Abstract
Here, we report a consanguineous family harboring a novel homozygous frame-shift mutation in ASPM leading to a truncation of the ASPM protein after amino acid position 1830. The phenotype of the patients was associated with microcephaly, epilepsy, and behavioral and cognitive deficits. Despite the obvious genetic similarity, the affected patients show a considerable phenotypic heterogeneity regarding the degree of mental retardation, presence of epilepsy and MRI findings. Interestingly, the degree of mental retardation and the presence of epilepsy correlates well with the severity of abnormalities detected in brain MRI. On the other hand, we detected no evidence for substantial nonsense-mediated ASPM transcript decay in blood samples. This indicates that other factors than ASPM expression levels are relevant for the variability of structural changes in brain morphology seen in patients with primary hereditary microcephaly caused by ASPM mutations.
1. Introduction
Mentally disabled patients suffering from epilepsy, and especially from drug-resistant epilepsy, need an exact and widespread work up, including genetic testing, as clear diagnosis helps the patients and their caregivers to understand and accept the diagnosis. Furthermore, it helps the treating clinician to find appropriate treatment regimens as well as prevents initiation of useless treatments [1,2].
Microcephaly, primary hereditary (MCPH), is a rare neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by microcephaly and intellectual disability [3] in absence of other congenital abnormalities [3,4]. ASPM (abnormal spindle-like microcephaly-associated) gene mutations (almost exclusively nonsense, frame-shift or splice site mutations) are the most frequent underlying genetic cause for autosomal recessive MCPH [3]. The ASPM gene maps at the locus 1q31.3.; it consists of 28 exons and encodes a protein that consists of 3477 amino acids. Animal data confirm the important role of ASPM in cell cycle division of neural progenitor cells and support the idea of ASPM dysfunction leading to a neuronal developmental dysfunction (for an overview see [5]). Seizures are found in up to 15% of ASPM-MCPH patients [6,7] and should lead to a diligent MRI work up.
Here, we report a consanguineous family with three siblings harboring a novel homozygous ASPM frame-shift mutation causing protein truncation after amino acid position 1830. Despite the obvious genetic similarity, all three patients show a considerable phenotypic heterogeneity regarding the degree of mental retardation, presence of epilepsy and MRI findings. These differences are unlikely related to differences in ASPM expression, since increased mutant ASPM expression in blood was detected in the most affected patient in comparison to controls and heterozygous carriers.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
Clinical information was derived from actual datasets collected at in- and outpatient appointments at the University Hospital Bonn, Department of Epileptology, in 2019 and 2021, as well as clinical information from previous examination. Written informed consent for publication of clinical data and clinical information was given by the caregiver.
2.2. Neuropsychological Rating
Two tests for estimation of intelligence were performed: Raven’s Progressive Matrices (RPM) [8], which is a nonverbal assessment of “general cognitive ability” in terms of inductive and deductive reasoning or ”meaning making”, reported as an Intelligence Quotient, and the Kaufman Assessment Battery for Children (Second Edition) [9], which covers a comprehensive range of skills, including sequential and simultaneous processing, learning, problem solving and crystalline skills, which are important for understanding children with learning difficulties or psychological problems.
Three scales were used for assessing severity of disability: the Global Assessment of Severity of Epilepsy Scale (GASE) [10], the SINGER scale [11] and the modified Rankin scale (mRS) [12]. mRS is a single-item, seven-point ordinal scale for clinicians ranging from zero (no disability) to six (death). Global Assessment of Severity of Epilepsy Scale (GASE) is a single-item, seven-point global rating scale to assess disease severity ranging from one (not severe) to seven (extremely severe) considering all aspects of a patient’s life with epilepsy. The SINGER scale assesses 20 functions including self-care, mobility and cognition, which are rated from zero (totally dependent on professional help) to five (independent without any assistance). A physical activity score, a cognition score, a household score and a total score can be extracted, as well as the Barthel Index. Individual SINGER outcomes are reported as percent achieved in regard to 100% independency. For SINGER physical activity, >75% is rated as “mild/no impairment”, 47–75% as “moderate impairment” and below 46% as “severe impairment”. For SINGER cognition, >86% is rated as “no/mild impairment”, 31–86% as “moderate impairment” and below 31% as “severe impairment”. For SINGER household, >80% is rated as “no/mild impairment”, 40–60% as “moderate impairment” and below as 40% as “severe impairment”.
