4mCpred-EL: An Ensemble Learning Framework for Identification of DNA N4-Methylcytosine Sites in the Mouse Genome
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
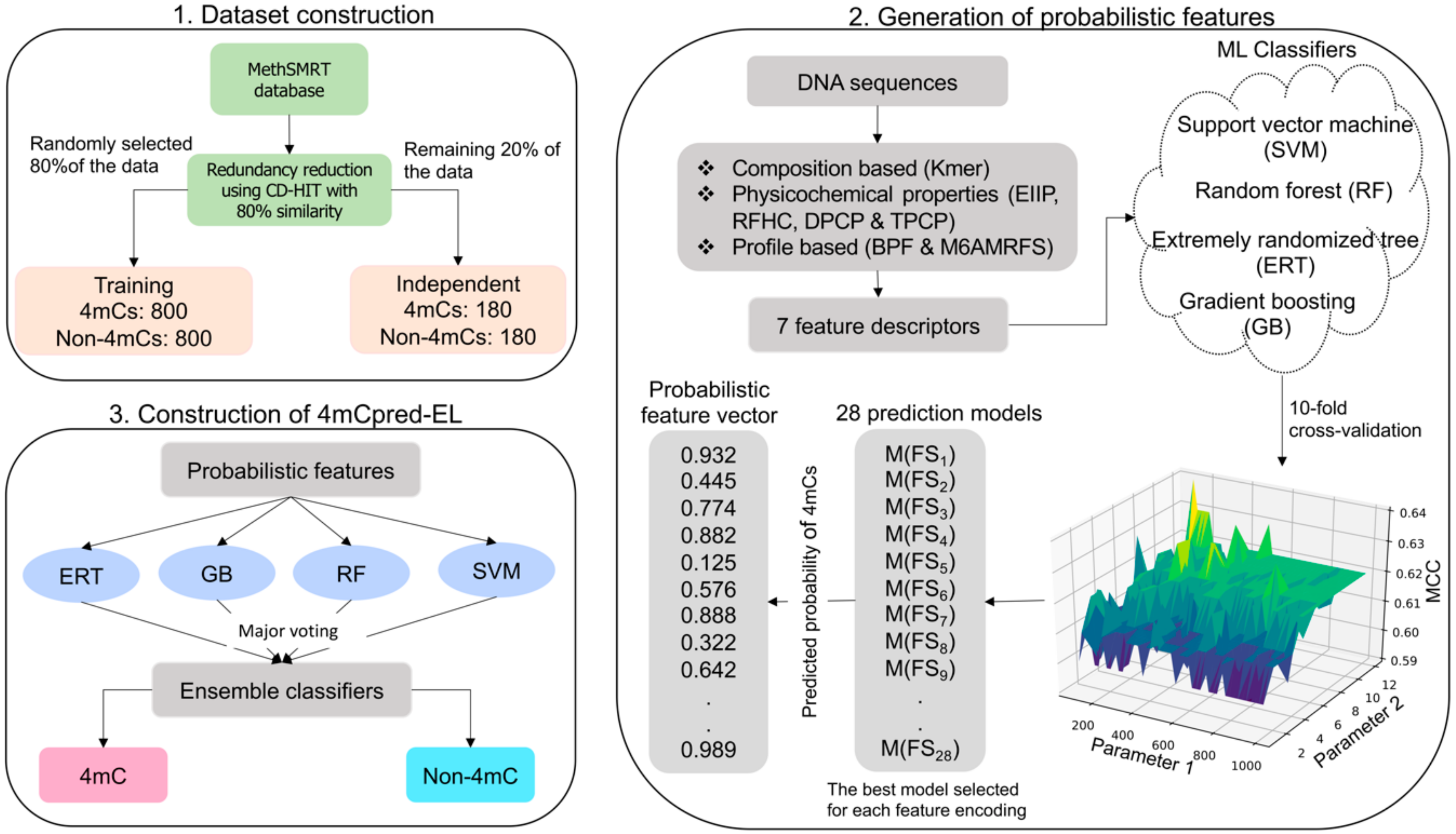
2.1. Dataset Construction
2.2. Feature Extraction
2.2.1. Kmer
2.2.2. M6AMRFS
2.2.3. RFHC
2.2.4. EIIP of Trinucleotides
2.2.5. BPF
2.2.6. DPCP
2.2.7. TPCP
2.3. Application of ML Algorithms in 4mCpred-EL
2.4. Performance Evaluation
3. Results and Discussion
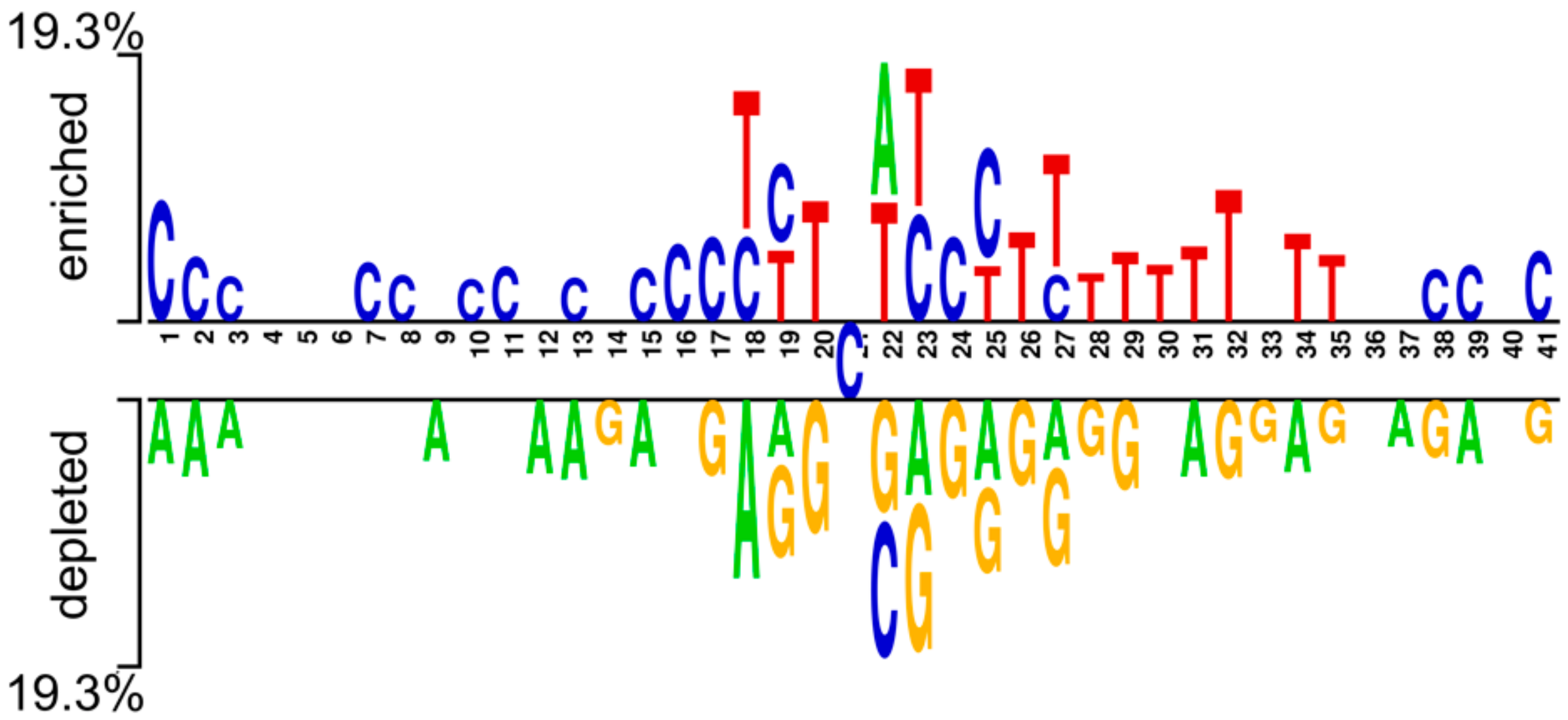
3.1. Evaluation of Nucleotide Composition Preference
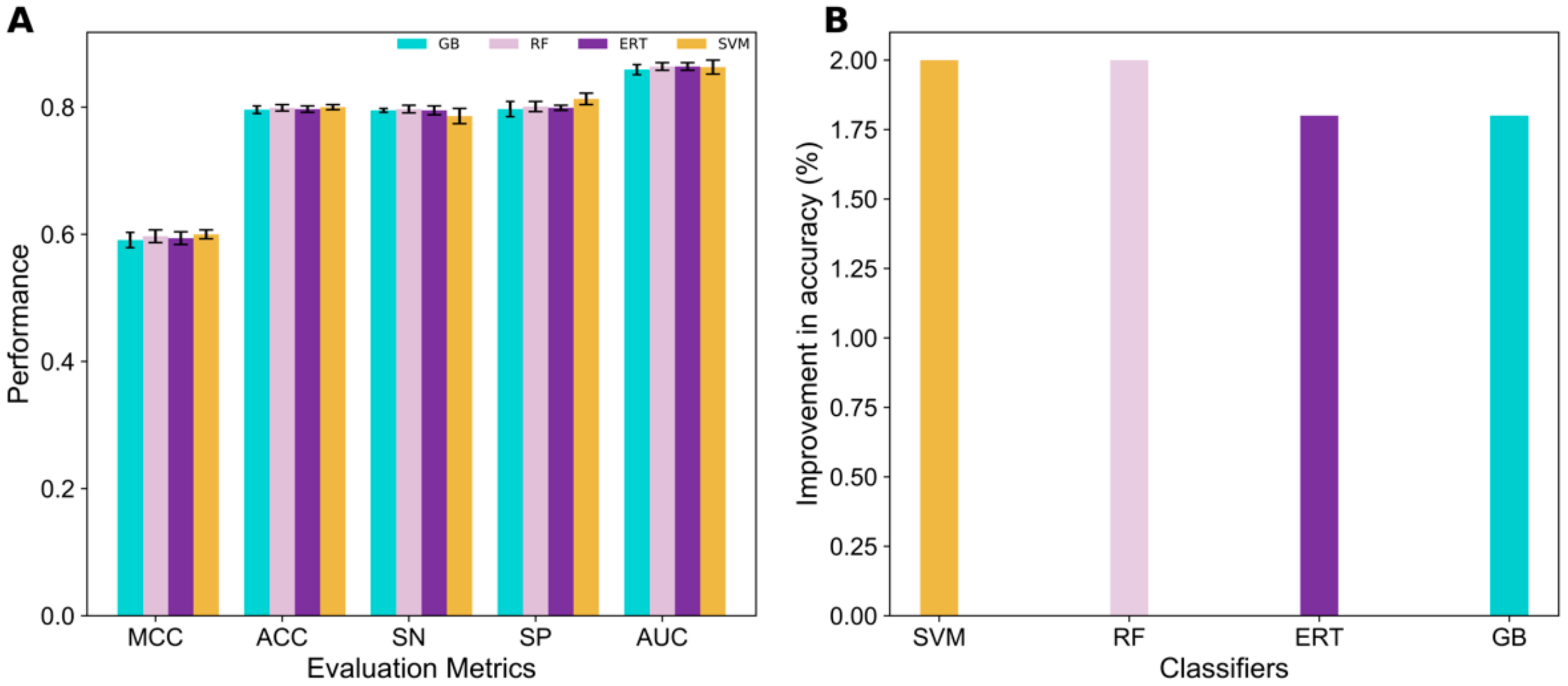
3.2. Performance Evaluation of Various ML Methods on Seven Feature Encodings
3.3. Construction of 4mCpred-EL
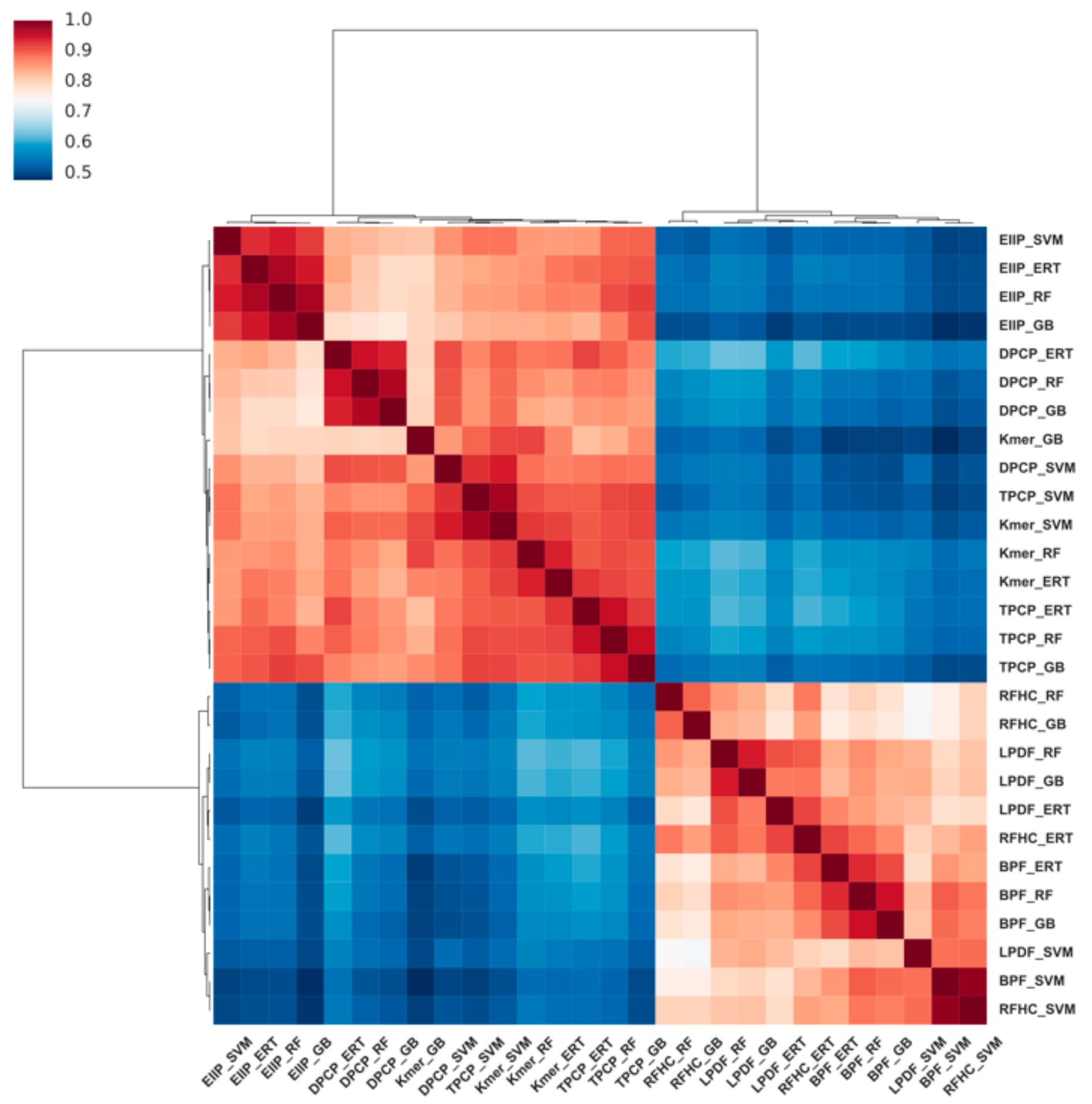
3.4. Feature Contribution and Relevance Analysis
3.5. Evaluation of Various Methods on the Independent Dataset
3.6. Web Server Implementation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jeltsch, A.; Jurkowska, R.Z. New concepts in DNA methylation. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2014, 39, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schubeler, D. Function and information content of DNA methylation. Nature 2015, 517, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pataillot-Meakin, T.; Pillay, N.; Beck, S. 3-methylcytosine in cancer: An underappreciated methyl lesion? Epigenomics 2016, 8, 451–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, B.M.; Chao, M.C.; Waldor, M.K. Entering the era of bacterial epigenomics with single molecule real time DNA sequencing. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2013, 16, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, M.M.; Bird, A. DNA methylation landscapes: Provocative insights from epigenomics. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2008, 9, 465–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, K.D. DNA methylation and human disease. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2005, 6, 597–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, P.A. Functions of DNA methylation: Islands, start sites, gene bodies and beyond. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2012, 13, 484–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, B.; Jin, P. Cytosine modifications in neurodevelopment and diseases. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2014, 71, 405–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, C.; Groop, L. Epigenetics: A molecular link between environmental factors and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 2009, 58, 2718–2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X. DNA modification by methyltransferases. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 1995, 5, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Zhao, B.S.; He, C. Nucleic Acid Modifications in Regulation of Gene Expression. Cell Chem. Biol. 2016, 23, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doherty, R.; Couldrey, C. Exploring genome wide bisulfite sequencing for DNA methylation analysis in livestock: A technical assessment. Front. Genet. 2014, 5, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flusberg, B.A.; Webster, D.R.; Lee, J.H.; Travers, K.J.; Olivares, E.C.; Clark, T.A.; Korlach, J.; Turner, S.W. Direct detection of DNA methylation during single-molecule, real-time sequencing. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 461–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boch, J.; Bonas, U. Xanthomonas AvrBs3 family-type III effectors: Discovery and function. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2010, 48, 419–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Yang, H.; Feng, P.; Ding, H.; Lin, H. iDNA4mC: Identifying DNA N4-methylcytosine sites based on nucleotide chemical properties. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 3518–3523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Chen, H.; Su, R. M6APred-EL: A Sequence-Based Predictor for Identifying N6-methyladenosine Sites Using Ensemble Learning. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2018, 12, 635–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Zhou, C.; Chen, H.; Song, J.; Su, R. ACPred-FL: A sequence-based predictor using effective feature representation to improve the prediction of anti-cancer peptides. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 4007–4016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manavalan, B.; Basith, S.; Shin, T.H.; Wei, L.; Lee, G. Meta-4mCpred: A Sequence-Based Meta-Predictor for Accurate DNA 4mC Site Prediction Using Effective Feature Representation. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2019, 16, 733–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Su, R.; Luan, S.; Liao, Z.; Manavalan, B.; Zou, Q.; Shi, X. Iterative feature representations improve N4-methylcytosine site prediction. Bioinformatics 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, P.; Luan, Y.; Chen, K.; Liu, Y.; Xiao, C.; Xie, Z. MethSMRT: An integrative database for DNA N6-methyladenine and N4-methylcytosine generated by single-molecular real-time sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D85–D89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espada, J.; Esteller, M. Mouse models in epigenetics: Insights in development and disease. Brief. Funct. Genom. 2013, 12, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uhl, E.W.; Warner, N.J. Mouse Models as Predictors of Human Responses: Evolutionary Medicine. Curr. Pathobiol. Rep. 2015, 3, 219–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, K.C. Some remarks on protein attribute prediction and pseudo amino acid composition. J. Theor. Biol. 2011, 273, 236–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, T.A.; Murray, I.A.; Morgan, R.D.; Kislyuk, A.O.; Spittle, K.E.; Boitano, M.; Fomenkov, A.; Roberts, R.J.; Korlach, J. Characterization of DNA methyltransferase specificities using single-molecule, real-time DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Niu, B.; Zhu, Z.; Wu, S.; Li, W. CD-HIT: Accelerated for clustering the next-generation sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 3150–3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Karchin, R.; Beer, M.A. Discriminative prediction of mammalian enhancers from DNA sequence. Genome Res. 2011, 21, 2167–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manavalan, B.; Shin, T.H.; Lee, G. DHSpred: Support-vector-machine-based human DNase I hypersensitive sites prediction using the optimal features selected by random forest. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 1944–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Li, K.; Huang, D.S.; Chou, K.C. iEnhancer-EL: Identifying enhancers and their strength with ensemble learning approach. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 3835–3842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiang, X.; Chen, H.; Ye, X.; Su, R.; Wei, L. M6AMRFS: Robust Prediction of N6-Methyladenosine Sites with Sequence-Based Features in Multiple Species. Front. Genet. 