Abstract
To investigate the concentration, seasonal variation, and sources of secondary organic aerosols (SOAs) in the inland areas of central China, 244 seasonal PM2.5 samples were collected from January to October 2019 at one urban site and one suburban site simultaneously in Bengbu of Anhui Province. Concentrations of organic carbon (OC), elemental carbon (EC), water-soluble organic carbon (WSOC), and typical organic tracers, including saccharides, tracers of SOAs from isoprene, terpenes, and toluene, were measured. Results showed that Bengbu has high pollution levels of organic aerosols, with annual average OC concentrations of about 9.5 μg m−3. About 60% of the OC in PM2.5 in Bengbu was water soluble. Different seasonal trends were found for the SOA tracers of isoprene, monoterpene, seisquiterpene, and toluene. The highest seasonal average concentration of the isoprene SOA tracers was observed in summer and of the monoterpene and seisquiterpene SOA tracers in autumn. A stronger correlation was found between the 2-methylglyceric acid-to-2-methyltetrol ratio (MGA/MTL) and ambient temperature than that between MGA/MTLs and NOX concentration, suggesting that temperature has an important impact on the MGA/MTL ratio besides NOX concentration. The OC/EC-based method, WSOC-based method, tracer yield method, and positive matrix factorization (PMF)-based method were used to estimate the concentration and sources of secondary organic carbon (SOC), and the PMF-based method was believed to be able to give reasonable results. SOC was the main contributor of WSOC in PM2.5 in Bengbu, while biomass burning made an important contribution to WSOC in autumn and winter (~40%). SOC was mainly associated with SOA tracers in summer and mainly associated with secondary ions in spring and winter, suggesting different formation mechanisms in different seasons.
1. Introduction
Secondary organic aerosols (SOAs) in atmospheric fine particles (PM2.5) are mainly formed by the homogeneous and heterogeneous reactions of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) emitted from biogenic [1] and anthropogenic [2] sources. SOA is an important component of PM2.5 and has adverse effects on climate change, air quality, and human health [3].
Isoprene, monoterpenes, and sesquiterpenes are major biological VOCs, and benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene, and xylene (BTEX) may be the most important anthropogenic VOCs for SOA formation [4,5,6,7,8,9,10]. Many studies on SOA formation from typical VOC precursors have been conducted, and a variety of SOA tracers have been found. For example, 2-methyltetrols (2-methyl-threitol and 2-methyl-erythritol) are proved to be tracers of isoprene SOAs [7,8]; 3-hydroxyglutaric acid (HGA), 3-hydroxy-4,4-dimethylglutaric acid (HDMGA), and 3-methyl-1,2,3-butyl-tricarboxylic acid (MBTCA) are tracers of monoterpene SOAs [8,9]; β-caryophyllinic acid is the tracer of β-caryophyllene SOAs [10]; and 2,3-dihydroxy-4-oxopentanoic acid (DHOPA) is the tracer of toluene SOAs [9]. The composition of SOA tracers can provide important information about the precursors and formation processes. For example, the 2-methylglyceric acid-to-2-methyltetrol ratio of isoprene SOAs formed under low and high NOx levels was found to be different [11,12]. The HGA-to-MBTCA ratio in SOAs from α-pinene was different from that from other monoterpenes [12,13].
On the global scale, it is believed that SOAs are mainly derived from biogenic VOCs [14]. However, anthropogenic VOCs are the main contributors to SOAs in urban areas [15,16]. Chamber experiments and field monitoring have shown that anthropogenic pollutants (e.g., O3, NOx.) have an important impact on the oxidation of VOCs and the formation of SOAs [17,18,19,20,21]. Therefore, long-term study of the chemical composition, temporal and spatial distribution of SOAs, and their relationship with other anthropogenic pollutants in ambient atmosphere is of great importance, which could provide basic information for the study of sources and formation mechanisms of SOAs [8,12].
Although the air quality in China has been continuously improving in recent years, severe haze episodes have occurred from time to time in central and northern regions of China. The air pollution problem in the inland cities of China is drawing increasing attention. Existing studies on SOAs in China have been mainly conducted in big cities and coastal areas, such as Beijing, Shanghai, and Guangzhou [22,23,24,25,26], while SOA studies in central inland areas are limited. Bengbu of Anhui Province is located on the Qinling–Huaihe line, the geographical demarcation between northern and southern China. The energy structure, industrial structure, and meteorological conditions of Bengbu are similar to those of many other small and medium-sized inland cities in central China. Moreover, the air quality in Bengbu is still poor, especially in autumn and winter [27]. The objective of this study is to investigate the concentration, seasonal variation, and potential sources of SOAs in PM2.5 in Bengbu based on the concentrations of carbonaceous components and typical SOA tracers, which could provide important information for the comprehensive understanding of China’s air pollution and contribute to the development of air pollution control strategies.
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Sampling
Two sampling sites were selected for the collection of PM2.5 samples, the rooftops of the Bengbu Municipal Bureau of Ecology and Environment (HBJ) and the Wuhe Municipal Bureau of Ecology and Environment (WH) (Figure 1). The HBJ site is located in the urban area of Bengbu and is surrounded mainly by office and residential areas; the WH site is about 40 km away from the urban area of Bengbu City and situated is in an area where lakes and river networks are densely distributed. Generally, the WH site is representative of a suburban environment but is also affected by local industrial activities and motor vehicles.
Figure 1.
Location of sampling sites (red solid stars).
The samples were collected simultaneously at the two sites with high-volume PM2.5 samplers (XT-1025; XTrust Instruments, Shanghai, China) in four seasons in 2019: 4–31 January (winter), 1–30 April (spring), 1–31 July (summer), and 1 October–2 November (autumn). Samples were collected on quartz fiber filters (QM-A, 20.0 cm × 25.4 cm, Whatman, UK) and baked at 500 °C for more than 4 h to remove organic residues before use [28]. The duration of each sample was about 23.5 h, from 9:00 a.m. to 8:30 a.m. of the next day. Field blanks were collected for each sampling period at both sites. A total of 244 samples were collected. Concentrations of NO2, SO2, and O3 at the two sites were monitored with online equipment, and temperature (T), relative humidity (RH), and wind speed during the sampling periods were collected from local meteorological monitoring stations.
2.2. Chemical Analysis
The concentrations of organic carbon (OC) and elemental carbon (EC) were measured by a thermal/optical carbon analyzer (DRI 2001A; Sunset Lab Inc., USA) with the IMPROVE temperature protocol in transmission mode. The detection limit (LOD) of the method was 0.2 μg·cm−2 filter, or about 0.05 μg·m−3.
