same set of parameters is calibrated for all the three rainfall events, the limitation of hydrological simulation of the 2006 event is possibly caused by the hydrological model and parameters, rather than the spatial uncertainty of rainfall records. The variation of the runoff coefficient is also regarded as a representation of the difficulty for model simulation in this infiltration-excess region, as mentioned in Section 4.4.
The proposed fitting of Equation (2) for the relationship between the NSE of simulated runoff and the DS would be capable to reveal the possible improvement of simulation when the number of stations increases to reduce the spatial uncertainty of rainfall. Therefore, this bootstrap method is useful in managing rainfall station density in river basins. Nevertheless, the deficiencies in model structure and model parameters also substantially contribute to the uncertainties of results in some cases, as shown in Figure 10c. The proposed bootstrap method would be promising to further quantify the fraction of rainfall input-caused uncertainty from the whole simulation error, after integrating some existing approaches (e.g., [34]).
5. Conclusions
This paper proposed a bootstrap method to quantify the spatial uncertainty of rainfall by resampling current rainfall stations. The bootstrap method was further adopted to evaluate the influence of rainfall spatial uncertainty on hydrological simulation, using the DYRIM hydrological model in the upstream of the Qingjian River basin.
For a certain rainfall event, the stations in the studied river basin represented statistically significant correlations, in terms of total rainfall depth and process and the stations clustered in the same group were generally in close geographic proximity. The spatial uncertainty of rainfall was introduced as the fluctuations of average basin rainfall using resampled partial stations and it was found to be smaller when a larger rainfall event covering the whole basin occurs. Through comparing the results in the Longxi River basin, the uncertainty of the average basin rainfall between different river basins was found with essential homogeneity.
The uncertainty of simulated runoff caused by the spatial uncertainty of rainfall was quantified by using the DYRIM hydrological model with the bootstrapped rainfall stations. The hydrological simulation was found to be sensitive to the spatial uncertainty of rainfall. The uncertainty of rainfall input was amplified remarkably through hydrological simulation, resulting in greater uncertainty of the simulated runoffs. Generally, with the reduction of rainfall input information, the effectiveness of hydrological simulation decreased and the fluctuation range of simulated runoff increased. Moreover, the data recorded at the rainfall center could reflect a higher weight for the simulation.
There should be an optimal layout of rainfall stations (including number and location) in a designated river basin. In this study, the relationship between the NSE of simulated runoff and the rainfall station density in the upstream of the Qingjian River basin was established and this relationship can be extrapolated to predict the runoff simulation improvement when station density increases. This can be regarded as a suggestion to plan the number of rainfall stations to strengthen rainfall observations. A precise description of the spatial distribution of rainfall is possible with a very dense distribution of rainfall stations, or by using other techniques. For example, the NSE value could be higher if there were more stations in the upstream of the Qingjian River basin. However, it should be noted that the relationship was proposed using a simple and straight-forward method, its application was the relation’s extrapolation and lacks rigorous theoretical derivation. Further works should be done to rationalize the method and to verify it in a densely measured river basin. Moreover, with reference to the location, additional rainfall stations should be installed as close to the rainfall center of a river basin as possible for better flow simulation, which can be obtained from the analysis of local historical high-resolution radar-based rainfall data. As a result, the analysis of rainfall uncertainty could be conducive to better understand of the rainfall spatial characteristic and its influence on model simulation.
It should also be noted that the method to estimate average basin rainfall has an influence on the uncertainty analysis. This study employed the Thiessen polygon method, but other methods, such as the Kriging method and the inverse distance weighted (IDW) method, may lead to different results, which need to be further studied and the results can also be easily obtained using the bootstrap method.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51579131, 51459003), the Natural Science Foundation of Qinghai Province project (Grant No. 2017-ZJ-911) and the State Grid of China (Grant No. 52283014000T).
Author Contributions
Tiejian Li conceived and designed the methodology and contributed to the organization of this paper; Ang Zhang performed the simulations; Ang Zhang and Haiyun Shi analyzed the data and wrote the paper. Xudong Fu guided this research and contributed to the improvement of this paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A
The pseudo-codes of the python script functions to calculate the basin average rainfall depth according to the bootstrap method are given as follow. The functions are easy-to-use and high compatible with the ArcGIS 10.0 environment, independent of hydrological processes.