2018, 9, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Lv, H.; Nie, F.; Lin, H. i6mA-Pred: Identifying DNA N6-methyladenine sites in the rice genome. Bioinformatics 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, P.; Yang, H.; Ding, H.; Lin, H.; Chen, W.; Chou, K.C. iDNA6mA-PseKNC: Identifying DNA N(6)-methyladenosine sites by incorporating nucleotide physicochemical properties into PseKNC. Genomics 2019, 111, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, A.S.; Sreenadhan, S.P. A coding measure scheme employing electron-ion interaction pseudopotential (EIIP). Bioinformation 2006, 1, 197. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- He, W.; Jia, C. EnhancerPred2. 0: Predicting enhancers and their strength based on position-specific trinucleotide propensity and electron–ion interaction potential feature selection. Mol. BioSyst. 2017, 13, 767–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, C.; Yang, Q.; Zou, Q. NucPosPred: Predicting species-specific genomic nucleosome positioning via four different modes of general PseKNC. J. Theor. Biol. 2018, 450, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, J.H. Greedy function approximation: A gradient boosting machine. Ann. Stat. 2001, 1189–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noble, W.S. What is a support vector machine? Nat. Biotechnol. 2006, 24, 1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geurts, P.; Ernst, D.; Wehenkel, L. Extremely randomized trees. Mach. Learn. 2006, 63, 3–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, A.; Pedregosa, F.; Eickenberg, M.; Gervais, P.; Mueller, A.; Kossaifi, J.; Gramfort, A.; Thirion, B.; Varoquaux, G. Machine learning for neuroimaging with scikit-learn. Front. Neuroinform. 2014, 8, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Feng, P.; Yang, H.; Ding, H.; Lin, H.; Chou, K.C. iRNA-3typeA: Identifying Three Types of Modification at RNA’s Adenosine Sites. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2018, 11, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiang, X.; Zhou, C.; Ye, X.; Du, P.F.; Su, R.; Wei, L. CPPred-FL: A sequence-based predictor for large-scale identification of cell-penetrating peptides by feature representation learning. Brief. Bioinform. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, R.; Wang, Z.; Cheng, J. Designing and evaluating the MULTICOM protein local and global model quality prediction methods in the CASP10 experiment. BMC Struct. Biol. 2014, 14, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manavalan, B.; Shin, T.H.; Lee, G. PVP-SVM: Sequence-Based Prediction of Phage Virion Proteins Using a Support Vector Machine. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boopathi, V.; Subramaniyam, S.; Malik, A.; Lee, G.; Manavalan, B.; Yang, D.C. mACPpred: A Support Vector Machine-Based Meta-Predictor for Identification of Anticancer Peptides. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Leier, A.; Marquez-Lago, T.; Yang, B.; Zhang, Z.; Akutsu, T.; Webb, G.I.; Daly, R.J. PhosphoPredict: A bioinformatics tool for prediction of human kinase-specific phosphorylation substrates and sites by integrating heterogeneous feature selection. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Xing, P.; Su, R.; Shi, G.; Ma, Z.S.; Zou, Q. CPPred-RF: A Sequence-based Predictor for Identifying Cell-Penetrating Peptides and Their Uptake Efficiency. J. Proteome Res. 2017, 16, 2044–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manavalan, B.; Shin, T.H.; Kim, M.O.; Lee, G. PIP-EL: A New Ensemble Learning Method for Improved Proinflammatory Peptide Predictions. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manavalan, B.; Shin, T.H.; Kim, M.O.; Lee, G. AIPpred: Sequence-Based Prediction of Anti-inflammatory Peptides Using Random Forest. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manavalan, B.; Subramaniyam, S.; Shin, T.H.; Kim, M.O.; Lee, G. Machine-Learning-Based Prediction of Cell-Penetrating Peptides and Their Uptake Efficiency with Improved Accuracy. J. Proteome Res. 2018, 17, 2715–2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicho, M.; de Bruyn Kops, C.; Stork, C.; Svozil, D.; Kirchmair, J. FAME 2: Simple and Effective Machine Learning Model of Cytochrome P450 Regioselectivity. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2017, 57, 1832–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawi, R.; Mall, R.; Kunji, K.; Shen, C.H.; Kwong, P.D.; Chuang, G.Y. PaRSnIP: Sequence-based protein solubility prediction using gradient boosting machine. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 1092–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Li, J.; Yang, B.; Xie, R.; Marquez-Lago, T.T.; Leier, A.; Hayashida, M.; Akutsu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Chou, K.C.; et al. Bastion3: A two-layer ensemble predictor of type III secreted effectors. Bioinformatics 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q.; Xiong, Y.; Dai, H.; Kumari, K.M.; Xu, Q.; Ou, H.Y.; Wei, D.Q. PDC-SGB: Prediction of effective drug combinations using a stochastic gradient boosting algorithm. J. Theor. Biol. 2017, 417, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Fang, T.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, B.; Zhu, X.; Xiong, Y. PseUI: Pseudouridine sites identification based on RNA sequence information. BMC Bioinform. 2018, 19, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Gao, H.; Zhu, X.; Chen, P. Protein-protein interface hot spots prediction based on a hybrid feature selection strategy. BMC Bioinform. 2018, 19, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Wang, Q.; Yang, J.; Zhu, X.; Wei, D.Q. PredT4SE-Stack: Prediction of Bacterial Type IV Secreted Effectors from Protein Sequences Using a Stacked Ensemble Method. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manavalan, B.; Basith, S.; Shin, T.H.; Wei, L.; Lee, G. mAHTPred: A sequence-based meta-predictor for improving the prediction of anti-hypertensive peptides using effective feature representation. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 2757–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manavalan, B.; Basith, S.; Shin, T.H.; Wei, L.; Lee, G. AtbPpred: A Robust Sequence-Based Prediction of Anti-Tubercular Peptides Using Extremely Randomized Trees. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2019, 17, 972–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basith, S.; Manavalan, B.; Shin, T.H.; Lee, G. SDM6A: A web-based integrative machine-learning framework for predicting 6mA sites in the rice genome. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2019, 18, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manavalan, B.; Govindaraj, R.G.; Shin, T.H.; Kim, M.O.; Lee, G. iBCE-EL: A New Ensemble Learning Framework for Improved Linear B-Cell Epitope Prediction. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, R.; Hu, J.; Zou, Q.; Manavalan, B.; Wei, L. Empirical comparison and analysis of web-based cell-penetrating peptide prediction tools. Brief. Bioinform. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crooks, G.E.; Hon, G.; Chandonia, J.M.; Brenner, S.E. WebLogo: A sequence logo generator. Genome Res. 2004, 14, 1188–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, B.; Xue, B. Decision-Tree Based Meta-Strategy Improved Accuracy of Disorder Prediction and Identified Novel Disordered Residues Inside Binding Motifs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanley, J.A.; McNeil, B.J. The meaning and use of the area under a receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve. Radiology 1982, 143, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, W.; Jia, C.; Zou, Q. 4mCPred: Machine Learning Methods for DNA N4-methylcytosine sites Prediction. Bioinformatics 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Luan, S.; Nagai, L.A.E.; Su, R.; Zou, Q. Exploring sequence-based features for the improved prediction of DNA N4-methylcytosine sites in multiple species. Bioinformatics 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, R.; Freitas, C.; Chan, L.; Sun, M.; Jiang, H.; Chen, Z. ProLanGO: Protein Function Prediction Using Neural Machine Translation Based on a Recurrent Neural Network. Molecules 2017, 22, 1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conover, M.; Staples, M.; Si, D.; Sun, M.; Cao, R. AngularQA: Protein model quality assessment with LSTM networks. Comput. Math. Biophys. 2019, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephenson, N.; Shane, E.; Chase, J.; Rowland, J.; Ries, D.; Justice, N.; Zhang, J.; Chan, L.; Cao, R. Survey of Machine Learning Techniques in Drug Discovery. Curr. Drug Metab. 2019, 20, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.H.; Joo, K.; Lee, J. ConDo: Protein domain boundary prediction using coevolutionary information. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 2411–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Method | MCC | ACC | SN | SP | AUC | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4mCpred-EL | 0.591 ± 0.001 | 0.795 ± 0.001 | 0.804 ± 0.002 | 0.787 ± 0.002 | 0.874 ± 0.001 | — |
| SVM | 0.559 ± 0.005 | 0.780 ± 0.002 | 0.775 ± 0.004 | 0.784 ± 0.005 | 0.854 ± 0.003 | 0.127 |
| ERT | 0.559 ± 0.008 | 0.779 ± 0.004 | 0.758 ± 0.008 | 0.800 ± 0.004 | 0.848 ± 0.005 | 0.049 |
| RF | 0.558 ± 0.009 | 0.779 ± 0.004 | 0.762 ± 0.014 | 0.796 ± 0.008 | 0.849 ± 0.007 | 0.058 |
| GB | 0.556 ± 0.011 | 0.778 ± 0.006 | 0.762 ± 0.011 | 0.793 ± 0.002 | 0.845 ± 0.010 | 0.029 |