To determine the concentration of water-soluble organic carbon (WSOC), 3 cm2 of the filter was ultrasonically extracted with 10 mL of ultrapure water at room temperature for 30 min. The extract was filtered with a 0.22 µm aqueous TEFLON filter membrane and then measured with a total organic carbon analyzer (TOC-LCSH; Shimadzu Corporation, Japan). The LOD of WSOC was about 0.06 μg·m−3.
About 60 cm2 of the sampled filter was cut with a puncher, and about 1000 ng of methyl-β-D-xylanopyranoside (MXP) was added onto the filter as a recovery standard and then extracted ultrasonically with 20 mL of a mixed solvent of dichloromethane and methanol (2:1 v/v) three times. The extracts were combined and concentrated to about 1 mL by a rotary evaporator and then filtered by a glass dropper filled with quartz wool. After being blown dry with gentle high-purity nitrogen, the extract was derivatized with 100 µL of BSTFA (with 1% TMCS) and 20 µL of anhydrous pyridine at 75 °C for 45 min. Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (Agilent 6890/5975 GC-MS, USA) analysis was performed on a DB-5MS (30 m × 0.25 mm × 0.25 μm) capillary column with high-purity helium as a carrier gas. Hexamethylbenzene was added before GC-MS analysis as an injection standard to check the recovery of MXP. The setup of GC-MS and the quantification method of the target compounds were the same as Feng et al. (2013) [24]. Using a signal-to-noise ratio of 5 as the quantification limit, the LOD of MXP was about 0.005 ng. In the experimental setup of this study, the LOD of the target species was about 0.002 ng·m−3.
2.3. Quality Assurance/Quality Control
Field blanks and procedure blanks (every 10 samples) were extracted and analyzed in the same way as the ambient samples. The target tracer compounds were not detected in the blanks. Recoveries of MXP in most samples were 70–110%. The results were reported after recovery correction, assuming that the target compounds had the same recovery as MXP. Duplicate analysis was conducted every 20 samples, and the results showed that our analyzing procedure has good repeatability (deviation less than 15%).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characteristics of Carbonaceous Components
3.1.1. OC and EC
Table 1 lists the seasonal average mass concentrations of OC, EC, and WSOC in PM2.5 at the HBJ and WH sites. The annual average concentrations of OC at the HBJ and WH sites were 9.20 and 9.67 μg·m−3, respectively, and of EC were 1.68 and 1.52 μg·m−3, respectively. The lower EC concentration at the WH site may be attributed to the fewer number of motor vehicles (number of motor vehicles was 225,375 in the urban area of Bengbu and 97,698 at the WH site according to the statistical yearbook of 2020, http://tjj.bengbu.gov.cn/gzdt/ztzl/tjnj/8668761.html. accessed on 30 June 2021). However, the differences in the OC and EC concentrations between the HBJ and WH sites were not statistically significant (p > 0.1 for the t-test). Significant correlation was found between the OC concentrations at the HBJ and WH sites (r = 0.92, p < 0.01), suggesting that concentrations of carbonaceous aerosols in PM2.5 in Bengbu have little spatial variation.

Table 1.
Concentrations of OC, EC, WSOC, and levoglucosan in PM2.5 in Bengbu.
An obvious seasonal variation was observed for OC and EC in PM2.5 in Bengbu: winter > autumn ≈ spring > summer. The concentrations of OC and EC in winter were significantly higher than those in other seasons. The main reason for the observed seasonal variation of OC and EC could be the seasonal difference in meteorological conditions. Lower temperature and weaker solar radiation in winter caused a lower atmospheric mixing height and thus the accumulation of pollutants. Much of the organic matter was semi-volatile and tended to exist in the particulate phase in winter but the gaseous phase in summer [28]. Extra emission from space heating and the frequent occurrence of atmospheric inversion were also important reasons for the higher concentration of OC and EC in winter.
A higher OC/EC ratio was found in summer than in other seasons (Table 1), in accordance with the higher formation rate of SOAs under higher temperature and stronger solar radiation in summer. It can also be found from Table 1 that the OC/EC ratio at the WH site was significantly higher than that at the HBJ site, indicating the stronger influence of SOAs at the WH site.
3.1.2. WSOC
The mass concentration of WSOC in PM2.5 in Bengbu ranged from 1.17 to 19.89 μg·m−3, and the annual average concentrations were 5.41 μg·m−3 at the HBJ site and 5.71 μg·m−3 at the WH site, higher than those in Shanghai in 2010 (5.0 μg·m−3) [24]. Like OC, the WSOC concentration had a seasonal trend of being higher in winter and lower in summer (Table 1). There was a significant correlation between the concentrations of WSOC at the HBJ and WH sites (R2 = 0.86, (WSOC)WH = 0.91 × (WSOC)HBJ + 0.75), indicating that the WSOC concentration in PM2.5 in Bengbu has little spatial variation.
WSOC accounted for 59% of OC at both the HBJ and WH sites, which indicated that the main part of OC in PM2.5 in Bengbu is water soluble. The WSOC/OC ratio in PM2.5 in Bengbu was higher than that reported in the summer of 2003 in Beijing, Shanghai, and Guangzhou (32%, 42%, and 43%, respectively, [28]) and 2010 in Shanghai [24] but lower than that of the Amazon forest [29] and the southeastern United States in summer (80%) [30]. The seasonal variation of the WSOC/OC ratio in PM2.5 in Bengbu was autumn > summer > spring > winter. The difference in SOA generation and biomass burning contribution in different seasons could be the main reason for the seasonal variation in the WSOC/OC ratio, which will be addressed later. In summer and autumn, the WSOC/OC ratio at the WH site was higher than that at the HBJ site, while in winter, the WSOC/OC ratio at the WH site was slightly lower than that at the HBJ site. The results suggested that SOA formation and biomass burning contribute more in rural areas (WH) in summer and autumn, while in winter, the WH site may be more affected by the scattered coal burning for space heating in rural areas.
There was a strong correlation between WSOC and levoglucosan in PM2.5 in Bengbu (Figure 2), indicating that biomass burning is an important contributor to WSOC. Mayol-Bracero et al. (2002) [29] found that most of the organic matter produced by biomass burning is water soluble. The results of simulated combustion experiments conducted by Zhang et al. (2007) [31] showed that the ratio of OC to levoglucosan in the fine particles emitted by biomass combustion is 8–16, and Ding et al. (2008) [30] used 10 as the WSOC/levoglucosan ratio to estimate the contribution of biomass burning to WSOC. The lowest ratio of WSOC/levoglucosan in PM2.5 in Bengbu was about 10, so a WSOC/levoglucosan ratio of 10 was used in this study to evaluate the contribution of biomass burning. It should be noted that using a fixed WSOC/levoglucosan ratio in different seasons would bring about a large uncertainty, because the WSOC/levoglucosan ratio depends on plant types and burning conditions. The estimation results showed that the highest contribution of biomass burning in PM2.5 in Bengbu occurred in winter at both sites, accounting for 41% (HBJ) and 37% (WH) of WSOC. The contribution of biomass burning to WSOC at the HBJ site was 26%, 21%, and 5% in autumn, spring, and summer, respectively, while the contribution of biomass burning at the WH site was higher in autumn (34%) and spring (31%).
