Abstract
Human induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC)-derived cardiomyocytes (CM) have been intensively used in drug development and disease modeling. Since iPSC-cardiomyocyte (CM) was first generated, their characterization has become a major focus of research. Multi-/micro-electrode array (MEA) systems provide a non-invasive user-friendly platform for detailed electrophysiological analysis of iPSC cardiomyocytes including drug testing to identify potential targets and the assessment of proarrhythmic risk. Here, we provide a systematical overview about the physiological and technical background of micro-electrode array measurements of iPSC-CM. We introduce the similarities and differences between action- and field potential and the advantages and drawbacks of MEA technology. In addition, we present current studies focusing on proarrhythmic side effects of novel and established compounds combining MEA systems and iPSC-CM. MEA technology will help to open a new gateway for novel therapies in cardiovascular diseases while reducing animal experiments at the same time.
1. Introduction
The first generation of induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) by Yamanka and co-workers in 2006 was a milestone for stem cell research as it allows the in vitro production of human cells without ethical concerns. Like embryonic stem cells, iPSCs have the capability to differentiate into any cell type, including cardiomyocytes, therefore providing an easy accessible cellular source for the generation of cardiac organoids and tissue structures [1,2,3].
One possible application for iPSC-derived cardiomyocytes (CMs) is their use in cell therapy replacing damaged tissue by in vitro generated CMs. As cardiovascular diseases are the major cause of death worldwide such regenerative approaches are needed for the development of novel treatment options. The potential and feasibility of iPSC-CM transplantation has been investigated in small and large animal models [4,5,6,7].
Thereby, an important future option of iPSC-CMs will be their generation from patient specific tissue enabling the implementation of autologous cell transplantation strategies. In this respect, iPSC-CMs can be used for the development of personalized drug screening approaches and clinically relevant diseases models. Therefore, iPSCs enable cost-effective methods to identify potential drug targets, even more accurately than animal models or other in vitro cell systems. Successful pre-clinical application of iPSC-derived cardiomyocytes for drug screening assays has been lately demonstrated by the CiPA initiative, which was initiated to assess the proarrhythmic risk of novel cardio therapeutics. A myriad of studies investigated in vitro drug effects on different ion channels of iPSC-CMs [8,9,10,11], reflecting the importance of electrophysiological measurements using stem cell derived cardiac cells.
However, the maturation of iPSC derived CMs is still a critical point for their application in cardiovascular research as well as for clinical applications. Besides metabolic and structural maturation, proper ion channel composition is crucial for the development of a mature cardiac phenotype. During the last decade, extensive analyses have been performed on the electrophysiological properties of iPSC-CMs [12,13,14,15]. Several ion channels and ion currents have been found to be present in iPSC-CMs, including sodium (INa), potassium (IK1 and IKr), L-type and T-type calcium channels, etc. Although multiple differentiation protocols have been developed, researchers failed to generate fully mature cardiomyocytes in vitro, possessing identical electrophysiological properties as their native adult counterparts [16,17,18]. Moreover, it has largely been shown that iPSC-CMs represent a heterogeneous population of electrophysiological phenotypes, i.e., atrial, ventricular and nodal-like cells [19], each characterized by a specific electrical profile. Therefore, it is important to obtain electrophysiological data for detailed characterization of iPSC-CMs, in particular when differentiation into a certain cardiac subtype is desired [20,21].
Typical approaches to investigate the electrophysiological properties of stem cell derived CMs will be discussed in the following paragraph.
2. Methods for Electrophysiological Characterization of iPSC-CMs
Several different techniques exist to study the electrophysiological properties of cardiac cells, including patch clamp analysis, MEA measurement and fluorescence dye-based assessment of the membrane potential. Each of these techniques has its own advantages and limitations, which are described in detail in the following.
2.1. Patch Clamping
Patch clamping is the gold standard technique for the acquisition of ion current data and detailed measurement of action potential (AP) properties in individual cells. The basic principle of patch clamp relies on a blunt ended glass pipette that is sealed onto the cellular membrane to obtain a so-called gigaseal [22].
In the “current patch clamp” mode the membrane potential is recorded while the current applied by the patch pipette is controlled by the operator [23]. The current patch clamp technique allows detection of APs that occur spontaneously or after stimulation with a current change induced by the recording pipette. Considering the fact that iPSC-CMs also contain non-beating populations, current patch clamp methodology allows the detection of AP patterns in these quiescent cells [23,24]. Moreover, detailed AP features, such as AP duration, amplitude, beating rate and mean diastolic potential can reliably be acquired with current patch clamping [25].
When precise characterization of ion channel subtypes is desired, “voltage patch clamp” is performed to measure individual ion currents. Unlike in the current patch clamp mode, the operator keeps the membrane potential at a certain value that enables detection of the net membrane current. In hiPSC-CMs, voltage patch clamp has been successfully applied to obtain data about ion channel density, voltage dependency and activation/deactivation characteristics [23].
However, these manual patch clamp methods are complex, technically challenging procedures that require high operator skills as well as a biophysical background for data interpretation. Another limitation is the low throughput since measurements are usually performed on the single cell level. Therefore, automated patch clamp devices have been developed to overcome the aforementioned drawbacks of manual patch clamp approaches [26]. Automatic platforms profoundly increase the efficiency of electrophysiological data recording by assessment of 10–700 cells at the same time [27]. However, while automated systems are capable to analyze hundreds of cells under variable experimental conditions, the accuracy of obtained data is reduced if compared to manual patch clamping [28,29]. High-throughput analysis is realized by analysis of single cell suspensions, in contrast to manual patch clamping where cells are usually processed in an adherent state. Recently developed systems are equipped with temperature control, optical stimulation and internal perfusion systems to ensure high data quality and reproducibility [27,30]. Data consistency and robustness is further determined by the homogeneity and density of the applied single cell suspension—a point that is particularly important for iPSC-CMs that are sensitive to dissociation as it can affect membrane proteins and electrical physiology of the cell, including ion channel expression [31,32]. Automatic techniques also do not provide the possibility of selective cell capturing. Hence, the system demands highly purified cell populations, which could be challenging when working with CMs differentiated from iPSCs that commonly represent a mixture of different cardiac subtypes [29].
2.2. Optical Recordings of the Membrane Potential
An indirect technique to assess electrophysiological data of iPSC-CMs is the application of voltage-sensitive dyes that change fluorescence intensity or emission spectra upon alteration of the membrane potential. Considering fluorescence microscopy as one of the most commonly used methods in cell research, utilizing voltage-sensitive dyes is operationally simple and does not require special instrumentation. Moreover, it is less invasive and it enables monitoring of voltage dynamics over thousands of cells with very high temporal resolution [33]. Several studies have proven feasibility of voltage sensor probes for drug screening experiments in iPSC-CMs [34,35,36]. Recently, Takaki and colleagues [37] applied voltage sensitive dyes for the identification of distinct cardiac subtypes in an iPSC-CM population. Further, the authors were able to detect differences in the AP pattern in iPSC-CMs obtained from patients suffering from the long QT syndrome, compared to control cells.
Alternatively, voltage sensitive probes can be engineered as fluorescent proteins that are stably expressed in target cells. Compared to voltage-sensitive dyes, these proteins possess lower phototoxicity, thus, facilitating long-term measurements. These genetically encoded probes are designed by conjugating a voltage-sensing domain to a single fluorescent protein, a fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) pair or rhodopsin proteins [38,39]. Changes of the membrane potential induce conformational rearrangement of the voltage-sensor, which in turn modulates the emission spectra of the attached fluorescent protein. The latest generation of genetically encoded voltage sensors, such as ArcLight, Archer1 or QuasAr1, show large fluorescence alteration upon depolarizing events (40%–80% for a 100 mV depolarization) associated with faster on/off kinetics (1–10 ms). Shaheen et al. generated ArcLight expressing human iPSC-CMs to establish a 2D cardiac tissue platform for optical mapping and pharmacological studies [40]. Former data confirmed the suitability of genetically encoded voltage sensors for iPSC-CM drug screening applications and disease modeling attributed to altered AP phenotypes [41,42,43,44]. However, there are certain limitations of this technology. Like fluorescence dyes, genetically encoded voltage indicators provide only relative, not absolute values for the membrane potential [45]. The lower on/off kinetics increase the probability of losing high frequency AP elements [41,45]. Furthermore, introduction of voltage-sensitive proteins like ArcLight could affect the electrophysiological properties of iPSC-CMs. This needs to be carefully addressed by the operator as well as proper folding and membrane integration of the voltage sensitive probe.
2.3. MEA-Based Analysis of Cell Behavior
A common MEA system is composed of dot-like electrodes arranged in two-dimensional grids that measure the fluctuations in the extracellular field potential (FP) of an attached cell layer in respect to a reference electrode placed outside the grid (Figure 1). MEA is a non-invasive, label free methodology that has been initially applied to investigate neuronal activity [46]. However, in recent years an increasing number of studies have taken advantage of MEAs to particularly analyze compound-induced cardiac toxicity in iPSC-CMs [47,48,49]. Like optical recordings of the membrane potential, MEA systems allow non-invasive and cost-effective measurements at high throughput scale, and long-term observations [46,50]. On the other hand, Rynnännen et al. published data of a custom-made MEA platform for FP detection based on a single cell analysis [51]. In contrast to conventional MEA systems, this optimized device demonstrated a modified layout of larger electrodes, most suitable for observation of single iPSC-CMs. Similarly, agarose micro-chambers printed on MEA have been found to facilitate single cell detection of FPs in stem cell-derived CMs [52]. Moreover, electrophysiological assessment using MEAs is not only restricted to cell culture but can also be performed on the tissue level to better simulate in vivo conditions, as shown for murine and human heart tissue slices [53,54,55].
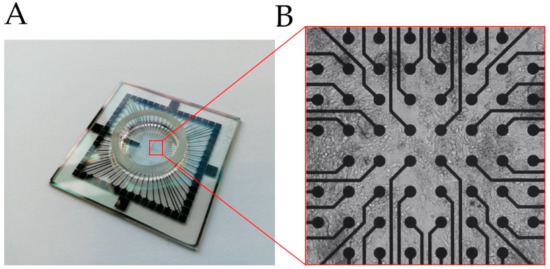
Figure 1.
(A) Glass multi-/micro-electrode array (MEA) chip used to detect field potential (FP) of cells. (B) Cells seeded on an MEA surface, grown on top of the electrodes (black dots), Video S1.
An advantage of the MEA technology is its high flexibility as it can be combined with other detection methodologies to multiply the number of parameters describing cellular functions. The main parameter assessed is the FP of spontaneously beating CMs that can be correlated with certain elements of the AP pattern. Additionally, newly developed platforms provide the possibility to detect impedance of the attached cell layer [56,57]. Unlike the FP that reflects the electrical activity, impedance corresponds to the mechanical movement of the cell on the electrode. It is influenced by cell density, cell number and the extent of cell adhesion. Thus, measuring impedance helps to acquire valuable information about beating behavior, proliferation, cell death and viability [22,58].
A relationship between contraction parameters and electrophysiological activity has also been investigated by combination of MEA and high-speed video microscopy, followed by motion based image analysis of beating cells [59]. Likewise, fluorescence microscopy was used to correlate FP measurements with subcellular information [60]. However, the combined setup of MEA platforms with optical techniques requires certain structural features to achieve optimal visualization of target cells, such as transparent electrodes [51,60,61].
In another study, Siemenov et al. developed a combined scanning ion conductance microscopy–MEA system for simultaneous detection of cell surface morphology and FP in cardiomyocytes [62]. The platform reveals morpho-dynamic parameters, including maximum displacement and cell volume changes in a time-dependent manner. Together with the FP data obtained from MEA measurements, the authors were able to reconstruct 3-dimensional motion of the cell surface over a complete contraction-relaxation cycle [62].
In order to obtain reproducible and reliable experimental data, a number of points need to be considered when working with MEA systems that are particularly important for drug screening assays. Since individual iPSC-CMs show variations in AP waveforms [63], confluent monolayer cell sheets are preferred to reduce the variability of the acquired FP patterns. In this regard, cell density needs to be carefully addressed by the operator as it was found to influence electrical remodeling of CMs derived from human iPSCs [64].
