Abstract
Marine aerosols are a globally significant contributor to aerosol-cloud-climate interactions; however, the impact that different sources of pollution and natural emissions from the ocean have on the water uptake properties of marine aerosols remains largely underexplored. Here we present measurements of the cloud condensation nuclei (CCN) activation of marine aerosols taken in a coastal, marine environment impacted by sea spray aerosol and different sources of pollution. The hygroscopicity parameter, κ, was found to range from <0.1 up to 1.4 with a campaign-average value of 0.22 ± 0.12. Smaller particles were less hygroscopic than larger ones, and κ varied diurnally and temporally as a function of air mass transport conditions. Measurements made using aerosol time-of-flight mass spectrometry (ATOFMS) revealed that heterogeneous reactions, sulfates, and temporal differences in the observed particle types had the largest impacts on the observed κ values. The aerosol mixing-state was also found to affect κ. Temporal differences between freshly-emitted soot and aged soot internally mixed with sulfates, likely emitted from ships, had the largest impact on diurnal variations in κ. Our results further demonstrate the significant impact that pollution and the aerosol mixing-state have on aerosol-cloud interactions in the marine boundary layer.
1. Introduction
Aerosols impact Earth’s climate directly by scattering and absorbing incoming solar radiation and indirectly by serving as nuclei for the formation of cloud droplets and ice crystals. The indirect radiative impact of aerosols is the least understood aspect of global climate change underscoring the need for observations that can better constrain aerosol-cloud-climate interactions [1]. The ability of aerosols to serve as cloud condensation nuclei (CCN) is dependent on their size, morphology, and chemical composition [2,3,4]. Oceans cover ~70% of the Earth’s surface; therefore, aerosols found in the marine atmosphere (e.g., marine aerosols) play an especially critical role in shaping aerosol-cloud-climate interactions on a global scale. The abundance of marine aerosols highlights the need for observations that can link the physicochemical properties of marine aerosols with their ability to nucleate cloud droplets in the atmosphere.
Several studies have measured or parameterized the water uptake properties of marine aerosols in different coastal and open ocean environments. A common way to represent the cloud forming potential of aerosols is by measuring their water uptake properties or hygroscopicity, which can be expressed as the single hygroscopicity parameter, κ [5]. This parameter denotes the water activity of a solution generated by the dissolved aerosol, and κ ranges from 0 for insoluble, but wettable, particles, up to 1.4 for salts. A single, average value of κ = 0.7 ± 0.2 has been prescribed for marine aerosols [6], and a similar value (e.g., κ = 0.72 ± 0.24) has been applied to global model simulations of aerosol hygroscopicity [7]. However, the hygroscopicity of marine aerosols has been shown to be highly variable depending on whether the sampling environment is representative of a polluted or a “clean” marine environment. During shipboard measurements in the tropical Atlantic Ocean, κ was observed to range from 0.75 during periods influenced by pollution from Europe up to 1.4, the same value as pure sea salt [8], during “clean” marine sampling conditions [9]. κ ranged between 0.59 to 1.11 during aircraft measurements over the pristine marine boundary layer in the Caribbean [10]. In contrast, κ was found to range from 0.33 to 0.5 for shipboard measurements conducted in the Arctic summertime during “clean” conditions [11]; the lower values of κ observed are proposed to be due to the contribution of insoluble to sparingly soluble marine organic material. Even lower hygroscopicities (e.g., κ ranging from 0.17 to 0.35) have been observed in coastal regions influenced by continental outflow and shipping emissions [10,12,13,14,15]. The range of observed values of κ demonstrates that marine aerosols show a large degree of heterogeneity in terms of their water uptake properties.
The diverse sources of marine aerosols play a major role in shaping the values of κ observed in the marine boundary layer. Sea spray aerosol, composed of sea salt and marine organic material, is a natural aerosol source emitted to the atmosphere when bubbles produced from breaking waves burst at the air-sea interface ejecting particulate matter into the atmosphere during the process [16,17,18]. Primarily composed of sodium chloride, sea salt has been shown to be the most hygroscopic aerosol with κ = 1.28–1.4 for fresh sea salt [8,19]. The hygroscopicity of biologically-derived marine organic aerosol remains uncertain; however, recent work has shown that κ can be as low as 0.14 when organics excreted from heterotrophic bacteria impact sea spray aerosol [8]. Continental emissions of biogenic organic aerosol produced from terrestrial sources have also been shown to contribute to the budget of CCN in the marine boundary layer [20]. Anthropogenic emissions contribute significantly to the marine aerosol burden and shape aerosol-cloud interactions in the marine environment. Biomass burning has been shown to be ubiquitous in the marine boundary layer both in coastal and open ocean environments [21,22]. Laboratory values for biomass burning aerosol range from 0.02 to 0.8 [23,24] while ambient air masses affected by biomass burning aerosol have been shown to have κ values ~0.2 [25]. Soot particles emitted from diesel engines have been shown to be non-hygroscopic (e.g., κ = 0) [26]. While shipping emissions have been shown to be poorly hygroscopic [15], these emissions can significantly increase the budget of CCN in the marine environment by acting as condensation sites for biogenic and anthropogenic sulfate that is hygroscopic (e.g., κ~0.6) [27,28,29]. Other continental emissions are also observed in the marine boundary layer including mineral dust, industrial emissions, and agricultural emissions [30]. Further, secondary processing or “aging” of aerosols through the condensation of gases, heterogeneous reactions, and multiphase chemistry also leads to the acquisition of particulate sulfate, secondary organic aerosol (SOA), and nitrate. A classic example in the marine boundary layer is the heterogeneous reaction between sea salt and gaseous nitrogen oxides (e.g., N2O5, HNO3) leading to the formation of sodium nitrate particles [31,32,33], which have a reduced κ (e.g., κ = 0.88) compared to fresh sea salt [5]. These secondary processes alter the size, chemical composition, and, therefore, the cloud nucleating potential of marine aerosols [34]. Understanding the factors that shape the physicochemical properties of marine aerosols, and how these processes affect aerosol hygroscopicity is essential for better constraining aerosol-cloud-climate interactions in the marine environment.
We present field measurements of aerosol hygroscopicity, given as values of κ, and the chemical mixing-state of individual particles observed during a campaign on the Scripps Pier, a site in coastal Southern California. Single-particle mass spectrometry is well-suited to differentiate the diverse particle sources and atmospheric processes that shape the physicochemical properties of marine aerosols [30,31,35,36,37,38]. We compare these measurements during time periods influenced by different air mass histories and, therefore, different particle sources and aging mechanisms in order to determine relationships between these factors and aerosol hygroscopicity. We explore whether diverse values of κ exist in the coastal marine boundary layer or whether a single, average value of κ is appropriate for marine aerosols sampled at this site. The influence of different aging processes, particle sources, and individual chemical compounds on observed values of aerosol hygroscopicity is also discussed.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Overview of Measurements Conducted on the Scripps Pier
Continuous measurements of the size, single-particle mixing state, and cloud nucleating properties of marine aerosols were conducted from 29 August to 2 October 2009 on the end of the Scripps Pier (Latitude: 32.8662° N, Longitude: 117.2544° W), which is 300 m west from shoreline and 8 m above sea level. Ambient particles were sampled through a stainless steel, 4 m long mast with an outer diameter of 1.9 cm and delivered to multiple instruments through a manifold connected to the end of the sampling mast. In addition to the single-particle, size distribution, and CCN measurements, black carbon (BC) was also measured using an aethalometer (AE-31, Magee Scientific, Berkeley, CA, USA). Gas-phase measurements of ozone (O3) (TEI 49C, Thermo Scientific) were also performed. Meteorological data (e.g., wind speed, wind direction, relative humidity, and temperature) was also continuously measured at the end of the Scripps pier [39]. Data is presented in local time, Pacific Daylight Time (PDT), which is 7 h behind Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). Figure S1 in the Supplementary Materials shows the temporal variation of temperature, relative humidity, wind speed, wind direction, ozone, and black carbon mass concentrations. Relative humidity and temperature were both stable throughout the majority of the field campaign with averages of 79.3 ± 8.2% and 20.3 ± 1.7 °C, respectively.
2.2. Chemical Analysis of Marine Aerosols Using ATOFMS
The chemistry of individual particles was measured, in real-time, using an aerosol time-of-flight mass spectrometer (ATOFMS) [40]. The ATOFMS measured the vacuum aerodynamic diameter (dva) and dual-polarity mass spectra of individual particles in the size range of ca. 200–3000 nm (dva). Particles are first focused in a conical-shaped inlet that accelerates them to their size-dependent terminal velocity. Then particles are optically detected by two continuous wave 532 nm lasers spaced 6.0 cm apart, measuring the terminal velocity of each particle and, consequently, dva. Polystyrene latex spheres of known diameter from 220–2500 nm were used to calibrate the particle size. The particle velocity was also used to time the firing of a Q-switched Nd:YAG laser (266 nm) operating at ~1.2 mJ laser power that simultaneously desorbed and ionized compounds from individual particles creating positive and negative ions, which were analyzed in a dual polarity time-of-flight mass spectrometer. Particle detection efficiencies are dependent on the ability of particles to interact with the 266 nm radiation [41,42,43]. Dual-polarity spectra provide complementary information that can be used to distinguish particle sources (e.g., ships vs. sea salt) and determine whether particles have undergone chemical aging on a particle-by-particle basis [36,37,44]. A lack of negative ion spectra indicates the presence of particle phase water, which suppresses negative ions produced by laser desorption/ionization [45,46]. During this campaign, a silica gel drier was used upstream of the ATOFMS in order to condition particles to 30% RH, which decreases some of this water and increases the formation of negative ion spectra.
The YAADA software toolkit (Available online: http://yaada.org/) was used to import single-particle mass spectra into MATLAB (The MathWorks, Inc., Natick, MA, USA) in order to process ATOFMS data [47]. Single-particle mass spectra were then analyzed using a clustering algorithm (ART-2a), which groups spectra with similar characteristics into distinct “clusters” that are then merged into distinct particle types based on the mass spectral ions and intensities [48]. Particle types were averaged into 1-h time bins and separated into submicron (0.2–1.0 um) and supermicron (1.0–3.0 um) particles. Each ion peak assignment presented in this paper corresponds to the most likely ion produced at a given mass-to-charge (m/z). Particle types described herein are defined by characteristic ion peaks and possible sources and do not reflect all of the species present within a particular particle class. Figure S2 shows the single particle spectra for the six major submicron particle types classified by ATOFMS, and a detailed description of the observed particle types can also be found in the Supplementary Materials.