2.3. Whole Exome Sequencing
Genomic DNA was isolated from blood by routine techniques. The index patient’s DNA was enriched for exons using the Agilent SureSelect Human All Exon V6 kit (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA). Paired-end reads of 100 bp resulted in a mean coverage of 82-fold (30-fold coverage for 78.5% and 10-fold coverage for 94.3% of target sequences). Reads were mapped and variants annotated as described [13]. Filtering and variant prioritization was performed using the VARBANK database and analysis tool at the Cologne Center for Genomics. In particular, we filtered for high-quality (coverage > 15-fold; phred-scaled quality > 25), rare homozygous variants (MAF ≤ 0.01 based on gnomAD; [14]) with predicted effects on protein sequence or splicing. To exclude pipeline-related artifacts, we filtered (MAF ≤ 0.01) against variants from in-house WES datasets from 511 epilepsy patients. Direct sequencing of purified PCR products was performed by a commercial service (Eurofins, Ebersberg, Germany).
2.4. ASPM Expression Analysis
Total blood RNA was obtained with the PAXgene system (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany). Complementary DNA (cDNA) was produced from RNA templates with the iScript Select cDNA synthesis kit (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Munich, Germany). A 1646 bp cDNA fragment between ASPM exon 17 and exon 18 was amplified using primers 5′-CAT CAC TTA TTC AGG GAT ATT G-3′ and 5′- TTG ATG TTC CCT TCT AAT CTG T -3′. Amplification was performed using RANGER DNA polymerase, under the following condition: 5 min at 95 °C; 35 cycles of 30 s at 95 °C, 25 s at 55 °C and 3 min at 68 °C; and finally, 10 min at 68 °C.
2.5. MRI Processing and Analysis
T1-weighted 3D whole-brain MR images of the three subjects (subjects II.2/II.4/II.3 with 1 mm/0.5 mm/0.8 mm isotropic resolution) were segmented into white matter, gray matter and CSF. Volumes of brain structures, including cerebrum and cerebellum, were determined by atlas-based volumetry (ABV), a fully automated, observer-independent method for volumetric analysis of MR images using algorithms of SPM12 and masks of diverse brain atlases [15,16]. The resulting volumes were adjusted by intracranial volume (ICV). ICV-normalized results were compared with an age-matched control group to obtain Z-scores. Additionally, a cortical reconstruction was performed, facilitating a gray matter surface and thickness assessment, using the recon-all pipeline of the Freesurfer [17] image analysis suite (version 7.1.1). Intermediate and final registrations and segmentations of Freesurfer analysis were inspected and manually corrected if required.
