RNA Sequencing on Muscle Biopsies from Exertional Rhabdomyolysis Patients Revealed Down-Regulation of Mitochondrial Function and Enhancement of Extracellular Matrix Composition
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Cohort and Clinical Information
2.2. Muscle Sample Collection
2.3. Total RNA Extraction and RNA Sequencing
2.4. RNA Sequencing Data Analysis
2.5. Functional and Pathway Enrichment Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Characteristics of ER Cases
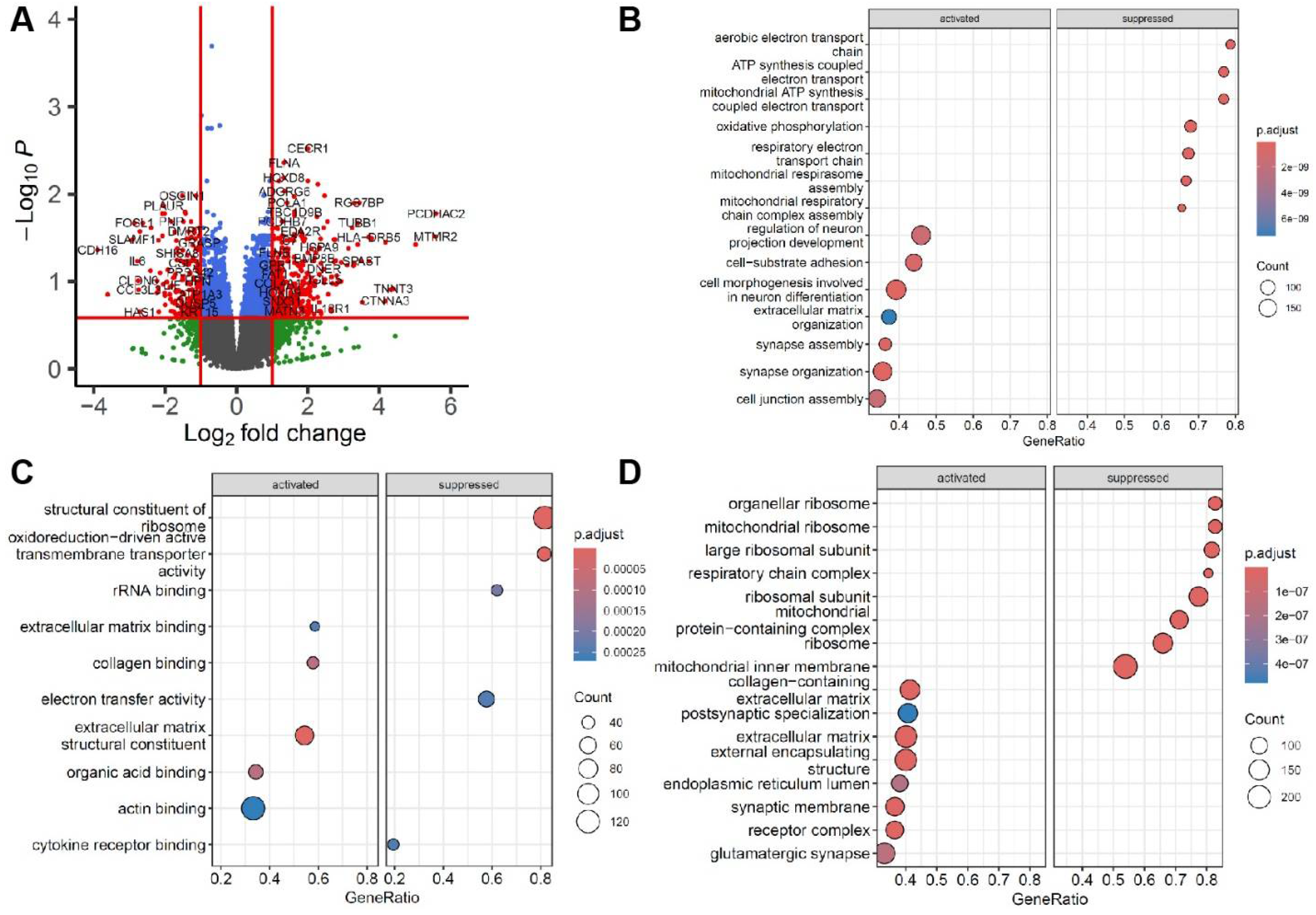
3.2. Overview of Differentiation Expression Analysis in Skeletal Muscle Expression Profiling
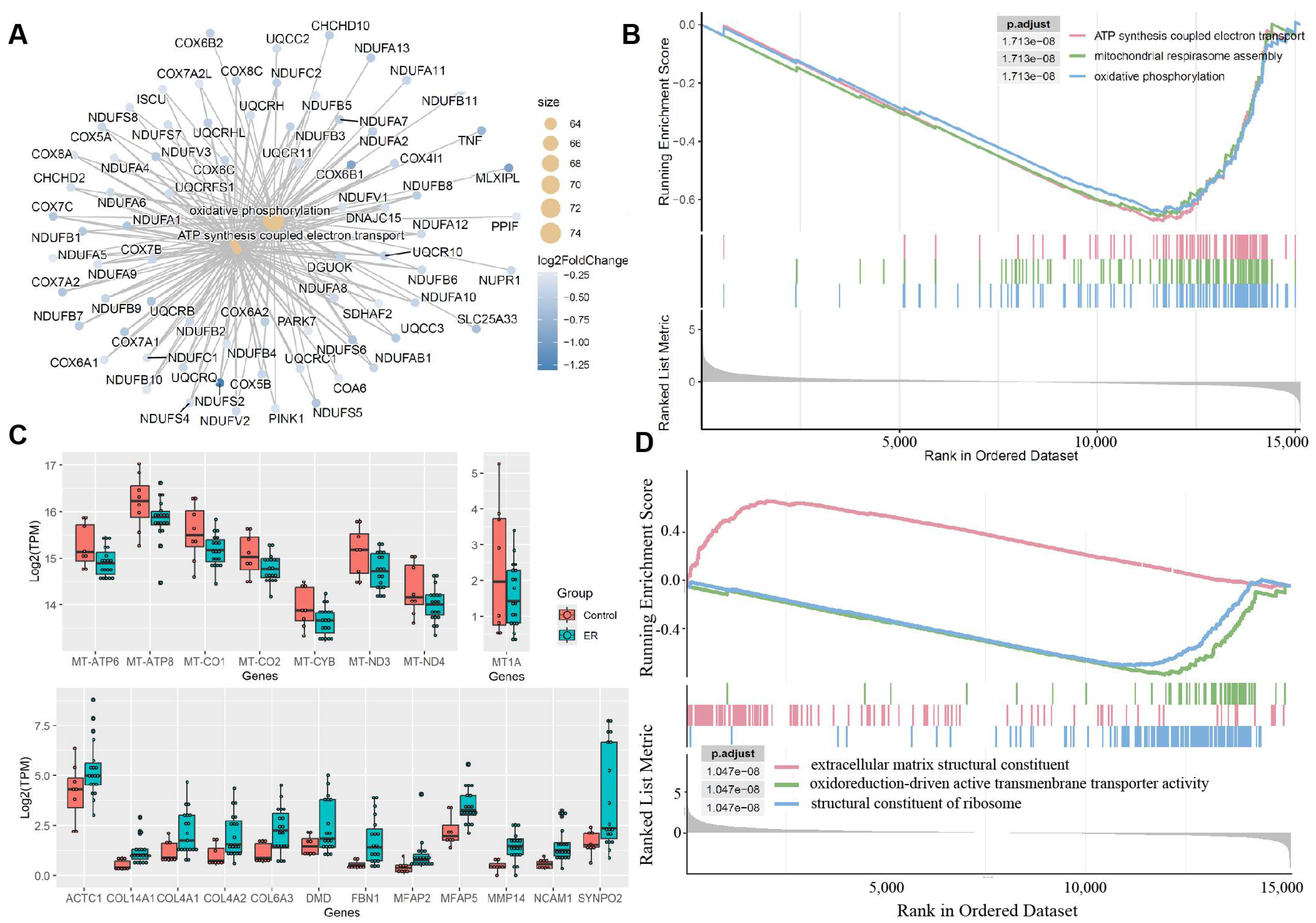
3.3. Functional Pathway Analysis of Significant Differential Gene Expression
3.4. Gene Set Enrichment Analysis of Significant Differential Gene Expression
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kruijt, N.; Laforet, P.; Vissing, J.; Bhai, S.; Stemmerik, M.G.; Kleefeld, F.; Voermans, N.C.; Fatehi, F.; Gupta, V.; Ferreiro, A.; et al. 276th ENMC International Workshop: Recommendations on optimal diagnostic pathway and management strategy for patients with acute rhabdomyolysis worldwide. 15th-17th March 2024, Hoofddorp, The Netherlands. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2025, 50, 105344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connnor, F.G.; Deuster, P.A. Rhabdomyolysis. In Goldman-Cecil Medicine; Goldman, L., Cooney, K.A., Eds.; Elsevier Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 714–717. [Google Scholar]
- Kruijt, N.; Bersselaar, L.R.v.D.; Kamsteeg, E.J.; Verbeeck, W.; Snoeck, M.M.J.; Everaerd, D.S.; Abdo, W.F.; Jansen, D.R.M.; Erasmus, C.E.; Jungbluth, H.; et al. The etiology of rhabdomyolysis: An interaction between genetic susceptibility and external triggers. Eur. J. Neurol. 2021, 28, 647–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nye, N.S.; Kasper, K.; Madsen, C.M.; Szczepanik, M.; Covey, C.J.; Oh, R.; Kane, S.; Beutler, A.I.; Leggit, J.C.; Deuster, P.A.; et al. Clinical Practice Guidelines for Exertional Rhabdomyolysis: A Military Medicine Perspective. Curr. Sports Med. Rep. 2021, 20, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melli, G.; Chaudhry, V.; Cornblath, D.R. Rhabdomyolysis: An evaluation of 475 hospitalized patients. Medicine 2005, 84, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, M.; Sambuughin, N.; Mungunshukh, O.; Edgeworth, D.B.; Hupalo, D.; Zhang, X.; Wilkerson, M.D.; Dalgard, C.L.; O’connor, F.G.; Deuster, P.A. Genome-Wide