2.3. Hygroscopicity Measurements of Marine Aerosols
The particle size distribution was continuously measured using a scanning mobility particle sizer (SMPS, Model 3080, TSI Inc., Shoreview, MN, USA), which characterized size distributions from 11 to 600 nm every 5 min. Total particle concentrations were measured every second by a condensation particle counter (CPC, model 3010, TSI Inc., Shoreview, MN, USA) and compared to the number concentrations of particles that activated cloud droplets within a cloud condensation nuclei counter (CCN-100, DMT) operated by scanning at the following supersaturations: 0.17% for 40 min, 0.71% for 10 min, 0.51% for 10 min, 0.29% for 10 min, and 0.10% for 10 min [49]. The supersaturation of the CCNc is a function of the column temperature gradient (dT), which was calibrated using (NH4)2SO4 (Aldrich, 99.999% purity).
The critical activation diameter (Dcrit) was calculated at each supersaturation using the size distribution data, total particle counts, and number concentrations of CCN. All data are presented as hourly averages. Dcrit was calculated using Equation (1) [15]:
where CN are the mean total particle counts measured by the CPC and the integrated size distribution made by the SMPS. From Equation (1), the number of particles measured by the SMPS in each size bin is integrated starting from the smallest diameter measured (e.g., Do = 11 nm in this case) and divided by the total number of particles measured by the SMPS (Ntotal). This fraction equals 1-CCN/CN, or the number fraction of particles that do not activate as CCN, when the SMPS size distribution is integrated up to Dcrit. The CCN activity of marine aerosols is presented as the single hygroscopicity parameter, κ, which was calculated using Equation (2) [5]:
where Dp is the dry particle diameter, Scrit is the supersaturation set by the CCN counter, and A is the Kelvin term calculated from Equation (3):
where σ is the surface tension of water (σ = 0.072 Jm−2), R is the universal gas constant, Mw is the molecular weight of water, and ρw is the density of water.
Uncertainties in κ reported in this paper refer to day-to-day and hourly differences in the average values of κ. A more detailed discussion of uncertainty in kappa can be found in the SI (see Figure S3 and discussion).
2.4. Classification of Air Masses
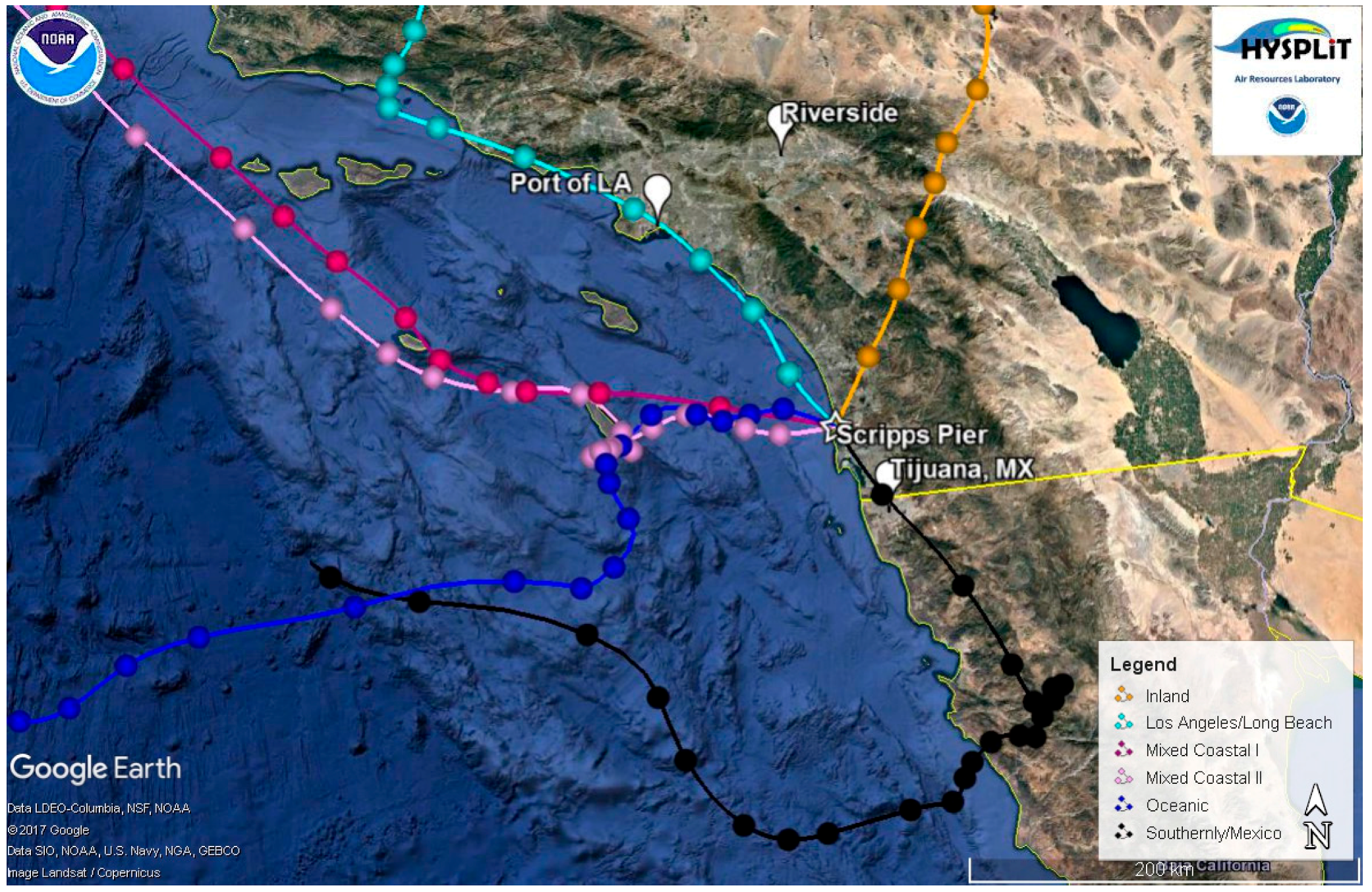
48-h, air mass back trajectories were calculated every 3 h for the entire campaign at heights of 200, 500, and 1000 m using NOAA’s Hybrid Single Particle Lagrangian Integrated Trajectory (HYSPLIT) model [50,51]. Figure 1 shows representative air mass back trajectories for the different types of air masses observed during the campaign at 200 m. For ease of comparison, we use similar air mass classifications at the same trajectory height (e.g., 200 m) as those presented in another study from the same site [52]. Oceanic air masses have westerly air mass back trajectories with transport over the open ocean; mixed coastal air masses have northwesterly back trajectories that hug the coast of California; Los Angeles and Long Beach air masses traverse the Ports of Los Angeles and Long Beach; Southerly/Mexico air masses have southerly back trajectories with many of these air masses crossing over parts of Mexico; and Inland air masses have easterly to northeasterly back trajectories with many of the air masses crossing over Riverside, CA, a polluted region of California that is impacted by aged emissions from Los Angeles [53,54,55]. Most of the inland trajectories also showed evidence of influence from the free troposphere. Two different periods classified as Mixed Coastal conditions were encountered that differed in the size distribution and observed particle types: (i) Mixed Coastal I conditions were observed before 14 September 2009 and (ii) Mixed Coastal II transport conditions were encountered from 14 September 2009 onward when back trajectories were slightly more stagnant. These periods will be discussed in more detail below. Figure S4 shows the average number size distributions for the five different air mass types encountered.
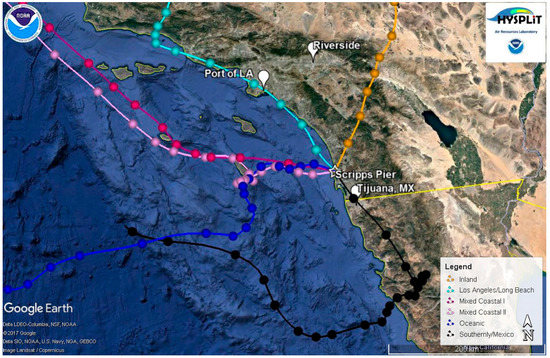
Figure 1.
