Abstract
Ryanodine receptors (RyRs) are large intracellular Ca2+ release channels primarily found in muscle and nerve cells and also present at low levels in pancreatic islet endocrine cells. This review examines the role of RyRs in islet cell function, focusing on calcium signaling and hormone secretion, while addressing the ongoing debate regarding their significance due to their limited expression. We explore conflicting experimental results and their potential causes, synthesizing current knowledge on RyR isoforms in islet cells, particularly in beta and delta cells. The review discusses how RyR-mediated calcium-induced calcium release enhances, rather than drives, glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. We examine the phosphorylation-dependent regulation of beta-cell RyRs, the concept of “leaky ryanodine receptors”, and the roles of RyRs in endoplasmic reticulum stress, apoptosis, store-operated calcium entry, and beta-cell electrical activity. The relationship between RyR dysfunction and the development of impaired insulin secretion in diabetes is assessed, noting their limited role in human diabetes pathogenesis given the disease’s polygenic nature. We highlight the established role of RyR-mediated CICR in the mechanism of action of common type 2 diabetes treatments, such as glucagon-like peptide-1, which enhances insulin secretion. By integrating findings from electrophysiological, molecular, and clinical studies, this review provides a balanced perspective on RyRs in islet cell physiology and pathology, emphasizing their significance in both normal insulin secretion and current diabetes therapies.
Keywords:
ryanodine receptors in islets cells; calcium-induced calcium release in islet cells; ryanodine receptors and insulin secretion; calcium signaling in beta cells; endoplasmic reticulum stress in beta cells; glucagon-like peptide-1 and ryanodine receptors; ryanodine receptors in delta cells; beta-cell electrical activity and ryanodine receptors; ryanodine receptors and diabetes; ryanodine receptors and store-operated calcium entry 1. Introduction
Ca2+ signaling is important for the secretion of various hormones from the endocrine cells in the islets of Langerhans [1,2]. In these cells, Ca2+ signaling is generated mainly by two mechanisms: (1) Ca2+ entry through the Ca2+ channels located on the plasma membrane and (2) Ca2+ release from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) via the intracellular Ca2+ release channels, specifically the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptors (IP3Rs) and the ryanodine receptors (RyRs). In islet endocrine cells, IP3Rs are more abundant than RyRs [3,4]. Ca2+-induced Ca2+ release (CICR) is a process whereby an increase in the cytosolic free Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]i) triggers more Ca2+ releases from the ER [5]. IP3Rs can mediate CICR in the presence of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3) [6,7,8]. Compared to IP3Rs, RyRs are more effective for CICR because Ca2+ can directly activate RyRs, and RyRs have a much higher Ca2+ conductance than IP3Rs [9,10]. The conductances of RyRs and IP3Rs with K+ as the charge carrier are ~700 and ~80 pS, respectively [10,11]. However, RyRs are much less abundant in islet cells, and partly for this reason, some investigators have found it difficult to demonstrate RyR-mediated CICR in these cells.
Since the discovery of CICR in 1992, more than three decades of research have generated enormous information about the roles of this process and RyRs in the regulation of Ca2+ signaling and secretion, especially in β-cells [12]. A head-to-head comparison between the relative importance of IP3Rs and RyRs in islet cell physiology is not the aim of this review. Instead, I will summarize the knowledge generated in recent years about the roles of CICR and RyRs in islet cells. I will also explain the potential reasons for the discrepancies in the results obtained by various researchers.
2. Effects of Different Agonists and Antagonists on RyRs
Investigators have used many exogenous or endogenous agonists and antagonists of RyRs to study CICR and RyRs in β-cells [13]. Interpretation of the results obtained with some of these pharmacological tools can sometimes be difficult, since many of these tools have off-target effects. Appropriate experimental protocols and cautious interpretations are necessary to avoid misleading conclusions. In the following paragraphs, I will discuss some of the agents used for studying RyRs and CICR in islet cells.