Analysis of Exertional Rhabdomyolysis in Sickle Cell Trait Positive African Americans. Genes 2024, 15, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boden, B.P.; Isaacs, D.J.; Ahmed, A.E.; Anderson, S.A. Epidemiology of Exertional Rhabdomyolysis in the United States: Analysis of NEISS Database 2000 to 2019. Physician Sportsmed. 2022, 50, 486–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makaryus, J.N.; Catanzaro, J.N.; Katona, K.C. Exertional rhabdomyolysis and renal failure in patients with sickle cell trait: Is it time to change our approach? Hematology 2007, 12, 349–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scalco, R.S.; Snoeck, M.; Quinlivan, R.; Treves, S.; Laforét, P.; Jungbluth, H.; Voermans, N.C. Exertional rhabdomyolysis: Physiological response or manifestation of an underlying myopathy? BMJ Open Sport Exerc. Med. 2016, 2, e000151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stožer, A.; Vodopivc, P.; Bombek, L.K. Pathophysiology of exercise-induced muscle damage and its structural, functional, metabolic, and clinical consequences. Physiol. Res. 2020, 69, 565–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valberg, S.J.; Velez-Irizarry, D.; Williams, Z.J.; Henry, M.L.; Iglewski, H.; Herrick, K.; Fenger, C. Enriched Pathways of Calcium Regulation, Cellular/Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Cell Proliferation Characterize Gluteal Muscle of Standardbred Horses between Episodes of Recurrent Exertional Rhabdomyolysis. Genes 2022, 13, 1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldrich, K.; Velez-Irizarry, D.; Fenger, C.; Schott, M.; Valberg, S.J. Pathways of calcium regulation, electron transport, and mitochondrial protein translation are molecular signatures of susceptibility to recurrent exertional rhabdomyolysis in Thoroughbred racehorses. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0244556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera-Serrano, M.; Ravenscroft, G. Recent advances in our understanding of genetic rhabdomyolysis. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2022, 35, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudo, R.T.; Cunha, L.B.P.; Carmo, P.L.; Matos, A.R.; Trachez, M.M.; Cardoso, L.A.M.; Aguiar, M.I.S.; Abreu, A.V.; Zapata-Sudo, G. Use of the caffeine-halothane contracture test for the diagnosis of malignant hyperthermia in Brazil. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2010, 43, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patro, R.; Duggal, G.; Love, M.I.; Irizarry, R.A.; Kingsford, C. Salmon provides fast and bias-aware quantification of transcript expression. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 417–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, A.; Ibrahim, J.G.; Love, M.I. Heavy-tailed prior distributions for sequence count data: Removing the noise and preserving large differences. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 2084–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.; Hu, E.; Xu, S.; Chen, M.; Guo, P.; Dai, Z.; Feng, T.; Zhou, L.; Tang, W.; Zhan, L.; et al. clusterProfiler 4.0: A universal enrichment tool for interpreting omics data. Innovation 2021, 2, 100141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniele, D.O.; Murray, J. Update: Exertional rhabdomyolysis, active component, U.S. Armed Forces, 2017–2021. MSMR 2022, 29, 15–20. [Google Scholar]
- Tietze, D.C.; Borchers, J. Exertional Rhabdomyolysis in the Athlete: A Clinical Review. Sports Health 2014, 6, 336–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillies, A.R.; Lieber, R.L. Structure and function of the skeletal muscle extracellular matrix. Muscle Nerve 2011, 44, 318–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, K.; Shaikh, S.; Chun, H.J.; Ali, S.; Lim, J.H.; Ahmad, S.S.; Lee, E.J.; Choi, I. Extracellular matrix: The critical contributor to skeletal muscle regeneration—A comprehensive review. Inflamm. Regen. 2023, 43, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Jin, Y.; He, J.; Jia, Z.; Liu, Y.; Xu, Y. Extracellular matrix in skeletal muscle injury and atrophy: Mechanisms and therapeutic implications. J. Orthop. Transl. 2025, 52, 404–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrey, E.; Jayr, L.; Mucher, E.; Gospodnetic, S.; Joly, F.; Benech, P.; Alibert, O.; Gidrol, X.; Mata, X.; Vaiman, A.; et al. Transcriptome analysis of muscle in horses suffering from recurrent exertional rhabdomyolysis revealed energetic pathway alterations and disruption in the cytosolic calcium regulation. Anim. Genet. 2012, 43, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.P.Z.; Thomas, S.; Gokmen, R.; Kariyawasam, D. Rhabdomyolysis and severe biphasic disturbance of calcium homeostasis secondary to COVID-19 infection. BMJ Case Rep. 2021, 14, e239611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Category | ER (n = 19) | Controls (n = 8) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Values | Counts | % | Values | Counts | % | |
