Abstract
Since airborne microplastics (AMPs) are a recent and unexplored field of study, there are several unresolved issues regarding their effects on plants. The accumulating potential of AMPs and their effect on the biochemical parameters of ten different plant species in an Indian city environment were assessed. The four types of AMPs deposited in the phyllosphere—fragment (30.76%), film (28.95%), fiber (22.61%), and pellet (17.68%)—were examined using stereomicroscopy and fluorescence microscopy. The air pollution tolerance index (APTI) was determined, and other biochemical parameters such as proline, phenol, malondialdehyde, carotenoids, superoxide dismutase, catalase, and peroxidase were also measured. The findings showed that in the case of polymers type, PE (30%) was more abundant than others, followed by PET (17%), PP (15%), PVC (13%), PVA (10%), PS (7%), ABS (5%), and PMMA (3%). Clerodendrum infortunatum L., Calotropis procera (Aiton) W.T. Aiton, and Mangifera indica L. all showed a strong APTI and also exhibited significantly higher amounts of AMP accumulation. Principal component analysis showed a stronger association between phyllospheric AMPs and biochemical parameters. Additionally, the correlation analysis revealed that the presence of accumulated AMPs may significantly influence the biochemical parameters of the plants. Thus, it can be concluded that the different plant species are uniquely specialized in AMP accumulation, which is significantly impacted by the plants’ APTI as well as other biochemical parameters.
1. Introduction
The past several decades have seen a significant increase in plastic pollution in the environment due to urbanization, population expansion, and the overuse of synthetic polymers and their poor waste management. The residues of synthetic plastic polymers break down into microplastics (MPs) when they enter the environment as a result of biotic and abiotic weathering. Furthermore, key sources of MPs (including tires, synthetic fabrics, and personal care items) may release MPs straight into the environment [1]. MPs are solid plastic particles that are insoluble in water, and those with sizes between 1 and 1000 μm are called “small MPs”, while those between 1000 and 5000 μm are called “large MPs” [2]. Concerns about MPs have grown over the past 10 years, and efforts to identify and quantify them in various biospheres have highlighted several catastrophes [2]. According to recent research on food, water, soil, and ambient air, MPs have already entered deeper trophic levels [3] and may have negative health impacts on humans and animals [4]. In addition to the most popular pathways (via food and drink), inhalation is a significant and dangerous way for MPs to enter the human body [5].
Due to developmental activities, the number of sources and concentrations of airborne dust particles are anticipated to be higher in the urban atmosphere than in the rural atmosphere [6]. Therefore, remediation strategies become essential to reduce airborne dust pollution, particularly in urban environments. By collecting airborne particulate matter (PM) and aerosols on the surfaces of leaves during gas diffusion, plants and green vegetation have long been utilized as passive air pollution remedies to enhance urban air quality. On the surface of their leaves, plants also collect air-suspended MPs (AMPs) and have effective removal ability [6]. These MPs, however, have the potential to have detrimental impacts by blocking stomatal openings, disrupting biochemical synthesis, and changing plants’ capacity to withstand air pollution [7]. There have been reports that MPs trigger plants to produce reactive oxygen species (ROS), inhibit chlorophyll production, reduce photosynthesis, impair hormone regulation, block the seed coat, and affect plant growth, besides affecting root nutrient uptake. According to a recent study, AMPs have a tendency to make microorganisms more pathogenic [8]. A further investigation demonstrated the intricate relationship between AMPs’ lipophilicity and leaves [9]. Therefore, it is generally known that plants are the first to recognize AMPs, which makes it easier for plants to interact with MPs.
Researchers have studied plants’ ability to withstand pollution in order to promote them as a green defense. Through the regulation of biochemical activities, plants can be degraded by some common air pollutants like PM and undergo significant changes with an accumulation of heavy metals in the phyllosphere [6], which is also called phytoremediation. Accordingly, it is possible to see plants as prospective high-efficiency AMP removers [10,11,12,13]. The increasing concentration of AMPs in ambient air may have an impact on plants, which offer preventative and remedial strategies against the growing problems of urban air pollution. Therefore, it is necessary to state that typical air contaminants that eventually reach plant leaves have an impact on biochemical parameters [14,15,16]. Therefore, ecologists working on green infrastructure must immediately evaluate how AMPs affect plants’ biochemical responses [9,10,11]. Recently, Sahu et al. [9] reported that Ficus benghalensis, Mangifera indica, and Polyalthia longifolia all showed effective MP accumulation and good APTI scores. Furthermore, their investigation concluded that the plant species are uniquely specialized in MP accumulation, which is significantly influenced by the plants’ APTI value, relative water content, leaf extract pH, and spatial changes.
Prior research has not adequately examined the effects of AMPs on the APTI, enzymatic antioxidants (catalase, peroxidase, and superoxide dismutase), and non-enzymatic antioxidants (proline, phenol, malondialdehyde, and carotenoids), as well as their accumulation on various plant species. Thus, the following goals governed the execution of this study: (1) to assess the dust deposition and MP retention (DDMP) on the leaves of different plant species, (2) to determine the impact of DDMP on the APTI and biochemical parameters (proline, phenol, malondialdehyde, carotenoids, superoxide dismutase, catalase, and peroxidase) of different plant species, and (3) to interpret species variety and geographical fluctuation in relation to MPs’ deposition on plant leaves in urban, suburban, and rural settings. We anticipate that DDMP influences the plants’ capacity to withstand air pollution and that the accumulation of AMPs on leaves depends on species and geographic variability in urban, suburban, and rural environments.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling Sites
The current study investigated Malda (geographical location: 24°40′20″ N to 25°32′08″ N and 87°45′50″ E to 88°28′10″ E) district (West Bengal, India), located in the Eastern Indo-Gangetic Plain. This district (3733 km2) is experiencing high pressure due to the dense population (1071 inhabitants/km), horizontal and vertical urban growth, and increasing commercial and residential buildings. As a result, land and vegetation destruction and energy consumption are rising. Therefore, this region is witnessing the rapid development of highways, such as national highways (NH-31, NH-12, and NH-131A) and a state highway (SH-10), as well as an international land port, a major border checkpoint (that connects to Bangladesh) [3]. The NH-12 traverses these sites, easing the continuous movement of ~10,000 vehicles daily [5]. Brick kilns, plastic recycling factories, jute, rice, mills, beverage and food manufacturers, cotton and silk factories, and beedi industries are the additional pollution sources that are located a short distance from these locations. So, for this study, we selected four study sites: Kaliachak (suburban type: dense population, close to NH-12, small number of plastic recycling factories), Sujapur (suburban type: moderate-level population density, close to NH-12, many small-scale plastic recycling factories), English Bazar (urban type: this site is more densely populated compared to the other sites, with the NH-12 and international boundary close to the sampling site), and Amriti (rural type: lower population density, absence of highways).
2.2. Sampling Process and Meteorological Parameters
The present work, which included leaf collection and biochemical analysis, was completed between December 2023 and February 2024. Since the highest levels of particle deposition on leaf surfaces have been seen during the winter, this season was selected for the current investigation [17]. The collection of mature leaf samples used in this investigation came from a minimum height of 1.96 m above the ground [18]. The sampling date was a minimum of 28 days from the last rainfall. Ten plant species (Aegle marmelos (L.) Correa, Ficus religiosa L., Ficus benghalensis L., Nerium oleander L., Clerodendrum infortunatum L., Calotropis procera (Aiton) W.T. Aiton, Mangifera indica L., Artocarpus heterophyllus Lam., Moringa oleifera Lam., Azadirachta indica A. Juss.), based on their dominance at and commonness to all study sites, were selected for the present work, the details of which are given in Table S1. The selected leaves were ~1.5 m above the ground and positioned on the outer crown of the tree [19]. A total of 30 leaf samples (10 samples per tree × three replicates from individual trees) were collected for each species from each site by carefully cutting the leaves using clean branch shears, and then sealing the samples in a sterile stainless-steel box. Before being brought to the laboratory, samples were placed on ice and maintained at 4 °C until analysis [20]. Thus, a total of 300 samples (10 species × 30 leaves) were collected for this study from each site (Table S2).
