Abstract
Urban particulate matter (PM) pollution critically impacts public health and climate. However, traditional ground-based monitoring fails to resolve vertical PM distribution, limiting understanding of transport and stratification-coupled mechanisms. Vertical profiles collected by an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) over Hangzhou, a core megacity in China’s Yangtze River Delta, reveal the spatiotemporal heterogeneity and multi-scale drivers of regional PM pollution during two intensive ten-day campaigns capturing peak pollution scenarios (winter: 17–26 January 2019; summer: 21–30 August 2019). Results show stark seasonal differences: winter PM1 and PM2.5 averages were 2.6- and 2.7-fold higher (p < 0.0001) than summer. Diurnal patterns were bimodal in winter and unimodal (single valley) in summer. Vertically consistent PM1 and PM2.5 distributions featured sharp morning (08:00) concentration increases within specific layers (winter: 250–325 m; summer: 350–425 m). Analysis demonstrates multi-scale coupling of synoptic systems, boundary layer processes, and vertical wind structure governing pollution. Key mechanisms include a winter “Transport-Accumulation-Reactivation” cycle driven by cold air, and summer typhoon circulation influences. We identify hygroscopic growth triggered by inversion-high humidity coupling and sea-breeze-driven secondary aerosol formation. Leveraging UAV-based vertical profiling over Hangzhou, this study pioneers a three-dimensional dissection of layer-coupled PM dynamics in the Yangtze River Delta, offering a scalable paradigm for aerial–ground networks to achieve precision stratified control strategies in megacities.
1. Introduction
Atmospheric particulate matter (PM) pollution, a persistent challenge of global urbanization, poses significant threats to public health and climate systems []. PM is classified by aerodynamic diameter, with PM2.5 (≤2.5 μm) and PM1 (≤1 μm) representing fine and submicron fractions, respectively []. Critically, PM1 constitutes over 70% of PM2.5 mass. Their high specific surface area and enhanced biological permeability facilitate the carriage of toxic components—including heavy metals and pathogens—amplifying risks for respiratory and cardiovascular diseases []. While China’s “Air Pollution Prevention and Control Action Plan” has reduced annual mean PM2.5 concentrations, megacities still experience frequent severe pollution episodes during winter []. Urban PM spatiotemporal heterogeneity arises from complex drivers: local sources (industrial emissions, vehicle exhaust, dust, secondary aerosols) interplay with meteorological conditions (e.g., temperature inversions, wind speed) and regional transport, governing pollutant dispersion and accumulation [,]. However, research predominantly focuses on horizontal distributions of PM pollution, leaving a critical gap in understanding vertical dynamics, which directly regulate dispersion efficiency, chemical transformation, and population exposure doses [,].
Traditional vertical profiling techniques—weather balloons, tall meteorological towers (>300 m), and remote sensing—face significant limitations. Balloons offer vertical profiles but lack sufficient spatiotemporal resolution. Towers enable stratified monitoring yet suffer from high costs, limited representativeness, and spatial constraints. Satellite remote sensing provides vertical data but lacks the fine-scale resolution required for urban process analysis []. Moreover, PM1 and PM2.5 exhibit potentially differentiated transport behaviors within the mixed layer due to particle size effects, but observational constraints prevent quantification of their environmental impacts []. Advances in unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) technology now offer solutions []. Early fixed-wing platforms enabled large-scale detection but were unsuitable for urban boundary-layer studies due to fuel emissions and demanding operational requirements []. Multirotor UAVs provide a promising platform for three-dimensional atmospheric sensing with vertical maneuverability and high spatial resolution (<5 m) [,], yet their measurement accuracy is significantly impacted by aerodynamic interference. Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations and field data reveal that rotor-induced turbulence causes systematic overestimation (~50%) of pollutant concentrations during descent phases, while ascent measurements maintain fidelity—a phenomenon exacerbated by sensor miniaturization limitations and payload-induced microclimates [].
This study employs a multirotor UAV system equipped with high-precision sensors to synchronously acquire vertical profiles (0–500 m) of PM1, PM2.5, and meteorological parameters via in situ measurements, achieving continuous high-resolution observations. By integrating air-mass trajectories, synoptic pattern analysis, and boundary-layer meteorology, we reveal the spatiotemporal (seasonal/diurnal) and vertical distribution characteristics of PM pollution, alongside its sources and transport mechanisms. These findings provide a multidimensional scientific basis for urban PM control strategies, enabling precise health risk warnings and informing integrated climate-air quality governance.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
This study selected Changkou Town (29°55′ N, 119°52′ E) in Hangzhou as a representative industrial-urban-rural transitional zone in eastern China (Figure S1). The research area exhibits complex atmospheric pollution characteristics, featuring dense industrial clusters dominated by chemical and machinery manufacturing sectors, major transportation corridors, and proximity to the Fuchun River watershed. The unique valley topography of the Fuchun River basin significantly modulates local meteorological patterns, generating frequent nocturnal radiation inversions during winter months while enhancing daytime convective mixing in summer. This distinctive convergence of anthropogenic emission sources (industrial production, vehicular traffic) and orographic-meteorological interactions creates an optimal natural laboratory for investigating the synergistic effects of multi-source pollution and vertical atmospheric processes on particulate matter (PM1 and PM2.5) stratification dynamics.
2.2. UAV Observations
This study employed a multi-rotor meteorological UAV platform (UAV6000, ZOGLAB Microsystem Co., Hangzhou, China) equipped with integrated atmospheric sensors for synchronous measurements of particulate matter (PM1/PM2.5), temperature, humidity, barometric pressure, and 3D wind fields. Technical specifications are provided in Table S1. Intensive vertical profiling campaigns were conducted during two seasonal periods: winter (17–26 January 2019) and summer (21–30 August 2019), with six daily flights scheduled at 3-h intervals from 08:00 to 23:00 local time. Operational protocols excluded measurements during precipitation events or when surface winds exceeded 10 m/s to maintain data integrity. A total of 98 UAV flight observations were made. All the observation data were used for subsequent analysis in this paper. Vertical observations covered altitudes of 0–500 m, stratified by function: surface layer (0–50 m), directly influenced by surface emission sources; mixed layer (50–500 m), reflecting the interaction between regional transport and vertical diffusion. The UAV executed stepped ascents at 25-m vertical resolution with controlled ascent rates <1 m/s, maintaining 10-s stabilization at each altitude before data acquisition. All flight operations adhered to Chinese aviation regulations, maintaining sub-500 m altitudes and visual-line-of-sight protocols for daytime missions.
2.3. Backward Trajectory Using the HYSPLIT Model
This study employed the Hybrid Single-Particle Lagrangian Integrated Trajectory (HYSPLIT) model, a NOAA-developed atmospheric dispersion system, to analyze long-range pollutant transport pathways. Meteorological inputs derived from the Global Data Assimilation System (GDAS) were used to compute 24-h backward trajectories at two representative altitudes (300 m and 500 m above ground level), synchronized with six daily observational timepoints (08:00–23:00 local time) [,,]. The 300 m level represents the typical transport height of the near-source region (initial stage of plume formation), while the 500-m level corresponds to the layer near the planetary boundary layer (PBL), where regional-scale transport is closely associated []. Multiple studies have confirmed that this configuration effectively captures long-distance pollutant transport pathways and accurately identifies regional pollution sources [,]. Trajectory clustering analysis, based on Euclidean distance, revealed 3–4 distinct air mass transport regimes.