2.1. Caffeine
Caffeine is the most commonly used pharmacological tool for activating RyRs. In insulin-secreting cells, caffeine triggers Ca2+ release from the ER under some experimental conditions [6,14,15,16,17,18,19,20], whereas it fails to do so in other conditions [12,21,22,23,24,25]. In intact β-cells, caffeine releases Ca2+ from the ER in some experiments [25,26,27], whereas it fails to do in others [21,22,23]. Many factors may account for these differences, including the filling state of the ER Ca2+ store, the phosphorylation status of the RyRs [28], and the experimental conditions used by different investigators.
There are some difficulties in interpreting the caffeine-induced increase in [Ca2+]i in intact β-cells. For instance, caffeine inhibits the KATP channel, leading to membrane depolarization and subsequent Ca2+ entry through voltage-gated Ca2+ channels (VGCCs) [22]. Caffeine also inhibits cAMP-phosphodiesterase enzymes, making it difficult to determine whether the effects of caffeine are mediated by caffeine itself or by increased cAMP [29].
2.2. Ryanodine
Ryanodine has been used for studying RyRs for over four decades, and so far, no notable off-target effects have been reported. Low concentrations of ryanodine open the channel, and high concentrations close the channel, but the channel can stay in different conformations other than in a simple “open” or “closed” state [30]. Ryanodine alters the open probability, conductance, and gating of the channel by binding to the high- and low-affinity sites of the channel [31]. At nanomolar concentrations, it binds to a single high-affinity site located within the pore of the channel, thereby increasing the open probability but reducing the conductance of the channels [32]. At micromolar concentrations, it binds to both the high-affinity site and one or more low-affinity sites, thereby locking the channel in a closed state [33]. In experiments, the actual concentrations at which ryanodine activates or inhibits RyRs may depend on numerous factors, such as whether it is being used in a cell-free system, permeabilized cells, intact cells, lipid bilayers, single cells, clusters of cells, tissue slices, and many other experimental conditions.
Since ryanodine can both activate and inhibit the channel, it may sometimes be difficult to interpret the results obtained from experiments in which ryanodine is used. For instance, while a high concentration of ryanodine inhibits RyRs during washout, one may see the stimulatory effect of ryanodine [34]. Investigators may need to try out different concentrations of ryanodine and different incubation times or follow the experimental protocols that have worked for other investigators in similar experiments. The use of inappropriate experimental protocols in experiments where ryanodine was used to inhibit RyRs has led to some misleading conclusions [35,36,37,38].
2.2.1. Activation of RyRs by Ryanodine
An increase in [Ca2+]i in any cell due to nanomolar concentrations of ryanodine is a highly reliable sign of the existence of functional RyRs in the cell. In dispersed human β-cells, nanomolar concentrations of ryanodine increase [Ca2+]i and insulin secretion [36]. In fresh mouse pancreatic tissue slices, activation of RyRs in β-cells by 100 nM ryanodine induced [Ca2+]i increase of short durations in a regenerative fashion [34].
2.2.2. Inhibition of RyRs by Ryanodine
To inhibit RyRs in β-cells, investigators have successfully used ryanodine at concentrations ranging from 10 to 400 μM and have used different experimental protocols [6,20,35,39,40,41]. When used at very high concentrations (e.g., >100 μM), ryanodine can inhibit channels completely in a relatively short time [13,34]. Ryanodine inhibits RyRs in a use-dependent manner [42]. Use-dependent means that ryanodine binds preferentially to open-state channels. To inhibit RyRs, it may be necessary to treat cells with high concentrations of ryanodine, often for prolonged periods. The kinetics of association of ryanodine with RyRs is slow, with the half-time for the association rate being as slow as 36 min [43]. For this reason, it may be necessary to incubate cells in 200 μM ryanodine for two hours [18]. The use of lower concentrations of ryanodine for shorter periods has led to the conclusion that ryanodine cannot inhibit glucose-induced increase in [Ca2+]i and insulin secretion [36]. In experiments where whole islets are used, it may take several hours to achieve sufficiently high concentrations of ryanodine inside the islets. Using the fluorescent ryanodine analog BODIPY FL-X ryanodine, Llanos et al. showed that it may take as long as 12 h for ryanodine concentration to increase to a sufficiently high level in all islet cells [35]. To inhibit insulin secretion from islets, it is necessary to incubate the islets in 200 μM ryanodine for as long as 12 h [35]. Ryanodine does not inhibit VGCCs and does not damage the cells [20,35]. Careful attention to experimental protocols is necessary to demonstrate the inhibitory action of ryanodine on RyR-dependent processes [20,39,44,45,46].
