Abstract
In China, blue sky defense is a crucial part of ecological environment governance. Objective environmental governance performance needs to be perceived by the public to more truly affect the public’s evaluation of the government’s environmental governance. This paper focuses on the public’s subjective perception of air pollution and evaluation of the local government’s environmental governance. Based on the Chinese General Social Survey data, the matched economic indicators, and air pollution data, we conduct a diachronic study on the public’s evaluation of local governments’ environmental protection work, and we analyze the relationship between the subjective perception of air pollution, the objective air pollution data, and the evaluation of local governments’ environmental protection work. The results showed the following: (1) People’s evaluation of local governments’ environmental protection work significantly improved from 2013 to 2021. The objective indicator improved, while the subjective perception declined. (2) The subjective perception of air pollution has a significant negative impact on the evaluation of local governments’ environmental protection work and needs to be better considered to improve air quality. At the same time, the effect of the objective indicator is insignificant.
1. Introduction
The public’s evaluation of the government’s performance regarding environmental protection is an essential topic, which is worthy of analysis. In recent decades, with remarkable economic development, China has suffered serious environmental problems and has become one of the countries with the heaviest air pollution [1,2,3]. China ranked 160th among 180 countries in the 2022 Global Environmental Performance Index (EPI) jointly released by Yale and the University of Columbia. Air pollution has become the biggest threat to public health and sustainable economic development in China [4]. Various consequences have raised public concerns about the government’s environmental governance and challenged China’s existing national governance system and governance capacity [5]. Therefore, analyzing the impact of air pollution on public government evaluation is of practical significance. Furthermore, previous studies have found that public support for the government is related to the implementation of government policies [6]. The performance of various government environmental policies cannot be separated from public support. Following severe challenges, the Chinese government’s approach to environmental governance is transforming from a system of top-down management, relying solely on executive orders, to a system that will gradually rely more on strengthening environmental legislation and seeking public participation and supervision [7]. Wang et al. [8] pointed to a new bottom-up force that might affect environmental governance in China.
Scholars have demonstrated that public perception of the environment plays a crucial role in the evaluation of the government [9]. The public directly perceives air quality, and the perception of air pollution forms an essential basis for the government’s decision-making on air pollution control. The subjective perception of the public can be used to optimize objective air pollution indicators. As early as the 1980s, some scholars used the threshold of public perception of air pollution to improve the air quality index [10]. Scholars have conducted much research on the factors affecting general air pollution perception. However, there are still some deficiencies and space for further research. First, the existing empirical evidence, regarding the perception of air pollution, mostly derives from developed countries, while evidence from developing countries is relatively rare [11]. The explanatory power of pertinent research findings in developing countries remains limited. Second, the areas of evaluation with respect to environmental improvements should be optimized. Only a few studies apply air pollution perception to government performance evaluations [12]. The Chinese government has regarded improving environmental quality as some of their most important work [13] and made great progress in improving air quality in recent years [14], with the annual average concentration of all six air quality indicators falling annually for the first time in 2021. Therefore, the diachronic change in government environmental governance evaluation deserves attention, and the factors affecting the public’s evaluation of government environmental protection require further analysis and discussion.
This research selected local governments as the main body of public environmental protection work evaluation. According to the provisions of China’s Environmental Protection Law, local governments are responsible for preserving local environmental quality. In recent years, the central government has incorporated local environmental performance into the performance evaluation system for local governments. In China, blue-sky defense is a crucial part of ecological and environmental governance. We choose the topic of air pollution to measure the objective performance of environmental protection work because air pollution is more easily perceived and is more of a concern for the public in daily life and work compared with water pollution, noise pollution and other problems. Firstly, this study analyzed the diachronic difference in the public’s evaluation of the government’s environmental protection effort. Then, this study used regression models to explain the evaluation of the local government’s environmental protection work in terms of the public’s subjective perception of air pollution, objective air pollution data, and social and economic variables. We mainly used the Chinese General Social Survey (CGSS) 2013 and CGSS2021, as well as the provincial economic and environmental indicators. The public’s evaluation of local governments’ environmental protection work significantly improved from 2013 to 2021. The objective indicator improved, while the subjective perception declined. The lower the public’s subjective perception of air pollution results, the higher their evaluation of the government’s environmental governance. However, the objective environmental governance performance does not directly affect the evaluation of the government’s environmental governance. Although subjective and objective indicators of air pollution are often tricky to match, governments could consider the feelings of the public to better contain pollution. These findings will be of significance when optimizing local government behavior and improving air quality.
This paper contributes to the studies on air quality, environmental pollution perception, and government environmental governance evaluation. First, it expands on previous studies. It more closely links air pollution perception and government environmental governance assessment, enriching the application of air pollution perception and contributing to a deeper understanding of this factor. Secondly, it is found that the public’s evaluation of the government’s environmental protection work is a process of subjective perception, individual factors, and macro-factors. When the government continues to make efforts to achieve specific results, the objective environmental pollution will not directly affect the public’s evaluation of the local government’s environmental governance. Third, the current empirical literature on the perception of air pollution by the Chinese people is mainly based on small survey samples of specific residents or extensive social surveys conducted nearly a decade ago [15,16]. This paper provides evidence based on reliable data and a recent representative social survey of China. The impact of public participation in local government-initiated environmental improvements will rise, along with the continuous expansion of citizens’ rights, regarding participation in environmental improvements [17].
The paper is structured as follows. Section 2 presents the literature review, focusing on air pollution perception, the objective performance of government governance, and public evaluation, and puts forward the research hypothesis. Section 3 describes the source of the survey data, the design of variables, and the methods. Section 4 introduces and analyzes the concrete empirical results. Finally, Section 5 and Section 6 provide discussions and the conclusion.