3. Action Potential vs. Field Potential
Both, AP and FP are parameters describing the membrane potential of cardiomyocytes or any other cell type that is electrically active. They are generated by ion currents between the extra- and intracellular space, tightly regulated by several different membrane-located ion channels [65]. In drug development, pharmacological compounds are classified in respect to their cardiotoxic effects based on the AP or/and FP pattern in iPSC-derived CMs [34]. In addition, electrophysiology is used to identify and characterize the different cardiac subtypes in iPSC derived CM populations, which is crucial for specific cell programming strategies [20,66,67].
3.1. Action Potential in Native Cardiac Cells and iPSC Derived CMs
The AP represents the time-dependent alterations of the membrane potential in CMs that occur during the contraction of heart tissue. This requires a well-defined orchestration of numerous ion channels. Since the human heart comprises different cardiomyocyte subtypes, the AP pattern varies significantly, depending on the regions of heart (e.g., atrium, sinus node and ventricle) [68].
Despite this electrical heterogeneity, each subtype specific pattern consists of five different phases, reflecting the activity of certain ion channels (Figure 2A). Based on an incoming depolarization stimulus, opening of voltage-gated Na+ channels induces sodium influx into the cytoplasm, resulting in a rapid depolarization of the membrane potential up to +20 to +40 mV (Phase 0). Subsequently, phase 1 is determined by time and voltage-dependent opening and closing of various ion transporters permeable to Na+, Ca2+ and K+, leading to a slight, transient hyperpolarization of the membrane potential (−10 to −30 mV). The following phase 2 is characterized by a relatively high capacity of the cell membrane and it is primarily driven by depolarization-dependent L-type Ca2+ channels. Due to a balanced interplay between inward currents of calcium and efflux of potassium phase 2 demonstrates a plateau period, which is particularly prominent in ventricular muscle cells [68,69]. During the plateau phase, Ca2+ channel conductance decreases while the outward current of K+ inclines. This in turn promotes further repolarization (phase 3) leading to a resting potential of ~−85 mV (phase 4).
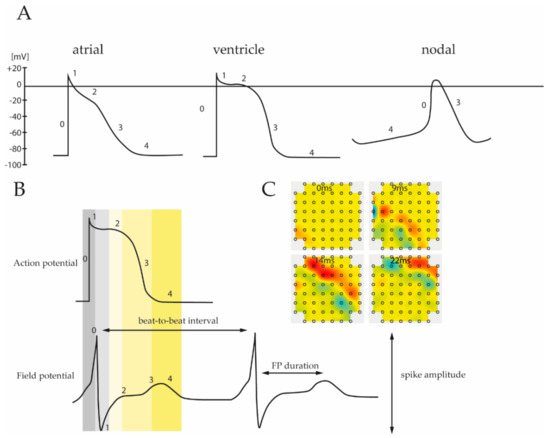
Figure 2.
(A) Subtype specific pattern of the cardiac action potential. Ventricular, atrial and nodal cells are characterized by unique depolarization and repolarization processes leading to different action potential (AP) waveforms. Numbers correspond to the different phases that reflect the activity of involved ion channels. (B) Comparison of the different phases between recorded action potential and field potential. As field potential measurements allow reconstruction of the corresponding action potential it provides important physiological parameters of electrically active cells, including spike amplitude, FP interval, etc. (C) Moreover, MEA analysis can be applied to obtain data about prolongation velocity and direction of the field potential spreading throughout the cell layer.
As stated above, AP patterns are unique for each cardiac subtype resulting from different ion channel composition within the cellular membrane (Figure 2A). Nodal cells, found in sinoatrial and an atrioventricular AV node or His-bundles, are capable to generate their own AP without an additional depolarizing stimulus. Compared to atrial and ventricular cells, the resting potential in nodal cells is unstable, begins at ~−60 mV (vs. ~−85 mV in atrial and ventricular cells) and gradually increases towards a threshold. This “pacemaker potential” is generated by K+ channels that open slowly upon depolarization and deactivates with time. Concurrently, depolarization of about −60 mV activates a nodal specific Na+ channel, known as the “funny channel”, causing an increase of the intracellular Na+ level. Once a threshold is reached, opening of voltage-gated Ca2+ channels induce a strong upstroke. This is in contrast to atrial and ventricular cells where a Na+ influx mainly contributes to the rapid depolarization in phase 0.
Differences in the AP pattern are also distinct between atrial and ventricular regions of the heart. Atrial CMs undergo a more rapid early repolarization and demonstrate a less profound plateau phase, followed by slow phase 3 repolarization (Figure 2A). These differences emanate from specific K+ channels, expressed in atrial cells, but not found in ventricular tissue [68].
Analysis and classification of AP patterns of iPSC-CMs is challenging as they demonstrate a large amount of variability, which supports the notion that CMs derived from iPSCs are a mixture of different cardiac subtypes of distinct maturation level [16,19,70]. Although multiple differentiation protocols have been established, researchers failed to generate fully mature cardiomyocytes in vitro possessing identical electrophysiological properties as their native adult counterparts [16,18]. For example, Ronaldson-Bouchard et al. have shown structural and metabolic maturity and adult-state like gene-expression of three iPSC cell lines after cultivation as cardiac tissues for four weeks, it remains to be seen whether this approach can be generally transferred to any iPSC cell line [71]. In addition, it is difficult to compare APs among different studies because of various experimental conditions used. Nevertheless, a common feature of iPSC-CMs compared to native CMs is their ability to generate APs without the need of an external, depolarizing signal, indicating a relative similarity with nodal tissue cells. Indeed, iPSC-CMs were found to express funny channels to drive spontaneous activity. Another nodal-cell characteristic of iPSC-CMs is their relatively positive resting potential of −60 to −70 mV that mainly relies on a lower or absent expression of the K+ channel IK1 [16,72], allowing the depolarizing funny current to trigger the AP. This low level of IK1 further evokes a slower upstroke velocity in phase 0. Computational simulations revealed that an increasing expression of IK1 in iPSC-CMs would induce a more negative and more stable resting potential [16,72,73,74]. These data also indicate an immature state of iPSC derived-CMs and suggests possible limitations for cardiovascular research and clinical applications.
3.2. Field Potential
Classically, the cardiac action potential of single cells is analyzed using patch clamp devices, which allow detection of each individual ion current contributing to the AP pattern [69,75]. In contrast, MEA does not directly measure the AP but rather record cardiac FP instead, shown in Figure 2B. The FP encompasses the spatiotemporal electrical activity of cell clusters attached to the electrode, thus, it is the superposition of all ionic processes, ranging from fast action potentials to slowest fluctuations [76,77]. The measured FP arises from spreading of the cardiac AP throughout the cell monolayer relative to the recording electrodes. Therefore, it is comparable to the clinical electrocardiogram signal that represents voltage change over time due to electrical activity of the heart [47].
Since the biophysical processes underlying the generation of FPs are well known, it is possible to reconstruct the corresponding AP pattern and to extract important physiological parameters [76]. Figure 2B depicts the different phases of a typical ventricular AP pattern and the corresponding FP measured by MEA. The FP waveform contains a strong transient spike attributed to the Na+ influx and associated membrane depolarization, followed by a gentle incline based on the intracellular increase of Ca2+ level and ending with repolarization associated with K+ efflux. In addition, a comparative analysis of patch clamp data and MEA recordings revealed that duration of the FPs correlate well with the length of the QT interval of APs [78]. Similar results were obtained by Asakura et al., showing that MEA-based FP detection can be applied to determine the prolongation of the QT interval following drug administration in iPSC-derived CMs [49]. In addition to the QT interval and K+/Ca+ flux, the FP pattern provides valuable information about the beating frequency as well as AP duration (Table 1, Figure 2B). Moreover, since MEA measurements are commonly performed on cell monolayers, propagation and direction of the AP can be determined (Figure 2C, Video S2).

Table 1.
Functional parameters acquired by FP measurements using MEA Systems.
For a more precise comparison of FPs and patch clamp measurements, MEA platforms have been developed that allow the detection of APs. These local extracellular AP assays, utilize electrodes capable to apply electrical stimulation in order to induce small pores in the cellular membrane for the acquisition of stable AP patterns over longer timescales [79,80]. In addition, the use of 3-dimensional electrodes can facilitate the coupling intensity and decrease the membrane resistance of individual cells required for intracellular recordings [81,82].
4. Application of MEAs for Cardiotoxic Risk Assessment
In 2014 the US department of health and human services estimated that nearly 1 million patients show adverse drug reactions each year—among these drug induced arrhythmias are the leading cause [83].
The comprehensive in vitro proarrhythmia assay (CiPA) initiative was originated for drug proarrhythmic potential assessment in order to analyze several known drugs and substances on their potential to affect the cardiac system. Thus, a list of 28 relevant drugs with a potential effect was published. The list reaches from vandatanib, clarithromycin, droperidol over metoprolol to tamoxifen and verapamil to name only a few. The drugs were categorized into high risk, intermediate risk and no or very low risk for torsade-de-pointes-tachycardia (TdP; Table 2). TdP is characterized by polymorphic ventricular tachyarrhythmias, which can follow drug induced delayed ventricular repolarization (OT interval prolongation) [84,85]. For the categorization the initiative recommends and describes assays that are mechanistically based in vitro assays and are composed of four different steps that in total should give a comprehensive overview of the possible proarrhythmic potential:

Table 2.
List of CiPA compounds defined by CiPA initiative * (May 2016) [86].
First, the effect of potential drugs and substances on several cardiac ion currents, which are defined as a core set of ion channel types needs to be analyzed. Second, the electrophysiological properties are simulated in in silico models. Since ventricular cardiomyocytes can be generated from human stem cells they represent a promising platform for drug testing, consequently the drug effects are measured in this in vitro setting as the third step. Finally, the expected and unexpected effects on the entire human organism need to be clinically evaluated [84].
Since the inception of the CiPA initiative in 2013, the analysis of the listed drugs was set into focus of research by the research community. Several cell lines (including self-generated and commercially available cell lines like iCell Cardiomyocytes (Fuji), Pluricytes (Pluriomics), Cor4u (Ncardia), Axol Bioscience, i-HCm (Cell applications), ASC (Applied Stem Cell, ix Cells Biotechnologies), CDI (Cellular Dynamics International), Cellartis (Clontech, Takara), ReproCardio (ReproCELL) and ACCEGEN (immortalized from patients or transdifferentiated from hSC) have been used to analyze the impact of compound administration on cardiomyocyte electrophysiology. The methodology used for the measurements range from (automated) patch clamp over MEA to optical measurement.
There is a tendency noticeable promoting the assessment of not only hERG inhibition or QT prolongation but also analysis of Nav1.5 (voltage gated Na+ channel), Cav1.2 (voltage gated Ca2+ channel) or of index of cardiac electrophysiological balance (assesses balance between OT interval and QRS duration).
The Consortium for Safety Assessment using Human iPS cells (CSAHI) was established in 2013 by the Japan Pharmaceutical Manufacturers Association in order to “give recommendations for the usage of human iPS-cell derived cardiomyocytes, hepatocytes and neurons in drug testing evaluation” [87]. The CSAHI study is also aiming at the analysis of potential unknown effects on the cardiac system and tries to overcome/decrease proarrhythmic-risk market withdrawal. There have been several substances being tested that are not listed on the CiPA list. CSAHI provides a generalizable platform with the promising method for prediction of cardiotoxicity [88]. There are different parameters that are analyzed for the named prediction, such as QT prolongation, arrhythmia, but not only using the hERG assay. The latter is known to be an inaccurate predictor, because it only focuses on the inhibition of this particular ion channel—yet for cardiac adverse effects, mostly a broader range of (different) ion channels is affected [89].
Using animal hearts as a model, (which is also done for drug testing approaches) or the guinea pig papillary muscle action potential assay (qpAPD), is also not sufficient due to interspecies differences in electrophysiological properties and different responding behavior to drugs [87,90].
The tested substances are modulating a range of cardiac ion currents and consequently can have multiple arrhythmogenic effects. Due to this fact, multiple parameters are required to be evaluated, especially when using MEA technology. The electrophysiological response to drugs can be analyzed using the heart rate, field potential duration (FPD) and the corrected FPD (cFPD), all indicating arrhythmia-like waveforms [85]. Moreover, further analytical parameters are available using impedance measurement, deformation analysis or high content imaging [87].
