Abstract
Against the backdrop of intensified global warming, extreme weather events such as dense fog, low visibility, heavy precipitation, and extreme temperatures have been increased and enhanced to a great extent. They are likely to pose severe threats to the operation of urban transportation and associated services, which has drawn much attention in recent decades. However, there are still plenty of issues to be resolved in improving the emergency meteorological services and developing targeted urban transportation meteorological services in modern cities. The present review briefly illustrates the current cutting-edge developments and trends in the field of urban transportation meteorology in China, including the establishment of observation networks and experiments and the development of early warning and prediction technologies, as well as the related meteorological commercial services. Meanwhile, reflections and discussions are provided in terms of the state-of-the-art observation channels and methods and the application of numerical model forecasts and artificial intelligence. With the advantages of various advanced technologies from multiple aspects, researchers could further expand explorations on urban transportation meteorological observations, forecasts, early warnings, and services. Associated theoretical studies and practical investigations are also to be carried out to provide solid scientific foundations for urban transportation disaster prevention and mitigation, for implementing the action of meteorological guarantees, and for the construction of a high-quality smart society.
Keywords:
urban meteorology; transportation meteorology; observation; forecast; early warning; review; China 1. Introduction
In the context of the accelerated development of state-of-the-art information technologies, the smart city is a new urban development model that fully utilizes cloud computing, Internet of Things, and other innovative technological means to make intelligent responses to various demands for public services, social management, industrial operations, and other activities [1]. Transportation is one of the basic and strategic industries of the national economy in China, providing crucial support for cities’ sustainable development [2]. Therefore, smart transportation is considered a priority area for the construction of smart cities and smart countries, of which the meteorological service is an inseparable part [3].
In fact, meteorology is one of the key factors affecting the safety and operation of urban transportation [4]. Taking China as an example, frequently occurring weather disasters tend to induce serious traffic accidents or blockages and to causes damage to traffic facilities. This is likely to generate severe threats to the safety and property of humans, as well as social and economic development. Meanwhile, changes in meteorological conditions would have an impact on the vehicle itself, the road conditions, the driver’s judgment, and their responsiveness in the driving process, as well as the vehicle’s interior environment. Moreover, different meteorological conditions may have different impacts on transportation. Compared with highways, although urban transportation is characterized by generally lower speeds of vehicles, it is confronted with a larger flow, more pedestrians, and more complex road conditions. Therefore, the impacts of meteorological conditions on urban roads and vehicle travel, as well as other traffic channels such as subways, are still significant and should not be ignored.
For instance, on 21 July 2012, Beijing suffered one of the most severe rainstorms in local history [5], causing the urban transportation system to be almost paralyzed. In total, 95 roads in the urban area were cut off due to the heavy precipitation. Severe waterlogging and circuit breakage brought huge losses to the citizens’ lives and property, with at least 79 deaths and 1.84 billion dollars in economic losses [6]. More recently, in 2021, the Zhengzhou 7·20 (20 July) torrential rain event registered a record hourly precipitation rate of 201.9 mm and the 24-h precipitation reached 624.1 mm [7]. The disaster led to serious water accumulation in the Wulongkou Parking Lot of Zhengzhou Metro Line 5 and the surrounding area, causing one metro operating train to stop in the section ahead of this and resulting in the deaths of 14 passengers. Moreover, a number of facilities and equipment were damaged, and the entire network of the Zhengzhou subway was forced to shut down for more than 50 days. Therefore, it is certainly necessary to carry out real-time monitoring, early warning, and forecasting studies and focus on the services of urban transportation meteorology. Effective predictions of the meteorological impacts on urban transportation contribute to the development of effective measures of transportation management regarding safety and smoothness, disaster prevention, and impact mitigation in advance.
From the perspective of national policies, taking China as an example, the China Meteorological Administration (CMA) released the “Action Plan for the Development of Smart Meteorological Services (2019–2023)” in 2018 [8], making “the demonstration of smart traffic meteorological services” one of the key assignments to adapt to the high-quality construction of meteorological modernization and to improve the intelligence of meteorological services. In terms of the urban transportation meteorology, further integrations of road monitoring, intelligent grid forecasts, traffic management, map navigation, and other associated elements are required to establish impact-based urban transportation meteorological service models and indicators. On this basis, the business capability could be improved to identify the risks of road sections and transportation safety levels affected by severe weather.
Subsequently, in November 2021, the CMA, together with the China Ministry of Public Security, the China Ministry of Transport, the China State Railway Administration, and the China State Post Bureau, jointly formulated the “14th Five-Year Plan for Transportation Meteorological Safeguard” [9]. It points out the current state, where (1) the construction of a transportation meteorological monitoring station network has been taking shape; (2) the business services of transportation meteorological forecasting and early warning are developing rapidly, and (3) the cooperation mechanisms among multiple departments have been basically formed. However, there are still issues waiting to be resolved, such as (1) the pertinence of the transportation meteorological service needs to be strengthened and (2) the information fusion of transportation and meteorology has not yet been analyzed in depth. Correspondingly, the goals of (1) developing digital transportation meteorological forecast products based on intelligent grid forecasts and (2) developing technologies for transportation meteorological forecasting and early warning are proposed to promote transportation meteorology innovation and to create a high-quality transportation meteorological service system.
Moreover, in May 2022, to optimize the supply of high-quality meteorological services for the social economy, the China State Council issued the “Outlines for High-quality Meteorological Development (2022–2035)” [10], which specifically refines the important role of the meteorological service in the transportation industry, especially in the urban area. It requires the further implementation of a meteorological safeguard for the construction of a strong transportation system; the exploration of a modern, comprehensive transportation meteorological service platform; the strengthening of the transportation meteorological monitoring, forecasting, and early warning capabilities, and finally the construction of a smart system of urban transportation meteorological services.
In recent decades, with the rapid development of the social economy and urbanization, the rising demand for urban meteorological services has posed new challenges for professional meteorological fields. It is also expected to accelerate the deepening and expanding processes of these fields, such as urban transportation meteorology. In fact, in the context of intensified global warming, extreme meteorological events occur from time to time and are likely to become increasingly frequent, including dense fog, low visibility, heavy precipitation, extreme temperatures, and other analogous phenomena [11,12,13,14], which pose severe threats to the operation of urban transportation and associated services. Currently, there are still many issues to be resolved in improving the emergency meteorological services and developing targeted urban transportation meteorological services in modern cities. The study of urban transportation meteorological monitoring, early warning, and forecasting is of great scientific significance and application value in dealing with weather disasters, the rational planning of urban facilities, and the improvement of urban operating quality.
The present paper briefly reviews the current cutting-edge developments and trends in the field of urban transportation meteorology, especially in China, including the establishment of observation networks and experiments in Section 2 and the development of early warning and prediction technologies in Section 3. Meanwhile, Section 4 describes the related meteorological commercial services. Finally, reflections and discussions are provided in Section 5 in terms of the state-of-the-art observation channels and methods, the application of numerical model forecasts, and artificial intelligence. These are to contribute to a scientific basis and reference towards the operational urban transportation meteorological safeguard and urban transportation disaster prevention and mitigation in China.
2. Urban Transportation Meteorological Observation
2.1. Urban Meteorological Observation Network
Since the beginning of the 21st century, European and American countries, as well as Japan, have carried out meteorological observation experiments for urban areas. Among them, short-term observation experiments on various factors, such as near-surface turbulence, the vertical structure of the urban boundary layer, and the traceability and dispersion of air pollution are mostly implemented for periods of within one year. Selected examples are provided in Table 1 and are briefly described in the following paragraphs. On the other hand, there are also several long-term observation experiments lasting for longer than this (Table 2). Such observations are effectively utilized not only to reveal the characteristics of the urban atmosphere but also to validate and promote the development of numerical models. Various data based on these urban observation networks could be produced for research institutions and the public.

Table 1.
Short-term urban meteorological observation experiments.

Table 2.
Long-term urban meteorological observation experiments.
In October 2000, the URBAN 2000 project [15] conducted several field experiments in Salt Lake City, which investigated the transportation and diffusion around a single downtown building, through the downtown area, and into the greater urban area. Moreover, meteorological measurements were conducted, including temperature and the 2D/3D wind field across the urban area. One mobile van was utilized to measure net radiation, sensible heat flux, and three levels of temperature to 18 m AGL. The project aims to evaluate and improve the hierarchy of atmospheric models being developed for simulating toxic agent dispersal from potential terrorist activities in urban environments. In the following Joint Urban 2003 project conducted in Oklahoma City [16], remote sensing instruments were used (radar profilers, lidars, sodars) to form a dense network. The network continuously measures the detailed wind and turbulence characteristics of the urban atmosphere from the ground through several kilometers above the ground, which lasts over one month. Another difference between URBAN 2000 and Joint Urban 2003 is that the former focuses on the urban nocturnal boundary layer (stable to neutral atmospheric conditions), while the latter focuses on the urban daytime boundary layer (neutral to unstable).