| AB | 0.537 ± 0.014 | 0.769 ± 0.007 | 0.755 ± 0.010 | 0.782 ± 0.006 | 0.777 ± 0.008 | <0.000001 |
| LR | 0.537 ± 0.003 | 0.768 ± 0.002 | 0.758 ± 0.003 | 0.778 ± 0.001 | 0.842 ± 0.004 | 0.016602 |
| KNN | 0.474 ± 0.003 | 0.736 ± 0.002 | 0.692 ± 0.010 | 0.780 ± 0.006 | 0.815 ± 0.003 | 0.000023 |
| Method | MCC | ACC | SN | SP | AUC | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4mCpred-EL | 0.596 ± 0.022 | 0.798 ± 0.011 | 0.804 ± 0.012 | 0.792 ± 0.028 | 0.897 ± 0.008 | — |
| RF | 0.562 ± 0.010 | 0.780 ± 0.005 | 0.736 ± 0.008 | 0.824 ± 0.014 | 0.862 ± 0.002 | 0.179 |
| ERT | 0.552 ± 0.012 | 0.775 ± 0.006 | 0.736 ± 0.008 | 0.814 ± 0.008 | 0.862 ± 0.011 | 0.179 |
| SVM | 0.544 ± 0.014 | 0.772 ± 0.007 | 0.742 ± 0.014 | 0.801 ± 0.009 | 0.870 ± 0.007 | 0.293 |
| GB | 0.544 ± 0.011 | 0.772 ± 0.005 | 0.743 ± 0.011 | 0.800 ± 0.020 | 0.862 ± 0.004 | 0.179 |
| LR | 0.536 ± 0.013 | 0.768 ± 0.006 | 0.753 ± 0.005 | 0.783 ± 0.010 | 0.863 ± 0.003 | 0.191 |
| AB | 0.524 ± 0.009 | 0.762 ± 0.005 | 0.747 ± 0.006 | 0.776 ± 0.008 | 0.793 ± 0.017 | 0.000371 |
| KNN | 0.508 ± 0.017 | 0.747 ± 0.008 | 0.625 ± 0.006 | 0.868 ± 0.012 | 0.826 ± 0.005 | 0.010668 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Manavalan, B.; Basith, S.; Shin, T.H.; Lee, D.Y.; Wei, L.; Lee, G. 4mCpred-EL: An Ensemble Learning Framework for Identification of DNA N4-Methylcytosine Sites in the Mouse Genome. Cells 2019, 8, 1332. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8111332
Manavalan B, Basith S, Shin TH, Lee DY, Wei L, Lee G. 4mCpred-EL: An Ensemble Learning Framework for Identification of DNA N4-Methylcytosine Sites in the Mouse Genome. Cells. 2019; 8(11):1332. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8111332
Chicago/Turabian StyleManavalan, Balachandran, Shaherin Basith, Tae Hwan Shin, Da Yeon Lee, Leyi Wei, and Gwang Lee. 2019. "4mCpred-EL: An Ensemble Learning Framework for Identification of DNA N4-Methylcytosine Sites in the Mouse Genome" Cells 8, no. 11: 1332. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8111332
APA StyleManavalan, B., Basith, S., Shin, T. H., Lee, D. Y., Wei, L., & Lee, G. (2019). 4mCpred-EL: An Ensemble Learning Framework for Identification of DNA N4-Methylcytosine Sites in the Mouse Genome. Cells, 8(11), 1332. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8111332






