Abstract
The westerly circulation and the monsoon circulation are the two major atmospheric circulation systems affecting the middle latitudes of the Northern Hemisphere (NH), which have significant impacts on climate and environmental changes in the middle latitudes. However, until now, people’s understanding of the long-term paleoenvironmental changes in the westerly- and monsoon-controlled areas in China’s middle latitudes is not uniform, and the phase relationship between the two at different time scales is also controversial, especially the exception to the “dry gets drier, wet gets wetter” paradigm in global warming between the two. Based on the existing literature data published, integrated paleoenvironmental records, and comprehensive simulation results in recent years, this study systematically reviews the climate and environmental changes in the two major circulation regions in the mid-latitudes of China since the Middle Pleistocene, with a focus on exploring the phase relationship between the two systems at different time scales and its influencing mechanism. Through the reanalysis and comparative analysis of the existing data, we conclude that the interaction and relationship between the two circulation systems are relatively strong and close during the warm periods, but relatively weak during the cold periods. From the perspective of orbital, suborbital, and millennium time scales, the phase relationship between the westerly and Asian summer monsoon (ASM) circulations shows roughly in-phase, out-of-phase, and anti-phase transitions, respectively. There are significant differences between the impacts of the westerly and ASM circulations on the middle-latitude regions of northwest China, the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau, and eastern China. However, under the combined influence of varied environmental factors such as BHLSR (boreal high-latitude solar radiation), SST (sea surface temperature), AMOC (north Atlantic meridional overturning circulation), NHI (Northern Hemisphere ice volume), NAO (North Atlantic Oscillation), ITCZ (intertropical convergence zone), WPSH (western Pacific subtropical high), TIOA (tropical Indian Ocean anomaly), ENSO (El Niño/Southern Oscillation), CGT/SRP (global teleconnection/Silk Road pattern), etc., there is a complex and close coupling relationship between the two, and it is necessary to comprehensively consider their “multi-factor’s joint-action” mechanism and impact, while, in general, the dynamic mechanisms driving the changes of the westerly and ASM circulations are not the same at different time scales, such as orbital, suborbital, centennial to millennium, and decadal to interannual, which also leads to the formation of different types of phase relationships between the two at different time scales. Future studies need to focus on the impact of this “multi-factor linkage mechanism” and “multi-phase relationship” in distinguishing the interaction between the westerly and ASM circulation systems in terms of orbital, suborbital, millennium, and sub-millennium time scales.
1. Introduction
The northern mainland of China is geographically located in the interaction zone of important branches of global atmospheric circulations, which is influenced by the convergence and interaction of atmospheric systems such as the westerly circulation from the Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea, the tropo-subtropical summer monsoon from the Pacific Ocean (East Asian monsoon), the tropical summer monsoon from the Indian Ocean (South Asian monsoon), and the winter monsoon from Siberia, and, moreover, under the influence of the special topography of the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau, a unique and complex climate and environmental pattern has been formed [1]. The mid-latitude westerlies in the Northern Hemisphere (NH) and the Asian monsoon are two important atmospheric circulation systems in Asia, wherein the westerlies play an important role in the interaction between low- and high-latitude climates, and exert an important influence on the global climate by regulating the transport and distribution of heat and moisture. As the most typical and wide-ranging monsoon circulation system in the global monsoon systems, the Asian monsoon can reach the temperate regions of the NH under the influence of seasonal migration of the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ). Therefore, there will be an interaction between the Asian monsoon circulation and the westerly circulation that both act on the mid-latitude regions of the NH, and the mid-latitudes of northern China are located in this interaction zone. Based on this, China’s mid-latitudes can be roughly divided into three different climate regions. The first is the eastern region controlled by monsoon circulation, which has a relatively humid environment and significant seasonal fluctuations in humidity [2]. The second is the northwest region controlled by the westerly circulation, which has a relatively arid climate [3]. The third is the interaction zone between the two major circulations (transition zone), which is affected by the changes and interactions of the two circulation systems, making the form of climate change in this area more complex.
In general, the study of climate and environmental changes in the mid-latitude regions of China is not only helpful in clarifying the specific role of different circulation systems, but is also of great significance for understanding the environmental effect of interactions between different circulation systems.
At present, a large number of studies have been conducted on climate and environmental changes within the dominant areas of the westerly and monsoon circulations in different periods, as well as their response relationships to each other (e.g., [4,5,6]). According to the records of paleoclimatic proxies, studies have found that, in the early Holocene, the Central Asian region controlled by the westerlies was abnormally dry and the East Asian monsoon region was relatively humid, and, in the middle Holocene, the climatic conditions in both regions were relatively humid, while, in the late Holocene, the westerly-dominated region was moderately humid and the East Asian monsoon region was relatively dry [4,7]. Due to the different driving factors that affect the changes of the westerly and monsoon regions, climate changes in these regions on the millennium scale exhibit out-of-phase characteristics [8,9]. Since the middle of the last century, analysis and research from a large amount of remote-sensing observations and meteorological data have shown that the climatic parameters such as rainfall and the humidity degree in northwestern China dominated by the Westerlies and in eastern China dominated by the monsoon circulation often exhibit opposite changes, making scholars believe that the climate and environment of the two regions exhibit inverse-phase (anti-phase) changes on the centennial to interannual time scale [9,10]. It can be seen from the above cognition that the intensities of the westerly circulation and the Asian monsoon circulation are different in different periods, and their impacts on the climatic environment of the regions under their control are also different. Meanwhile, due to the different driving mechanisms that cause the changes between the two, the phase relationship between them in different time scales is also very different.
However, up to now, there is no unified understanding of the long-term paleoclimate and paleo-environmental changes in the westerly- and East-Asian-monsoon-controlled regions in the middle latitudes of China, and there are also divergent opinions on the correlation between the two circulations at different time scales. Due to the continuous expansion of geochronological methods and climatic proxies in the past decade, more and more paleoenvironmental records have been accumulated and significant progress has been made in the academic circle. It is necessary to further focus on systematic comparison and reanalysis.
Based on the existing research in recent years, this paper systematically reviews the climate and environmental changes in the two major climate regions in the middle latitudes of China since the Middle Pleistocene. It also explores the degree of interactions, the changes in phase relationships, and the dynamic mechanisms of the two climate systems at different time scales. This study not only provides a valuable reference for the comprehensive understanding of the indicative significance of the circulations in the middle latitudes of the NH, but also provides theoretical and scientific support for predicting future climate change in the two major climate regions.
2. Background—Characteristics of the Westerly Circulation and Asian Summer Monsoon
2.1. Westerly Circulation
The Westerly circulation is an interplanetary wind system formed in the middle latitudes of the northern and southern hemispheres between the subtropical high and the sub-polar low. It is formed by the gradual deflection of airflow from the subtropical high to the sub-polar low under the influence of the geostrophic deflection force. As a perennial stable planetary wind system, the westerlies play a crucial role in driving ocean circulation and regulating the exchange of heat, momentum, and carbon between the ocean and the atmosphere, and influence the changes of climate and environment in most areas of the middle latitudes of the northern and southern hemispheres [11]. For the middle latitudes of China, the Westerly circulation not only brings more water vapor to northwestern China [12], but also acts as a bridge link between the North Atlantic region and the East Asian monsoon region, transmitting the signals of climate change in the North Atlantic to the East Asian monsoon region through Central Asia [13]. Therefore, the Westerlies have a significant impact on the climatic and environmental changes in northwestern region and the East Asian monsoon region of China.
The basic state of the Westerly circulation can be divided into two major types, namely, the latitudinal type and the meridional type. The latitudinal type is a relatively flat circulation with long and east–western waves expanded in the Westerly circulation, which transports water vapor from the North Atlantic Ocean to the northwestern region of China and plays an important role in the change of climate and environment in the region [12]. The meridional type is a north–south wavy airflow developed in the Westerly circulation, in which the blocking high pressure and teleconnection wave train also have important impacts on the climate and environmental changes in northwestern China and the East Asian monsoon region [12]. Studies on the average structure of the latitudinal circulations in the NH in winter show that the latitudinal circulation of the Westerly wind system has an important impact on the winter temperature and precipitation in the monsoon region of China [14]. When the westerly latitudinal circulation is strong, the intensity of the Siberian high is weakened and the southward activity of the cold airflow also weakens accordingly, which leads to an increase in temperature in most regions of China in winter [13]. At the same time, it will also lead to an increase in precipitation in the northern part of the monsoon region of China [13]. Therefore, the interaction between the Westerly latitudinal circulation and the East Asian monsoon is relatively complicated.
In order to quantify the strength of the westerly latitudinal circulation, we can use the “westerly index” to quantitatively describe its intensity. The westerly index, also known as the zonal index, WI or ZI, was first proposed by [15] in the late 1930s. The latitudinal mean sea level pressure difference between 35° N and 55° N in the NH is used to reflect the strength of the Westerly circulation in temperate regions of the NH. Subsequently, some scholars partially adjusted the calculation method of the WI according to different research objectives and objects, so as to better fit the actual Westerly circulation intensity in different regions [14,16]. According to the relationship between the estimated WI and precipitation intensity in different regions in recent decades, it has been found that the larger the WI, the greater the precipitation in the regions of northwestern China and North China [17], and the lower the precipitation in the Yangtze River Basin and its southern regions [18].
The wavy meridional westerly circulation plays an effect on climate and environmental change in China mainly through the blocking high pressure systems. For example, the different location and duration of blocking high pressure will have a great difference in their impact on climate change in China. When the blocking high is located in the Ural Mountains, the temperature in most parts of northern China decreases [19]. While it is located in the high latitudes of East Asia, the summer in North China is severely dry [20]. In addition, the wavy meridional westerly circulation also causes the existence of a quasi-steady Rossby teleconnection wave train from North Africa to the Eurasian continent in the NH in summer [21]. The change in the teleconnective wave train will have a certain impact on the precipitation in different regions of China, such as the Silk Road teleconnection pattern (SRP), which is one of the teleconnective wave trains and is more typical in Eurasia. When the SRP is in a negative phase, it can lead to an increase in precipitation in northwestern China and a decrease in precipitation in the East Asian monsoon region of China [22], and, conversely (a positive phase of the SRP), the opposite is true [22].
2.2. Asian Summer Monsoon
The monsoon is a manifestation of the seasonal migration of the intertropical convergence zone (ITCZ), also known as the equatorial convergence zone, equatorial low-pressure zone, or equatorial trough. Its variation is influenced by natural forcing (solar and volcanic activities), anthropogenic forcing (greenhouse gases and aerosols), internal variability (interannual and interdecadal variation of sea–air interaction), and other factors [23,24].
At present, there are six major monsoon regions worldwide, including the Asian monsoon, North American monsoon, South American monsoon, North African monsoon, South African monsoon, and Australia–Indonesia monsoon [25]. As early as 1686, Halley proposed that a monsoon is formed by the temperature gradient between the ocean and land generated by the solar radiation over the two regions, and it can be seen as a giant sea–land wind system [23]. This is the definition of monsoon in the traditional understanding [23]. In recent years, with the development of space information technology and the increase of remote-sensing and telemetry data, people have gradually realized that, although the scope of monsoons is regional, its causes have global characteristics, and they are all related to the seasonal north–south movement of ITCZ.
Among the six major monsoon systems in the world, the Asian summer monsoon (ASM) has the widest, most typical, and most complex coverage. It consists of two subsystems, the East Asian summer monsoon (EASM) and the South Asian summer monsoon (SASM) [26]. Due to the comprehensive impact of the low-latitude equatorial ocean (Pacific and India Oceans), the subtropical Pacific, and the temperate Pacific, the EASM can be further divided into the tropical monsoon derived from the South China Sea and the West Pacific Ocean, the subtropical monsoon, and the temperate monsoon derived from the East China Sea and the Japanese Sea. The SASM, also known as the Indian summer monsoon (ISM), is mainly a tropical monsoon system. It is influenced by the north–south movement of the equatorial convergence zone and the sea–land thermal differences between the Eurasian continent and the Indian Ocean, bringing a large amount of water vapor to China. The water vapor content of the SASM is much higher than that of the EASM. As important components of the ASM, both those of the EASM and SASM have a profound impact on the climatological, hydrological, and ecological environments of central and eastern China, and even western China.
As a seasonal atmospheric circulation, the Asian monsoon has different coverage and intensity in different periods and exerts different effects on different land coverage areas. During the period from winter to summer in the NH, the ASM gradually advances northward, and this process is generally divided into three stages. The first is the outbreak of the SASM on the east coast of the Bay of Bengal, the second is the outbreak of the EASM in the South China Sea, and the third is the outbreak of the Indian monsoon (ISM) [27]. The northernmost boundary they can reach is the northern edge of the ASM. According to the meteorological data and monitoring/remote-sensing data in recent decades, the northern boundary of the ASM roughly follows a southwest–northeast trend along the southeastern part of the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau, the eastern section of the Qilian Mountains, the southern foot of the Helan Mountains, the Daqingshan Mountains, and the western side of the Greater Khingan (Daxing-Anling) Mountains [28]. The advance and retreat of the ASM will control the north–south displacement of the rainbelt in China, directly affecting the establishment and disappearance of the rainy season in regions of Jiangnan and North China. The onset time of the rainy season in these regions, as well as the speed and intensity of its northward movement, have a direct impact on the spatiotemporal distribution of atmospheric precipitation and the occurrence of droughts and floods in Eastern Asia [29].
In addition to the above-mentioned air–sea interaction, the ASM is also affected by other circulation systems such as the Westerlies, the subtropical high, and the South Asian high (SAH, also called the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau high, QTPH), etc. The abnormal activity of the ASM is often accompanied by changes in other circulation systems, which, together, cause precipitation changes in East Asia and climate change at the NH scale.
The research on the intensity of the Asian monsoon, especially the ASM intensity, has a long history. For the changes of the ASM in the geological and historical periods, the academic community often reflects the intensity of the ASM in corresponding period according to some paleoclimatic proxy indices, such as deep-sea sediments [30], ice cores [31], cave stalagmites in southern China [32], loess–paleosoil sedimentary sequences [33], tree rings [34], lake sediments [35], spores and pollens [36], etc. By establishing the continuous or periodic variation curves of these climate proxies, the researchers have reconstructed hydrological and ecological paleoenvironment information such as regional precipitation, sources of atmospheric precipitation, vegetation growth types, and lake level heights in a specific period based on the transformation functions, so as to further trace the monsoonal climate information at that time. In recent decades, in order to reflect the physical characteristics and intensity of monsoon circulation as much as possible, on the basis of a comprehensive analysis of big data remote-sensing and long-term meteorological data, the “monsoon index” (MI) is commonly used to quantitatively describe the intensity and positional changes of the ASM circulation, and, then, it is combined with paleoclimatic proxies to reflect the strength of the ASM in different periods [37,38,39].