2.4. Synoptic Systems and Boundary Layer Analysis
Synoptic systems analysis focused on three characteristic heavy pollution episodes (20 January and 25 January 2019 in winter; 23 August 2019 in summer) with consistent 08:00 local time initialization to examine meteorological drivers of PM spatiotemporal patterns. We utilized ERA5 reanalysis data from the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF) with 0.25° × 0.25° spatial resolution and hourly temporal resolution []. Key parameters, including geopotential height, temperature fields, wind vectors, and relative humidity at multiple isobaric levels (sea-level pressure, 925 hPa, and 850 hPa), were systematically analyzed to reconstruct synoptic-scale circulation patterns. In the visualization of the atmospheric background field, NCL 6.2.1 (NCAR Command Language) was employed for data processing and analysis.
The hourly planetary boundary layer height (PBLH) data were obtained from the ERA5 (ECMWF Reanalysis v5) global atmospheric reanalysis dataset, developed by the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF). These data were retrieved through the Copernicus Climate Data Store (CDS) platform and processed using Python-based data extraction tools. The PBLH was calculated based on the bulk Richardson number method, with a spatial resolution of 0.25° latitude × 0.25° longitude.
2.5. Data Processing and Analysis
This study implemented rigorous data quality assurance protocols through a three-stage analytical pipeline. Atmospheric measurements underwent initial filtering to remove PM concentration anomalies caused by rotor-induced turbulence (defined as values exceeding 3 thresholds in moving 10-s windows) and sensor-range-exceeding meteorological outliers. Subsequent standardization involved height-normalized particulate concentrations using 5-m vertical bins and temporal alignment to Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) for cross-dataset comparability.
Statistical evaluation comprised paired t-tests for comparisons and Pearson correlation analysis assessing parameter covariation. All analytical workflows were executed in Python 3.12.7 with statistical significance thresholds maintained at 0.05. Visualization architectures leveraged Python to generate publication-grade figures.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Temporal Variability in PM Distribution
Figure 1a illustrates the contrasting PM regimes observed during two intensive campaigns conducted in January (winter) and August (summer). While the present data cover 10-day snapshots, the winter-to-summer reduction (Winter means: PM1 = 76.3 ± 12.1, PM2.5 = 92.7 ± 18.4 μg m−3; Summer means: PM1 = 29.5 ± 4.2, PM2.5 = 35.2 ± 5.1 μg m−3; Analysis of variance (ANOVA), p < 0.0001) in mean concentrations aligned quantitatively with the ranges reported in those longer records, supporting the validity of the seasonal comparison. Unimodal distributions were diagnosed when the Hartigan–Hartigan dip-test p-value > 0.05 and the distance between the first and second peaks (Δpeak) was <10 µg m−3; otherwise the distribution was classified as bimodal. On this basis, winter PM1 and PM2.5 both exhibited bimodal distributions (dip-test p < 0.01; Δpeak = 18.6 µg m−3 for PM1 and 19.2 µg m−3 for PM2.5), spanning 5.1–269.9 µg m−3 (PM1) and 5.5–327.4 µg m−3 (PM2.5). These modes were punctuated by frequent high-pollution episodes (50–100 µg m−3) and extreme outliers (>200 µg m−3 PM2.5), reflecting the compounded effects of elevated anthropogenic emissions and stagnant meteorological conditions. [,]. Summer distributions showed leptokurtic patterns (PM1: kurtosis = 4.0; PM2.5: kurtosis = 4.8; reference Gaussian kurtosis = 3.0) concentrated below 50 μg m−3, forming stable low-concentration plateaus.
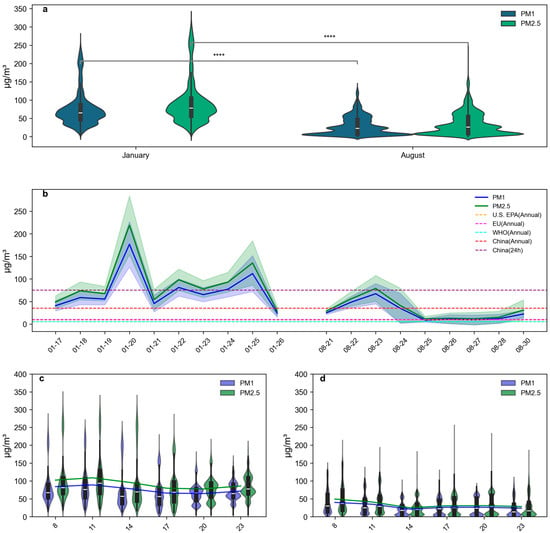
Figure 1.
Seasonal, daily, and diurnal distribution of PM1 and PM2.5. (a) The seasonal distribution. The shaded areas represent the probability density of the data, with wider sections indicating higher data density at those values. The black boxes within the violins denote the interquartile range, with the white line inside representing the median. The vertical lines extend to the minimum and maximum values, excluding outliers. The asterisks indicate significant differences in concentration between the two months, with **** denoting a p-value < 0.0001 based on a t-test, highlighting highly statistically significant differences. (b) The daily distribution. The shaded area represents the standard deviation. (c) The diurnal distribution in January. (d) The diurnal distribution in August. The solid lines represent the mean values of PM1 and PM2.5 at each time point.
Figure 1b revealed episodic pollutant dynamics during monitoring periods. Winter displayed acute pollution surges, notably a PM2.5 spike to ≈ 250 μg m−3 (20 January) coinciding with anticyclonic stagnation, contrasting with summer’s stable baseline (PM2.5 < 35 μg m−3). Winter concentrations systematically exceeded China’s 24-h PM2.5 standard (75 μg m−3) and WHO annual guidelines (10 μg m−3) by factors of 3–5, particularly during the 20 January event, where PM2.5 surpassed 200 μg m−3, attributable to combined emission intensity and temperature inversion [,].
Diurnal patterns (Figure 1c,d) exhibited seasonally modulated cycles []. Winter profiles showed distinct morning (08:00–11:00) and evening (20:00–23:00) peaks with positive skewness in violin plots, indicating episodic pollution accumulation (PM2.5: 102.2–108.6–77.4 μg m−3). The upward-broadened quartile distributions (>75th percentile spanning 120–250 μg m−3 PM2.5) reflect episodic pollution accumulation. Noon-time symmetric distributions (14:00–17:00) correlated with enhanced convective mixing, where interquartile ranges contract by 40–60%. Summer displayed dampened variability with progressive daytime declines (PM2.5 at 08:00 = 49.4 to PM2.5 at 14:00 = 25.1 μg m−3) followed by nocturnal rebounds, consistent with stable boundary layer dynamics [,].