With a distinct perspective, the Pentagon Shield field program was implemented from 9 April to 16 May 2004 in Washington, D.C. [17]. It focuses on the effects of a single building (the Pentagon) on the flow field, chemical tracer transport, and dispersion. A unique aspect is the use of two higher-resolution scanning Doppler lidars with overlapping and synchronized scan patterns that work together, providing detailed data with 100-m resolution. Moreover, the Madison Square Garden field experiment [18] in New York City addresses its goal in cities with tall skyscrapers. They found that the mean wind speed and direction on the tops of tall downtown buildings are approximately equal to those near the surface at a nearby airport, but the mean wind speed is three times larger than that at street level. The HEAT program [19], conducted in Houston, Texas during the summer of 2005, mainly collected electrical data from the National Lightning Detection Network and a lightning-mapping system (LDAR II), and atmospheric variables such as temperature, moisture, winds, and aerosol from balloon-borne soundings, tethered atmospheric observation systems, and wind profilers, as well as mobile sounding units, airborne instruments, and three Doppler radar devices.
Similar field observation experiments were conducted in France, the UK, Switzerland, and Japan. The ESCOMPTE program [20], conducted in the Marseilles-Berre area in the south of France during Summer 2001, covered an area of 120 × 120 km. By utilizing surface measurement networks, remote sensing, and ship-borne, balloon-borne, and airplane measurements, the mean standard meteorological parameters and turbulent fluxes, ozone, ozone precursors, photochemically active trace gases, and aerosols were measured, and a database was therefore established. The CAPITOUL experiment [21], in the city of Toulouse in Southwest France, was conducted for one year from February 2004. Focusing on the urban climate, it revealed that the urban surface energy balance differs between summer and winter, while the city impacts the boundary layer when an urban breeze is observed. Aiming at improving the understanding of the physical processes affecting the street- and neighborhood-scale flow of air, traffic, and people, the DAPPLE project [22] was conducted at the intersection of Marylebone Road and Gloucester Place, London, in 2003. Data included the mean and turbulent winds at the intersection, carbon monoxide and nitrogen dioxide, traffic flow and composition, as well as personal exposure measurements of PM2.5, ultrafine particle counts, etc.
With respect to the urban meteorological observation networks in China, they have been developed and generally matured in the three major urban clusters, i.e., Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei, the Yangtze River Delta, and the Pearl River Delta. In addition to aiding scientific research, these observation networks also effectively support the forecasts of urban meteorology and transportation meteorology, as well as the decision making of associated departments [31,32].
In the area of Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei, scientific experiments in the Study of Urban Impacts on Rainfall and Fog/Haze (SURF) were conducted during 2014–2019, among which there were three main observational experiments [33]. Two of them focused on the summer thunderstorm processes (July–August 2015 and July–September 2016) to study the effects of urbanization on precipitation-triggering mechanisms, movement, and intensity. The other experiment focused on the winter haze (November 2015–January 2016) to study aerosol sources and processes of transportation and transformation. In this area, 1992 automatic weather stations were utilized, and the meteorological data were collected every 5 min. Radiosondes were launched twice-daily at 0000 and 1200 UTC, with additional soundings at 0600 UTC during flood seasons at the Nanjiao site. Based on existing operational instruments, the planetary boundary layer network was augmented with 5 wind profilers, 1 scanning Doppler lidar, 2 aerosol micropulse lidar, and 10 ceilometers. The turbulent flux and associated meteorological data were collected at the towers in Beijing and Tianjin. Based on these combined observations, the hockey-stick transition turbulence–wind relationships over the urban canopies [34,35] have been confirmed, which describes the roles of non-local large coherent turbulence eddies during turbulence intensity and mean wind speed under near-neutral conditions.
As for the Yangtze River Delta region, an urban meteorological and environmental meteorological observation network has been formed, consisting of transportation meteorology, urban environmental meteorology, ecological meteorology, agricultural meteorology, marine meteorology, climate resources, drought monitoring, lightning monitoring, hydrometeorology, and some other specialized observation systems. Aiming at extensive urban meteorological observations for megacities, Shanghai has built a combined ground-based and space-based system named Shanghai’s Urban Integrated Meteorological Observation Network (SUIMON) [30]. By utilizing a dense observation network and various instrument types, the network collects wind, temperature, humidity, rain, and pressure every 1 min, and it has extended the observation to the vertical plane, thus providing a four-dimensional dataset of the area. A high frequency of severe convective precipitation events was found over the urban area and the mouth of the Yangtze River, which matches well with the spatial distribution of cloud-to-ground flash density. Suzhou has also constructed an urban heat island monitoring network for urban heat island-associated investigations. It was found that when the tree cover rate reached 40%, the daily average concentration of major air pollutants in the urban area decreases significantly [36]. In Hangzhou, a comprehensive detection system for compound atmospheric pollution has been established with a full range of detection items. Results show that the most recent decade of urban development in Hangzhou substantially reduced the atmospheric diffusion, and pollutant concentrations rose quickly in the urban area [37]. In Nanjing and Hefei, city-wide traffic visibility monitoring networks have been constructed for urban transportation meteorological services.
In the urban cluster of the Pearl River Delta, a comprehensive urban meteorological observation system has been developed, including a dense network of ground-based automatic stations, a variety of ground-based remote sensing equipment (e.g., wind profile radar, aerosol radar, and Doppler radar), a network of urban atmospheric composition monitoring stations, and a Global Positioning System/Meteorology (GPS/MET) water vapor monitoring network. Taking Shenzhen as an example, a generally complete urban meteorological disaster monitoring system has been formed since 1994, as well as a climate monitoring system [38]. Over the last few decades, the Shenzhen Urban Meteorological Observing Network (SUMON) has been developed comprehensively, with its spatial and temporal resolutions reaching 3.5 km and 1 min, respectively.
In addition, the meteorological observation towers also provide important support in the study of urban boundary layer physics and the atmospheric environment, as well as in the observation and monitoring of transportation meteorological-related elements. For instance, the 325-m flux tower (39°58′ N, 116°22′ E) at the Institute of Atmospheric Physics in Beijing, the 255-m flux tower (39°06′ N, 117°10′ E) at the Tianjin Meteorological Service in Tianjin, and the 356-m flux tower (22°40′ N, 113°54′ E) at the Shiyan Meteorological Observatory in Shenzhen provide diversified and solid foundations for local urban meteorological observations [39,40,41]. Databases of turbulent and gradient wind, temperature, and humidity are obtained at different layers, favoring more comprehensive studies of turbulent statistic characteristics and turbulent fluxes over the urban areas, as well as their synoptic and climatological features [42,43,44].
In recent years, via ground-based remote sensing techniques including wind profilers, microwave radiometers, and laser lidar, etc., three-dimensional observations of atmospheric temperature, humidity, wind field, water condensate, and aerosol have been well observed to enrich the local urban observation networks in several megacities and to further enhance the usage of these thermal and dynamic factors in numerical models [45]. Moreover, it is suggested that the effective combination of this equipment would help to obtain atmospheric profiles with higher spatial and temporal resolutions, which is also to be further developed in the future.
In general, during the construction of urban meteorological observation networks such as the abovementioned ones, the characteristics and development directions have been proposed to include five aspects [30]: multiple platforms, multiple variables, multiple scales, multiple linkages, and multiple functions. Detailed information is provided in Figure 1. In simple terms, the multiple platforms detecting multiple variables and considering multiple scales are to compose the comprehensive observation network via multiple linkages, which ultimately serve the users with multiple functions.
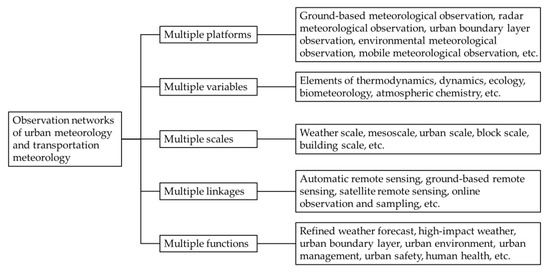
Figure 1.
Characteristics and development directions of urban transportation meteorological observation network.