2.3. Extent of the Westerly and ASM
There are great spatial differences in climate in the extensive middle latitudes of China, but they can be generally divided into three climate subsystems: the eastern region affected by the ASM (monsoonal zone), the northwest region affected by the Westerly circulation (westerly zone), and the transitional region such as the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau affected by the above two circulations with a relatively high altitude (mixed zone).
In different periods of the past, the intensities of the ASM and westerly systems has varied, resulting in differences in the ranges of the westerly- and monsoon-controlled regions, as well as their transition region [7].
Among the three, the interannual variation in the intensity of the current ASM circulation is the largest [40]. In years of different intensities, the range reached by the northward expansion of the ASM occasionally undergoes adjustments [41]. If the transition region is not considered, the northern boundary line of the ASM can be regarded as the approximate boundary between the ASM and the Westerly (Figure 1) [7]. In weak monsoon years, the edge of the ASM can roughly reach North China to the north and the eastern part of the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau to the west, and, in strong monsoon years, the ASM can reach the border between China and Mongolia to the north and the eastern part of Xinjiang to the west [42]. The intensity variation of the ASM in different periods leads to the change of the areas of the Westerly and transitional regions. At the same time, the spatial distribution pattern of the local climate and ecological vegetation within each climate zone will also change [43].
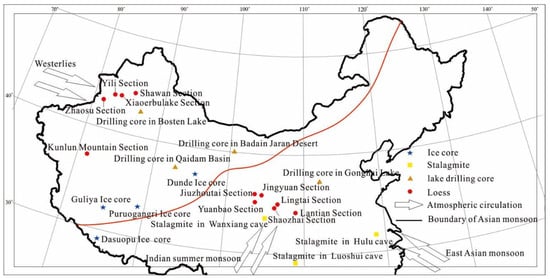
Figure 1.
Distribution and location of paleoenvironmental records cited in the paper (the red line represents the approximate boundary line between the Westerly and monsoon circulations).
3. The Relationship and Interaction between the Westerlies and ASM: A Review and Discussion on the Spatiotemporal Scales and Driving Mechanisms
In this paper, we will review and discuss the mid-latitude regions of China affected by the two major circulation systems in terms of the different temporal and spatial scales. Our study method mainly focuses on systematically organizing, reviewing, comparing, and discussing some existing and typical paleoenvironmental records shown and listed in Figure 1 and Table 1, and then puts forward some questions, opinions, and prospects. On a temporal scale, we discuss the changes in the intensities of westerly and monsoon circulations and their potential mechanisms over different historical periods. On a spatial scale, we divide the middle-latitude region of China into the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau region (mixed zone), the northwest region of China (westerly zone), and the eastern region of China (monsoon zone) to explore the intensities of the two major circulation systems and their interrelationships in different regions. Finally, we discuss the dynamic mechanisms and influencing factors of the interaction/interrelationship between monsoon and westerly circulations, and make some summaries and prospects.

Table 1.
Climate proxies, locations and distributions of sediment samples, and their literature sources cited in this paper for regions controlled by the two major atmospheric circulation.
3.1. Changes of the Westerlies and ASM at Different Time Scales and Their Relationships
3.1.1. Initial Period
The Westerly circulation is a kind of planetary wind system formed by the uneven heating and rotation deflection of the Earth. It has been formed for a long time and its origin is not a controversial issue. Based on the sedimentary records of deep-sea cores in the North Pacific Ocean, Rea et al. [30] speculated that the aeolian material transported by the Westerly circulation in northwest China had already reached a considerable scale at least before 20 Ma B.P. They found a significant increase in the ocean deposition rate around 8 Ma B.P. based on the characteristics of deep-sea sediments in the North Pacific at different periods, indicating a sudden increase in the dust transport strength of the Westerlies.
Regarding the origin of the EASM, Liu et al. [1] inferred the approximate paleoenvironmental conditions of different periods in China since the Cenozoic based on the distribution ranges and temporal changes of geological indicators such as Chinese flora and fauna, salt deposits (potassium, halite, and gypsum), and coal seams in China. They pointed out that, before the Oligocene, the climate in China was mainly controlled by the planetary wind system (i.e., the westerlies) and the climate pattern was basically zonal. They also suggested that the embryonic EAM may have appeared during the Oligocene period (38–24 Ma B.P.) based on the reduction of salt deposits such as gypsum and halite in the southeastern region of China during this period. Further research by Wu F et al. [58] found that, before and after 26 Ma B.P., sediments such as mudstone, shale, and other sediments indicating a humid environment in the Linxia Basin in western China gradually replaced gypsum, halite, and other evaporites indicating a dry environment. It suggests that the precipitation increased in southeastern China (no longer being a desert environment controlled by the subtropical high climate), and the EAM may have already appeared and reached the temperate zone regions at that time driven by the strongly periodic uplift of the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau, forming an environmental distribution pattern similar to that of today.
Regarding the origin of the SASM, it may appear later than the EASM. Shi and Tang [59] proposed that the SASM may have originated around 22 Ma B.P., based on the characteristics of humification shown by spore pollen records in the Linxia Basin.
According to the large-scale occurrence and distribution of red clay deposits on the Loess Plateau in the late Cenozoic, Cao et al. [60] proposed that the East Asian winter monsoon (EAWM) started from 6–8 Ma, and then existed and evolved to this day. However, according to the existence of continuous dust accumulation in northern China since the early Miocene, Guo [61] pointed out that different circulations carrying large amounts of wind dust and water vapor, respectively, formed an arid inland Asian environment and an Asian-monsoon-dominated environment, and their formation time was at least 22 Ma B.P. ago and has since developed to this day. Therefore, the Siberian high pressure system should have formed earlier than 22 Ma B.P. Subsequently, the EAM system characterized by the combination of winter and summer monsoons was initially established [62]. At the same time, the alternations of the dominant periods of winter and summer monsoons also suggest that the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau had reached a certain height when the EAM system was established, which lead to the aridification in northwest China and Central Asia, as well as the northward shift and strengthening of the Siberian high [63,64].
3.1.2. From the Middle Pleistocene to the Last Interglacial Period (1200–130 ka B.P.)
The 1.2 Ma B.P. period is considered to be the beginning of the global mid-Pleistocene climate transition (MPT) in the Quaternary. Since then, the fluctuation cycle of global climate and environmental changes has gradually changed from 41 ka to 100 ka. This period is mainly characterized by changes in global climate such as an increase in the amplitude of climate fluctuations [65], a significant increase in global ice volume, a decrease in ocean temperature, and an intensification of land drought [66]. The impact of the MPT on the atmospheric circulation and climate environment in the middle latitudes of China is of great significance and deserves to be emphatically studied.
Through the study of the stable isotopes of carbonates in the sediment cores from the hinterland of the Badanjilin Desert, one of the typical areas of interaction of the westerlies and ASM in the desert zone of northern China, Wang F et al. [44] found that, during the period of 1200–600 ka B.P, the δ18O and δ13C values showed a common trend of collaborative increase (Figure 2C). This is consistent with the research results of carbonate carbon isotopes in the Cretaceous red layers dominated by the planetary wind system before the Late Oligocene, reflecting intense evaporation under the control of a dry climate. Therefore, it is argued that, during the period of 1200–600 ka B.P., the area was controlled by the Westerly circulation [44]. In addition, the carbonate isotopes of δ18O and δ13C from sediment cores in the western Qaidam Basin in the northern Qinghai–Tibet Plateau, which is dominated by the Westerlies, also showed a synergistic increase trend during the period of 1200–600 ka B.P. (Figure 2B), indicating strong evaporation, intensified drought, and the relatively stronger influence of the Westerlies in this region during this period [45]. In addition, the sediment characteristics of loess–paleosol profiles in the Kunlun Mountains and Tianshan Mountains in northwestern China (Figure 2A) also reflect the relatively strong Westerly climate during this period [46,47].
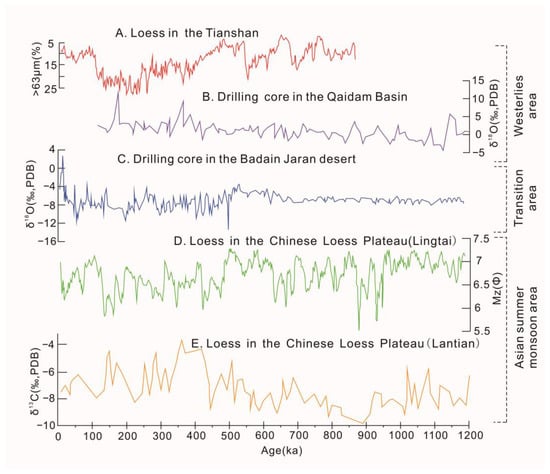
Figure 2.
Paleo-sedimentary records from the areas controlled by the Westerly and monsoon circulations since 1200 ka B.P. (A) The percentage of grain size > 63 μm in the loess sediment profile on the northern slope of the Tianshan Mountains [47]. (B) Variation of δ18O content in carbonates in the core of the Qaidam Basin [45]. (C) Variation of δ18O content in carbonates in the cores from the hinterland of the Badanjilin Desert [44]. (D) Particle size variation of loess sediments in the Lingtai Section of the Loess Plateau [44]. (E) Variation of δ18O content in carbonates of loess sediments in the Lantian Section of the Loess Plateau [33].
However, in the Loess Plateau of China, the ASM climate reflected by paleo-aeolian sedimentary sequences showed the opposite changing characteristics during this period. Variations of grain size and carbonate δ13C values of the Lingtai and Lantian sections of the Loess Plateau (Figure 2D,E) indicate that the sediment particle size is relatively fine and the carbon isotope enrichment degree is weak during this period. The results indicated that the C4 plant biomass in the Loess Plateau was lower, the precipitation in the warm season was less, and the ASM is relatively weak during this period [33,67].
All of the above evidence suggests that, during the period of 1200–600 ka B.P. since the Middle Pleistocene, the Westerly circulation in the middle latitudes of China was relatively strong, while the monsoon circulation was relatively weak. This may be due to the continuous cooling in the high latitudes of the NH during the global MPT and the significant increase in global ice volume, which led to the enhancement of the meridional temperature gradient, the stronger Westerly circulation, the decrease in ocean temperature, and the relative weakening of monsoons [45].
The extensive uplift of the Pamir Plateau and the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau (Kunhuang Movement) that occurred about 600 ka B.P. ago had a profound impact on the changes of the ASM and Westerlies [68], resulting in significant changes in the atmospheric circulations and climatic environment after 600 ka B.P.
In northwest China, where the Westerly climate is dominant, the grain sizes of loess sediments on the northern slopes of the Kunlun Mountains [46] and the Tianshan Mountains [47] were coarsened at around 500 ka B.P., reflecting a significant climatic aridity. This indicates that the substantial uplift of the terrains around the Tarim and Guerbantonggute Basins leads to a decrease of water vapor content brought by atmospheric circulations and a weakening of the Westerly circulation [46,47]. At the same time, the climate in the western Qaidam Basin, which is dominated by the Westerlies, also exhibits similar aridification, because the δ13C and δ18O values of the core carbonates from the basin have shown a phased increase since 600 ka B.P. [45], indicating a relative decrease in water vapor content and an intensification of drought compared to the 1200–600 ka B.P. period, that is, a relative weakening of the westerly circulation since 600 ka B.P.
In addition, in the Badanjilin Desert in northern China, which is jointly affected by the westerly circulation and the Asian summer monsoon circulation, the δ13C and δ18O values of the core carbonates in its hinterland area showed significant changes during the 600 ka B.P. period, manifested as the significant increase in the δ18O values at 600–450 ka B.P. [69]. This indicates a significant increase in the water vapor sources in the region and a significant strengthening of the ASM during this period, while the δ13C values of carbonates showed an intermittent increase after 600 ka B.P. [69], reflecting the continuous increase of precipitation in the warm season and the increase in the C4 plant biomass. This indicates the subsequent Westerly circulation was relatively weakened and the ASM relatively increased after 600 ka B.P. Therefore, the environment in the Badanjilin Desert during this period was dominated by the ASM climate.
In addition, the loess–paleosol sequences in the Loess Plateau of China dominated by the ASM showed a gradual increase of δ13C and an expansion of C4 plants since 600 ka B.P [33]. This further reflects the significant strengthening of the ASM after 600 ka B.P. and its strong trend continued until the 450 ka B.P. period [33]. This period is also corresponding to the paleosol layer S5 of the interglacial period in the loess paleosol sequences of the Loess Plateau [67], indicating that it has a certain relationship with the global temperature change.
From 450 ka B.P. to 130 ka B.P. in the Last Interglacial period, the climatic environment of the ASM region exhibited relatively large alternating fluctuations corresponding to the glacial–interglacial cycle, and the ASM was exceptionally strong during the interglacial period [51]. During this fluctuation process, the ASM extended northward and westward in the mid-latitude region during the interglacial period, resulting in a relatively strong interaction between the ASM and the Westerly circulation. During the glacial period, the intensity of the ASM is relatively weakened and its impact range is relatively small, so the interaction with the Westerly circulation is also relatively weak.
3.1.3. Last Interglacial Period (130–70 ka B.P.)
During the Last Interglacial period, the global climate and environmental conditions were similar to the current Holocene, which is reflected in many paleoclimate records.
In the aeolian sediment records of the Loess Plateau in China, climate reconstruction for the Holocene and the early Last Interglacial (Eemian interglacial) periods shows that there was a period of arid climate in the middle of both periods, with the duration of the Holocene drought being 6–5 ka B.P. [70]. The evidence shows that, during the Holocene, the S0 paleosol in the sedimentary profile of the Loess Plateau was interrupted by loess deposition [71], lakes in northern China shrank [72], the amount of terrigenous dust in the seafloor sediments of the North Pacific and the ice cores of Greenland increased [73], and drought events occurred during the Eemian interglacial period similar to the Holocene [74]. In addition, different climatic records also show that there were relatively humid periods during the Holocene and Eemian interglacial ages, which were in the 5–3 ka B.P. and 124.2–121.3 ka B.P. periods, respectively [74]. The similarity in the patterns of climate change between the Eemian interglacial and Holocene periods revealed by the above cases suggests that research on climate change during the Last Interglacial period may provide some support for predicting the future climate change on Earth [52].
During the Last Interglacial period, records of aeolian sedimentation showed that the atmospheric circulations in the EAM region and the northwest region (westerly region) of China at the middle latitudes were relatively strong (Figure 3), with a relatively high precipitation and strong pedogenesis of loess. However, during this period, the intensity of atmospheric circulation and precipitation in different regions may out of phase at the suborbital scale.