The study area exhibited critically elevated PM levels, particularly during winter. Seasonal and diurnal patterns manifest through: (1) Winter’s high-amplitude diurnal cycles (ΔPM2.5 ≈ 50 μg m−3) driven by morning emission peaks and nocturnal stagnation versus summer’s meteorologically regulated stability; (2) Frequent winter exceedance events; (3) Consistent PM1/PM2.5 covariation confirming fine particulate dominance in pollution episodes and possibly the same source.
3.2. Vertical Distribution Profiles of PM
Seasonally modulated vertical stratification patterns of PM1 and PM2.5 across diurnal cycles were shown in Figure 2.
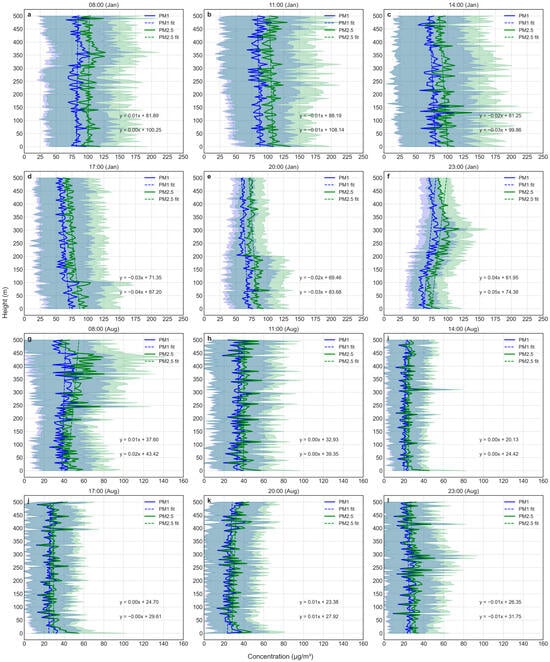
Figure 2.
The vertical profiles of PM concentrations. (a–f) at different times in January, 2019. (g–l) at different times in August, 2019. The solid lines represent the concentration changes of vertical observation, and the shaded areas are the standard deviations. The dashed lines are the linear fitting results.
During the winter season, the vertical profiles of PM1 and PM2.5 concentrations can typically be categorized into two groups. The first group, observed between 14:00 and 20:00, exhibited PM concentrations that decrease as altitude increases (Figure 2b–e). Specifically, at 14:00, 17:00, and 20:00, PM concentrations were relatively high near the surface layer with significant fluctuations. Beyond certain heights (17:00: 100 m; 20:00: 200 m), the concentrations were progressively attenuated (Figure 2d,e). The second group showed overall PM concentrations increasing with altitude. At 23:00–11:00, PM concentrations showed elevated pollution layers through three-phase stratification: surface depletion (0–150 m), mid-altitude maxima (150–300 m at 23:00, 250–400 m at 08:00), and upper-level stabilization (Figure 2a,f). Linear regression slopes for winter vertical gradients reached −0.02 at 14:00 versus +0.04 at 23:00, confirming dynamic inversion-driven stratification.
Summer profiles contrasted sharply (Figure 2g–l), demonstrating vertically homogeneous distributions except at 08:00 when residual layer interactions created elevated PM layers (200–450 m) (Figure 2g). Daytime convective mixing (14:00–17:00) produced uniform vertical gradients (lower slopes), likely due to strong turbulent mixing during summer daytime, which facilitates rapid vertical diffusion of pollutants (Figure 2i,j). Nocturnal profiles showed dampened recirculation patterns compared to winter, with PM2.5 vertical gradients reduced (slope = 0.01 at 20:00 and slope = −0.01 at 23:00) (Figure 2k,l), further confirming the influence of seasonal changes on pollutant vertical distribution characteristics [,].
Meanwhile, size-segregation dynamics (Figure S2) revealed altitude-dependent PM1/PM2.5 ratio divergences. Under winter conditions (Figure S2a), the PM1/PM2.5 ratio generally increased with height, and the curves for different time periods within a day showed similar trends, indicating progressive fine-particle enrichment with height. The PM1/PM2.5 ratio fluctuated notably within the 250–325 m height range, suggesting a significant increase in PM2.5 concentrations, especially at 08:00 in the morning. In contrast, the PM1/PM2.5 ratio in summer (Figure S2b) followed a similar overall trend with height as in winter but exhibited more intense fluctuations, particularly within the 350–425 m height range (at 08:00 in the morning), where PM2.5 concentrations surge relative to PM1 concentrations.
In summary, although the vertical variation trends of PM1 and PM2.5 concentrations were largely consistent, likely originating from the same pollution sources, smaller-sized PM1 accounted for a higher proportion at higher altitudes in general. Specific vertical distribution features were observed for PM concentrations at 08:00 and 23:00 in winter (250–325 m) and at 08:00 in summer (350–425 m). PM2.5 concentrations exhibited sudden increases. Below 500 m altitude, PM concentrations generally maintained stable vertical gradients except during the aforementioned critical periods. Comparative analysis revealed winter profiles exhibited enhanced vertical heterogeneity compared to summer, with near-surface concentration maxima diminishing gradually with height in most diurnal phases. These spatiotemporal distribution characteristics, including seasonal contrasts in vertical variability and diurnal stratification patterns, appear principally governed by multiscale thermal-dynamic processes governing boundary layer evolution, particularly the interplay between surface emissions, turbulent mixing regimes, and inversion layer dynamics [,,]. To gain a deeper understanding of the mechanisms behind PM spatiotemporal distribution, further interpretation incorporating relevant meteorological parameters is necessary.
3.3. Driving Factors of PM Spatial-Temporal Distribution
Complex interactions among multifaceted meteorological determinants govern the spatiotemporal distribution of PM concentrations, encompassing source-specific emission patterns and transboundary transport mechanisms, synoptic-scale atmospheric circulation dynamics, and regional-scale thermodynamic structural parameters within the PBL [,]. These interdependent factors collectively modulate aerosol vertical stratification and horizontal dispersion through mechanisms including but not limited to adjective transport modulated by pressure gradient forces, convective mixing driven by surface-atmosphere energy exchanges, and stability regimes dictated by ABL height oscillations and temperature inversion characteristics [,].
3.3.1. Long Distance Transport
Figure 3 presents a 24-h HYSPLIT backward trajectory clustering analysis of PM-laden air parcels at distinct sampling altitudes (300 m/500 m) during contrasting seasonal periods (January vs. August 2019), revealing marked seasonal and altitudinal heterogeneity in aerosol transport mechanisms and source apportionment [].
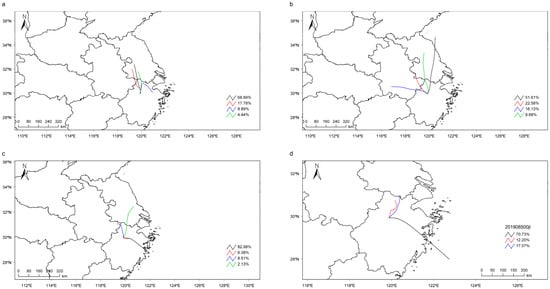
Figure 3.