Representative 48-h back trajectories taken at 200 m for the different air masses observed during the measurement campaign: (a) Inland (orange; taken 22 September 2009 at 6:00); (b) Los Angeles/Long Beach (cyan; taken 11 September 2009 at 9:00); (c) Mixed Coastal I (magenta; taken 3 September 2009 at 21:00); (d) Mixed Coastal II (light pink; taken 15 September 2009 at 0:00); (e) Oceanic (dark blue; taken 14 September 2009 at 12:00), and (f) Southerly/Mexico (black; taken 1 September 2009 at 12:00). Points represent 2-h time intervals.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Observed Hygroscopicity of Marine Aerosols
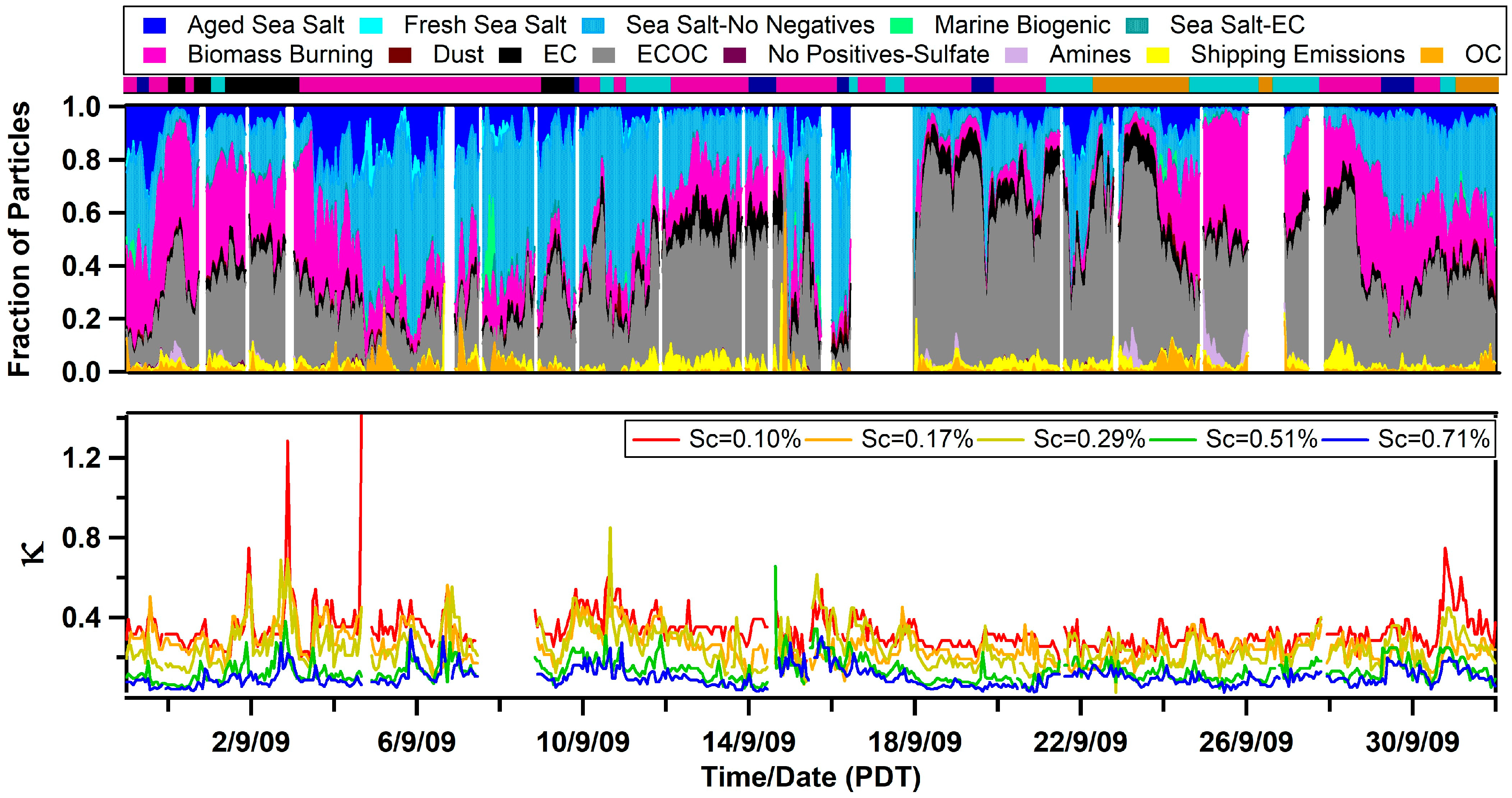
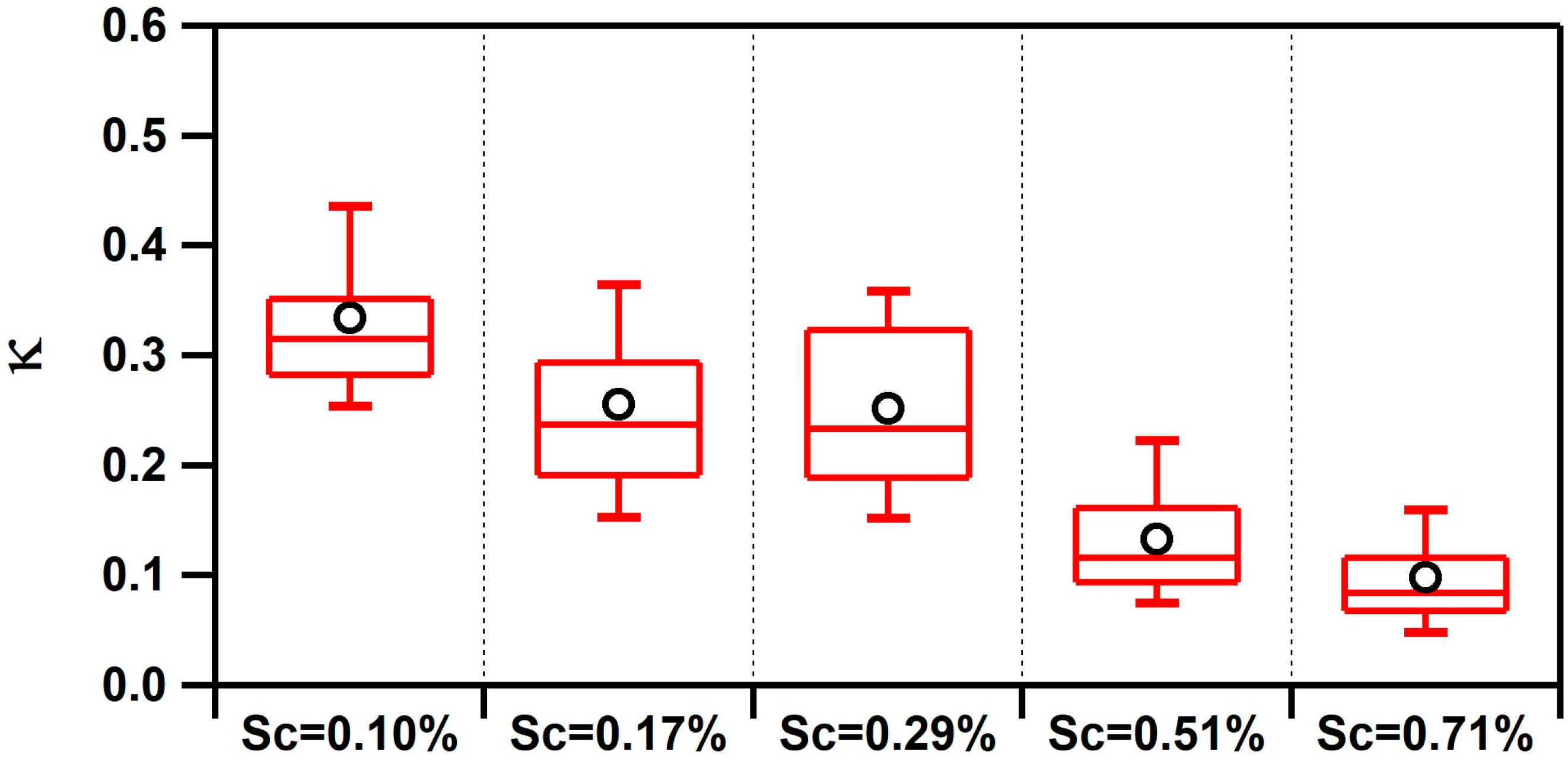
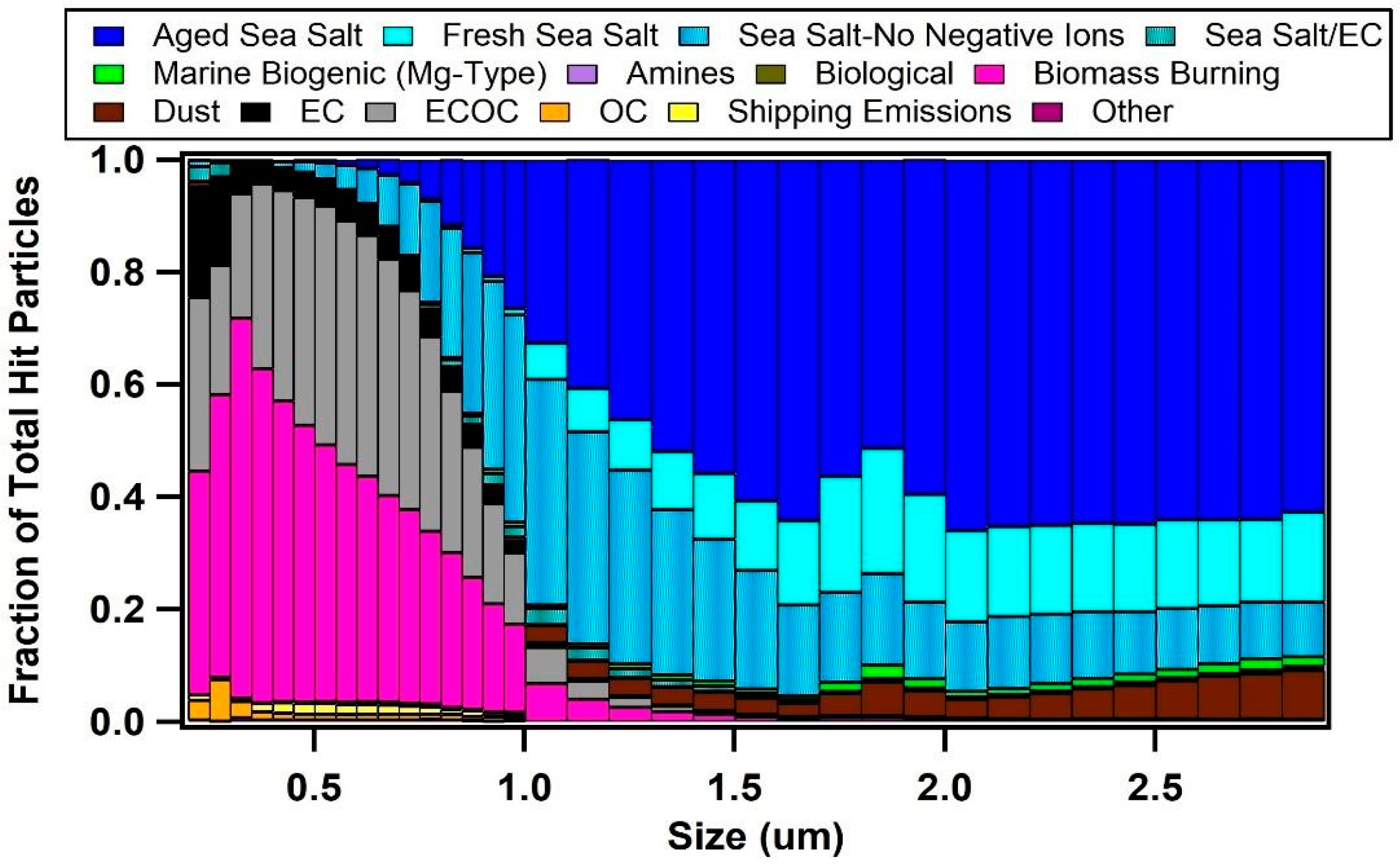
Values of κ measured at the Scripps Pier were found to be influenced by the air mass history and aerosol mixing-state. κ ranged from <0.1 up to 1.4, and the overall campaign average κ for all supersaturations was 0.22 ± 0.12. This single, average value is significantly lower than the value predicted for a marine environment (e.g., κ = 0.7 ± 0.2) [6] or values modeled for the polluted marine boundary layer that is influenced by continental outflow (e.g., κ ranges from 0.4 to 0.6) [7]. However, similar low values of κ have been observed along the California coast (e.g., κ = 0.17–0.35) [10,13,14,15] and in inland California (e.g., κ = 0.05–0.40) [56,57]. To determine the factors influencing κ, we explored the influence of the air mass history and chemical composition. Figure 2 compares the temporal variability of the air mass transport conditions, submicron particle types observed by ATOFMS, and values of κ calculated at different supersaturations (values of fCCN and Dcrit can be found in Figure S5 in the Supplementary Materials). Of note, Figure 2 shows the spread in the values of κ as a function of Scrit, which is further illustrated by the box and whisker plot shown in Figure 3. Values of κ were found to sharply decrease for larger values of Scrit with average values of κ = 0.33 ± 0.10 for 0.10% supersaturation, κ = 0.26 ± 0.08 for 0.17% supersaturation, κ = 0.25 ± 0.10 for 0.29% supersaturation, κ = 0.13 ± 0.06 for 0.51% supersaturation, and κ = 0.10 ± 0.05 for 0.71% supersaturation. Since larger particles are more likely to activate at lower values of supersaturation, our findings suggest that smaller particles were less hygroscopic than larger ones. While a field campaign conducted on the island of Crete found the opposite trend (e.g., larger particles were less hygroscopic) [12], our finding agrees with shipboard measurements conducted in the tropical Atlantic Ocean [9] and with measurements conducted in a boreal forest [58]. Our observation is likely due to the presence of larger hygroscopic sea salt and small, carbonaceous particle types, which is further supported by the size-resolved chemistry observed by ATOFMS shown in Figure 4. The fact that κ reaches up to 1.4, the same value as pure sea salt, for the smallest value of Scrit further supports this conclusion.