3. Results
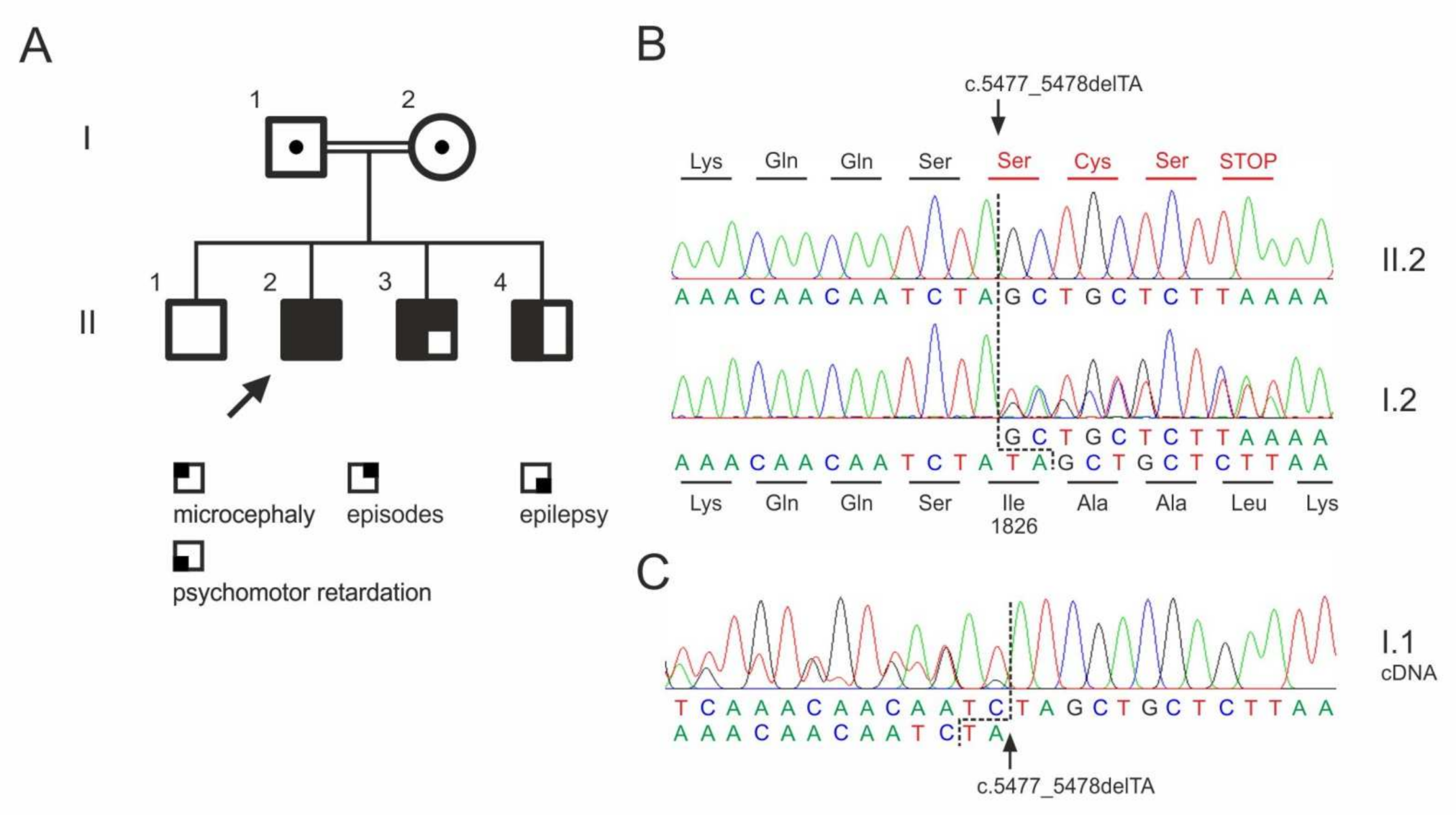
We report on three affected sons of a consanguine relation (the parents are first degree cousins), Figure 1A. A fourth, 23-year-old son (II.1) was not affected. The parents are clinically unaffected, respectively. The family originally comes from Iraq. Samples from the unaffected brother (II.1) were not available.
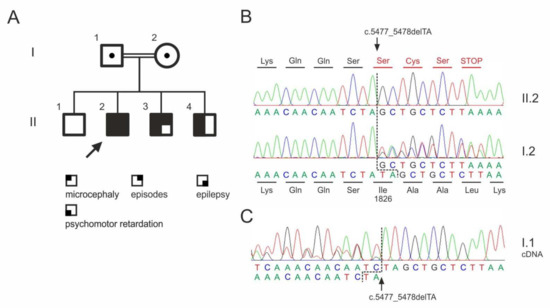
Figure 1.
ASPM mutation in a consanguineous family. (A) Pedigree. Dots indicate heterozygous carriers. No material was available from the unaffected sibling (II.1) for genotyping. (B) Sequencing chromatograms of the index patient (II.2) and his unaffected mother (I.2). (C) Sequencing chromatogram from cDNA obtained from whole blood RNA sample, confirming the heterozygous mutation in the father (I.1). Please note the presence of the mutant transcript in the sequencing chromatogram showing the absence of significant nonsense-mediated decay.
3.1. Case A (II.2)
This 21-year-old man was referred to us at the age of 19 years because of drug-resistant epilepsy. He was born after an uneventful pregnancy to healthy parents.
Already in early childhood, moderate psychomotor delay became obvious with left-side mild spastic hemiparesis, leading to inability to walk as late as at the age of four. A global delay of childhood development was reported by the parents, with first words at the age of five. Apart from shyness, no behavioral abnormality impairing everyday life was reported by the parents. Difficulties in falling asleep and a shift in the day-night rhythm were reported with a moderate impact on everyday life. At the age of ten, he started to display focal impaired awareness seizures as well as focal impaired awareness seizures to bilateral tonic-clonic seizures. Initially treated with carbamazepine monotherapy, add-on with levetiracetam did not achieve long-term seizure freedom. At the first appointment, we saw a moderately mentally disabled young man with microcephalus, with mild left spastic hemiparesis of normal height. No other congenital abnormalities were found.
He was suffering from weekly seizures. Further antiseizure treatment regimen including valproate and oxcarbazepine were unsuccessful. A 24 h long-term EEG recording displayed right central and temporal epileptiform discharges and three similar focal impaired awareness seizures showing an ictal pattern frontocentral, once accentuated in the right hemisphere. This high seizure frequency within 24 h with adequate blood levels of antiseizure medication as well as the registered mild semiology of seizures suggests a higher seizure frequency as reported by the family.