2.2. Urban Meteorological Outfield Observation Experiments
From the end of the last century to the beginning of this century, a series of large-scale outfield observation experiments have been successfully explored throughout the world, focusing on plenty of topics, among which the urban boundary layer meteorology and urban air pollution are two important and popular aspects [46]. In Beijing, China, the Beijing City Atmospheric Pollution Observation Field Experiment (BECAPEX, 2001–2003) and the Beijing Urban Boundary Layer Experiment (BUBLEX, 2004–2005) have been implemented to obtain three-dimensional structure integrated images of Beijing’s atmospheric dynamics and chemical process [47]. More details have also been included, such as urban observations of the boundary layer, rainstorm adaptability, complex terrain and atmospheric circulation, flux and energy balance, as well as the urban thermal environment [48]. Associated studies have revealed that the air pollution in Beijing usually comes from local sources, but the sources in the vicinity also have a prominent influence [49]. Nanjing City has also carried out several experiments (e.g., periods in 2004 and 2006) with urban boundary layer observations to investigate the urban mixed layer, convective entrainment zone, and cloud feedback processes via LIDAR (Light Detection and Ranging), radiosonde, meteorological towers, turbulence measurements, and many other techniques [50,51,52], based on which the transition features of the mixed layer and the entrainment zone over Nanjing City have been revealed by comparison between urban and suburban areas. During the past decade, the urban meteorological observation experiments have been mainly focused on the research of high-impact weather mechanisms and their mitigation countermeasures, on the urban effects on weather and climate, and on the mutual feedback between urban aerosols and weather climate [53]. Meanwhile, the observation scope has been expanded from a single city in the past to multiple cities (city clusters and metropolitan areas) nowadays. These investigations could assist cities in facing, detecting, and discussing hazards such as storm surges, flooding, heatwaves, and air pollution episodes, especially in the changing climate.
There are also downscaling outfield experiments conducted. For instance, Sun Yat-sen University carried out an urban climate experiment in 2016–2017 in the suburbs of Guangzhou on a reduced scale [54]. The experimental site covered an area of 4800 m2, which was far from surrounding buildings and had an impermeable surface. Two ideal street valley models were composed of roughly 2000 concrete building models, each with a height of 1.2 m, a width of 0.5 m, and a wall thickness of 1.5 cm. The effects of building heat capacities and street aspect ratios on the turbulence and temperature spatiotemporal characteristics of two-dimensional street valleys were investigated through outfield experiments under the typical non-stationary real meteorological conditions.
Moreover, through these outfield experiments on urban and transportation meteorology, the associated air pollution and source emission regarding PM2.5, CO, SO2, O3, and even various heavy metals were also analyzed to investigate their spatial and temporal distributions and developing trends [55,56]. Studies have also revealed that, in winter, volatile organic compounds (VOCs) including benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene, and xylene (BTEX) could mainly be attributed to urban transportation, posing hazards for human health [57,58]. At the same time, corresponding assessments of health risks related to human exposure to urban transportation pollution and emissions are also currently under investigation using the databases from multiple experiments [59,60].
2.3. Urban Transportation Meteorological Monitoring System
Since the 1980s, the Standing International Road Weather Commission (SIRWEC) has been established worldwide by several countries to carry out studies on winter road weather predictions, winter road treatment methods, the Road Weather Information System (RWIS), and the Intelligent Transportation System (ITS). The frequent information exchange and technology sharing among members have promoted the development of urban transportation meteorology to a great extent in various countries [61].
In China, transportation meteorological monitoring mainly started in 2005, which is relatively late compared to developed countries [62]. At the early stage, it mostly focused on the highways outside of cities, while less attention has been paid to urban transportation [63,64]. At present, meteorological monitoring along urban transportation lines is being vigorously developed, and automatic meteorological monitoring stations have been deployed along the major roads. However, such monitoring equipment arrangements are still not sufficient; they are unevenly distributed, with little coverage in many provinces, especially in mountainous areas [65]. There is currently an urgent requirement to further increase and construct urban transportation meteorological stations [66].
In addition, remote sensing techniques have been widely used and have allowed effective progress in urban transportation meteorological monitoring applications due to the improvement in quantification precision, wide monitoring range, fast update time, and relatively low cost [67]. For instance, the unmanned aerial vehicle for remote sensing has such advantages as real-time measurement (wireless communication transmission), flexibility (fixed or mobile stations), high resolution (horizontally 3–5 m and vertically ~1 m), cost-effectiveness, etc., and can gather information in dangerous environments without any risk to flight crews, providing a powerful supplement for spaceborne remote sensing and airborne remote sensing [68]. Such technology has been increasingly used in obtaining spatial data, e.g., the conventional meteorological elements and urban transportation flow [69,70]. These improvements provide fundamental support for the implementation of the real-time monitoring of roads [71].
On the other hand, the usage of Internet of Things technology, which transmits data among multiple pieces of equipment via the internet in near-real time, provides an effective channel for the combination of meteorological information and urban transportation derived from multiple sensors [72,73,74]. By means of the automatic and timely communication between different equipment, it has generally realized the construction of urban transportation meteorological monitoring frameworks and plays a crucial role in the business operation of transportation management and emergency management [75,76]. Taking the Beijing Municipal Commission of Transportation as an example, based on the project titled “The internet of things application demonstration project of maintaining road traffic unblocked in extreme meteorological conditions”, under the framework of the first batch of Internet of Things projects in Beijing, the meteorological information obtained by meteorological sensors is combined with transportation information, with schemes of prediction and early warning proposed regarding the depth of waterlogging, snow cover, ice formation, visibility, and others [77]. It has been successfully attempted and plays an important role in road transportation management under complex weather conditions [78]. Moreover, the Wuxi Meteorological Bureau of Jiangsu Province has also deployed Internet of Things-based urban waterlogging monitoring stations at some specific locations on main traffic roads [79]. Subsequently, a system of urban waterlogging monitoring and early warning has been constructed, realizing the automated, digitalized, and refined real-time online management of urban transportation meteorological conditions, especially the waterlogging risk [80].
With respect to rail-based urban transportation, based on sufficient experience in event prevention and emergency disposal, the Shanghai Urban Rail Transportation and Shanghai Meteorological Service Center jointly developed the Shanghai Rail Transportation Meteorological Assistant Decision-Making System in 2020, using the basic geographic data, observations, and monitoring information of local automatic weather stations within the Shanghai Meteorological Bureau. The real-time monitoring and risk warning of urban transportation meteorological disasters, as well as other functions, are therefore achieved [81]. In general, the system mainly consists of six main sections: a central map, risk warning, weather forecasts, impact, early warning information, and extreme weather statistics. By adopting technologically advanced monitoring methods and obtaining timely and effective early warning information, the meteorological risks of rail-based urban transportation could be “moved forward”, building a solid foundation for improved operational urban rail transportation safety.
3. Urban Transportation Meteorological Early Warning and Forecast
The early warning and forecasting of urban transportation meteorology is closely related to the development of urban smart transportation, transportation planning, city management, and the improvement of citizen life. Previous studies [82] have pointed out that the existing issues needing to be addressed for the user mainly include street and channel wind speeds, precipitation and its phase state, road surface conditions, surface observation representativeness, refined forecasting (e.g., at the road scale), road surface temperature and visibility etc. In recent years, researchers have conducted diverse investigations on urban transportation meteorology in the field of smart cities based on a variety of statistical analysis techniques.
Silva et al. [83] pointed out that a precise weather forecast is one of the most crucial aspects in urban transportation and smart city big data analysis, which provides the underlying design basis for safe construction and production and stable system operation. Lu et al. [84] proposed to collect and analyze severe weather data reported on social media, and to use regression-based early warning models to estimate the urban transportation conditions. This could assist in urban transportation perception, forecasting, early warning, and decision-making, with intuitive visualization solutions. Wessel [85] statistically analyzes the impact of different weather phenomena on the cycling population, including not only the real-time weather conditions but also weather forecasts, especially regarding cloud, rainfall, snow, and thunderstorms, etc. They have a variety of leading or lagging impacts on the number of cyclists, which could be analyzed and obtained via statistical methodologies. The corresponding results could be beneficial for the formulation and promotion of policies in urban transportation planning and civilization construction. Taking the factors of seasons and weekday/non-working days into consideration, Simunek and Smutny [86] have established a transportation speed prediction conceptual model for lead times of within 1 week, combining meteorological elements such as air temperature, wind direction, wind speed, humidity, air pressure, and cloud cover, etc. It enriches the high-quality prediction of the urban transportation information, and it especially has a significant improvement effect on the estimation of arrival times and could aid the intelligent transportation system and urban transportation prediction.