| Age (year) | ||||||
| Range | 20–44 | 19–62 | ||||
| Mean ± SD | 29.9 ± 6.7 | 30.4 ± 14.1 | ||||
| Gender | ||||||
| Male | 17 | 89.5 | 7 | 87.5 | ||
| Female | 2 | 10.5 | 1 | 12.5 | ||
| Ethnicity | ||||||
| African | 6 | 31.6 | 1 | 12.5 | ||
| Caucasian | 12 | 63.2 | 1 | 12.5 | ||
| Unknown | 1 | 5.3 | 6 | 87.5 | ||
| CK level (IU/L) | ||||||
| Range | 2000–170,000 | N/A | ||||
| Mean | 52,272.5 | N/A | ||||
| Symptoms | ||||||
| Single episodes | 6 | 31.6 | 0 | |||
| >2 episodes | 13 | 68.4 | 0 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ren, M.; Michaelson, L.P.; Mungunsukh, O.; Bedocs, P.; Friel, L.; Cofer, K.; Dartt, C.E.; Sambuughin, N.; O’Connor, F.G. RNA Sequencing on Muscle Biopsies from Exertional Rhabdomyolysis Patients Revealed Down-Regulation of Mitochondrial Function and Enhancement of Extracellular Matrix Composition. Genes 2025, 16, 930. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16080930
Ren M, Michaelson LP, Mungunsukh O, Bedocs P, Friel L, Cofer K, Dartt CE, Sambuughin N, O’Connor FG. RNA Sequencing on Muscle Biopsies from Exertional Rhabdomyolysis Patients Revealed Down-Regulation of Mitochondrial Function and Enhancement of Extracellular Matrix Composition. Genes. 2025; 16(8):930. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16080930
Chicago/Turabian StyleRen, Mingqiang, Luke P. Michaelson, Ognoon Mungunsukh, Peter Bedocs, Liam Friel, Kristen Cofer, Carolyn E. Dartt, Nyamkhishig Sambuughin, and Francis G. O’Connor. 2025. "RNA Sequencing on Muscle Biopsies from Exertional Rhabdomyolysis Patients Revealed Down-Regulation of Mitochondrial Function and Enhancement of Extracellular Matrix Composition" Genes 16, no. 8: 930. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16080930
APA StyleRen, M., Michaelson, L. P., Mungunsukh, O., Bedocs, P., Friel, L., Cofer, K., Dartt, C. E., Sambuughin, N., & O’Connor, F. G. (2025). RNA Sequencing on Muscle Biopsies from Exertional Rhabdomyolysis Patients Revealed Down-Regulation of Mitochondrial Function and Enhancement of Extracellular Matrix Composition. Genes, 16(8), 930. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16080930