Data for meteorological parameters such as the all sky surface UV index (W m−2 × 40), precipitation (mm/day), relative humidity (%), temperature maximum (°C), temperature minimum (°C), wind speed maximum (m/s), and wind speed minimum (m/s) were recorded using the NASA POWER website (https://power.larc.nasa.gov/, accessed on 1 July 2025). The wind rose plots were made using WRPLOT view ver. 7.0.0 (Lakes Software, Waterloo, ON, Canada). The air mass backward trajectories were computed using the NOAA (National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration) Hybrid single-particle Lagrangian Integrated Trajectory (HYSPLIT) model (https://www.ready.noaa.gov/HYSPLIT.php, accessed on 1 July 2025).
2.3. Dust Capturing Potentiality of Leaves
All of the leaves’ top and bottom surfaces were cleaned using a tiny brush to gather dust on tracing paper that had been previously weighed. We used the millimeter graph paper approach to compute the individual leaf area (m2) [19,21]. An electronic balance was used to weigh the samples, and the following formula was used to determine the dust weight:
where W is dust accumulation (mg/cm2), W1 is the initial weight of the tracing paper, W2 is the final weight of the tracing paper with dust, and a is the total area of the leaf (m2).
W (mg/cm2) = (W2 − W1)/a
Dust holding capacity (%) = (W × 100)/weight of cleaned leaves
2.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) of Leaves
For the SEM study, firstly, we cut one cm2 disks from unwashed plant leaves and let them air-dry in a closed and sterile chamber. These leaves were cut into thin pieces from the space between the leaf border and midrib. We used double-sided sticky tape to place each leaf strip on an aluminum stub, and after that, gold coating was performed to enable high-quality imaging. SEM was conducted (model: EVO18, Zeiss; Oberkochen, Germany) with ~15 kV accelerating voltage and a magnification range of 100–10,000x; leaf disks were inspected under vacuum conditions and captured on the camera in environmental mode.
2.5. Isolation, Identification, and Quantification of Microplastics
2.5.1. Isolation Procedure
The 1 gm dust samples were first treated with 10 mL 30% H2O2 to remove the organic materials, and they were then kept overnight at room temperature. The MP extraction followed a procedure used in recent studies, based on density separation using a saturated ZnCl2 solution (1.6 g/cm3) that was added to all samples in a 25 mL glass tube. To break down the largest aggregates, the samples were placed in an ultrasonic bath and then shaken. To settle larger particles and separate lighter particles (density < 1.6 g/cm3), including MPs, from the supernatant, the samples were centrifuged for 30 min at 5000 rpm. The supernatant containing MPs with a density of up to 1.6 g/cm3 was then filtered through a 60 μm pore size stainless-steel mesh, and the residue on the steel sieve was washed with Milli-Q water to remove other contamination. The above processes were repeated two more times. Finally, the MP sample-containing stainless-steel mesh was dried at 40–50 °C in a hot-air even. After that, samples were brushed from the mesh onto a glass Petri dish and stored for further analysis [9,22,23].
2.5.2. Stereomicroscope
The identification and quantification of the MPs followed the same method used by Leitao et al. [23]. The MPs were placed onto a glass slide to be analyzed using a stereomicroscope (model: GOKO, MX-99; Ambala, Haryana, India) equipped to take a photo of the particles using a digital camera. We used a pixel size of 3.9 μm and a 6.7x magnification for taking the pictures. Suspected particles were subjected to the break- and hot-point tests (hot needle grasped with tweezers). Plastic will get sticky and leave a mark when heated to a high temperature [24]. A number of photographs were cross-checked, and the plastic particles were detected by comparing the images taken before and after heating and observing changes in their size, shape, and color [5,24,25,26,27,28]. This cross-check suggested that the analyst’s impact on the measures would be minimal. Image J software (version 1.53) was used to measure and count the MP particles. The MPs were numbered and grouped according to size, color (white, black, red, blue, green, yellow, and transparent), and shape (film, fiber, fragment, and pellet). According to their size, they were classified into four groups: group 1 (≥60–<100 μm), group 2 (≥100–<500 μm), group 3 (≥500–<1000 μm), and group 4 (≥1000–≤5000 μm).
2.5.3. Fluorescent Microscope
Due to environmental deterioration, MPs decolorized and were formed into primarily white- and transparent-color MPs, rendering stereomicroscope identification difficult; thus, a fluorescent microscope was utilized for possible confirmation [3]. Additionally, the fluorescent microscope (model: Carl Zeiss, Axioscope 5 FL; Oberkochen, Germany) can visualize the comparatively smaller range of MPs and partially identify polymer types using fluorescent images when exposed to UV (254–365 nm), blue (430–495 nm), and green (495–570 nm) light [3]. Nile Red (NR) solution (0.5 mg/l) was used for this analysis, followed by the procedure of Mandal et al. [5].
2.5.4. Attenuated Total Reflectance Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
MPs cannot be completely and consistently detected with NR staining-based techniques and eye inspection alone [5]. We used attenuated total reflectance Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (ATR-FTIR) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA; model: Thermo Nicolet 5700) to determine the polymer composition of all putative MPs from each group. Prior to sample scanning, the background spectrum was acquired and utilized to calibrate carbon dioxide and vapor interference. In order to co-scan targeted compounds in a diamond pressure pool 16 times scan at a resolution of 4 cm−1 in transmission mode for each MP, midinfrared waves (400–4000 cm−1) were used. The resulting background interference was automatically calibrated, and the spectra were recorded using Thermo Fisher Scientific’s OMNIC PictaTM software ver. 1.9. Following meticulous spectra interpretation, the resulting spectra were matched to the OMNIC polymer spectra collection in order to verify the suspected particles’ chemical makeup with a minimum of 60% similarity. Only four pieces of fragmented particle were proven to be a plastic matrix with a ratio of 65% because of their tiny size, whereas the majority (n = 60) of the validated MPs had a match ratio of more than 75%. The OriginPro (version 9.1) program was used to create FTIR graphs [5] (Table S2).
2.6. Biochemical Characterization of Plant Leaves
We used fresh leaf samples for the biochemical investigation of the ascorbic acid (AA), total chlorophyll (TC), relative water content (RWC), and pH of leaf extract. Through the use of the 2,6 di-chlorophenol indophenol (DCPIP) method, the AA content (in mg/g) of leaves was calculated in accordance with Keller and Schwager’s [29] protocol. Similarly, the RWC was estimated using the oven-drying method [30], which involves calculating three leaf weights and using the following formula:
where Wd is the dry weight (weight after being oven-dried after an overnight immersion), Wf is the fresh leaf weight, and Wt is the turgid weight (weight of the leaf after an overnight immersion in water). In contrast, freshly homogenized leaves (leaf/deionized water = 1:5) were extracted in order to test the pH (P) of the leaf extract electrochemically [31]. Three fresh leaf samples weighing 0.2 g each were extracted overnight using 80% acetone (5 mL) before being pulverized and homogenized in order to detect the photosynthetic pigments (Chl-a, Chl-b, TC, and carotenoids). After filtering the homogenized solutions, 80% acetone was added to each sample to increase the filtrate to 25 mL. Through the use of a spectrophotometer (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA; model: Agilent Cary 60 spectrophotometer) and the Arnon [14] technique, the absorbance of the filtrates was measured at different wavelengths (663, 645, and 480 nm). The following is the calculation of the integrated formula for the air pollution tolerance index (APTI) [30,32]:
RWC (%) = [(Wf − Wd)/(Wt − Wd)] × 100
APTI = [AA (TC + P) + RWC]/10
Proline content was determined according to Bates et al. [16]. Total phenolic content (TPC) was determined by the Folin–Ciocalteu method [33]. Lipid peroxidation was analyzed in plant tissues by measuring malondialdehyde (MDA) [34]. We used spectrophotometry to measure antioxidant enzymes, including peroxidase (POD), catalase (CAT), and superoxide dismutase (SOD). Three fresh leaf samples, each weighing about 0.5 g, were mashed. The resulting homogenized mixture was then filtered through muslin fabric and centrifuged at 12,000× g for 10 min at 4 °C. After photochemical reduction was inhibited by nitro blue tetrazolium (NBT), SOD activity was measured. Through the use of a UV-1900 BMS (Waltham, MA, USA) spectrophotometer, the quantity of enzyme needed to provide 50% blockage of the NBT reduction at 560 nm was used to calculate one unit of SOD activity. Monitoring the absorbance drop at 240 nm due to H2O2 disappearance (ε = 39.4 mM−1cm−1) allowed for the determination of CAT activity. In accordance with the standard protocol, POD activity was measured. At 470 nm, the absorbance varied according to guaiacol [34,35,36,37].