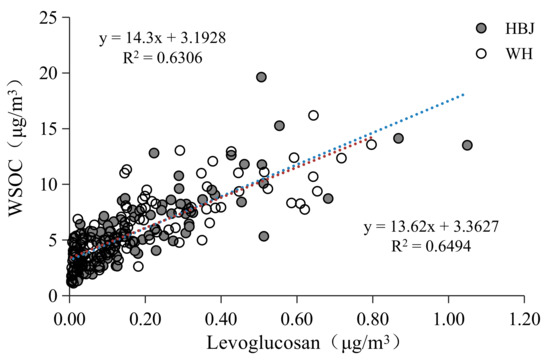
Figure 2.
Correlation between levoglucosan and WSOC at the HBJ and WH sites.
3.2. Concentration and Composition of SOA Tracers
The seasonal average concentrations of the SOA tracers generated from natural and anthropogenic precursors in PM2.5 in Bengbu are shown in Table 2, including isoprene SOA tracers (I1~I6), α-pinene SOA tracers (A1~A3), a sesquiterpene SOA tracer (β1), and a toluene SOA tracer (T1). The total concentrations of the measured SOA tracers in PM2.5 at the HBJ and WH sites during the sampling periods were 0.26~148.65 ng·m−3 (with an average of 17.80 ng·m−3) and 0.42~155.77 ng·m−3 (averaged at 20.66 ng·m−3), respectively. The difference between the SOA concentrations at the two sites was not statistically significant (p > 0.05 for the t-test).

Table 2.
Concentrations of SOA tracers in PM2.5 in Bengbu.
3.2.1. Isoprene SOA Tracers
The total concentration of isoprene SOA tracers in PM2.5 during the whole sampling periods were 14.98 ng·m−3 at the HBJ site and 17.98 ng·m−3 at the WH site, similar to those in other places in China [22,24]. The WH site had a slightly higher average concentration of isoprene SOA tracers, but no significant difference between the two sites could be found (p > 0.1), suggesting that the sources and reaction process of isoprene at the two sites are similar. It can be seen from Table 2 that the concentrations of isoprene SOA tracers in PM2.5 in Bengbu had a distinct seasonal trend, with the highest concentration in summer and the lowest in winter. The average concentration in summer was about 6–17 times that in the other seasons, which was similar to that found for the isoprene SOA tracers in PM2.5 in Shanghai [24]. The strong dependence of isoprene emission on the atmospheric temperature could be the main reason for the high summer concentration of isoprene SOA tracers, and higher temperature and stronger solar radiation in summer promote the photochemical oxidation of isoprene [32].
2-Methyltetrols (MTLs, I5 and I6) and C5-alkene triols (I2~I4) accounted for about 90% of the total isoprene SOA tracers in summer but contributed less in other seasons (Table 2). Studies have shown that isoprene epoxydiols (IEPOX) are the intermediates for isoprene oxidation under low-NOx (or no-NOx) conditions, and IEPOX are then further converted to MTLs and C5-alkene triols through acid-catalyzed ring opening and subsequent nucleophilic addition [33]. A recent study found that MTLs and C5-alkene triols could be formed from the thermal decomposition of IEPOX SOAs during analytical workup [34]. Significant correlation (r = 0.75) between MTLs and C5-alkene triols in PM2.5 in Bengbu proved that the formation mechanism of these two types of tracers is similar.
The concentration of 2-methylglyceric acid (MGA) also showed a seasonal trend of being the highest in summer and the lowest in winter, but the range of the seasonal variation (summer/winter ratio of ~4) was much smaller than that of MTLs and C5-alkene triols (Table 2). It was found that MGA is a tracer of isoprene SOAs generated under high-NOx conditions [33], and a higher-NOx condition is favorable for the formation of MGA [35]. Therefore, the MGA/MTL ratio at different NOx levels may reflect the impact of the NOx level on the formation of isoprene SOAs. Lewandowski et al. (2013) [12] found that the MGA/MTL ratio in the suburbs of the southeastern United States (0.13–0.35) is significantly smaller than that in the urban areas of California (0.87–1.80), which is consistent with the understanding of high NOx promoting the formation of MGA. In this study, the MGA/MTL ratio at the HBJ site was 1.93, 0.28, 0.88, and 1.98 in spring, summer, autumn, and winter, respectively, and 1.09, 0.18, 0.72, and 2.39 at the WH site, respectively. The seasonal trend of being higher in winter and lower in summer for the MGA/MTL ratio in PM2.5 in Bengbu was in agreement with seasonal NOx concentrations. The MGA/MTL ratio at the WH site in spring, summer, and autumn was lower than that at the HBJ site, which matched with the lower NO2 concentration at the WH site (annual average of 18 μg·m−3) than that at the HBJ site (30 μg·m−3). However, the higher MGA/MTL ratio at the WH site in winter could not be verified by the NO2 concentration.
To investigate the potential factors affecting the distribution of the MGA/MTL ratio, correlation analysis between the seasonal average MGA/MTL ratio and the NO2 concentration and ambient temperature was conducted. The results showed that the MGA/MTL ratio in PM2.5 in Bengbu is positively correlated with the NO2 concentration (r = 0.67), just as expected, and negatively correlated with ambient temperature (r = −0.90). Therefore, it seems that temperature may play a more important role in the MGA/MTL ratio in PM2.5 in Bengbu, in addition to the influence of the NO2 concentration. The higher temperature and stronger solar radiation in summer promote the formation of MTLs by generating more radicals, and the lower concentration of NOx reduces the formation of MGA, resulting in the lowest MGA/MTL ratio in summer. In winter, the higher NOx concentration favors the formation of MGA [35], and the lower temperature is unfavorable for the formation of MTLs, which relies on the concentrations of free radicals.
3.2.2. Monoterpene SOA Tracers
Monoterpenes account for about 35% of the global natural VOC emissions [3], among which α-pinene is the single largest monoterpene compound. 3-Hydroxyglutaric acid (HGA, A1 in Table 2), 3-hydroxy-4,4-dimethylglutaric acid (HDMGA), and 3-methyl-1,2,3-butyltricarboxylic acid (MBTCA) were the typical monoterpene SOA tracers. The annual average concentrations of monoterpene SOA tracers in PM2.5 at the HBJ and WH sites were 1.81 and 1.79 ng·m−3, respectively. Compared with other cities in China, the concentration of monoterpene SOA tracers in PM2.5 in Bengbu was at a lower level (e.g., annual average of 4.6 ng·m−3 in Shanghai in 2010 and >10 ng·m−3 in summer in Beijing, Hefei, and Wuxi) [22,24,26,36,37]. In addition to geographical differences, the differences in analytical methods adopted by different labs should be an important cause of the variations between different studies.