Currently, artificial intelligence theories such as machine learning are flourishing, which brings not only new opportunities but also challenges to the field of urban transportation meteorology. Researchers are also trying to adopt relevant theories and techniques to explore the laws behind various meteorological phenomena [87]. In particular, deep learning models, with their high robustness and strong nonlinearity, have been widely used in the field of meteorological forecasting, including extrapolation forecasting of elements such as temperature and precipitation, multivariate statistical forecast modeling, and numerical model product applications, and also in urban transportation meteorological early warning and forecasting [88,89,90]. Some cases for nowcasting and predictions of short-term and even longer timescales are provided as follows.
For nowcasting and short-term urban transportation meteorological predictions, Jia et al. [91] introduced the precipitation factor into the deep neural network and Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) methods, achieving a more accurate prediction of urban transportation flow than the raw deep learning networks. Nagy and Simon [92] have also demonstrated that both weather forecasts and their seasonal effects have important impacts on the prediction of urban transportation. Intelligent integrations of various temporal and spatial elements, such as weather, season, weekday/non-weekday, random events, and road conditions, could effectively improve the prediction of nonlinear transportation flows via deep learning frameworks such as the convolutional neural network (CNN) and LSTM. On this basis, Lee and Min [93] have constructed a Long Short-Term Memory Recurrent Neural Network (LSTM-RNN) model for urban transportation prediction using hourly observations and forecasts of temperature and precipitation, as well as the characteristics of urban activities affecting transportation operations. The model has been attempted and examined in Seoul, South Korea, and is demonstrated to be effective in improving the accuracy of urban transportation prediction. Moreover, Ali et al. [94] successfully established a deep hybrid neural network prediction model for urban transportation flow by using weather reality and forecasts as external factors affecting urban transportation flow, together with the spatiotemporal characteristics of daily urban transportation. Deb et al. [95] made full use of various deep learning methods to statistically analyze the time series correlations between weather status changes and transportation congestion magnitudes, and afterwards they conducted prediction experiments on transportation congestion by using regression analysis on the weather factors, which hence effectively improved the prediction ability regarding the urban transportation time. Based on the four situational factors of weather, season, weekday/non-weekday, and holiday/non-holiday, Ma et al. [96] constructed a daily urban transportation flow prediction model with a convolutional recurrent neural network and experimentally demonstrated the effectiveness and stability of the established scheme. Considering the nonlinear characteristics of traffic flow and the complex spatiotemporal correlations between transportation and weather, Nigam and Srivastava [97] defined a soft time threshold to capture the long-term impact of weather elements on transportation flow and proposed a hybrid CNN-LSTM model, which is capable of efficiently learning and predicting the transportation speed and flow issues in smart transportation operation and management. Tukymbekov et al. [98,99] designed an intelligent autonomous street light system based on the LSTM network using forecasts of weather and solar radiation, achieving the adaptive adjustment of the lighting system to effectively reduce energy consumption and serving urban transportation in a stable and safe manner. Moreover, with a weather-based transportation analysis method, Nasser and Simon [100] studied the relationship between transportation flow and weather factors at different frequencies and time intervals. It helps to reasonably determine and estimate the transportation flow under different meteorological conditions and to develop intelligent urban transportation systems in the construction of smart cities.
In addition, at longer timescales, based on urban transportation networks, social statistics, human flow data, and calendar data, as well as meteorological elements such as rainfall, snow, temperature, wind, etc., Zhou [101] simulated the correlation between the abovementioned factors and transportation events through deep learning algorithms, which helps to predict the frequency of possible accidents with cross-domain datasets and contributes to emergency management and decision-making in relevant departments. Furthermore, Ryu et al. [102] have constructed a time- and weather-aware deep learning neural network model with multiple modules using refined weather forecasts. It produces generally reliable and comprehensive long-term urban transportation condition predictions and effectively facilitates long-term urban transportation planning and management.
4. Commercial Services of Urban Transportation Meteorology
In the early 20th century, commercial meteorological services began to emerge worldwide and have been well developed, such as the numerical forecasts of the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts [103,104], the marine meteorological navigation of the United States, the aviation meteorological services of Japan and New Zealand, and the transportation meteorological services of the United Kingdom and Finland [105,106]. At the beginning of the 21st century, several countries, including the United States, the United Kingdom, Germany, the Netherlands, Japan, and Singapore, etc., had already carried out the practice of smart transportation in the construction of smart cities and achieved practical success [107,108]. In October 2011, the United States National Weather Service of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration installed multifunctional sensors on over 2000 passenger buses in New York. As the bus moves, data on temperature, humidity, and light levels can be collected every 10 s along the route, which are then immediately transmitted back to the National Weather Service center. Afterwards, the center integrates the collected meteorological, geographic, and many other types of data with official surveys. The natural disaster data network is also merged to capture the keys, to generate early warning system information, and to provide transportation meteorological services [109]. In 2014, Chicago launched the installation of street light sensors to collect urban pavement information and to detect meteorological data on temperature and wind. Using Internet of Things technology, all these sources are digitally connected, detected, analyzed, and integrated to allow the practical application of the intelligent transportation concept and to contribute to the construction and development of smart cities [110]. To date, a number of states in the United States have successively established regional transportation meteorological monitoring and forecasting systems, which provide real-time forecasts on transportation factors such as pavement temperature according to their respective road conditions [111,112].
As for China, in recent years, with the progress of meteorological monitoring, early warning and forecasting systems, as well as the rapid development of transportation-associated construction, the meteorological department has developed rapidly in terms of the research and application of transportation meteorological business [113]. In fact, according to the Chinese Ministry of Public Security’s statistics, severe weather conditions account for nearly 40% of transportation accidents and roughly 65% of direct economic losses [114,115]. The CMA officially carried out a survey on the hidden risks of transportation meteorological hazards in 31 provinces during 2013–2015 by means of questionnaire distribution, on-the-spot investigation, and expert evaluation [116]. After quality control, a nationwide transportation meteorological disaster risk census database was then constructed, containing geographic information associated with hidden risks, meteorological information for observation, early warning, and prediction, accident information on transportation under certain disaster conditions, etc., favoring the establishment of a corresponding business system for early warning and forecasting [117]. Combining automation and human–computer interaction, transportation meteorological disaster early warning service products focusing on four high-impact meteorological elements, including low visibility, strong wind, heavy precipitation, and freezing rain and snow, would be generated for lead times of 3 days [118,119].
Moreover, meteorological departments and commercial companies in various provinces have also cooperated with transportation departments to jointly carry out research and development on a series of specific service products and platforms. For instance, the Key Laboratory of Transportation Meteorology of the China Meteorological Administration and the Nanjing Joint Institute for Atmospheric Sciences (formerly known as the Jiangsu Institute of Meteorological Sciences) have conducted investigations on the establishment of a transportation meteorological information service system and on the distributed transportation meteorological information sharing technology based on a web service, which is an early practice in smart city construction [120]. The Hebei Meteorological Service Center has also carried out research on data quality control methods for the monitoring of transportation conditions in Hebei Province, which provides accuracy assessments for the local transportation meteorological service business [121]. In Guangdong Province, Foshan has actively set up a large database of transportation meteorology, which integrates multi-source data to monitor the whole transportation flow and to optimize the route plan system [122]. From a broader perspective, the CMA Public Meteorological Service Center, the Huafeng Meteorological Media Group, and some other departments have also focused on transportation meteorology, including monitoring data fusion, road inversion algorithms, applied meteorological forecasting, as well as service system construction, and have achieved great progress [123]. A corresponding transportation meteorological service system platform combining information on transportation and meteorology is therefore established for decision-making and for specific users from multiple fields of traffic management, map navigation, logistics distribution, autopilot, Internet of Vehicles, vehicle–road collaboration, and many others [124,125].
Beijing, as the center of China from many perspectives, including culture, science, education, and international communication, has developed a generally complete framework for urban transportation meteorological services. The Beijing Municipal Commission of Transport and the Beijing Meteorological Bureau have cooperated closely to provide professional, refined, and targeted transportation meteorological services for associated departments, enterprises, and the public based on the intelligent grid forecast system [126]. They mainly focus on the safe operation of meteorological safeguard services through the development of professional meteorological monitoring and specific forecast products, as well as the construction of multifunctional service platforms. In addition, according to the demand of the Beijing Traffic Management Bureau for guiding and maintaining the transportation order on the city’s roads, it is critical to determine and release the road closure standards when visibility levels of less than 50 m are observed [127]. However, the current refined monitoring techniques cannot reach this criterion; thus, they need to be further strengthened at the later stage of research and development, especially in the application of technologies such as real-time remote sensing and image recognition [128].