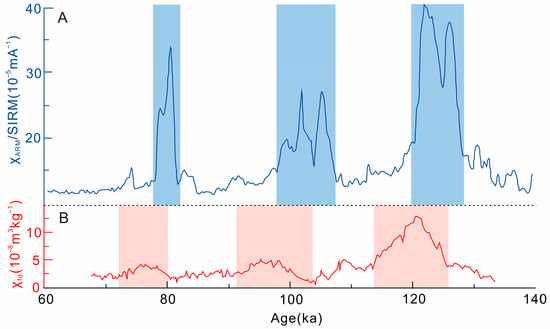
Figure 3.
Comparison of the magnetic susceptibility records between the Westerly- and ASM-dominated regions during the Last Interglacial period. (A) Changes in magnetic susceptibility recorded in the JZT (Jiuzhoutai) loess sediment profiles on the Loess Plateau of China during the Last Interglacial Period (χARM to SIRM ratio, [2]. (B) Changes in frequency magnetic susceptibility in the KS (Kesang) loess sediment profiles in the Yili Basin, northwest China, during the Last Interglacial period [2].
Many paleoclimate records show a lack of co-ordination between the dominant regions of the Westerlies and the ASMs in China in terms of environmental changes during the Last Interglacial period, such as the long-term “out-of-phase” relationship between the moisture evolution patterns of the two regions on the suborbital time scale [75]. For example, in the Loess Plateau dominated by the ASM, the sediment records of loess–paleosol sequences reflect that the moisture content in this area peaked at 78.8, 99.5, 101.5, 103.5, 121.6, and 126.3 ka B.P., indicating that the ASM was relatively strong during these periods and brought a large amount of precipitation to the region [2]. However, in the Yili River Valley of Xinjiang, where the Westerly climate is dominant, the peak values of local moisture reflected by paleoclimatic records such as loess deposits occurred during the periods of 76, 95, 97, 98, 107, and 120.8 ka B.P., respectively [2]. This shows a significant delay of 3–5 ka in the moisture peak values in the Loess Plateau region dominated by the ASM (Figure 3), indicating that the moisture evolution patterns of the two during the Last Interglacial period have an out-of-phase relationship on the suborbital time scale.
3.1.4. Last Glacial Period (70–12 ka B.P.)
In the 1980s, paleoenvironmental records from the Greenland ice cores showed that the predominant characteristic of environmental changes on Earth during the Last Glacial Period (LGP, 70–12 ka B.P.) was the repeated occurrence of abrupt climate changes on millennium time scales [76,77].
During the LGP, 25 D-O cycle events occurred in the North Atlantic region [76], and six significant Heinrich events were recorded by the North Atlantic marine sediments during the coldest interval of the D-O cycles (Figure 4a), which contained a large amount of coarse-grained sediments from the land [77].
In the early stage of the LGP (Deep Sea Oxygen Isotope Stage 4, MIS4, 73–61 ka B.P.), more fine-grained sediments (>40 μm) and quartz particles appeared in the loess–paleosol profiles in the Yili region in Central Asia (Figure 4b,c). The increase in these materials indicates an enhanced Westerly circulation, leading to coarser dust transport and strong dust storms [48]. While over the Loess Plateau in the ASM region during this period, more coarse particles in the loess profiles (Figure 4d) indicated stronger winter monsoon and weaker summer monsoon [53]. However, the low oxygen isotope values of stalagmites from this monsoon region (Figure 4e) revealed a strong summer monsoon precipitation [32,56]; that is, a strong summer monsoon occurred.
The changing trends of the Westerlies and monsoons seems to be different during different periods of the LGP. During the MIS4 period, the two regions exhibited a relatively strong Westerly circulation and weak summer monsoon circulation (Figure 4). Before MIS3b, the Westerly circulation showed a tendency of decreasing fluctuations, while the summer monsoon circulation showed a trend of increasing fluctuations (Figure 4). During the MIS3b-MIS3a period, the fluctuations of the Westerly circulation increased while the fluctuations of the summer monsoon circulation weakened (Figure 4).
From these trends, it can be seen that, during the LGP, there may be an inverse correlation between the Westerly and monsoon circulations on the suborbital time scale of the glacial period, but it is not obvious on the whole. Compared with the interglacial period, the ASM during the glacial period was significantly lower [78], and its influence in China was relatively smaller than that during the interglacial period. Thus, its interaction with the Westerly circulation may also be relatively weak. At present, it is still unclear whether there is a complete inverse correlation between the two systems during the glacial period, and more detailed data are needed in the future to explore the interaction between the Westerly and ASM circulations during the glacial period.
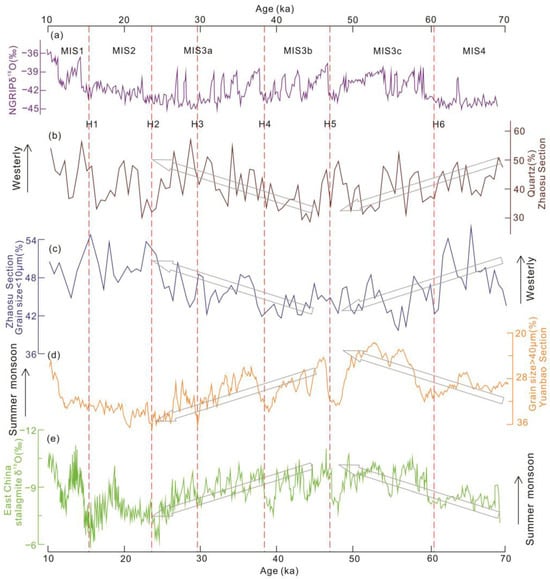
Figure 4.
Comparison of records between the Westerly and monsoon regions during the LGP. (a) NGRIP Ice Core δ18O records [79]. (b) Changes of quartz content in the Zhaosu section in Yili area dominated by the Westerly climate [48]. (c) The percentage variation of sediment grain size < 10 μm in the Zhaosu section [48]. (d) The percentage variation of sediment grain size > 40 μm in the Yuanbao section in the monsoon region of South China [53]. (e) δ18O variation of stalagmites in the monsoon region of East China [32]. The arrows indicate the pronounced increase (or decrease) with approximately monotonic trend of the proxies in the corresponding time period.
3.1.5. The Holocene (12 ka B.P.–1 ka B.P.)
Before the Holocene, the global climate mainly shown a pattern of warm and cold alternation with large fluctuations, while, during the Holocene, it was generally warm with small fluctuations.
For the Westerly-dominated arid region of mid-latitude in China, the climate in this area during the early Holocene (around 11–8 ka B.P.) was drier than it is today (Figure 5). During this period, most of the lakes in the region were in a dry state or had extremely low water levels [3,80], indicating A less precipitation, stronger evaporation, and A weaker Westerly intensity in the region [3,80].
During the middle Holocene (8–4 ka), climate conditions in the arid areas dominated by the Westerlies were relatively humid (Figure 5). The ancient records show that the regional precipitation is directly proportional to the intensity of the Westerlies, with an increase in precipitation, and many lakes in the region have the highest water levels in history [4]. This indicates that the strength of the Westerlies has reached its strongest state since the Holocene.
In the late Holocene since 4 ka B.P., the humidity of the climate in the Westerly region decreased (Figure 5). The lake water levels in the region were relatively lower, but still higher than in the early Holocene [75]. This indicates that the intensity of the Westerlies in this period had relatively weakened, but the degree of the weakening was small.
Compared with the Westerly region, the climatic conditions in the ASM region during the early Holocene were relatively humid (Figure 5). Paleoenvironmental records such as lake sediments in the monsoon region all reflect a higher amount of precipitation [40,81]. The humidification of the monsoon region was mainly related to the relatively strong ASM [82], so the intensity of the ASM in the early Holocene was relatively strong.
From the early Holocene to the middle Holocene, the precipitation in the monsoon region increased relatively, and the degree of humidity and monsoon intensity also gradually increased, reaching the maximum intensity of the Holocene in the middle Holocene [79,83]. This pattern of climate change, which gradually became humid from the early to middle Holocene and reached its strongest level, exhibits different and even opposite characteristics from the pattern of transition from drought to humidity in the Westerly regions during the same period (Figure 5).
From the middle to late Holocene, the climate in the monsoon region gradually became arid (Figure 5). Compared with the middle Holocene, the precipitation in the monsoon region during this period decreased significantly, and the monsoon intensity showed a continuous weakening trend on the whole [57].
As we have mentioned above, the Holocene and the Last Interglacial periods were relatively similar in terms of global climate. In fact, in addition to the overall similarity in climatic environment, the intensity variations of the Westerly and ASM circulations in the middle latitudes of Asia during the Holocene, as well as the moisture-changing patterns in their respective influencing areas, were also similar to those in the Last Interglacial period, also showing out-of-phase relationships on the suborbital time scale, as shown in Figure 5.
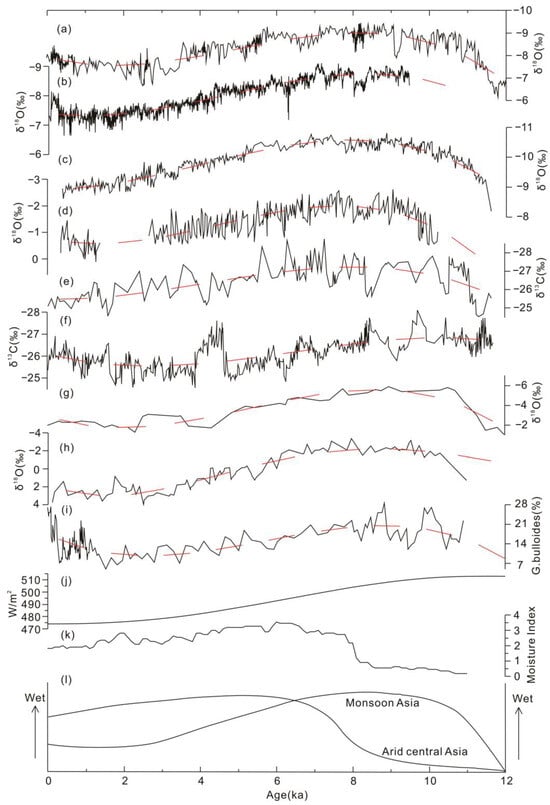
Figure 5.
Comparison of paleoenvironmental records between the ASM region and the arid Central Asian region (ACA, the Westerly region) since the Holocene (cited from [4]). (a) Dongge Cave D4, China (after [84]); (b) Dongge Cave DA, China (after [85]); (c) Shanbao Cave SB10-26, China (after [86]); (d) Qunf Cave, Oman (after [87]); (e) Hongyuan Peat, and (f) Hani Peat, China (after [87,88]); (g) Siling Lake, China (after [89]); (h) Qinghai Lake (after [90]); and (i) Arabian Sea (after [91]. All curves in panels (a–i) show the same direction of moisture change with increasing moisture upward. The long-term trend for each proxy curve is showed by smooth dashed line. Summer insolation at 30°N ((j) after [92]) and synthesized Holocene effective-moisture evolution line (k) after [4] are also shown. The out-of-phase relationship of Holocene moisture evolution between monsoon Asia and ACA is illustrated in (l).
3.1.6. Over the Past Thousand Years (1 ka B.P.–Present)
A comparative study of regional paleoenvironmental records from the Westerly region of Central Asia and the monsoon region of East Asia over the past thousand years (1 ka B.P.) has shown that the precipitation in the two regions presents a completely opposite trend during this period [4].
Lake core records from the Westerly-dominated Bosten Lake in Xinjiang show that, during the past 1–0.5 ka B.P. period, the carbonate content of core sediments was relatively high, the coarse particle content was low, and the average particle size was small [50]. This indicates that the humidity of the climate during this period was relatively low, the water vapor content of the atmospheric circulation was less, and the strength of the Westerly circulation was relatively weak. During the period of 0.5–0.1 ka B.P., the regional climate was within the range of the Little Ice Age (LIA), during which the carbonate content in the sediments reached the lowest value, with a higher content of coarse particles and a relatively coarse mean particle size [50]. This indicates that the Westerlies move southward in the NH, the Westerly circulation intensifies and brings more water vapor to the arid areas of Central Asia, resulting in a relatively humid climate. After 0.1 ka B.P., the mean particle size and coarse particle content of lake sediments decreased, while the carbonate content increased again, indicating that the strength of the Westerly circulation weakened again [50]. Therefore, these paleoenvironmental records suggest that the Westerly circulation has exhibited a “weak-strong-weak” changing pattern and trend over the past 1 ka.
In the monsoon-dominated East Asian area, oxygen isotope records of stalagmites from the Vientiane Cave reveal a significant fluctuation of the monsoon intensity during the period of 1–0.6 ka B.P., but the overall intensity maintained a strong trend [58]. This strong monsoon trend was maintained and continued in the region up to 0.6 ka B.P. [93,94], followed by significant fluctuations and an overall weakening [95], until it began to increase sharply around 0.1 ka B.P. [96], showing a strengthening trend of the monsoon. Therefore, these paleoenvironmental records indicate that the ASM circulation has exhibited a “strong-weak-strong” pattern and trend over the past 1 ka. It clearly shows a completely opposite trend to the intensity changes of the Westerly circulation mentioned above.
3.1.7. Differential Evolution and Interrelationships of the Westerlies and Monsoons since the Middle Pleistocene
By elaborating on the evolution of the two major circulation systems in different periods since the Middle Pleistocene, it can be seen that there are significant differences in the strength changes of the Westerly and ASM circulations that affect the middle latitudes of China in different periods. Moreover, the phase relationship between the two also varies at different time scales and environmental backgrounds.
When the global climate background is in a relatively cold period (such as the MPT, LGP, etc.), the ASM generally exhibits a relatively weak intensity. This results in a relatively small range of northward and westward extension of the ASM in China, and it brings relatively less precipitation to its affected area, resulting in a relatively weak connection and interaction between the monsoon and Westerly circulations.
At this time, the wetness of the climate in the joint influence zone (transition zone) of the two systems may be mainly affected by the ASM. It does not mean that the Westerlies are relatively strong at this time. This is because, in general, the influence of the ASM is stronger than that of the Westerlies in the transition zone, because the distance at that the summer monsoon carries moisture into the inland region of China is much smaller than the Westerly circulation sourced from the Atlantic and Mediterranean areas.
It should be noted that, during the LGP, the interaction and feedback between the Westerly and ASM circulations in the transition zone were not significant. This may be due to the relative narrowing and southward retreat of the ASM, resulting in reduced interaction with the mid-latitude Westerly winds. Therefore, the coupling relationship between the two circulation systems is relatively weak.