2.7. Quality Control and Quality Assurance for Microplastic Analysis
To get rid of any possible impurities, glass wares were used in the analysis and were carefully cleaned with deionized water. Deionized water is essential for avoiding the entry of contaminants that might jeopardize the samples’ integrity. Additional steps were taken to reduce the possibility of airborne contamination, given the sensitivity of the MP analysis. Pieces of equipment like the sieves and glass beakers were wrapped in aluminum foil after the initial cleaning. Adopting rigorous personal protection measures was an additional move. Nitrile gloves were used to handle samples and reduce the possibility of external contamination, and cotton lab coats were worn to prevent external contamination. To maintain the integrity of the results and assure that any MPs found were representative of the sample content and not of outside contaminants, these procedures were followed continuously throughout the study. Laboratory blanks were used to assess MP contamination during analysis and identification, and results were discarded for self-contamination.
2.8. Statistical Analysis
Sankey diagrams were employed to study the size and shape diversity of MPs, and pie charts represent the color and polymer abundance of MPs. Principal component analysis (PCA) was used to identify the regulatory factors using biplots. Pearson’s correlation analysis was employed to recognize the interrelationship between various parameters such as DDMP, wind speed, precipitation, and biochemical parameters of plants. A structural equation model was drawn to study the direct and indirect relationships between various MPs and biochemical parameters of plants on the meteorological parameters (such as wind speed and precipitation). Multiple linear regression models were used to predict the impact of wind and precipitation parameters on the biochemical parameters of plants and DDMP concentration. The Microsoft Excel platform was used to represent the graphs of bar plots and pie charts, and the rest of the analyses were conducted through R 4.2.0 software.
3. Results and Discussion
This study was carried out during the post-monsoon season, with an average temperature of 27.61 ± 2.12 °C and a relative humidity of 69.4 ± 6.7% throughout the study period (December–February). Throughout the study period, the average daily precipitation was 0.69 ± 0.21 mm (Table S1). Of the days, 1.92% were calm, and there was an average maximum wind speed of 3.99 ± 0.58 m/s. The wind rose plot (Figure 1) indicates that northwest wind accounted for the majority of the wind throughout the study period. Meteorological parameters have a great influence on the air quality of an urban agglomeration [5]. Lower wind speeds generally have the potential to impede the dispersion of air pollutants and decrease vertical dispersion, which increases the likelihood that DDMP will become trapped in the limited mixing layer and exacerbate the concentration of contaminants [9]. Pollutant concentrations in the atmosphere that accumulated in the phyllosphere increased dramatically over the research period due to lower temperatures, medium-to-high humidity, moderate wind speeds, and little precipitation (Table S1). Moreover, urbanized regions’ complicated topography and land use patterns can impede complex wind flow and produce internal boundary layers, which might worsen the impact [9]. For instance, the investigated area includes both industrialized regions (such as Sujapur area, plastic recycling factories) and heavily inhabited cities (such as Kaliachak, English Bazar area). The HYSPLIT model was used to generate 72 h backward air mass trajectories at various altitudes above ground level that highlight the origin of DDMP pollutants at the study site [5]. The analysis revealed that the air mass in the study area came from Indian states such as Uttar Pradesh, Punjab, Haryana, Delhi, Bihar, Jharkhand, Meghalaya, and Assam and other countries such as, mainly, Bhutan, Pakistan, and Afghanistan (Figure 1). However, the trajectory data show many crisscross lines in the study area that may be due to the air mass being dominated by local sources. So, we can assume that DDMP in the phyllosphere primarily comes from local sources (Figure 2).
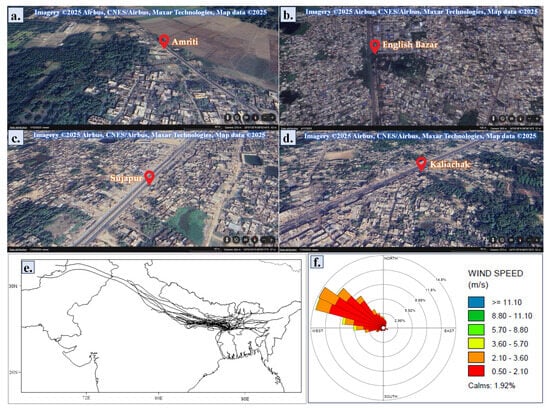
Figure 1.
The sampling sites represented via the satellite images obtained from Google Earth (https://earth.google.com/web; accessed on 1 July 2025): (a) Amriti; (b) English Bazar; (c) Sujapur; (d) Kaliachak. (e) Air mass backward trajectory data of the study area during the study period (December 2023–February 2024) was obtained using the NOAA HYSPLIT model. (f) The wind rose diagram illustrates the wind patterns of the study area during the study period (December 2023–February 2024).
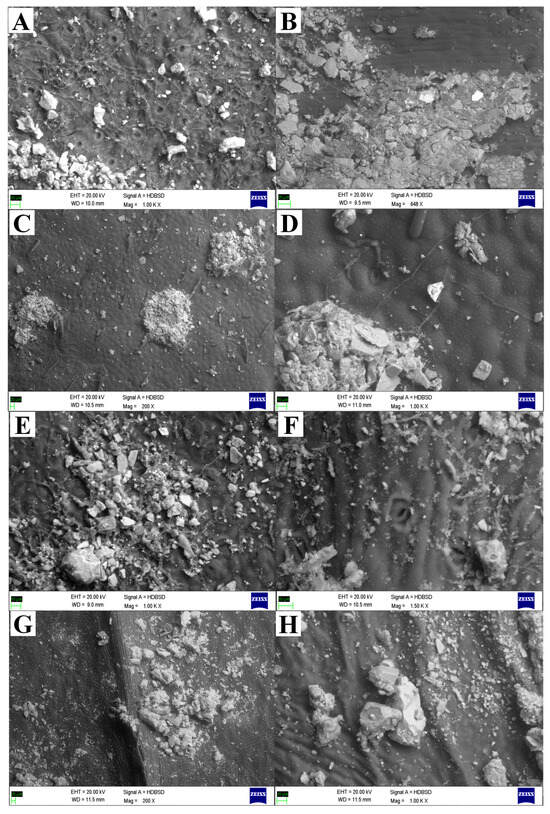
Figure 2.
Scanning electron microscopic (SEM) representations showed the heterogeneous mixture of different-sized dust particles deposited on the leaf surfaces. The following plant species showed dust accumulation in and around stomata that block the stomata, disturbing the plants’ physicochemical activity and altering the microenvironment of the leaf surfaces: (A,B) Mangifera indica L., (C,D) Moringa oleifera Lam., (E,F) Aegle marmelos (L.) Correa, and (G,H) Azadirachta indica A. Juss.