Compared with isoprene SOA tracers, the seasonal distribution of monoterpene SOA tracers was more complicated. The concentration of HDMGA in PM2.5 in Bengbu was the highest in autumn, followed by summer, and was lower in winter at both sites, while the highest seasonal average concentration of HGA and MBTCA appeared in summer at the HBJ site but in autumn at the WH site (Table 2). HGA had the lowest seasonal concentration in spring, while MBTCA had a significantly lower concentration in winter. The complexity of the seasonal variation in monoterpene SOA tracers suggests the complicated influencing factors in the emission and oxidation of monoterpenes.
Previous studies have showed that the concentration ratio of HGA to MBTCA (HGA/MBTCA) could be used to distinguish the contribution of different monoterpenoid precursors. SOAs from α-pinene had a much lower HGA/MBTCA ratio than the SOAs from β-pinene or δ-limonene, and the increase in the HGA/MBTCA ratio thus indicated a decrease in contribution from α-pinene [12,13,22,37]. The HGA/MBTCA ratios at the HBJ site were 0.80, 0.78, 0.71, and 4.86 in spring, summer, autumn, and winter, respectively, and 1.08, 0.81, 0.97, and 4.97 at the WH site, respectively. The seasonal HGA/MBTCA ratio in PM2.5 in Bengbu was comparable with that in other places in China [22,37]. The significantly higher HGA/MBTCA ratio in PM2.5 in Bengbu in winter suggested that the precursors of monoterpene SOAs in winter might be significantly different from those in other seasons, and the contribution of α-pinene was lower in winter. The usage of cosmetic products might be the possible cause of the seasonal difference, because limonene is widely used in many cosmetic products [38].
3.2.3. β-caryophyllene SOA Tracers
Similar to monoterpenes, the emission of β-caryophyllene was closely dependent on meteorological conditions, such as temperature and solar radiation. β-caryophyllinic acid is the oxidation product of β-caryophyllene and is well recognized to be a tracer of sesquiterpene SOAs [10]. The concentration of β-caryophyllinic acid in PM2.5 in Bengbu showed a seasonal trend of being the highest in autumn and the lowest in summer (Table 2), which was significantly different from that of isoprene or monoterpene SOA tracers but was similar to that found in Guangzhou and Hong Kong [23,25].
3.2.4. Toluene SOA Tracers
Aromatic VOCs are important anthropogenic VOCs in the atmosphere and can be from vehicle exhaust, industrial activities, solvent usage, biomass burning, etc. Toluene is the most abundant aromatic VOC and is an important precursor of SOAs. 2,3-Dihydroxy-4-oxopentanoic acid (DHOPA) is found to be a typical oxidation product of toluene in chamber experiments and is proved to be a tracer of toluene SOAs [39]. The annual average concentration of DHOPA in PM2.5 was 1.08 ng·m−3 at the HBJ site and 1.06 ng·m−3 at the WH site. Compared with other cities in China, the concentration of DHOPA in PM2.5 in Bengbu was similar to that in Shanghai (annual average of 1.2 ng·m−3 in 2010) [24], Hefei (2.62 ng·m−3 in summer of 2012) [22], and Hong Kong (1.67 ng·m−3 in summer of 2006) [25].
It can be seen from Table 2 that the seasonal concentration of DHOPA was the highest in summer, followed by autumn and winter, and the lowest in spring. The higher concentration in summer could be attributed to the enhanced oxidation rate and the increased emission rate of the precursors under higher temperature and stronger solar radiation. The results also showed that the concentration of DHOPA at the WH site was lower than that at the HBJ site in spring and summer, while it was higher at the WH site than at the HBJ site in autumn and winter, indicating that the emission sources of toluene are different to some extent between the two sites.
3.3. Estimation of the Concentration and Contribution of SOC
Although secondary organic carbon (SOC) has received widespread attention, so far, there is still no direct method to determine the SOC concentration in OC. A variety of indirect methods has been applied to the estimation of SOC, for example, the OC/EC-based method [40], the WSOC-based method [41], the SOA tracer-based method [9], the reception model such as PMF and CMB [42], and the AMS method [43]. Among them, the OC/EC- and WSOC-based methods have been widely used because of their simplicity.
3.3.1. Estimation of SOC Based on the OC/EC Ratio
Since EC is emitted directly from pollution sources and does not undergo chemical changes in the atmosphere, EC is a good indicator of primary aerosols and can be used as a tracer to estimate the concentration of primary organic carbon (POC) and the contribution of SOC [40]. As the OC/EC ratio of fine particles from different emission sources is different and the OC/EC ratio changes during the atmospheric aging process, it is almost impossible to obtain the OC/EC ratio for primary particles in the atmosphere. The minimum OC/EC ratio ((OC/EC)min) during a certain period is usually used as the OC/EC ratio of primary aerosols [44], and the SOC concentration can be estimated by the following equation:
SOCEC-based = OC – EC × (OC/EC)min
From the estimated SOC concentration in Table 3, the annual average concentrations of SOCEC-based were 2.97 and 4.06 μg·m−3 at the HBJ and WH sites, respectively, accounting for 32% and 42% of the OC, respectively. A higher concentration and contribution of SOC at the suburban site were in accordance with the weaker anthropogenic activities and stronger impact of transported particles at the WH site. The SOCEC-based concentration had a seasonal trend of being the highest in winter and lower in summer and autumn, while the SOCEC-based/OC ratio was the highest in summer (39% at the HBJ site and 53% at the WH site). The highest SOCEC-based/OC ratio in summer was consistent with the consensus that higher temperatures and stronger sunlight are beneficial to the formation of SOAs [23,45]. However, the lower SOCEC-based/OC ratio in autumn than that in winter was inconsistent with the recognition that SOAs are not easily generated in winter, suggesting the insufficient representativeness of (OC/EC)min for primary aerosols.

Table 3.
Estimated SOC concentrations (μg·m−3) and contributions to OC based on OC/EC and WSOC.
3.3.2. Estimation of SOC Based on WSOC Concentration
Previous studies have shown that the WSOC in fine particles mainly comes from SOC and biomass burning [41] and that the main part of SOAs is water soluble [46]. Therefore, the part of WSOC other than the contribution of biomass burning could be regarded as SOC (SOCWSOC-based), that is, the SOC concentration can be estimated by the following equation:
SOCWSOC-based = WSOCtotal − WSOCBB
WSOCBB is the WSOC contributed by biomass burning, which was estimated in Section 3.1.2.