When used at high concentrations, the binding of ryanodine to RyRs is usually irreversible in the time frame of single-channel experiments. However, in the time frame of the experiments reported by Postić et al., the activation was reversible on washout of ryanodine [34]. Apparently, in intact cells, ryanodine can be inactivated presumably by cytochrome P450 enzymes.
2.3. 9-Methyl-7-bromoeudistomin D (MBED)
MBED is about 1000 times more potent than caffeine and activates RyRs in a caffeine-like manner [47]. MBED increases [Ca2+]i and stimulates insulin secretion from insulin-secreting cells [42,48]. Unlike caffeine, MBED does not inhibit cAMP-PDE activity in these cells [48]. However, MBED is not readily available from commercial sources.
2.4. Thimerosal
Thimerosal, a sulfhydryl oxidizing agent, activates RyRs by interacting with critical thiol groups associated with the channel [49]. It releases Ca2+ from the ER by activating RyRs in RINm5F cells, MIN6 cells, and mouse islet cells [12,25,50]. Thimerosal can also activate IP3Rs, but these cells express inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor, type 3 (IP3R3) [51], which is not activated but rather inhibited by thimerosal [52].
2.5. Dantrolene
Dantrolene, even at low concentrations (e.g., 10 μM), inhibits RyR1 and RyR3 [53]. In β-cells that express RyR1, glucose-induced [Ca2+]i oscillations are inhibited by 10 μM dantrolene [54]. In MIN6 cells, which express both RyR1 and RyR2, harmane-induced Ca2+ increase and insulin secretion are inhibited by 10 μM dantrolene [25]. Glucose-induced insulin secretion from rat or mouse islets is inhibited by 10 μM dantrolene [55,56], but 10 μM dantrolene does not inhibit insulin secretion from human islets [36].
To inhibit RyR2, high concentrations of dantrolene are usually needed, but if RyR2 becomes phosphorylated, the channel becomes more susceptible to inhibition by dantrolene [57,58,59]. Since human β-cells mainly express RyR2 [3], it is not surprising that glucose-induced insulin secretion from human β-cells is not inhibited by 10 μM dantrolene [36]. In insulin-secreting INS-1E cells, which also mainly express RyR2, insulin secretion mediated by RyR2-mediated CICR is inhibited by a high concentration (e.g., 75 μM) of dantrolene [48]. Dantrolene is only slightly soluble in water. For experiments requiring high concentrations, such as 100 μM, it is recommended to freshly dissolve dantrolene in polyethylene glycol 600 before each experiment [55].
It is possible that alternative splicing of RyR2 may determine the channel’s sensitivity to inhibition by dantrolene. β-cells express the “islet type” RyR2 that is generated by alternative splicing of exons 4 and 75 [60]. The sensitivity of this splice variant to inhibition by dantrolene is unknown.
Dantrolene may have broader effects, and some of its effects are poorly understood. For instance, it can bind to the IP3-binding domain of IP3Rs [61] and inhibit IP3-induced Ca2+ increase in some cells [62]. A paradoxical effect of dantrolene, characterized by an increase in insulin secretion through mechanisms that are not yet fully understood, has also been described [63,64]. Another effect of high concentrations of dantrolene is the inhibition of glucose oxidation, which can complicate the interpretation of the insulin secretion data [55].