There has been much research on the existence of MPs in soils, sediments, marine habitats, and some organisms. Even though it is known that AMPs may travel great distances as suspended air particles, fewer investigations have concentrated on them [38]. They could therefore be part of the pollution of plants and land. Since a higher level of AMPs was seen in urban air compared to rural regions, it was determined that industrialization, population density, exposure to rapid traffic, and civic and other developmental activities are major factors in understanding the distribution of AMPs (Figure 3b). Therefore, corrective action is required to reduce DDMPs, particularly in urban environments [39].
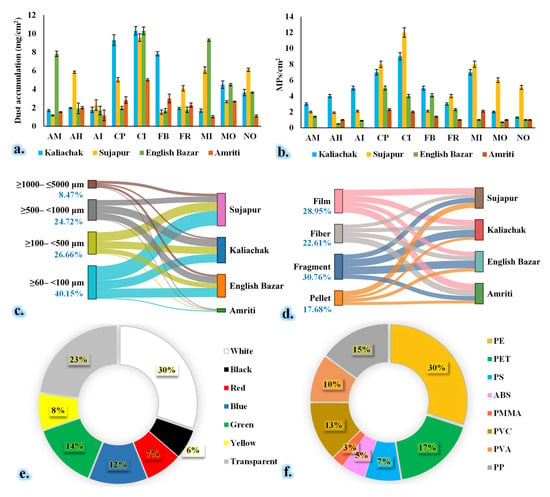
Figure 3.
Total dust load (a) and MP abundance (b) in different species. MP diversity at different sampling sites: (c) size, (d) shape, (e) color, and (f) polymer abundance throughout the study period. Kaliachak: suburban type, dense population, and small number of plastic recycling factories; Sujapur: suburban type, moderate-level population density, and large number of plastic recycling factories; English Bazar: urban type, dense population; Amriti: rural type and lower population density. AM: Aegle marmelos (L.) Correa; AH: Artocarpus heterophyllus Lam.; AI: Azadirachta indica A. Juss.; CI: Clerodendrum infortunatum L.; CP: Calotropis procera (Aiton) W.T. Aiton; FR: Ficus religiosa L.; FB: Ficus benghalensis L.; MO: Moringa oleifera Lam.; MI: Mangifera indica L.; NO: Nerium oleander L.
In addition to being a conventional solution for bioremediation, plants make a multifaceted contribution to the fight against urban air pollution [40]. Given this, adding the accumulation of DDMPs that cleanse the surrounding air to its characteristics might increase its advantages. This study’s evaluation can help identify the best plant species for a certain land use type to help reduce developing DDMP problems in ambient air. This study demonstrated that MP accumulation varied greatly by plant species. The physical traits of leaves might be the cause of this (Table S2). Despite other plants’ noticeable pubescent or hairy features, our study found that Clerodendrum infortunatum L., Calotropis procera (Aiton) W.T. Aiton, and Mangifera indica L. collected more DDMPs than others. Prior research has shown that plant leaves’ hairy features aid in PM retention [41]. However, in terms of DDMPs, the current study found no evidence of a hairy structure’s significance in DDMP accumulation. Conversely, leaves with epicuticular wax showed a higher concentration of MPs. This suggests that, more than any other morphological feature, including hairy features, epicuticular wax may promote the formation of AMPs (Figure 2). This might be a result of MPs’ lipophilic nature, which entails a higher affinity for lipids [42]. This result is in line with the findings of Liu et al. [43], who also suggested that waxy deposition would have a greater impact on air pollutant capture than the presence of pubescens. In a specific plant species, we additionally observed significant variances in cumulative and other types of DDMP accumulation (Figure 3). This might be because the plant species showed a selective accumulation of MPs, or it could be because of the chemistry of the MP–plant interaction, which requires more research. However, as shown in Figure 4, the results clearly show the substantial species heterogeneity in MP accumulation from ambient air.
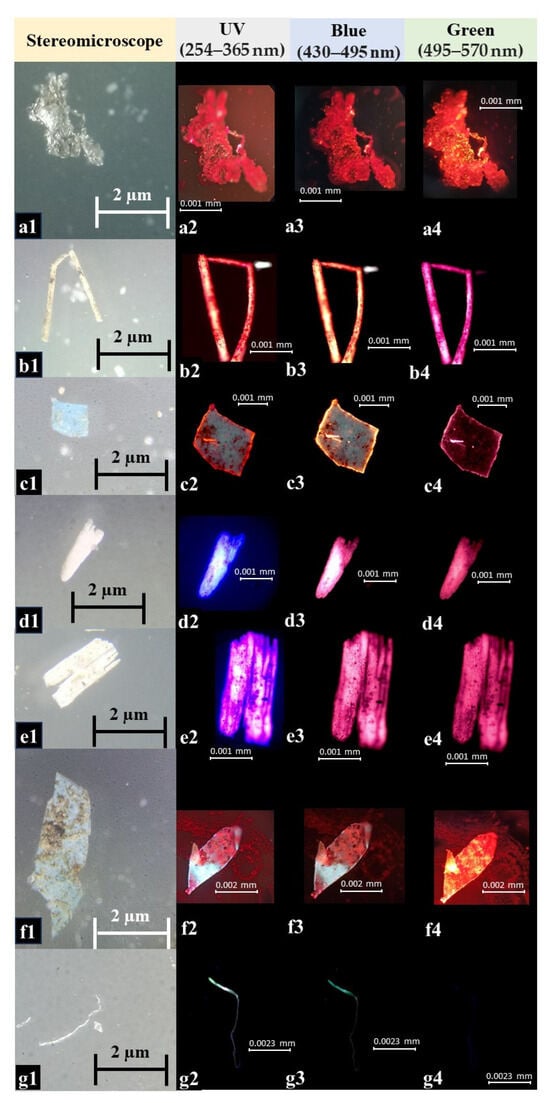
Figure 4.
Fluorescent microscopy images of selected microplastics from leaf phyllosphere, which show the different sizes of microplastics. The fluorescent microscopy images are taken with different filters; based on the fluorescent intensities in different filters, the probable polymer type can be identified [5]. (a) Film type with white color (a1): PE/PP/PA/PU/PS with strong (a2–a4; in UV, blue, and green) fluorescence intensity; (b) fiber type with white color (b1): PE/PP/PA/PU/PS with strong (b2–b4; in UV, blue, and green) fluorescence intensity; (c) fragment type with blue color (c1): PE/PP/PA/PU/PS with strong (c2–c4, in UV, blue, and green) fluorescence intensity; (d,e) fragment type with white color (d1,e1): PE/PP/PA/PU/PS with strong (d2–d4,e2–e4; in UV, blue, and green) fluorescence intensity; (f) fragment type with blue color (f1): PE/PP/PA/PU/PS with strong (f2–f4; in UV, blue, and green) fluorescence intensity; (g) fiber type with white color (g1): CA with strong (g2,g3; in UV and blue) and weak (g4; in green) fluorescence intensity. PE: Polyethylene; PP: Polypropylene; PA: Polyamide; PU: Polyurethane; PS: Polystyrene; CA: Cellulose acetate.
The fragment type of MPs was more prevalent than the other types in the current investigation (Figure 3). The smaller-size (≥60–<100 µm) AMPs had the highest abundance, followed by medium- (≥100–<1000 µm) and larger-size AMPs. In the case of color, we found that white-color AMPs were more prevalent than the other types of AMPs. The PE-type polymer had the highest percentage (30%), followed by PET (17%), PP (15%), PVC (13%), PMMA (10%), and others (Figure 5). This outcome is consistent with the findings of Yadav et al. [44], who also documented the presence of the aforementioned MP types in urban ambient air. Nonetheless, the size density of the MPs may be the reason for the fragments’ dominance over their counterparts in other MPs (Figure 3). Prior research has demonstrated that tiny MP structures can travel large distances, which explains why they are so common [5,45,46]. In this investigation, we found that the top three MP accumulators were C. infortunatum L., C. procera, and M. indica. Green belts and urban forests, which may improve a plant’s vegetative functions, or plantations in residential and sensitive locations can all benefit from these species. The study also points out that the gradient of MP levels in ambient air may directly contribute to the variation in MP accumulation by plant species.