The SOC and SOC/OC ratio estimated by the WSOC-based method are listed in Table 3. The annual average concentrations of SOCWSOC-based were 3.94 μg·m−3 at the HBJ site and 3.99 μg·m−3 at the WH site, accounting for 43% and 42% of OC, respectively. Similar to what was found for SOCEC-based, the SOCWSOC-based concentration was the highest in winter and the lowest in summer, but the SOCWSOC-based/OC ratio was the highest in summer (57% at the HBJ site and 61% at the WH site) and the lowest in winter (33% and 32% at the HBJ and WH sites, respectively). The concentration and contribution of SOCWSOC-based in autumn were obviously higher than those of SOCEC-based. Generally, the seasonal trend in the SOCWSOC-based concentration and the SOCWSOC-based/OC ratio is consistent with the seasonal trend in the meteorological conditions in Bengbu.
3.3.3. Estimation of SOC with the Tracer Yield Method
Based on the concentrations of 11 SOA tracers measured in this study, the concentration of SOC in PM2.5 in Bengbu was estimated using the tracer yield method. The tracer yield in SOC generated by various VOCs in chamber experiments (fSOC) reported by Kleindienst et al. (2007) [9] was used, and the formula is as follows:
where ∑[tri] is the sum of the concentrations of tracers. The fSOC of different precursors was 0.155 for isoprene, 0.231 for α-pinene, 0.023 for β-caryophyllene, and 0.0079 for toluene.
The estimation results in Table 4 show that the annual concentration of tracer-based SOC (SOCtracer-based) in PM2.5 was 0.25 μg·m−3 at the HBJ site and 0.27 μg·m−3 at the WH site. The concentration of SOCtracer-based in PM2.5 in Bengbu was similar to that in Shanghai (range 0.02–2.8 μg·m−3, averaged at 0.30 μg·m−3) [24] but significantly lower than that in Guangzhou (3.1 μg·m−3 in summer, 2.0 μg·m−3 in autumn and winter) [23].

Table 4.
Seasonal concentration (µg m−3) and contribution (%) of SOC estimated by the tracer yield method in Bengbu.
There was a big difference between the concentrations of SOCtracer-based and SOCEC-based and SOCWSOC-based. The concentration of SOCtracer-based in summer was only about 30% of SOCEC-based or SOCWSOC-based, while the concentration of SOCtracer-based was less than 10% of SOCEC-based in other seasons, which was similar to the results in Shanghai [24]. In addition to the uncertainties in quantitative methods, the possible reasons for the gap were as follows: First, the conditions of the chamber experiments were different from actual atmospheric conditions, and the yield of tracers in ambient SOAs might be different from the ones obtained from chamber experiments. Second, many of the SOA precursors in the actual atmosphere were not studied in the chamber experiments, so estimation based on the existing chamber experiments would underestimate the SOC concentration. Third, there may be other mechanisms different from the chamber experiments contributing to the formation of SOAs in the actual atmosphere, such as aqueous reactions, which would also lead to the underestimation of the SOC concentration by the current tracer-based method.
Despite the large uncertainties in the estimation of the SOC concentration, the tracer-based method could give important information about the sources of SOAs in PM2.5 in Bengbu and their seasonal variations (Table 4). In summer, biogenic VOCs are the main sources of SOA in PM2.5 in Bengbu, and the contribution of isoprene SOAs dominates, while in other seasons, especially in winter, the SOAs in Bengbu mainly come from anthropogenic VOCs. In general, based on the results of the tracer-based method, anthropogenic pollutants, such as toluene, are the main contributors to SOAs in PM2.5 in Bengbu.
3.3.4. Estimation of SOC with PMF
To better understand the sources of SOAs in PM2.5 in Bengbu, source apportionment of SOC was conducted using positive matrix factorization (PMF; U.S. EPA version 5.0). WSOC, nitrate and sulfate ions (NO3−, SO42−), six saccharide compounds (arabitol, fructose 1, fructose 2, glucose 1, glucose 2, manni-tol), levoglucosan, and 11 SOA tracers were included in the PMF analysis, and six factors/sources were retrieved (Figure 3).
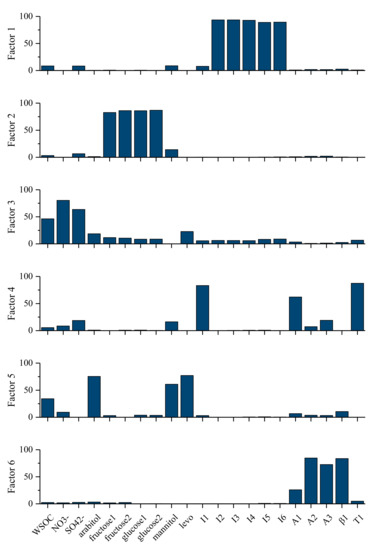
Figure 3.
PMF source profile (% of species) of WSOC in PM2.5 in Bengbu.
Based on the high-loading species in each factor, factors 1–6 were identified as SOAs from isoprene, WSOC from soil [47], SOAs associated with secondary inorganic ions, SOAs from toluene, WSOC from biomass burning, and SOAs from terpenes, respectively. Among them, WSOC in F2 and F5 should be primary in nature, while WSOC associated with F1, F3, F4, and F6 were secondary, and the sum of the WSOC concentrations in these sources was regarded as SOCPMF-based. It should be noted that MGA (I1) and HGA (A1) also had high loadings in factor 4, in addition to DHOPA (T1). So in addition to toluene SOAs, there may be some contribution of isoprene SOAs and monoterpene SOAs in F4. Analysis showed that T1, I1, and A1 are significantly correlated with each other (r > 0.6), suggesting that the emission pattern or oxidation pathway of their precursors is similar. Therefore, it was not surprising to find them in the same factor in PMF analysis. A different number of factors was tried in PMF analysis, but we failed to separate them. Factor 3 was characterized by the high weight of nitrate and sulfate, WSOC also had a high weight, while the weight of the SOA tracers was small, indicating that a large part of SOC might be formed in a similar way with sulfate and nitrate but different from that of the measured SOA tracers. More studies on the chemical composition of the secondary organic matter associated with nitrate and sulfate are needed.
The concentration and contribution of SOCPMF-based are listed in Table 5. The annual average concentrations of SOCPMF-based were 3.02 μg·m−3 at the HBJ site and 3.54 μg·m−3 at the WH site, accounting for 33% and 37% of OC, respectively. The concentration of SOCPMF-based had a seasonal trend of being the highest in winter and the lowest in autumn, but the differences between spring, summer, and autumn were relatively small. The contribution of SOCPMF-based to WSOC was the highest in summer, followed by spring, and the lowest in autumn. In summer, almost all of the WSOC was secondary, while in autumn, more than half of the WSOC came from primary emissions. Therefore, the reason for the low contribution of SOCPMF-based to OC in autumn (Table 5) could be the high contribution of biomass burning in autumn (BB in Table 6).