In periods of relatively warm global climate (such as the Last Interglacial and Holocene), the ASM is much stronger than during the glacial period, and the interaction and connection between the ASM and Westerly circulations are also stronger. This leads to a significant correlation/phase relationship between the two during the warm periods. It may produce an “out-of-phase” relationship due to changes in the driving factors of the two on the millennium time scale, or it may produce an “anti-phase” relationship due to changes in the driving factors on the centennial and interdecadal time scales.
Therefore, the reasons for the differential changes and interrelationships between the Westerly and ASM circulations since the Pleistocene need to be explored and explained from the dynamic driving mechanisms of the two on different time scales. This will be discussed later.
3.2. Regional Impacts of the Westerly and ASM
The middle latitudes of China have a vast area with significant diversity in geological, geographical, topographical, and ecological conditions. Therefore, the climatic environment in different subregions also exhibits significant spatial differences under the influence of the Westerly and ASM circulations.
In the past, scholars often divided China’s climate regionalization into several sub-regions according to the interaction of topographical and meteorological conditions in different regions, which is conducive to identifying and analyzing the influence of different atmospheric circulations on each sub-region [97,98]. Based on previous studies, this paper divides the mid-latitude region of northern China into three sub-regions. They are the arid region of northwest China located in Central Asia (Westerly region), the humid region of eastern and southern China in East Asia (monsoon region), and the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau region in southwest China (transition/composite/mixed region). Based on the collected paleoclimatic records/indicators (as shown in Table 1 and Figure 1) and modern meteorological data, this paper discusses the degree of influence of different atmospheric circulations in the three regions, with a view to more comprehensively understanding the climate and environmental changes that occur in different mid-latitude regions under the joint effects of the Westerly, ASM, and other atmospheric systems such as the South Asian high (SAH).
3.2.1. Qinghai–Tibet Plateau Region (QTP, Mixed Zone)
As the highest geographical unit on Earth, the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau (QTP) is highly sensitive to environmental changes in response to global climate change, including permafrost melting, runoff changes, ecological environment changes, and the intensification of natural disasters [99].
The atmospheric circulation system that dominates water vapor transport over the QTP mainly includes two parts, the SASM circulation and the Westerly circulation. According to the different sources of water vapor in the plateau, the academic circle often divides it into two regions, the southern and the northern regions, with a boundary of 32°N [100]. The southern region of the plateau is mainly controlled by the SASM, and the water vapor comes from the slender conveyor belt from the western equatorial Indian Ocean to the Arabian Sea and the Bay of Bengal, which provide about 51.4% of the water vapor for the precipitation on the plateau [101]. The northern region of the plateau is mainly controlled by the low-level Westerlies, and the water vapor comes from Eurasia and the North Atlantic Ocean on the northwest side of the plateau, which provide about 38.9% of the water vapor for the precipitation on the plateau [101].
The QTP has the largest mountain glacier in the world, and its ice core deposits are the best archives to record paleoclimate changes such as precipitation in the past period of the QTP. Research on the paleoenvironmental reconstruction from different ice cores in the northern part of the plateau, such as the Guliya ice core, Dunde ice core, and Puruogangri ice core, has found that the variation trend of precipitation in the northern QTP from west to east had been relatively consistent since the 15th century. That is, the entire northern part of the plateau has experienced a fluctuational increase in precipitation before 1740, a fluctuational decrease in precipitation during 1740–1850, and a fluctuational increase in precipitation after 1850 (Figure 6). The consistency of changes in precipitation in this large area indicates that the northern region of the QTP is controlled by an atmospheric circulation system as a whole [31]. Studies of δ18O in local precipitation have identified that the source of water vapor in the northern plateau is closely related to water vapor transported by the Westerlies [102].
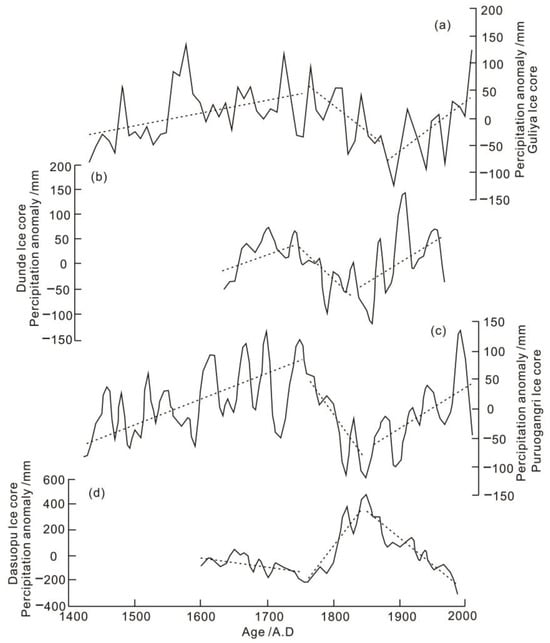
Figure 6.
Changes in precipitation over the QTP in recent period as reflected by ice core records (cited from [31]). (a) Guiya Ice core. (b) Dunde Ice core. (c) Puruogangri Ice core. (d) Dasuopu Ice core.
However, compared with the precipitation records in the northern part of the QTP, the precipitation records reflected by the Dasopu ice core in the southern part of the QTP show the opposite characteristics [102]. The precipitation in the southern plateau was fluctuationally decreased before 1740, fluctuationally increased during 1740–1850, and then fluctuationally decreased after 1850 [102]. The δ18O records of regional precipitation show that the source of water vapor in the southern plateau is closely related to water vapor transported by the Indian summer monsoon (ISM) [102].
The QTP is a typical region where the Westerly and monsoon circulations interact, and the coupling state of the two is mainly affected by the variation of monsoon intensity. When the intensity of monsoon is relatively strong, the position of the Westerlies is northward and the intensity of the Westerlies is relatively weak [103]. On the contrary, when the monsoon intensity is weak, the position of the Westerlies is southward and the intensity of the westerlies is relatively strong [103].
When the intensity of the monsoon or Westerlies changes, the precipitation in their respective control areas will also change, which will affect the area of glaciers and lakes of the QTP. Based on the changes in remote-sensing areas of 7090 glaciers and inland lake areas in seven representative regions of the QTP from 1990 to 2010, it is found that, under the control of the SASM, the glaciers in the southeastern part of the QTP have significantly retreated and both lake areas and water volumes have decreased over the past thirty years [99]. During the same period, the glacier area in the northwest of the plateau changed less under the control of the westerlies, while the lake area and water volume increased significantly [99]. This corresponds to the characteristics of the weakening of monsoons and the strengthening of Westerlies in this period mentioned above; that is, in the past 30 years, the strengthening of the Westerlies has led to an increase in precipitation and the lake area in the northern part of the plateau, while the weakening of the monsoon has led to the retreat of glaciers and the decrease of lake area in the southern part of the plateau. It can be seen that, in different regions of the QTP, the plateau environment changes differently under the control of different atmospheric circulation systems.
3.2.2. Northwest China (Westerly Zone)
Compared with the humid environment under the control of monsoon circulation, the climate in northwest China under the control of Westerly circulation is relatively arid due to its long distance from the source areas of water vapor such as the Atlantic Ocean. The main area of the vast mid-latitude desert zone in the NH is mainly distributed in these regions. Therefore, in terms of environmental change, the climate humidification in northwest China is the focus of attention.
Currently, multiple studies have shown that the climate in northwest China has an overall trend of warming and wetting since the mid-20th century. During this period, the lake area in northwest China generally expanded [104], and some dry lake beds that had desertified became lakes again [105]. The soil moisture in the region continued to increase [106], and the annual average precipitation and seasonal average precipitation in the region showed an increasing trend [107]. These environmental events all reflect the evidence of increasing precipitation in northwest China.
Although the Westerly circulation from the ocean (Atlantic) and land seas (Mediterranean, Black Sea, Caspian Sea, etc.) is the main source of water vapor in northwest China, the mechanism that cause increased precipitation in the region is relatively complex. It may not only be a partial response to global warming, but maybe also be related to the Siberian high and the Arctic Oscillation (AO), as well as the latitudinal oscillation of the Westerly jet and the northward movement of the subtropical high belt [107]. However, the essence of the above reasons is that they can promote the enhancement of the Westerly circulation and cause warming and humidification in the northwest China.
However, in addition to the strengthening of the Westerly circulation, the humidification of northwest China may also be affected by the weakening of the EASM.
Some studies have found that the increase of precipitation in the northwest China in recent years is partly related to the weakening of the EASM [104]. According to the reanalysis data of precipitation days, studies have revealed that, in addition to the North Atlantic water vapor transported by the Westerlies, the water vapor of northwest China may also be transported from the tropical Indian Ocean (SASM) and the South China Sea monsoon (EASM) under extreme climatic conditions [104,108].
When the EASM weakens, it is conducive to the westward movement of the western Pacific subtropical high (WPSH) and the increase of Mongolian anticyclone activity [109]. The westward extension of the WPSH promotes the westward transport of water vapor from the eastern Pacific and northern Indian Oceans in summer. The increase of Mongolian anticyclones leads to continuous easterly winds in northern China, which can travel along the northern QTP to the western Tarim Basin in Xinjiang [109]. The two jointly promote the water vapor transport of the monsoon system from the tropical Indian Ocean and the South China Sea along the eastern and northern QTP into the lower troposphere water vapor in northwest China, as well as from the tropical Indian Ocean into the middle and upper troposphere water vapor in northwest China [109].
In fact, on 30 July 2018, the Wensu rainstorm that caused serious loss of life and property in Aksu, Xinjiang, and the Hami rainstorm on the next day (31 July) were formed under this circulation system [104]. It can be seen that some extreme rainfall phenomena in northwest China are closely related to the extreme westward extension of the subtropical high pressure caused by the weakening of the EASM.
The eastern and western parts of northwest China have different responses to the Westerly and ASM circulations. Although both the strengthening of the Westerly circulation and the weakening of the ASM lead to humidification in northwest China, the latter’s impact only occurs under extreme precipitation conditions, rather than conventional effects. However, the extensive area of northwest China, especially its eastern part, is subject to both the conventional influences of the Westerly and ASM as it crosses the northern boundary line of the ASM [28]. Based on the average northern boundary line of the ASM, some studies divided the area of northwest China into two parts: the eastern and western parts (Figure 7a). The area east of the boundary line is controlled by the ASM and the area west of the boundary line is controlled by the Westerlies [10].
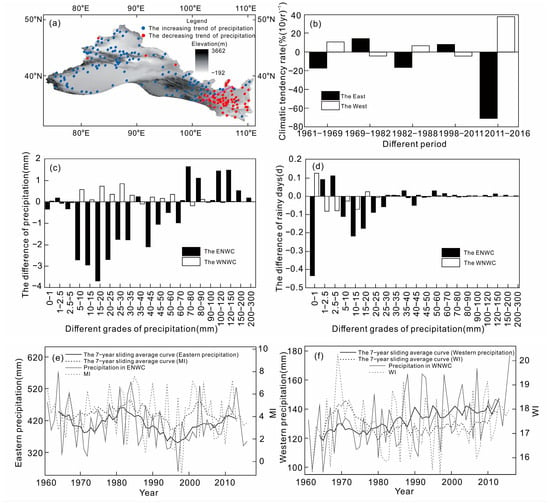
Figure 7.
Precipitation seesaw phenomenon in the eastern (ENWC) and western (WNWC) parts of Northwest China (NWC) (modified after [10]). (a) Regional division of ENWC and WNWC and the precipitation tendency distribution of stations in the same period. (b) The tendency distribution of variation of precipitation anomaly percentage in ENWC and WNWC during flood season from 1961 to 2016. The difference distribution of precipitation (c) and rainy days (d) in ENWC and WNWC under the WA-EH and WH-EA styles (the WA-EH style means precipitation increases in ENWC and decreases in WNWC, while the WH-EA style is the opposite). The comparison of EASM index and precipitation variation in ENWC (e) and the comparison of WI and precipitation variation in WNWC (f).
Through the analysis of the differences in precipitation variation between the eastern and western parts of northwest China and their interrelationships with the Westerly and ASM, Zhang Q et al. [10] found that the precipitation variations between the eastern and western parts of northwest China exhibit a significant “seesaw” phenomenon in the interannual, decadal, and overall times scales (Figure 7a–d). This phenomenon is related to the anti-phase variation between the ASM index and the Westerly circulation index; that is, the precipitation in the eastern part of northwest China is positively correlated with the summer monsoon index, and the precipitation in the western part is positively correlated with the Westerly index (Figure 7e,f). This indicates that the strengthening of the ASM will lead to an increase in precipitation in the eastern part of northwest China, while the strengthening of the Westerly circulation will lead to an increase in precipitation in the western part.
It can also be seen that there is an anti-phase variation relationship between the EASM index and the Westerly index (Figure 7e,f). It is not only related to the interaction between the EASM and Westerly circulation through the subtropical high, but also to the common but almost opposite effect of the South Asian high on the EASM and Westerly circulations under the influence of the QTP [10].
3.2.3. Eastern China (Monsoon Zone)
The impact of the ASM on the climate of East Asia is usually that, when the intensity of the ASM from the ocean changes, its water-vapor-carrying capacity also changes, resulting in an increase or decrease of the total precipitation in East Asia [110].
For the world’s largest monsoon system, namely, the ASM, its large-scale precipitation requires not only sufficient water vapor, but also needs to have another condition, that is, the dynamic conditions for water vapor to rise. In this regard, the WPSH (western Pacific subtropical high) and the SAH (South Asian high, also called the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau high, QTPH) play important roles in it [111]. This process is influenced by both local and middle- and high-latitude circulation factors, which result in a complexity in the relationship between the ASM and precipitation in East Asia.
Studies have shown that many factors can affect the intensity variation of the EASM and its corresponding precipitation configuration, such as the changes of sea surface temperature (SST) in different years [112], the WPSH [113], the SAH [114], the blocking high pressure situation in middle to high latitudes and related water vapor transport [115], etc. In other words, the anomalies of the EASM are usually accompanied by the anomalies of the WPSH and the SAH. The precipitation in the EASM region is influenced by the northward movement of the WPSH, the eastward shift of the SAH center, and the blocking situation in the Ural region. Moreover, these impacts are not static, but the combination of different factors brings different effects.
In order to better understand the response of precipitation in East Asia to the intensity of the ASM, studies have divided the relationship between monsoon intensity and precipitation into four types [110], namely, the strong monsoon and strong precipitation type, strong monsoon and weak precipitation type, weak monsoon and strong precipitation type, and weak monsoon and weak precipitation type. The strong monsoon and heavy precipitation type often corresponds to the background conditions of a high SST in the North Pacific Ocean, northward movement of the position of the WPSH, and westward movement of the center of the SAH. The strong monsoon and weak precipitation type corresponds to the background conditions of a significantly lower SST in the North Pacific, southward position of the WPSH, and eastward position of the center of the SAH. The weak monsoon and strong precipitation type corresponds to the background conditions of a high SST in the North Pacific, northward position of the WPSH, and westward position of the center of the SAH. The weak monsoon and weak precipitation type corresponds to the background conditions of a low SST in the North Pacific, southward position of the WPSH, and eastward position of the center of the SAH. Therefore, the precipitation in the ASM region will form different types of precipitation under the influence of the ASM and multiple atmospheric systems.