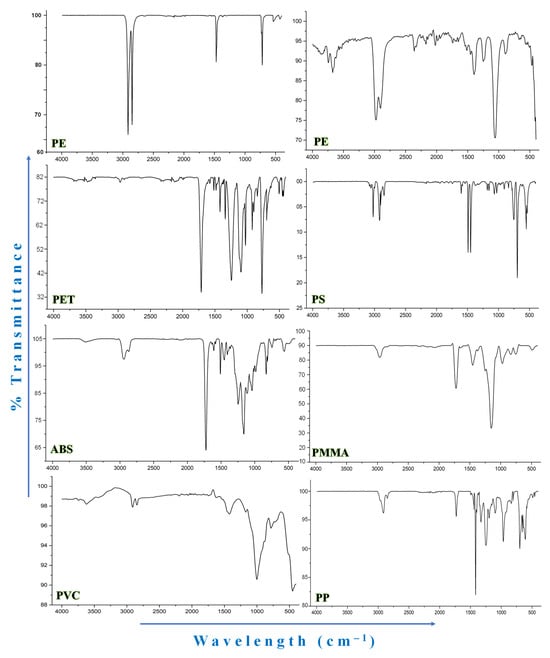
Figure 5.
Selected FTIR graphs of microplastics. PE: Polyethylene; PMMA: Polymethyl methacrylate; PET: Polyethylene terephthalate; PS: Polystyrene; PVC: Polyvinyl chloride; PP: Polypropylene; ABS: Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene.
C. procera had the greatest levels of chl-a and b and total chlorophylls, which are primarily responsible for the production of food in plants. Regarding various plant species, there was a notable variance in the chlorophyll content. The urban biotope and sensitive region had the highest levels of chlorophyll, whereas the industrial and residential sectors had the lowest levels overall (Figure 6). Additionally, our findings point to a negative relationship between the APTI and chlorophyll contents. This confirms that plants’ decreased capacity for tolerance lowers the synthesis of chlorophyll and impacts production, which is significantly influenced by exposure to air pollution [47].
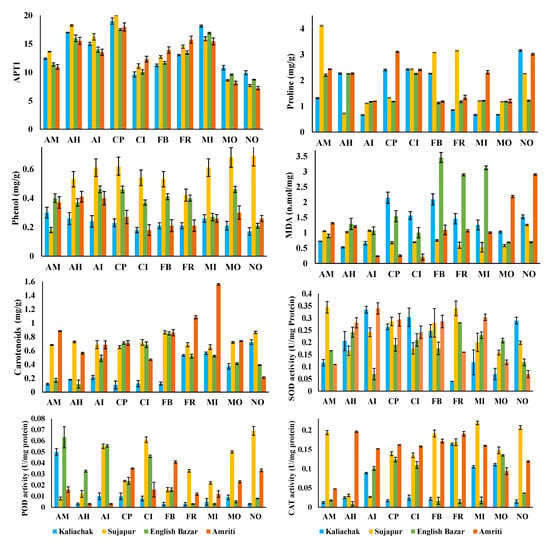
Figure 6.
APTI and non-enzymatic antioxidant (proline; phenol; MDA: malondialdehyde; and carotenoids) and enzymatic antioxidant (CAT: catalase; POD: peroxidase; and SOD: superoxide dismutase) activity in different plant species. Kaliachak: suburban type, dense population, and small number of plastic recycling factories; Sujapur: suburban type, moderate-level population density, and large number of plastic recycling factories; English Bazar: urban type and dense population; Amriti: rural type and lower population density. AM: Aegle marmelos (L.) Correa; AH: Artocarpus heterophyllus Lam.; AI: Azadirachta indica A. Juss.; CI: Clerodendrum infortunatum L.; CP: Calotropis procera (Aiton) W.T. Aiton; FR: Ficus religiosa L.; FB: Ficus benghalensis L.; MO: Moringa oleifera Lam.; MI: Mangifera indica L.; NO: Nerium oleander L.
A high RWC is thought to improve a plant’s tolerance by preventing wilting and combating unfavorable and drought circumstances [48]. In this investigation, the RWC demonstrated a noteworthy function in controlling the plant species’ APTI. This suggests that the water content of a plant’s leaves has the greatest impact on its tolerance (Figure 6). This study’s PCA biplot analysis further supports this, showing that RWC clearly outperforms other criteria in determining the tolerance of plants. Conversely, AA and the pH of leaf extract had a negative correlation with plants’ capacity for tolerance. While a high AA concentration protects plants against reactive oxygen species, a high leaf extract pH causes plants to exhibit greater pollution tolerance [49]. Acidic air pollution may be the cause of the leaf extract’s pH being < 7 in most cases [9]. In a comparison of the air in residential, sensitive, and biotope zones to that in industrial and traffic areas, the higher ascorbic acid content in leaves may be the result of exposure to higher levels of reactive oxygen species. Changes in a number of factors, such as the kind of land use, the ambient air, and plant response, might affect the biochemical characteristics. The cumulative effect of several elements supported by MPs in the air may thus be responsible for the observed changes with regard to the biochemical parameters of plants and their capacity for tolerance (Figure 7). The concentration of MPs on the leaf surface has a major effect on the metabolic parameters and tolerance capacity of plants. The findings imply that MPs in general and MP fiber and fragment shape in particular were primarily in charge of influencing the plants’ metabolic parameters. The PCA biplot reveals some linkages of MPs with SOD, the APTI, and AA, being described under the same component, while the correlation analysis shows substantial correlations (particularly with leaf extract pH) (Figure 7a). There was a substantial positive association between the pH of the leaf extract and the MPs, suggesting that the pH level was higher at higher MP concentrations. Lower biological activity in plants under MP stress may be the cause of this. In their evaluation of MPs’ impacts, Li et al. [40] hypothesized that MPs impair biological processes, which in turn affect physiological and pH processes [50]. Additionally, our data showed a negative correlation between MPs and chl-b concentration, supporting the findings of Gao et al. [25], who showed that exposure to MPs impairs the formation of chlorophyll. Khatiwada et al. [35] observed similar results of a decreased chlorophyll content with MP buildup.
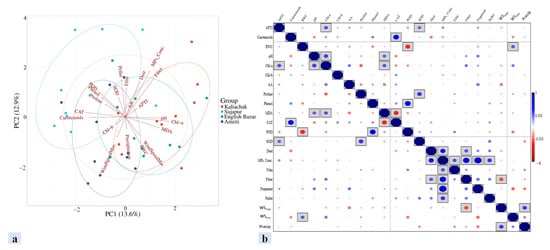
Figure 7.
(a) Principal component analysis (biplot) and (b) correlation analysis among the amount of DDMP, wind speed, precipitation, and various biochemical parameters in plants of the study area. WSmax: wind speed maximum; WSmin: wind speed minimum; Precip: precipitation; APTI: air pollution tolerance index; RWC: relative water content; Chl: chlorophyll; MDA: malondialdehyde; CAT: catalase; POD: peroxidase; SOD: superoxide dismutase; MPs_Conc.: microplastic concentration.