2.6. Other Agonists of RyRs
2.6.1. 4-Chloro-m-cresol (4-CmC) and 4-Chloro-3-ethylphenol (4-CEP)
4-Chloro-m-cresol (4-CmC) is a potent and clinically relevant activator of RyR1, but when used at high concentrations, it can also activate RyR2 and RyR3 [65,66,67]. 4-Chloro-3-ethylphenol (4-CEP), which has a more hydrophobic ethyl group instead of a methyl group at the 3-position, is more bioactive [66]. These agents do have some off-target effects; for instance, they inhibit the ORAI1-3 channels [68]. We and other investigators have reported that 4-CmC and 4-CEP activate RyRs in insulin-secreting cells [20,28,69,70,71].
2.6.2. Nitric Oxide (NO)
NO can activate RyRs either directly or through oxidation or poly-S-nitrosylation of critical thiol groups associated with the channel [13,72]. Glucose stimulates the formation of NO in β-cells [73,74]. Low concentrations of gaseous NO increase [Ca2+]i by activating RyRs and stimulate insulin secretion from rat β-cells [18].
2.6.3. Arachidonic Acid
Previous studies have shown that arachidonic acid releases Ca2+ from the sarcoplasmic reticulum through the activation of RyRs [75,76]. Arachidonic acid increases [Ca2+]i in β-cells by activating the RyRs [39]. In this context, it is noteworthy that glucose stimulation increases arachidonic acid in β-cells [77].
3. Role of RyRs in Mediating CICR in β-Cells
By using a variety of methods, many groups have confirmed that β-cells express RyRs, but their expression levels are lower than in many other tissues [14,28,44,54,78]. The presence of RyRs in β-cells has been confirmed by RNAse protection assay, real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction, and RNA sequencing [3,28,44,54,78]. RyRs are more effective than IP3Rs in mediating CICR because they can be directly activated by Ca2+, and in the physiological range of [Ca2+]i, RyRs act solely as Ca2+-activated channels [10,11]. RyRs also have very high conductance and thus are more effective than IP3Rs in amplifying Ca2+ signals through CICR [11].
An increase in [Ca2+]i caused by Ca2+ entry through VGCCs triggers CICR through RyRs in β-cells [14,20,44,46]. However, this activation is not like the activation of RyRs and CICR in skeletal muscle or heart, where VGCCs and RyRs are distributed in an orderly dyadic or triadic pattern [79]. Thus, in single mouse β-cells, a 100 ms depolarizing voltage clamping step does not always trigger CICR [80]. Unlike in the heart, where RyRs are closely coupled to and rapidly activated by VGCCs during each action potential, β-cells appear to have a “loose” coupling, similar to smooth muscle cells [81]. This is likely due to the low abundance of RyRs in β-cells. Consequently, RyR activation in β-cells seems to depend on a global increase in [Ca2+]i resulting from VGCC-mediated Ca2+ influx rather than a localized, tightly coupled interaction between VGCCs and RyRs.
There is no certainty that an increase in [Ca2+]i caused by depolarization-induced Ca2+ entry through VGCCs will always trigger substantial CICR in β-cells. Usually, a sufficiently high [Ca2+]i is required for activating RyRs [10]. The density of VGCCs in β-cells is low [34,82]. Depolarization of β-cells upon stimulation by glucose alone often leads to an increase of [Ca2+]i to only about 300 nM. This concentration of [Ca2+]i is usually not sufficient for triggering CICR. However, such concentrations of cytoplasmic Ca2+ can initiate CICR in the presence of cAMP generating agents, high luminal Ca2+ concentration, and positive modulatory factors of RyRs like ATP, NO, glycolytic intermediates, and arachidonic acid [13].