Table 5.
Concentration (μg·m−3) and contribution of SOCPMF-based to WSOC and OC (%).

Table 6.
Contributions of different sources to WSOC by PMF in different seasons (%).
It can be seen from the seasonal contributions of different sources to WSOC (Table 6) that WSOC associated with secondary nitrate and sulfate (SOCNS in Table 6) and biomass burning (BB in Table 6) are the main contributors to WSOC in PM2.5 in Bengbu. On an annual basis, SOCNS contributed 46% of WSOC and biomass burning contributed 34%. The contribution of the soil (dust) to WSOC (F2) was significant only in spring and could be ascribed to the dry weather and stronger soil microbial activity in spring. The SOC associated with the measured SOA tracers accounted for 72% of SOCPMF-based in summer and dropped to 28% of SOCPMF-based in autumn and less than 10% in spring and winter. In general, SOCPMF-based was mainly associated with secondary inorganic ions, except in summer.
PMF results showed that the contributions of different sources to SOCPMF-based at the two sites is similar in spring, autumn, and winter. However, in summer, the average contribution of toluene SOAs to SOCPMF-based at the HBJ site (24%) was significantly higher than that at the WH site (14%), and the contribution of SOCNS at the HBJ site (18%) was significantly lower than that at the WH site (36%), indicating that the sources of SOC in urban and suburban areas in summer are different.
3.3.5. Comparison of Different Methods
The annual average concentration of SOC in PM2.5 in Bengbu estimated with the OC/EC-based (3.52 μg·m−3), WSOC-based (3.96 μg·m−3), and PMF-based method (3.28 μg·m−3) was comparable, indicating that all these methods could give reasonable results. The SOC concentration at the WH site obtained by different methods was higher than that at the HBJ site, indicating that the suburban site has a higher contribution of secondary organic matter. However, the SOC concentration estimated by different methods had some differences in different seasons. For example, in autumn, the SOC concentration obtained by the WSOC-based method was significantly higher than that obtained by the OC/EC- and PMF-based methods. The possible reason might be that the WSOC/levoglucosan ratio of biomass-burning-produced particles in autumn was different from that in other seasons. The SOC concentration estimated by the OC/EC-based method in winter at the WH site was significantly higher than that by the WSOC- and PMF-based methods, suggesting that (OC/EC)min in winter may not be representative of the primary OC/EC ratio.
To compare the results from the different methods, the correlations between the concentrations of SOCEC-based, SOCWSOC-based, and SOCPMF-based were analyzed. The results showed that the linear fitting equations were SOCWSOC-based = 0.41 × SOCEC-based + 2.57 (R2 = 0.31, p < 0.01), SOCPMF-based = 0.40 × SOCEC-based + 1.85 (R2 = 0.38, p < 0.01), and SOCPMF-based = 0.57 × SOCWSOC-based + 1.05 (R2 = 0.36, p < 0.01). The significant correlations between these results indicated the rationality of the estimation methods, but the large positive intercepts in the equations related to SOCEC-based suggested that the OC/EC-based method may underestimate the SOC concentration when the concentration is low, because part of the POC from the OC/EC method may still be secondary. Some oxidation products with a high C/O ratio have poor water solubility, so the WSOC-based estimation method might underestimate the amount of SOC. Meanwhile, other sources besides secondary generation and biomass burning, such as WSOC from soil, may also contribute to WSOC; therefore, the WSOC-based method would overestimate the SOC concentration in some cases.
The correlation analysis between SOCTracer-based and the contribution of (F1 + F4 + F6) in SOCPMF-based showed that they are strongly correlated (r = 0.93, p < 0.01). However, SOCTracer-based only accounted for about 30% of the contribution of (F1 + F4 + F6) in SOCPMF-based, indicating that the tracer yield method used in this study underestimates the concentration of SOC [24]. Further analysis showed that the concentration of SOCIsoprene in SOCTracer-based (Table 4) and the isoprene SOC (F1) in PMF results have a strong linear correlation (R2 = 0.92, slope = 0.21), SOCTerpene in SOCTracer-based is strongly correlated with the terpene SOC (F6) in PMF (R2 = 0.76, slope = 0.12), and SOCToluene in SOCTracer-based is strongly correlated with the toluene SOC (F4) in PMF (R2 =0.72, slope = 0.52). It was thus quite obvious that the contribution of terpene and isoprene SOAs was seriously underestimated in the tracer yield method compared with the PMF-based method.
In summary, when estimating the concentration of SOC, the OC/EC-based method suffers from difficulties in determining the primary OC/EC ratio; the variation in the WSOC/levoglucosan ratio in the primary particles generated by the combustion of different types of plants or under different burning conditions would bring uncertainties to the WSOC-based method; and there are great uncertainties in the selection of the fSOC value in the tracer yield method. In comparison, the PMF-based method with WSOC and organic tracers can avoid the uncertainties mentioned above to a certain extent and can resolve the sources and contributions of SOC more reasonably.