2. Literature Review
2.1. Subjective Perception of Air Pollution
Environmental pollution improvements have long been a concern in academia [18,19,20]. Hao et al. [21] provided evidence that public concern about environmental pollution would force the government to take measures. The research regarding government evaluation must first consider the public’s perception of government services. Earlier studies on public evaluation have found that the public’s perception of service quality affects the public’s satisfaction with the service [22]. If the research on government satisfaction is extended to an evaluation of government environmental governance, it is necessary to consider the public perception of the condition of the environment. Of course, the environmental pollution perceived by the public is not necessarily consistent with the actual level of environmental pollution [23]. If the public’s perception of environmental pollution is wrong, there will be bias in their evaluation of the respective local government. If we focus on the risk of environmental problems brought by the public, the perception is defined as environmental risk perception. Risk perception is one of the most important indicators of public concern about air pollution [24]. By reviewing the rich literature on environmental risk perceptions, we identify three theoretical strands: risk determinism, socio-demographic approaches, and socio-cultural approaches [25,26,27,28,29]. These points help us systematically understand the key factors that influence the public’s perception of air pollution in China.
Air pollution perception research originated in the US in the 1950s. Based on the experience of developed countries, three major research orientations, namely “pollution perception bias”, “information framework theory”, and “social construction theory”, gradually developed [30,31,32,33]. Although some studies have found that fine air pollution can be perceived by the people, the public perception of pollution is affected by a series of variables, including information, region, and personal social background [34]. The literature on air pollution perception in China has recently increased, especially after successive national smog incidents in 2013. Public awareness of air pollution has also recently increased [35]. A survey conducted by Huang et al. [36], in big cities such as Beijing, revealed great differences in public health risk perception and pointed out that experiencing severe air pollution and being exposed to the related harm significantly increased people’s awareness of and familiarity with PM2.5. Li et al. [37,38] documented how air pollution awareness was raised among the urban middle class and what public engagement followed. Some social psychologists have also cooperated to explore the ultimate effects of air pollution perception through experiments [39]. The literature on air pollution perception is of great significance when thinking about the evaluation of government environmental protection work.
Although research on air pollution perception has a long history, it has not been systematically included in the framework of public evaluation of environmental governance. The objective environmental governance performance needs to be perceived by the public to more honestly influence the public’s evaluation of the government’s environmental governance. Therefore, we assume the following:
Hypothesis 1 (H1).
The public’s evaluation of the government’s environmental protection work significantly correlates with the perceived air pollution level.
2.2. Objective Performance and Public Evaluation
Environmental protection is a basic function of a modern state [40]. The public’s evaluation of the government’s environmental protection actions has become a crucial means of government performance evaluation. Different studies have found that many factors affect the public’s evaluation of the government. The relationship between the objective performance of government governance and the subjective evaluation of the public has always been a focus of debate. There are two very different schools of thought. Some people believe that the government performance affects public evaluation. That is to say that functioning public services help to improve general satisfaction. This view is supported by many empirical studies. For example, in Seoul, South Korea, evidence was found supporting a positive correlation between the quality of public service and public satisfaction [41].
However, this view is also challenged by numerous theories and empirical evidence showing that the objective performance of government governance is not consistent with the public’s evaluation. In theory, the public needs sufficient information to make rational judgments, but evaluations of public services contain information asymmetry. The public cannot make a rational judgment based on insufficient data. Madumere [42] held the opinion that an effective model for public participation in the environment consists of enabling all stakeholders to access each other’s information. Stipak [43] not only believes that surveys of public satisfaction cannot accurately reflect the actual performance of the government but also that the analysis of subjective attitudes is too complex to accurately reflect reality. At the empirical level, the correlation between public evaluation and actual performance is also supported by some evidence. Kelly and Swindell’s [44] study of local governments in the US found that, only in some areas, some objective performance indicators correlated with public evaluations.
In environmental governance, local governments are considered critical to air quality improvements [45]. The objective performance of the government was found to be inconsistent with the public’s evaluation of the government’s environmental protection work. The same applies to air quality. Graves [30] documented an apparent paradox between the reality and evaluations of air quality improvement in the US. Schwartz [46] found that most US respondents believed that air pollution had worsened or would grow worse in the future, although the US government had made significant progress in reducing air pollution in recent decades. Domestic research in China revealed a similar pattern [47]. Most studies model objective and subjective air pollution separately, although both pathways can exist simultaneously [48]. Although the associations between actual air pollution level and the public evaluation of government environmental protection work have been a focus for researchers in developed countries, the related associations have not yet been thoroughly examined in China [49]. It is essential to complement the empirical evidence regarding China. Therefore, to examine the above two viewpoints, we assume the following:
Hypothesis 2 (H2).
Public evaluations of government environmental protection work significantly correlate with the actual air pollution level.
2.3. Other Factors
At present, some of the literature has emphasized the influence of individuals’ social and economic characteristics on their attitudes from the perspective of different disciplines. For example, economics focuses on the influence of individual income and employment status on the evaluation of government work [50]; sociology focuses on the influence of education level, political orientation, gender, and age on the evaluation of government-related policies [51]; social psychology examines influence on the evaluation of government work from the perspective of public trust level and understanding of risks [52]. This paper attempts to combine the individual level with the social level, adopting a multidimensional and comprehensive perspective to study the factors that affect the public’s evaluation of the government’s environmental protection work.
At the individual level, the most common analyses focus on the individuals’ demographic socioeconomic characteristics. The research shows that the social and economic characteristics of individual populations impact their evaluation of the government’s public policies. For example, some scholars have pointed out that age, gender, and political orientation are significantly correlated with attitude towards the government’s environmental policies [53,54,55]. Most of these studies were conducted in Western contexts, where environmental governance is built upon widespread citizen participation and strong government accountability from its local constituents. Relatively little is known about the relationship between public evaluation of government environmental protection work and individual subjective perception in China [56].
The variables related to the formulation of identity are personal environmental knowledge (EK) and environmental value (EV). EK includes general knowledge, concepts, and relationships regarding the natural environment and its main ecosystems [57,58]. Previous studies found that EK has a significant impact on environmental concern, environmental awareness, environmental risk assessment, and environmental quality perception [59,60,61]. Since the late 1990s, latent value variables have become the focus of environmental behavior researchers. Stern et al. [62] believed that environmental attitudes are variable and can change over time, while values are relatively stable, and they put forward the Value-Belief-Norm Theory. EV refers to individuals’ fundamental views on the environment and environmental issues based on their outlooks on life. Stern [63] divided EV into egoism and altruism. He believed that the two had a significant impact on public garbage classification behavior. Scholars verified that people with EV were friendlier to the environment and changed their behavioral habits according to changes in the environment [64].