Cluster diagrams of 24-h backward trajectories at 300 and 500 m above ground level over sampling points during various time periods (8:00, 11:00, 14:00, 17:00, 20:00, 23:00 BJT). (a) 300 m, January; (b) 500 m, January; (c) 300 m, August; (d) 500 m, August.
Winter analyses (January 2019) demonstrated pronounced boundary layer stratification effects, with the 300 m level (Figure 3a) dominated by four mesoscale clusters originating from proximate industrial corridors in southern Jiangsu, Hangzhou, and Ningbo. This low-altitude confinement (frequency >65%) reflects strong near-surface pollutant accumulation under winter-specific meteorological constraints, including persistent temperature inversions and subsidence-driven atmospheric compression []. In contrast, trajectories at the 500 m altitude (Figure 3b) exhibited long-range transport features, with air masses mainly originating from central Yangtze River Delta regions and parts of Anhui, potentially driven by high-altitude wind fields and persistent anticyclonic conditions that facilitated long-distance pollutant transport [,].
Summer observations (August 2019) exhibited fundamentally altered transport dynamics shaped by East Asian monsoon circulation. At 300 m (Figure 3c), four dominant clusters demonstrated enhanced marine influence, with 82.98% frequency from eastern Zhejiang coastal zones, contrasting with winter’s continental dominance. This coastal predominance intensified at 500 m (Figure 3d), where 70.73% trajectories originate from maritime sectors, correlating with strengthened southeasterlies from the West Pacific subtropical high []. In summer, the prevailing trajectory clusters decline from four to three relative to winter, reflecting a thermally driven intensification of convective mixing that more effectively disperses air masses in the horizontal plane and, consequently, suppresses cluster formation [].
Overall, the seasonal differences in airflow transport mechanisms above the sampling points were aligned with meteorological dynamic processes. Winter conditions (e.g., temperature inversion and weak vertical mixing) promoted local PM accumulation, primarily driven by emissions from local or neighboring areas, with most pollutants originating from inland regions. In contrast, summer thermal convection and stronger synoptic-scale wind fields enhanced cross-regional pollution dispersion. The high transport efficiency (mostly exceeding 70%) from maritime to inland areas at both 300 m and 500 m altitudes in August further demonstrated that vertical atmospheric structures (e.g., monsoon circulation or frontal systems) coupled with seasonal meteorological conditions (notably summer land-sea thermal contrasts) played a critical role in regulating PM dispersion processes. This highlights the potential contribution of maritime air masses to cross-border regional PM pollution transport during summer.
3.3.2. Synoptic-Scale Meteorological Drivers
Synoptic-scale meteorological systems may exhibit significant regulatory effects on the transport pathways and spatiotemporal heterogeneity of PM []. Our investigation reveals pronounced meteorological regulation of PM transport dynamics through two distinct cold-air events in January 2019 and contrasting typhoon-influenced conditions in August 2019 (Figure 4).
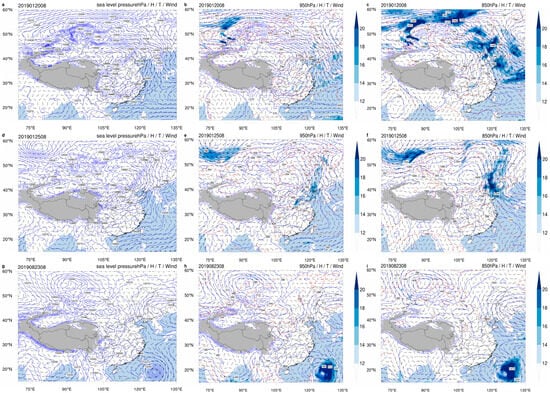
Figure 4.
Synoptic weather pattern at 08:00 (UTC+8) on 20 January 2019, 25 January 2019, 23 August 2019. (a) sea level pressure, 20 January 2019. (b) 950 hPa, 20 January 2019. (c) 850 hPa, 20 January 2019. (d) sea level pressure, 25 January 2019. (e) 950 hPa, 25 January 2019. (f) 850 hPa, 25 January 2019. (g) sea level pressure, 23 August 2019. (h) 950 hPa, 23 August 2019. (i) 850 hPa, 23 August 2019. Meteorological elements on the isobaric surface were extracted, and the atmospheric circulation field at this level was visualized. The wind field was represented using vector arrows, with wind speed indicated by both the length of the arrows and the presence of barbs. The geopotential height field was depicted as solid blue contour lines, while the temperature field was represented by dashed red lines.
During Phase I (20–24 January) in winter, a vertically coherent transport corridor emerged as 850 hPa trough positioned (Korean Peninsula–Zhejiang axis) synchronized with surface northerly flows (wind speed > 6 m/s), facilitating rapid PM advection (Figure 4a,b). Lower-tropospheric dynamics proved critical: by 21 January, a 950 hPa trough departure permitted anticyclogenesis at low levels (<850 hPa), generating vertical wind shear between surface convergence and upper-level northwesterlies (>6 m/s) (Figure 4c). This configuration suppressed vertical mixing while sustaining horizontal transport, culminating in PM accumulation through inertial trapping. Phase II (25 January) commenced as a Xinjiang cold vortex propagated southeastward, reestablishing 850 hPa–surface wind coherence with renewed northerly dominance (Figure 4d–f). Backward trajectories corroborated dual pollution sources: frontal advection of northern aerosols superimposed on local emissions during trough passages.
August observations contrasted sharply, with Typhoon Bailu’s peripheral circulation altering PM dispersion (Figure 4g–i). As the typhoon approached Taiwan, 850 hPa wind convergence between typhoon-induced southeasterlies and subtropical high westerlies initiated convective precipitation (Figure 4h). Concurrently, weak easterlies (<3 m/s) at 925 hPa and surface levels enhanced vertical mixing, demonstrating tropical cyclones’ capacity to paradoxically improve air quality through enhanced atmospheric ventilation (Figure 4g,i).
In summary, the vertical consistency of cold air southward pathways, the development of lower-level anticyclones, and the superimposed effects of typhoon peripheral circulation collectively shaped potential PM transport pathways and dispersion characteristics under different weather conditions []. The demonstrated seasonality in transport mechanisms—frontal dominance in winter versus convective modulation in summer—provides a conceptual framework for predicting transboundary pollution events under changing climatic regimes [,,,].
3.3.3. Synergistic Effects of Meteorological Factors
The synergistic interplay between PM concentration dynamics and meteorological parameters within the boundary layer demonstrates pronounced spatiotemporal heterogeneity []. Current research reveals that the spatial-temporal distribution patterns of atmospheric particulates may be substantially modulated by the three-dimensional configuration and diurnal variation characteristics of critical meteorological elements, particularly through complex interactions involving temperature stratification, humidity gradients, and wind field patterns across different atmospheric layers [,,].