The blockage of stomatal pores (Figure 2) or distortions or deformities in cellular structures caused by DDMPs are a likely cause of the observed positive significant associations between RWC and MPs (Figure 7b). Longer water retention in plants may have resulted from stomatal pore blockage, which decreased water loss through transpiration (Figure 6). DDMPs can therefore be quite important in causing abnormalities in the architecture of outer cells [51,52,53]. However, research has also shown that MPs are in charge of plants’ increased ROS levels [54]. The effect of MPs in raising AA and SOD concentration in this study may have been significant since AA and SOD have an inherent defense against all ROS (Figure 6). Furthermore, MPs are hydrophobic [55], which prevents them from entering cells. As a result, once they adhere to the leaf surface, they stay there until they are expelled as washouts or fallout. This led to the finding that the APTI, which, in this study, showed a substantial positive relationship with AA, increased as enzymatic and non-enzymatic antioxidant concentrations increased, with MP accumulation serving as a guide. As the accumulation density of MPs on the leaf surface rises, plants may respond more strongly to airborne MPs [56]. On the other hand, wind speed (max. and min.) and precipitation negatively correlated with DDMP concentration. This result from the study indicates that the wind patterns and precipitation did not affect the DDMP concentration in the phyllosphere. This may be due to the local sources in this study being significantly more impactful than the distant sources (Figure 7).
Similarly, linear regression analysis also indicated that the wind speed maximum, wind speed minimum, and precipitation did not significantly impact plant biochemical parameters (Table 1), where the biochemical parameters and DDMP were the dependent variables and wind and precipitation were the independent variables. So, from both analyses, we can assume that meteorological variables such as wind patterns and precipitation did not directly affect the MP diversity and as well as plant biochemical parameters. In contrast, a previous study reported that MPs (fiber and fragment) showed a general ability to predicting the pH, AA, and APTI in the case of M. indica and Chl-a and b and total chlorophyll concentration in the case of Tectona grandis, despite the significant species diversity. Therefore, it is clear that the MP concentration in ambient air controls and regulates the biochemical parameters in plants. This is in contrast to Leonard et al.’s report [37,38], as they found a clear geographical influence on MP accumulation in their investigation. But in the case of our study, MP diversity and DDMP concentrations affected the biochemical parameters, but the meteorological parameters had a non-significant effect on plant biochemical parameters and DDMP concentrations [57]. This is only an observation of this study, though, and further research along these lines would provide detailed and tangible information.

Table 1.
Multiple linear regression analysis highlighting the relationship between wind and precipitation and biochemical parameters or DDMP.
Additionally, our study discovered that residential and sensitive regions had higher levels of MP deposition on leaves. There are two possible explanations for this intriguing but worrisome finding: either (a) the ambient air in sensitive and residential areas contains higher concentrations of DDMPs due to human behavior patterns or, maybe, the migration of these DDMPs from other areas, or (b) the same plant species perform better in these areas because of reduced air pollution (because of criteria pollutants). Due to the widespread usage of plastic items in daily life, including medical packaging in hospital units, the former explanation appears to be more credible [58]. The primary MPs (deliberately created by manufacturers for use in paints, cosmetics, etc.) are the principal cause of high levels of MPs entering the environment [59]. It is also commonly recognized that increased DDMP entrance into the atmosphere is a result of disintegration from the source [60]. Since there are several sources of MPs, it is evident that there is a large buildup of MPs in sensitive regions, such as hospitals and residential areas.
A secondary finding of this study, as represented via the structural equation mode (Figure 8), is that between the biochemical parameters and the effect of microplastics on the meteorological parameters, there were significant differences. This demonstrates that the size and makeup of the various MP categories (forms) may be causing plants to exhibit selective accumulation of MPs. The varying magnitude of MP production at various locations might also be the cause of this phenomenon. Therefore, differences in spatial scale are important for the production of MPs in the air as well as for their deposition on plant leaves (Figure 2).
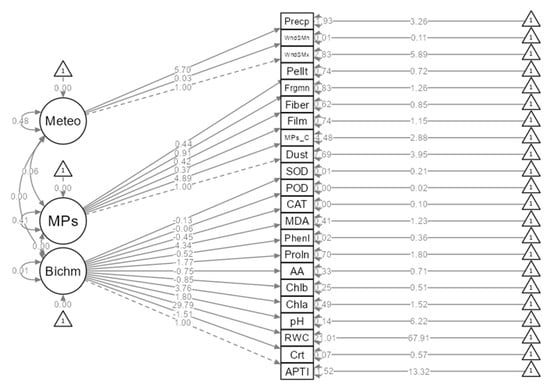
Figure 8.
Direct and indirect relationships between the biochemical (Bichm) parameters and the effect of microplastics (MP type) on the meteorological (Meteo) parameters through a structural equation model. WndSMx: wind speed maximum; WndSMn: wind speed minimum; Precp: precipitation; APTI: air pollution tolerance index; RWC: relative water content; Chla: chlorophyll-a; Chlb: chlorophyll-b; MDA: malondialdehyde; CAT: catalase; POD: peroxidase; SOD: superoxide dismutase; MPs_C: microplastic concentration; Pellt: pellet; Frgmn: fragment; Phenl: phenol; Proln: proline; AA: ascorbic acid; Crt: carotenoid.
There is currently a lack of comprehensive research on the determination of MPs in urban air foliage. As a result, a comparative evaluation has very little chance of succeeding. Nevertheless, comparable research (although with a relatively small sample size) reveals that the number of MPs accumulating on leaf surfaces can vary from 1000 MPs/m2 to 70,000 MPs/m2 [9,61,62]. Plants provide dependable help in lowering the concentration of MPs in urban air, as is clear. In addition, it was shown that, in addition to being influenced by the kind of urban area, plants exhibit species specialization in the accumulation of MPs on their leaf surfaces [63,64,65]. Therefore, to successfully combat the growing MP problem in urban air, schematic planning utilizing heterosporous planting methods beneath urban green belts, urban biotopes, urban transit corridors, etc., must be used.
4. Conclusions
Understanding how DDMPs vary on the leaf surfaces of different plant species across different geographic scales validated the study’s findings on the uniqueness of MP accumulation. The most prevalent form of MPs deposited was the fragment form. However, the fiber and fragment forms provided insight into the biochemical characteristics. The plants’ RWC regulated the APTI. Furthermore, the strong correlation between MP accumulation and plant tolerance suggests that the MP concentration increases plants’ resilience to air pollution. This characteristic improves the plants’ capacity for phytoremediation. Additionally, it was noted that some plant species in sensitive and residential regions were effective MP trappers. This might be because of the high ambient concentration brought on by varying degrees of plastic usage. Thus, it can be concluded that the specialization of plant species in MP accumulation is controlled by RWC, the plant’s APTI value, and spatial scale differences. This study helps give baseline data on the study region, despite its one-time study period limitation. To address this issue, however, further research that includes seasonal fluctuations in DDMP accumulation and the ensuing effects on plant physiological processes and morphological characteristics, including the function of meteorology in MP accumulation, may be helpful.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/atmos16070861/s1, Table S1: Meteorological parameters of the Malda district; Table S2: Morphological characteristics of the selected plant species under this study; Table S3: Peak assignments for attenuated total reflection-fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (ATR-FTIR) characteristics for several kinds of microplastics. References [66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73,74] are cited in the Supplementary Materials.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.S. and M.M.; methodology, M.M.; validation, M.M.; formal analysis, M.M., S.K.D. and T.G.; investigation, M.M., S.G. and A.M.; resources, A.S. and A.P.; data curation, M.M.; writing—original draft preparation, M.M.; writing—review and editing, A.R., A.P., R.P., G.K.A., R.R. and A.S.; visualization, M.M.; supervision, A.S.; project administration, A.S. and M.M.; funding acquisition, R.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data could be made available by the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
M.M. acknowledges the University Grants Commission (UGC, New Delhi, Govt. of India), as the author receives fellowship in the form of the Senior Research Fellowship (CSIR-UGC SRF; Award No. 16–6(DEC.2018)/2019(NET/CSIR); UGC-Ref. No.: 900/(CSIR-UGC NET DEC.2018); dated: 02.04.2019). A.R. acknowledges the Council of Scientific Research (CSIR), New Delhi, for providing fellowship in the form of the Junior Research Fellowship (CSIR-HRDG Ref No: Sept/06/22(i)EU-V) from GoI. All authors also acknowledge the infrastructural support in the form of the DBT-BOOST program, Department of Science & Technology and Biotechnology, GoWB, GoI (vide Ref. No. 1089/BT(Estt)/1 P-07/2018; dated: 24.01.2019) provided to the Department of Botany, University of Gour Banga, Malda, West Bengal, India. Additionally, all the authors are also grateful to the Central facility of Bose Institute, EN-80, Sector-V, Bidhan Nagar, Kolkata, Pin—700091, West Bengal, India.