4. Conclusions
Analysis of the concentrations of OC, EC, WSOC, and organic tracers in seasonal PM2.5 samples in 2019 at one urban and one suburban site showed the high pollution levels of organic aerosols in Bengbu. About 60% of OC was water soluble, secondary organic aerosols were the main contributor to WSOC, and biomass burning had an important contribution to WSOC in autumn and winter (~40%). The concentrations of isoprene SOA tracers show strong seasonal variations in being the highest in summer and the lowest in winter. The seasonal variation in monoterpene and sesquiterpene SOA tracers was different from that of isoprene SOA tracers, indicating different emission characteristics of their precursors. Concentrations of the toluene SOA tracer in spring and summer were higher at the urban site than at the suburban site, while they were higher at the suburban site in autumn and winter, suggesting different emission sources of anthropogenic VOCs in urban and suburban areas. A comparison was made of the estimated concentrations of SOC from the OC/EC-based method, the WSOC-based method, the SOA tracer yield method, and the PMF-based method, and the results showed that the PMF analysis using WSOC and organic tracers can reasonably resolve the sources and contribution of SOC. The annual average concentration of SOC in PM2.5 in Bengbu was 3.02 μg m−3 at the urban site and 3.54 μg m−3 at the suburban site, accounting for 33% and 37% of OC, respectively. SOC was mainly associated with the SOA tracers in summer and with secondary ions but not the measured SOA tracers in other seasons, suggesting different formation mechanisms in different seasons. Based on our results, reducing biomass burning and anthropogenic VOC emissions is an important measure that should be taken to improve the air quality in Bengbu.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.F. and L.L. (Li Li); methodology, J.F.; data curation, L.L. (Liang Li); investigation, S.Z., H.T., and Q.L.; formal analysis, S.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, S.Z.; writing—review and editing, J.F. and L.L. (Li Li); project administration, L.L. (Liang Li) and C.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was financially supported by the Bengbu Municipal Bureau of Ecology and Environment (project C-2018-ZFCG-Z-563) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 41877373).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Claeys, M.; Graham, B.; Vas, G.; Wang, W.; Vermeylen, R.; Pashynska, V.; Cafmeyer, J.; Guyon, P.; Andreae, M.O.; Artaxo, P.; et al. Formation of secondary organic aerosols through photooxidation of isoprene. Science 2004, 303, 1173–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jang, M.S.; Czoschke, N.M.; Lee, S.; Kamens, R.M. Heterogeneous atmospheric aerosol production by acid-catalyzed particle-phase reactions. Science 2002, 298, 814–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimenez, J.L.; Canagaratna, M.R.; Donahue, N.M.; Prevot, A.S.H.; Zhang, Q.; Kroll, J.H.; DeCarlo, P.F.; Allan, J.D.; Coe, H.; Ng, N.L.; et al. Evolution of organic aerosols in the atmosphere. Science 2009, 326, 1525–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffin, R.J.; Cocker, D.R.; Seinfeld, J.H.; Dabdub, D. Estimate of global atmospheric organic aerosol from oxidation of biogenic hydrocarbons. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1999, 26, 2721–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guenther, A.; Karl, T.; Harley, P.; Wiedinmyer, C.; Palmer, P.I.; Geron, C. Estimates of global terrestrial isoprene emissions using MEGAN (Model of Emissions of Gases and Aerosols from Nature). Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2006, 6, 3181–3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duhl, T.R.; Helmig, D.; Guenther, A. Sesquiterpene emissions from vegetation: A review. Biogeosciences 2008, 5, 761–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Surratt, J.D.; Murphy, S.M.; Kroll, J.H.; Ng, N.L.; Hildebrandt, L.; Sorooshian, A.; Szmigielski, R.; Vermeylen, R.; Maenhaut, W.; Claeys, M.; et al. Chemical composition of secondary organic aerosol formed from the photooxidation of isoprene. J. Phys. Chem. A 2006, 110, 9665–9690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, C.M.; Kawamura, K.; Fu, P.Q. Seasonal variations of biogenic secondary organic aerosol tracers in Cape Hedo, Okinawa. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 130, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleindienst, T.E.; Jaoui, M.; Lewandowski, M.; Offenberg, J.H.; Lewis, C.W.; Bhave, P.V.; Edney, E.O. Estimates of the contributions of biogenic and anthropogenic hydrocarbons to secondary organic aerosol at a southeastern US location. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 8288–8300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaoui, M.; Lewandowski, M.; Kleindienst, T.E.; Offenberg, J.H.; Edney, E.O. beta-caryophyllinic acid: An atmospheric tracer for beta-caryophyllene secondary organic aerosol. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L05816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Wang, X.M.; Xie, Z.Q.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, L.G. Impacts of Siberian biomass burning on organic aerosols over the North Pacific Ocean and the Arctic: Primary and secondary organic tracers. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 3149–3157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewandowski, M.; Piletic, I.R.; Kleindienst, T.E.; Offenberg, J.H.; Beaver, M.R.; Jaoui, M.; Docherty, K.S.; Edney, E.O. Secondary organic aerosol characterisation at field sites across the United States during the spring-summer period. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2013, 93, 1084–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaoui, M.; Kleindienst, T.E.; Lewandowski, M.; Offenberg, J.H.; Edney, E.O. Identification and quantification of aerosol polar oxygenated compounds bearing carboxylic or hydroxyl groups. 2. Organic tracer compounds from monoterpenes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 5661–5673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farina, S.C.; Adams, P.J.; Pandis, S.N. Modeling global secondary organic aerosol formation and processing with the volatility basis set: Implications for anthropogenic secondary organic aerosol. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2010, 115, D09202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, X.; Wang, X.M.; Gao, B.; Fu, X.X.; He, Q.F.; Zhao, X.Y.; Yu, J.Z.; Zheng, M. Tracer-based estimation of secondary organic carbon in the Pearl River Delta, south China. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2012, 117, D05313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Schneidemesser, E.; Zhou, J.B.; Stone, E.A.; Schauer, J.J.; Shpund, J.; Brenner, S.; Qasrawi, R.; Abdeen, Z.; Sarnat, J.A. Spatial variability of carbonaceous aerosol concentrations in East and West Jerusalem. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 1911–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, M.M.H.; Ortiz-Montalvo, D.L.; Hennigan, C.J. The effects of isoprene and NOx on secondary organic aerosols formed through reversible and irreversible uptake to aerosol water. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 1171–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, L.; Guo, H.Y.; Boyd, C.M.; Klein, M.; Bougiatioti, A.; Cerully, K.M.; Hite, J.R.; Isaacman-VanWertz, G.; Kreisberg, N.M.; Knote, C.; et al. Effects of anthropogenic emissions on aerosol formation from isoprene and monoterpenes in the southeastern United States. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, D.F.; Schmitt, S.H.; Wang, M.J.; Acir, I.H.; Tillmann, R.; Tan, Z.F.; Novelli, A.; Fuchs, H.; Pullinen, I.; Wegener, R.; et al. Effects of NOx and SO2 on the secondary organic aerosol formation from photooxidation of alpha-pinene and limonene. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 1611–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Froyd, K.D.; Murphy, S.M.; Murphy, D.M.; de Gouw, J.A.; Eddingsaas, N.C.; Wennberg, P.O. Contribution of isoprene-derived organosulfates to free tropospheric aerosol mass. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 21360–21365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.J.; Tang, L.L.; Sun, Y.L.; Favez, O.; Canonaco, F.; Albinet, A.; Couvidat, F.; Liu, D.T.; Jayne, J.T.; Wang, Z.; et al. Limited formation of isoprene epoxydiols-derived secondary organic aerosol under NOx-rich environments in Eastern China. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 2035–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, X.; He, Q.F.; Shen, R.Q.; Yu, Q.Q.; Wang, X.M. Spatial distributions of secondary organic aerosols from isoprene, monoterpenes, beta-caryophyllene, and aromatics over China during summer. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2014, 119, 11877–11891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.A.; Wang, X.M.; Zheng, M. The influence of temperature and aerosol acidity on biogenic secondary organic aerosol tracers: Observations at a rural site in the central Pearl River Delta region, South China. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 1303–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.L.; Li, M.; Zhang, P.; Gong, S.Y.; Zhong, M.A.; Wu, M.H.; Zheng, M.; Chen, C.H.; Wang, H.L.; Lou, S.R. Investigation of the sources and seasonal variations of secondary organic aerosols in PM2.5 in Shanghai with organic tracers. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 79, 614–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Bian, Q.; Li, T.W.Y.; Lau, A.K.H.; Yu, J.Z. Contributions of isoprene, monoterpenes, beta-caryophyllene, and toluene to secondary organic aerosols in Hong Kong during the summer of 2006. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2008, 113, D22206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, R.Z.; Wu, Z.P.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.J.; Shang, D.J.; Xiao, Y.; Li, M.R.; Zeng, L.M.; Wu, Z.J.; Hallquist, M.; et al. Primary and secondary organic aerosols in summer 2016 in Beijing. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 4055–4068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, R.; Li, Q.; Xu, J.; Li, L.; Ge, C.J.; Huang, L.; Sun, D.H.; Liu, Z.Y.; Zhang, K.; Zhou, G.Z.; et al. Regional air pollution process in winter over the Yangtze River Delta and its influence on typical northern cities. Huan Jing Ke Xue 2020, 41, 1520–1534. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.L.; Hu, M.; Chan, C.K.; Lau, P.S.; Fang, M.; He, L.Y.; Tang, X.Y. A comparative study of the organic matter in PM2.5 from three Chinese megacities in three different climatic zones. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 3983–3994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayol-Bracero, O.L.; Guyon, P.; Graham, B.; Roberts, G.; Andreae, M.O.; Decesari, S.; Facchini, M.C.; Fuzzi, S.; Artaxo, P. Water-soluble organic compounds in biomass burning aerosols over Amazonia—2. Apportionment of the chemical composition and importance of the polyacidic fraction. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2002, 107, 8091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Zheng, M.; Yu, L.P.; Zhang, X.L.; Weber, R.J.; Yan, B.; Russell, A.G.; Edgerton, E.S.; Wang, X.M. Spatial and seasonal trends in biogenic secondary organic aerosol tracers and water-soluble organic carbon in the southeastern United States. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 5171–5176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.X.; Shao, M.; Zhang, Y.H.; Zeng, L.M.; He, L.Y.; Zhu, B.; Wei, Y.J.; Zhu, X.L. Source profiles of particulate organic matters emitted from cereal straw burnings. J. Environ. Sci.-China 2007, 19, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.H.; Knipping, E.M.; Edgerton, E.S.; Shaw, S.L.; Surratt, J.D. Investigating the influences of SO2 and NH3 levels on isoprene-derived secondary organic aerosol formation using conditional sampling approaches. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 8457–8470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Surratt, J.D.; Chan, A.W.H.; Eddingsaas, N.C.; Chan, M.N.; Loza, C.L.; Kwan, A.J.; Hersey, S.P.; Flagan, R.C.; Wennberg, P.O.; Seinfeld, J.H. Reactive intermediates revealed in secondary organic aerosol formation from isoprene. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 6640–6645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- D’Ambro, E.L.; Schobesberger, S.; Gaston, C.J.; Lopez-Hilfiker, F.D.; Lee, B.; Liu, J.; Zelenyuk, A.; Bell, D.; Cappa, C.D.; Helgestad, T.; et al. Chamber-based insights into the factors controlling epoxydiol (IEPOX) secondary organic aerosol (SOA) yield, composition, and volatility. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 11253–11265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Surratt, J.D.; Lin, Y.H.; Bapat, J.; Kamens, R.M. Effect of relative humidity on SOA formation from isoprene/NO photooxidation: Enhancement of 2-methylglyceric acid and its corresponding oligoesters under dry conditions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 6411–6424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, P.Q.; Kawamura, K.; Kanaya, Y.; Wang, Z.F. Contributions of biogenic volatile organic compounds to the formation of secondary organic aerosols over Mt Tai, Central East China. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 4817–4826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, Z.Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.R.; Xu, L.L.; Liu, T.T.; Xiao, H.; Hong, Y.W.; Chen, J.S.; Li, M.R.; Deng, J.J.; et al. Secondary organic aerosol of PM2.5 in a mountainous forest area in southeastern China: Molecular compositions and tracers implication. Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 653, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesonen, M.; Suomela, S.; Kuuliala, O.; Henriks-Eckerman, M.-L.; Aalto-Korte, K. Occupational contact dermatitis caused by d-limonene. Contact Dermat. 2014, 71, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleindienst, T.E.; Conver, T.S.; McIver, C.D.; Edney, E.O. Determination of secondary organic aerosol products from the photooxidation of toluene and their implications in ambient PM2.5. J. Atmos. Chem. 2004, 47, 79–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turpin, B.J.; Huntzicker, J.J. Identification of secondary organic aerosol episodes and quantitation of primary and secondary organic aerosol concentrations during SCAQS. Atmos. Environ. 1995, 29, 3527–3544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, R.J.; Sullivan, A.P.; Peltier, R.E.; Russell, A.; Yan, B.; Zheng, M.; de Gouw, J.; Warneke, C.; Brock, C.; Holloway, J.S.; et al. A study of secondary organic aerosol formation in the anthropogenic-influenced southeastern United States. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2007, 112, D13302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Zheng, M.; Edgerton, E.S.; Jansen, J.J.; Wang, X.M. Contemporary or fossil origin: Split of estimated secondary organic carbon in the southeastern United States. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 9122–9128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, R.; Takegawa, N.; Zheng, M.; Kondo, Y.; Miyazaki, Y.; Miyakawa, T.; Hu, M.; Shao, M.; Zeng, L.; Gong, Y.; et al. Characterization and source apportionment of submicron aerosol with aerosol mass spectrometer during the PRIDE-PRD 2006 campaign. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 6911–6929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castro, L.M.; Pio, C.A.; Harrison, R.M.; Smith, D.J.T. Carbonaceous aerosol in urban and rural European atmospheres: Estimation of secondary organic carbon concentrations. Atmos. Environ. 1999, 33, 2771–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szidat, S.; Jenk, T.M.; Synal, H.A.; Kalberer, M.; Wacker, L.; Hajdas, I.; Kasper-Giebl, A.; Baltensperger, U. Contributions of fossil fuel, biomass-burning, and biogenic emissions to carbonaceous aerosols in Zurich as traced by C-14. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2006, 111, D07206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kondo, Y.; Miyazaki, Y.; Takegawa, N.; Miyakawa, T.; Weber, R.J.; Jimenez, J.L.; Zhang, Q.; Worsnop, D.R. Oxygenated and water-soluble organic aerosols in Tokyo. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2007, 112, D01203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simoneit, B.; Elias, V.O.; Kobayashi, M.; Kawamura, K.; Rushdi, A.I.; Medeiros, P.M.; Rogge, W.F.; Didyk, B.M. Sugars-dominant water-soluble organic compounds in soils and characterization as tracers in atmospheric particulate matter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 5939–5949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).