Chemical Characterization, Source, and SOA Production of Intermediate Volatile Organic Compounds during Haze Episodes in North China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling Collection
2.2. Chemical Analysis
2.3. PMF Model
2.4. Estimation of SOA Production Based on Different Methods
2.5. QA/QC
3. Results and Discussion
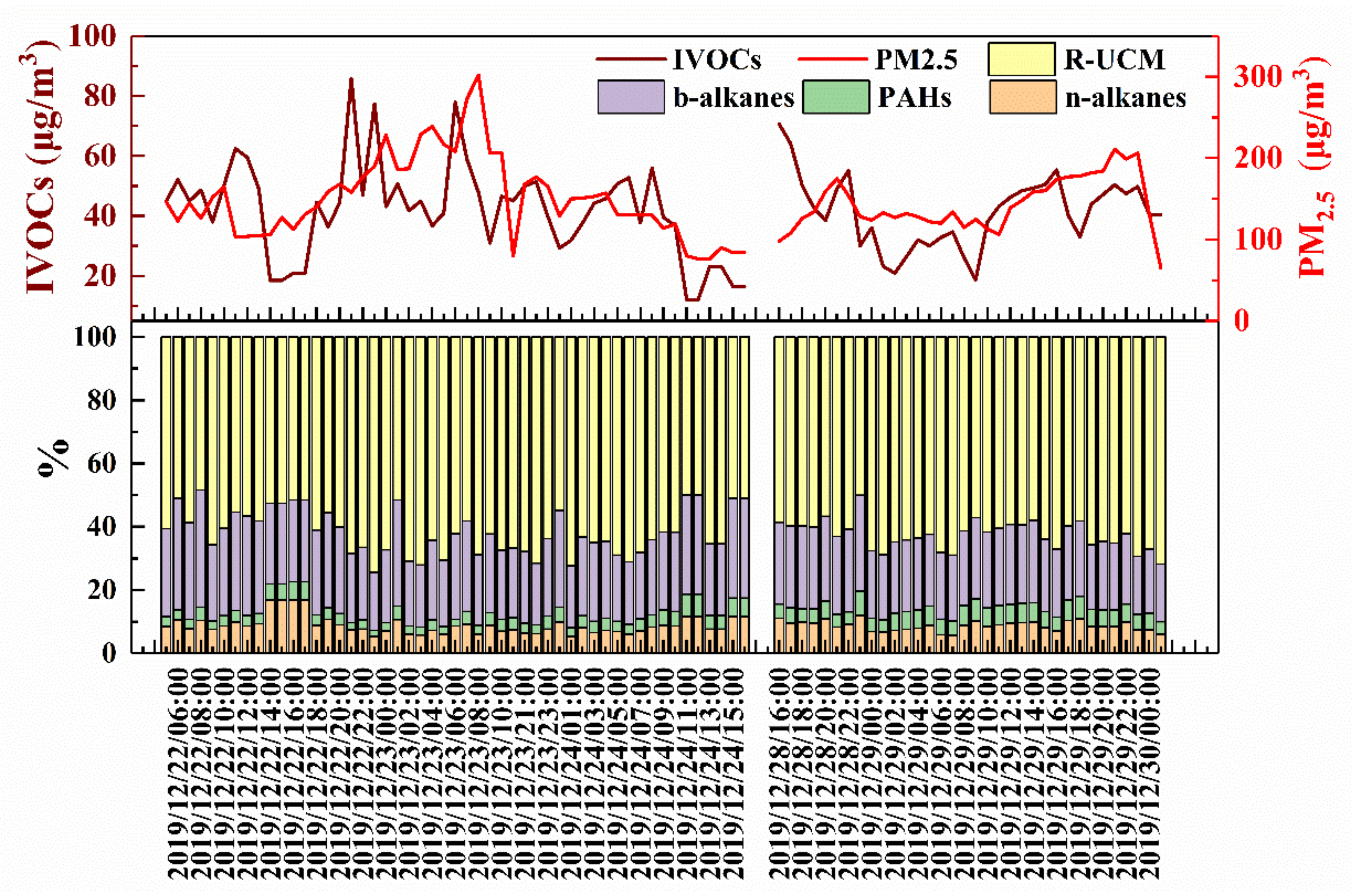
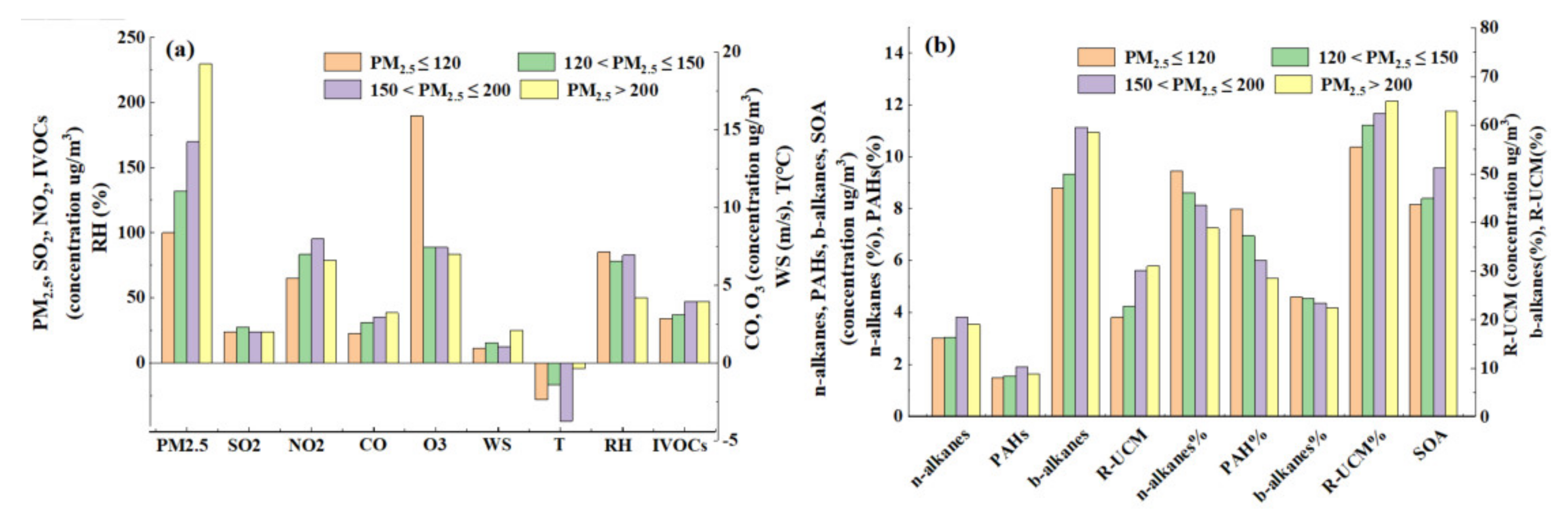
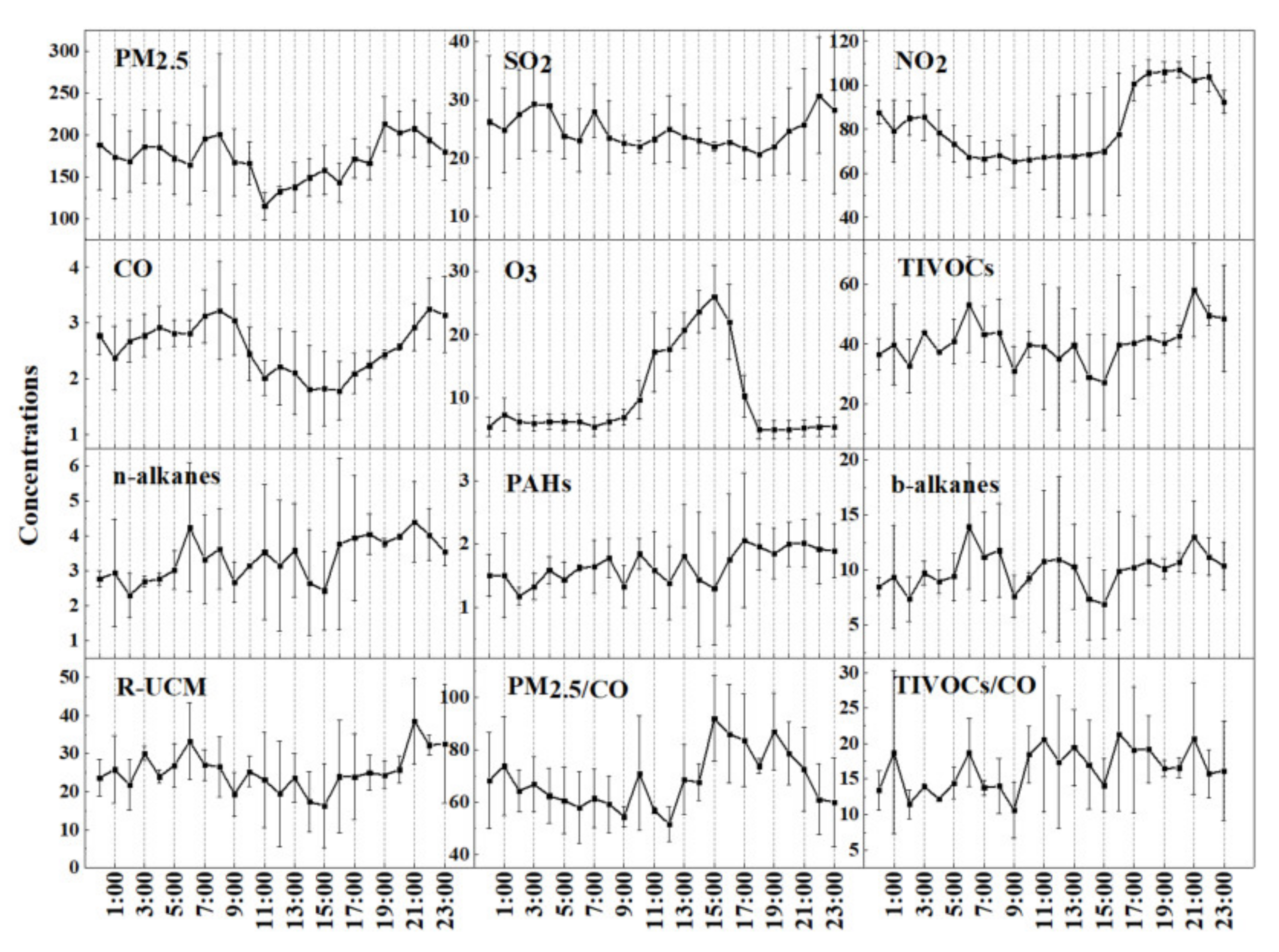
3.1. Concentration Levels of IVOCs during the Haze Episodes
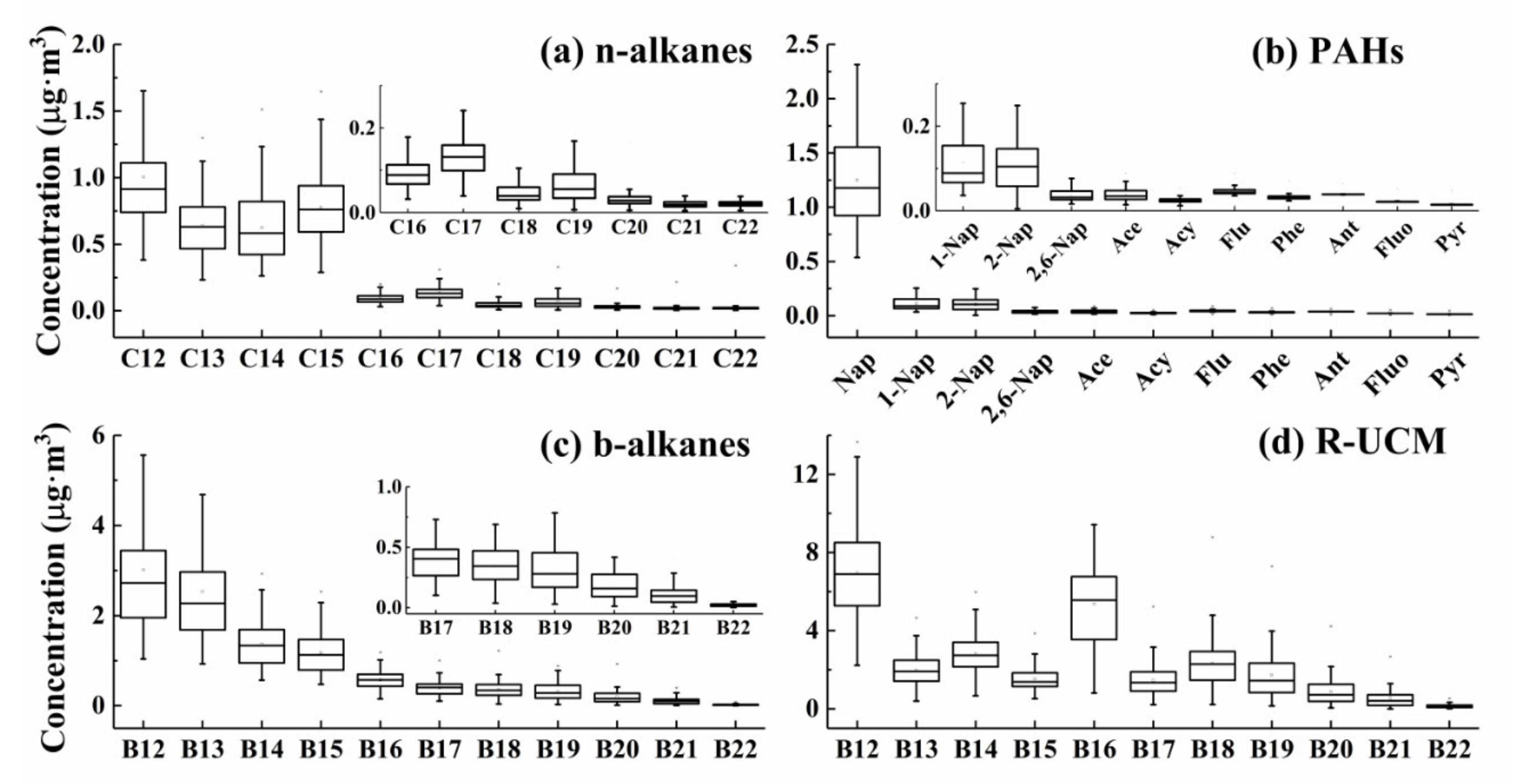
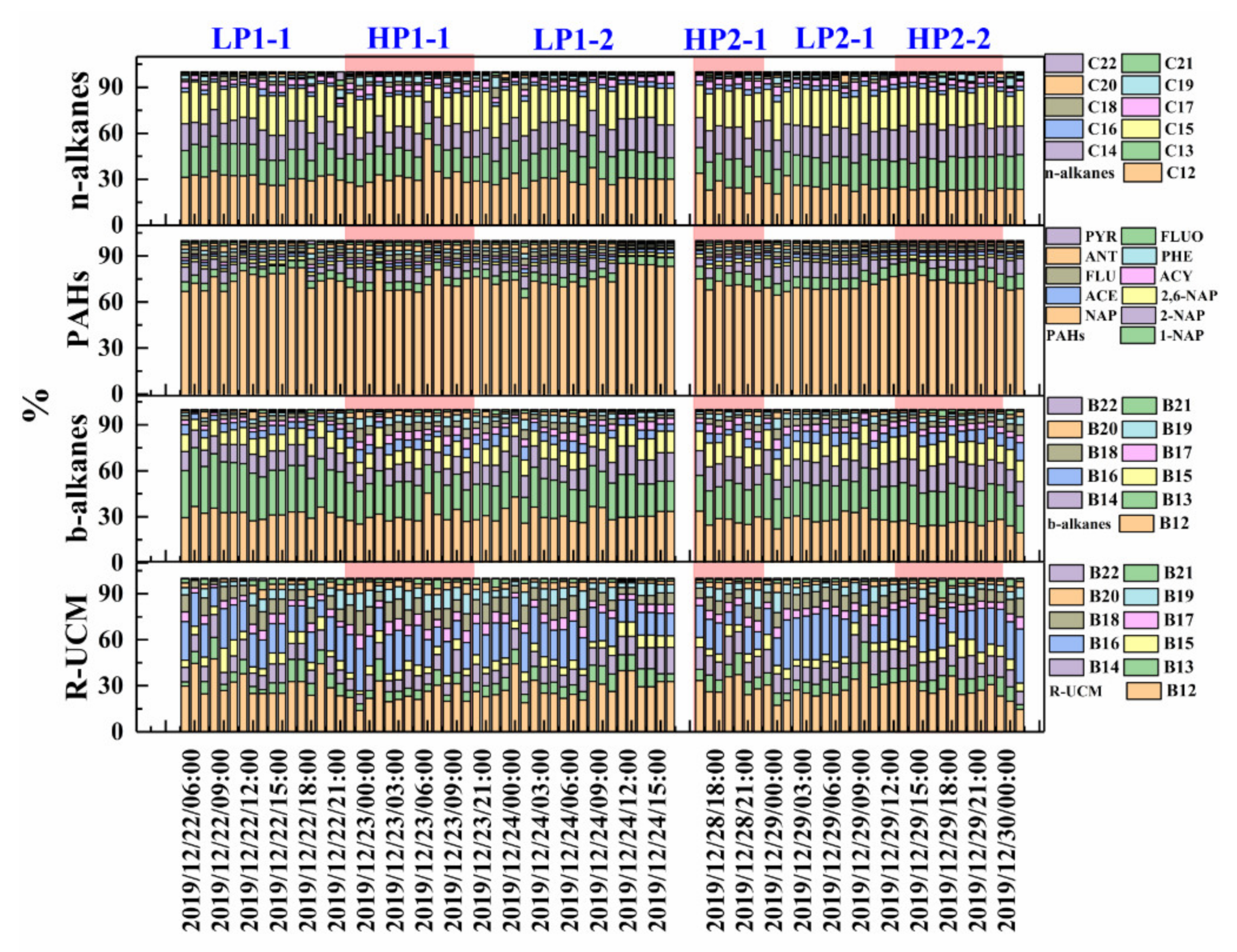
3.2. Component Characteristics of IVOCs during Haze Episodes
3.3. Sources of IVOCs
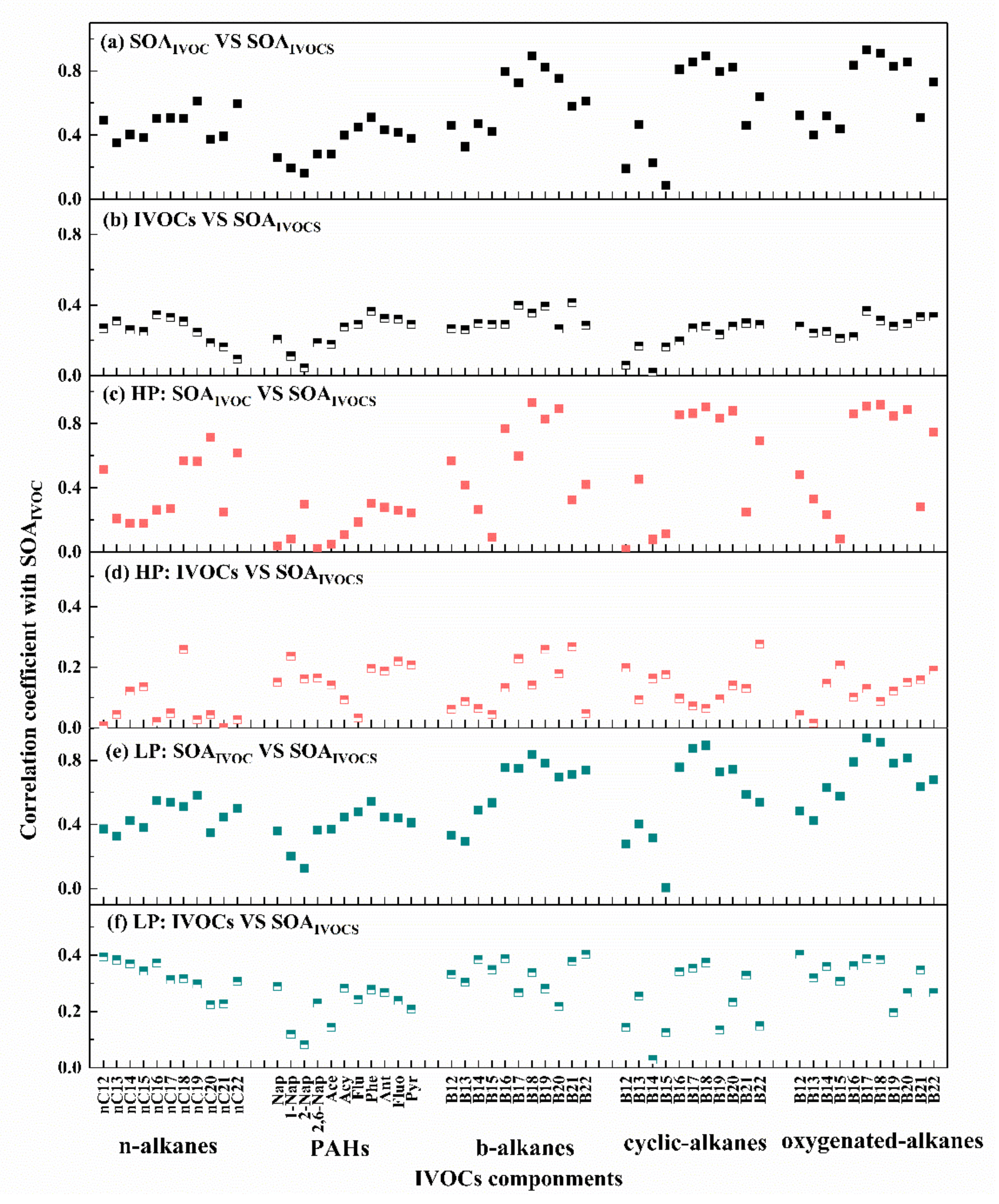
3.4. Estimation of SOA Production
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, X.J.; Zhao, P.S.; Xu, J.; Meng, W.; Pu, W.W.; Dong, F.; He, D.; Shi, Q.F. Analysis of a winter regional haze event and its formation mechanism in the North China Plain. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2013, 13, 5685–5696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Li, J.; Liu, D.; Ding, P.; Shen, C.; Mo, Y.; Wang, X.; Luo, C.; Cheng, Z.; Szidat, S.; et al. Source apportionment and dynamic changes of carbonaceous aerosols during the haze bloom-decay process in China based on radiocarbon and organic molecular tracers. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2016, 16, 2985–2996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kautzman, K.E.; Surratt, J.D.; Chan, M.N.; Chan, A.W.H.; Hersey, S.P.; Chhabra, P.S.; Dalleska, N.F.; Wennberg, P.O.; Flagan, R.C.; Seinfeld, J.H. Chemical composition of gas- and aerosol-phase products from the photooxidation of naphthalene. J. Phys. Chem. A 2010, 114, 