References
- Beven, K.J. Rainfall-Runoff Modelling; John Wiley & Sons Press: Chichester, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, V.P.; Prevert, D.K. Mathematical Models of Large Watershed Hydrology; Water Resources: Highlands Ranch, CO, USA, 2002; p. 891. [Google Scholar]
- Fares, A.; Awal, R.; Michaud, J.; Chu, P.S.; Fares, S.; Kodama, K.; Rosener, M. Rainfall-runoff modeling in a flashy tropical watershed using the distributed HL-RDHM model. J. Hydrol. 2014, 519, 3436–3447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.Y.; Li, T.J.; Liu, R.H.; Chen, J.; Li, J.Y.; Zhang, A.; Wang, G.Q. A service-oriented architecture for ensemble flood forecast from numerical weather prediction. J. Hydrol. 2015, 527, 933–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taormina, R.; Chau, K.W.; Sivakumar, B. Neural network river forecasting through baseflow separation and binary-coded swarm optimization. J. Hydrol. 2015, 529, 1788–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholami, V.; Chau, K.W.; Fadaee, F.; Torkaman, J.; Ghaffari, A. Modeling of groundwater level fluctuations using dendrochronology in alluvial aquifers. J. Hydrol. 2015, 529, 1060–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olyaie, E.; Banejad, H.; Chau, K.W.; Melesse, A.M. A comparison of various artificial intelligence approaches performance for estimating suspended sediment load of river systems: A case study in United States. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.Y.; Chau, K.W. A hybrid double feedforward neural network for suspended sediment load estimation. Water Resour. Manag. 2016, 30, 2179–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.C.; Xu, D.M.; Chau, K.W.; Lei, G.J. Assessment of river water quality based on theory of variable fuzzy sets and fuzzy binary comparison method. Water Resour. Manag. 2014, 28, 4183–4200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chau, K.W. Use of meta-heuristic techniques in rainfall-runoff modelling. Water 2017, 9, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMillan, H.; Jackson, B.; Clark, M.; Kavetski, D.; Woods, R. Rainfall uncertainty in hydrological modelling: An evaluation of multiplicative error models. J. Hydrol. 2011, 400, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavetski, D.; Kuczera, G.; Franks, S.W. Bayesian analysis of input uncertainty in hydrological modeling: 1. Theory. Water Resour. Res. 2006, 42, W03407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavetski, D.; Kuczera, G.; Franks, S.W. Bayesian analysis of input uncertainty in hydrological modeling: 2. Application. Water Resour. Res. 2006, 42, W03408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bárdossy, A.; Das, T. Influence of rainfall observation network on model calibration and application. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2008, 12, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulin, L.; Gaume, E.; Obled, C. Uncertainties on mean areal precipitation: Assessment and impact on streamflow simulations. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2009, 13, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivapalan, M.; Blöschl, G. Transformation of point rainfall to areal rainfall: Intensity-duration-frequency curves. J. Hydrol. 1998, 204, 150–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Xu, C.Y.; Sælthun, N.R.; Zhou, B.; Xu, Y. Evaluation of reanalysis and satellite-based precipitation datasets in driving hydrological models in a humid region of Southern China. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2015, 29, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athira, P.; Sudheer, K.P. A method to reduce the computational requirement while assessing uncertainty of complex hydrological models. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2015, 29, 847–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, M.; Huang, Y.F.; El-Shafie, A.; Shatirah, A. Application of the generalized likelihood uncertainty estimation (GLUE) approach for assessing uncertainty in hydrological models: A review. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2015, 29, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarini, G.; Mandapaka, P.V.; Krajewski, W.F.; Moore, R.J. Rainfall and sampling uncertainties: A rain gauge perspective. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113, D11102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, C.B.; Valdes, J.B.; Rodriguez-Iturbe, I. On the influence of the spatial distribution of rainfall on storm runoff. Water Resour. Res. 1979, 15, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faurès, J.M.; Goodrich, D.C.; Woolhiser, D.A.; Sorooshian, S. Impact of small-scale spatial rainfall variability on runoff modeling. J. Hydrol. 1995, 173, 309–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, V.L. On the effect of uncertainty in spatial distribution of rainfall on catchment modelling. Catena 1996, 28, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casper, M.C.; Herbst, M.; Grundmann, J.; Buchholz, O.; Bliefernicht, J. Influence of rainfall variability on the simulation of extreme runoff in small catchments. Hydrol. Wasserbewirtsch. 2009, 53, 134–139. [Google Scholar]