We focus on the impact of the level of economic development. Previous studies have shown a complex relationship between macroeconomic growth and environmental pollution, the most famous of which is the Environment Kuznets Curve (EKC) hypothesis [65]. However, the validity of this hypothesis remains controversial. Empirical results indicate that CO2–economy interactions dynamically changed over time in Guangdong—one of the most representative provinces of China [66]. Hao et al. [67] found that sustainable economic growth may help reduce PM2.5 concentrations. Generally, with the increase in economic development and residents’ income, the public demand for a good environment also increases. Therefore, the public will make a corresponding evaluation of the government’s actions.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Data
3.1.1. Individual-Level Data
The data used in this paper are mainly from CGSS2013 and CGSS2021. Launched in 2003, CGSS is China’s first nationwide, comprehensive, and continuous large-scale social survey project, jointly carried out by Renmin University of China and academic institutions across the country. This project adopted a multi-level stratified probability sampling design and carried out nationwide household access work. The data for 2013 and 2021 were chosen because their surveys both included environmental modules.
The environmental module of CGSS2013 surveyed adults, aged 18 and above, from 28 provincial-level administrative regions, including Liaoning, Shaanxi, Jiangsu, and Fujian province. The environmental module of CGSS2021 surveyed adults, aged 18 and above, from 19 provincial-level administrative regions. The 28 provinces involved in the data of 2013 include 19 provinces involved in the data of 2021. For the purpose of this research, only the samples of 19 provincial administrative regions, with data for 2013 and 2021, were retained in this paper. After processing, the proper sample size for the 2013 data was 6783, and the proper sample size for 2021 was 2741. Mean or median values were used to fill the missing values of variables in some samples.
3.1.2. Provincial Hierarchical Data
This paper also used the economic and environmental indicators of the 19 provinces in 2012 and 2020. The economic data were taken from China Statistical Yearbook (2013) and China Statistical Yearbook (2021), while the corresponding environmental data were taken from the provincial ecological environment state bulletin. The macro-level and survey sample data were not strictly synchronized in time because respondents’ perception of air pollution and evaluation of government protection work may lag [68]. However, the macro-level data adopted in this study also have certain limitations. City-level or county-level data are more accurate than provincial-level, but we could only locate the interviewees in their provinces. Due to the restrictions of CGSS data disclosure, the interviewees’ respective cities and counties could not be located, so the macro-level data could only be collected at the provincial level.
3.2. Variables
3.2.1. The Dependent Variable
The dependent variable of this paper is the individual’s evaluation of the local government’s environmental performance. In the CGSS2021 questionnaire, the specific question about dependent variables was “How well do you think the local government has done in solving environmental problems in your area in the past five years” with a total of six possible answers. The ranking was as follows: 1 meant “one-sided emphasis on economic development, ignoring environmental protection work”, 2 meant “insufficient attention, insufficient investment in environmental protection”, 3 meant “although the government has tried its best, but the effect is not good”, 4 meant “government has made great efforts and achieved certain results”, 5 meant “government has made great achievements”, and 98 meant “I can not choose”. The CGSS2013 survey also set the same questions. Finally, in the modeling, we assumed a neutral attitude for “I can not choose” and assigned this the middle value, “3”. We treated the ordinal variable as the interval variable, which was widely adopted, and the result did not significantly change.
3.2.2. Independent Variables
For a subjective indicator of air pollution, we selected the public’s subjective perception of air pollution. In the CGSS2021 questionnaire, respondents’ had seven possible answers regarding the severity of air pollution in their local areas. These answers were as follows: 5 meant “very serious”, 4 meant “relatively serious”, 3 meant “generally”, 2 meant “not too serious”, 1 meant “not serious”, 7 meant “the problem doesn’t exist”, and 8 meant “I can not choose”. The CGSS2013 survey set a similar question. For the sake of analysis, we combined and assigned values to the answers, ending with “the problem doesn’t exist” = 0, “generally” = 1, “not serious” = 2, “not too serious” = 3, “relatively serious” = 4, and “very serious” = 5.
For an objective indicator of air pollution, we selected the PM10 index and matched the annual average PM10 concentration in the provinces in which the respondents lived. The concentration index PM10 was adopted for theoretical and practical considerations. Theoretically, SO2, NO2, and PM10 are the primary atmospheric pollutants. The report from the Ministry of Environmental Protection of China (2013) found that PM10 caused great harm to physical health, and it was the primary pollutant affecting air quality in China. Previous studies have also adopted PM10 as the independent variable of air pollution perception [49,69]. PM10 is more likely to be perceived than other pollutants. PM10 has a large diameter and is more likely to affect air visibility compared to other pollutants. Accordingly, it is more likely to affect residents’ mental health [70]. At the practical level, PM10 monitoring was completed in 2006 for all prefecture-level cities in China, while PM2.5 monitoring was completed in 2015. Therefore, the average annual PM10 concentration index in 2012 and 2020, for the respondents’ provinces, provided an objective indicator of the local government’s environmental performance. The study also collected the average density of PM2.5 in 2020.
As an objective indicator of air pollution, we also collected the percentage of days exceeding the standard as pollution days in the provinces in which the respondents lived. Air Quality Index (AQI) is a dimensionless index that quantitatively describes air quality. With the introduction of Ambient Air Quality Standards (GB3095-2012) in China, AQI, a special air quality evaluation method for public release, was also stipulated, so the public could judge the air quality level and whether it met the standards. As the implementation year of AQI was later than 2012, it could not be used for diachronic analysis. The study collected the percentage of days exceeding the standard in 2020.