913–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, B.; Hu, W.W.; Shao, M.; Wang, M.; Chen, W.T.; Lu, S.H.; Zeng, L.M.; Hu, M. VOC emissions, evolutions and contributions to SOA formation at a receptor site in eastern China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2013, 13, 8815–8832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Couvidat, F.; Kim, Y.; Sartelet, K.; Seigneur, C.; Marchand, N.; Sciare, J. Modeling secondary organic aerosol in an urban area: Application to Paris, France. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2013, 13, 983–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Presto, A.A.; Miracolo, M.A.; Kroll, J.H.; Worsnop, D.R.; Robinson, A.L.; Donahue, N.M. Intermediate-Volatility Organic Compounds A Potential Source of Ambient Oxidized Organic Aerosol. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 43, 4744–4749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Y.; Shao, M.; Li, Y.; Chen, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Wu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Hu, M.; et al. Potentially Important Contribution of Gas-Phase Oxidation of Naphthalene and Methylnaphthalene to Secondary Organic Aerosol during Haze Events in Beijing. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 1235–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, A.W.H.; Kautzman, K.E.; Chhabra, P.S.; Surratt, J.D.; Chan, M.N.; Crounse, J.D.; Kürten, A.; Wennberg, P.O.; Flagan, R.C.; Seinfeld, J.H. Secondary organic aerosol formation from photooxidation of naphthalene and alkylnaphthalenes: Implications for oxidation of intermediate volatility organic compounds (IVOCs). Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 3049–3060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pye, H.O.T.; Seinfeld, J.H. A global perspective on aerosol from low-volatility organic compounds. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2010, 10, 4377–4401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, B.; Wang, S.; Donahue, N.M.; Jathar, S.H.; Huang, X.; Wu, W.; Hao, J.; Robinson, A. Quantifying the effect of organic aerosol aging and intermediate-volatility emissions on regional-scale aerosol pollution in China. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pye, H.O.T.; Pouliot, G. Modeling the Role of Alkanes, Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons, and Their Oligomers in Secondary Organic Aerosol Formation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 6041–6047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woody, M.C.; West, J.J.; Jathar, S.H.; Robinson, A.L.; Arunachalam, S. Estimates of non-traditional secondary organic aerosols from aircraft SVOC and IVOC emissions using CMAQ. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2015, 15, 6929–6942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qian, Z.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Z.; Han, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, Y.; Shang, Y.; Guo, H.; Li, Q.; Shen, G.; et al. Intermediate Volatile Organic Compound Emissions from Residential Solid Fuel Combustion Based on Field Measurements in Rural China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 5689–5700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Zhu, L.; Wang, S.; Wisthaler, A.; Li, Q.; Jiang, J.; Hao, J. Time-Resolved Intermediate-Volatility and Semivolatile Organic Compound Emissions from Household Coal Combustion in Northern China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 9269–9278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Nguyen, N.T.; Presto, A.A.; Hennigan, C.J.; May, A.; Robinson, A. Intermediate Volatility Organic Compound Emissions from On-Road Gasoline Vehicles and Small Off-Road Gasoline Engines. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 4554–4563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Nguyen, N.T.; Presto, A.A.; Hennigan, C.J.; May, A.; Robinson, A. Intermediate Volatility Organic Compound Emissions from On-Road Diesel Vehicles: Chemical Composition, Emission Factors, and Estimated Secondary Organic Aerosol Production. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 11516–11526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cross, E.S.; Sappok, A.G.; Wong, V.W.; Kroll, J.H. Load-Dependent Emission Factors and Chemical Characteristics of IVOCs from a Medium-Duty Diesel Engine. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 13483–13491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, H.; Hao, Y.; Zhang, W.; Su, P.; Zhang, F.; Chen, Y.; Feng, D.; Li, Y. Emission of intermediate volatility organic compounds from a ship main engine burning heavy fuel oil. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 84, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Liu, H.; Shen, X.; Fu, M.; Huang, F.; Man, H.; Deng, F.; Shaikh, A.A.; Wang, X.; Dong, R.; et al. Intermediate-Volatility Organic Compound Emissions from Nonroad Construction Machinery under Different Operation Modes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 13832–13840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cross, E.S.; Hunter, J.F.; Carrasquillo, A.J.; Franklin, J.P.; Herndon, S.C.; Jayne, J.T.; Worsnop, D.R.; Miake-Lye, R.C.; Kroll, J.H. Online measurements of the emissions of intermediate-volatility and semi-volatile organic compounds from aircraft. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2013, 13, 7845–7858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, P.P.; Li, Y.J.; Zhang, F.; Chen, Y.J.; Feng, Y.L.; Xu, J.M.; Ma, Y.G.; Huang, C.; Li, L.; Li, J.; et al. Concentration, composition and variation of ambient IVOCs in Shanghai Port during the G20 summit. GEOCHIMICA 2018, 47, 313321. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Ren, B.; Qiao, Z.; Zhu, J.; Wang, H.; Zhou, M.; Qiao, L.; Lou, S.; Jing, S.; Huang, C.; et al. Characteristics of atmospheric intermediate volatility organic compounds (IVOCs) in winter and summer under different air pollution levels. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 210, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Hennigan, C.; May, A.; Tkacik, D.S.; de Gouw, J.; Gilman, J.B.; Kuster, W.; Borbon, A.; Robinson, A. Intermediate-Volatility Organic Compounds: A Large Source of Secondary Organic Aerosol. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 13743–13750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, M.; Chen, Y.; Tian, C.; Zhang, F.; Yan, C.; Zheng, M. Chemical composition of PM 2.5 from two tunnels with different vehicular fleet characteristics. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 550, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, M.; Chen, Y.; Feng, Y.; Li, C.; Zheng, J.; Tian, C.; Yan, C.; Zheng, M. Measurement of PM and its chemical composition in real-world emissions from non-road and on-road diesel vehicles. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2017, 17, 6779–6795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lv, L.; Chen, Y.; Han, Y.; Cui, M.; Wei, P.; Zheng, M.; Hu, J. High-time-resolution PM2.5 source apportionment based on multi-model with organic tracers in Beijing during haze episodes. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 772, 144766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopke, P.K. Review of receptor modeling methods for source apportionment. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2015, 66, 237–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paatero, P. The multilinear engine—A table-driven, least squares program for solving multilinear problems, including the n-way parallel factor analysis model. J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 1999, 8, 854–888. [Google Scholar]
- Aumont, B.; Valorso, R.; Mouchel-Vallon, C.; Camredon, M.; Lee-Taylor, J.; Madronich, S. Modeling SOA formation from the oxidation of intermediate volatility n-alkanes. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 7577–7589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, J.; Lee, S.; Ho, K.F.; Zou, S.; Fung, K.; Li, Y.; Watson, J.; Chow, J.C. Spatial and seasonal variations of atmospheric organic carbon and elemental carbon in Pearl River Delta Region, China. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 4447–4456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Dennis, R.L.; Bhave, P.V.; Eder, B.K. Primary and secondary organic aerosols over the United States: Estimates on the basis of observed organic carbon (OC) and elemental carbon (EC), and air quality modeled primary OC/EC ratios. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 5257–5268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.G. Characteristics and Source Apportionment of Atmospheric Intermediate-Volatility Organic Compounds (IVOCs) in Selected Chinese Cities. Ph.D. Thesis, Guangzhou Institute of Geochemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou, China, 2020. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Xie, M.; Hannigan, M.; Barsanti, K. Gas/particle partitioning of n-alkanes, PAHs and oxygenated PAHs in urban Denver. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 95, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozaffar, A.; Zhang, Y.-L.; Fan, M.; Cao, F.; Lin, Y.-C. Characteristics of summertime ambient VOCs and their contributions to O3 and SOA formation in a suburban area of Nanjing, China. Atmos. Res. 2020, 240, 104923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, R.; Fu, H.; Zhou, D.; Chen, J. Observation and analysis of atmospheric volatile organic compounds in a typical petrochemical area in Yangtze River Delta, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 71, 233–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olumayede, E.G. Atmospheric Volatile Organic Compounds and Ozone Creation Potential in an Urban Center of Southern Nigeria. Int. J. Atmos. Sci. 2014, 2014, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.J.; Feng, Y.L.; Qian, Z.; Han, Y.; Chen, Y.J. Emission Characteristics of IVOCs from the Combustion of Residential Solid Fuels and the Impact of Burning Temperature. Environ. Sci. 2019, 40, 4404–4411. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.; Hu, Q.; Li, Y.; Tian, J.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Feng, J.; An, J.; Qiao, L.; Wang, H.; et al. Intermediate Volatility Organic Compound Emissions from a Large Cargo Vessel Operated under Real-World Conditions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 12934–12942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Emission Sources | n-Alkanes/b-Alkanes | Sampling Methods | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Biomass burning | Rice straw | 0.18 | Laboratory simulation | Lu et al. [37] |
| Pine wood | 0.08 | Laboratory simulation | Lu et al. [37] | |
| Crop straw | 0.43 ± 0.17 | Filed measurement | Qian et al. [13] | |
| Fuelwood | 0.38 ± 0.12 | Filed measurement | ||