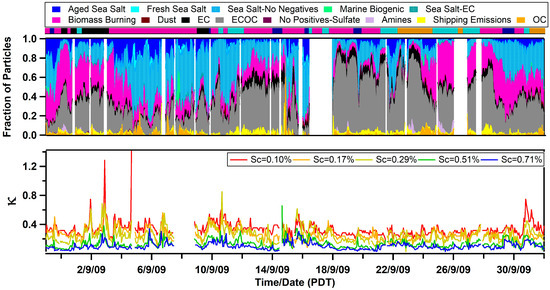
Figure 2.
Temporal profile of the hygroscopicity parameter, κ, as a function of Scrit (Sc, bottom panel), the submicron single-particle composition measured by the ATOFMS (middle panel), and the airmass classification (top panel, magenta is Mixed Coastal, black is Southerly/Mexico, cyan is Los Angeles/Long Beach, orange is Inland, and dark blue is Oceanic).
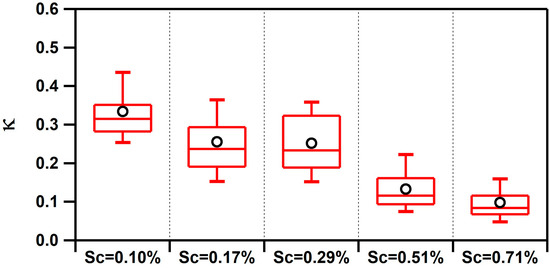
Figure 3.
Box and whisker plots of κ values calculated at different values of Scrit (Sc). Average values are denoted by black circles.
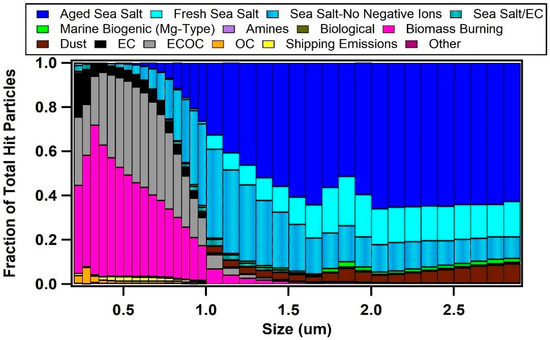
Figure 4.
Particle types observed by ATOFMS shown as a function of particle size. Submicron particles are spaced by 0.05 um bins, while supermicron particles are spaced by 0.1 um bins.
Three spikes in κ are also shown in Figure 2. These spikes were observed on September 1, September 2, and September 4. ATOFMS data is unavailable for the first two spikes in κ. However, during the third spike, a decrease in submicron carbonaceous particle types and an increase in fresh sea salt was observed. Further, black carbon concentrations measured by an aethalometer dropped below the detection limit of the instrument during this time period indicating that “clean” marine conditions were observed.
Overall, the different air masses sampled were found to account for some of the temporal variability of κ. Surprisingly, the highest average value of κ was not observed during Oceanic transport conditions, when κ = 0.23 ± 0.07 at a supersaturation of 0.17% (see Table 1). Instead the highest values of κ were measured during Southerly/Mexico transport conditions (κ = 0.31 ± 0.11) and during Mixed Coastal I transport (κ = 0.28 ± 0.09) while Inland air masses had the lowest values of κ (i.e., κ = 0.21 ± 0.05). Because values of κ range from ~0.5 to 1.4 during “clean” marine conditions [9,10], the observed low average values of κ suggest that pollution constantly influences the hygroscopicity of marine aerosols off the coast of Southern California. Overall, our low values of κ are in agreement with recent field campaigns that have shown that “clean” marine conditions are rarely observed near the coast of California [27,28].

Table 1.
Air mass transport conditions, average black carbon (BC) mass concentrations, observed particle types, and average values of κ, fCCN, and Dcrit observed at 0.17% supersaturation. The standard deviation is given in brackets.
3.2. Single Particle Composition of Marine Aerosols
Particle composition was shown to vary based on the origin of the sampled air mass (see Table 1 and the top and middle panels of Figure 2). We focus only on the submicron particles in Figure 2, as supermicron particles are assumed to be CCN active due to their large size and, therefore, smaller Kelvin effect, while the composition of the submicron particles is more important for explaining the observed κ values. Temporal trends of both submicron and supermicron particle types can be found in Figure S6.
The highest number fractions of submicron ocean-derived particle types (e.g., sea salt particles with no negative ion spectra, aged sea salt, and fresh sea salt) were observed during Oceanic (~41% of observed submicron particles) and Mixed Coastal I transport conditions (~49% of observed submicron particles). Notably, few Mg-type particles and no methanesulfonic acid (MSA, 95CH3SO3−) were detected by ATOFMS, which indicates that marine biological activity did not significantly impact the mixing-state or hygroscopicity of marine aerosols sampled during this campaign [36,59]. Instead, the number fraction of fresh soot particles (e.g., elemental carbon (EC) particles) with little secondary nitrate and/or sulfate was higher during Oceanic transport conditions and is likely due to shipping emissions. Since fresh soot is non-hygroscopic (e.g., κ = 0), the higher number fractions of soot observed during Oceanic transport conditions likely explains why κ was lower under these air mass conditions. Lower values of κ were also observed during Mixed Coastal II than during Mixed Coastal I transport conditions, likely due to the lower number fraction of sea salt and higher number fractions of shipping emissions and soot particles (e.g., EC and elemental carbon/organic carbon (ECOC) particle types) detected during Mixed Coastal II conditions. Soot particle types and shipping emissions were also prevalent (e.g., 36% and 2%, respectively) when air masses from the Ports of Los Angeles and Long Beach were sampled. It is important to note that the ATOFMS signature for shipping emissions contains iron (56Fe+), vanadium (51V+, 67VO+), and nickel (58Ni+), indicative of high sulfur residual fuel combustion, while ships combusting diesel fuel emit EC and ECOC particle types [35,60]. Thus, it is likely that many of the observed soot particles were also emitted from ships, particularly during onshore winds and when air masses transported over the open ocean (e.g., during Oceanic transport conditions) were impacted by ocean-going ships.