Conflicts of Interest
Authors Ganesh Kumar Agrawal and Randeep Rakwal were employed by the company GRADE Academy (Pvt.) Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Mandal, M.; Roy, A.; Sarkar, A. Understanding the possible cellular responses in plants under micro (nano)-plastic (MNPs): Balancing the structural harmony with functions. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 957, 177732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO. Plastics—Environmental Aspects—State of Knowledge and Methodologies. 2020. Available online: https://www.iso.org/obp (accessed on 1 July 2025).
- Mandal, M.; Roy, A.; Binha, S.K.; Popek, R.; Przybysz, A.; Koczoń, P.; Prasad, D.; Sarkar, A. Waste dumps as microplastic hotspots: A comparative investigation at urban, suburban, and rural areas of Eastern India and associated risk assessment. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2025, 44, 1869–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, E.; Lee, J.Y.; Redwan, M. Animal exposure to microplastics and health effects: A review. Emerg. Contam. 2024, 10, 110369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, M.; Roy, A.; Singh, P.; Sarkar, A. Quantification and Characterization of Airborne Microplastics and their Possible Hazards: A Case Study from an Urban Sprawl in Eastern India. Front. Environ. Chem. 2024, 5, 1499873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, M.; Das, S.; Roy, A.; Rakwal, R.; Jones, O.A.; Popek, R.; Agrawal, G.K.; Sarkar, A. Interactive relations between plants, phyllosphere microbial community, and particulate matter pollution. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 890, 164352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, N.; Zhong, H.; Zhou, F.; Zhang, X.; Liu, C.; Huang, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, Y.; et al. A global estimate of multiecosystem photosynthesis losses under microplastic pollution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2025, 122, e2423957122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, M.; Sarkar, M.; Khan, A.; Biswas, M.; Masi, A.; Rakwal, R.; Agrawal, G.K.; Srivastava, A.; Sarkar, A. Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) and Reactive Nitrogen Species (RNS) in Plants—Maintenance of structural individuality and functional blend. Adv. Redox Res. 2022, 5, 100039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, C.; Dash, P.K.; Basti, S. Accumulation of airborne microplastics and its impact on pollution tolerance ability of plants in an urban setup in India. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2025, 18, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natsu, S.; Okochi, H.; Niida, Y.; Miyazaki, A. Accumulation of Airborne Microplastics on Forest Canopy Leaves: Insights from Trichomes and Epicuticular Waxes. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2023; preprint. [Google Scholar]
- Bi, M.; He, Q.; Chen, Y. What roles are terrestrial plants playing in global microplastic cycling? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 5325–5327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, C.B.; Quinn, B. Plastic production, waste and legislation. In Microplastic Pollutants; Crawford, C.B., Quinn, B., Eds.; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 39–56. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, L.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, W.; Liu, X.; Wang, Q.; Tanveer, M.; Huang, L. Microplastic stress in plants: Effect on plant growth and their remediations. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1226484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnon, D.I. Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts. Polyphenoloxidase in Beta vulgaris. Plant Physiol. 1949, 24, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atugoda, T.; Vithanage, M.; Wijesekara, H.; Bolan, N.; Sarmah, A.K.; Bank, M.S.; You, S.; Ok, Y.S. Interactions between microplastics, pharmaceuticals and personal care products: Implications for vector transport. Environ. Int. 2021, 149, 106367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bates, L.S.; Waldren, R.P.; Teare, I.D. Rapid determination of free proline for water-stress studies. Plant Soil 1973, 39, 205–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batool, I.; Qadir, A.; Levermore, J.M.; Kelly, F.J. Dynamics of airborne microplastics, appraisal and distributional behavior in atmosphere; A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, S.S.; Sahu, C.; Basti, S.; Sahu, S.K. Particle and heavy metal accumulation by two plant species in a coal mining area of Odisha, India. Int. J. Phytoremediation 2023, 26, 838–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, N.; Zhang, H.; Salam, M.M.A.; Li, H.; Chen, G. Foliar dust particle retention and metal accumulation of five garden tree species in Hangzhou: Seasonal changes. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 306, 119472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, P.K.; Sahu, C.; Basti, S.; Sahu, S.K. Altitude governs the air pollution tolerance and heavy metal accumulation in plants. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowarah, K.; Patchaiyappan, A.; Thirunavukkarasu, C.; Jayakumar, S.; Devipriya, S.P. Quantification of microplastics using Nile red in two bivalve species Perna viridis and Meretrix meretrix from three estuaries in Pondicherry, India and microplastic uptake by local communities through bivalve diet. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 153, 110982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dris, R.; Gasperi, J.; Saad, M.; Mirande, C.; Tassin, B. Synthetic fibers in atmospheric fallout: A source of microplastics in the environment? Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 104, 290–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitão, I.A.; Van Schaik, L.; Iwasaki, S.; Ferreira, A.J.D.; Geissen, V. Accumulation of airborne microplastics on leaves of different tree species in the urban environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 948, 174907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falakdin, P.; Rosales, A.L.; Andrade, J.; Terzaghi, E.; Guardo, A.D.; Lorenzo, S.M. Comparison of microplastic type, size, and composition in atmospheric and foliage samples in an urban scenario. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 349, 123911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, G.; Zhao, X.; Jin, P.; Gao, K.; Beardall, J. Current understanding and challenges for aquatic primary producers in a world with rising micro- and nano-plastic levels. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 406, 124685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Wang, D.; Wei, L.; Zhang, X.; Song, B. Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in plant leaves from Yan’an city of the Loess Plateau, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2014, 110, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Li, T.; Li, M.; Cai, Z.; Wang, X.; Gong, H.; Yan, M. Mangrove plants are promising bioindicator of coastal atmospheric microplastics pollution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 465, 133473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javanmard, Z.; Kouchaksaraei, M.T.; Pandey, H.S.M.; Pandey, A.K. Assessment of anticipated performance index of some deciduous plant species under dust air pollution. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 38987–38994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, T.; Schwager, H. Air pollution and ascorbic acid. Eur. J. For. Pathol. 1977, 7, 338–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmarkar, D.; Padhy, P.K. Air pollution tolerance, anticipated performance, and metal accumulation indices of plant species for greenbelt development in urban industrial area. Chemosphere 2019, 237, 124552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, M.; Nagpal, A. Evaluation of air pollution tolerance index and anticipated performance index of plants and their application in development of green space along the urban areas. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 18881–18895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmakar, D.; Deb, K.; Padhy, P.K. Ecophysiological responses of tree species due to air pollution for biomonitoring of environmental health in urban area. Urban Clim. 2021, 35, 100741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noreen, H.; Semmar, N.; Farman, M.; McCullagh, J.S. Measurement of total phenolic content and antioxidant activity of aerial parts of medicinal plant Coronopus didymus. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2017, 10, 792–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalofah, A.; Migdadi, H.; El-Harty, E. Antioxidant enzymatic activities and growth response of quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa willd) to exogenous selenium application. Plants 2021, 10, 719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanoranga, K.S. Phytomonitoring of air pollution around brick kilns in Balochistan province Pakistan through air pollution index and metal accumulation index. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 229, 727–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatiwada, J.R.; Madsen, C.; Warwick, C.; Shrestha, S.; Chio, C.; Qin, W. Interaction between polyethylene terephthalate (PET) microplastic and microalgae (Scenedesmus spp.): Effect on the growth, chlorophyll content, and hetero-aggregation. Environ. Adv. 2023, 13, 100399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, J.; Borthakur, A.; Koutnik, V.S.; Brar, J.; Glasman, J.; Cowger, W.; Dittrich, T.M.; Mohanty, S.K. Challenges of using leaves as biomonitoring system to assess airborne microplastic deposition on urban tree canopies. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2023, 14, 101651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, J.; El Rassi, L.A.; Samad, M.A.; Prehn, S.; Mohanty, S.K. The relative importance of local climate and land use on the deposition rate or airborne microplastics on terrestrial land. Atmos. Environ. 2024, 318, 120212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Li, K.; Bai, X.; Zhang, G.; Tian, X.; Tang, Q.; Zhang, M.; Hu, M.; Huang, Y. Microplastics in the atmosphere: Adsorb on leaves and their effects on the phyllosphere bacterial community. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 462, 132789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zheng, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, S.; Li, Y.; Zhang, W.; Li, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, X.; et al. Effect and mechanism of microplastics exposure against microalgae: Photosynthesis and oxidative stress. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 905, 167017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yang, Y.; Chen, X.; He, Y.; Bolan, N.; Rinklebe, J.; Lam, S.S.; Peng, W.; Sonne, C. A discussion of microplastics in soil and risks for ecosystems and food chains. Chemosphere 2023, 313, 137637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Wei, C.; Jiao, M.; Wang, Y.; Sun, H. Mangrove leaves: An undeniably important sink of MPs from tidal water and air. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 426, 128138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Wang, X.; Song, Z.; Wei, N.; Li, D. Terrestrial plants as a potential temporary sink of atmospheric microplastics during transport. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 742, 140523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, H.; Sethulekshmi, S.; Shriwastav, A. Estimation of microplastic exposure via the composite sampling of drinking water, respirable air, and cooked food from Mumbai, India. Environ Res. 2022, 214, 113735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, L.; Ma, Z.; Xu, Y.; Sun, F.; Lun, X.; Liu, X.; Chen, J.; Yu, X. Assessing the capacity of plant species to accumulate particulate matter in Beijing, China. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohanty, S.P.; Mishra, R.; Basti, S.; Sahu, C. Chemical fractionation of elements in leaf-deposited particulate matter of an urban area in India. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2024, 17, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnar, V.E.; Simon, E.; Tothmeresz, B.; Ninsawat, S.; Szabo, S. Air pollution induced vegetation stress—The air pollution tolerance index as a quick tool for city health evaluation. Ecol. Ind. 2020, 113, 106234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadgorska-Socha, A.; Kandziora-Ciupa, M.; Trzesicki, M.; Barczyk, G. Air pollution tolerance index and heavy metal bio-accumulation in selected plant species from urban biotopes. Chemosphere 2017, 183, 471–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharti, S.K.; Trivedi, A.; Kumar, N. Air pollution tolerance index of plants growing near an industrial site. Urban Clim. 2018, 24, 820–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prajapati, S.K.; Tripathi, B.D. Anticipated performance index of some tree species considered for green belt development in and around an urban area: A case study of Varanasi city, India. J. Environ. Manag. 2008, 88, 1343–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, P.K. Particulate matter tolerance of plants (APTI and API) in a biodiversity hotspot located in a tropical region: Implications for eco-control. Part. Sci. Technol. 2019, 38, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redondo-Bermudez, M.C.; Gulenc, I.T.; Cameron, R.W.; Inkson, B.J. Green barriers’ for air pollutant capture: Leaf micromorphology as a mechanism to explain plants capacity to capture particulate matter. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 288, 117809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Bhattacharya, T.; Kumari, M. Air pollution tolerance, metal accumulation and dust capturing capacity of common tropical trees in commercial and industrial sites. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 722, 137622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, C.; Basti, S.; Sahu, S.K. Air pollution tolerance index (APTI) and expected performance index (EPI) of trees in Samabalpur town of India. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, C.; Basti, S.; Sahu, S.K. Particulate collection potential of trees as a means to improve the air quality in urban areas in India. Environ. Process. 2021, 8, 377–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, C.; Sahu, S.K. Ambient air quality and air pollution index of Sambalpur: A major town in Eastern India. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 16, 8217–8228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahrukh, S.; Hossain, S.A.; Huda, M.N.; Moniruzzaman, M.; Islam, M.M.; Shaikh, M.A.A.; Hossain, M.E. Air pollution tolerance, anticipated performance, and metal accumulation indices of four ever green tree species in Dhaka, Bangladesh. Curr. Plant Biol. 2023, 35–36, 100296. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, O.P. Plant Taxonomy; Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Company Limited: New Delhi, India, 1993; p. 482. [Google Scholar]
- Shrestha, S.; Baral, B.; Dhital, N.B.; Yang, H.H. Assessing air pollution tolerance of plant species in vegetation traffic barriers in Kathmandu Valley, Nepal. Sustain. Environ. Res. 2021, 31, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, K.; Ziajahromi, S.; Nash, S.B.; Leusch, F.D. Evaluating the retention of airborne microplastics on plant leaf: Influence of leaf morphology. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 346, 123673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, M.; Lu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Hu, L.; Huang, X.; Liu, X. Distribution patterns of microplastics in various tissues of the Zhikong scallop (Chlamys farreri) and in the surrounding culture seawater. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 160, 111595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Li, H.; Guo, X.; Sun, Y.; Li, S. Capacity of six shrub species to retain atmospheric particulates with different diameters. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 2643–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaid, M.; Mehra, K.; Gupta, A. Microplastics as contaminants in Indian environment: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 68025–68052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vattanasit, U.; Kongpran, J.; Ikeda, A. Airborne microplastics: A narrative review of potential effects on the human respiratory system. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 904, 166745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, S.L.; Gouin, T.; Koelmans, A.A.; Scheuermann, L. Development of screening criteria for microplastic particles in air and atmospheric deposition: Critical review and applicability towards assessing human exposure. Microplastics Nanoplastics 2021, 1, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noda, S.; Fujita, M.; Asano, T. Spontaneous-emission control by photonic crystals and nanocavities. Nat. Photonics 2007, 1, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikida, K.; Coates, J. Infrared and Raman analysis of polymers. In Handbook of Plastics Analysis; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003; pp. 198–328. [Google Scholar]
- Chércoles Asensio, R.; San Andrés Moya, M.; De la Roja, J.M.; Gómez, M. Analytical characterization of polymers used in conservation and restoration by ATR-FTIR spectroscopy. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 395, 2081–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mecozzi, M.; Pietroletti, M.; Monakhova, Y.B. FTIR spectroscopy supported by statistical techniques for the structural characterization of plastic debris in the marine environment: Application to monitoring studies. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 106, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, M.R.; Horgen, F.D.; Orski, S.V.; Rodriguez, V.; Beers, K.L.; Balazs, G.H.; Jones, T.T.; Work, T.M.; Brignac, K.C.; Royer, S.-J.; et al. Validation of ATR FT-IR to identify polymers of plastic marine debris, including those ingested by marine organisms. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 127, 704–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verleye, G.A.; Roeges, N.P.; De Moor, M.O. Easy Identification of Plastics and Rubbers; iSmithers Rapra Publishing: Shrewsbury, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Beltran, M.; Marcilla, A. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy applied to the study of PVC decomposition. Eur. Polym. J. 1997, 33, 1135–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharazmi, A.; Faraji, N.; Hussin, R.M.; Saion, E.; Yunus, W.M.M.; Behzad, K. Structural, optical, opto-thermal and thermal properties of ZnS–PVA nanofluids synthesized through a radiolytic approach. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2015, 6, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).