| Coal combustion | Coal | 0.57 ± 0.17 | Filed measurement | Qian et al. [13] |
| Coal | 0.47 ± 0.09 | Laboratory simulation | Lu et al. [37] | |
| Gasoline emission | GV | 0.10 | On/off-road measurement | Zhao et al. [15] |
| GV | 0.83 ± 0.11 | On-road measurement | Unpublished | |
| EGV | 0.84 ± 0.35 | On-road measurement | ||
| Diesel emission | DV | 0.55 ± 0.26 | On-road measurement | Unpublished |
| DV | 0.38 | On-road measurement | Zhao et al. [16] | |
| HFOV | 0.42 | Filed measurement | Huang et al. [38] | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, X.; Zhao, J.; Feng, Y.; Cai, J.; Yan, C.; Chen, Y. Chemical Characterization, Source, and SOA Production of Intermediate Volatile Organic Compounds during Haze Episodes in North China. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1484. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12111484
Feng X, Zhao J, Feng Y, Cai J, Yan C, Chen Y. Chemical Characterization, Source, and SOA Production of Intermediate Volatile Organic Compounds during Haze Episodes in North China. Atmosphere. 2021; 12(11):1484. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12111484
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Xinxin, Jinhu Zhao, Yanli Feng, Junjie Cai, Caiqing Yan, and Yingjun Chen. 2021. "Chemical Characterization, Source, and SOA Production of Intermediate Volatile Organic Compounds during Haze Episodes in North China" Atmosphere 12, no. 11: 1484. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12111484
APA StyleFeng, X., Zhao, J., Feng, Y., Cai, J., Yan, C., & Chen, Y. (2021). Chemical Characterization, Source, and SOA Production of Intermediate Volatile Organic Compounds during Haze Episodes in North China. Atmosphere, 12(11), 1484. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12111484