3.2.3. Control Variables
For EK, a series of indicators of cognition of environmental problems were adopted. After reverse assignment, the score of each hand was added up to obtain the EK score. A high score means that the respondents have a higher level of EK. EV was obtained using series of indicators regarding general perceptions of the relationship between human society and the environment. Some of the answers were assigned in reverse. The scores for each hand were added together to obtain the EV score. The Cronbach’s Alpha of EK and EV are 0.820 and 0.814, respectively, indicating that EK and EV are two high-level reliability indicators.
For the topic of social trust, due to the limitations of the question design in the CGSS questionnaire, we chose the measurement of general belief to determine the social trust variable. In the CSGG questionnaire, the specific question is: “Generally speaking, do you think most people can be trusted”. There are four possible answers: 1 means “people can almost always be trusted”, 2 means “people can often be trusted”, 3 means “you often have to deal with people with caution”, and 4 means “you almost always deal with people with caution”. We inverted the assignment for the answers.
We also controlled for the socioeconomic demographic variables of the respondents. The educational variable adopted the linear measurement method to measure the total number of years of school education. The income data were derived from the questionnaire about annual income in 2020. Health status was assessed as an ordered variable (very unhealthy = 1, relatively unhealthy = 2, average = 3, relatively healthy = 4, very healthy = 5). The variables of political status were dummy variables (a member of the Communist Party = 1, others = 0). Other variables included age, gender (female = 1, male = 0), and whether the survey was conducted in an urban or rural area (urban = 1, rural = 0).
For the economic development of the respondents’ provinces, we used two indicators. The first was the per capita GDP of each province (ten thousand yuan) and the second was the GDP growth rate of each province.
Table 1 reports descriptive statistics of the main variables used in our regression analysis from the CGSS2021 survey, as well as air pollution and economic indicators for 2020. The relevant data from CGSS2013 and 2012 are not included in the regression and are not reported in this paper.

Table 1.
Descriptive statistics of variables included in the regression.
3.3. Methods
With the help of STATA15.0 software (StataCorp LLC, College Station, TX, USA), this paper firstly completed a diachronic assessment of the air pollution perception and environmental governance evaluation of local governments, as investigated by CGSS2013 and CGSS2021 at the provincial level. PM10 in 2012 and 2020 was also compared, and t-test was used to compare the differences at different timepoints. Then, through regression, this paper explored the influencing factor model of public evaluation of government environmental protection work from the perspectives of individual socioeconomic and demographic variables, social psychological characteristics, macroeconomic development, and the air pollution level of the province.
For regression, we used the following analysis steps. First, the null model, also known as the one-way analysis of variance model, means that there are no explanatory variables at the personal level and the regional level. The purpose of this model is to decompose the total variance at the individual level and regional level, respectively, but it can also compute the intra-class correlation coefficient (ICC). A high coefficient indicates more inter-group variation and vice versa; more total variance can be explained by intra-group variation. If there were significant differences in the per capita evaluation scores among provinces, we used the linear stratification model. If there was no significant difference, we used a multivariate linear model. The above models are standard, so they are not explained in detail in this paper. As there are different measurement levels and significant differences in the size of variables, we standardized all variables for the convenience of comparison.
4. Results
4.1. The Diachronic Nature of the Government’s Environmental Protection Work
The changes in the provincial mean value of evaluating local governments’ environmental protection work are as follows. We know how each person from the CGSS survey rated the government’s environmental work, as well as which province each person lived in, so we can calculate the average of the government’s environmental work evaluation for each province (Figure 1). In 2013, the score was 3.073. In 2021, the score was 3.663, showing a significant improvement (p < 0.001). Other surveys provide evidence for the public’s assessment of government environmental protection. In 2021, the Policy Research Center for the Environment and Economy of the Ministry of Ecology and Environment released the Survey Report on Citizens’ Ecological and Environmental Behavior (2021) in China. According to the report, most respondents believed that the major environmental problems near their homes improved, to varying degrees, in 2021, based on the continuous work of the government. The respondents generally recognized the effectiveness of the government’s environmental protection efforts.
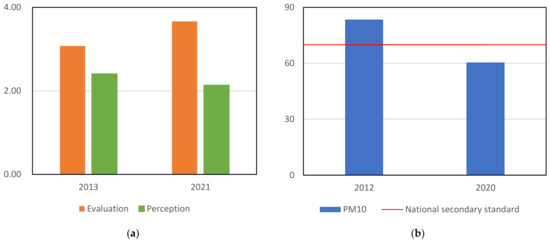
Figure 1.
Provincial-level data at different timepoints. (a) Evaluation of local governments’ environmental governance and perception of air pollution; (b) PM10 (μg/m3) and national secondary standard used to determine whether it exceeds the standard.
The changes in the provincial mean value of air pollution perception are as follows. All the respondents’ perception of air pollution was documented in the CGSS survey, as well as each respondent’s province; this information was used to calculate the average for each province’s perception of air pollution. The two timepoints in 2013 and 2021 were 2.407 and 2.133, respectively, with a specific decrease (p < 0.05). Other surveys have provided similar results. Public environmental awareness surveys have been carried out in Beijing for years. In 2021, the Beijing Municipal Bureau of Ecological Environment commissioned a third-party organization to carry out a public environmental awareness survey. It was found that the public’s satisfaction with air quality was the highest, and the score significantly increased from 7.79 in 2020 to 8.14 in 2021. In other words, perceived air pollution is improving. Ruan et al. [71] found that most respondents believed that the perception of environmental pollution was low, and the satisfaction with environmental governance was good in recent years.
The changes in the provincial average annual concentration of PM10 are as follows. In China, the current yearly mean level 2 standard is ≤70 μg/m3. In 2012, it was 83.421 μg/m3, obviously exceeding the standard, and in 2020, it was 60.474 μg/m3, showing a significant decline (p < 0.001) and a change toward meeting the standard. According to the state media, China saw the fastest improvement in air quality worldwide, between 2013 and 2020, and China’s air quality has improved as much as it did in the three decades since the Clean Air Act was launched in the US.