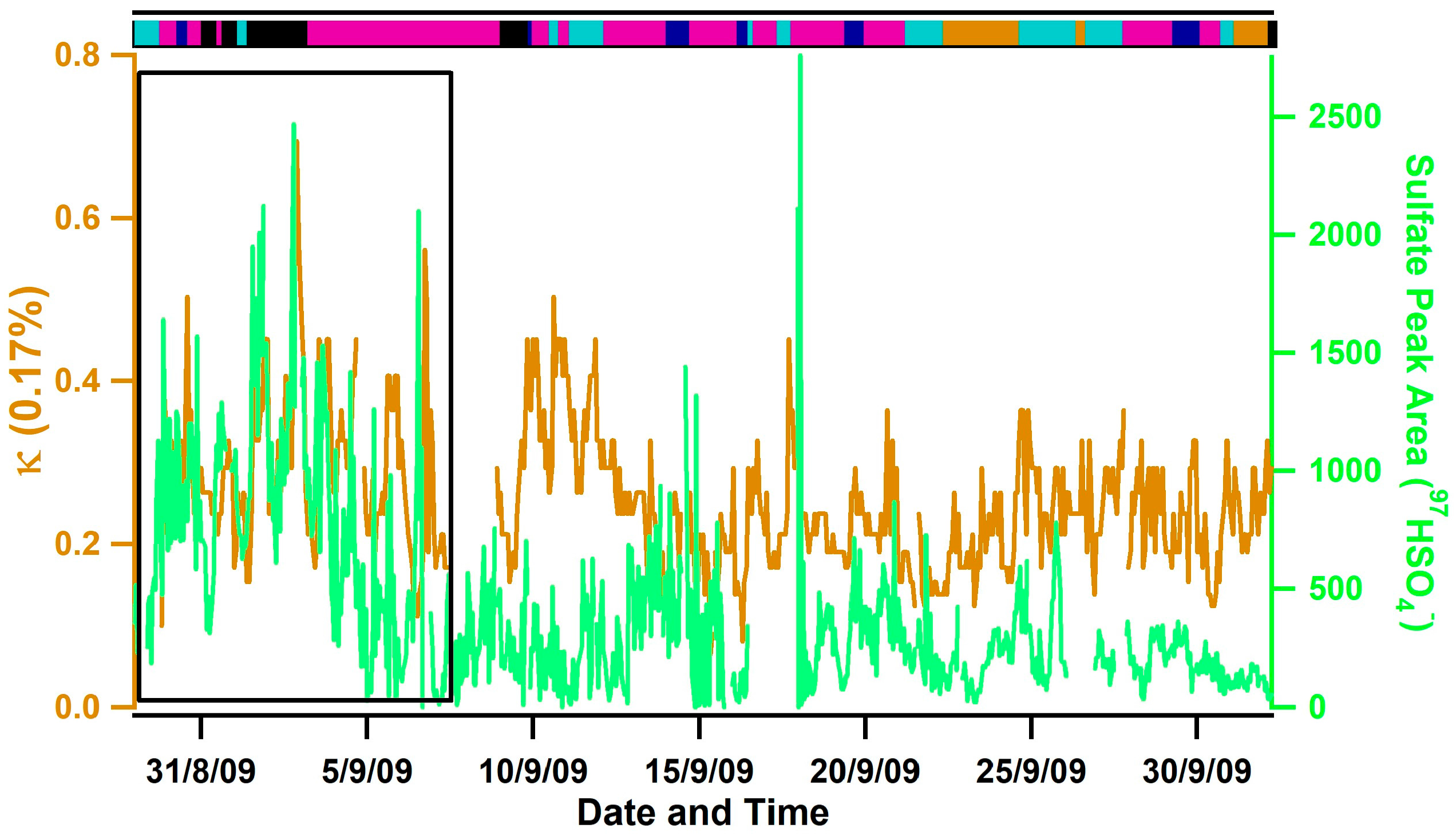
The lowest hygroscopicities were observed during Inland transport conditions due to a lack of sea salt and the high number fractions of carbonaceous (e.g., soot and organic carbon (OC)) particle types (e.g., ~56% on average). OC measured during this campaign contained ion peaks indicative of aromatic compounds typically derived from the secondary processing of vehicle exhaust and industrial emissions (e.g., 51C4H3+, 63C5H3+, 77C6H5+) [61,62,63], indicating a combustion rather than a biogenic source. The highest values of κ were observed during Southerly/Mexico transport conditions, even though lower number fractions of sea salt and higher number fractions of OC and ECOC were observed compared to Oceanic and Mixed Coastal I transport conditions. High number fractions of biomass burning aerosols were also observed (e.g., ~25% on average and up to 46%) and No Positives-Sulfates were also present that contained sulfuric acid ion peaks (e.g., 195H2SO4SO4−). Notably, the highest ion peak areas of sulfate, which is indicative of the amount of sulfate present [64,65], were also observed during this time period and were temporally correlated with κ (see the boxed region in Figure 5). The higher levels of sulfate during Southerly transport conditions are likely due to strict regulations in California on particulate sulfate and sulfur levels in fuels [66] compared to Mexico. We speculate that the combined influence of highly acidic aerosol and high amounts of sulfate observed during this time period explains the higher values of aerosol hygroscopicity observed during Southerly transport conditions. While very high number fractions of biomass burning aerosol (e.g., 59% on average) were also observed during Los Angeles and Long Beach transport conditions from 24 September 2009–26 September 2009 due to the Guiberson fire that burned in Ventura County, lower values of κ were observed during this time period. The most likely explanation is that less sulfate was observed (see Figure 5) and a higher number of fractions of soot particles emitted from ships and diesel trucks were transported from the Ports of Los Angeles and Long Beach that lowered the observed κ values.
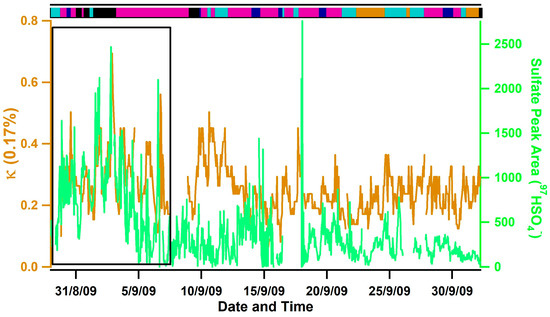
Figure 5.
Temporal plot of the average κ observed at 0.17% supersaturation (orange trace) and the average sulfate ion peak area observed by ATOFMS (green trace). A bar illustrating the airmass classification (top panel, magenta is Mixed Coastal, black is Southerly/Mexico, cyan is Los Angeles/Long Beach, orange is Inland, dark blue is Oceanic) is also shown. The black box highlights the time period when sulfate and κ were high during Southerly transport conditions.
3.3. Diurnal Variability of Κ and the Role of Chemical Aging
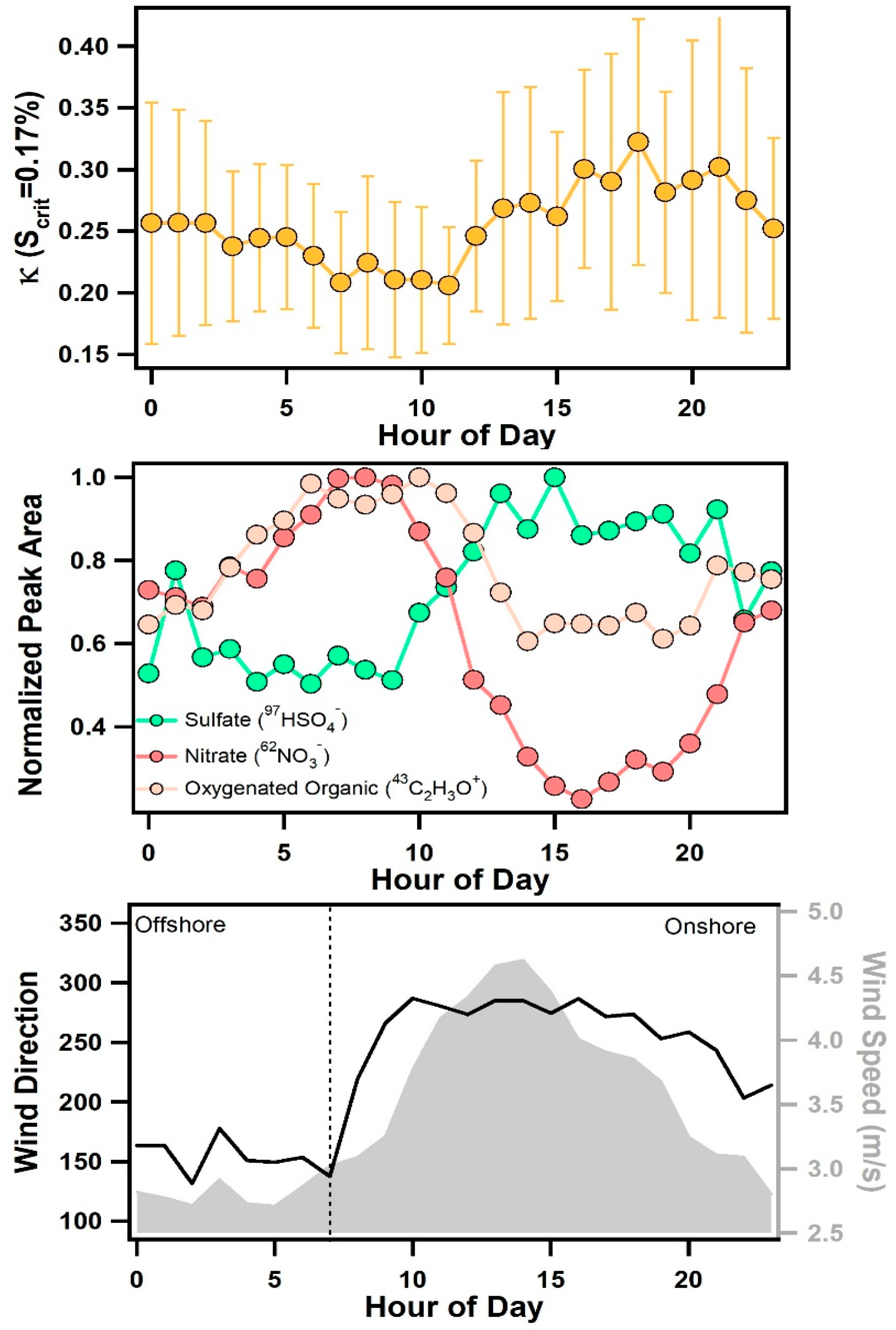
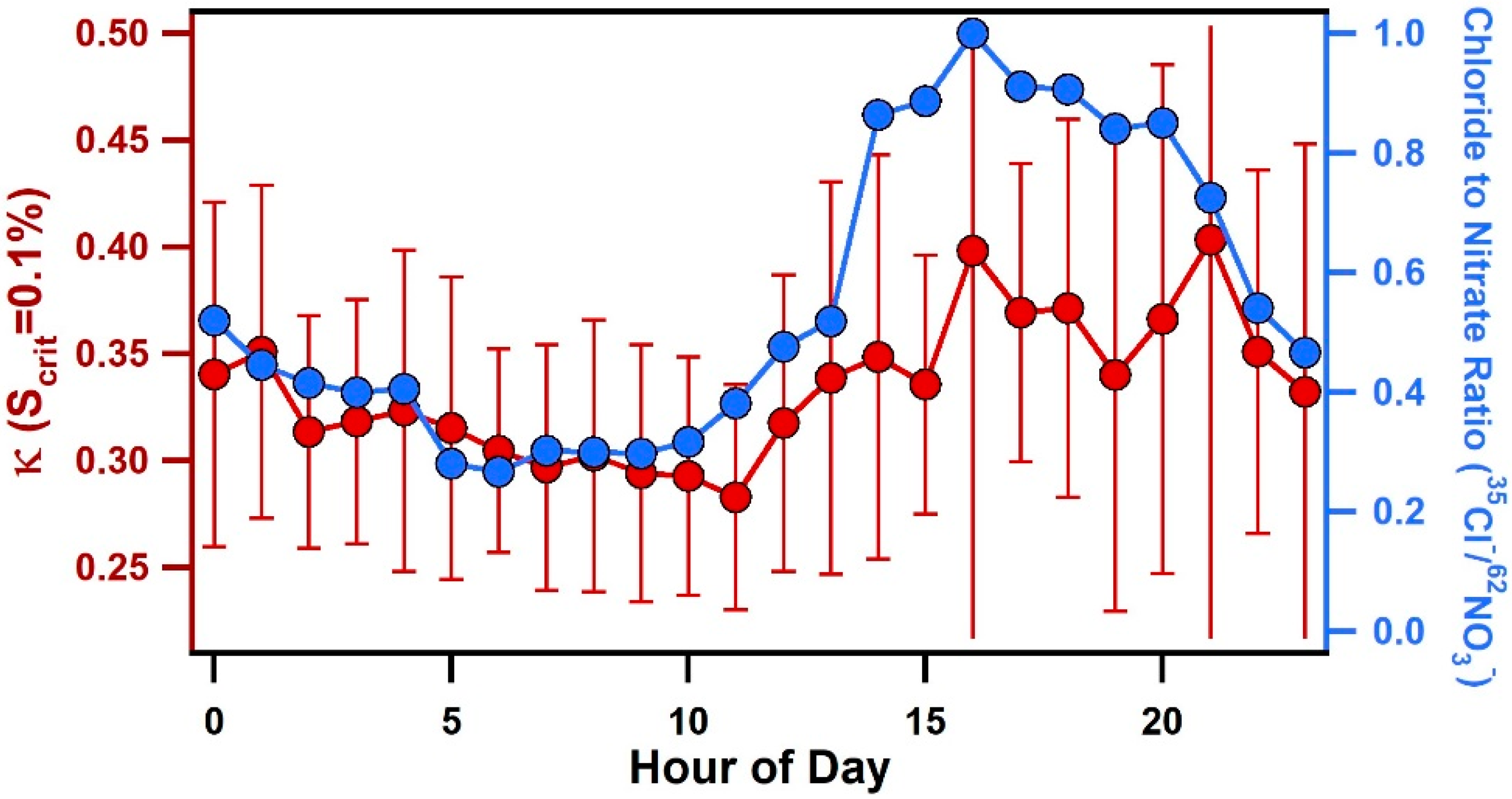
In addition to the influence of air mass transport conditions, another striking feature of Figure 2 is the consistent, diurnal variations in κ for all values of Scrit. Figure 6 shows the average diurnal pattern of κ. At a supersaturation of 0.17%, κ was found to decrease slightly between 7:00–9:00 to an average value of 0.21 ± 0.01, then increase throughout the afternoon and reach a peak, average value of 0.29 ± 0.02 between 14:00–18:00. Values of κ began to rise after 9:00 when wind speeds increased and a change from offshore to onshore winds was observed (see Figure 6). Diurnal patterns of individual chemical compounds measured by ATOFMS are also shown in Figure 6. Particulate nitrate (e.g., 62NO3−) was primarily associated with aged sea salt and was found to peak during offshore winds in the early morning, which is the opposite diurnal pattern of κ, likely due to nitrogen oxide emissions associated with morning traffic. Notably, the chloride (35Cl−) to nitrate (62NO3−) ratio, shown in Figure 7, was found to peak in the late afternoon and evening due to onshore winds and increased wind speeds that enhanced the production of fresh sea salt. This ratio shows a nearly identical pattern as κ, particularly at 0.1% supersaturation (see Figure 7), suggesting that variations in the relative amounts of fresh and heterogeneously reacted sea salt contribute to the observed diurnal cycle of κ, particularly for larger submicron particles.