In terms of the interaction between the monsoon and westerly circulations, not only will the changes of the ASM affect the precipitation variation in the northwest of China dominated by the westerly system, but the changes of the Westerly intensity will also affect the precipitation in the ASM region. The impact of the Westerlies on the precipitation in the monsoon region is mainly achieved by affecting the position variation of the subtropical high pressure.
Normally, the strengthening of the Westerlies will “attract” the northward uplift and westward extension of the subtropical high. The area covered by the subtropical high is usually characterized by a prevailing downdraft, sunny weather, and prolonged drought, and its edge area is the convergent and rising area of warm and moist air in the lower layer, which is prone to the formation of thunderstorms and precipitation belts. Therefore, where the subtropical high is located, the central control area of the subtropical high is dry and hot, while the marginal area forms a large amount of monsoon precipitation. In this context, changes in the position of subtropical high pressure will lead to different water-and-heat-combination characteristics in the south and north of the ASM region.
When the intensity of the Westerlies is strong, the subtropical high extends northward and westward, and its northern edge can reach the area north of the Yellow River, resulting in an increase in summer precipitation in the northern monsoon region, while the southern monsoon region located in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River is covered by the subtropical high, resulting in less precipitation and occasional drought [18]. The overall situation of the ASM region is characterized by “flood in the north and drought in the south” [18]. On the contrary, when the intensity of the Westerlies is relatively weak, the subtropical high is located south of the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River, and the northern edge of the subtropical high is also located in the Yangtze River or Jiangnan area of the southern monsoon region; as a result, the precipitation is mostly concentrated in this region, while most areas of the northern monsoon region north of the Yellow and Huaihe Rivers have relatively less precipitation. The entire ASM region presents a situation of “southern flooding and northern drought” [18].
Through the analysis of atmospheric circulations in the three mid-latitude regions mentioned above, it can be seen that the Westerly system and the SAM system have different impacts on different regions and interact with each other. The southern and northern regions of the QTP are under the influence of the SASM and the Westerly circulations, respectively, and the circulation intensities in the two parts of the plateau exist with a relation of “as one falls, another rises”. Not only is the northwest region of China affected by the Westerly circulation, but, under extreme weather conditions, the ASM may also extend westward and bring it a large amount of precipitation. The monsoon region in eastern China is not only affected by the ASM, but also by the abnormal Westerly circulation, which can cause changes in the position and intensity of other atmospheric circulations in the ASM region (such as the WPSH, SAH, and the blocking high in the middle and high latitudes), thereby affecting the meteorological environment of the EASM region. Therefore, it can be said that the impact of the Westerly and ASM circulations on the middle latitudes of China is complex, diverse, and mutually coupled.
3.3. Dynamic Mechanism and Influencing Factors of Changes in Monsoon and Westerly Circulations
3.3.1. Orbital Time Scale
On the orbital time scale of the glacial/interglacial cycles, the climate and environmental change patterns in northwest China dominated by the westerlies is consistent with that of eastern China dominated by the monsoons [7], showing glacial-to-interglacial-to-glacial cyclical changes. A comparative study on the paleoenvironments between the Chashmanigar loess in Tajikistan bordering northwest China (Westerly region) and the Lingtai loess in the central Loess Plateau of China (monsoon region) has found that not only do they exhibit obvious alternation of loess layers and paleosol layers, but the loess and paleosol layers in both places also have a good consistency in age [67,116], which accords with the Earth’s orbital changes in the cycles of glacial and interglacial periods.
In terms of genesis, it is well known that the environmental conditions for the formation of loess and paleosols are different. The loess layer is mainly formed during the cold and dry glacial period, while the paleosol layer is often formed during the warm and humid interglacial period [117,118]. Although the sedimentary rhythms of the Lingtai loess profile in China and the Chashmanigar loess profile in Tajikistan are consistent and the climatic conditions for the formation of loess and paleosol are similar, the atmospheric circulations (wind systems) of the two are fundamentally different.
In the Tajikistan area dominated by the Westerlies, the climate of the loess layer formation was dry, windy, and cold with a high dust content in the atmosphere. The transport and deposition of loess dust were influenced by the Westerlies throughout the year and the Siberian north wind in winter. The climate of the paleosol layer formation in this region was relatively wet, warm, and windy. It was not only affected by the warm temperature during the interglacial period, but also had a richer water vapor content compared to the loess formation period, and the main source of water vapor was the Westerly circulation. It carries a large amount of water vapor from the North Atlantic region and promotes the formation of ancient soil layers in Tajikistan [67,116].
In the Loess Plateau of China under the control of the ASM, the loess layers were formed during the cold and dry glacial period and were mainly influenced by the Siberian northwest wind (winter monsoon). The climate for the formation of the paleosol layers was relatively warm and humid, which is not only related to the global warm climate in the interglacial period, but also related to the large amount of water vapor brought by the strong ASM from the ocean, and the combined effect of the two promoted the formation of the local paleosol [67,116,117,118].
Tajikistan and China, two regions controlled by different atmospheric circulation systems, have formed relatively consistent profiles of loess and paleosol cycles, indicating that, on the orbital time scale of glacial–interglacial cycles, the Westerly circulation that promotes the formation of paleosols in Central Asia and the ASM circulation that promotes the formation of paleosols in the Loess Plateau exhibit consistent intensity changes on this time scale, which proves that the two have an in-phase relationship.
In addition to the consistency on the glacial–interglacial scale, the changes of the Central Asian Westerlies and the ASM also have good consistency with the variations of the NH solar radiation in July on the orbital scale of the 20,000-year precession period [119].
Studies on the paleoenvironmental reconstruction from the areas in Israel and Uzbekistan in Central Asia controlled by the Westerlies have shown that the variation of local westerly circulation intensity is in-phase with the variation of solar radiation in July in the NH [29,53,120]. This indicates that the precession and solar radiation on the orbital time scale dominate the changes of the Westerly circulation intensity. The δ18O records of cave stalagmite carbonates from the Sanbao and Huludong Caves in southeastern China have shown that the summer precipitation in the EASM region is also in good consistency with the variation of solar radiation controlled by the precession period [32]. This indicates that the ASM circulation is also driven by the solar radiation and has an in-phase relationship with the variation of the NH summer solar radiation.
Therefore, the Westerly circulation and the ASM circulation both respond to the changes in solar radiation in the NH on the glacial–interglacial scale and the precession time scale of 20,000 years, and they have an in-phase relationship on the Earth’s orbital time scale.
3.3.2. Suborbital Time Scale
On the suborbital time scale, comprehensive comparisons of various paleoenvironmental records have shown that the changes of solar radiation and SST at high latitudes in the NH may be important factors influencing the paleoenvironmental changes in the arid Central Asia (ACA) since the Holocene (Figure 8). Moreover, these factors may also have significant impacts on the variation of the monsoon circulation intensity in the mid-latitudes [4]. Under the influence of multiple factors, the climate and environmental changes in the Westerly and monsoon regions may be asynchronous on the suborbital time scale (that is, exhibiting an out-of-phase relationship). This was observed during the relatively warm Last Interglacial and Holocene periods.
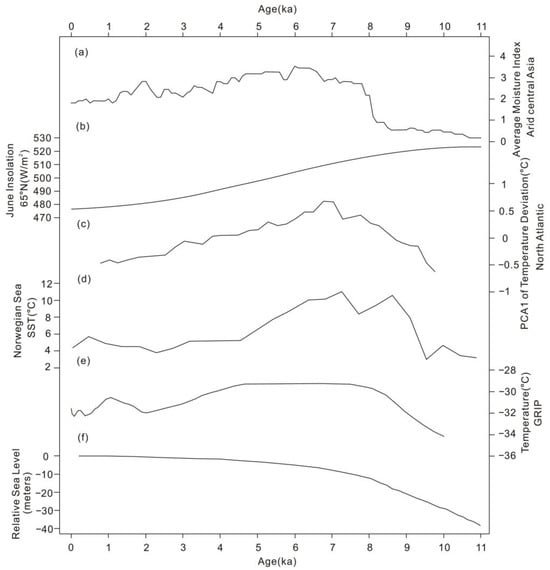
Figure 8.
A comprehensive comparison of the Westerlies with multiple global environmental records at the Holocene suborbital scale (cited from [4]). (a) Synthesized Holocene mean moisture index in arid Central Asia (ACA); (b) correlation with Northern Hemisphere summer insolation [92]; (c) sea surface temperature (SST) of the North Atlantic region [121]; (d) SST of the Norwegian Sea [122]; (e) air temperature from GRIP ice-core [123]; and (f) relative sea-level change from Barbados [124].
The loess profiles from the Yili Basin in the Westerly region and the Loess Plateau in the monsoon region both show that, during the Last Interglacial period, the variation of humidity in northwest China lagged behind that in the monsoon region by about 3–5 ka [2]. This reveals that the atmospheric circulation systems that caused the humidity changes in the two regions were not synchronized during this period. During the Holocene period, as discussed above, the climate and environmental changes in the arid Central Asia and the ASM regions were also asynchronous (Figure 5). Environmental changes in the arid region of northwest China are characterized by the early Holocene drought, the middle Holocene humidity, and the late Holocene moderate humidity, while the ASM region exhibits the early Holocene humidity, the middle Holocene relative humidity, and the late Holocene relative drought [4]. This indicates that the Westerly circulation and the ASM circulation exhibit an out-of-phase relationship on the suborbital time scale within the interglacial period.
The reasons for the asynchronous (out-of-phase) evolution of the Westerlies and monsoons at the suborbital scale can be explored by taking the changes of solar radiation and SST during the Holocene as examples.
In the early Holocene, the rise in global temperature and the increase in solar radiation (Figure 5) led to an increase of the sea–land temperature gradient and evaporation in East Asia, and the intensity of the ASM was enhanced and a large amount of water vapor was carried from the ocean to East Asia [84]. Therefore, the climatic environment of the ASM region was relatively humid in the early Holocene. However, for the northwest region of China at the middle latitudes, the strong solar radiation in summer in the early Holocene would lead to intense local evaporation. At the same time, due to the significant melting of the ice sheet in Greenland, the sea water temperature in the North Atlantic Ocean was lower and the sea surface evaporation was reduced, so the water vapor content brought by the Westerly circulation decreased, leading to a dry climate in northwest China (Figure 9). In winter, the increase of solar radiation also leads to an increase of SST in the north Atlantic Ocean, a decrease of meridional temperature gradient, a decrease of the Westerly intensity, a decrease of evaporation due to the lower winter temperature, and a decrease of water vapor content brought by the Westerlies, leading to further drought in northwest China [82].
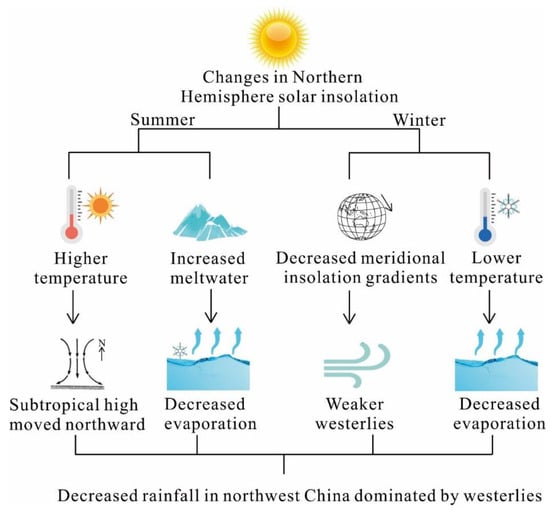
Figure 9.
Changes in solar radiation in the early Holocene in the NH led to climatic drought in the Westerly region [7].
After the middle Holocene, the solar radiation in the NH was slightly weaker than in the earlier period but still relatively strong (Figure 8). Due to the relative decrease in solar radiation, the ASM also showed a weakening trend in the middle Holocene [84], but the climate in the monsoon region was still relatively humid at this time, with only a decrease in the degree of humidity compared to the early Holocene (Figure 5). For the Westerly region during this period, because the ice sheet in the NH gradually decreases but the SST in the North Atlantic began to rise, the water vapor content of the Westerly circulation increased and the activity of low-level cyclones increased, resulting in a large increase in the wetness of northwest China. Therefore, under the influence of a high SST in the North Atlantic and high temperature in the middle latitudes, the enhanced water vapor transport of the Westerly circulation and increased cyclone activity in the region led to a higher degree of humidity in northwest China during this period [7].
In summary, the ASM was mainly controlled by the amount of summer solar radiation since the Holocene [97]; coupled with the changes of SST and regional surface processes, these factors collectively contributed to the key driven mechanism that caused the environmental changes in the Westerly and ASM regions to show they were out-of-phase at the suborbital scale during the Holocene [82].
3.3.3. Millennial to Centennial Time Scale
Multiple paleoenvironmental records and modeling studies have shown that the weakening of the North Atlantic overturning circulation (AMOC) and the expansion of ice volume in the NH since the penultimate and last glacial periods can lead to rapid climate change in the North Atlantic region on a millennium to centennial time scale (Figure 10). At the same time, it affects the intensity and location changes of the Westerly circulation, and then transmits to eastern Asia through the Westerly circulation, causing rapid climate and environmental changes in the SAM region [84,125,126,127,128].
Abrupt climate change events on the millennium time scale that occurred during the LGP (such as the Heinrich and DO events) were largely associated with the weakening of the AMOC [129,130]. The link between rapid cold events in the North Atlantic Ocean and weak ASM on a centennial to millennium time scale since the LGP has also been confirmed by various climatic records (Figure 10). For example, during the Younger Dryas (YD) event and 9.5–8.5 ka B.P., the EASM precipitation on the millennium time scale showed a significant weakening, which corresponded to the weakening of the AMOC [131,132].
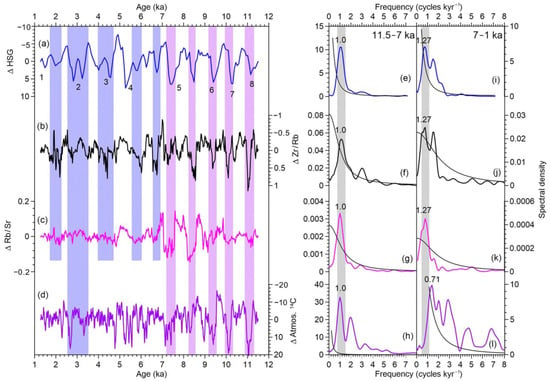
Figure 10.