Table 2 reports the results of the diachronic values and t-test. The t-test shows significant differences in the evaluation of local governments’ environmental protection work, subjective perception of air pollution, and annual average PM10 concentration at different timepoints. From 2013 to 2021, the evaluation of local governments’ environmental work has significantly increased, while the perception of air pollution has significantly decreased. Both of these are subjective assessments made by the public. We hypothesize that they are directly related. PM10 also significantly decreased, and the objective index of air pollution decreased, which is the government’s actual achievement in environmental protection, but it is not clear that PM10 has a direct impact on the evaluation of the local government’s environmental protection work. Previous research in China showed an inconsistent relationship between environmental quality improvements and local government job evaluation from 2003 to 2013 [47]. Possible reasons for this include a lack of publicity, a lack of public trust in government, and high public expectations for environmental quality improvements. According to the findings of Lu et al. [68], the public is more sensitive to short-term fluctuations in air quality.

Table 2.
Changes in provincial level data at different timepoints.
4.2. Influencing Factors of Public Evaluation of Government Environmental Protection Work
Table 3 reports the setting of the model and the results of regression analysis. Among the variables used in this paper, the objective index of air pollution and the level of economic development belong to the provincial level, while other variables belong to the individual level. Regression analysis was used to explore the variables’ impact on the public evaluation of local governments’ environmental protection work in 2021.

Table 3.
Factors influencing evaluation of local governments’ environmental work.
Model 1 shows a two-tier, completely unconditional model. This was calculated by Stata, and we determined how much of the total variance can be explained by the individual level and the regional level, respectively. We can report that the intra-group variance is 0.906, which is much larger than the inter-group variance (0.024). After calculating ICC, the value is 0.026, which means that the per capita variance of 2.6% regarding the government’s environmental performance evaluation score is the difference between provinces. The empirical rule, whether the ICC value is more significant than 0.059, was used to judge whether the layered model is worth using [72]. Therefore, the layered model was not used in this study, and multiple linear regression was used instead.
All the individual-level variables were added to Model 2. The results show that pollution perception (β = −0.087, p < 0.001), age (β = 0.007, p < 0.001), health (β = 0.064, p < 0.001), social trust (β = 0.080, p < 0.01), and EK (β = −0.015, p < 0.05) are significantly correlated with local government environmental protection scores. The more serious the air pollution is perceived to be by the public, the more dissatisfied they are with the environmental protection work of the local government, and they think that the environmental protection work of the local government is not good. Therefore, Hypothesis 1 is supported by the data. Older men have a higher assessment of local governments’ environmental work. Better health also correlates with higher evaluation of the government’s environmental protection work. There is a significant positive correlation between the trust level and the subjective evaluation of the government’s environmental protection work, indicating that the higher the public’s trust in society, the higher their evaluation of the government’s environmental protection work, which is consistent with the findings of Konisky et al. [53] and Pu et al. [73]. Individual EK has a significant, direct, negative effect on the government’s evaluation work, indicating that the higher the individual EK, the lower their evaluation of the government’s environmental protection work. It is not difficult to understand that, if individuals have a higher EK, they are more likely to realize the importance of environmental problems and the harm they cause, and they may have more stringent requirements regarding environmental governance. However, it is surprising that EV (β = 0.002, p > 0.05) has no significant effect on the evaluation of the government’s environmental protection work. This may be because the environmental protection concept has been widely accepted in China, while EK is more professional.
Objective indicators of air pollution and economic development were added to Model 3. According to the data in Table 3, regions with higher per capita GDP (β = −0.016, p < 0.01) have a significant negative correlation with the evaluation of the government’s environmental protection work, which indicates that the public has more urgent requirements for a suitable environment after specific material needs are met. The richer the region, the more acute the public demand for a good atmosphere and the stricter the evaluation of the government’s environmental protection work. However, there is no significant correlation between the growth rate of GDP (β = 1.039, p > 0.05) and the evaluation of the government’s environmental protection. This indicates that the economic growth rate will not necessarily lead to improvements in the government’s environmental performance evaluation because the economic growth rate is not necessarily related to financial stock and, therefore, is not necessarily related to actual living standards and environmental pollution. Naturally, it is not necessarily associated with the evaluation of the government’s environmental work. As an objective indicator of air quality, PM10 (β = −0.001, p > 0.05) has no significant direct effect on the public’s evaluation of the local government’s environmental protection work. Hypothesis 2 is not supported by the data. This is consistent with the findings of Bickerstaff et al. [32] and Brody et al. [74]. Governments should fulfill their environmental responsibility and increase their performance exposure [75].
On the basis of Model 3, Model 4 replaces PM10 with pollution days when the AQI index exceeds the standard. Only the influence that GDP per capita (β = −0.016, p < 0.01 in Model 3; β = −0.014, p < 0.05 in Model 4) has on evaluation showed a slight change, with no significant changes in other variables. Pollution days (β = −0.152, p > 0.05) have no significant direct effects on the public’s evaluation of the local government’s environmental protection work. Hypothesis 2 is still not supported by the data. Combined with the above models, this study also replaces the independent variable PM10 with PM2.5. The evaluation of the dependent variable of local government environmental performance changed from a quantitative variable to a sequential variable. However, the results do not significantly vary, so they are not presented in this paper.
5. Discussion
In combination with the survey data of the CGSS, the matching provincial-level economic indicators, and air pollution data, this study determined the following. From 2013 to 2021, the public’s evaluation of local governments’ environmental protection work significantly improved. The objective indicator improved, while the subjective perception declined. It is imperative to improve the public’s subjective perception of environmental pollution. The public’s subjective perception affects their evaluation of the government’s environmental protection work. It is not proven that public evaluation of government environmental protection work significantly correlates with actual air pollution levels.