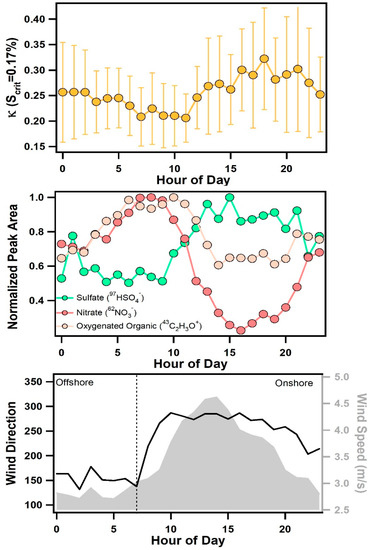
Figure 6.
Diurnal profile of κ at 0.17% supersaturation with error bars representing the standard deviation (top panel), sulfate, nitrate, and oxygenated organic aerosol ion peaks measured by ATOFMS (middle panel), and wind speed and direction (bottom panel).
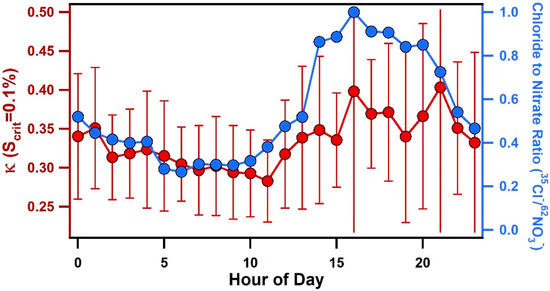
Figure 7.
Diurnal profile of κ at 0.1% supersaturation with error bars representing the standard deviation and the chloride/nitrate ratio measured by ATOFMS.
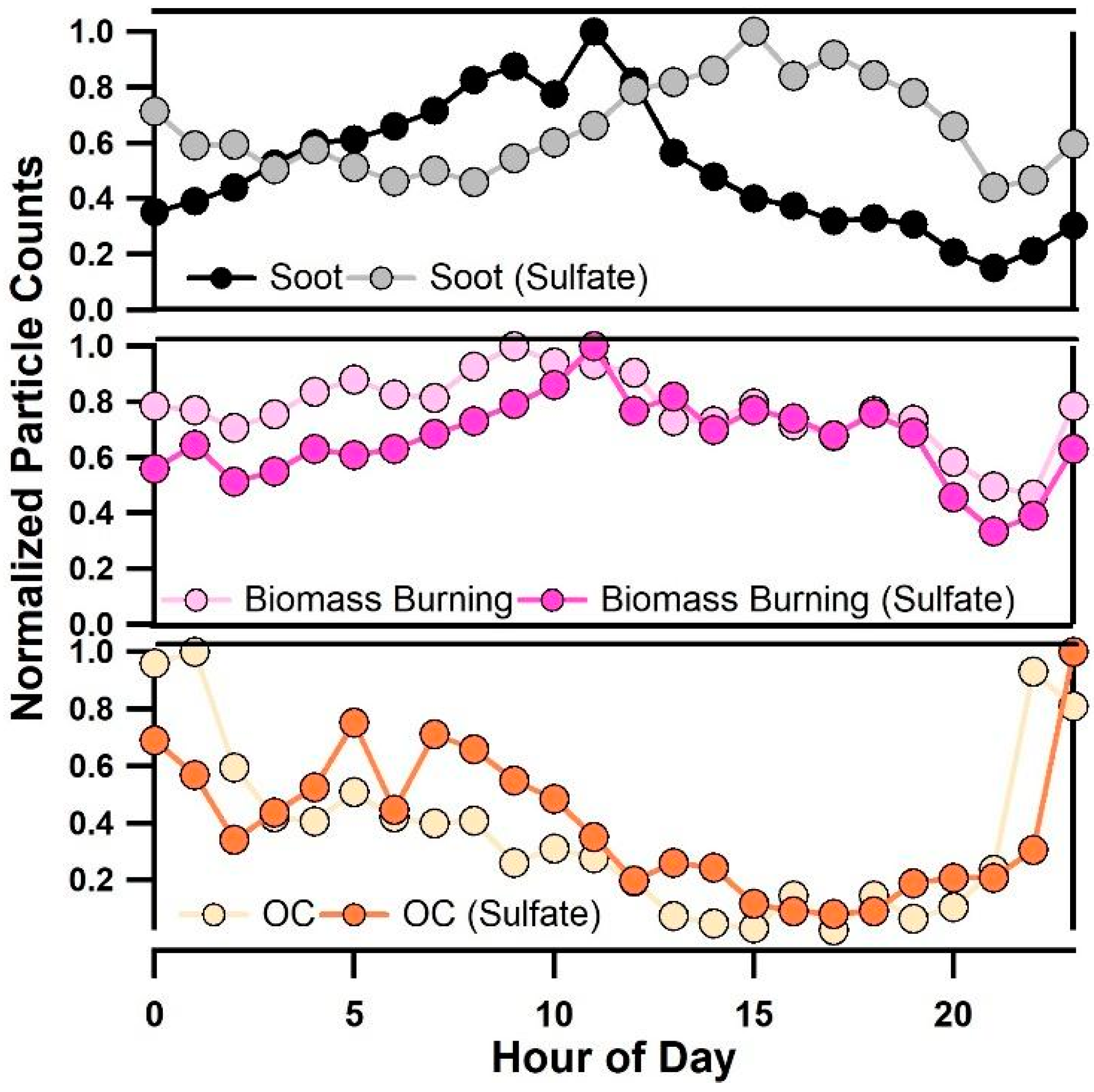
Figure 6 also clearly shows that the diurnal pattern of particulate sulfate (97HSO4−) is nearly identical to variations in κ. To gain further insight into how the mixing state of sulfate-containing particles impacted κ, Figure 8 shows a comparison of the diurnal profile of normalized number counts of soot (e.g., EC and ECOC), biomass burning, and OC particles with and without sulfates. From Figure 8, soot particles with and without sulfates showed diurnal patterns that matched observed κ values. Fresh soot particle types peaked in the morning between 8:00–10:00, when the lowest values of κ were observed, while soot particles internally mixed with sulfate peaked in the late afternoon from 14:00–18:00 when the highest values of κ were observed. The diurnal trends in the mixing state of soot particles are likely due to contributions of local emissions in the morning during offshore winds, while aged shipping emissions contributed internal mixtures of soot and sulfate that were observed in the afternoon during onshore winds. Ocean-going vessels emit large quantities of carbonaceous particles and SO2(g) [35], and the observed soot particles in the afternoon are likely due to soot emitted from marine diesel engines that acts as a condensation site for sulfate. This finding is in agreement with previous work showing that ships emit carbonaceous material that acquires sulfate and contributes to budgets of CCN in the marine boundary layer [27,28,29]. This finding also agrees with previous work showing that the most dramatic increases in κ occur when non-hygroscopic aerosols acquire trace amounts of hygroscopic material [67]. In contrast, OC and OC-(Sulfate) particles were found to peak in the evening and in the morning between 8:00–10:00 during offshore winds. Interestingly, 43C2H3O+, an ATOFMS marker associated with oxygenated, aged OC [53] was not found to increase at the same time as κ, suggesting that the aging of purely organic particles did not significantly impact κ. Biomass burning aerosol and internal mixtures of this particle type with sulfate were both found to be abundant during all hours of the day likely due to the major wildfires that burned in Southern California during most of this study.