From a broader perspective, such as a national one, documents from multiple departments have proposed the task of developing smart transportation meteorological service demonstration [129,130]. In practical procedures, based on the vigorous development of artificial intelligence and computer technology, the role of deep learning algorithms such as deep neural networks is becoming increasingly prominent in urban transportation meteorological services, such as real-time monitoring and early warning systems [9]. In general, the implementation of deep learning in smart urban transportation meteorology could be separated mainly into three steps/subsystems: (1) data collection, storage, and query; (2) construction of an intelligent recognition algorithm; and (3) identification of the urban transportation meteorological risk. Corresponding measures are further described in detail in Figure 2.
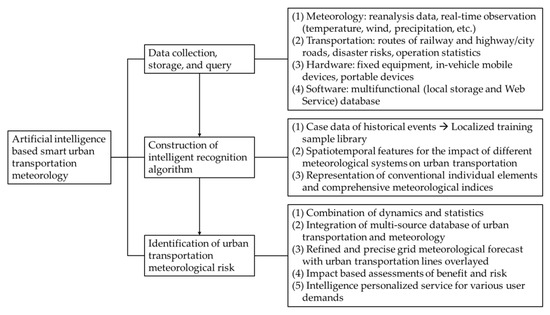
Figure 2.
Detailed procedures of artificial intelligence-based smart urban transportation meteorology system.
5. Discussion
In the present era, a new round of scientific and technological revolution and industrial change is accelerating worldwide, in addition to Chinese social and economic development. It brings new strategic opportunities to the regional construction of urban transportation. With the construction progress of smart cities and modern transportation, targeted transportation meteorological monitoring, forecasting, and early warning systems are significantly ameliorating the problems of urban road resource shortages and traffic congestion, playing an important role in the construction of smart urban transportation. Nevertheless, in the context of intensified global warming, extreme meteorological events are becoming increasingly frequent, including dense fog, low visibility, heavy precipitation, extreme temperatures, and other analogous phenomena, which pose severe threats to the operation of urban transportation and associated services [131]. It has drawn much attention in recent decades, and there are still plenty of issues to be resolved in improving the emergency meteorological services and developing targeted urban transportation meteorological services in modern cities. These involve the research, development, and transformation of a new generation of meteorological service systems, but also cooperation among multiple departments and their own internal business adjustments.
In brief, the in-depth development of urban transportation meteorological services and the corresponding advancement of both theoretical and technological explorations are of great significance to improve the construction of smart cities and modern transportation. Hence, the following perceptions and discussions are to be proposed based on the above review and analyses.
- (1)
- With the rapid development of observation facilities and methodologies, equipment such as radar, satellite, microwave radiometers, unmanned aerial vehicles, and mobile observations would further enrich the existing urban transportation meteorological observation system. The in-depth and effective integration of multi-source observations is favorable to establish a more comprehensive and more reliable urban transportation meteorological observation big data system with higher spatial and temporal resolutions. This would help to further reveal the spatiotemporal distribution and variation characteristics of urban transportation meteorology-associated factors and to provide solid support with a database for more accurate and effective forecasts and early warnings.
- (2)
- Thus far, numerical weather prediction models have become the most important tool for meteorological forecasts around the world, which discretize the dynamical and physical equations of the atmosphere. Increasingly, operational business agencies have begun to develop a series of global numerical models with high spatial and temporal resolutions, generating more complete forecast systems. In this context, the quality of numerical forecast products has been continuously improved, with the product sources also being continuously expanded. However, their applications in the field of transportation meteorology, especially urban transportation meteorology, are still relatively lacking. The corresponding refinement and postprocessing of the model outputs are important scientific and technical issues that need to be investigated.
- (3)
- Along with the recent advancement of machine learning, plenty of complex but efficient deep learning models (a branch of machine learning and artificial intelligence) are nowadays emerging in an endless stream and they have been considered as core technologies in many fields. However, many of them have not yet been timely and effectively applied in the field of meteorology, especially urban transportation meteorology, which needs extensive and in-depth experiments and analyses. At the same time, facing specific application scenarios such as urban transportation meteorology, it is always necessary to construct targeted, high-resolution meteorological observation datasets based on multi-source observation systems and collaborative observation experiments, which could give full play to the advantages of artificial intelligence’s nonlinearity in data modeling and generate more reasonable and more accurate urban transportation meteorological forecast and early warning products.
- (4)
- With regard to the different meteorological conditions and elements, they certainly tend to result in different impacts on urban transportation due to their different mechanisms of onset, development, and retreat. Respective research and development towards their optimal observation schemes, forecasts, and early warning technologies are necessary to predict the impacts of various meteorological conditions and complex weather events on all aspects of urban transportation in advance and to ultimately provide stable and reliable safeguarding services.
In summary, advances in meteorological observations and numerical models, as well as many other aspects, would bring great progress to urban transportation meteorology. Meanwhile, with the advantages of the vast range of data-driven statistical models and artificial intelligence frameworks, the urban transportation meteorological forecast and early warning system could also be continuously improved and optimized, providing a solid scientific foundation and high application value for the efficient prevention and mitigation of disasters and the high-quality construction of smart city transportation.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.Z., H.Y. and D.L.; validation, H.W. (Hongbin Wang), L.Z. (Linyi Zhou) and C.Z.; formal analysis, S.Z. and H.Y.; investigation, Y.L., Y.Z. and Y.F.; resources, H.W. (Hongbin Wang), Y.X., L.Z. (Ling Zhang) and X.Z.; data curation, F.Z. and H.W. (Hong Wu); writing—original draft preparation, S.Z. and H.Y.; writing—review and editing, D.L. and H.W. (Hongbin Wang). All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was jointly funded by the Basic Research Fund of the Chinese Academy of Meteorological Sciences (Grant Nos. 2022Y027 and 2021Y011), the research project of the Jiangsu Meteorological Bureau (Grant Nos. KQ202209 and KQ202114), the 333 Project of Jiangsu Province (Grant No. BRA2018420), the Beijing Foundation of NJIAS (Grant Nos. BJG201906, BJG202104 and BJG202209) and the General Program of Key Science and Technology in Transportation, the Ministry of Transport (Grant Nos. 2018-MS4-102 and ZL-2018-04).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Belli, L.; Cilfone, A.; Davoli, L.; Ferrari, G.; Adorni, P.; Di Nocera, F.; Dall’Olio, A.; Pellegrini, C.; Mordacci, M.; Bertolotti, E. IoT-enabled smart sustainable cities: Challenges and approaches. Smart Cities 2020, 3, 1039–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Li, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Xu, X. Analysis of spatial associations in the energy–carbon emission efficiency of the transportation industry and its influencing factors: Evidence from China. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2022, 97, 106905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Li, X.; Cai, Y.; Lorenzo, B.; Fang, Y. Intelligent data transportation in smart cities: A spectrum-aware approach. IEEE/ACM Trans. Netw. 2018, 26, 2598–2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crevier, L.-P.; Delage, Y. METRo: A new model for road-condition forecasting in Canada. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2001, 40, 2026–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Liu, Y. The possible impact of urbanization on a heavy rainfall event in Beijing. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 8132–8143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Sun, J.; Xu, J.; Yang, S.; Zong, Z.; Chen, T.; Fang, C.; Sheng, J. Analysis and thinking on the extremes of the 21 July 2012 torrential rain in Beijing Part I: Observation and thinking. Meteorol. Mon. 2012, 38, 1255–1266. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yu, M.; Liang, X.; Xia, R.; Gao, Y.; Gao, X.; Yin, J. On the influences of urbanization on the extreme rainfall over Zhengzhou on 20 July 2021: A convection-permitting ensemble modeling study. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2022, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China Meteorological Administration. Action Plan for the Development of Smart Meteorological Services (2019–2023); China Meteorological Administration: Beijing, China, 2018.
- China Meteorological Administration; China Ministry of Public Security; China Ministry of Transport; China State Railway Administration; China State Post Bureau. The 14th Five-Year Plan for Transportation Meteorological Safeguard; China Meteorological Administration: Beijing, China, 2021.
- China State Council. Outlines for High-quality Meteorological Development (2022–2035); China State Council: Beijing, China, 2022.