The usage of human iPSC-CMs for drug testing is a promising tool due to their large-scale production circumventing the lack of a source for human adult cells [85]. However, they are displaying/carrying the disadvantage of not being identical to isolated primary adult cardiomyocytes and showing indicators for immature state, iPSC-CM are comparable in expression of cardiomyocyte marker. Especially the expression of relevant cardiac ion channels such as INa, ICaL, If, Ito, IK1, IKr and IKs has been analyzed [91,92]. Compared to previously used single ionic current model approaches they have shown a higher sensitivity and specificity [85]. Techniques such as qpAPD evaluated several false negative results [87], leading to possibly high risk in drug administration on patients. Many attempts have been carried out to analyze the response of human iPSC-CM to the administration of not only cardiogenic drugs and to further compare it to human adult cardiomyocytes. Yet, limitations must be kept in mind when transferring results from cell models to the human organism.
Since comparability within CiPA associated data generation is crucial Kanda et al. aimed to develop a standardized protocol for the experimental data generation including experimental conditions and calibration compounds providing it to a big community [63].
In order to validate the reliability and comparability of iPSC-CM based drug testing CiPA associated studies have been examined using a batch of known (formerly analyzed) drugs, various commercial cell lines, different electrophysiological platforms and multiple experimental sites [85,93]. Differences between the various analyzed combinations could be seen but also representative effects on depolarization, confirming the utility of the CiPA paradigm. Promoting the concept of CiPA, the CSAHI study from Japan HEART TEAM could not detect any inter-facility variability [90] and is providing new insights from their large scale drug testing combining electrophysiological data (from the MEA platform) with gene expression profiles [87,88]. A comprehensive overview of tested substances on their proarrhythmic risk/cardiac side effects using the combination of MEA technology with iPSC-CM is given in Table 3 and Table 4. Table 3 summarizes drugs with a primarily non-cardiac medical indication such as antibiotic or antipsychotic drugs. Anti-arrhythmic drugs and cardiac ion-channel blocker are included in Table 4, containing cardiogenic substances.
To consider the influence of serum containing medium during administration and measurement of potential cardiotoxic drugs Schocken et al. compared serum containing and serum free medium in pro-arrhythmia risk assessment. The solubility of a drug connected with the precise drug concentration as well as cardiomyocyte electrophysiology may be affected by the serum. Mostly the precise serum composition is unknown. Using a high-throughput MEA 25 substances have been analyzed, showing differences in drug availability and the tendency of serum to influence the FPD in an increasing or decreasing manner for several drugs [94].
To further improve and expand the system of iPSC-CM drug testing, Zeng et al. addressed the diversity of iPSC-CM models from different gender and ethnical origin with known pharmaceuticals, detecting possible inter-sex differences [95]. Therefore, they prefer/vote for generalized pre-set acceptance criteria for iPSC-CMs. Burnett et al. recently published a study using not only a population-based CM model, generated from cells of 43 individuals (both gender and diverse ancestry) to defeat the drawback of inter-individual variability but also tested a large scale of substances of pharmaceuticals, environment and food. Both for control and substrate administration they found inter-individual variability, increasing the requirement of population based-models (to reproduce a whole population) [96].

Table 3.
MEA based safety testing of drugs without cardiac indication using human induced pluripotent stem cell cardiomyocyte (hiPSC-CM).
Table 3.
MEA based safety testing of drugs without cardiac indication using human induced pluripotent stem cell cardiomyocyte (hiPSC-CM).
| Substance | (Site of) Action | Effect | Min. Effective Conc. | Cell Type/ Subtype | Differentiation Protocol | Age/ Maturation State | Platform | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alfuzosin | Treatment of benign prostatic enlargement, a hERG-channel blocker | Clinical QT prolongation | 30 nM | hiPSC-CM iCell™ (mixture of ventricular, atrial, nodal cells) | n/a | 32 days of differentiation +15–26 days | MEA | [87,88] |
| Astemizole | Antihistaminergic drug, H1 receptor antagonist, multi-channel block | Repolarization prolongation/arrhythmogenic effects, hERG channel blockade | 3–10 nM | hiPSC-CM iCell™/iCell2™/Cor4U® (mixture of ventricular, atrial, nodal cells) | n/a | 32 days of differentiation (+15–26 days) n/a | MEA | [87,88,93] |
| BaCl2 | Digitalis like activity, stimulation tonic contraction in muscle, used as contrast agent | Chronotropic effect K+ and Ca2+ modulation | - | hiPSC-CM iCell™ (mixture of ventricular, atrial, nodal cells) | n/a | 32 days of differentiation +15–26 days | MEA | [87] |
| Blebbistatin | Myosin II ATPase inhibitor | Increase in beating frequency, beating arrest (30 µM) | 1–30 µM | hiPSC-CM iCell™ (mixture of ventricular, atrial, nodal cells) | n/a | Min. 32 days of differentiation | MEA | [88] |
| Carbachol | Parasympathomimetic drug cholinergic agonist KAch- channel, glaucoma treatment | Negative chronotropic effects, FPDc prolongation, decrease in beating frequency | 10 µM | Double reporter cell line, subtypes: ventricular, atrial, nodal, TBX5 Nkx2.5/hiPSC-CM (iCell™ mixture of ventricular, atrial, nodal cells) | 2D n/a | 35-40 day of differentiation 32 days of differentiation | Patch clamp, MEA | [21,88] |
| Chlorpromazine | Anti-psychotic drug, multi-channel block | Early afterdepolarization, beating arrest | 10 µM | hiPSC-CM iCell™ mixture of ventricular, atrial, nodal cells) | n/a | 32 days of differentiation | MEA | [88] |
| Chromanol 293B | IKv7.1 channel Blocker | Prolong FPD in control cells, | LQTS cells and control (patient- derived cells) n/a | 3D | 30-60 days of differentiation +50 days | MEA | [97] | |
| Cisapride | Prokinetic gastrointestinal drug, multi-channel block | Prolongation of FPD, Repolarization delays/arrhythmogenic effects Prolongation of QT from patients with long QT syndrome | 100 nM | hiPSC-CM Cor4U® and iCell™ mixture of ventricular, atrial, nodal cells Wt iPSC, and from patient with LQTS (n/a) | n/a 3D | 10 days after differentiation, min. 32 days of differentiation n/a | MEA, automated patch clamp | [26,87,88,93,98,99] |
| Clarithromycin | Antibiotic drug | Repolarization prolongation, arrhythmogenic effects | - | hiPSC-CM iCell2™/Cor4U® (mixture of ventricular, atrial, nodal cells) | n/a | 32 days of differentiation n/a | MEA/VSO | [93] |
| Clozapine | Anti-psychotic drug, multi-channel block | Shortening of FPDc, increase in beat frequency | 0.3–1 µM | hiPSC-CM iCell™ mixture of ventricular, atrial, nodal cells) | n/a | 32 days of differentiation | MEA | [88] |
| Domperidone | Dopamine-antagonist, anti-nausea drug hERG- channel blocker | Repolarization prolongation, arrhythmogenic effects | 10 nM | hiPSC-CM iCell™/iCell2™/Cor4U® mixture of ventricular, atrial, nodal cells) | n/a | 32 days of differentiation n/a | MEA/VSO | [88,93] |
| Doxorubicin | anthracycline chemotherapy agent | Decrease in FPD, beat frequency and spike amplitude | 1 µM | hiPSC-CMs iCell™ 50% ventricular, 10% atrial cells patient derived cells (n/a) | n/a 2D | 32 days of differentiation 20–30 days of differentiation | MEA | [100,101] |
| Droperidol | Neuroleptic drug | Repolarization prolongation, arrhythmogenic effects | - | hiPSC-CM iCell2™/Cor4U® (mixture of ventricular, atrial, nodal cells) | n/a | 32 days of differentiation n/a | MEA/VSO | [93] |
| Fluoxetine | Anti-depressant drug | Clinical QT prolongation | - | hiPSC-CM iCell™ (mixture of ventricular, atrial, nodal cells) | n/a | 32 days of differentiation +15–26 days | MEA | [87] |
| Isoproterenol | Bronchodilator | Chronotropic effect, K+ and Ca2+ Modulation, FPDc shortening, increasing beating frequency | 3–100 nM | hiPSC-CM iCell™ (mixture of ventricular, atrial, nodal cells) | n/a | 32 days of differentiation +15–26 days | MEA | [87,88] |
| Loratadine | Anti- histaminergic drug, H1 receptor block, multi-channel block | Increase in beating frequency | 0.1–3 µM | hiPSC-CM iCell™ (mixture of ventricular, atrial, nodal cells) | n/a | 32 days of differentiation | MEA | [88] |
| Moxifloxacin | Anti-biotic drug, multi-channel block | Repolarization delay | 10 µM | hiPSC-CM iCell™/Cor4U® (mixture of ventricular, atrial, nodal cells) GE Healthcare (Cytiva™), Stanford Cardiac Institute | n/a | 32 days of differentiation +14–24 days n/a | MEA | [85] |
| Ondansetron | Antiemetic drug, serotonin-receptor block | Repolarization prolongation, arrhythmogenic effects | 30 nM | hiPSC-CM iCell2 ™/Cor4U® (mixture of ventricular, atrial, nodal cells) | n/a | 32 days of differentiation n/a | MEA/VSO | [93] |
| Pimozide | Anti-psychotic drug, multi-channel block | Repolarization prolongation/arrhythmogenic effects | 3–10 nM | hiPSC-CM iCell™/iCell2 ™/Cor4U® (mixture of ventricular, atrial, nodal cells) | n/a | 32 days of differentiation +15–26 days n/a | MEA | [87,93] |
| Risperidon | Anti-psychotic drug, serotonin-receptor block | Repolarization prolongation | 3–30 nM | hiPSC-CM iCell2™/Cor4U® (mixture of ventricular, atrial, nodal cells) | n/a | 32 days of differentiation n/a | MEA | [93] |
| Sunitinib | Anti-cancer drug, tyrosine kinase inhibitor | FPDc prolongation, early afterdepolarization | 0.3–10 µM | hiPSC-CM iCell™ (mixture of ventricular, atrial, nodal cells) | n/a | 32 days of differentiation | MEA | [88] |
| Terfenadine | Anti-histaminergic drug, H1 receptor block | FPDc prolongation, decrease in spike amplitude, repolarization prolongation | 100–1000 nM | hiPSC-CM iCell™/iCell2™/Cor4U® (mixture of ventricular, atrial, nodal cells) | n/a | 32 days of differentiation n/a | MEA | [93,98] |
| Tetrodotoxin (TTX) | Neurotoxic drug, (voltage sensitive) Nav (1.1, 1.7, 1.5)- channel block | Decrease in slope, depolarization potential and action potential duration | 10 µM | hiPSC-CM Cor4U® mixture of ventricular, atrial, nodal cells | n/a | 10 days after differentiation | Automated patch clamp | [26] |
| Thioridazine | Sedative, anti- psychotic drug, multi-channel block | Repolarization delays/arrhythmogenic effects | 100 nM | hiPSC-CM iCell™ (mixture of ventricular, atrial, nodal cells) | n/a | 32 days of differentiation +15–26 days | MEA | [87,88] |
| Tolterodine | Treatment of urinary incontinence, muscarinic receptor antagonist | clinical QT prolongation, early afterdepolarization | 100–300 nM | hiPSC-CM iCell™ (mixture of ventricular, atrial, nodal cells) | n/a | 32 days of differentiation +15–26 days | MEA | [87] |
| Vanoxerine | Serotonin-dopamine reuptake inhibitor | Clinical QT prolongation, multiple ion-channel effects, early afterdepolarizations | 100 nM | hiPSC-CM iCell™ (mixture of ventricular, atrial, nodal cells) | n/a | 32 days of differentiation +15–26 days | MEA | [87] |
| Vandetanib | Anti-cancer drug for thyroid gland, kinase inhibitor | Repolarization prolongation, arrhythmia like events | 0.1–1 µM | hiPSC-CM iCell2™/Cor4U® (mixture of ventricular, atrial, nodal cells) | n/a | 32 days of differentiation n/a | MEA/VSO | [93] |

Table 4.
MEA based safety testing of drugs with cardiac indication using hiPSC-CM.
Table 4.