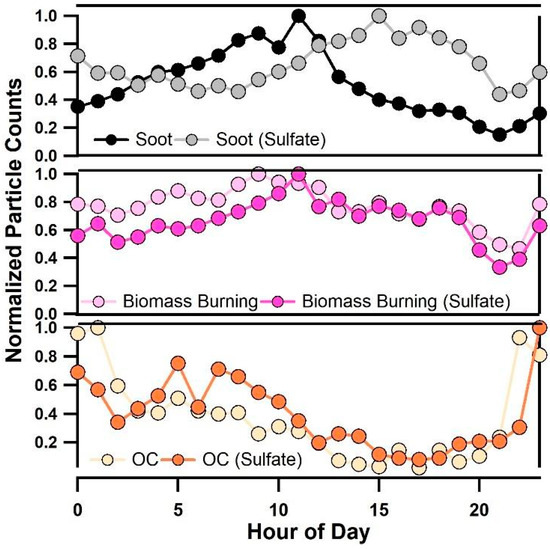
Figure 8.
Diurnal profile of soot and soot internally mixed with sulfate (top panel), biomass burning and biomass burning aerosol internally mixed with sulfate (middle panel), and OC and OC internally mixed with sulfate (bottom panel).
4. Conclusions
Our results provide insight into the water uptake and physicochemical properties of marine aerosols at a polluted coastal site. κ was found to vary as a function of particle size and the origin of the air mass sampled. During different air mass transport conditions, variations in the number fractions of highly hygroscopic particle types, including sea salt, and less hygroscopic particle types, including OC and soot, shaped the observed values of κ. During Inland transport conditions, a high number fractions of both soot and OC particles and mixtures of these particle types (e.g., ECOC particles) resulted in the lowest values of κ observed during the campaign. In addition to the presence or absence of specific particle types, particulate sulfate was also found to significantly affect κ. During Southerly/Mexico transport conditions, the highest values of both κ and particulate sulfate were observed further demonstrating the important role that sulfate plays in the water uptake properties of marine aerosols.
Particulate sulfate and the aerosol mixing-state also influenced the observed diurnal variability of κ. Daily variations in the chloride-to-nitrate ratio were found to match the diurnal variability of κ for larger submicron particles, suggesting that heterogeneous processing of fresh sea salt, which displaces chloride with nitrate, decreases κ in the polluted marine boundary layer. For smaller particles, the observed diurnal pattern of κ covaried with the afternoon production of particulate sulfate. Notably, particulate nitrate and ion peak indicators of aged OC had the opposite trend as κ illustrating the important role of sulfate in the observed aerosol hygroscopicity. A clear diurnal pattern was observed for soot particles whereby freshly-emitted soot particles peaked in the morning and aged soot particles that were internally mixed with sulfate peaked along with κ in the afternoon. In contrast, OC and biomass burning aerosol were highly aged by the time they reached the Scripps Pier, which caused these particles to play a less significant role in the observed diurnal variations in κ. The diurnal cycle of κ also followed the daily changes in wind direction, suggesting that the observed fresh soot particles were from local emissions while internal mixtures of soot and sulfate observed during onshore winds were due to aged diesel combustion particles, likely emitted from ships. Our results agree with previous work showing that the aging of anthropogenic aerosols has the largest impact on particle hygroscopicity [15] and that pollution significantly impacts CCN activation along the coast of California [27,28].
During this study, κ ranged from poorly hygroscopic (e.g., κ < 0.1) up to highly hygroscopic (e.g., κ = 1.4, the same value as fresh sea salt) [5,8]. The overall campaign average κ was 0.22 ± 0.12, which is on par with average values of continental aerosol [6], and significantly lower than the average κ of 0.72 ± 0.24 expected for marine environments and κ of 0.4–0.6 predicted for marine aerosols impacted by continental outflow [7]. In fact, most studies conducted in coastal regions, including along the California coast, have reported significantly lower values of κ than expected for marine environments, in the range of 0.17 to 0.35, due to the large impact of pollution on the hygroscopicity of marine aerosols [12,13,14,15,68]. Even in the summertime Arctic Ocean during “clean” marine conditions, lower values of κ have been observed, likely due to the influence of biologically-derived marine organic aerosol [11]. These findings suggest that the average predicted value of κ may not capture the variability of aerosol hygroscopicity observed in coastal and open oceanic environments and likely overpredicts κ values for coastal environments.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at http://www.mdpi.com/2073-4433/9/2/52/s1, Figure S1. Temporal profiles of black carbon mass concentrations, ozone, wind speed, and wind direction, temperature, and relative humidity; Figure S2. Average spectra and descriptions of particle types sampled by the ATOFMS; Figure S3. uncertainties in κ; Figure S4. Average size distributions during different air mass transport conditions; Figure S5. Values of Dcrit and the fraction of particles activated (fCCN); and Figure S6. Temporal trends of submicron and supermicron particles.
Acknowledgments
Dan Cziczo (Massachusetts Institute of Technology) is acknowledged for use of a cloud condensation nuclei counter during this field campaign. PNNL and the ARCS fellowship are acknowledged for support of C.J.G. C. McDonald is acknowledged for use of the Scripps Pier during measurements. The authors gratefully acknowledge the NOAA Air Resources Laboratory (ARL) for the provision of the HYSPLIT transport and dispersion model and/or READY website (http://www.ready.noaa.gov) used in this publication.
Author Contributions
C.J.G. led measurements to collect ATOFMS, CCN, CPC, SMPS, black carbon, and ozone data, processed ATOFMS data, and wrote the manuscript. J.F.C., D.B.C., and K.J.S. also collected ATOFMS, CCN, CPC, SMPS, black carbon, and ozone data. J.Y.G. and A.E.B. processed SMPS, CCN, and CPC data. K.A.P. conceived the experiment and administered the project. All authors read and edited the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Myhre, G.; Shindell, D.; Bréon, F.-M.; Collins, W.; Fuglestvedt, J.; Huang, J.; Koch, D.; Lamarque, J.-F.; Lee, D.; Mendoza, B.; et al. Anthropogenic and Natural Radiative Forcing; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- McFiggans, G.; Artaxo, P.; Baltensperger, U.; Coe, H.; Facchini, M.C.; Feingold, G.; Fuzzi, S.; Gysel, M.; Laaksonen, A.; Lohmann, U.; et al. The effect of physical and chemical aerosol properties on warm cloud droplet activation. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2006, 6, 2593–2649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruppacher, H.R.; Klett, J.D. Microphysics of Clouds and Precipitation, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Quinn, P.K.; Bates, T.S.; Coffman, D.J.; Covert, D.S. Influence of particle size and chemistry on the cloud nucleating properties of aerosols. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2008, 8, 1029–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petters, M.D.; Kreidenweis, S.M. A single parameter representation of hygroscopic growth and cloud condensation nucleus activity. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2007, 7, 1961–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreae, M.O.; Rosenfeld, D. Aerosol-cloud-precipitation interactions. Part 1. The nature and sources of cloud-active aerosols. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2008, 89, 13–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pringle, K.J.; Tost, H.; Pozzer, A.; Poschl, U.; Lelieveld, J. Global distribution of the effective aerosol hygroscopicity parameter for CCN activation. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 5241–5255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, D.B.; Ault, A.P.; Moffet, R.C.; Ruppel, M.J.; Cuadra-Rodriguez, L.A.; Guasco, T.L.; Corrigan, C.E.; Pedler, B.E.; Azam, F.; Aluwihare, L.I.; et al. Impact of marine biogeochemistry on the chemical mixing state and cloud forming ability of nascent sea spray aerosol. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 8553–8565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Good, N.; Topping, D.O.; Allan, J.D.; Flynn, M.; Fuentes, E.; Irwin, M.; Williams, P.I.; Coe, H.; McFiggans, G. Consistency between parameterisations of aerosol hygroscopicity and CCN activity during the RHaMBLe discovery cruise. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 3189–3203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, J.G. Variability of the relationship between particle size and cloud-nucleating ability. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M.; Chang, R.Y.W.; Sierau, B.; Sjogren, S.; Swietlicki, E.; Abbatt, J.P.D.; Leck, C.; Lohmann, U. Cloud condensation nuclei closure study on summer arctic aerosol. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 11335–11350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bougiatioti, A.; Nenes, A.; Fountoukis, C.; Kalivitis, N.; Pandis, S.N.; Mihalopoulos, N. Size-resolved CCN distributions and activation kinetics of aged continental and marine aerosol. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 8791–8808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, G.C.; Day, D.A.; Russell, L.M.; Dunlea, E.J.; Jimenez, J.L.; Tomlinson, J.M.; Collins, D.R.; Shinozuka, Y.; Clarke, A.D. Characterization of particle cloud droplet activity and composition in the free troposphere and the boundary layer during INTEX-B. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 6627–6644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, R.H.; Cerully, K.; Bahreini, R.; Brock, C.A.; Middlebrook, A.M.; Nenes, A. Hygroscopicity and composition of California CCN during summer 2010. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furutani, H.; Dall’osto, M.; Roberts, G.C.; Prather, K.A. Assessment of the relative importance of atmospheric aging on CCN activity derived from field observations. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 3130–3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchard, D.C.; Woodcock, A.H. Bubble formation and modification in the sea and its meteorological significance. Tellus 1957, 9, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Dowd, C.D.; De Leeuw, G. Marine aerosol production: A review of the current knowledge. Philos. Trans. A 2007, 365, 1753–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prather, K.A.; Bertram, T.H.; Grassian, V.H.; Deane, G.B.; Stokes, M.D.; DeMott, P.J.; Aluwihare, L.I.; Palenik, B.P.; Azam, F.; Seinfeld, J.H.; et al. Bringing the ocean into the laboratory to probe the chemical complexity of sea spray aerosol. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 7550–7555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, S.M.; Butcher, A.C.; Rosenoern, T.; Coz, E.; Lieke, K.I.; de Leeuw, G.; Nilsson, E.D.; Bilde, M. Investigating Primary Marine Aerosol Properties: CCN Activity of Sea Salt and Mixed Inorganic-Organic Particles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 10405–10412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coggon, M.M.; Sorooshian, A.; Wang, Z.; Craven, J.S.; Metcalf, A.R.; Lin, J.J.; Nenes, A.; Jonsson, H.H.; Flagan, R.C.; Seinfeld, J.H. Observations of continental biogenic impacts on marine aerosol and clouds off the coast of California. J. Geophys. Res. 2014, 119, 6724–6748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.-H.; Xie, Z.-Q.; Wang, X.-M.; Kang, H.; Zhang, P. Levoglucosan indicates high levels of biomass burning aerosols over oceans from the Arctic to Antarctic. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brioude, J.; Cooper, O.R.; Feinfeld, G.; Trainer, M.; Freitas, S.R.; Kowal, D.; Ayers, J.R.; Prins, E.; Minnis, P.; McKeen, S.A.; et al. Effect of biomass burning on marine stratocumulus clouds off the California coast. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 8841–8856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petters, M.D.; Carrico, C.M.; Kreidenweis, S.M.; Prenni, A.J.; DeMott, P.J.; Collett, J.L.; Moosmuller, H. Cloud condensation nucleation activity of biomass burning aerosol. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelhart, G.J.; Hennigan, C.J.; Miracolo, M.A.; Robinson, A.L.; Pandis, S.N. Cloud condensation nuclei activity of fresh primary and aged biomass burning aerosol. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 7285–7293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lathem, T.; Beyersdorf, A.J.; Thornhill, K.L.; Winstead, E.L.; Cubison, M.J.; Hecobian, A.; Jimenez, J.L.; Weber, R.J.; Anderson, B.E.; Nenes, A. Analysis of CCN activity of Arctic aerosol and Canadian biomass burning during summer 2008. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 2735–2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dua, S.K.; Hopke, P.K.; Raunemaa, T. Hygroscopicity of diesel aerosols. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1999, 112, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coggon, M.M.; Sorooshian, A.; Wang, Z.; Metcalf, A.R.; Frossard, A.A.; Lin, J.J.; Craven, J.S.; Nenes, A.; Jonsson, H.H.; Russell, L.M.; et al. Ship impacts on the marine atmosphere: Insights into the contribution of shipping emissions to the properties of marine aerosol and clouds. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 8439–8458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegg, D.A.; Covert, D.S.; Jonsson, H.H.; Woods, R.K. The contribution of anthropogenic aerosols to aerosol light-scattering and CCN activity in the California coastal zone. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 7341–7351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langley, L.; Leaitch, W.R.; Lohmann, U.; Shantz, N.C.; Worsnop, D. Contributions from DMS and ship emissions to CCN observed over the summertime North Pacific. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 1287–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaston, C.J.; Quinn, P.K.; Bates, T.S.; Gilman, J.B.; Bon, D.M.; Kuster, W.C.; Prather, K.A. The impact of shipping, agricultural, and urban emissions on single particle chemistry observed aboard the R/V Atlantis during CalNex. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gard, E.E.; Kleeman, M.J.; Gross, D.S.; Hughes, L.S.; Allen, J.O.; Morrical, B.D.; Fergenson, D.P.; Dienes, T.; Galli, M.E.; Johnson, R.J.; et al. Direct observation of heterogeneous chemistry in the atmosphere. Science 1998, 279, 1184–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saul, T.D.; Tolocka, M.P.; Johnston, M.V. Reactive uptake of nitric acid onto sodium chloride aerosols across a wide range of relative humidities. J. Phys. Chem. A 2006, 110, 7614–7620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thornton, J.A.; Abbatt, J.P.D. N2O5 reaction on submicron sea salt aerosol: Kinetics, products, and the effect of surface active organics. J. Phys. Chem. A 2005, 109, 10004–10012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farmer, D.K.; Cappa, C.D.; Kreidenweis, S.M. Atmospheric processes and their controlling influence on cloud condensation nuclei activity. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 4199–4217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ault, A.P.; Gaston, C.J.; Wang, Y.; Dominguez, G.; Thiemens, M.H.; Prather, K.A. Characterization of the single particle mixing state of individual ship plume events measured at the Port of Los Angeles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 1954–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaston, C.J.; Furutani, H.; Guazzotti, S.A.; Coffee, K.R.; Bates, T.S.; Quinn, P.K.; Aluwihare, L.I.; Mitchell, B.G.; Prather, K.A. Unique ocean-derived particles serve as a proxy for changes in ocean chemistry. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116, D18310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guazzotti, S.A.; Coffee, K.R.; Prather, K.A. Continuous measurements of size-resolved particle chemistry during INDOEX-Intensive Field Phase 99. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2001, 106, 28607–28627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, R.C.; Guazzotti, S.A.; Sodeman, D.A.; Tang, Y.; Carmichael, G.R.; Prather, K.A. Mineral dust is a sink for chlorine in the marine boundary layer. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 7166–7179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Scripps Pier Page. Available online: http://www.sccoos.org/data/piers/ (accessed on 30 November 2017).
- Gard, E.; Mayer, J.E.; Morrical, B.D.; Dienes, T.; Fergenson, D.P.; Prather, K.A. Real-time analysis of individual atmospheric aerosol particles: Design and performance of a portable ATOFMS. Anal. Chem. 1997, 69, 4083–4091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dall’Osto, M.; Harrison, R.M.; Beddows, D.C.S.; Freney, E.J.; Heal, M.R.; Donovan, R.J. Single-particle detection efficiencies of aerosol time-of-flight mass spectrometry during the North Atlantic marine boundary layer experiment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 5029–5035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, X.Y.; Bhave, P.V.; Prather, K.A. Comparison of two methods for obtaining quantitative mass concentrations from aerosol time-of-flight mass spectrometry measurements. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 6169–6178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenzel, R.J.; Liu, D.Y.; Edgerton, E.S.; Prather, K.A. Aerosol time-of-flight mass spectrometry during the Atlanta Supersite Experiment: 2. Scaling procedures. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108, 8427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noble, C.A.; Prather, K.A. Real-time measurement of correlated size and composition profiles of individual atmospheric aerosol particles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1996, 30, 2667–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neubauer, K.R.; Johnston, M.V.; Wexler, A.S. Humidity effects on the mass spectra of single aerosol particles. Atmos. Environ. 1998, 32, 2521–2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neubauer, K.R.; Johnston, M.V.; Wexler, A.S. On-line analysis of aqueous aerosols by laser desorption ionization. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. Ion Process. 1997, 163, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, J.O. YAADA Software Toolkit to Analyze Single-Particle Mass Spectral Data: Reference Manual Version 1.1. Arizona State University, 2002. Available online: http://www.yaada.org (accessed on 30 November 2017).
- Song, X.H.; Hopke, P.K.; Fergenson, D.P.; Prather, K.A. Classification of single particles analyzed by ATOFMS using an artificial neural network, ART-2a. Anal. Chem. 1999, 71, 860–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, G.C.; Nenes, A. A continuous-flow streamwise thermal-gradient CCN chamber for atmospheric measurements. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 206–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, A.F.; Draxler, R.R.; Rolph, G.D.; Stunder, B.J.B.; Cohen, M.D.; Ngan, F. Noaa’s Hysplit Atmospheric Transport and Dispersion Modeling System. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 96, 2059–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolph, G.; Stein, A.; Stunder, B. Real-time Environmental Applications and Display sYstem: READY. Environ. Model. Softw. 2017, 95, 210–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Day, D.A.; Shields, J.E.; Russell, L.M. Ozone-driven daytime formation of secondary organic aerosol containing carboxylic acid groups and alkane groups. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 8321–8341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Pratt, K.A.; Shields, L.G.; Toner, S.M.; Prather, K.A. Seasonal comparisons of single-particle chemical mixing state in Riverside, CA. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 59, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor, S.H.; Allen, J.O.; Hughes, L.S.; Bhave, P.; Cass, G.R.; Prather, K.A. Ambient single particle analysis in Riverside, California by aerosol time-of-flight mass spectrometry during the SCOS97-NARSTO. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 239–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denkenberger, K.A.; Moffet, R.C.; Holecek, J.C.; Rebotier, T.P.; Prather, K.A. Real-time, single-particle measurements of oligomers in aged ambient aerosol particles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 5439–5446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, F.; Hayes, P.L.; Ortega, A.; Taylor, J.W.; Allan, J.D.; Gilman, J.; Kuster, W.; de Gouw, J.; Jimenez, J.L.; Wang, J. Droplet activation properties of organic aerosols observed at an urban site during CalNex-LA. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 2903–2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, F.; Setyan, A.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, J. CCN activity of organic aerosols observed downwind of urban emissions during CARES. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 12155–12169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerully, K.M.; Raatikainen, T.; Lance, S.; Tkacik, D.; Tiitta, P.; Petaja, T.; Ehn, M.; Kulmala, M.; Worsnop, D.R.; Laaksonen, A.; et al. Aerosol hygroscopicity and CCN activation kinetics in a boreal forest environment during the 2007 EUCAARI campaign. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 12369–12386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaston, C.J.; Pratt, K.A.; Qin, X.Y.; Prather, K.A. Real-time detection and mixing state of methanesulfonate in single particles at an inland urban location during a phytoplankton bloom. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 1566–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ault, A.P.; Moore, M.J.; Furutani, H.; Prather, K.A. Impact of emissions from the Los Angeles port region on San Diego air quality during regional transport events. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 3500–3506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, P.J.; Prather, K.A. Interpretation of mass spectra from organic compounds in aerosol time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2000, 72, 3553–3562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shields, L.G.; Suess, D.T.; Prather, K.A. Determination of single particle mass spectral signatures from heavy-duty diesel vehicle emissions for PM2.5 source apportionment. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 3841–3852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toner, S.M.; Shields, L.G.; Sodeman, D.A.; Prather, K.A. Using mass spectral source signatures to apportion exhaust particles from gasoline and diesel powered vehicles in a freeway study using UF-ATOFMS. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 568–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhave, P.V.; Allen, J.O.; Morrical, B.D.; Fergenson, D.P.; Cass, G.R.; Prather, K.A. A field-based approach for determining ATOFMS instrument sensitivities to ammonium and nitrate. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 4868–4879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Gross, D.S.; Galli, M.E.; Silva, P.J.; Prather, K.A. Relative sensitivity factors for alkali metal and ammonium cations in single particle aerosol time-of-flight mass spectra. Anal. Chem. 2000, 72, 416–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CARB. Final Regulation Order. Fuel Sulfur and Other Operational Requirements for Ocean-Going Vessels within California Waters and 24 Nautical Miles of the California Baseline; California Air Resources Board: Sacramento, CA, USA, 2009.
- Roberts, G.C.; Artaxo, P.; Zhou, J.C.; Swietlicki, E.; Andreae, M.O. Sensitivity of CCN spectra on chemical and physical properties of aerosol: A case study from the Amazon Basin. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2002, 107, 8070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lee, Y.N.; Daum, P.H.; Jayne, J.; Alexander, M.L. Effects of aerosol organics on cloud condensation nucleus (CCN) concentration and first indirect aerosol effect. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2008, 8, 6325–6339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).