- Ge, F.; Zhu, S.; Peng, T.; Zhao, Y.; Sielmann, F.; Fraedrich, K.; Zhi, X.; Liu, X.; Tang, W.; Ji, L. Risks of precipitation extremes over Southeast Asia: Does 1.5 °C or 2 °C global warming make a difference? Environ. Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 044015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Ge, F.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, L.; Sielmann, F.; Fraedrich, K.; Zhi, X. Conspicuous temperature extremes over Southeast Asia: Seasonal variations under 1.5 °C and 2 °C global warming. Clim. Chang. 2020, 160, 343–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Ge, F.; Sielmann, F.; Pan, M.; Fraedrich, K.; Remedio, A.R.C.; Sein, D.V.; Jacob, D.; Wang, H.; Zhi, X. Seasonal temperature response over the Indochina Peninsula to a worst-case high emission forcing: A study with the regionally coupled model ROM. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2020, 142, 613–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, F.; Zhu, S.; Luo, H.; Zhi, X.; Wang, H. Future changes in precipitation extremes over Southeast Asia: Insights from CMIP6 multi-model ensemble. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 24013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allwine, K.J.; Shinn, J.H.; Streit, G.E.; Clawson, K.L.; Brown, M. Overview of URBAN 2000. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2002, 83, 521–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allwine, K.J.; Leach, M.J.; Stockham, L.W.; Shinn, J.S.; Hosker, R.P.; Bowers, J.F.; Pace, J.C. Overview of Joint Urban 2003: An atmospheric dispersion study in Oklahoma City. In Proceedings of the Symposium on Planning, Nowcasting, and Forecasting in the Urban Zone, Seattle, WA, USA, 10–15 January 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Warner, T.; Benda, P.; Swerdlin, S.; Knievel, J.; Argenta, E.; Aronian, B.; Balsley, B.; Bowers, J.; Carter, R.; Clark, P.; et al. The Pentagon Shield Field Program: Toward Critical Infrastructure Protection. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2007, 88, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, S.; White, J.; Zhou, Y.; Kosheleva, A. Analysis of Joint Urban 2003 (JU2003) and Madison Square Garden 2005 (MSG05) Meteorological and Tracer Data. In Proceedings of the 6th Symposium on the Urban Environment, Atlanta, GA, USA, 27 January–3 February 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Orville, R.; Zhang, R.; Nielsen-Gammon, J.; Collins, D.; Ely, B.; Steiger, S. Houston Environmental Aerosol Thunderstorm (HEAT) Project; Texas A&M University Department of Atmospheric Sciences: College Station, TX, USA, 2004; p. 57. [Google Scholar]
- Cros, B.; Durand, P.; Cachier, H.; Drobinski, P.; Fréjafon, E.; Kottmeier, C.; Perros, P.; Peuch, V.-H.; Ponche, J.-L.; Robin, D.; et al. The ESCOMPTE program: An overview. Atmos. Res. 2004, 69, 241–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masson, V.; Gomes, L.; Pigeon, G.; Liousse, C.; Pont, V.; Lagouarde, J.P.; Voogt, J.; Salmond, J.; Oke, T.R.; Hidalgo, J.; et al. The Canopy and Aerosol Particles Interactions in TOulouse Urban Layer (CAPITOUL) experiment. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2008, 102, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, S.; ApSimon, H.; Barlow, J.; Belcher, S.; Bell, M.; Boddy, J.; Britter, R.; Cheng, H.; Clark, R.; Colvile, R.; et al. Introduction to the DAPPLE Air Pollution Project. Sci. Total Environ. 2004, 332, 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, R.M.; Dall’Osto, M.; Beddows, D.C.S.; Thorpe, A.J.; Bloss, W.J.; Allan, J.D.; Coe, H.; Dorsey, J.R.; Gallagher, M.; Martin, C.; et al. Atmospheric chemistry and physics in the atmosphere of a developed megacity (London): An overview of the REPARTEE experiment and its conclusions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 3065–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohnenstengel, S.I.; Belcher, S.E.; Aiken, A.; Allan, J.D.; Allen, G.; Bacak, A.; Bannan, T.J.; Barlow, J.F.; Beddows, D.C.S.; Bloss, W.J.; et al. Meteorology, Air Quality, and Health in London: The ClearfLo Project. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 96, 779–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotach, M.W.; Vogt, R.; Bernhofer, C.; Batchvarova, E.; Christen, A.; Clappier, A.; Feddersen, B.; Gryning, S.-E.; Martucci, G.; Mayer, H.; et al. BUBBLE—An urban boundary layer meteorology project. Arch. Meteorol. Geophys. Bioclimatol. Ser. B 2005, 81, 231–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakatani, T.; Misumi, R.; Shoji, Y.; Saito, K.; Seko, H.; Seino, N.; Suzuki, S.-I.; Shusse, Y.; Maesaka, T.; Sugawara, H. Tokyo metropolitan area convection study for extreme weather resilient cities. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 96, ES123–ES126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicks, B.B.; Callahan, W.J.; Pendergrass, W.R., III; Dobosy, R.J.; Novakovskaia, E. Urban turbulence in space and in time. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2012, 51, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koskinen, J.T.; Poutiainen, J.; Schultz, D.M.; Joffre, S.; Koistinen, J.; Saltikoff, E.; Gregow, E.; Turtiainen, H.; Dabberdt, W.F.; Damski, J.; et al. The Helsinki Testbed: A mesoscale measurement, research, and service platform. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 92, 325–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Takahashi, K.; Mikami, T.; Takahashi, H. Influence of the urban heat island phenomenon in Tokyo in land and sea breezes. In Proceedings of the Seventh International Conference on Urban Climate, Yokohama, Japan, 29 June–3 July 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, J.; Yang, L.; Grimmond, C.S.B.; Shi, J.; Gu, W.; Chang, Y.; Hu, P.; Sun, J.; Ao, X.; Han, Z. Urban integrated meteorological observations: Practice and experience in Shanghai, China. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 96, 85–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, S.; Jiang, W.; Liang, P.; Liu, H.; Wang, X.; Tan, J.; Zhang, N.; Li, J.; Du, W.; Pei, L. Advances in urban meteorological research in China. J. Meteorol. Res. 2020, 34, 218–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Dou, J.; Miao, S.; Chu, Y.; Sun, D. Advances of urban meteorological research: International conference on urban climate. Adv. Meteorol. Sci. Technol. 2019, 9, 16–22. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, X.; Miao, S.; Li, J.; Bornstein, R.; Zhang, X.; Gao, Y.; Chen, F.; Cao, X.; Cheng, Z.; Clements, C.; et al. SURF: Understanding and Predicting Urban Convection and Haze. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2018, 99, 1391–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Mahrt, L.; Banta, R.M.; Pichugina, Y.L. Turbulence regimes and turbulence intermittency in the stable boundary layer during CASES-99. J. Atmos. Sci. 2012, 69, 338–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Lenschow, D.H.; LeMone, M.A.; Mahrt, L. The role of large-coherent-eddy transport in the atmospheric surface layer based on CASES-99 Observations. Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 2016, 160, 83–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Liu, H.; Shen, J.; Ji, Y. Influence of urban heat island on pollution diffusion in Suzhou. Plateau Meteorol. 2016, 35, 1584–1594. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Ma, W.; Qian, J.; Cai, J.; Ye, X.; Li, J.; Wang, X. Effect of urbanization on the urban meteorology and air pollution in Hangzhou. J. Meteorol. Res. 2015, 29, 950–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Jiang, Y.; Zhuang, H.; Rao, H.; Tan, M. A brief introduction to Shenzhen urban meteorological observing network of networks. Adv. Meteorol. Sci. Technol. 2013, 3, 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, F.; Li, X.; Chen, H.; Liu, G. Turbulence characteristics in the rough urban canopy layer. Clim. Environ. Res. 1999, 3, 252–258. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, S.; Dou, J.; Chen, F.; Li, J.; Li, A. Analysis of observations on the urban surface energy balance in Beijing. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2012, 55, 1881–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Lu, C.; Chan, P.-W.; Zhang, X.; Yang, H.-L.; Lan, Z.-J.; Zhang, W.-H.; Liu, Y.-W.; Pan, L.; Zhang, L. Tower observed vertical distribution of PM2.5, O3 and NOx in the Pearl River Delta. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 220, 117083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, S.; Chen, F. Enhanced modeling of latent heat flux from urban surfaces in the Noah/single-layer urban canopy coupled model. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2014, 57, 2408–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Li, Y.; Han, S.; Wu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Li, C. Turbulent statistic characteristic of the urban boundary layer in Tianjin. Plateau Meteorol. 2011, 30, 1481–1487. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Y.; Wu, C.; Wu, D.; Liu, B.; Li, Y.J.; Sun, J.; Yang, H.; Mao, X.; Tan, J.; Xia, R.; et al. Vertical distributions of atmospheric black carbon in dry and wet seasons observed at a 356-m meteorological tower in Shenzhen, South China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 853, 158657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Mao, J.; Ji, C. Overview of ground-based remote sensing observation techniques for air temperature, humidity and wind profiles. Meteorol. Hydrol. Mar. Instrum. 2018, 35, 109–116. [Google Scholar]