- Bedient, P.B.; Hoblit, B.C.; Gladwell, D.C.; Vieux, B.E. NEXRAD radar for flood prediction in Houston. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2000, 5, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.B.; Koren, V.I.; Zhang, Z.; Reed, S.M.; Pan, J.J.; Moreda, F. Runoff response to spatial variability in precipitation: An analysis of observed data. J. Hydrol. 2004, 298, 267–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Sonnenborg, T.O.; Refsgaard, J.C.; Vejen, F.; Jensen, K.H. Evaluation of the value of radar QPE data and rain gauge data for hydrological modeling. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 5989–6005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vischel, T.; Lebel, T.; Massuel, S.; Cappelaere, B. Conditional simulation schemes of rain fields and their application to rainfall–runoff modeling studies in the sahel. J. Hydrol. 2009, 375, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renard, B.; Kavetski, D.; Leblois, E.; Thyer, M.; Kuczera, G.; Franks, S.W. Toward a reliable decomposition of predictive uncertainty in hydrological modeling: Characterizing rainfall errors using conditional simulation. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47, W11516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaramillo, F.; Baccard, M.; Narinesingh, P.; Gaskin, S.; Cooper, V. Assessing the role of a limestone quarry as sediment source in a developing tropical catchment. Land Degrad. Dev. 2016, 27, 1064–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaubey, I.; Haan, C.T.; Grunwald, S.; Salisbury, J.M. Uncertainty in the model parameters due to spatial variability of rainfall. J. Hydrol. 1999, 220, 48–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blume, T.; Zehe, E.; Bronstert, A. Rainfall—runoff response, event-based runoff coefficients and hydrograph separation. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2007, 52, 843–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichert, P.; Mieleitner, J. Analyzing input and structural uncertainty of nonlinear dynamic models with stochastic, time-dependent parameters. Water Resour. Res. 2009, 45, W10402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Giudice, D.; Reichert, P.; Bareš, V.; Albert, C.; Rieckermann, J. Model bias and complexity—Understanding the effects of structural deficits and input errors on runoff predictions. Environ. Model. Softw. 2015, 64, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Shao, Q.; Xu, Z.; Cai, X. Analysis of parameter uncertainty in semi-distributed hydrological models using bootstrap method: A case study of SWAT model applied to Yingluoxia watershed in northwest China. J. Hydrol. 2010, 385, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uboldi, F.; Sulis, A.N.; Lussana, C.; Cislaghi, M.; Russo, M. A spatial bootstrap technique for parameter estimation of rainfall annual maxima distribution. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 981–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Li, Y.; Shin, J.; Kim, T. Constructing confidence intervals of extreme rainfall quantiles using Bayesian, bootstrap and profile likelihood approaches. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2016, 59, 573–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legates, D.R.; McCabe, G.J., Jr. Evaluating the use of “goodness-of-fit” measures in hydrologic and hydroclimatic model validation. Water Resour. Res. 1999, 35, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.S.; Kim, H.S.; Seoh, B.H. Streamflow simulation and skewness preservation based on the bootstrapped stochastic models. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2004, 18, 386–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Soidán, P.; Menezes, R.; Rubiños, Ó. Bootstrap approaches for spatial data. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2014, 28, 1207–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesterberg, T.; Moore, D.S.; Monaghan, S.; Clipson, A.; Epstein, R. Bootstrap methods and permutation tests. In Introduction to the Practice of Statistics; W.H. Freeman & Company: New York, NY, USA, 2005; Volume 5, pp. 1–70. [Google Scholar]
- DiCiccio, T.J.; Efron, B. Bootstrap confidence intervals. Stat. Sci. 1996, 11, 189–228. [Google Scholar]