4. Magnitude of [Ca2+]i Increase Achieved Through RyR-Mediated CICR
Numerous studies have measured [Ca2+]i in β-cells upon glucose stimulation using fluorescent Ca2+ indicators. Some studies report raw fluorescence changes implying [Ca2+]i changes, while others calibrate fluorescence signals to [Ca2+]i changes using different methods. These studies show that at low glucose concentrations, [Ca2+]i is about 100 nM. Upon high glucose stimulation, [Ca2+]i typically increases three-fold. This relatively modest increase may be due to experimental conditions not supporting the optimal engagement of the CICR process.
CICR amplifies Ca2+ signals in β-cells to varying degrees depending on the experimental conditions [28,42,46]. The magnitude of the global [Ca2+]i increase at the peak of CICR depends on how effectively the process is engaged. Agents that increase cAMP play a crucial role in this process [28]. In the presence of cAMP-elevating agents, peak [Ca2+]i increase during the CICR upstroke can reach high levels, typically 0.5–2 μM [6,42,83].
Optimal stimulation of β-cells by nutrients can likely increase [Ca2+]i to very high levels, potentially around 10 μM. Such high [Ca2+]i levels are achieved through CICR and the fusion of multiple Ca2+ events. However, these high concentrations cannot be detected by commonly used high-affinity Ca2+ indicators. Low-affinity Ca2+ indicators like Calbryte are more suitable for measuring such high concentrations [84].
[Ca2+]i increase caused by CICR often occurs in the form of large regenerative Ca2+ spikes of short duration [6,28,34,46]. Local [Ca2+]i increases caused by CICR may be even higher, but measuring these local increases is challenging. Relatively high [Ca2+]i increases are necessary for mediating certain cellular processes, such as 1. insulin exocytosis (requiring approximately 1 μM Ca2+) [85], and 2. activation of the large-conductance BK (KCa1.1) channels (requiring Ca2+ concentrations of around 10 μM [86].
These high [Ca2+]i levels highlight the importance of CICR in β-cell function and the need for appropriate experimental techniques to accurately measure and study this process.
5. Regulation of RyRs in β-Cells by Phosphorylation
The regulation of RyRs in β-cells through phosphorylation is a critical process that influences Ca2+ signaling and insulin secretion. This section will focus on the effects of phosphorylation by two key kinases: Ca2+-calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII) and protein kinase A (PKA).
5.1. CaMKII-Mediated Phosphorylation
Glucose stimulation of β-cells activates CaMKII, leading to the phosphorylation of RyR2 [87]. This phosphorylation enhances the sensitivity of RyR2 to trigger Ca2+, thereby amplifying CICR [88]. The primary site for CaMKII-mediated phosphorylation on mouse RyR2 is the serine residue at position 2814 (S2814). Phosphorylation of S2814 increases RyR2 channel activity. When S2814 of mouse RyR2 is replaced by aspartic acid (D) (S2814D), it mimics constitutive pseudo-phosphorylation of RyR2 by CAMKII. In S2814D knock-in mice, the channel has a gain-of-function defect. In these mice, there is enhanced Ca2+ leak from the ER, reduced ER Ca2+ pool size, and decreased frequency and amplitude of glucose-stimulated Ca2+ oscillations in β-cells. These mice exhibit basal hyperinsulinemia, glucose intolerance, and reduced glucose-induced insulin secretion, closely resembling β-cells defects observed in human type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Indeed, increased CaMKII-mediated phosphorylation at S2814 has been reported in the β-cells of individuals with T2DM [87]. It is conceivable that overstimulation of β-cells (e.g., due to overeating) leads to increased [Ca2+]i, chronic activation of CaMKII, and CaMKII-mediated hyperphosphorylation of RyR2. Chronic activation of RyR2 by CaMKII leads to Ca2+ leak, resulting in higher basal insulin secretion and impairment of glucose-induced insulin secretion.