- Grimmond, C.S.B. Progress in measuring and observing the urban atmosphere. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2006, 84, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Ding, G.; Bian, L.; Xie, L. Characteristics of atmospheric environment of boundary layer structure of city community in BECAPEX and integrate influence. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 2004, 5, 663–671. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Shu, W. Observation and analysis of nocturnal low-level jet characteristics over Beijing in summer. Chin. J. Geophys. 2008, 51, 360–368. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Dou, J. Progress in urban meteorological experiments in Beijing. Adv. Meteorol. Sci. Technol. 2014, 4, 36–45. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Jiang, W.; Sun, J.; Liu, G. An observation and analysis of the micrometeorological characteristics of the Nanjing urban boundary layer, eastern China. J. Nanjing Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2008, 1, 99–106. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, M.; Jiang, W.; Wu, X.; Qi, F.; Yuan, R.; Fang, H.; Liu, D.; Zhou, J. LIDAR exploring of the UBL in downtown of the Nanjing City. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2006, 26, 1723–1728. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, M.; Jiang, W.; Gu, J.; Xie, C.; Zhou, J. Study on the mixed layer, entrainment zone, and cloud feedback based on lidar exploration of Nanjing city. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baklanov, A.; Grimmond, C.; Carlson, D.; Terblanche, D.; Tang, X.; Bouchet, V.; Lee, B.; Langendijk, G.; Kolli, R.; Hovsepyan, A. From urban meteorology, climate and environment research to integrated city services. Urban Clim. 2018, 23, 330–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Wang, D.; Wang, Q.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Hang, J.; Gao, P.; Ou, C.; Wang, K. Scaled outdoor experimental studies of urban thermal environment in street canyon models with various aspect ratios and thermal storage. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 726, 138147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajizadeh, Y.; Jafari, N.; Fanaei, F.; Ghanbari, R.; Mohammadi, A.; Behnami, A.; Jafari, A.; Aghababayi, M.; Abdolahnejad, A. Spatial patterns and temporal variations of traffic-related air pollutants and estimating its health effects in Isfahan city, Iran. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2021, 19, 781–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleimani, A.; Toolabi, A.; Mansour, S.N.; Abdolahnejad, A.; Akther, T.; Fouladi-Fard, R.; Miri, M.; Mohammadi, A. Health risk assessment and spatial trend of metals in settled dust of surrounding areas of Lake Urmia, NW Iran. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2022, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojarrad, H.; Fard, R.F.; Rezaali, M.; Heidari, H.; Izanloo, H.; Mohammadbeigi, A.; Mohammadi, A.; Sorooshian, A. Spatial trends, health risk assessment and ozone formation potential linked to BTEX. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2019, 26, 2836–2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Bai, Y.; Zhi, X.; Wu, K.; Zhao, T.; Zhou, Y.; Xiong, J.; Zhu, S.; Zhou, W.; Hu, W.; et al. Two typical patterns of regional PM2.5 transport for heavy air pollution over Central China: Rapid transit transport and stationary accumulation transport. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtari, M.; Jafari, N.; Mohammadi, A.; Hajizadeh, Y.; Ghanbari, R.; Nemati, S.; Abdolahnejad, A. Temporal and spatial trends of airborne asbestos fiber concentrations in the urban areas of Yazd, Iran. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 16, 2657–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraji, M.; Mohammadi, A.; Najmi, M.; Fallahnezhad, M.; Sabetkish, N.; Kazemnejad, A.; Shoormasti, R.S.; Fazlollahi, M.R.; Pourpak, Z.; Moin, M. Exposure to ambient air pollution and prevalence of asthma in adults. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2021, 14, 1211–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, K.; Yang, J.; Zhang, H. Advance on highway traffic meteorological research in foreign country. J. Meteorol. Environ. 2019, 35, 79–86. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, C.; Wang, B. Advances in road weather forecasting system and its future development. J. Trop. Meteorol. 2007, 23, 652–658. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Lin, Z.; Cheng, T. Research progress on temperature prediction method for road icing. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2020, 20, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Telang, S.; Chel, A.; Nemade, A.; Kaushik, G. Intelligent Transport System for a Smart City. In Security and Privacy Applications for Smart City Development; Tamane, S.C., Dey, N., Hassanien, A.E., Eds.; Studies in Systems, Decision and Control; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; Volume 308. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Z.; Liu, Z.; Li, Y.; Jia, A.; Ye, R. Research on highway traffic meteorological monitoring system. Meteorol. Hydrol. Mar. Instrum. 2021, 38, 16–19. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, Y. On the system of road traffic’s meteorological monitoring and early warning based on GIS. J. Liaoning Police Coll. 2017, 19, 58–62. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Li, X.; Bao, Y.; Shao, Y. Research progress of remote sensing application on transportation meteorological disasters. Remote Sens. Land Resour. 2018, 30, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Shen, L.; Wang, H.; Lei, T. The research on unmanned aerial vehicle remote sensing and its applications. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Advanced Computer Control, Shenyang, China, 27–29 March 2010; pp. 644–647. [Google Scholar]
- Whitehead, K.; Hugenholtz, C.H.; Myshak, S.; Brown, O.; LeClair, A.; Tamminga, A.; Barchyn, T.E.; Moorman, B.; Eaton, B. Remote sensing of the environment with small unmanned aircraft systems (UASs), part 1: A review of progress and challenges. J. Unmanned Veh. Syst. 2014, 2, 69–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehead, K.; Hugenholtz, C.H.; Myshak, S.; Brown, O.; LeClair, A.; Tamminga, A.; Barchyn, T.E.; Moorman, B.; Eaton, B. Remote sensing of the environment with small unmanned aircraft systems (UASs), part 2: Scientific and commercial applications. J. Unmanned Veh. Syst. 2014, 2, 86–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barmpounakis, E.N.; Vlahogianni, E.I.; Golias, J.C. Unmanned Aerial Aircraft Systems for transportation engineering: Current practice and future challenges. Int. J. Transp. Sci. Technol. 2016, 5, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atzori, L.; Iera, A.; Morabito, G. The Internet of Things: A survey. Comput. Netw. 2010, 54, 2787–2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, L.; Muller, C.L.; Young, D.T.; Warren, E.; Grimmond, S.; Cai, X.-M.; Ferranti, E. The Birmingham urban climate laboratory: An open meteorological test bed and challenges of the smart city. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 96, 1545–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Chen, H.; Chen, X.; Chen, J. Semantic framework of Internet of Things for smart cities: Case studies. Sensors 2016, 16, 1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Ke, L. Cloud assisted Internet of things intelligent transportation system and the traffic control system in the smart city. J. Control Decis. 2022, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Liu, B.; Wang, D. Design and research of urban intelligent transportation system based on the Internet of Things. In Internet of Things. Communications in Computer and Information Science; Wang, Y., Zhang, X., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; Volume 312, pp. 572–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The People’s Government of Beijing Municipality. Overall Plan for Internet of Things Application Construction in Beijing’s Urban Safe Operation and Emergency Management; Beijing Government General Office: Beijing, China, 2011; p. 14.
- Beijing Municipal Commission of Transportation. The Feasibility Study of “The Internet of Things Application Demonstration Project of Maintaining Road Traffic Unblocked in Extreme Meteorological Conditions”; Beijing Municipal Commission of Transportation: Beijing, China, 2011; pp. 127–130.