3.2. Case B (II.3)
This 19-year-old man was referred to us at the age of 17 years as epilepsy was suspected. He was born at the expected date after an uneventful pregnancy to healthy parents. In early childhood, mild psychomotor delay was reported by the parents. Moderate behavioral abnormality including aggression and reduced tolerance to frustration leading to intrafamiliar distress was the main problem reported by the parents. Difficulties in falling asleep were reported, though without impact on everyday life. According to his parents, at the age of eighteen, he started to display weekly episodes with non-responsiveness and gazing for about 30 seconds; initial treatment with levetiracetam monotherapy did not lead to freedom of episodes. Episodes have never been observed at school or elsewhere.
At the first appointment, we saw a slightly mentally disabled young man with microcephalus and reduced body height (third percentile); no other congenital abnormalities were found. He was suffering from weekly episodes. A 96 h long-term EEG recording displayed neither epileptiform discharges no epileptic seizures. Epilepsy could not be verified.
3.3. Case C (II.4)
This 16-year-old boy who was referred to us at the age of 16 years to test for epilepsy. He was born at expected date after an uneventful pregnancy to healthy parents. In early childhood, mild psychomotor delay was reported by the parents. He has never displayed episodes which were suspicious for seizures. Behavioral abnormality including irritability and easy frightening was reported, although with minor impact on everyday life. Moreover, difficulty sleeping through the night was reported, although this only had a mild impact on everyday life.
At the first appointment, we saw a mild mentally disabled boy with microcephalus and of normal height. No other congenital abnormalities were found. He was not suffering from any episodes. A 96 h long-term EEG recording displayed neither epileptiform discharges no epileptic seizures. Epilepsy could not be verified.
3.4. Cognitive and Disability Assessment of the Individual Patients
The cognitive function and the degree of disability of the individual patients in the family (II.2, II.3, II.4; Figure 1A) were assessed by tests of intelligence (intelligence quotient) and standardized behavioral rating scales (Table 1). While the global intellectual level in all three patients turned out to be very low (<intelligence quotient 55), the patients in part differed considerably in regard to their independency on others as defined according to the international classification of functioning related ratings. Accordingly, patient II.2 showed epilepsy and the highest overall impairment, while patient II.3 was affected to a much lesser degree.

Table 1.
Cognitive and disability assessment by rating scales.
3.5. Whole Exome Sequencing