5.2. Phosphorylation by PKA
The primary site for the PKA-mediated phosphorylation of RyR2 is serine at 2808 (S2808) [64,89]. In β-cells, PKA-mediated phosphorylation of RyR2 is essential for the functional recruitment and activation of the channel by its agonists [28,90]. This phosphorylation appears to play a crucial role in overcoming the inhibitory effects of cytoplasmic Mg2+ on RyR2 [91]. PKA phosphorylation also enhances the sensitivity of RyR2 to the stimulatory effects of cytoplasmic Ca2+, thereby promoting CICR from the ER [44,64,92]. While the consequences of CaMKII-mediated hyperphosphorylation on RyR2 in β-cells are well established, the effects of PKA-mediated hyperphosphorylation require further investigation.
6. FK506-Binding Protein 12.6 (FKBP12.6) and RyR2
FKBP12.6 (product of FKBP1B gene), also known as calstabin2, binds to and stabilizes the closed state of RyR2, reducing the probability of channel opening. Its dissociation from RyR2 increases the excitability of the channel. One study has demonstrated that cADPR binds to FKBP12.6, thereby releasing Ca2+ through RyR2 in rat islet microsomes [93]. While several subsequent studies have investigated the functional relationship between cADPR, and FKBP12.6, no other study has directly replicated the binding assay. The view that cADPR is the endogenous ligand for FKBP12.6 remains controversial and not widely accepted.
Chen et al. have shown that in Fkbp1b knock-out mice, glucose-induced [Ca2+]i increase in β-cells is enhanced, and consistent with this, glucose-induced insulin secretion is also increased [94]. FKBP12.6 has a stabilizing effect on RyR2, and in the absence of FKBP12.6, the channel becomes more sensitized to trigger by Ca2+, leading to enhanced CICR. On the other hand, Noguchi et al. reported dramatically different results. They showed that in their Fkbp1b knock-out mice, glucose-induced insulin secretion was markedly decreased [95].
The reasons for such contradictory results may be because in the study by Chen et al., exon 3 was deleted, and in the study by Noguchi et al., exon 1 was deleted. The different exon deletions effectively created distinct “splice variants” of Fkbp1b. Exon 1 deletion might lead to a more complete loss of FKBP12.6 function, leading to Ca2+ leak through RyR2, which can explain impaired insulin secretion [96]. Exon 3 deletion might result in a partially functional protein that increases RyR2 excitability in a way that enhances insulin secretion.
The contradictory findings could also be due to the different genetic backgrounds of the mouse models used (129/Sv/Ev mice in the study by Chen et al. and ICR mice in the study by Noguchi et al. It is possible that different genetic backgrounds trigger different levels of compensatory mechanisms and modify the expression of different genes involved in glucose metabolism and insulin secretion.
The dramatic alterations in insulin secretion observed in two different Fkbp1b knock-out mouse models, showing either increased or decreased secretion, suggest a significant role for RyR2-mediated CICR in regulating insulin secretion.
7. Cyclic ADP-Ribose (cADPR) and RyRs of β-Cells
cADPR plays a complex role in modulating RyRs, particularly RyR2. While cADPR can activate RyR2 directly [97], its primary function is to enhance RyR2’s sensitivity to Ca2+, thereby amplifying CICR [98]. Notably, cADPR does not bind directly to RyRs but interacts with them through intermediary proteins such as FKBP12.6 [93] and GAPDH [99].
In β-cells, whether cADPR releases Ca2+ from the ER depends on the specific cells, rodent models, experimental conditions, or labs performing the experiments. Some studies published in this field have not been replicated. cADPR does not activate RyRs in β-cells obtained from ob/ob mice or rat insulinoma cells [24,50,100].
Nevertheless, it is evident that glucose, especially in the presence of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), increases cADPR level in β-cells [101]. Like several other small molecules, cADPR appears to sensitize RyRs in β-cells to enhance CICR [101]. Direct evidence that cADPR enhances CICR by sensitizing RyRs in β-cells is lacking, whereas evidence that cAMP does the same is robust [6,28,46,48].