It is ultimately up to the people to evaluate the effectiveness of environmental protection, and the government’s work needs to include surveys and data collection regarding the public’s subjective feelings. The Chinese government attaches great importance to environmental problems and has introduced many environmental protection policies [76]. In China, air quality has been used to assess the performance of local officials [77]. Ultimately, it is up to the people to evaluate the effectiveness of the government’s work. In recent years, the problem of environmental pollution has aroused broad public concern. The people are in the best position to determine how the government’s environmental governance performance will work, and they should receive a real sense of gain. This study found that people’s subjective perception of environmental pollution is critical, and the perception has a direct impact on the public’s evaluation of the government’s environmental protection efforts. Therefore, the government needs to investigate and collect data on the public’s subjective feelings. It is useless to just work hard and not know how the people feel. Existing studies have suggested that it is critical for policymakers to realize that subjective perceptions can be combined with objective indicators to obtain a comprehensive understanding of urban environmental governance [23]. Individuals’ direct perception of environmental issues, such as air pollution and its effects, enhances their understanding of the importance of environmental policy measures. This makes the policy more acceptable [78,79].
Government evaluation is a comprehensive topic which needs to be based on performance and information disclosure. In recent years, public participation in the performance evaluation of local government has become a focus of general management. In reality, there are many “public participation” performance evaluations across China. With the improvement in public awareness of participation, the public’s satisfaction with environmental governance has become an essential part of evaluations of the government’s environmental governance [80]. For example, the environmental protection department in Zhejiang Province conducted a provincial public satisfaction survey on the ecological environment in 2022, hoping that the survey would reflect the effectiveness of local ecological and environmental protection work. It should be pointed out that the public often lacks the opportunity to personally experience special public services, such as environmental emergency response, and the government management is relatively closed and lacks transparency and openness. Hence, it is challenging to conduct an evaluation. Public participation is an integral part of the modern environmental governance system, and it is closely related to the disclosure of government environmental information [81]. Improving government transparency or information disclosure can effectively improve environmental governance. Based on CGSS2021 survey samples and 2020 air pollution data, the public’s subjective evaluation may not directly reflect the honest and objective performance of the government, as it is subject to the influence of various factors. However, our t-test also shows that this evaluation is not a pie in the sky. It is also based on the objective achievements of environmental governance.
6. Conclusions
The public’s evaluation of the government has always been a significant issue in government governance. This paper takes the Chinese public’s evaluation of local governments’ environmental governance as an example. Based on a quantitative analysis of CGSS data, the matched socioeconomic indicators, and air pollution data, this work conducted a diachronic study on the public’s evaluation of local governments’ environmental protection work and analyzed the relationship between the subjective perception of air pollution, objective indicators of environmental governance performance, and the evaluation of local governments’ environmental protection work. This study finds that people’s evaluation of local governments’ environmental protection work has significantly improved, and the subjective perception of air pollution substantially affects individuals’ evaluations. Therefore, the government needs to effectively improve its objective social governance and services to improve people’s well-being; it also needs to strengthen investigation and data collection regarding people’s subjective feelings.
As Bickerstaff et al. [82] put it: “What does air pollution mean to the ordinary people? How do people give meaning to air pollution? When some people see air pollution as a problem, why not others?” Our study finds that only when objective environmental pollution is perceived by the public can it be used as a basis for judging the government’s environmental governance. The public’s subjective perception of the government’s social governance performance is a process of the social structure. For example, Wang et al. [8] examined the influence of social media, and future research should pay more attention to the internal mechanisms of the social construction of personal perception.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.L.; methodology, J.Z. and C.L.; formal analysis, C.L.; investigation, Z.W.; data curation, Z.W.; writing—original draft preparation, J.Z.; writing—review and editing, C.L.; funding acquisition, J.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by General Project of Philosophy and Social Sciences Research in Colleges and Universities in Jiangsu Province, grant number 2022SJYB1048.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all the subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The dataset used in this study can be obtained from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
Authors acknowledge the support given by partner institution that provided the Chinese General Social Survey data. The institution is Renmin University of China.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Zhao, S.P.; Yu, Y.; Yin, D.Y.; He, J.J.; Liu, N.; Qu, J.J.; Xiao, J.H. Annual and diurnal variations of gaseous and particulate pollutants in 31 provincial capital cities based on in situ air quality monitoring data from China National Environmental Monitoring Center. Environ. Int. 2016, 86, 92–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Z.; Luo, L.N.; Wang, S.X.; Wang, Y.G.; Sharma, S.; Shimadera, H.; Wang, X.L.; Bressi, M.; Miranda, R.M.D.; Jiang, J.K.; et al. Status and characteristics of ambient PM2.5 pollution in global megacities. Environ. Int. 2016, 89–90, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.B.; Wu, L.; Xie, Y.C.; He, J.J.; Chen, X.; Wang, T.; Lin, Y.C.; Jin, T.S.; Wang, A.X.; Liu, Y.; et al. Air pollution in China: Status and spatiotemporal variations. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 227, 334–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.X.; Cai, W.J.; Chen, X.T.; Chen, X.; Zhao, Z.J.; Ma, Z.Y.; Yang, F.; Zhang, S.H. Synergies of carbon neutrality, air pollution control, and health improvement–A case study of China energy interconnection scenario. Glob. Energy Interconnect. 2022, 5, 531–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guttman, D.; Young, O.; Jing, Y.J.; Bramble, B.; Bu, M.L.; Chen, C.; Furst, K.; Hu, T.; Li, Y.F.; Logan, K.; et al. Environmental governance in China: Interactions between the state and “nonstate actors”. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 220, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetherington, M.J. The political relevance of political trust. Am. Political Sci. Rev. 1998, 92, 791–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munro, N. Explaining public participation in environmental governance in China. Environ. Values 2021, 30, 453–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.S.; Jia, Y.H. Social media’s influence on air quality improvement: Evidence from China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 298, 126769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.M. Effects and drawbacks of environmental impact assessment in avoiding NIMBY. Ekoloji 2018, 27, 149–154. [Google Scholar]