Whole exome sequencing in the index patients revealed a previously not described homozygous mutation in the ASPM gene (NM_18136.5:c.5477_5478del; p.Ile1826Serfs*4), which was verified by Sanger sequencing (Figure 1B). The mutation classifies as pathogenic according to the criteria by the American Collage of Medical Genetics (PVS1, PM2, PM3; [18]). The two affected brothers were also homozygous for the mutation. The clinically unaffected parents were heterozygous carriers.
As a result of the deletion of two bases, the reading frame in the ASPM gene shifts from codon 1826 and leads to a premature termination of the protein synthesis (Figure 2B). The other homozygous variants detected in the index patient (Table 2) were either described in ClinVar as benign variants (APP) or were present in homozygous state in controls.
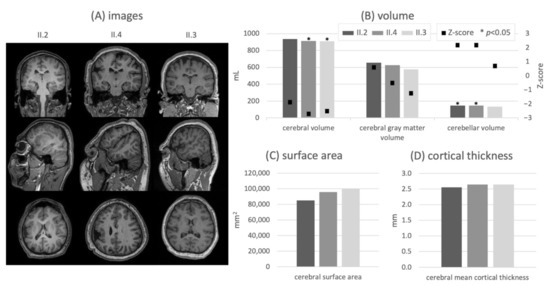
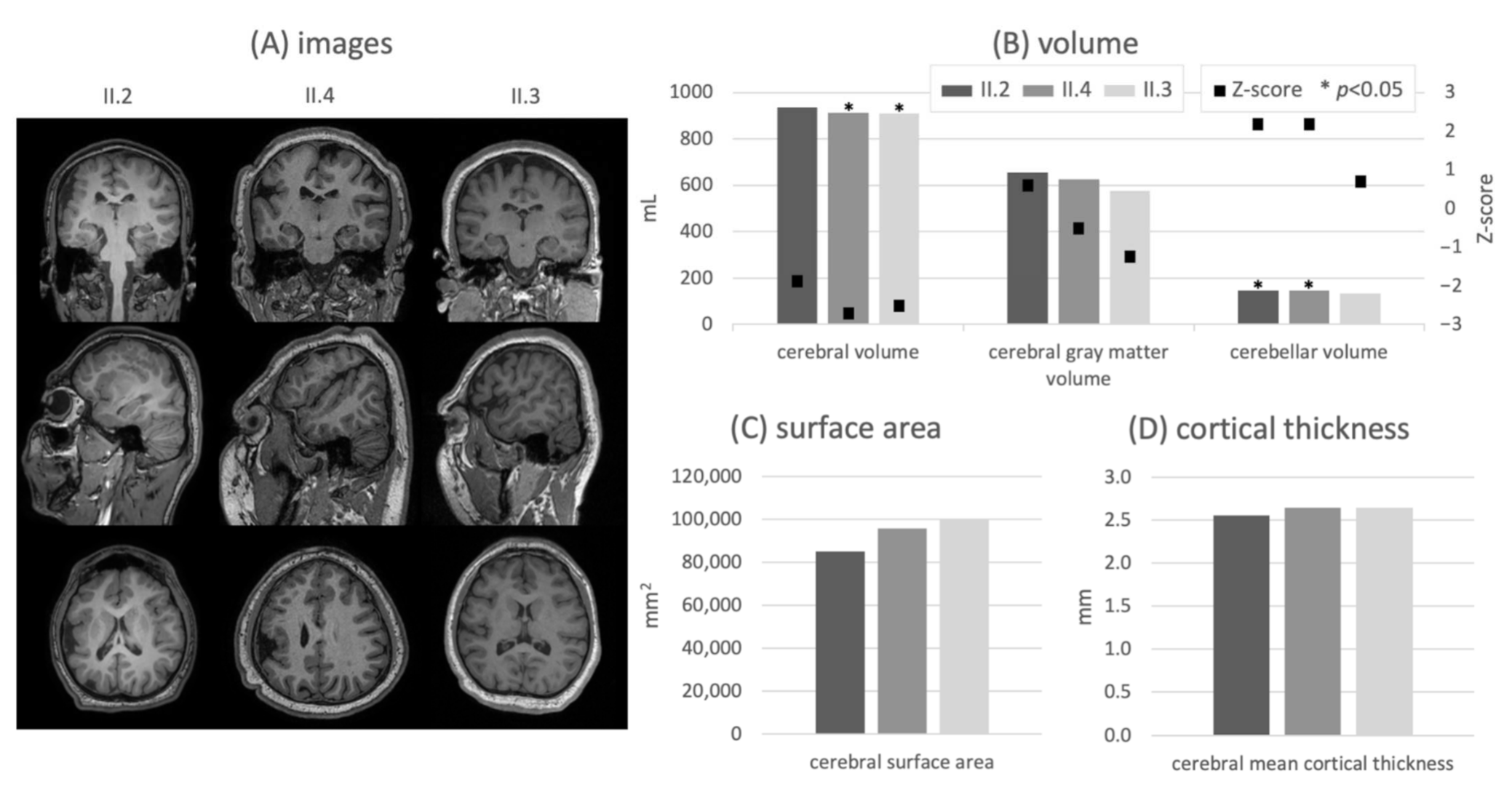
Figure 2.
T1-weighted MR images in all orientations with a sagittal view of the right hemisphere (A), ICV-normalized volumes and corresponding Z-scores obtained by comparison with an age-matched control group per subject (B), brain surface area (C) and cortical gray matter thickness (D) for all subjects. The quantitative results are consistent with the MR abnormalities and match the highest disease severity seen in patient II.2. * p < 0.05.

Table 2.
Homozygous and hemizygous variants with CADD * score > 20 detected in the index patient (II.2).
Interestingly, the ASPM frame shift mutation does not cause nonsense-mediated transcript decay as visible in the cDNA sequencing chromatogram from the heterozygous father (I.1) (Figure 2C).
3.6. MRI Processing and Analysis
Radiological assessment showed microcephaly and microgyria in the right hemi-spheres, which were most pronounced in subjects II.2 and II.4. These abnormalities are evident in the quantified measures: All three subjects show a reduced ICV compared to the age-matched control group (Z-scores of subjects II.2/II.4/II.3: −5.1/−3.9/−4.0, p < 0.01). Thereby, the subject with the highest severity of cognitive impairment presents the strongest deviation. Likewise, ICV-normalized results (Figure 2B) indicate a subaverage expression of the cerebrum (Z-scores of subjects II.2/II.4/II.3: −1.9/−2.7/−2.5). In contrast, a volumetric overrepresentation of the cerebellum relative to the control group is apparent (positive Z-scores for subjects II.2/II.4/II.3: +2.2/+2.2/+0.7). No significant difference in cerebral relative gray matter volume relative to the control group is found. The volumetric results are complemented by corresponding brain surface area characteristics (Figure 2C), which show a clearly reduced cortical surface according to the degree of cognitive disability. Again, the strongest reduction is visible in the most impaired subject. The same relationship appears in the cortical thickness distribution (Figure 2D), as a decrease of the cerebral mean cortical thickness is present in the most severely affected subject (II.2).