A comparison between the records of the Asian summer monsoon and North Atlantic abrupt events (cited from [132]). (a–d) Centennial components of (b) Zr/Rb and (c) Rb/Sr with (a) the North Atlantic HSG [133] and (d) atmosphere 14C record [134]. The purple and blue bars indicate abrupt monsoon events. The numbers 1–8 in figure (a) indicate the selected event cycles which are used for the spectral analyses of periodicity in figure (e–l). Plots (e–l) show the spectra of the proxy records during the (e–h) Early and (i–l) Late Holocene [132]. Spectral peaks that are above the 80% confidence levels (black lines) are marked. The grey vertical bands indicate the most significant cycle [132].
Regarding the effect of AMOC weakening on climate change in the NH, modelling experiments have shown that, when the AMOC weakens, the ability of low-latitude high temperature and high-salinity seawater to transport northward to high-latitude areas is weakened, resulting in a substantial reduction of heat in the NH [135], and the climate in most parts of the NH, including Greenland, will respond to cooling over several decades or even shorter periods of time [136].
The decrease of SST in the North Atlantic Ocean increases the meridional temperature gradient in the NH, leading to an enhancement of the Westerly circulation [49]. At the same time, the cooling of the North Pacific Ocean causes the Atlantic and Pacific intertropical convergence zone (ITCZ) to move southward in summer, and the pressure difference between the two sides of the tropical Pacific Ocean is decreased. As a result, more water vapor flows eastward in the western Pacific and the monsoon blowing from the ocean to the land is correspondingly weakened, so the precipitation in the monsoon area also decreases synchronously [136].
In addition to the weakening of the AMOC, other factors, such as increased ice volume in the NH, also play a role. During the winter period of the LGP, the expansion of sea ice in the northern Atlantic Ocean led to an increase of the meridional temperature gradient in the NH, which also resulted in an enhancement of the mid-latitude Westerly circulation [49]. At this time, most of the loess deposits in northern China showed a strengthening of the winter monsoon and a relative weakening of the ASM in the dust source areas in the northwest Loess Plateau in China and northern Asia, leading to an increase of sandstorm events and the coarsening of loess sediment particles in northern China [119]. This indicates that both the Westerly circulation and the Asian winter monsoon (AWM) were strengthened to a certain extent when the rapid cooling events occurred on a millennium time scale in the NH.
Therefore, the weakening of AMOC and the expansion of ice volume in the NH during the glacial period have an important role in promoting the climate cooling events on a millennium time scale in the NH. At the same time, the intensities of the Westerly and ASM circulations, which affect the climatic environment in middle latitudes of China, showed a trend of strengthening and weakening, respectively [137], so that the two circulation systems showed an anti-phase (or out-of-phase) relationship on the centennial to millennium time scale.
3.3.4. Interannual to Interdecadal Time Scales
On the interdecadal to interannual time scales, climate teleconnections generated by the North Atlantic Oscillation (NAO), the Arctic Oscillation (AO), the El Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO), and some Rossby wave trains have important effects on the intensity variations of the Westerly and ASM circulations in the middle latitudes of the NH. The coupling effects of these multiple factors at the sea–land and regional scales also lead to the anti-phase (or out of phase) relationship between climate and environmental changes in the Westerly and monsoon regions in the middle latitudes on the interdecadal to interannual time scales [138,139,140].
The NAO (and/or AO) plays an important role in the change of the Westerlies’ position [2,141]. The positive phase of the NAO generally corresponds to the northward moving of the Westerlies in the middle latitudes, resulting in wetter conditions in northern Europe and drier conditions in southern Europe [138]. On the contrary, the negative phase of the NAO usually corresponds to the southward moving of the Westerlies, resulting in increased winter precipitation in southern Europe and possibly in Central Asia. That is, for northwest China, a weak NAO corresponds to more precipitation, and a strong NAO corresponds to less precipitation in northwest China [138,139,140].
Some studies have revealed through modelling experiments that the drought in Central Asia in the early Holocene is related to the strong positive phase of the NAO [80]. During this period, the northward movement of the Westerlies and the reduction of evaporation in inland lakes (such as the Caspian Sea) and the North Atlantic Ocean at the upstream of the Westerly circulation led to drought in northwest China [80]. However, the wetness in the inland region of northwest China during the middle Holocene was correlated with the negative phase of the NAO [142], because the negative phase of the NAO is conducive to increasing the meridional pressure gradient in the NH and causing the Westerlies to move extremely southward, leading to more water vapor being transported to the middle-latitude regions [142]. Therefore, the NAO can effectively change the position of the Westerlies and enhance or weaken the intensity of the Westerlies [141].
The strength of the NAO not only affects the climatic environment in the Westerly-dominated region, but also has an impact on the environment in the ASM region. The analysis of interannual- and interdecadal-scale meteorological data over the last 70 years shows a clear correlation between the NAO and the climate of East Asia [143]. When the NAO is in a positive phase, the EASM is relatively strong, with more summer precipitation in the northern part of East Asia and less precipitation in the southern and southwestern parts of East Asia. When the NAO is in a negative phase, the EASM is relatively weak, with less summer precipitation in the northern part and more in the southern part [143]. Therefore, the different phases of NAO lead to an out-of-phase relationship between the Westerly and ASM circulations on the interdecadal scale, which plays an important role in the climate and environmental changes in northwest and eastern regions of China.
ENSO also has a great influence on the climate change in the arid northwest and monsoonal eastern regions of China at the interdecadal or interannual scale. In the past century, there has been a trend of reduced precipitation, climate warming, and drying in the monsoon region of North China. One of the important reasons is from ENSO: it can affect the intensity of the SASM by influencing the Walker circulation, thereby affecting the precipitation intensity in the EASM region [144].
Compared with the environmental effect of ENSO from the Pacific Ocean on a regional scale, the migration of the Earth’s intertropical convergence zone (ITCZ), which is caused by the seasonal transition between the northern and southern hemispheres driven by solar radiation changes, has a more profound impact on the ASM. The increase of summer solar radiation in the NH will make ITCZ move northward and strengthen the ASM, which, together with the tropical Pacific SST under the influence of ENSO, will cause the change of precipitation in the EASM region. Therefore, the locations of ITCZ, SST, and ENSO in the tropical Pacific were strongly correlated with each other during the Holocene, which, together, affected the climatic environment of the wide middle-latitude region in China during the Holocene [139,145].
The correlation analysis between the ENSO index and precipitation in the EASM region shows that there is a significant negative correlation between the two [139]. When El Niño occurs, the western Pacific Ocean exhibits cyclonic circulation, which reduces water vapor transport over East Asia and weakens the intensity of the summer monsoon that year. In the following year, anticyclonic circulation often appears over the western Pacific Ocean, which will strengthen water vapor transport over East Asia and make the intensity of the summer monsoon relatively strong [139]. Therefore, ENSO has an important effect on the precipitation in the EASM region at the interannual scale.
Moreover, studies have shown that ENSO affects the deep circulation rate and surface heat distribution in the Atlantic Ocean by controlling water vapor transport between the tropical Atlantic and Pacific Oceans, thereby affecting the NAO and, consequently, affecting Westerly circulation [145,146]. For example, the appearance of La Niña will lead to SST anomalies in the Pacific Ocean, which will force the changes in the intensity and location of water vapor propagation and transport in the ocean and lead to the phase anomalies of the NAO under the influence of atmospheric Rossby wave train propagation [147].
The existence of atmospheric Rossby wave trains usually leads to an anti-phase relationship between climate changes in the EASM region and the Central Asian Westerly region on interannual and interdecadal time scales [22]. This is often associated with the type of climatic teleconnections. Teleconnection in climatology is a nonlinear process of the Earth’s climate system, which can link climate anomalies over long distances (thousands of kilometers away) to each other under the influence of atmospheric Rossby wave train propagation [148].
For example, on the interdecadal time scale, when the North Atlantic SST warms up, the warm ocean surface influences the atmosphere through air–sea interactions, triggering wave trains over the North Atlantic Ocean that propagate eastward from the western North Atlantic to the east and split into two shifting paths over the eastern North Atlantic, one of which propagates horizontally from the North Atlantic to East Asia. Its waveform is similar to the negative phase of the Silk Road teleconnection pattern (SRP) [149].
SRP, as a regional manifestation of the circumglobal teleconnection (CGT), plays an important role in the climatic environment and precipitation changes in the middle latitudes of Asia. CGT/SRP is caused by the abnormal non-adiabatic heating of the Indian Summer monsoon (ISM) precipitation. When CGT/SRP shows a negative phase, it causes abnormal water vapor transport from the Indian Ocean to northwest China, thereby increasing the summer precipitation in the northwest region [109]. Meanwhile, the negative phase CGT/SRP will also weaken water vapor transport from the western Pacific Ocean, leading to a decrease in precipitation in the EASM region [109]. Therefore, CGT/SRP may play an important role in the anti-phase relationship of summer precipitations between the Westerly region of northwest China and the monsoon region of east China.
In the context of continuous global warming, the atmospheric environment tends to stabilize, while the CGT/SRP pattern tends to weaken [150]. It may be a partial reason for the increase of precipitation in northwest China and the decrease of precipitation in the monsoon region of eastern China over the past half century.
It is worth noting that the formation of CGT/SRP is influenced by the temperature anomaly of the Indian Ocean, and studies have also shown that the temperature anomaly of the Indian Ocean also affects the intensity of the SASM, the location of the SAH [151], and the emergence of ENSO [152]. Therefore, CGT/SRP can be regarded as a link connecting the Westerly circulation, SASM, SAH, and ENSO, and influence the climatic environment changes in the Westerly and monsoon regions in the middle latitudes of China on an interdecadal or interannual time scale.
Overall, the driving factors that cause climate changes of the middle latitudes of China at different time scales are not the same. In different time scales, the phase relationship between the Westerly circulation and the ASM circulation is different from each other. On the orbital time scale of glacial to interglacial cycles, the relationship between them is in phase. On the suborbital time scale, due to the influence of solar radiation and SST, there is an out-of-phase relationship between them. On the millennium to decadal time scale, the two exhibit an anti-phase relationship under the influence of a variety of climate factors. In view of this, we should understand the climate change of different regions in the middle latitudes of China on a clear time scale.
4. Summary and Outlook
The interaction between the Westerly circulation and the ASM circulation in the middle latitudes of China is very complicated. In different time scales, since the formation of the Asian monsoon, it has interacted with the Westerly circulation at different intensities. In the warm period when the global temperature is higher, the Asian monsoon is relatively strong, with a relatively large range extending northward and westward, and the intensity of interaction with the Westerly circulation is also relatively obvious. In the cold period when the global temperature is relatively low, the Asian monsoon is relatively weak, and the interaction intensity and correlation between it and the Westerly circulation are weak. On the spatial scale, different subregions in the middle latitudes of China are affected to different degrees by the Westerly circulation and the ASM circulation due to the differences in their geographical locations and topographies, resulting in significant differences in their climatic environment. At the same time, the interaction between the Westerly circulation and the ASM circulation is also affected many other atmospheric systems, such as the WPSH and the Siberian high. Under the joint influence of multiple atmospheric systems, the interaction and relationship between the two become more complicated.
The Westerly circulation and the ASM circulation are subject to different driving factors on different time scales, and the phase relationship between them also presents different changes. On the orbital time scale, the relationship between the two is in phase under the influence of the glacial–interglacial cycle. On the suborbital time scale, the relationship is out of phase under the influence of solar radiation and SST. On the millennium to decadal time scale, there is an anti-phase relationship between the two under the influences of a variety of atmospheric and environmental factors such as the AMOC, ice volume in the NH, NAO, ENSO, and SRP, etc.
It is worth noting that some of the issues discussed in this study have a certain degree of uncertainty due to the complexity of paleoclimate indicators and the contradictions and conflicts between them to a certain extent. For example, during the LGP, what was the relationship between the Westerly circulation and the ASM on different time scales? In the future, it should be further explored with the support of more paleoclimate indicators. At the same time, why is the phase relationship between the two in the LGP not similar to that in the Last Interglacial and Holocene periods? That is, why is the relationship between the Westerly circulation and the ASM at the suborbital time scale out of phase? In addition, many studies have found that the climate change during the current Holocene period is somewhat similar to that of the Last Interglacial period. However, under the current global warming and intense human activities, will the climatic environment in the future have certain differences or will it still be similar to that of the previous Last Interglacial period? The answer to these questions may require more adequate climate indicators or precise climate simulation models in the future. It is hoped that this study can provide a certain theoretical basis for solving these problems in the future, and provide some scientific basis for responding to extreme climatic environments in the future.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.-Q.Z. and X.-J.L.; methodology, B.-Q.Z. and X.-J.L.; software, X.-J.L.; validation, B.-Q.Z. and X.-J.L.; formal analysis, B.-Q.Z. and X.-J.L.; investigation, B.-Q.Z. and X.-J.L.; resources, B.-Q.Z. and X.-J.L.; data curation, X.-J.L.; writing—original draft preparation, B.-Q.Z. and X.-J.L.; writing—review and editing, B.-Q.Z.; visualization, B.-Q.Z. and X.-J.L.; supervision, B.-Q.Z.; project administration, B.-Q.Z.; funding acquisition, B.-Q.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Third Xinjiang Scientific Expedition Program (2021XJKK0803), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41930640), and the Project of the Second Comprehensive Scientific Investigation on the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau (2019QZKK1003).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article and the related references cited.