Temperature Stratification and Inversion Layers
Winter PM vertical distributions exhibited strong dependence on temperature inversion dynamics []. Observations revealed frequent nocturnal-to-dawn (20:00–11:00) inversion layers near 250 m altitude (Figure 5a,b,e,f), effectively suppressing vertical mixing and reducing boundary layer height (Figure S3) []. This thermal structure drives significant PM accumulation with enhanced concentration variability between 250–350 m at 08:00 and 100–300 m at 23:00 (Figure 2a,f). Mechanistic analysis showed that near-surface originated pollutants (<250 m/100 m) encounter inversion cap restrictions on upward diffusion []. The 250–350 m layer became a semi-closed reservoir under inversion stabilization. Notably, the positive correlation between temperature and PM1/PM2.5 ratios at 250–325 m (Figure S4a) suggested thermal modulation of particle size distribution, where elevated temperatures preferentially enhanced PM1 concentrations through possible volatilization mechanisms [,,]. Above 400 m, neutral stratification with reduced thermal gradients corresponded to dampened PM concentration fluctuations. Diurnally, enhanced solar radiation (14:00–17:00) established super-adiabatic lapse rates, triggering turbulent mixing (Figure 5c,d) and boundary layer expansion (Figure S3) []. This convective regime homogenized vertical PM distributions, evidenced by decreased concentration gradient slopes (Figure 2c,d).
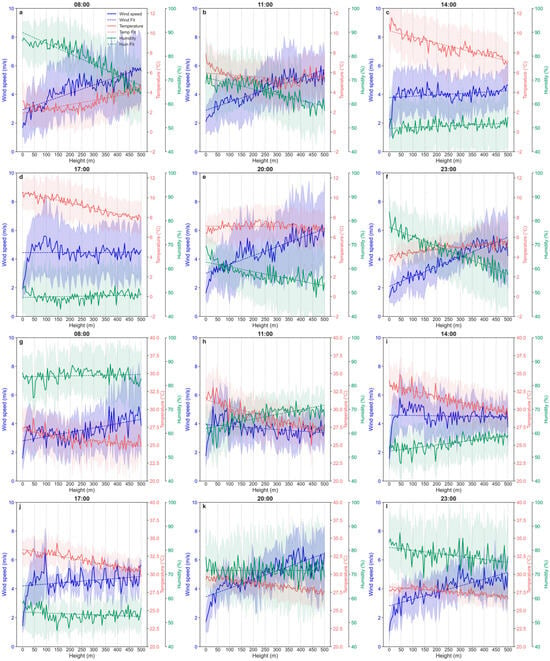
Figure 5.
The vertical profiles of wind speed, temperature, and humidity at different times in January and August, 2019. (a–f) at different times in January, 2019. (g–l) at different times in August, 2019. The shaded areas are the standard deviations. The solid lines represent the observed results, while the dashed lines indicate the linear fitting results.
Summer exhibited fundamentally distinct thermal-PM coupling patterns dominated by turbulence-driven dispersion. The absence of persistent inversions (Figure 5g–l) and elevated boundary layer heights (Figure S3) facilitated efficient vertical mixing, yielding flatter PM gradients. Unique dawn phenomena emerge under weak stabilization: 08:00 observations revealed attenuated thermal gradients near 350 m, coinciding with abrupt PM1/PM2.5 ratio fluctuations in the 350–425 m layer (Figure S2b). This transitional regime demonstrates dual thermal effects, PM1 enhancement through potential secondary aerosol formation and partial mixing suppression via shallow inversions (Figure S4e) [,]. However, compared to winter inversions, summer’s weaker thermal controls result in smaller vertical PM variability amplitudes, reflecting less constrained pollutant redistribution.
Humidity Coupling Effect
Humidity-PM coupling demonstrated pronounced seasonal divergence through aerosol hygroscopic modulation (Figure 5a–f) []. Winter observations revealed moisture-dominated PM enhancement mechanisms. High near-surface humidity (>60% RH at 08:00, 11:00, 23:00) amplified PM2.5 concentrations via hygroscopic growth (Figure 5a,b,f), particularly evident in the 250–325 m layer where PM1/PM2.5 ratios exhibited inverse correlation with humidity (Figure S4b) []. A sharp humidity gradient transition at inversion layer tops (~400 m) created a desiccation boundary, corresponding to inflection points in PM vertical profiles (Figure 2a). Nocturnal moisture retention further exacerbated surface-level pollution through suppressed wet deposition []. Daytime humidity reduction (<50% RH) synergized with turbulent mixing to homogenize PM distributions (Figure 2c,d) [,].
Near-surface humidity levels during summer were generally higher than in winter across all time periods, but the humidity gradient with altitude was significantly weaker than in winter (Figure 5g–l). Specifically, the high-humidity environment in the surface layer during morning (8:00) and nighttime (23:00) led to relatively elevated PM concentrations (Figure 5g,l), whereas midday (11:00–17:00) humidity dropped markedly to typical winter levels (approximately 50%), resulting in substantially weakened hygroscopic growth effects of PM (Figure 5h–k). The unique weak-gradient vertical humidity distribution in summer, combined with strong daytime turbulent mixing, reduced humidity’s regulatory efficiency on PM concentrations compared to winter. Notably, similar to winter conditions, at specific altitude layers during summer mornings (8:00), increasing humidity with height promotes PM2.5 concentration growth (Figure S2b), subsequently triggering drastic fluctuations in the PM1/PM2.5 ratio (Figure S4f). This phenomenon may stem from differential responses of various particle sizes to humidity variations [,].
Wind Speed Disturbance
Wind-PM interactions exhibited marked seasonal contrasts through differential vertical transport dynamics (Figure 5). Winter mornings (08:00, 11:00) and nights (20:00, 23:00) showed steep vertical wind gradients with height-dependent velocity amplification (Figure S5a,b). Weak surface winds combined with opposing vertical wind directions generated turbulent shear layers, driving PM variability at critical altitudes (08:00: 250–400 m; 23:00: 150–400 m) []. Daytime enhancement (14:00–17:00) elevated wind speeds with coherent vertical mixing, flattening PM gradients (Figure 5c,d).
Summer wind regimes diverged through reduced vertical gradients and turbulent “plume-rise” effects (Figure 5g–l). Despite comparable surface winds, daytime turbulence intensity promoted uniform PM distributions (Figure 5c,d). Morning/evening surface calm periods exhibited distinct vertical wind directionality, coupled with diminished humidity gradients, preventing altitude-specific PM accumulation (Figure S5c,d).
Comparative analysis revealed that solar-driven turbulent mixing induces convergent midday homogenization of PM vertical distributions, yet fundamental seasonal divergences emerged through distinct thermodynamic and dynamic couplings. Summer exhibited amplified thermal gradients and altitude-dependent wind variability, synergistically enhancing horizontal pollutant dispersion. Conversely, winter nocturnal stabilization (20:00–08:00) combines strong inversion layers with elevated humidity to trap pollutants in the 250–400 m reservoir layer, prolonging residence times. Particle size modulation follows thermally and hygroscopically divergent pathways: temperature-driven PM1 formation contrasts with humidity-enhanced PM2.5 growth. These results provide critical observational evidence for investigating the formation mechanisms of PM pollution in the study area.