4. Discussion
ASPM is a microtubule-associated protein found at the spindle poles and centrosomes and is essential for normal mitotic spindle function in embryonic neuroblasts of developing CNS. In humans, it comprises 63 IQ domains (the single letter code for the amino acids isoleucine and glutamine), which mediate interaction with the EF-hand motifs of calmodulin- and calmodulin-related proteins (Figure 3) [20] and are believed to be essential for cerebral cortical neurogenesis.
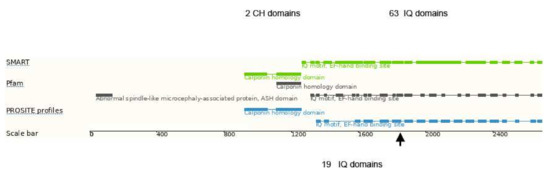
Figure 3.
Domain structure of the human ASPM protein. CH domains–calponin homology domains, IQ domains–isoleucine-glutamine domains. The arrow indicates the truncation position due to the homozygous p.Ile1826Serfs*4 mutation, leaving 19 intact IQ domains. Modified according to [21].
In earlier work, ASPM expression, in particular the number of IQ domains, were suggested to be correlated with cortical development and it is discussed as one of the essential genes important for the increase of the cortical size during primate evolution [22,23,24]. Mutations in ASPM, the most common recessive microcephaly gene, reduce the cortical volume by at least 50% in humans, but have little effect on the brains of mice, which probably reflects evolutionarily divergent functions of this protein. The major role of ASPM in the early cortical development and gyration has been later confirmed in Aspm knockout ferrets [20], which are a better model than mice for the cortical gyration pattern of the human brain. The authors propose an evolutionary mechanism by which ASPM regulates cortical expansion during evolution by controlling the affinity of ventricular radial glial cells for the ventricular surface, thus modulating the ratio of ventricular radial glial cells, the most undifferentiated cell type, to outer radial glia, a more differentiated progenitor. Accordingly, differences in the phenotypic expression of available ASPM transcripts leading to different cortical surface areas have been attributed to the large phenotypic variability of primary hereditary microcephaly (MCPH) patients due to ASPM mutations. This transcript variability could be caused by a different degree of nonsense-mediated decay of ASPM transcripts harboring nonsense mutations. This would explain why so far, only nonsense, splice-site or frame-shift mutations in this particular gene have been associated with autosomal recessive MCPH caused by ASPM mutations [25]. In contrast to this, we have observed in blood samples no evidence for a substantial nonsense-mediated ASPM transcript decay. Therefore, the missing non-functional protein with the appropriate amount of IQ domains (Figure 3) seems to be essential to explain the fact that even a small deletion in the C-terminus is sufficient to cause severe microcephaly [5]. Thus, a decrease of IQ domain numbers in the potentially expressed truncated forms of the protein, rather than a decrease of its total amount, might be relevant for the dramatic decrease of cerebral surface area and the reduced cortical gyration pattern of MCPH patients.
The three brothers with microcephaly and mental retardation reported here carry a novel homozygous ASPM mutation, leading to a premature termination of the ASPM protein at amino acid position 1830. As indicated in Figure 3, this truncated ASPM protein contains only 19 IQ domains. All affected brothers show a significantly reduced cerebral volume compared to sex- and age-matched controls. Though carrying the same loss-of-function mutation at a very similar genetic background (male siblings from consanguineous parents), the phenotype differs substantially between the affected patients: one individual (II.2) exhibited severe epilepsy, high degree of mental retardation and a low cortical surface area, while his sibling (II.3) had no epilepsy, only mild psychomotor delay and an almost normal cerebral surface area. A rather high intrafamiliar phenotype variability in ASPM mutation in MCPH patients has been mentioned before [5], but no reasons were identified.
These large phenotypic differences are unlikely to be related to differences in ASPM transcript levels due to different degrees of nonsense-mediated decay of the mutated ASPM transcript. This result does not exclude potential expression differences in the developing nervous system but makes other possible mechanisms more likely to explain the phenotypic variability in MCPH due to ASPM nonsense or frame-shift mutations. Potentially other variants in the genome (genetic modifiers) may alleviate or exacerbate the severity of the disease, resulting in the variability of phenotypic outcomes [26]. Especially in consanguineous families, differences in the segregation pattern of further rare homozygous variants could contribute to the phenotypic variability. In our reported family, this can be excluded, since only a very limited number of frequent and obviously nonpathogenic additional homozygous variants was observed (Table 2). Therefore other, potentially epigenetic mechanisms might contribute to this phenomenon.