Acknowledgments
We thank Xiaoping Yang, Xunming Wang, and other scholars for their help with the authors’ research work.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Liu, D.; Zheng, M.; Guo, Z. Initiation and evolution of the Asian monsoon system timely coupled with the ice-sheet growth and the tectonic movements in Asia. Quat. Sci. 1998, 18, 194–204. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, J.; Gao, F.; Xia, D.; Huang, W.; Chen, F. Moisture variations in arid Central Asia and its out-of-phase relationship with the Asian Monsoon during MIS 5: Evidence from loess records. J. Quat. Sci. 2018, 33, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Chen, J.; Huang, W. A discussion on the westerly-dominated climate model in mid-latitude Asia during the modern interglacial period. Earth Sci. Front. 2009, 16, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Yu, Z.; Yang, M.; Ito, E.; Wang, S.; Madsen, D.B.; Huang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Sato, T.; Birks, H.J.B.; et al. Holocene moisture evolution in arid Central Asia and its out-of-phase relationship with Asian monsoon history. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2008, 27, 351–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; An, C.; Wang, H. Holocene climatic and environmental changes in the arid and semi-arid areas of China: A review. Holocene 2006, 16, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Xiao, J.; Li, Y.; Tian, F.; Nakagawa, T. Pollen-based quantitative reconstruction of Holocene climate changes in the Daihai Lake area, Inner Mongolia, China. J. Clim. 2010, 23, 2856–2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Chen, J.; Huang, W.; Chen, S.; Huang, X.; Jin, L.; Jia, J.; Zhang, X.; An, C.; Zhang, J.; et al. Westerlies Asia and monsoonal Asia: Spatiotemporal differences in climate change and possible mechanisms on decadal to sub-orbital timescales. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2019, 192, 337–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, N.; Chen, H.; Li, Z.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, C. Tracking millennial-scale climate change by analysis of the modern summer precipitation in the marginal regions of the Asian monsoon. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2012, 58, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Chen, J.; Zhang, X.; Feng, S.; Chen, F. Definition of the core zone of the “westerlies-dominated climatic regime”, and its controlling factors during the instrumental period. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2015, 58, 676–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Lin, J.; Liu, W.; Han, L. Precipitation seesaw phenomenon and its formation mechanism in the eastern and western parts of Northwest China during the flood season. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2019, 62, 2083–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abell, J.T.; Winckler, G.; Anderson, R.F.; Herbert, T.D. Poleward and weakened wester lies during Pliocene warmth. Nature 2021, 589, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, C.; Jia, R.; Huang, J. An overview of the influence of atmospheric circulation on the climate in arid and semi-arid region of Central and East Asia. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2018, 61, 1183–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, W.; Zhang, X.; Wang, D.; Shen, Z.; Mei, F.; Cheng, Y.; Yan, L. The important significance of westerly wind study. Mar. Geol. Quat. Geol. 2004, 24, 125–132. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, D.; Wang, S. Structure of zonal-mean circulation over the northern hemisphere and its impact on climate of China in winter. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2001, 21, 108–112. [Google Scholar]
- Rossby, C.G. Relation between variations in the intensity of the zonal circulation of the atmosphere and the displacements of the semi-permanent centers of action. J. Mar. Res. 1939, 2, 38–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wang, K.; Fu, S.; Jiang, H. The Interrelationship between regional westerly index and the water vapor budget in Northwest China. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2008, 30, 28–34. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, W.; Wu, X.; Chen, J.; Chen, F. Tropospheric Biennial Oscillations and abrupt changes of precipitation in the arid Central Asia. Clim. Chang. Res. 2012, 8, 448–455. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, H.; Hu, J.; Fan, K.; Zhang, Y. The analysis of relationship between the variation of westerly index in summer and precipitation during the flood period over China in the last 50 years. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2007, 31, 717–726. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, M.; Huang, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, X.; Zheng, Z.; Ge, J. Winter blocking episodes and impact on climate over East Asia. Plateau Meteorol. 2008, 27, 415–421. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, A.; Gao, B. A diagnostic analyses of serious flood-drought during summer season in the North China plane. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2000, 24, 393–402. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, R.; Oh, J.; Kim, B. A teleconnection pattern in upper-level meridional wind over the North African and Eurasian continent in summer. Tellus Ser. A-Dyn. Meteorol. Oceanogr. 2002, 54, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Huang, R. Excitation mechanisms of the teleconnection patterns affecting the July precipitation in Northwest China. J. Clim. 2012, 25, 7834–7851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P. Global monsoon in a geological perspective. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2009, 54, 535–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Q.; Zhang, R.; Wang, P.; Wang, B. Monsoons across multi-scales: Summary of fourth conference on Earth system science. Adv. Earth Sci. 2016, 31, 689–699. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Ding, Q. Global monsoon: Dominant mode of annual variation in the tropics. Dyn. Atmos. Ocean. 2008, 44, 165–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, S. A review of recent research on the East Asian summer monsoon in China. In Monsoon Meteorology; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1987; pp. 60–92. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, G.; Zhang, Y. Tibetan Plateau forcing and the timing of the monsoon onset over South Asia and the South China Sea. Mon. Weather Rev. 1998, 126, 913–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Huang, W.; Jin, L.; Chen, J.; Chen, S. A climatological northern boundry index for the East Asian summer and its interannual variability. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2018, 61, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; He, J.; Guan, Z.; Chen, X. Review of the Chinese research on the East Asian tropical and subtropical monsoons. J. Trop. Meteorol. 2008, 24, 724–731. [Google Scholar]
- Rea, D.K.; Snoeckx, H.; Joseph, L.H. Late Cenozoic Eolian deposition in the North Pacific: Asian drying, Tibetan uplift, and cooling of the northern hemisphere. Paleoceanography 1998, 13, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, K.; Yao, T.; Wang, N.; Tian, L.; Xu, B. The difference in precipitation variability between the north and south Tibetan Plateaus. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2008, 30, 726–732. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, H.; Edwards, R.L.; Sinha, A.; Sptl, C.; Yi, L.; Chen, S.; Kelly, M.; Kathayat, G.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; et al. The Asian monsoon over the past 640,000 years and ice age terminations. Nature 2016, 534, 640–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Z.; Huang, Y.; Liu, W.; Guo, Z.; Clemens, S.; Li, L.; Prell, W.; Ning, Y.; Cai, Y.; Zhou, W.; et al. Multiple expansions of C4 plant biomass in East Asia since 7 Ma coupled with strengthened monsoon circulation. Geology 2005, 33, 705–708. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Park, W.K.; Cai, Q.; Seo, J.W.; Jung, H.S. Changes in East Asian summer monsoon precipitation since 1840: Taking tree ring records from China and South Korea as an example. Sci. China (Ser. D) 2003, 33, 543–549. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Wang, K.; Jiang, H.; Li, Z.; Sun, J.; Luo, X.; Zhu, Q. A numerical simulation of the effects of westerly and monsoon on precipitation in the Heihe River basin. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2010, 32, 489–496. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Yu, Z.; Ni, Z. Holocene climate evolution in the monsoonal margin region revealed by the pollen record from Jilantai Playa. Lake Sci. 2018, 30, 1161–1176. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Yan, Z. The East Asian summer monsoon circulation anomaly index and its interannual variations. Chin. Sci. Bull. 1999, 44, 421–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Chen, L.; He, J. Interannual variation of index of East Asian land-sea thermal difference and its relation to monsoon circulation and rainfall over China. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 2001, 15, 71–85. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Cheng, H.; Edwards, R.L.; Kong, X.; Shao, X.; Chen, S.; Wu, J.; Jiang, X.; Wang, X.; An, Z. Millennial- and orbital-scale changes in the East Asian monsoon over the past 224,000 years. Nature 2008, 451, 1090–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Xu, Q.; Chen, J.; Birks, H.J.B.; Liu, J.; Zhang, S.; Jin, L.; An, C.; Telford, R.J.; Cao, X.; et al. East Asian summer monsoon precipitation variability since the last deglaciation. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.; Chen, B.; Liang, P.; Qian, W. Definition and features of the north edge of Asian summer monsoon. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 2009, 67, 83–89. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, W.; Ding, T.; Hu, H.; Lin, X.; Qin, A. An overview of dry-wet climate variability among monsoon-westerly regions and the monsoon northernmost marginal active zone in China. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2009, 26, 630–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhu, B.; Yang, J.; Ma, P.; Liu, X.; Lu, G.; Wang, Y.; Yu, H.; Liu, W.; Wang, D. New characteristics about the climate humidification trend in Northwest China. Sci. Bull. 2021, 66, 3757–3771. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Li, Z.; Sun, X.; Li, B.; Wang, X.; Chen, F. A 1200 ka stable isotope record from the center of the Badain Jaran Desert, northwestern China: Implications for the variation and interplay of the westerlies and the Asian summer monsoon. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2021, 22, e2020GC009575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Fang, X.; Ye, C.; Teng, X.; Zhang, T. Tibet forcing Quaternary stepwise enhancement of westerly jet and Central Asian aridification: Carbonate isotope records from deep drilling in the Qaidam salt playa, NE Tibet. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2014, 116, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Lv, L.; Yang, S.; Li, J.; An, Z.; Jiang, P.; Chen, X. Loess in Kunlun Mountains and its implications on desert development and Tibetan Plateau uplift in West China. Sci. China Ser. D-Earth Sci. 2002, 45, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Shi, Z.; Yang, S.; Yan, M.; Li, J.; Jiang, P. Loess in the Tian Shan and its implications for the development of the Gurbantunggut Desert and drying of northern Xinjiang. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2002, 47, 1381–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zeng, M.; Chen, X.; Li, Y.; Chang, H.; An, Z.; Guo, X. Abrupt climatic events recorded by the Ili loess during the last glaciation in Central Asia: Evidence from grain-size and minerals. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2018, 155, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Song, Y.; Lai, Z.; Han, L.; An, Z. Rapid and cyclic dust accumulation during MIS 2 in Central Asia inferred from loess OSL dating and grain-size analysis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Huang, X.; Zhang, J.; Holmes, J.A.; Chen, J. Humid Little Ice Age in and Central Asia documented by Bosten Lake, Xinjiang, China. Sci. China Ser. D-Earth Sci. 2006, 49, 1280–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Zhang, C.; Fu, Y.; Wu, H.; Hao, Q.; Qiao, Y.; Guo, Z. Clay mineralogical and geochemical record from a loess-paleosol sequence in Chinese Loess Plateau during the past 880 ka and the implication on the East Asian Summer Monsoon. Quat. Sci. 2022, 42, 921–938. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, J.; Xia, D.; Wang, Y.; Wang, B.; Lu, H.; Zhao, S. East Asian monsoon evolution during the Eemian, as recorded in the western Chinese Loess Plateau. Quat. Int. 2016, 399, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, Z.; Chen, F.; Cheng, H.; Liu, W.; Wang, G.; Lai, Z.; Bloemendal, J. High-resolution summer precipitation variations in the western Chinese Loess Plateau during the last glacial. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Bloemendal, J.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Oldfield, F. High-resolution multi-proxy climate records from Chinese loess, evidence for rapid climatic changes over the last 75 kyr. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 1997, 130, 323–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Chen, S.; Wang, Z.; Yang, S.; Wang, Y.; Shao, Q. The response of Asian monsoon events to the north south high latitude climate in the Last Glacial period. Quat. Sci. 2020, 40, 864–876. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Cheng, H.; Edwards, R.L.; An, Z.; Wu, J.; Shen, C.; Dorale, J.A. A high-resolution absolute-dated late Pleistocene monsoon record from Hulu Cave, China. Science 2001, 294, 2345–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Cheng, H.; Edwards, R.L.; Chen, F.; Wang, Y.; Yang, X.; Liu, J.; Tan, M.; Wang, X.; Liu, J.; et al. A test of climate, sun, and culture relationships from an 1810-Year Chinese cave record. Science 2008, 322, 940–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.; Fang, X.; Yang, Y.; Dupont-Nivet, G.; Nie, J.; Fluteau, F.; Zhang, T.; Han, W. Reorganization of Asian climate in relation to Tibetan Plateau uplift. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2022, 3, 684–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Tang, M. Discussion on the relationship between the second stage uplift of the Qinghai Tibet Plateau and the development of the Asian monsoon. Sci. China (Ser. D) 1998, 28, 263–271. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, J.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, Y.; Lu, H. Size distribution of the late Cenozoic red clay and the winter monsoon variations. Mar. Geol. Quat. Geol. 2001, 21, 99–106. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Z. The Evolution History of the Monsoon Recorded by the 22-8 Ma Wind Dust Deposition See: Ding Zhongli et al. Research on the Integration of Environmental Evolution in Western China; Meteorological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- An, Z. The history and variability of East Asian monsoon climate. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2000, 45, 238–249. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, D.; Shaw, J.; An, Z.; Cheng, M.; Yue, L. Magnetostratigraphy and paleoclimatic interpretation of a continuous 7.2 Ma late Cenozoic eolian sediments from the Chinese Loess Plateau. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1998, 25, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X. Influences of Qinghai-Xizang (Tibet) Plateau uplift on the atmospheric circulation, global climate and environment changes. Plateau Meteorol. 1999, 18, 321–332. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, G.; Pan, B.; Guan, Q.; Gao, H. Reviews of studies on the Mid-Pleistocene climatic transition and 100 ka cycle. Adv. Earth Sci. 2002, 17, 605–611. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Sun, Y.; Liu, X. Mid-Pleistocene climate transition: Characteristic, mechanism and perspective. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2017, 62, 3861–3872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Ranov, V.; Yang, S.; Finaev, A.; Han, J.; Wang, G. The loess record in southern Tajikistan and correlation with Chinese loess. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2002, 200, 387–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Fang, X. Uplift of the Tibetan Plateau and environmental changes. Chin. Sci. Bull. 1999, 44, 2117–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, H.; Rohling, E.J.; Stringer, C.; Roberts, A.P.; Dekkers, M.J.; Dupont-Nivet, G.; Yu, J.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, P.; Liu, Z.; et al. Two-stage mid-Brunhes climate transition and Mid-Pleistocene human diversification. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2020, 210, 103354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Pang, J.; Huang, P.; Hou, C.; Han, Y. High-resolution studies of the oldest cultivated soils in the southern Loess Plateau of China. Catena 2002, 47, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Pang, J.; Chen, S.; Zhang, Z. Holocene dust accumulation and the formation of polycyclic cinnamon soils (luvisols) in the Chinese Loess Plateau. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2003, 28, 1259–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Lan, H.; Lou, J.; Chen, Y. The dry Holocene megathermal in inner Mongolia. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2003, 193, 181–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pye, K.; Zhou, L. Late Pleistocene and Holocene aeolian dust deposition in North China and the Northwest Pacific Ocean. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 1989, 73, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linsley, B.K. Oxygen-isotope record of sea level and climate variations in the Sulu Sea over the past 150,000 years. Nature 1996, 380, 234–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Jia, J.; Chen, J.; Li, G.; Zhang, X.; Xie, H.; Xia, D.; Huang, W.; An, C. A persistent Holocene wetting trend in arid Central Asia, with wettest conditions in the late Holocene, revealed by multi-proxy analyses of loess-paleosol sequences in Xinjiang, China. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2016, 146, 134–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dansgaard, W. North Atlantic climatic oscillations revealed by deep Greenland ice cores. Clim. Process. Clim. Sensit. 1984, 29, 288–298. [Google Scholar]