MEA based safety testing of drugs with cardiac indication using hiPSC-CM.
| Substance | (Side of) Action | Effect | Min. Effective Conc. | Cell Type | Differentiation Protocol | Age/Maturation State | Platform | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amiodarone | Class III anti-arrhythmic drug, multi-channel block | Clinical QT prolongation | 0.1–1 µM | hiPSC-CM iCell™ (mixture of ventricular, atrial, nodal cells) | n/a | 32 days of differentiation +15–26 days | MEA | [87,88] |
| Azimilide | Class III anti-arrhythmic drug | FPDc prolongation, decrease in beating frequency, early after depolarization | 0.3–1 µM | hiPSC-CM iCell™ (mixture of ventricular, atrial, nodal cells) | n/a | 32 days of differentiation | MEA | [88] |
| Bay K 8644 | Agonist of voltage sensitive dihydropyridine (DHP; L-Typ) Calcium channel | FPDc prolongation, decrease in beat frequency, positive inotropic | 0.3–3 nM | hiPSC-CM iCell™ (mixture of ventricular, atrial, nodal cells) | n/a | 32 days of differentiation +15–26 days | MEA | [87,88] |
| Bepridil | Class IV anti-arrhythmic drug, multi-channel block | Repolarization delays/arrhythmogenic effects | 0.1–1 µM | hiPSC-CM iCell™/iCell2™/Cor4U® (mixture of ventricular, atrial, nodal cells) | n/a | 32 days of differentiation +15–26 days n/a | MEA | [87,88,93] |
| Dofetilide | Class III anti-arrhythmic drug, multi-channel block | Increase in FPD, TdP arrhythmias | 3–100 nM | hiPSC-CM iCell™/iCell2™/Cor4U® (mixture of ventricular, atrial, nodal cells) Pluricytes™ | n/a | 32 days of differentiation n/a n/a | MEA | [88,93,102] |
| E-4031 | Class III anti-arrhythmic drug, hERG- channel block | prolonged FPD, severe arrhythmia in LQTS iPSC-CM | 30–100 nM | hiPSC-CM iCell™/Cor4U® (mixture of ventricular, atrial, nodal cells) GE Healthcare (Cytiva™), Stanford Cardiac Institute LQTS cells and control | n/a3D | 32 days of differentiation +14–24 days n/a 30–60 days of differentiation +50 days | MEA | [85,97,98] |
| Flecainide | Class Ic anti-arrhythmic drug, multi-channel block | Decrease in spike amplitude, FPDc prolongation | 1 µM | hiPSC-CM iCell™/Cor4U® (mixture of ventricular, atrial, nodal cells) GE Healthcare (Cytiva™), Stanford Cardiac InstituteCPVT cells and control | n/a 2D/3D | 32 days of differentiation +14–24 days n/a 20–30 days of beating | MEA Patch clamp | [85,98,103] |
| Ibutilide | Class III Anti-arrhythmic drug, multi-channel block | Arrhythmia like events, early after depolarizations | 1–100 nM | hiPSC-CM iCell™/iCell2™/Cor4U® (mixture of ventricular, atrial, nodal cells) | n/a | 32 days of differentiation n/a | MEA/VSO | [88,93] |
| Ivabradin | Treatment of stable angina pectoris, If-channel inhibitor, heart rate reducing drug | Prolongation in APD, decrease in beating frequency | 1 µM | Double reporter cell line, subtypes: ventricular, atrial, nodal, TBX5 Nkx2.5/hiPSC-CM | 2D | 35–40 days of differentiation | Patch clamp | [21] |
| JNJ303 | IKv7.1- channel inhibitor | Small prolongation of FPDc | 300 nM | hiPSC-CM iCell™/Cor4U® (mixture of ventricular, atrial, nodal cells) GE Healthcare (Cytiva™), Stanford Cardiac Institute | n/a | 32 days of differentiation n/a | MEA | [85] |
| Levocromakalim | Vasodilating drug, KATP opener | Membrane hyperpolarization, decrease in FPDc and beating frequency | 1–3 µM | hiPSC-CM iCell™ (mixture of ventricular, atrial, nodal cells) | n/a | 32 days of differentiation +15–26 days | MEA | [87,88] |
| Metoprolol | Anti- arrhythmic, anti- hypertonic drug, ß1-adreno receptor block | Induced arrhythmias, hERG block at higher concentrations | 100 µM | hIPSC CM iCell2™/Cor4U® (mixture of ventricular, atrial, nodal cells) CPVT cells and control | n/a 2D/3D | 32 days of differentiation n/a 20–30 days of beating | MEA/VSO Patch clamp | [93,103] |
| Mexiletine | Class Ib anti-arrhythmic drug, Inhibiting Nav1.5- also hERG block | Reduce spike amplitude, cessation of spontaneous beating (100 µM) | 1–10 µM, | hIPSC-CM iCell™/iCell2™ Cor4U® (mixture of ventricular, atrial, nodal cells) GE Healthcare (Cytiva™), Stanford Cardiac Institute | n/a | 32 days of differentiation +14–24 days n/a | MEA | [85,88,93,98] |
| Mibefradil | Treatment of angina pectoris and hypertension, multi-channel block | Shortening in FPDc, increase in beat frequency | 0.3–1 µM | hiPSC-CM iCell™ (mixture of ventricular, atrial, nodal cells) | n/a | 32 days of differentiation +15–26 days | MEA | [87,88] |
| Nifedipin | Vasodilating drug, ICaL block | Shortening of FPDc, increase in beating rate | 0.3–1 µM | hiPSC-CM iCell™/Cor4U® (mixture of ventricular, atrial, nodal cells) GE Healthcare (Cytiva™), Stanford Cardiac Institute | n/a | 32 days of differentiation +10 days n/a | MEA, automated patch clamp | [26,85,98] |
| NS- 1643 | hERG-channel activator | Repolarization effect, decrease in FPDc, increase in beating frequency | 3 µM | hiPSC-CM iCell™ (mixture of ventricular, atrial, nodal cells) | n/a | 32 days of differentiation +15–26 days | MEA | [87,88] |
| Ouabain | Cardiac glycoside, Na+-K+- ATPase inhibitor | Repolarization effects, decrease in FPDc | 10–100 nM | hiPSC-CM iCell™ (mixture of ventricular, atrial, nodal cells) | n/a | 32 days of differentiation +15–26 days | MEA | [87,88] |
| Propranolol | Class II anti-arrhythmic drug, beta- receptor block | Early afterdepolarization, decrease in beating frequency | 10 µM | hiPSC-CM iCell™ (mixture of ventricular, atrial, nodal cells) | n/a | 32 days of differentiation | MEA | [88] |
| Quinidine | Class Ia anti-arrhythmic drug, multi-channel block (Nav1.5, Cav1.2, hERG) | FPDc prolongation, reduced spike amplitude, repolarization delays/arrhythmogenic effects | 0.3–10 µM | hiPSC-CM iCell™/iCell2™ Cor4U® (mixture of ventricular, atrial, nodal cells) GE Healthcare (Cytiva™), Stanford Cardiac Institute Fibroblast-derived iPSC-CM (67% ventricular, 5% nodal, 28% atrial) | n/a 3D | 32 days of differentiation +15–26 days 65–95 days after differentiation induction | MEA, Low impedance MEA | [85,87,88,93,98,104] |
| Ranolazine | Angina pectoris treatment, multichannel (Na and hERG block) | FPDc prolongation, clinical QT prolongation, repolarization prolongation | 0.3 µM, clinical conc. <100 µM | hiPSC-CM iCell iCell2™ Cor4U® (mixture of ventricular, atrial, nodal cells) GE Healthcare (Cytiva™), Stanford Cardiac Institute | 32 days of differentiation +15–26 days (14–24 days) n/a | MEA | [85,87,88,93] | |
| Sotalol | Anti-arrhythmic drug, beta adreno receptor block | Repolarization prolongation, arrhythmogenic effects, hERG- channel block | 15 µM | hiPSC-CMs iCell2™/Cor4U® (mixture of ventricular, atrial, nodal cells) Fibroblast-derived iPSC-CM (67% ventricular,5% nodal, 28% atrial) | n/a 3D | 32 days of differentiation n/a 65–95 days after differentiation induction | Low impedance MEA | [93,104] |
| Verapamil | Class VI anti-arrhythmic drug, inhibits hERG, ICal-typ calcium channels, Multi-channel block | Shortening of FPDc, increase in spontaneous beat rate; shortening in APD20 and APD90 | 0.1–0.3 µM; 1 µM | hiPSC-CM iCell™ (mixture of ventricular, atrial, nodal cells) Pluricytes™ | n/a | 32 days of differentiation n/a | MEA; patch clamp | [98,102] |
| Vernakalant | Class III anti-arrhythmic drug, used for cardioversion of atrial fibrillation, atrial potassium- channel block | APD prolongation, partly arrhythmogenic effects, | - | Double reporter cell line, different subtypes (ventricular phenotype) | 2D | 20–30 days post induction of differentiation | Patch clamp | [21] |
| ZD 7288 | Selective hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated channel blocker, If- current inhibitor | Negative chronotropic effect, FPDc prolongation | 3–30 nM | hiPSC-CM iCell™ (mixture of ventricular, atrial, nodal cells) | n/a | 32 days of differentiation +15–26 days | MEA | [87,88] |
5. Disease Modeling Using hiPSC-CM
Cardiovascular diseases (CVD) are the number one cause of death globally according to the WHO. This group of disease is not only present in developed countries but also in low income countries. CVD affects both the blood vessels and the heart and range from coronary heart disease, thrombosis, over structural abnormalities of the heart and arrhythmias to stroke and heart failure [83].
In order to understand the pathological mechanisms of the disease iPSC-derived cardiomyocytes generated from patient cells like dermal fibroblasts or blood cells showed high potential as a tool to not only generate immortalized cell lines from healthy donors but also from diseased patients [105]. The generated cell lines can show disease-specific phenotypes [99]. Especially physiological characteristics can be determined when carrying the mutations in the cardiac relevant genes. This suggests that the disease phenotype can be recapitulated in vitro. To further analyze the pathogenic mechanisms causing the disease and the disease specific phenotype patient originated iPSC-CM were analyzed and afterwards genetically fixed. Here, RNA interference can be used for silencing or suppressing mutant genes [106]. To determine and control the effects caused by mutations the initial genetic defect was induced and replicated in hESC derived CM on the contrary. A correction of the defect led to a normalization of the analyzed parameter whereas the induction led to the diseased phenotype [107]. Besides a better understanding of heart disease, the transgenic models should contribute to testing of cardiogenic drugs on their positive therapeutic as well as detrimental side effects. Moreover, the sensitivity of patients for side effects of drugs can be evaluated and, the clinical vulnerability of high-risk groups (population) to drug induced-cardiotoxicity can be set into consideration. This testing of therapies in vitro is another promising tool [99,108].
For the analysis and validation of the generated iPSC-CM based disease models patch clamp analyses are still the gold standard, despite the number of MEA based measurements in increasing (Figure 3). In this part we want to give a selective overview about already developed disease models for cardiac disease generated from human iPSCs, where the usage of MEA platform is additionally mentioned.
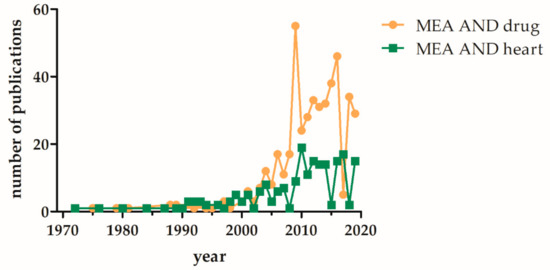
Figure 3.
Increase of PubMed listed publications involving MEA based analysis of “heart” or “drugs” over the last five decades. The terms (multielectrode array and drug) or (microelectrode array and drug) and (multielectrode array and heart) or (microelectrode array and heart) were used for the PubMed search (date: Sept 2019).
6. Overview of Developed Disease Models
Ping Liang et al. generated a library of iPSC-derived CM from patients suffering from various hereditary cardiac disorders to show that cardiac drug toxicity differs between different pathophysiological conditions. The iPSC-CM was generated from patients with hereditary long-QT syndrome, familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and familial dilated cardiomyopathy. They have shown that patients that already suffer from a heart disease have a higher incidence to show adverse effects arising from their medical treatment. They seem to have a higher sensitivity to cardiotropic drugs and can have a higher risk for arrhythmias, which possibly are leading to death [99].