- Zhi, X.; Cui, B.; Ji, Y.; Zhu, S.; Ma, Z.; Zhang, X. Prediction of water level in urban waterlogging area based on deep learning approach. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Electrocommunication, Intelligent Computing and Systems, Xi’an, China, 18–19 June 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Sun, H.; Zhang, L. Discussion on locations of road weather information system station on smart expressway. Highway 2022, 67, 248–254. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, K. Strategy for refined control of meteorological risks in Shanghai urban rail transit. Urban Mass Transit. 2022, 25, 86–90. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, S.; Wang, Y. Advances and prospects of urban meteorology research: Meeting users’ needs. Adv. Meteorol. Sci. Technol. 2014, 4, 6–14. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, B.N.; Khan, M.; Han, K. Big Data Analytics Embedded Smart City Architecture for Performance Enhancement through Real-Time Data Processing and Decision-Making. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2017, 2017, 9429676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Zhu, Y.; Shi, K.; Lv, Y.; Shi, P.; Niu, Z. Using Adverse Weather Data in Social Media to Assist with City-Level Traffic Situation Awareness and Alerting. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessel, J. Using weather forecasts to forecast whether bikes are used. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2020, 138, 537–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simunek, M.; Smutny, Z. Traffic Information Enrichment: Creating Long-Term Traffic Speed Prediction Ensemble Model for Better Navigation through Waypoints. Appl. Sci. 2020, 11, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichstein, M.; Camps-Valls, G.; Stevens, B.; Jung, M.; Denzler, J.; Carvalhais, N.; Prabhat. Deep learning and process understanding for data-driven Earth system science. Nature 2019, 566, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taillardat, M.; Mestre, O.; Zamo, M.; Naveau, P. Calibrated ensemble forecasts using quantile regression forests and ensemble model output statistics. Mon. Weather Rev. 2016, 144, 2375–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handler, S.L.; Reeves, H.D.; McGovern, A. Development of a probabilistic subfreezing road temperature nowcast and forecast using Machine Learning. Weather Forecast. 2020, 35, 1845–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Xu, J.; Yan, M.; Liu, Z. Using multiple linear regression and BP neural network to predict critical meteorological conditions of expressway bridge pavement icing. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0263539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Wu, J.; Xu, M. Traffic flow prediction with rainfall impact using a deep learning method. J. Adv. Transp. 2017, 2017, 6575947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, A.M.; Simon, V. Survey on traffic prediction in smart cities. Pervasive Mob. Comput. 2018, 50, 148–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-J.; Min, O. Long short-term memory recurrent neural network for urban traffic prediction: A case study of Seoul. In Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC), Maui, HI, USA, 4–7 November 2018; pp. 1279–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Yu, J.; Cai, H. Leveraging spatio-temporal patterns for predicting citywide traffic crowd flows using deep hybrid neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE 25th International Conference on Parallel and Distributed Systems (ICPADS), Tianjin, China, 4–6 December 2019; pp. 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, B.; Khan, S.R.; Tanvir Hasan, K.; Khan, A.H.; Alam, M.A. Travel Time Prediction using Machine Learning and Weather Impact on Traffic Conditions. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 5th International Conference for Convergence in Technology (I2CT), Pune, India, 29–31 March 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Song, X.; Li, P. Daily traffic flow forecasting through a contextual convolutional recurrent neural network modeling inter- and intra-day traffic patterns. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2020, 22, 2627–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigam, A.; Srivastava, S. Macroscopic traffic stream variables prediction with weather impact using hybrid CNN-LSTM model. In Adjunct Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Distributed Computing and Networking (ICDCN ’21); Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Tukymbekov, D.; Saymbetov, A.; Nurgaliyev, M.; Kuttybay, N.; Nalibayev, Y.; Dosymbetova, G. Intelligent energy efficient street lighting system with predictive energy consumption. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Smart Energy Systems and Technologies (SEST), Porto, Portugal, 9–11 September 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Tukymbekov, D.; Saymbetov, A.; Nurgaliyev, M.; Kuttybay, N.; Dosymbetova, G.; Svanbayev, Y. Intelligent autonomous street lighting system based on weather forecast using LSTM. Energy 2021, 231, 120902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasser, A.; Simon, V. A novel method for analyzing weather effect on smart City traffic. In Proceedings of the IEEE 22nd International Symposium on a World of Wireless, Mobile and Multimedia Networks (WoWMoM), Pisa, Italy, 7–11 June 2021; pp. 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z. Attention based stack ResNet for citywide traffic accident prediction. In Proceedings of the 20th IEEE International Conference on Mobile Data Management (MDM), Hong Kong, China, 10–13 June 2019; pp. 369–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, S.; Kim, D.; Kim, J. Weather-Aware Long-Range Traffic Forecast Using Multi-Module Deep Neural Network. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Y.; Zhi, X.; Zhu, S.; Fan, Y.; Pan, M. Statistical calibrations of surface air temperature forecasts over East Asia using pattern projection methods. Weather Forecast. 2021, 36, 1661–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Zhi, X.; Ge, F.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, L.; Gao, J. Subseasonal forecast of surface air temperature using superensemble approaches: Experiments over Northeast Asia for 2018. Weather Forecast. 2021, 36, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haltiner, G.J.; Williams, R.T. Some recent advances in numerical weather prediction. Mon. Weather Rev. 1975, 103, 571–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, P.; Thorpe, A.; Brunet, G. The quiet revolution of numerical weather prediction. Nature 2015, 525, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa, J.M.; Holm, E.; White, M. Part 3: Technology: Creating Intelligent, Coordinated Transit: Moving New Mexico the Smart Way. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2005, 1927, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kueper, D. The smart transportation guidebook: Planning and designing highways and streets that support sustainable and livable communities. ITE J. 2008, 78, 38–42. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C. Big data will change several major thinking categories. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. (Soc. Sci. Ed.) 2015, 29, 120–125. [Google Scholar]
- English, N.; Zhao, C.; Brown, K.L.; Catlett, C.; Cagney, K. Making Sense of Sensor Data: How Local Environmental Conditions Add Value to Social Science Research. Soc. Sci. Comput. Rev. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minhoto, M.J.C.; Pais, J.C.; Pereira, P.A.A.; Picado-Santos, L.G. Predicting asphalt pavement temperature with a three-dimensional finite element method. Transp. Res. Rec. 2005, 1919, 96–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, F.; Hossain, S.M.K.; Fu, L.; Johnson, M.; Fei, Y. Prediction of pavement surface temperature using meteorological data for optimal winter operations in parking lots. In Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Cold Regions Engineering, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 19–22 July 2015; pp. 440–451. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, Y.; Li, X. Advances in traffic meteorological service under the influence of disastrous weather. J. Catastrophol. 2015, 30, 144–147. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, Y.; Wang, S.; Yang, X.; Li, J.; Xu, W.; Shang, K. Progress of traffic meteorological researches about monitoring and forecasting services on express highways. J. Arid. Meteorol. 2016, 34, 591–603. [Google Scholar]
- China Intelligent Transportation Association. Framework and Technical Specification for Expressway Traffic Meteorological System; China Intelligent Transportation Association: Beijing, China, 2022; p. 11. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, B.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X. Analysis and research on the characteristics of hidden risks of highway meteorological disasters. In Proceedings of the 32nd Annual Conference of the Chinese Meteorological Society, Tianjin, China, 14–16 October 2015; pp. 29–33. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, F.; Xia, W.; Chen, X. Investigation of highway system during survey on disaster bearing body. City Disaster Reduct. 2021, 137, 35–38. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, C.; Zhang, C. Development and verification of a numerical forecast model for road meteorological services. J. Appl. Meteorol. Sci. 2012, 23, 451–458. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, N.; Meng, X.; Ma, C.; Qu, X.; Zhang, J. Weather forecast indexes of dense fogs based on traffic weather monitoring data. Meteorol. Sci. Technol. 2015, 43, 145–150. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, D.; Tang, W.; Liu, Y.; Wang, M.; Li, A.; Qu, H. Design and development of an early risk warning system of highway traffic meteorological disasters. Meteorol. Sci. Technol. 2018, 46, 822–828. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, X.; Ma, C.; Liu, J.; Yang, G.; Zhou, Y. Methods for controlling quality of meteorological monitoring data on expressway surface state. Meteorol. Sci. Technol. 2012, 40, 203–206. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, N.; Shi, H.; Han, G.; Wang, B.; Shu, L. Dynamic path planning algorithms with load balancing based on data prediction for smart transportation systems. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 15907–15922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Xi, S.; Wang, L. Research on refined forecast test and correction of maximum wind speed along expressway in Henan province. Meteorol. Environ. Sci. 2022, 45, 29–35. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Han, Y.; Li, A. Advance in research and operation in traffic meteorological service in China. Adv. Meteorol. Sci. Technol. 2017, 7, 85–89. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Song, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L. Analysis of the current status and innovative models of “immersive” specialized meteorological services in meteorological departments. Bull. Sci. Technol. 2021, 37, 18–23. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Liao, H. Weather, travel mode choice, and impacts on subway ridership in Beijing. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2020, 135, 264–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Wu, H.; Liu, Y.; Yang, J.; Tian, H.; Pan, J. Risk assessment and region partition of low visibility disasters on highway in China. Meteorol. Mon. 2018, 44, 676–683. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, H.; Wu, H.; Yang, J.; Gao, J.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, K. Demand analysis of meteorological decision-making service for highway traffic. Meteorol. Environ. Sci. 2018, 41, 70–76. [Google Scholar]
- China Meteorological Administration; China National Development and Reform Commission. The 14th Five-Year Plan for National Meteorological Development; China Meteorological Administration: Beijing, China, 2021; p. 52.
- China Meteorological Administration; Ministry of Science and Technology of the People´s Republic of China; Chinese Academy of Sciences. Development Strategy of Meteorological Science and Technology in China (2021–2035); China Meteorological Administration: Beijing, China, 2022; p. 46.
- Lu, H.; Chen, M.; Kuang, W. The impacts of abnormal weather and natural disasters on transport and strategies for enhancing ability for disaster prevention and mitigation. Transp. Policy 2019, 98, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).