- Heinrich, H. Origin and consequences of cyclic ice rafting in the Northeast Atlantic Ocean during the past 130,000 years. Quat. Res. 1988, 29, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; An, Z.; Wang, Y.; Ji, J.; Chen, Y.; Lu, H. Rb/Sr distribution and paleomonsoon changes in the recent 800ka Luochuan loess profile. Sci. China (Ser. D) 1998, 28, 498–504. [Google Scholar]
- Andersen, K.K.; Azuma, N.; Barnola, J.M.; Bigler, M.; Biscaye, P.; Caillon, N.; Chappellaz, J.; Clausen, H.B.; Dahljensen, D.; Fischer, H.; et al. High-resolution record of northern hemisphere climate extending into the last interglacial period. Nature 2004, 431, 147–151. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, L.; Chen, F.; Morrill, C.; Otto-Bliesner, B.L.; Rosenbloom, N. Causes of early Holocene desertification in arid Central Asia. Clim. Dyn. 2012, 38, 1577–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzschuh, U. Palaeo-moisture evolution in monsoonal Central Asia during the last 50,000 years. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2006, 25, 163–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Jin, L.; Huang, W.; Chen, F. Forcing mechanisms of orbital-scale changes in winter rainfall over northwestern China during the Holocene. Holocene 2016, 26, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, D.; Cheng, H.; Edwards, R.L.; Dykoski, C.A.; Kelly, M.J.; Zhang, M.; Qing, J.; Lin, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wu, J.; et al. Timing, duration, and transitions of the Last Interglacial Asian monsoon. Science 2004, 304, 575–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Cheng, H.; Edwards, R.L.; He, Y.; Kong, X.; An, Z.; Wu, J.; Kelly, M.J.; Dykoski, C.A.; Li, X. The Holocene Asian monsoon: Links to solar changes and North Atlantic climate. Science 2005, 308, 854–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, H.; Kong, X.; Wu, J. Long-term trend and abrupt events of the Holocene Asian monsoon inferred from a stalagmite d18O record from Shennongjia in Central China. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2006, 51, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleitmann, D.; Burns, S.J.; Mudelsee, M.; Neff, U.; Kramers, J.; Mangini, A.; Matter, A. Holocene Forcing of the Indian Monsoon recorded in a stalagmite from Southern Oman. Science 2003, 300, 1737–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Y.; Hong, B.; Lin, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Shibata, Y.; Hirota, M.; Uchida, M.; Leng, X.; Jiang, H.; Xu, H.; et al. Correlation between Indian Ocean summer monsoon and North Atlantic climate during the Holocene. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2003, 211, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Hhong, B.; Lin, Q.; Shibata, Y.; Hirota, M.; Zhu, Y.; Leng, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Yi, L. Inverse phase oscillations between the East Asian and Indian Ocean summer monsoons during the last 12000 years and paleo-El Nio. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2005, 231, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Liu, J.; Yuan, B.; Liu, D.; Liu, R.; Liu, Y.; Yaskawa, K. Monsoon variations of the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau during the last 12,000 years—Geochemical evidence from the sediments in the Siling Lake. Chin. Sci. Bull. 1993, 38, 577–581. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Shen, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Liu, W. Southwest monsoon changes indicated by oxygen isotope of ostracode shells from sediments in Qinghai Lake since the Lateglacial. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2007, 52, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.K.; Anderson, D.M.; Overpeck, J.T. Abrupt changes in the Asian southwest monsoon during the Holocene and their links to the North Atlantic Ocean. Nature 2003, 421, 354–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, A.; Loutre, M.F. Insolation values for the climate of the last 10,000,000 years. Quat. Sci. Rev. 1991, 10, 297–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G. Pollen evidence for increased summer rainfall in the Medieval warm period at Maili, northeast China. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1998, 25, 1931–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Tan, M.; Cheng, H.; Liu, T. Stable isotope records of plant cover change and monsoon variation in the past 2200 years: Evidence from laminated stalagmites in Beijing, China. Boreas 2003, 32, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Hendrson, G.M.; Huang, J.; Xie, S.; Sun, Y.; Johnson, K.R. Quantification of Holocene Asian monsoon rainfall from spatially separated cave records. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2008, 266, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, P.; Cheng, H.; Chen, F.; Yang, X.; Zhang, D.; Zhou, J.; Jia, J.; An, C.; Sang, W.; et al. The relationship between monsoon precipitation changes recorded by oxygen isotopes of stalagmites and the sea air system during AD 1875–2003 on the western edge of the Loess Plateau. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2008, 53, 2801–2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Schneider, B.; Park, W.; Latif, M.; Khon, V.; Zhang, X. The spatial-temporal patterns of Asian summer monsoon precipitation in response to Holocene insolation change: A model-data synthesis. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2014, 85, 47–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Z.; Porter, S.C.; Kutzbach, J.E.; Wu, X.; Wang, S.; Liu, X.; Li, X.; Zhou, W. Asynchronous Holocene optimum of the East Asian monsoon. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2000, 19, 743–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.; Park, S.; Shen, M.; Gao, J.; Yang, W.; Zhang, G.; Lei, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zhu, L.; Xu, B.; et al. Chained impacts on modern environment of interaction between westerlies and Indian monsoon on Tibetan Plateau. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2017, 32, 976–984. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.; Xu, X.; Yang, S.; Zhang, W. On the origin and destination of atmospheric moisture and air mass over the Tibetan Plateau. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2012, 110, 423–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Gao, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W. Water vapor transport processes on Asian water tower. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2019, 34, 1210–1219. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, T.; Masson-Delmotte, V.; Gao, J.; Yu, W.; Yang, X.; Risi, C.; Sturm, C.; Werner, M.; Zhao, H.; He, Y. A review of climatic controls δ18O in precipitation over the Tibetan Plateau: Observations and simulations. Rev. Geophys. 2013, 51, 525–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Zhu, C. Coupling mode of westerly–monsoonal flow over the Tibetan Plateau and its seasonal variation. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2022, 46, 1017–1029. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Zhang, X.; Lu, H.; Jin, L.; Du, Y.; Chen, F. Increasing summer precipitation in arid Central Asia linked to the weakening of the East Asian summer monsoon in the recent decades. Int. J. Climatol. 2021, 41, 1024–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Jiang, F.; Wang, Y.; Fan, Z. A study on signals and effects of climatic pattern change from warm-dry to warm-wet in Xinjiang. Arid Land Geogr. 2002, 25, 194–200. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Gou, X.; Cook, E.R.; Chen, F. Tree-ring based drought reconstruction for the Central Tien Shan area in northwest China. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L07715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Huang, W.; Jin, L.; Chen, J.; Wang, J. Spatiotemporal precipitation variations in the arid Central Asia in the context of global warming. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2011, 41, 1647–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Chen, J.; Huang, W. Weakened East Asian summer monsoon triggers increased precipitation in Northwest China. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2021, 64, 835–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Feng, S.; Chen, J.; Chen, F. Physical Mechanisms of summer precipitation variations in the Tarim Basin in northwestern China. J. Clim. 2015, 28, 3579–3591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, H.; Jiang, D. The configurable relationships between summer monsoon and precipitation over East Asia. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2004, 28, 699–712. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Q. The variations of summer monsoon in East Asia and the rainfall over China. J. Trop. Meteorol. 1985, 1, 44–52. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Xu, H.; Deng, J. Long-term rising of SST over the marginal seas of China in winter and its impact on precipitation in China. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 2015, 73, 505–514. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.; Wang, S.; Qian, Z.; Song, M.; Wang, A. Climatic linkages between SHWP position and EASM rainy-belts and areas in east part of China in summer half year. Plateau Meteorol. 2013, 32, 1510–1525. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Wei, L.; Liu, K. Effects of south Asia high and western Pacific subtropical high on the summer precipitation anomalies over southwest China. J. Arid Meteorol. 2013, 31, 464–470. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Tao, S. Influence of Asian mid-high latitude circulation on East Asian summer rainfall. Acta Meteorol. Sinia 1998, 56, 199–211. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.; Ding, F.; Ding, Z. Pleistocene chemical weathering history of Asian arid and semi-arid regions recorded in loess deposits of China and Tajikistan. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2006, 70, 1695–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T. Loess and the Environment; China Ocean Press: Beijing, China, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, H.; An, Z. The paleoclimatic significance of grain size composition of Loess Plateau. Sci. China (Ser. D) 1998, 28, 278–283. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Song, Y.; Yin, Q.; Han, L.; Wang, Y. Orbital and millennial northern mid-latitude westerlies over the last glacial period. Clim. Dyn. 2019, 53, 3315–3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Spotl, C.; Breitenbach, S.F.M.; Sinha, A.; Wassenburg, J.A.; Jochum, K.P.; Scholz, D.; Li, X.; Yi, L.; Peng, Y.; et al. Climate variations of Central Asia on orbital to millennial timescales. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, M.R.; Wolfe, A.P. Spatial and temporal variability of Holocene temperature in the North Atlantic region. Quat. Res. 2006, 65, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koc, N.; Jansen, E.; Haflidason, H. Paleoceanographic reconstructions of surface ocean conditions in the Greenland, Iceland and Norwegian Seas through the last 14 ka based on diatoms. Quat. Sci. Rev. 1993, 12, 115–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahl-Jensen, D.; Mosegaard, K.; Gundestrup, N.; Clow, G.D.; Johnsen, S.J.; Hansen, A.W.; Balling, N. Past temperatures directly from the Greenland ice sheet. Science 1998, 282, 268–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peltier, W.R.; Fairbanks, R.G. Global glacial ice volume and Last Glacial maximum duration from an extended Barbados sea level record. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2006, 25, 3322–3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Liu, T.; Guiot, J.; Wu, N.; Lu, H.; Han, J.; Liu, J.; Gu, Z. High frequency pulses of East Asian monsoon climate in the last two glaciations: Link with the North Atlantic. Clim. Dyn. 1996, 12, 701–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanase, W.; Abe-Ouchi, A. The LGM surface climate and atmospheric circulation over East Asia and the North Pacific in the PMIP2 coupled model simulations. Clim. Past 2007, 3, 439–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Henderson, G.M.; Hu, C.; Mason, A.J.; Charnley, N.; Johnson, K.R.; Xie, S. Links between the East Asian monsoon and North Atlantic climate during the 8200-year event. Nat. Geosci. 2013, 6, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, S.C.; An, Z.S. Correlation between climate events in the North-Altantic and China during last glaciation. Nature 1995, 375, 305–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Chen, F.; Ganopolski, A.; Claussen, M. Response of East Asian climate to Dansgaard/Oeschger and Heinrich events in a coupled model of intermediate complexity. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2007, 112, D06117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcmanus, J.F.; Francois, R.; Gherardi, J.M.; Keigwin, L.D.; Brown-Leger, S. Collapse and rapid resumption of Atlantic meridional circulation linked to deglacial climate changes. Nature 2004, 428, 834–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Praetorius, S.K.; Mcmanus, J.F.; Oppo, D.W.; Curry, W.B. Episodic reductions in bottom-water currents since the last ice age. Nat. Geosci. 2008, 1, 449–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Sun, Y.; Vandenberghe, J.; Cheng, P.; Zhang, X.; Gowan, E.J.; Lohmann, G.; An, Z. Centennial- to millennial-scale monsoon changes since the last deglaciation linked to solar activities and North Atlantic cooling. Clim. Past 2020, 16, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, G.; Kromer, B.; Beer, J.; Muscheler, R.; Evans, M.N.; Showers, W.; Hoffmann, S.; Lotti-Bond, R.; Hajdas, I.; Bonani, G. Persistent solar influence on North Atlantic climate during the Holocene. Science 2001, 294, 2130–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reimer, P.J.; Bard, E.; Bayliss, A.; Beck, J.W.; Blackwell, P.G.; Ramsey, C.B.; Buck, C.E.; Cheng, H.; Edwards, R.L.; Friedrich, M.; et al. IntCal13 and Marine13 radiocarbon age calibration curves 0–50,000 years cal BP. Radiocarbon 2013, 55, 1869–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.I.; Liu, Z.; Otto-Bliesner, B.; Brady, E.C.; Kutzbach, J.E.; Harrison, S.P. A simulation of the last glacial maximum climate using the NCAR-CCSM. Clim. Dyn. 2003, 20, 127–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Clemens, S.C.; Morrill, C.; Lin, X.; Wang, X.; An, Z. Influence of Atlantic meridional overturning circulation on the East Asian winter monsoon. Nat. Geosci. 2012, 5, 46–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Z.; Colman, S.M.; Zhou, W.; Li, X.; Brown, E.T.; Jull, A.J.T.; Cai, Y.; Huang, Y.; Lu, X.; Chang, H.; et al. Interplay between the Westerlies and Asian monsoon recorded in Lake Qinghai sediments since 32 ka. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aizen, E.M.; Aizen, V.B.; Melack, J.M.; Nakamura, T.; Ohta, T. Precipitation and atmospheric circulation patterns at mid-latitudes of Asia. Int. J. Climatol. 2001, 21, 535–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Chen, F.; Feng, S.; Chen, J.; Zhang, X. Interannual precipitation variations in the mid-latitude Asia and their association with large-scale atmospheric circulation. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2013, 58, 3962–3968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Yang, L. Desertification and related climate change in the Alashan Plateau since the last 40 ka of the last glacial period. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, C.; Lu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Tao, S.; Dong, W.; Li, H.; Jin, M.; Wang, Z. A high-resolution record of Holocene environmental and climatic changes from Lake Balikun (Xinjiang, China): Implications for Central Asia. Holocene 2012, 22, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Morrill, C. Multiple factors causing Holocene lake-level change in monsoonal and arid Central Asia as identified by model experiments. Clim. Dyn. 2010, 35, 1115–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q. The characteristics of the North Atlantic Oscillation and its impact on East Asia. Adv. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Wu, Y. The influence of ENSO on the summer climate change in China and its mechanism. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 1989, 6, 21–32. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, R. Interannual variation of North China rainfall in rainy season and SSTs in the equatorial eastern Pacific. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2005, 50, 2069–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Tian, J.; Huang, E.; Ma, W. Earth System and Evolution; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, S.; Chen, W.; Feng, J.; Graf, H.F. Combined impacts of PDO and two types of La Nina on climate anomalies in Europe. J. Clim. 2017, 30, 3253–3278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenberth, K.E.; Branstator, G.W.; Karoly, D.; Kumar, A.; Lau, N.C.; Ropelewski, C. Progress during TOGA in understanding and modeling global teleconnections associated with tropical sea surface temperatures. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1998, 103, 14291–14324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; He, S.; Gao, Y.; Chen, H.; Wang, H. North Atlantic modulation of interdecadal variations in hot drought events over northeastern China. J. Clim. 2020, 33, 4315–4332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Wang, B.; Seo, K.; Kug, J.; Choi, Y.; Kosaka, Y.; Ha, K. Future change of northern hemisphere summer tropical-extratropical teleconnection in CMIP5 Models*. J. Clim. 2014, 27, 3643–3664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Zhang, R.; Wen, M.; Kim, B.; Nam, J. Interannual variation of the South Asian High and its relation with Indian and East Asian summer monsoon rainfall. J. Clim. 2015, 28, 2623–2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Q.; Wang, B. Circumglobal teleconnection in the Northern Hemisphere summer. J. Clim. 2005, 18, 3483–3505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).