5. Conclusions
The large phenotypic variability seen in patients with primary hereditary microcephaly due to ASPM mutations correlates well with the degree of structural brain abnormalities. The expression levels of the transcript for the truncated ASPM protein suggest that differences in the degree of structural cerebral changes cannot be explained by nonsense-mediated decay causing differences in ASPM expression.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.v.W. and W.S.K.; methodology, R.v.W., T.R., C.H. and W.S.K.; Software: H.-J.H.; Validation: R.v.W., T.R. and W.S.K.; formal analysis, M.S., T.R., T.B., G.Z. and K.H.; investigation: R.v.W., M.S., H.-J.H., T.R., A.I., T.B., K.H., G.Z. and C.H.; Resources: R.v.W., T.R., A.I., C.H. and W.S.K.; data curation, R.v.W., T.R. and W.S.K.; writing—original draft preparation, R.v.W. and W.S.K.; writing—review and editing, R.v.W., R.S. and W.S.K.; visualization, T.R. and G.Z.; supervision, R.v.W. and W.S.K.; project administration, R.v.W. and W.S.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received funding from DFG (Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft) KU 911/21-2 to W.S.K. and ZS 99/3-2 to G.Z.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee of University of Bonn (approval code: 040/07 and date of approval 24 April 2009).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Acknowledgments
The technical support of Susanne Beyer is gratefully acknowledged.
Conflicts of Interest
R.v.W. has received fees as a speaker, consultant or travel support by Arvelle, Cerbomed, Desitin, G.W. pharmaceuticals, EISAI and UCB. M.S. has not received any fees or grants. T.R. has received travel support by EISAI. H.-J.H. has not received any fees or grants. K.H. has not received any fees or grants. A.I. has received travel support by EISAI. T.B. has received fees as a speaker and consultant by EISAI and UCB. C.H. has received grants from the EU, travel support by Desitin, honoraria for talks, counseling and advisory boards by G.W. pharmaceuticals, EISAI and UCB, as well as license fees by EISAI and UCB. R.S. has received fees as speaker or consultant from Bial, Cyberonics, Desitin, EISAI, LivaNova, Novartis and UCB Pharma, and grants from Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG), Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung (BMBF), the Bundesministerium für Gesundheit and Marga and Walter Boll Stiftung. W.S.K. and G.Z. have received grants from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG).
References
- Weber, Y.G.; Biskup, S.; Helbig, K.L.; Von Spiczak, S.; Lerche, H. The role of genetic testing in epilepsy diagnosis and management. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2017, 17, 739–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Møller, R.S.; Hammer, T.B.; Rubboli, G.; Lemke, J.R.; Johannesen, K.M. From next-generation sequencing to targeted treatment of non-acquired epilepsies. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2019, 19, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaqout, S.; Morris-Rosendahl, D.; Kaindl, A.M. Autosomal Recessive Primary Microcephaly (MCPH): An Update. Neuropediatrics 2017, 48, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woods, C.G.; Bond, J.; Enard, W. Autosomal recessive primary microcephaly (MCPH): A review of clinical, molecular, and evolutionary findings. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2005, 76, 717–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Létard, P.; Drunat, S.; Vial, Y.; Duerinckx, S.; Ernault, A.; Amram, D.; Arpin, S.; Bertoli, M.; Busa, T.; Ceulemans, B.; et al. Autosomal recessive primary microcephaly due to ASPM mutations: An update. Hum. Mutat. 2018, 39, 319–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passemard, S.; Titomanlio, L.; Elmaleh, M.; Afenjar, A.; Alessandri, J.-L.; Andria, G.; de Villemeur, T.B.; Boespflug-Tanguy, O.; Burglen, L.; Del Giudice, E.; et al. Expanding the clinical and neuroradiologic phenotype of primary microcephaly due to ASPM mutations. Neurology 2009, 73, 962–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Hamid, M.S.; Ismail, M.F.; Darwish, H.A.; Effat, L.K.; Zaki, M.S.; Abdel-Salam, G.M.H. Molecular and phenotypic spectrum of ASPM-related primary microcephaly: Identification of eight novel mutations. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2016, 170, 2133–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raven, J.; Court, J.H. Manual for Raven’s Progressive Matrices and Vocabulary Scales. In Research Supplement No. 4: Additional National and American Norms, and Summaries of Normative, Reliability, and Validity Studies; Oxford Psychologists Press: Oxford, UK, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman, A.S.; Kaufman, N.L. Kaufman Assessment Battery for Children, 2nd ed.; American Guidance Service: Circle Pines, MN, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, C.J.; Zou, G.; Wiebe, S.; Speechley, K.N. Global assessment of the severity of epilepsy (GASE) scale in children: Validity, reliability, responsiveness. Epilepsia 2015, 56, 1950–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funke, U.-N.; Schüwer, U.; Themann, P.; Gerdes, N. Selbständigkeits- Index für die Neurologische und Geriatrische Rehabilitation SINGER: Manual zur Stufenzuordnung. 2., Vollständig Überarbeitete und Erweitertete Auflage; S. Roderer Verlag: Regensburg, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Berzina, G.; Sveen, U.; Paanalahti, M.; Sunnerhagen, K.S. Analyzing the modified Rankin Scale using concepts of the international classification of functioning, disability and health. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2016, 52, 203–213. [Google Scholar]
- Basmanav, F.B.; Oprisoreanu, A.-M.; Pasternack, S.M.; Thiele, H.; Fritz, G.; Wenzel, J.; Größer, L.; Wehner, M.; Wolf, S.; Fagerberg, C.; et al. Mutations in POGLUT1, encoding protein O-glucosyltransferase 1, cause autosomal-dominant Dowling-Degos disease. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2014, 94, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karczewski, K.J.; Francioli, L.C.; Tiao, G.; Cummings, B.B.; Alföldi, J.; Wang, Q.; Collins, R.L.; Laricchia, K.M.; Ganna, A.; Birnbaum, D.P.; et al. The mutational constraint spectrum quantified from variation in 141,456 humans. Nature 2020, 581, 434–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huppertz, H.-J.; Kröll-Seger, J.; Klöppel, S.; Ganz, R.E.; Kassubek, J. Intra- and interscanner variability of automated voxel-based volumetry based on a 3D probabilistic atlas of human cerebral structures. Neuroimage 2010, 49, 2216–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huppertz, H.-J.; Möller, L.; Südmeyer, M.; Hilker, R.; Hattingen, E.; Egger, K.; Amtage, F.; Respondek, G.; Stamelou, M.; Schnitzler, A.; et al. Differentiation of neurodegenerative parkinsonian syndromes by volumetric magnetic resonance imaging analysis and support vector machine classification. Mov. Disord. 2016, 31, 1506–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dale, A.M.; Fischl, B.; Sereno, M.I. Cortical surface-based analysis. I. Segmentation and surface reconstruction. Neuroimage 1999, 9, 179–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: A joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rentzsch, P.; Schubach, M.; Shendure, J.; Kircher, M. CADD-Splice—Improving genome-wide variant effect prediction using deep learning-derived splice scores. Genome Med. 2021, 13, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.B.; Sun, X.; Kodani, A.; Borges-Monroy, R.; Girskis, K.M.; Ryu, S.C.; Wang, P.P.; Patel, K.; Gonzalez, D.M.; Woo, Y.M.; et al. Aspm knockout ferret reveals an evolutionary mechanism governing cerebral cortical size. Nature 2018, 556, 370–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ensembl Genome Browser. Available online: https://www.ensembl.org/Homo_sapiens/Transcript/ProteinSummary?db=core;g=ENSG00000066279;r=1:197084121-197146694;t=ENST00000367409 (accessed on 21 December 2021).
- Bond, J.; Roberts, E.; Mochida, G.H.; Hampshire, D.J.; Scott, S.; Askham, J.M.; Springell, K.; Mahadevan, M.; Crow, Y.J.; Markham, A.F.; et al. ASPM is a major determinant of cerebral cortical size. Nat Genet. 2002, 32, 316–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekel-Bobrov, N.; Gilbert, S.L.; Evans, P.D.; Vallender, E.J.; Anderson, J.R.; Hudson, R.R.; Tishkoff, S.A.; Lahn, B.T. Ongoing adaptive evolution of ASPM, a brain size determinant in Homo sapiens. Science 2005, 309, 1720–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouprina, N.; Pavlicek, A.; Collins, N.K.; Nakano, M.; Noskov, V.N.; Ohzeki, J.; Mochida, G.H.; Risinger, J.I.; Goldsmith, P.; Gunsior, M.; et al. The microcephaly ASPM gene is expressed in proliferating tissues and encodes for a mitotic spindle protein. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2005, 14, 2155–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OMIM. Available online: https://www.omim.org/entry/605481?search=ASPM&highlight=aspm (accessed on 21 December 2021).
- Rahit, K.M.; Tarailo-Graovac, M. Genetic modifiers and rare Mendelian disease. Genes 2020, 11, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).