4. Conclusions
This study employed UAV vertical profiling coupled with multidimensional system analysis to elucidate the spatiotemporal heterogeneity of PM pollution and its multiscale drivers. Key findings revealed marked seasonal contrasts: winter PM1 and PM2.5 concentrations exceed summer levels by 2.6- and 2.7-fold, respectively (p < 0.0001), with an extreme pollution episode on 20 January recording PM2.5 peaks of 327 μg/m3, 4.4 times China’s 24-h air quality standard. Diurnal patterns exhibited winter bimodal peaks (11:00 and 23:00) versus summer monomodal trough configurations (14:00 minimum). Vertical profiling identified consistent PM1-PM2.5 covariation, with distinct stratification during winter mornings/nights (08:00/23:00) and summer mornings (08:00), characterized by elevated PM1 fractions at higher altitudes and abrupt PM2.5 surges in critical layers (winter: 250–325 m; summer: 350–425 m). Outside these periods, PM concentrations below 500 m generally followed surface-dominant decay profiles, though winter exhibits 38% stronger vertical variability than summer.
Mechanistically, three-scale meteorological couplings governed pollution dynamics. Synoptic systems orchestrated 3D transport pathways, winter cold surges drove cyclical “transport-accumulation-reactivation” processes, while summer typhoon peripheries enhanced dispersion efficiency []. Within the boundary layer, thermo-dynamic interactions regulated vertical structures: winter inversions (250 m) coupled with high humidity (RH > 60%) amplified hygroscopic PM2.5 spikes, contrasting with summer’s sea breeze-driven secondary aerosol formation (350–425 m altitude PM2.5 surges, highly positively correlated with temperature). Vertical wind shear regimes further modulated dispersion. Winter’s low-speed winds with strong shear generate wave-like profiles, whereas summer’s homogeneous winds facilitate efficient lofting. These processes collectively explain extreme pollution genesis through turbulent mixing, inversion evolution, and altitude-resolved transport dynamics [].
The findings transcend traditional ground-based monitoring limitations, establishing a novel framework for tracing pollution transformation pathways. By quantifying the interplay between synoptic systems and boundary layer processes, this work provides critical insights for early warning systems and a new theoretical paradigm for regional atmospheric complex pollution control.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/atmos16080968/s1, Figure S1: The location of the sampling site and the study area at Changkou, Fuyang, Hangzhou, China; Figure S2: Vertical profiles of PM1 to PM2.5 ratio at different times in January and August. (a) in January. (b) in August; Figure S3: Average boundary layer height at different times in January and August; Figure S4: Pearson correlation between PM1 to PM2.5 ratio and temperature, humidity, as well as horizontal and vertical wind speed at different times and altitudes in January and August; Figure S5: The average horizontal and vertical wind speed profiles at different times in January and August; Table S1: Main measurement parameters of UAV6000.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.Z. and B.Q.; methodology, Z.Z. and Y.P.; software, Z.Z.; validation, Y.P.; formal analysis, Z.Z.; investigation, Z.Z.; resources, Y.P., B.Q., C.Z. and M.Y.; writing—original draft preparation, Z.Z.; writing—review and editing, Z.Z., B.Q. and X.Y.; visualization, Z.Z.; supervision, X.Y. and B.Q.; funding acquisition, B.Q., M.Y. and Y.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Key Research and Development Program of China, grant number “2023YFC3706300”. The Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number “LZJMY23D050006” and “LZJMY24D050009”. Science and Technology Program of Zhejiang Meteorological Service, grant number “2023ZDZL04” and “2024YB12”. Science and Technology Cooperation Project of Zhejiang Academy of Agricultural Sciences and Shaoxing, grant number “ZJTY2024-A-57”. Program of the Bureau of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of Keqiao District, grant number “Lin [2025] 910”.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Zheng, H.; Wu, D.; Wang, S.; Li, X.; Jin, L.N.; Zhao, B.; Li, S.; Sun, Y.; Dong, Z.; Wu, Q.; et al. Control of Toxicity of Fine Particulate Matter Emissions in China. Nature 2025, 643, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrone, M.R.; Becagli, S.; Garcia Orza, J.A.; Vecchi, R.; Dinoi, A.; Udisti, R.; Cabello, M. The Impact of Long-Range-Transport on PM1 and PM2.5 at a Central Mediterranean Site. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 71, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Xu, W.; Zhou, W.; Lei, L.; Sun, J.; You, B.; Wang, Z.; Sun, Y. Insights into the Compositional Differences of PM1 and PM2.5 from Aerosol Mass Spectrometer Measurements in Beijing, China. Atmos. Environ. 2023, 301, 119709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, G.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, S.; Cheng, J.; Yan, L.; Wu, N.; Hu, H.; Tong, D.; Zheng, B.; et al. Efficacy of China’s Clean Air Actions to Tackle PM2.5 Pollution between 2013 and 2020. Nat. Geosci. 2024, 17, 987–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Rong, B.; Kang, L.; Zhang, N.; Qin, C. Measuring the Urban-Rural and Spatiotemporal Heterogeneity of the Drivers of PM2.5-Attributed Health Burdens in China from 2008 to 2021 Using High-Resolution Dataset. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 346, 118940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Luo, X.-S.; Xu, J.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wu, L.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, D. Spatio-Temporal Variations and Factors of a Provincial PM2.5 Pollution in Eastern China during 2013–2017 by Geostatistics. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.; Li, B.; Li, X.-B.; Wang, Z.; Li, S.-Y.; Peng, Z.-R. Vertical and Horizontal Distributions of Traffic-Related Pollutants beside an Urban Arterial Road Based on Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Observations. Build. Environ. 2021, 187, 107401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Huang, J.; Wang, Y.; Tao, X.; Hu, C.; Deng, L.; Xu, J.; Xiao, H.-W.; Luo, L.; Xiao, H.-Y.; et al. Vertical Distribution of PM2.5 and Interactions with the Atmospheric Boundary Layer during the Development Stage of a Heavy Haze Pollution Event. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 704, 135329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, R.; Patra, A.K.; Nazneen. Vertical Profile of Particulate Matter: A Review of Techniques and Methods. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2022, 15, 979–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossein Motlagh, N.; Kortoçi, P.; Su, X.; Lovén, L.; Hoel, H.K.; Bjerkestrand Haugsvær, S.; Srivastava, V.; Gulbrandsen, C.F.; Nurmi, P.; Tarkoma, S. Unmanned Aerial Vehicles for Air Pollution Monitoring: A Survey. IEEE Internet Things J. 2023, 10, 21687–21704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, B.; Zhong, Z.; Jiang, X. A High Accuracy and Large-Scale Detection for Fixed-Wing UAV Autonomous Ground Landing with GNSS-Denied. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 45898–45911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Li, X.-B.; Song, R.; Wang, H.-W.; Li, B.; He, H.-D.; Peng, Z.-R. Development and Utilization of Hexacopter Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Platform to Characterize Vertical Distribution of Boundary Layer Ozone in Wintertime. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2020, 11, 1073–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishal; Sharma, M.; Jain, S. Unmanned Aerial Vehicles and Low-Cost Sensors for Air Quality Monitoring: A Comprehensive Review of Applications across Diverse Emission Sources. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2025, 127, 106409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedworth, H.; Page, J.; Sohl, J.; Saad, T. Investigating Errors Observed during UAV-Based Vertical Measurements Using Computational Fluid Dynamics. Drones 2022, 6, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rößler, T.; Stein, O.; Heng, Y.; Baumeister, P.; Hoffmann, L. Trajectory Errors of Different Numerical Integration Schemes Diagnosed with the MPTRAC Advection Module Driven by ECMWF Operational Analyses. Geosci. Model Dev. 2018, 11, 575–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Zheng, J.; Fang, F.; Liang, F.; Yang, M.; Tong, L.; Xiao, H. Unveiling PM2.5 Transport Pathways: A Trajectory-Channel Model Framework for Spatiotemporally Quantitative Source Apportionment. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, N.; Fujii, Y.; Khan, M.F.; Hien, T.T.; Minh, T.H.; Okochi, H.; Takenaka, N. Source Apportionment of Ambient PM2.5 in Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam. Asian J. Atmos. Environ. 2024, 18, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shikhovtsev, M.Y.; Obolkin, V.A.; Khodzher, T.V.; Molozhnikova, Y.V. Variability of the Ground Concentration of Particulate Matter PM1–PM10 in the Air Basin of the Southern Baikal Region. Atmos. Ocean. Opt. 2023, 36, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, R.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, S.; Xu, H. Spatiotemporal Evolution of PM2.5 Concentrations and Source Apportionment in Henan Province, China. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2021, 30, 4815–4826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhao, T.; Wang, R.; Zhang, L. Backward Trajectory and Multifractal Analysis of Air Pollution in Zhengzhou Region of China. Math. Probl. Eng. 2022, 2022, 2226565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Hirahara, S.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D.; et al. The ERA5 Global Reanalysis. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 146, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maltare, N.N.; Vahora, S.; Jani, K. Seasonal Analysis of Meteorological Parameters and Air Pollutant Concentrations in Kolkata: An Evaluation of Their Relationship. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 436, 140514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Shen, Z.; Cao, J.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, L.; Huang, R.-J.; Zheng, C.; Wang, L.; Liu, S.; Xu, H.; et al. Variations in PM2.5, TSP, BC, and Trace Gases (NO2, SO2, and O3) between Haze and Non-Haze Episodes in Winter over Xi’an, China. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 112, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Tong, D.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Lei, Y.; Yan, G.; Yan, L.; Yu, S.; Cui, R.Y.; Clarke, L.; et al. Pathways of China’s PM2.5 Air Quality 2015–2060 in the Context of Carbon Neutrality. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2021, 8, nwab078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO Global Air Quality Guidelines: Particulate Matter (PM2.5 and PM10), Ozone, Nitrogen Dioxide, Sulfur Dioxide and Carbon Monoxide. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34662007/ (accessed on 13 July 2025).
- Biancardi, M.; Zhou, Y.; Kang, W.; Xiao, T.; Grubesic, T.; Nelson, J.; Liang, L. Exploring Spatiotemporal Dynamics, Seasonality, and Time-of-Day Trends of PM2.5 Pollution with a Low-Cost Sensor Network: Insights from Classic and Spatially Explicit Markov Chains. Appl. Geogr. 2024, 172, 103414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-L.; Cao, F. Fine Particulate Matter (PM2.5) in China at a City Level. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zong, L.; Yang, Y.; Gao, M.; Wang, H.; Wang, P.; Zhang, H.; Wang, L.; Ning, G.; Liu, C.; Li, Y.; et al. Large-Scale Synoptic Drivers of Co-Occurring Summertime Ozone and PM2.5 Pollution in Eastern China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 9105–9124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wang, W.; Li, L.; Li, J.; Wei, L.; Chi, W.; Hong, L.; Zhao, Q.; Jiang, J. Seasonal Concentration Distribution of PM1.0 and PM2.5 and a Risk Assessment of Bound Trace Metals in Harbin, China: Effect of the Species Distribution of Heavy Metals and Heat Supply. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Martin, R.V.; van Donkelaar, A.; Jimenez, J.L.; Zhang, Q.; Turner, J.R.; Liu, X.; Rowe, M.; Meng, J.; Yu, W.; et al. Estimates of Submicron Particulate Matter (PM1) Concentrations for 1998–2022 across the Contiguous USA: Leveraging Measurements of PM1 with Nationwide PM2.5 Component Data. Lancet Planet. Heath 2025, 9, e491–e502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Ding, S.; Liu, D. Exploring the Spatiotemporal Pattern of PM2.5 Distribution and Its Determinants in Chinese Cities Based on a Multilevel Analysis Approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 659, 1513–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Du, P.; Samat, A.; Xia, J.; Che, M.; Xue, Z. Spatiotemporal Pattern of PM2.5 Concentrations in Mainland China and Analysis of Its Influencing Factors Using Geographically Weighted Regression. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, Y.; Li, J.; Miao, S.; Che, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, R.; Liu, S. Interaction between Planetary Boundary Layer and PM2.5 Pollution in Megacities in China: A Review. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2019, 5, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Chen, L.; Liao, H.; Dang, R. Correlations between PM2.5 and Ozone over China and Associated Underlying Reasons. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Yuan, Z.; Fung, J.C.H.; Lau, A.K.H. A Comparison of HYSPLIT Backward Trajectories Generated from Two GDAS Datasets. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 506–507, 527–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Wei, S.; Wang, S. Temperature Inversions in the Atmospheric Boundary Layer and Lower Troposphere over the Sichuan Basin, China: Climatology and Impacts on Air Pollution. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 726, 138579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Archer, C.L.; Caldeira, K. Global Assessment of High-Altitude Wind Power. Energies 2009, 2, 307–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Hu, Q.; Hu, B.; Wang, S.; Liu, H.; Xing, C.; Lin, H.; Lin, J. Vertical Structure of Air Pollutant Transport Flux as Determined by Ground-Based Remote Sensing Observations in Fen-Wei Plain, China. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Cai, W.; Huang, G.; Hu, K.; Ng, B.; Wang, G. Increased Variability of the Western Pacific Subtropical High under Greenhouse Warming. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2120335119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernov, J.B.; Beddows, D.; Thomas, D.C.; Dall’Osto, M.; Harrison, R.M.; Schmale, J.; Skov, H.; Massling, A. Increased Aerosol Concentrations in the High Arctic Attributable to Changing Atmospheric Transport Patterns. npj Clim. Atmos. Sci. 2022, 5, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Zhao, T.; Meng, K.; Zhou, Y.; Xiong, J.; Sun, X.; Shen, L.; Yue, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Hu, W.; et al. Quasi-Weekly Oscillation of Regional PM2.5 Transport over China Driven by the Synoptic-Scale Disturbance of the East Asian Winter Monsoon Circulation. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2025, 25, 1273–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, M.; Xu, C.; Lv, S.; Jin, X.; Mu, Q.; Zhu, J. Mechanisms of O3 and PM2.5 Evolution along the Cold Wave Passage in Eastern China. npj Clim. Atmos. Sci. 2025, 8, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J.; Chen, H.; Wang, Y.; Lu, Z.; Wang, R.-Q.; Fung, J.C.-H.; Ng, C.W.W. Escalating Tropical Cyclone Precipitation Extremes and Landslide Hazards in South China under Global Warming. npj Clim. Atmos. Sci. 2024, 7, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Wu, N.; Chen, J.; Chan, P.; Tang, J.; Wang, N. Vertical Exchange and Cross-Regional Transport of Lower-Tropospheric Ozone over Hong Kong. Atmos. Res. 2023, 292, 106877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Zhai, P.; Chen, Y. Contribution of Changes in Synoptic-Scale Circulation Patterns to the Past Summer Precipitation Regime Shift in Eastern China. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2020GL087728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, X.; Chen, W.; Hu, P.; Chen, S.; Sheng, L. Intraseasonal Variation of the Northeast Asian Anomalous Anticyclone and Its Impacts on PM2.5 Pollution in the North China Plain in Early Winter. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2022, 22, 6507–6521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhong, S.; Dai, Z.; Yu, L. Comprehensive Analyses Linking PM2.5 to Its Precursors and Meteorological Conditions across Regions and Time Scale in China. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2025, 16, 102469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Tian, H.; Liu, X.; Wu, B.; Liu, S.; Hao, Y.; Luo, L.; Liu, W.; Zhao, S.; Lin, S.; et al. Spatial-Temporal Variation Characteristics of Air Pollution and Apportionment of Contributions by Different Sources in Shanxi Province of China. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 244, 117926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, C.; Collaud Coen, M.; Andrews, E.; Lin, Y.; Bossert, I.; Lund Myhre, C.; Tuch, T.; Wiedensohler, A.; Fiebig, M.; Aalto, P.; et al. Seasonality of the Particle Number Concentration and Size Distribution: A Global Analysis Retrieved from the Network of Global Atmosphere Watch (GAW) near-Surface Observatories. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 17185–17223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Wang, J.; Xue, K.; Fang, C. Spatial and Temporal Distribution Characteristics and Influencing Factors Analysis of Particulate Matter Pollution in Jinan City. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2021, 14, 1267–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Xie, Z.; Yao, X.; Wang, S.; Dong, L. Multilayer Temperature Inversion Structures and Their Potential Impact on Atmospheric Pollution in Northwest China. Atmos. Environ. 2025, 343, 120998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhang, C.; Li, Y.; Sun, J.; Chen, Z.; Li, L. Concurrence of Temperature and Humidity Inversions in Winter in Qingdao, China. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2024, 51, e2024GL108350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Gao, J.; Wang, Z.; Guo, Z. Influence of Particle Size Distribution on Agglomeration/Defluidization of Iron Powders at Elevated Temperature. ISIJ Int. 2017, 57, 649–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Huang, X. Simultaneous Inversion of Particle Size Distribution, Thermal Accommodation Coefficient, and Temperature of In-Flame Soot Aggregates Using Laser-Induced Incandescence. Materials 2024, 17, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Moon, J.; Kim, H. Understanding the Driving Forces of Summer PM1 Composition in Seoul, Korea, with Explainable Machine Learning. ACS ES&T Air 2024, 1, 960–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, H.; Cai, X.; Song, Y.; Zhu, T. The Impacts of the Atmospheric Boundary Layer on Regional Haze in North China. npj Clim. Atmos. Sci. 2021, 4, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Wu, Z.; Man, R.; Zong, T.; Liu, Y.; Meng, X.; Chen, J.; Chen, S.; Yang, S.; Yuan, B.; et al. Secondary Aerosol Formation Drives Atmospheric Particulate Matter Pollution over Megacities (Beijing and Seoul) in East Asia. Atmos. Environ. 2023, 301, 119702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, H.; Huang, Y.; Yang, S.; Cui, S.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, N.; Feng, L.; Ge, X.; Chen, M.; Wang, J.; et al. Characteristics of Wintertime Atmospheric PM1 in a Megacity in the Yangtze River Delta, China: A Comparative Study of 2015 and 2022. Aerosol Sci. Eng. 2025, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, R.; Yu, W. The Effects of PM2.5 Concentrations and Relative Humidity on Atmospheric Visibility in Beijing. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 2235–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; He, K.; Du, Z.; Zheng, M.; Duan, F.; Ma, Y. Humidity Plays an Important Role in the PM2.5 Pollution in Beijing. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 197, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Qin, Y.; Xu, X.; He, G.; Liu, N.; Miao, S.; Lu, X.; Wang, H.; Fan, S. Measurement Report: Nocturnal Subsidence behind the Cold Front Enhances Surface Particulate Matter in Plains Regions: Observations from the Mobile Multi-Lidar System. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2024, 24, 2267–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Yim, S.H.; Yang, Y.; Lee, O.S.; Lam, D.H.; Cheng, J.C.; Guo, J. Observation of Turbulent Mixing Characteristics in the Typical Daytime Cloud-Topped Boundary Layer over Hong Kong in 2019. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparks, N.; Toumi, R. Numerical Simulations of Daytime Temperature and Humidity Crossover Effects in London. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2015, 154, 101–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattarai, C.; Khlystov, A. Derivation of Particle-Size Changes from Polydisperse Size Distribution Measurements: Numerical and Experimental Verification. Aerosol Sci. Eng. 2021, 5, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, A.; Shen, X.; Ma, Q.; Lu, J.; Hu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Liang, L.; Liu, L.; Liu, S.; et al. Size-Resolved Hygroscopicity and Volatility Properties of Ambient Urban Aerosol Particles Measured by a Volatility Hygroscopicity Tandem Differential Mobility Analyzer System in Beijing. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2025, 25, 3389–3412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Wang, Y.; Riemer, M.; Li, Q. Effect of Unidirectional Vertical Wind Shear on Tropical Cyclone Intensity Change—Lower-Layer Shear versus Upper-Layer Shear. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 6265–6282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogozovsky, I.; Ansmann, A.; Hofer, J.; Chudnovsky, A. Unveiling Atmospheric Layers: Vertical Pollution Patterns and Prospects for High-Resolution Aerosol Retrievals Using the Eastern Mediterranean as a Case Study. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2025, 59, 12181–12195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndlovu, Z. Turbulent Diffusion and Air Pollution: A Comprehensive Review of Mechanisms, Impacts, and Modeling Approaches. World J. Adv. Res. Rev. 2024, 23, 1511–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).