- Flachsbart, P.G.; Phillips, S. An index and model of human response to air quality. J. Air Pollut. Control. Assoc. 1980, 30, 759–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galinato, G.I.; Chouinard, H.H. Strategic interaction and institutional quality determinants of environmental regulations. Resour. Energy Econ. 2018, 53, 114–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, D.Y.; Xia, M.Y.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Elahi, E.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, H.M. The impact of public appeals on the performance of environmental governance in China: A perspective of provincial panel data. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 231, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.M.; Yu, S.F.; Xu, Z.H. Does environmental pollution weaken the positive effect of government public expenditure on residents’ subjective wellbeing? A case study in China. Energy Environ. 2022, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zheng, Y.X.; Tong, D.; Shao, M.; Wang, S.X.; Zhang, Y.H.; Xu, X.D.; Wang, J.N.; He, H.; Liu, W.Q.; et al. Drivers of improved PM2.5 air quality in China from 2013 to 2017. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 24463–24469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Folmer, H.; Xue, J. Perception of air pollution in the Jinchuan mining area, China: A structural equation modeling approach. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, W.; Wei, Y.M.; Wang, S.Y. Left behind in perception of air pollution? A hidden form of spatial injustice in China. Environ. Plan. C Politics Space 2022, 40, 666–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okubo, N. The development of the Japanese legal system for public participation in land use and environmental matters. Land Use Policy 2016, 52, 492–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.X.; Jin, R.L. Theoretical exploration of carbon emissions dynamic evolutionary system and evolutionary scenario analysis. Energy 2012, 40, 376–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, G.C.; Tian, L.X.; Fu, M.; Sun, M. Government control or low carbon lifestyle? Analysis and application of a novel selective-constrained energy–saving and emission–reduction dynamic evolution system. Energy Policy 2014, 68, 498–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.X.; Ye, Q.; Zhen, Z.L. A new assessment model of social cost of carbon and its situation analysis in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 211, 1434–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Liu, S.; Lu, Z.N.; Huang, J.B.; Zhao, M.Y. The impact of environmental pollution on public health expenditure: Dynamic panel analysis based on Chinese provincial data. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 18853–18865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeithaml, V.A.; Berry, L.L.; Parasuraman, A. The behavioral consequences of service quality. J. Mark. 1996, 60, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiarini, B.; D’Agostino, A.; Marzano, E.; Regoli, A. The perception of air pollution and noise in urban environments: A subjective indicator across European countries. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 263, 110272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ban, J.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, Y.; Anderson, G.B.; Li, T.T. The health policy implications of individual adaptive behavior responses to smog pollution in urban China. Environ. Int. 2017, 106, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleury-Bahi, G. Environmental risk: Perception and target with local versus global evaluation. Psychol. Rep. 2008, 102, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shusterman, D.; Lipscomb, J.; Neutra, R.; Satin, K. Symptom prevalence and odor-worry interaction near hazardous waste sites. Environ. Health Perspect. 1991, 94, 25–30. [Google Scholar]
- Flynn, J.; Slovic, P.; Mertz, C.K. Gender, race, and perception of environmental health risks. Risk Anal. 1994, 14, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeola, F.O. Nativity and environmental risk perception: An empirical study of native-born and foreign-born residents of the USA. Hum. Ecol. Rev. 2007, 14, 13–25. [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson, I. Social theories of risk perception: At once indispensable and insufficient. Curr. Sociol. 2001, 49, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graves, P.E. Environmental perceptions and environmental reality: When more is less? Environ. Plan. A 2003, 35, 951–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebler, C.M.; Bendix, J. Old-growth forests on network news: News sources and the framing of an environmental controversy. Journal. Mass Commun. Q. 1996, 73, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bickerstaff, K.; Walker, G. Public understandings of air pollution: The ‘localisation’ of environmental risk. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2001, 11, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bush, J.; Moffatt, S.; Dunn, C.E. Keeping the public informed? Public negotiation of air quality information. Public Underst. Sci. 2001, 10, 213–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyslop, N.P. Impaired visibility: The air pollution people see. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 182–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.W.; Yao, N.Z.; Guo, Q.Z.; Wang, F.B. Public risk perception and willingness to mitigate climate change: City smog as an example. Environ. Geochem. Health 2020, 42, 881–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Rao, C.; Kuijp, T.J.V.E.; Bi, J.; Liu, Y. A comparison of individual exposure, perception, and acceptable levels of PM2.5 with air pollution policy objectives in China. Environ. Res. 2017, 157, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Tilt, B. Perceptions of quality of life and pollution among China’s urban middle class: The case of smog in Tangshan. China Q. 2018, 234, 340–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Tilt, B. Public engagements with smog in urban China: Knowledge, trust, and action. Environ. Sci. Policy 2019, 92, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, L.N.; Wu, Z.D.; Zhang, S.H.; Zhou, K.X. The end effect in air pollution: The role of perceived difference. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 232, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, D.J.; Hironaka, A.; Schofer, E. The nation–state and the natural environment over the twentieth century. Am. Sociol. Rev. 2000, 65, 96–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, T.; Lee, S.J. Does management performance impact citizen satisfaction? Am. Rev. Public Adm. 2012, 42, 419–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madumere, N. Public enlightenment and participation—A major contribution in mitigating climate change. Int. J. Sustain. Built Environ. 2017, 6, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stipak, B. Citizen satisfaction with urban services: Potential misuse as a performance indicator. Public Adm. Rev. 1979, 39, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, J.M.; Swindell, D. Service quality variation across urban space: First steps toward a model of citizen satisfaction. J. Urban Aff. 2002, 24, 271–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Sun, J.W.; Jiang, J.J.; Wang, J. The effect of environmental regulation competition on haze pollution: Evidence from China’s province-level data. Environ. Geochem. Health 2022, 44, 3057–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, J. Clearing the air. Regulation 2003, 26, 22–29. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, C.T.; Hong, D.Y. Research on the model of factors influencing the public evaluation of government environmental protection. Soc. Sci. Res. 2015, 2, 108–115. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.T.; Folmer, H.; Xue, J.H. To what extent does air pollution affect happiness? The case of the Jinchuan mining area, China. Ecol. Econ. 2014, 99, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, M.; Zhang, H.; Evans, R.D.; Zhong, X.; Yang, K. Actual air pollution, environmental transparency, and the perception of air pollution in China. J. Environ. Dev. 2019, 28, 78–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinder, D.R.; Kiewiet, D.R. Economic discontent and political behavior: The role of personal grievances and collective economic judgments in congressional voting. Am. J. Political Sci. 1979, 23, 495–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietz, T.; Dan, A.; Shwom, R. Support for climate change policy: Social psychological and social structural influences. Rural Sociol. 2007, 72, 185–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cin, C.K. Blaming the government for environmental problems: A multilevel and cross-national analysis of the relationship between trust in government and local and global environmental concerns. Environ. Behav. 2012, 45, 971–992. [Google Scholar]
- Konisky, D.M.; Milyo, J.; Richardson, L.E. Environmental policy attitudes: Issues, geographical scale, and political trust. Soc. Sci. Q. 2008, 89, 1066–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, T.; Lægreid, P. Trust in government: The relative importance of service satisfaction, political factors, and demography. Public Perform. Manag. Rev. 2005, 28, 487–511. [Google Scholar]
- Pampel, F.C.; Hunter, L.M. Cohort change, diffusion, and support for environmental spending in the United States. Am. J. Sociol. 2012, 118, 420–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.L.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.J. Understanding individual environmental concern in the context of local environmental governance in China: A multi-level analysis. Soc. Nat. Resour. 2018, 31, 1283–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fryxell, G.E.; Lo, C.W.H. The influence of environmental knowledge and values on managerial behaviors on behalf of the environment: An empirical examination of managers in China. J. Bus. Ethics 2003, 46, 45–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkes, F.; Colding, J.; Folke, C. Rediscovery of traditional ecological knowledge as adaptive management. Ecol. Appl. 2000, 10, 1251–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadler, M.; Haller, M. Global activism and nationally driven recycling: The influence of world society and national contexts on public and private environmental behavior. Int. Sociol. 2011, 26, 315–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omanga, E.; Ulmer, L.; Berhane, Z.; Gatari, M. Industrial air pollution in rural Kenya: Community awareness, risk perception and associations between risk variables. BMC Public Health 2014, 14, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thepaksorn, P.; Siriwong, W.; Neitzel, R.L.; Somrongthong, R.; Techasrivichien, T. Relationship between noise-related risk perception, knowledge, and the use of hearing protection devices among para rubber wood sawmill workers. Saf. Health Work. 2018, 9, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, P.C.; Dietz, T.; Guagnano, G.A. A brief inventory of values. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 1998, 58, 984–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, P.C. Psychology and the science of human-environment interactions. J. Am. Psychol. 2000, 55, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopper, J.R.; Nielsen, M.C. Recycling as altruistic behavior: Normative and Behavioral Strategies to Expand Participation in a Community Recycling Program. Environ. Behav. 1991, 23, 195–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossman, G.M.; Krueger, A.B. Environmental Impacts of a North American Free Trade Agreement. Available online: https://www.nber.org/papers/w3914 (accessed on 14 December 2022).
- Jiang, J.J.; Ye, B.; Zhou, N.; Zhang, X.L. Decoupling analysis and environmental Kuznets curve modelling of provincial-level CO2 emissions and economic growth in China: A case study. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 212, 1242–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Peng, H.; Temulun, T.; Liu, L.Q.; Mao, J.; Lu, Z.N.; Chen, H. How harmful is air pollution to economic development? New evidence from PM2.5 concentrations of Chinese cities. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 743–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.L.; Wang, Y.; Zuo, J.; Jiang, H.Q.; Huang, D.C.; Rameezdeen, R. Characteristics of public concern on haze in China and its relationship with air quality in urban areas. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 637–638, 1597–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, K.E. Chicago residents’ perceptions of air quality: Objective pollution, the built environment, and neighborhood stigma theory. Population and Environment 2015, 37, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Power, M.C.; Kioumourtzoglou, M.A.; Hart, J.E.; Okereke, O.I.; Laden, F.; Weisskopf, M.G. The relation between past exposure to fine particulate air pollutant and prevalent anxiety: Observational cohort study. BMJ 2015, 350, h1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, H.B.; Li, Q.; Chen, J.; Liu, S.; Ma, Z.Y. Government trust, environmental pollution perception, and environmental governance satisfaction. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 9929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Science, 2nd ed.; Lawrence Erlbaum Associates: Hillsdale, NJ, USA, 1988; pp. 407–415. [Google Scholar]
- Pu, S.; Shao, Z.J.; Fang, M.R.; Yang, L.; Liu, R.Y.; Bi, J.; Ma, Z.W. Spatial distribution of the public’s risk perception for air pollution: A nationwide study in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 655, 454–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brody, S.D.; Peck, B.M.; Highfield, W.E. Examining localized patterns of air quality perception in Texas: A spatial and statistical analysis. Risk Anal. 2004, 24, 1561–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.J.; Bian, Q.; Mao, Q.D. How can internet use and environmental risk perception encourage pro-environmental behaviors? The mediating role of government performance perception. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2022, 31, 5621–5631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X. Factors influencing the environmental satisfaction of local residents in the coal mining area, China. Soc. Indic. Res. 2015, 120, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Li, X.; Chen, X.; Zhang, L. Objective air quality index versus subjective perception: Which has a greater impact on life satisfaction? Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2022, 24, 6860–6877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, D.J. Public attitudes on environment, energy and the economy-implications for policy. Environ. 1981, 1, 187–195. [Google Scholar]
- Wallner, A.; Hunziker, M.; Kienast, F. Do natural science experiments influence public attitudes towards environmental problems? Glob. Environ. Change 2003, 13, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.L.; Shen, L.W.; Li, Y.W.; Li, Y. The impact of environmental information disclosure on environmental governance satisfaction. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Huang, Y.X.; Wang, K.M. How do environmental concerns and governance performance affect public environmental participation: A case study of waste sorting in urban China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 9947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bickerstaff, K.; Walker, G. The place(s) of matter: Matter out of place-public understandings of air pollution. Prog. Hum. Geogr. 2003, 27, 45–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).