In 2014 Zhang et al. generated cardiomyocytes derived from iPSC from patients with recessive, life-threatening cardiac arrhythmia of Jarvell and Lang–Nielsen syndrome. They gave new insights into the pathological mechanisms and showed enhanced sensitivity to proarrhythmic drugs in the generated cell-based disease model using MEA technology and patch clamp [109].
Considering the literature of the last years for ion channelopathies, these appear to be in focus of disease modeling, revealing many well-established human iPSC generated disease models. Among these the long QT syndrome is the most common. The first model has been developed by Moretti et al. (2010). Ventricular and atrial cells in contrast to nodal type or healthy control cells, have shown significantly increased APDs [110]. The response of sporadic Long QT1-iPSC-CM to small molecule inhibitors has been analyzed measuring changes in the FPD with the MEA platform [97].
A mutation in the gene of the sodium voltage-gated channel (Nav1.5) alpha subunit 5 (SCN5A) for example is leading to conduction defects, phenotypes of the LQT3 and Brugada syndrome due to a gain and loss of function [24]. A review on modeling long QT syndrome with the aid of iPSC-CM can be found by Sala et al. [111].
Another channelopathy that has been used for the generation of a disease model is the catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (CPVT). An incorrect and insufficient Ca2+ handling (inclusive spontaneous release or sequestration) is leading to this adrenergically mediated polymorphic ventricular tachycardia [112]. Sasaki et al. generated CM from CPVT patient- derived iPSCs and identified S107 as a potential therapeutic agent since a pre-incubation with S107 led to a reduction of isoprenaline induced delayed afterdepolarizations [113]. Acimovic et al. (2018) developed a CPVT model using a novel ryanodine receptor mutation and further analyzed the response to a treatment with flecainide and metoprolol [103].
Furthermore, models of structural myopathies have been developed: among these, the hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) and the familial dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) are the most common being analyzed. HCM associated death is mostly caused by ventricular fibrillation developed from ventricular arrhythmias. Despite that not all pathophysiological mechanisms are known yet, some detected mutations have been the basis of developed disease models. HCM iPSC derived cardiomyocytes have shown enhanced sarcomere arrangement [114], deviating electromechanical properties such as delayed after depolarizations and calcium handling [115]. DCM is leading to systolic dysfunction such as decreased ejection fraction due to an expanded size of the left ventricle combined with decreased chamber thickness. Several known mutations have been fundamental for the generation of a DCM model, including MYH7 [116], TNNT [117], LMNA (laminin A/c) [118], Desmin [119], Titin [120] and RBM20 RNA-binding motif protein 20 [121,122]. On the cellular level an increase in cell size, abnormal sarcomere structure and organization e.g., sarcomeric α actinin and defective calcium handling (altering calcium machinery) [121] could be seen within these models. For further detailed and completely information we would recommend the review by Giacomelli et al. [123].
Moreover, cardiomyocytes have been generated from patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy iPSCs showing phenotypical deficiency of dystrophin and increased Ca levels in resting cells. The before mentioned disease caused by a high quantity of mutations is characterized by a knockout of the dystrophin protein resulting in muscle degeneration [124]. For further detailed reading we recommend the systematic review on cardiomyopathy phenotypes in iPSC-CM (HCM and DCM) by Eschenhagen and Carrier [125].
Besides the generation of disease models from patient derived cells, new gene editing technologies find application: de la Roche et al. generated a model for the Brugada syndrome carrying the A735V mutation in the SCN5A gene introduced by CRISPR/Cas9 in order to be independent of the patient’s genetic background. The generated CM showed electrophysiological alteration such as decreased upstroke velocity and sodium current density [126].
Among the current literature the number of developed models that are not primarily heart diseases (structural caused heart disease) but show heart related symptoms is increasing. For example a model for Chagas disease, a parasite caused infection by Trypanosoma cruzi that is associated with cardiomyopathy symptoms since the parasites are replicating in the cardiomyocytes, was developed by Bozzi et al. after infection of iPSC-CM with Trypanosoma cruzi [127]. Lee et al. developed a model for autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) form patient derived iPSC-CM showing mutations in the PKD1/PKD2 gene [128], to name only two of them.
Since the generation of disease models with patient derived iPSC-CM was developed and practiced within the last years, the first scientific outcome has been produced in a more detailed understanding of the pathophysiological mechanisms that underlie known symptoms. Several recent studies were performed:
Using patient derived iPSC-CM from Fabry disease combined with gene editing technology Birket et al. analyzed the functional consequences of underlying genetic defects. They have shown the accumulation of GL-3 and alterations in excitability and calcium handling in cardiomyocytes. Moreover LIMP-2, shown to accumulate in the cells, was detected as a new potential biomarker [129].
Caluori et al. developed a system combining MEA platform with cantilever of atomic force microscopy (AFM) in order to analyze the topography, beating force and electric events simultaneously of control and DCM-derived iPSC-CM. Meanwhile substances for the cell characterization and toxicity testing have been administrated [130].
Moreover, microtissues have been generated from the disease model cardiomyocytes for hypertrophic cardiomyopathy HCM [131] and for catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia CPVT [132]. The HCM model was used to analyze contraction force development and calcium transient under mechanical overload revealing that both genetic defects and environmental stress reinforce dysfunctions in contractility [131]. The CPVT tissue construct examined molecular and cellular abnormalities and is confirming the approach of generating tissue like structures for the analysis of arrhythmia, which is mostly generated by the connection of many cells [132].
Another approach for the further use of these disease models and an improved reliability of the results/predictions are large scale simulations in in silico models. In order to enable this approach for the LQT syndrome with regards to the phenotypical variation (due to the large amount of different mutations) this system was developed and showed comparable results to experimental data concerning electrophysiological properties. Additionally, this simulation can facilitate the understanding of further biophysical mechanisms [133].
7. Conclusions and Outlook
Cardiomyocytes generated from human iPSCs are used to study heart development, cardiac function and heart diseases, and to develop novel pharmacological therapeutics [11,21,23,134]. This involves a detailed electrophysiological characterization of these cardiomyocytes under physiological and pathological conditions. Due to its non-invasive, label-free character MEA methodology has become a widely used tool to assess the electrical properties of cells in vitro. Besides iPSC-derived cardiomyocytes, acquisition of the FP by MEA assays can also be applied to any other cell type that shows electrical activity, including adult cardiomyocytes or neuronal cells. However, MEA measurements are not only restricted to cell monolayers, but can also be performed on slices of cardiac and brain tissue to better simulate in vivo conditions. Similarly, the replication of human physiology can be enhanced when MEA technology is combined with in vitro generated organoids. Therefore, MEA platforms can become a valuable tool in organ-on-a-chip engineering, promoting the clinical translation of acquired data [135,136].
As a high-throughput technology, MEA devices are particular important for the identification of novel therapeutics in drug research. The combination of MEA systems and iPSCs has been successfully applied in pharmacological studies and disease modeling, suggesting iPSC-based MEA measurements as a powerful approach for the development of personalized therapies that allow a more specific therapeutic intervention compared to conventional treatment options [137,138,139]. In this concept, patient-derived iPSCs are obtained by reprogramming of fibroblasts and induced to differentiate into cardiomyocytes. Subsequent analyses, e.g., transcriptomics and proteomics, enable the identification of molecular targets needed for pharmacological therapy. In a second step, the potency and efficiency of tested drugs is evaluated by MEA measurements, which in turn can provide important information to establish personalized drug treatments. Thus, MEA technology will help to open a new gateway for novel therapies in cardiovascular diseases.
Supplementary Materials
The supplementary materials are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4409/8/11/1331/s1.
Funding
This work was supported by the EU structural Fund (ESF/14-BM-A55-0024/18). In addition, R.D. and H.L. are supported by the DFG (DA1296/6-1), the German Heart Foundation (F/01/12), the FORUN Program of Rostock University Medical Centre (889001 and 889003) and the Josef and Käthe Klinz Foundation (T319/29737/2017). R.D. and S.K. are supported by the DAMP Foundation and the BMBF (VIP+ 00240).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Abbreviations
| 2D | Two-dimensional |
| ADPKD | Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease |
| AFM | Atomic force microscopy |
| AP | Action potential |
| APD | Action potential duration |
| ATM | Atomic force microscopy |
| AV Node | Atrioventricular node |
| HCM | Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy |
| Ca2+ | Calcium |
| CiPA | Comprehensive in vitro proarrhythmia assay |
| CM | Cardiomyocytes |
| CPVT | Catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia |
| CSAHI | Consortium for Safety Assessment using Human iPS cells |
| CVD | Cardiovascular disease |
| DCM | Familial dilated cardiomyopathy |
| FP | Field potential |
| FPDc | Field potential duration (corrected) |
| FRET | Fluorescence resonance energy transfer |
| GL-3 | Basic helix-loop-helix proteins, GLABRA3 |
| gpAPD | Guinea pig papillary muscle action potential assay |
| hERG | Human ether-a-go-go Related gene-voltage sensitive potassium channel |
| hiPSC | Human induced pluripotent stem cell |
| K+ | Potassium |
| LIMP-2 | Lysosomal integral membrane protein 2 |
| LMNA | Lamin A/C |
| MEA | Multi-/micro-electrode array |
| MYH7 | Myosin heavy chain 7 |
| Na+ | Sodium |
| PKD1/2 | Polycystic kidney disease 1 |
| RNA | Ribonucleic acid |
| SCN5A | Sodium voltage-gated channel alpha subunit 5 |
| TBX5 | T-box transcription factor |
| TdP | Torsade-de-Pointes-Tachycardia |
| TnnT | TroponinT |
| VSO | Voltage-sensitive optical system |
| WT | Wild type |
References