- Efron, B. Bootstrap Methods: Another Look at the Jackknife. Ann. Stat. 1979, 7, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, R.M.; Shallcross, A.L. The moving blocks bootstrap versus parametric time series models. Water Resour. Res. 1996, 32, 1875–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaramillo, F.; Cory, N.; Arheimer, B.; Laudon, H.; van der Velde, Y.; Hasper, T.B.; Teutschbein, C.; Uddling, J. Dominant effect of increasing forest biomass on evapotranspiration: Interpretations of movement in Budyko space. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 567–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lall, U.; Sharma, A. A nearest neighbor bootstrap for time series resampling. Water Resour. Res. 1996, 323, 679–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortin, V.; Bernier, J.; Bobée, B. Simulation, Bayes and bootstrap in statistical hydrology. Water Resour. Res. 1997, 33, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiessen, A.H. Precipitation averages for large areas. Mon. Weather Rev. 1911, 39, 1082–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivakumar, B.; Woldemeskel, F.M. A network-based analysis of spatial rainfall connections. Environ. Model. Softw. 2015, 69, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, P.J.; Manjourides, J.; Bonetti, M.; Pagano, M. A permutation test for determining significance of clusters with applications to spatial and gene expression data. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2009, 53, 4290–4300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.Q.; Wu, B.; Li, T.J. Digital yellow river model. J. Hydro-Environ. Res. 2007, 1, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.Q.; Fu, X.D.; Shi, H.Y.; Li, T.J. Watershed Sediment Dynamics and Modeling: A Watershed Modeling System for Yellow River; Advances in Water Resources Engineering; Springer International Publishing: Basel, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 1–40. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.J.; Wang, G.Q.; Chen, J.; Wang, H. Dynamic parallelization of hydrological model simulations. Environ. Model. Softw. 2011, 26, 1736–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Fu, X.D.; Wang, G.Q.; Li, T.J.; Gao, J. A common parallel computing framework for modeling hydrological processes of river basins. Parallel Comput. 2011, 37, 302–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Li, T.J.; Si, Y.; Liu, R.H.; Shi, H.Y.; Li, X.; Li, J.Y.; Wu, X. Double-layer parallelization for hydrological model calibration on HPC systems. J. Hydrol. 2016, 535, 737–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.J.; Wang, G.Q.; Huang, Y.F.; Fu, X.D. Modeling the Process of Hillslope Soil Erosion in the Loess Plateau. J. Environ. Inform. 2009, 14, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.Y.; Li, T.J.; Wang, K.; Zhang, A.; Wang, G.Q.; Fu, X.D. Physically-based simulation of the streamflow decrease caused by sediment-trapping dams in the middle Yellow River. Hydrol. Process. 2016, 30, 783–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.Y.; Li, T.J. Estimating hydrological parameters based on rainfall patterns in river basins with no long-term historical observations. J. Hydrol. 2017, 553, 651–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.Y.; Chen, J.; Li, T.J.; Wang, G.Q. A new method for estimation of spatially distributed rainfall through merging satellite observations, raingauge records and terrain digital elevation model data. J. Hydro-Environ. Res. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.J.; Wang, G.Q.; Chen, J. A modified binary tree codification of drainage networks to support complex hydrological models. Comput. Geosci. 2010, 36, 1427–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, R.; Li, T.J.; Huang, Y.F.; Li, J.Y.; Wang, G.Q. An efficient and comprehensive method for drainage network extraction from DEM with billions of pixels using a size-balanced binary search tree. Geomorphology 2015, 238, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTER GDEM Validation Team. ASTER Global DEM Validation Summary Report; METI & NASA: Washington, DC, USA, 2009.
- ASTER GDEM Validation Team. ASTER Global DEM Version 2—Summary of Validation Results; METI & NASA: Washington, DC, USA, 2011.
- Holland, J. Adaptation in Natural and Artificial Systems; University of Michigan Press: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Deb, K. Genetic algorithm in search and optimization: The technique and applications. In Proceedings of the International workshop on Soft Computing & Intelligent Systems, Calcutta, India, 12–13 January 1997; pp. 58–87. [Google Scholar]
- Nash, J.E.; Sutcliffe, J.V. River flow forecasting through conceptual models. J. Hydrol. 1970, 10, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.N.; Li, Z.J.; Chen, J.; Li, Q.L.; Yao, C. Event-based hydrological modeling for detecting dominant hydrological process and suitable model strategy for semi-arid catchments. J. Hydrol. 2016, 542, 292–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).