- Takahashi, K.; Yamanaka, S. Induction of Pluripotent Stem Cells from Mouse Embryonic and Adult Fibroblast Cultures by Defined Factors. Cell 2006, 126, 663–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, Y.; Yamanaka, S. Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells 10 Years Later. Circ. Res. 2017, 120, 1958–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuppinger, C. 3D Cardiac Cell Culture: A Critical Review of Current Technologies and Applications. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2019, 6, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojas, S.V.; Kensah, G.; Rotaermel, A.; Baraki, H.; Kutschka, I.; Zweigerdt, R.; Martin, U.; Haverich, A.; Gruh, I.; Martens, A. Transplantation of purified iPSC-derived cardiomyocytes in myocardial infarction. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0173222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.; Gregorich, Z.R.; Zhu, W.; Mattapally, S.; Oduk, Y.; Lou, X.; Kannappan, R.; Borovjagin, A.V.; Walcott, G.P.; Pollard, A.E.; et al. Large Cardiac Muscle Patches Engineered From Human Induced-Pluripotent Stem Cell–Derived Cardiac Cells Improve Recovery From Myocardial Infarction in Swine. Circulation 2018, 137, 1712–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shadrin, I.Y.; Allen, B.W.; Qian, Y.; Jackman, C.P.; Carlson, A.L.; Juhas, M.E.; Bursac, N. Cardiopatch platform enables maturation and scale-up of human pluripotent stem cell-derived engineered heart tissues. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Chen, H.; Xiao, D.; Yang, H.; Itzhaki, I.; Qin, X.; Chour, T.; Aguirre, A.; Lehmann, K.; Kim, Y.; et al. Comparison of Non-human Primate versus Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Cardiomyocytes for Treatment of Myocardial Infarction. Stem Cell Rep. 2018, 10, 422–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeiffer-Kaushik, E.R.; Smith, G.L.; Cai, B.; Dempsey, G.T.; Hortigon-Vinagre, M.P.; Zamora, V.; Feng, S.; Ingermanson, R.; Zhu, R.; Hariharan, V.; et al. Electrophysiological characterization of drug response in hSC-derived cardiomyocytes using voltage-sensitive optical platforms. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2018, 99, 106612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, J.; Wei, F.; Cai, C.; Lyn-Cook, B.; Pang, L. Sex-Related Differences in Drug-Induced QT Prolongation and Torsades de Pointes: A New Model System with Human iPSC-CMs. Toxicol. Sci. 2018, 167, 360–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izumi-Nakaseko, H.; Hagiwara-Nagasawa, M.; Naito, A.T.; Goto, A.; Chiba, K.; Sekino, Y.; Kanda, Y.; Sugiyama, A. Application of human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes sheets with microelectrode array system to estimate antiarrhythmic properties of multi-ion channel blockers. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 137, 372–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, S.L.; Zlochiver, V.; Conrad, D.B.; Vaidyanathan, R.; Valiquette, A.M.; Joshi-Mukherjee, R. A Multiwell Cardiac μGMEA Platform for Action Potential Recordings from Human iPSC-Derived Cardiomyocyte Constructs. Stem Cell Rep. 2018, 11, 522–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itzhaki, I.; Maizels, L.; Huber, I.; Zwi-Dantsis, L.; Caspi, O.; Winterstern, A.; Feldman, O.; Gepstein, A.; Arbel, G.; Hammerman, H.; et al. Modelling the long QT syndrome with induced pluripotent stem cells. Nature 2011, 471, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braam, S.R.; Tertoolen, L.; van de Stolpe, A.; Meyer, T.; Passier, R.; Mummery, C.L. Prediction of drug-induced cardiotoxicity using human embryonic stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes. Stem Cell Res. 2010, 4, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goineau, S.; Castagné, V. Electrophysiological characteristics and pharmacological sensitivity of two lines of human induced pluripotent stem cell derived cardiomyocytes coming from two different suppliers. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2018, 90, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimm, F.A.; Blanchette, A.; House, J.S.; Ferguson, K.; Hsieh, N.-H.; Dalaijamts, C.; Wright, A.A.; Anson, B.; Wright, F.A.; Chiu, W.A.; et al. A human population-based organotypic in vitro model for cardiotoxicity screening. ALTEX 2018, 35, 441–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goversen, B.; van der Heyden, M.A.G.; van Veen, T.A.B.; de Boer, T.P. The immature electrophysiological phenotype of iPSC-CMs still hampers in vitro drug screening: Special focus on IK1. Pharm. Ther. 2018, 183, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paci, M.; Hyttinen, J.; Rodriguez, B.; Severi, S. Human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived versus adult cardiomyocytes: An\textlessi\textgreaterin silico\textless/i\textgreater electrophysiological study on effects of ionic current block. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 5147–5160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.H.; Ye, L. Maturation of Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Cardiomyocytes: A Critical Step for Drug Development and Cell Therapy. J. Cardiovasc. Transl. Res. 2018, 11, 375–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakikes, I.; Ameen, M.; Termglinchan, V.; Wu, J.C. Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Cardiomyocytes: Insights into Molecular, Cellular, and Functional Phenotypes. Circ. Res. 2015, 117, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hausburg, F.; Jung, J.J.; David, R. Specific cell (re-)programming: Approaches and perspectives. In Advances in Biochemical Engineering/Biotechnology; Springer: Basel, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 163, pp. 71–115. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.Z.; Termglinchan, V.; Shao, N.-Y.; Itzhaki, I.; Liu, C.; Ma, N.; Tian, L.; Wang, V.Y.; Chang, A.C.Y.; Guo, H.; et al. A Human iPSC Double-Reporter System Enables Purification of Cardiac Lineage Subpopulations with Distinct Function and Drug Response Profiles. Cell Stem. Cell 2019, 24, 802–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obergrussberger, A.; Stölzle-Feix, S.; Becker, N.; Brüggemann, A.; Fertig, N.; Möller, C. Novel Screening Techniques For Ion Channel Targeting Drugs. Channels 2015, 9, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Casini, S.; Verkerk, A.O.; Remme, C.A. Human iPSC-Derived Cardiomyocytes for Investigation of Disease Mechanisms and Therapeutic Strategies in Inherited Arrhythmia Syndromes: Strengths and Limitations. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 2017, 31, 325–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, R.P.; Casini, S.; van den Berg, C.W.; Hoekstra, M.; Remme, C.A.; Dambrot, C.; Salvatori, D.; Oostwaard, D.W.; Wilde, A.A.M.; Bezzina, C.R.; et al. Cardiomyocytes derived from pluripotent stem cells recapitulate electrophysiological characteristics of an overlap syndrome of cardiac sodium channel disease. Circulation 2012, 125, 3079–3091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sallam, K.; Li, Y.; Sager, P.T.; Houser, S.R.; Wu, J.C. Finding the Rhythm of Sudden Cardiac Death. Circ. Res. 2015, 116, 1989–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheel, O.; Frech, S.; Amuzescu, B.; Eisfeld, J.; Lin, K.-H.; Knott, T. Action Potential Characterization of Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell–Derived Cardiomyocytes Using Automated Patch-Clamp Technology. Assay Drug Dev. Technol. 2014, 12, 457–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obergrussberger, A.; Goetze, T.A.; Brinkwirth, N.; Becker, N.; Friis, S.; Rapedius, M.; Haarmann, C.; Rinke-Weiß, I.; Stölzle-Feix, S.; Brüggemann, A.; et al. An update on the advancing high-throughput screening techniques for patch clamp-based ion channel screens: Implications for drug discovery. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2018, 13, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franz, D.; Olsen, H.L.; Klink, O.; Gimsa, J. Automated and manual patch clamp data of human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived dopaminergic neurons. Sci. Data 2017, 4, 170056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yajuan, X.; Xin, L.; Zhiyuan, L. A Comparison of the Performance and Application Differences Between Manual and Automated Patch-Clamp Techniques. Curr. Chem. Geno. 2012, 6, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, D.C.; Dallas, M.L. Using automated patch clamp electrophysiology platforms in pain-related ion channel research: Insights from industry and academia. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 175, 2312–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.-L.; Hsing, H.-W.; Lai, T.-C.; Chen, Y.-W.; Lee, T.-R.; Chan, H.-T.; Lyu, P.-C.; Wu, C.-L.; Lu, Y.-C.; Lin, S.-T.; et al. Trypsin-induced proteome alteration during cell subculture in mammalian cells. J. Biomed. Sci. 2010, 17, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajamohan, D.; Kalra, S.; Duc Hoang, M.; George, V.; Staniforth, A.; Russell, H.; Yang, X.; Denning, C. Automated Electrophysiological and Pharmacological Evaluation of Human Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Cardiomyocytes. Stem Cells Dev. 2016, 25, 439–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Storace, D.; Rad, M.S.; Han, Z.; Jin, L.; Cohen, L.B.; Hughes, T.; Baker, B.J.; Sung, U. Genetically encoded protein sensors of membrane potential. In Membrane Potential Imaging in the Nervous System and Heart; Springer: Basel, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 493–509. [Google Scholar]
- del Álamo, J.C.; Lemons, D.; Serrano, R.; Savchenko, A.; Cerignoli, F.; Bodmer, R.; Mercola, M. High throughput physiological screening of iPSC-derived cardiomyocytes for drug development. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2016, 1863, 1717–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedut, S.; Seminatore-Nole, C.; Lamamy, V.; Caignard, S.; Boutin, J.A.; Nosjean, O.; Stephan, J.-P.; Coge, F. High-throughput drug profiling with voltage- and calcium-sensitive fluorescent probes in human iPSC-derived cardiomyocytes. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2016, 311, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hortigon-Vinagre, M.P.; Zamora, V.; Burton, F.L.; Green, J.; Gintant, G.A.; Smith, G.L. The use of ratiometric fluorescence measurements of the voltage sensitive dye Di-4-ANEPPS to examine action potential characteristics and drug effects on human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes. Toxicol. Sci. 2016, 154, 320–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takaki, T.; Inagaki, A.; Chonabayashi, K.; Inoue, K.; Miki, K.; Ohno, S.; Makiyama, T.; Horie, M.; Yoshida, Y. Optical Recording of Action Potentials in Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Cardiac Single Cells and Monolayers Generated from Long QT Syndrome Type 1 Patients. Stem Cells Int. 2019, 2019, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St-Pierre, F.; Chavarha, M.; Lin, M.Z. Designs and sensing mechanisms of genetically encoded fluorescent voltage indicators. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2015, 27, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Jin, L.; Platisa, J.; Cohen, L.B.; Baker, B.J.; Pieribone, V.A. Fluorescent Protein Voltage Probes Derived from ArcLight that Respond to Membrane Voltage Changes with Fast Kinetics. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaheen, N.; Shiti, A.; Huber, I.; Shinnawi, R.; Arbel, G.; Gepstein, A.; Setter, N.; Goldfracht, I.; Gruber, A.; Chorna, S.V.; et al. Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Cardiac Cell Sheets Expressing Genetically Encoded Voltage Indicator for Pharmacological and Arrhythmia Studies. Stem Cell Rep. 2018, 10, 1879–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leyton-Mange, J.S.; Mills, R.W.; Macri, V.S.; Jang, M.Y.; Butte, F.N.; Ellinor, P.T.; Milan, D.J. Rapid cellular phenotyping of human pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes using a genetically encoded fluorescent voltage sensor. Stem Cell Rep. 2014, 2, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinnawi, R.; Huber, I.; Maizels, L.; Shaheen, N.; Gepstein, A.; Arbel, G.; Tijsen, A.J.; Gepstein, L. Monitoring human-induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes with genetically encoded calcium and voltage fluorescent reporters. Stem Cell Rep. 2015, 5, 582–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Awari, D.W.; Han, E.Y.; Uche-Anya, E.; Park, S.-H.E.; Yabe, Y.A.; Chung, W.K.; Yazawa, M. Dual optical recordings for action potentials and calcium handling in induced pluripotent stem cell models of cardiac arrhythmias using genetically encoded fluorescent indicators. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2015, 4, 468–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herron, T.J. Calcium and voltage mapping in hiPSC-CM monolayers. Cell Calcium. 2016, 59, 84–90. [Google Scholar]
- Herron, T.J.; Lee, P.; Jalife, J. Optical Imaging of Voltage and Calcium in Cardiac Cells & Tissues. Circ. Res. 2012, 110, 609–623. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhang, R.; Zhao, B.; Lossin, C.; Cao, Z. Cardiotoxicity screening: A review of rapid-throughput in vitro approaches. Arch. Toxicol. 2016, 90, 1803–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, W.; Asakura, K.; Ando, H.; Taniguchi, T.; Ojima, A.; Uda, T.; Osada, T.; Hayashi, S.; Kasai, C.; Miyamoto, N.; et al. Electrophysiological characteristics of human iPSC-derived cardiomyocytes for the assessment of drug-induced proarrhythmic potential. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0167348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sala, L.; Ward-van Oostwaard, D.; Tertoolen, L.G.J.; Mummery, C.L.; Bellin, M. Electrophysiological Analysis of human Pluripotent Stem Cell-derived Cardiomyocytes (hPSC-CMs) Using Multi-electrode Arrays (MEAs). J. Vis. Exp. 2017, 123, e55587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asakura, K.; Hayashi, S.; Ojima, A.; Taniguchi, T.; Miyamoto, N.; Nakamori, C.; Nagasawa, C.; Kitamura, T.; Osada, T.; Honda, Y.; et al. Improvement of acquisition and analysis methods in multi-electrode array experiments with iPS cell-derived cardiomyocytes. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2015, 75, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Scharnhorst, K.S.; Stieg, A.Z.; Gimzewski, J.K.; Minami, I.; Nakatsuji, N.; Nakano, H.; Nakano, A. Two dimensional electrophysiological characterization of human pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocyte system. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryynänen, T.; Pekkanen-Mattila, M.; Shah, D.; Kreutzer, J.; Kallio, P.; Lekkala, J.; Aalto-Setälä, K. Microelectrode array for noninvasive analysis of cardiomyocytes at the single-cell level. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2018, 57, 117001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, T.; Toriumi, H.; Shimada, J.; Nomura, F. Extracellular field potential recording of single cardiomyocytes in agarose microchambers using microelectrode array. J. Appl. Phys. 2018, 57, 03EB03. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C.; Qiao, Y.; Li, G.; Baechle, K.; Camelliti, P.; Rentschler, S.; Efimov, I.R. Human Organotypic Cultured Cardiac Slices: New Platform For High Throughput Preclinical Human Trials. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, J.D.; Montaigne, D.; Tinker, A. Tissue-Level Cardiac Electrophysiology Studied in Murine Myocardium Using a Microelectrode Array: Autonomic and Thermal Modulation. J. Membr. Biol. 2017, 250, 471–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, R.A.; Tzortzis, K.N.; Dupont, E.; Selvadurai, S.; Perbellini, F.; Cantwell, C.D.; Ng, F.S.; Simon, A.R.; Terracciano, C.M.; Peters, N.S. Concurrent micro-to macro-cardiac electrophysiology in myocyte cultures and human heart slices. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doerr, L.; Thomas, U.; Guinot, D.R.; Bot, C.T.; Stoelzle-Feix, S.; Beckler, M.; George, M.; Fertig, N. New Easy-to-Use Hybrid System for Extracellular Potential and Impedance Recordings. J. Lab. Autom. 2015, 20, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, F.; Huang, C.; Lin, Y.D.; Ivanovskaya, A.N.; O’Hara, T.J.; Booth, R.H.; Creek, C.J.; Enright, H.A.; Soscia, D.A.; Belle, A.M.; et al. Simultaneous electrical recording of cardiac electrophysiology and contraction on chip. Lab. A Chip 2017, 17, 1732–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takasuna, K.; Asakura, K.; Araki, S.; Ando, H.; Kazusa, K.; Kitaguchi, T.; Kunimatsu, T.; Suzuki, S.; Miyamoto, N. Comprehensive in Vitro Cardiac Safety Assessment Using Human Stem Cell Technology: Overview of Csahi Heart Initiative. J. Pharma. Toxico. Meth. 2017, 83, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, T.; Kunihiro, T.; Ando, T.; Kobayashi, S.; Matsui, E.; Yada, H.; Kanda, Y.; Kurokawa, J.; Furukawa, T. Image-based evaluation of contraction-relaxation kinetics of human-induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes: Correlation and complementarity with extracellular electrophysiology. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2014, 77, 178–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cools, J.; Jin, Q.; Yoon, E.; Alba Burbano, D.; Luo, Z.; Cuypers, D.; Callewaert, G.; Braeken, D.; Gracias, D.H. A Micropatterned Multielectrode Shell for 3D Spatiotemporal Recording from Live Cells. Adv. Sci. 2018, 5, 1700731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarah, J.M.; Stowasser, A.; Parker, R.L.; Asari, H.; Wagenaar, D.A. Optically transparent multi-suction electrode arrays. Front. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simeonov, S.; Schäffer, T.E. Ultrafast imaging of cardiomyocyte contractions by combining scanning ion conductance microscopy with a microelectrode array. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 9648–9655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanda, Y.; Yamazaki, D.; Kurokawa, J.; Inutsuka, T.; Sekino, Y. Points to consider for a validation study of iPS cell-derived cardiomyocytes using a multi-electrode array system. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2016, 81, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uesugi, M.; Ojima, A.; Taniguchi, T.; Miyamoto, N.; Sawada, K. Low-density plating is sufficient to induce cardiac hypertrophy and electrical remodeling in highly purified human iPS cell-derived cardiomyocytes. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2014, 69, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, A.S.; Tan, H.L.; Wilde, A.A.M. Cardiac ion channels in health and disease. Heart Rhythm. 2010, 7, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, J.J.; Husse, B.; Rimmbach, C.; Krebs, S.; Stieber, J.; Steinhoff, G.; Dendorfer, A.; Franz, W.-M.; David, R. Programming and Isolation of Highly Pure Physiologically and Pharmacologically Functional Sinus-Nodal Bodies from Pluripotent Stem Cells. Stem Cell Rep. 2014, 2, 592–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Protze, S.I.; Liu, J.; Nussinovitch, U.; Ohana, L.; Backx, P.H.; Gepstein, L.; Keller, G.M. Sinoatrial node cardiomyocytes derived from human pluripotent cells function as a biological pacemaker. Nat. Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Laksman, Z.; Backx, P.H. The electrophysiological development of cardiomyocytes. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 96, 253–273. [Google Scholar]
- Feher, J. The Cardiac Action Potential. In Quantitative Human Physiology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 528–536. [Google Scholar]
- Du, D.T.M.; Hellen, N.; Kane, C.; Terracciano, C.M.N. Action potential morphology of human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes does not predict cardiac chamber specificity and is dependent on cell density. Biophys. J. 2015, 108, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronaldson-Bouchard, K.; Ma, S.P.; Yeager, K.; Chen, T.; Song, L.; Sirabella, D.; Morikawa, K.; Teles, D.; Yazawa, M.; Vunjak-Novakovic, G. Advanced maturation of human cardiac tissue grown from pluripotent stem cells. Nature 2018, 556, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidyanathan, R.; Markandeya, Y.S.; Kamp, T.J.; Makielski, J.C.; January, C.T.; Eckhardt, L.L. IK1-enhanced human-induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes: An improved cardiomyocyte model to investigate inherited arrhythmia syndromes. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2016, 310, 1611–1621. [Google Scholar]
- Goversen, B.; Becker, N.; Stoelzle-Feix, S.; Obergrussberger, A.; Vos, M.A.; van Veen, T.A.B.; Fertig, N.; de Boer, T.P. A Hybrid Model for Safety Pharmacology on an Automated Patch Clamp Platform: Using Dynamic Clamp to Join iPSC-Derived Cardiomyocytes and Simulations of Ik1 Ion Channels in Real-Time. Front. Physiol. 2018, 8, 1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonsson, M.K.B.; Vos, M.A.; Mirams, G.R.; Duker, G.; Sartipy, P.; De Boer, T.P.; Van Veen, T.A.B. Application of human stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes in safety pharmacology requires caution beyond hERG. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2012, 52, 998–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tertoolen, L.G.J.; Braam, S.R.; van Meer, B.J.; Passier, R.; Mummery, C.L. Interpretation of field potentials measured on a multi electrode array in pharmacological toxicity screening on primary and human pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 497, 1135–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clements, M. Multielectrode array (MEA) assay for unit 22.4 profiling electrophysiological drug effects in human stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes. Curr. Protoc. Toxicol. 2016, 2016, 1–32. [Google Scholar]
- Buzsáki, G.; Anastassiou, C.A.; Koch, C. The origin of extracellular fields and currents — EEG, ECoG, LFP and spikes. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2012, 13, 407–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halbach, M.D.; Egert, U.; Hescheler, J.; Banach, K. Estimation of action potential changes from field potential recordings in multicellular mouse cardiac myocyte cultures. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2003, 13, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayes, H.B.; Nicolini, A.M.; Arrowood, C.A.; Chvatal, S.A.; Wolfson, D.W.; Cho, H.C.; Sullivan, D.D.; Chal, J.; Fermini, B.; Clements, M.; et al. Novel method for action potential measurements from intact cardiac monolayers with multiwell microelectrode array technology. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jans, D.; Callewaert, G.; Krylychkina, O.; Hoffman, L.; Gullo, F.; Prodanov, D.; Braeken, D. Action potential-based MEA platform for in vitro screening of drug-induced cardiotoxicity using human iPSCs and rat neonatal myocytes. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2017, 87, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, C.; Lin, Z.; Hanson, L.; Cui, Y.; Cui, B. Intracellular recording of action potentials by nanopillar electroporation. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2012, 7, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fendyur, A.; Spira, M.E. Toward on-chip, in-cell recordings from cultured cardiomyocytes by arrays of gold mushroom-shaped microelectrodes. Front. Neuroeng. 2012, 5, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Cardiovascular diseases. 2019. Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/cardiovascular-diseases (accessed on 28 October 2019).
- Fermini, B.; Hancox, J.C.; Abi-Gerges, N.; Bridgland-Taylor, M.; Chaudhary, K.W.; Colatsky, T.; Correll, K.; Crumb, W.; Damiano, B.; Erdemli, G.; et al. A New Perspective in the Field of Cardiac Safety Testing through the Comprehensive In Vitro Proarrhythmia Assay Paradigm. J. Biomol. Screen 2016, 21, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millard, D.; Dang, Q.; Shi, H.; Zhang, X.; Strock, C.; Kraushaar, U.; Zeng, H.; Levesque, P.; Lu, H.-R.; Guillon, J.-M.; et al. Cross-Site Reliability of Human Induced Pluripotent stem cell-derived Cardiomyocyte Based Safety Assays Using Microelectrode Arrays: Results from a Blinded CiPA Pilot Study. Toxicol. Sci. 2018, 164, 550–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CiPA Initiative. 2019. Available online: https://cipaproject.org (accessed on 28 October 2019).
- Kitaguchi, T.; Moriyama, Y.; Taniguchi, T.; Maeda, S.; Ando, H.; Uda, T.; Otabe, K.; Oguchi, M.; Shimizu, S.; Saito, H.; et al. CSAHi study: Detection of drug-induced ion channel/receptor responses, QT prolongation, and arrhythmia using multi-electrode arrays in combination with human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2017, 85, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozaki, Y.; Honda, Y.; Watanabe, H.; Saiki, S.; Koyabu, K.; Itoh, T.; Nagasawa, C.; Nakamori, C.; Nakayama, C.; Iwasaki, H.; et al. CSAHi study-2: Validation of multi-electrode array systems (MEA60/2100) for prediction of drug-induced proarrhythmia using human iPS cell-derived cardiomyocytes: Assessment of reference compounds and comparison with non-clinical studies and clinical information. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2017, 88, 238–251. [Google Scholar]
- Sager, P.T.; Gintant, G.; Turner, J.R.; Pettit, S.; Stockbridge, N. Rechanneling the cardiac proarrhythmia safety paradigm: A meeting report from the Cardiac Safety Research Consortium. Am. Heart J. 2014, 167, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitaguchi, T.; Moriyama, Y.; Taniguchi, T.; Ojima, A.; Ando, H.; Uda, T.; Otabe, K.; Oguchi, M.; Shimizu, S.; Saito, H.; et al. CSAHi study: Evaluation of multi-electrode array in combination with human iPS cell-derived cardiomyocytes to predict drug-induced QT prolongation and arrhythmia — Effects of 7 reference compounds at 10 facilities. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2016, 78, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Guo, L.; Fiene, S.J.; Anson, B.D.; Thomson, J.A.; Kamp, T.J.; Kolaja, K.L.; Swanson, B.J.; January, C.T. High purity human-induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes: Electrophysiological properties of action potentials and ionic currents. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2011, 301, 2006–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van den Heuvel, N.H.L.; van Veen, T.A.B.; Lim, B.; Jonsson, M.K.B. Lessons from the heart: Mirroring electrophysiological characteristics during cardiac development to in vitro differentiation of stem cell derived cardiomyocytes. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2014, 67, 12–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blinova, K.; Dang, Q.; Millard, D.; Smith, G.; Pierson, J.; Guo, L.; Brock, M.; Lu, H.R.; Kraushaar, U.; Zeng, H.; et al. International Multisite Study of Human-Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Cardiomyocytes for Drug Proarrhythmic Potential Assessment. Cell Rep. 2018, 24, 3582–3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schocken, D.; Stohlman, J.; Vicente, J.; Chan, D.; Patel, D.; Matta, M.K.; Patel, V.; Brock, M.; Millard, D.; Ross, J.; et al. Comparative analysis of media effects on human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes in proarrhythmia risk assessment. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2018, 90, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Wang, J.; Clouse, H.; Lagrutta, A.; Sannajust, F. HiPSC-CMs from different sex and ethnic origin donors exhibit qualitatively different responses to several classes of pharmacological challenges. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2019, 99, 106598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett, S.D.; Blanchette, A.D.; Grimm, F.A.; House, J.S.; Reif, D.M.; Wright, F.A.; Chiu, W.A.; Rusyn, I. Population-based toxicity screening in human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2019, 381, 114711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egashira, T.; Yuasa, S.; Suzuki, T.; Aizawa, Y.; Yamakawa, H.; Matsuhashi, T.; Ohno, Y.; Tohyama, S.; Okata, S.; Seki, T.; et al. Disease characterization using LQTS-specific induced pluripotent stem cells. Cardiovasc. Res. 2012, 95, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, K.; Aylott, M.; Cui, Y.; Louttit, J.B.; McMahon, N.C.; Sridhar, A. Comparison of Electrophysiological Data From Human-Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell–Derived Cardiomyocytes to Functional Preclinical Safety Assays. Toxicol. Sci. 2013, 134, 412–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, P.; Lan, F.; Lee, A.S.; Gong, T.; Sanchez-Freire, V.; Wang, Y.; Diecke, S.; Sallam, K.; Knowles, J.W.; Wang, P.J.; et al. Drug Screening Using a Library of Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell–Derived Cardiomyocytes Reveals Disease-Specific Patterns of Cardiotoxicity. Circulation 2013, 127, 1677–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maillet, A.; Tan, K.; Chai, X.; Sadananda, S.N.; Mehta, A.; Ooi, J.; Hayden, M.R.; Pouladi, M.A.; Ghosh, S.; Shim, W.; et al. Modeling Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity in Human Pluripotent Stem Cell Derived-Cardiomyocytes. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burridge, P.W.; Li, Y.F.; Matsa, E.; Wu, H.; Ong, S.-G.; Sharma, A.; Holmström, A.; Chang, A.C.; Coronado, M.J.; Ebert, A.D.; et al. Human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes recapitulate the predilection of breast cancer patients to doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulder, P.; de Korte, T.; Dragicevic, E.; Kraushaar, U.; Printemps, R.; Vlaming, M.L.H.; Braam, S.R.; Valentin, J.-P. Predicting cardiac safety using human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes combined with multi-electrode array (MEA) technology: A conference report. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2018, 91, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acimovic, I.; Refaat, M.; Moreau, A.; Salykin, A.; Reiken, S.; Sleiman, Y.; Souidi, M.; Přibyl, J.; Kajava, A.; Richard, S.; et al. Post-Translational Modifications and Diastolic Calcium Leak Associated to the Novel RyR2-D3638A Mutation Lead to CPVT in Patient-Specific hiPSC-Derived Cardiomyocytes. JCM 2018, 7, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarrete, E.G.; Liang, P.; Lan, F.; Sanchez-Freire, V.; Simmons, C.; Gong, T.; Sharma, A.; Burridge, P.W.; Patlolla, B.; Lee, A.S.; et al. Screening Drug-Induced Arrhythmia Using Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Cardiomyocytes and Low-Impedance Microelectrode Arrays. Circulation 2013, 128, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebert, A.D.; Svendsen, C.N. Human stem cells and drug screening: Opportunities and challenges. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2010, 9, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, E.; Howard, L.; Liu, M.; O’Brien, T.; Ward, D.; Shen, S.; Prendiville, T. Long QT Syndrome: Genetics and Future Perspective. Pediatr Cardiol 2019, 40, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellin, M.; Casini, S.; Davis, R.P.; D’Aniello, C.; Haas, J.; Ward-van Oostwaard, D.; Tertoolen, L.G.J.; Jung, C.B.; Elliott, D.A.; Welling, A.; et al. Isogenic human pluripotent stem cell pairs reveal the role of a KCNH2 mutation in long-QT syndrome: Isogenic pairs of LQT2 pluripotent stem cells. Embo J. 2013, 32, 3161–3175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandão, K.O.; Tabel, V.A.; Atsma, D.E.; Mummery, C.L.; Davis, R.P. Human pluripotent stem cell models of cardiac disease: From mechanisms to therapies. Dis. Model. Mech. 2017, 10, 1039–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; D’Aniello, C.; Verkerk, A.O.; Wrobel, E.; Frank, S.; Ward-van Oostwaard, D.; Piccini, I.; Freund, C.; Rao, J.; Seebohm, G.; et al. Recessive cardiac phenotypes in induced pluripotent stem cell models of Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome: Disease mechanisms and pharmacological rescue. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 5383–5392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moretti, A.; Bellin, M.; Welling, A.; Jung, C.B.; Lam, J.T.; Bott-Flügel, L.; Dorn, T.; Goedel, A.; Höhnke, C.; Hofmann, F.; et al. Patient-Specific Induced Pluripotent Stem-Cell Models for Long-QT Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 1397–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sala, L.; Gnecchi, M.; Schwartz, P.J. Derived from Human-induced Pluripotent Stem Cells. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. Rev. 2019, 8, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; Ruan, Y.; Priori, S.G. Catecholaminergic Polymorphic Ventricular Tachycardia. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2008, 51, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, K.; Makiyama, T.; Yoshida, Y.; Wuriyanghai, Y.; Kamakura, T.; Nishiuchi, S.; Hayano, M.; Harita, T.; Yamamoto, Y.; Kohjitani, H.; et al. Patient-Specific Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell Model Assessed with Electrical Pacing Validates S107 as a Potential Therapeutic Agent for Catecholaminergic Polymorphic Ventricular Tachycardia. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0164795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvajal-Vergara, X.; Sevilla, A.; D’Souza, S.L.; Ang, Y.-S.; Schaniel, C.; Lee, D.-F.; Yang, L.; Kaplan, A.D.; Adler, E.D.; Rozov, R.; et al. Patient-specific induced pluripotent stem-cell-derived models of LEOPARD syndrome. Nature 2010, 465, 808–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, F.; Lee, A.S.; Liang, P.; Sanchez-Freire, V.; Nguyen, P.K.; Wang, L.; Han, L.; Yen, M.; Wang, Y.; Sun, N.; et al. Abnormal Calcium Handling Properties Underlie Familial Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Pathology in Patient-Specific Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells. Cell Stem Cell 2013, 12, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.-C.; Breitbart, A.; De Lange, W.J.; Hofsteen, P.; Futakuchi-Tsuchida, A.; Xu, J.; Schopf, C.; Razumova, M.V.; Jiao, A.; Boucek, R.; et al. Novel Adult-Onset Systolic Cardiomyopathy Due to MYH7 E848G Mutation in Patient-Derived Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells. JACC Basic Transl. Sci. 2018, 3, 728–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, N.; Yazawa, M.; Liu, J.; Han, L.; Sanchez-Freire, V.; Abilez, O.J.; Navarrete, E.G.; Hu, S.; Wang, L.; Lee, A.; et al. Patient-Specific Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells as a Model for Familial Dilated Cardiomyopathy. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012, 4, 47–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siu, C.-W.; Lee, Y.-K.; Ho, J.C.-Y.; Lai, W.-H.; Chan, Y.-C.; Ng, K.-M.; Wong, L.-Y.; Au, K.-W.; Lau, Y.-M.; Zhang, J.; et al. Modeling of lamin A/C mutation premature cardiac aging using patient-specific induced pluripotent stem cells. Aging 2012, 4, 803–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tse, H.-F.; Ho, J.C.Y.; Choi, S.-W.; Lee, Y.-K.; Butler, A.W.; Ng, K.-M.; Siu, C.-W.; Simpson, M.A.; Lai, W.-H.; Chan, Y.-C.; et al. Patient-specific induced-pluripotent stem cells-derived cardiomyocytes recapitulate the pathogenic phenotypes of dilated cardiomyopathy due to a novel DES mutation identified by whole exome sequencing. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2013, 22, 1395–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinson, J.T.; Chopra, A.; Nafissi, N.; Polacheck, W.J.; Benson, C.C.; Swist, S.; Gorham, J.; Yang, L.; Schafer, S.; Sheng, C.C.; et al. Titin mutations in iPS cells define sarcomere insufficiency as a cause of dilated cardiomyopathy. Science 2015, 349, 982–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Streckfuss-Bömeke, K.; Tiburcy, M.; Fomin, A.; Luo, X.; Li, W.; Fischer, C.; Özcelik, C.; Perrot, A.; Sossalla, S.; Haas, J.; et al. Severe DCM phenotype of patient harboring RBM20 mutation S635A can be modeled by patient-specific induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2017, 113, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wyles, S.P.; Li, X.; Hrstka, S.C.; Reyes, S.; Oommen, S.; Beraldi, R.; Edwards, J.; Terzic, A.; Olson, T.M.; Nelson, T.J. Modeling structural and functional deficiencies of RBM20 familial dilated cardiomyopathy using human induced pluripotent stem cells. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2016, 25, 254–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacomelli, E.; Mummery, C.L.; Bellin, M. Human heart disease: Lessons from human pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2017, 74, 3711–3739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Li, Y.; Han, L.; Kaplan, A.D.; Ao, Y.; Kalra, S.; Bett, G.C.L.; Rasmusson, R.L.; Denning, C.; Yang, L. Modeling and study of the mechanism of dilated cardiomyopathy using induced pluripotent stem cells derived from individuals with Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Dis. Models Mech. 2015, 8, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eschenhagen, T.; Carrier, L. Cardiomyopathy phenotypes in human-induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes—a systematic review. Pflug. Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 2019, 471, 755–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Roche, J.; Angsutararux, P.; Kempf, H.; Janan, M.; Bolesani, E.; Thiemann, S.; Wojciechowski, D.; Coffee, M.; Franke, A.; Schwanke, K.; et al. Comparing human iPSC-cardiomyocytes versus HEK293T cells unveils disease-causing effects of Brugada mutation A735V of NaV1.5 sodium channels. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozzi, A.; Sayed, N.; Matsa, E.; Sass, G.; Neofytou, E.; Clemons, K.V.; Correa-Oliveira, R.; Stevens, D.A.; Wu, J.C. Using Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Cardiomyocytes as a Model to Study Trypanosoma cruzi Infection. Stem Cell Rep. 2019, 12, 1232–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-J.; Cheng, S.-J.; Huang, C.-Y.; Chen, C.-Y.; Feng, L.; Hwang, D.-Y.; Kamp, T.J.; Chen, H.-C.; Hsieh, P.C.H. Primary cardiac manifestation of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease revealed by patient induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes. EBioMedicine 2019, 40, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birket, M.J.; Raibaud, S.; Lettieri, M.; Adamson, A.D.; Letang, V.; Cervello, P.; Redon, N.; Ret, G.; Viale, S.; Wang, B.; et al. A Human Stem Cell Model of Fabry Disease Implicates LIMP-2 Accumulation in Cardiomyocyte Pathology. Stem Cell Rep. 2019, 13, 380–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caluori, G.; Pribyl, J.; Pesl, M.; Jelinkova, S.; Rotrekl, V.; Skladal, P.; Raiteri, R. Non-invasive electromechanical cell-based biosensors for improved investigation of 3D cardiac models. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 124, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.; Huebsch, N.; Koo, S.; Mandegar, M.A.; Siemons, B.; Boggess, S.; Conklin, B.R.; Grigoropoulos, C.P.; Healy, K.E. Contractile deficits in engineered cardiac microtissues as a result of MYBPC3 deficiency and mechanical overload. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 2, 955–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.-J.; Zhang, D.; Qi, Y.; Li, Y.; Lee, K.Y.; Bezzerides, V.J.; Yang, P.; Xia, S.; Kim, S.L.; Liu, X.; et al. Insights Into the Pathogenesis of Catecholaminergic Polymorphic Ventricular Tachycardia From Engineered Human Heart Tissue. Circulation 2019, 140, 390–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paci, M.; Casini, S.; Bellin, M.; Hyttinen, J.; Severi, S. Large-Scale Simulation of the Phenotypical Variability Induced by Loss-of-Function Long QT Mutations in Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell Cardiomyocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satsuka, A.; Kanda, Y. Cardiotoxicity assessment of drugs using human iPS cell-derived cardiomyocytes: From proarrhythmia risk to cardiooncology. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Korolj, A.; Lai, B.F.L.; Radisic, M. Advances in organ-on-a-chip engineering. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2018, 3, 257–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maoz, B.M.; Herland, A.; Henry, O.Y.F.; Leineweber, W.D.; Yadid, M.; Doyle, J.; Mannix, R.; Kujala, V.J.; FitzGerald, E.A.; Parker, K.K.; et al. Organs-on-Chips with combined multi-electrode array and transepithelial electrical resistance measurement capabilities. Lab. Chip 2017, 17, 2294–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Sanzo, M.; Cipolloni, L.; Borro, M.; La Russa, R.; Santurro, A.; Scopetti, M.; Simmaco, M.; Frati, P. Clinical Applications of Personalized Medicine: A New Paradigm and Challenge. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2017, 18, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, I.Y.; Matsa, E.; Wu, J.C. Induced pluripotent stem cells: At the heart of cardiovascular precision medicine. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2016, 13, 333–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamazaki, T.; El Rouby, N.; Fredette, N.C.; Santostefano, K.E.; Terada, N. Concise Review: Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell Research in the Era of Precision Medicine. Stem Cells 2017, 35, 545–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).