8. Role of RyRs in Mediating Insulin Secretion
Ca2+ entry through VGCCs can cause a modest increase in [Ca2+]i, which is sufficient to trigger some insulin secretion. However, under certain conditions, this Ca2+ entry leads to CICR, resulting in a much higher [Ca2+]i. This elevated Ca2+ level substantially contributes to Ca2+-dependent insulin secretion.
The involvement of RyRs in glucose-stimulated insulin secretion is well established through both pharmacological and molecular experiments. Pharmacological agonists of RyRs, such as caffeine and MBED, enhance insulin secretion [47,48,102], while inhibitors like high concentrations of ryanodine and dantrolene suppress it [35,48,102]. Molecular studies have shown that deletion of RyR2 inhibits glucose-stimulated insulin secretion [103], and islets from knock-in mice with a RyR2 mutation exhibit impaired secretion [87]. Furthermore, humans and mice with a mutant leaky RyR2 also demonstrate impaired glucose-stimulated insulin secretion [96].
CICR mediates insulin secretion in a context-dependent manner, i.e., it increases insulin secretion only when the glucose concentration is high, and the RyRs are sensitized by exogenous agents like caffeine or endogenous modulators like cAMP [6,28,48].
The RyR2 isoform in β-cells differs from that in the heart [60]. Specifically, RyR2 mRNA in beta cells lacks both exon 4 and exon 75 [60]. This splice variant is more effective in mediating glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. Evidence for this comes from studies showing that insulin secretion is impaired in mice expressing the “exon 75-containing RyR2”, whereas it remains normal in mice expressing the “exon 75-deficient RyR2” [104].
9. Role of RyR-Mediated CICR in GLP-1-Induced Insulin Secretion
GLP-1 increases insulin secretion primarily at high glucose concentrations and halts secretion when glucose levels drop, thus preventing hypoglycemia [105]. Drugs that stimulate insulin secretion via the GLP-1 receptor and coupled G-protein activation are commonly used to treat T2DM. GLP-1 increases insulin secretion by generating cAMP, which affects various ion channels, including RyRs [106]. It has been established that GLP-1 stimulates insulin secretion by enhancing RyR-mediated CICR (Figure 1) [6,15,41,105,107].
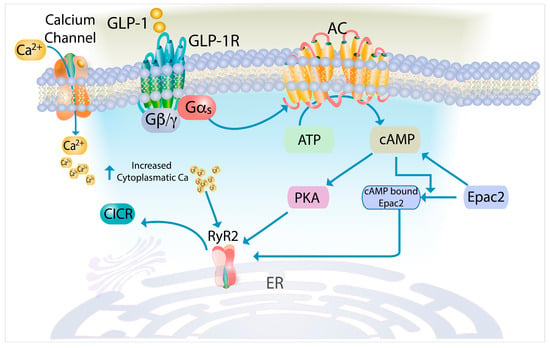
Figure 1.
Schematic of GLP-1-mediated CICR in β-cells. The figure illustrates the sequential signaling events through which GLP-1 potentiates CICR. Binding of GLP-1 to its G-protein-coupled receptor activates Gαs subunit, which stimulates adenylyl cyclase to generate cAMP. Elevated cAMP levels activate protein kinase A and bind to the exchange protein directly activated by cAMP 2 (Epac2). The cAMP-bound Epac2 directly interacts with RyR2, while PKA phosphorylates RyR2. These dual actions enhance RyR2 sensitivity to cytoplasmic Ca2+, resulting in enhanced CICR. Abbreviations: AC, adenylyl cyclase; Gαs, stimulatory G-protein α-subunit; PKA, protein kinase A.
GLP-1 sensitizes RyR2 through the protein kinase A (PKA) and the exchange protein activated by cAMP 2 (Epac2) pathways [90,108]. PKA phosphorylates RyR2 at Ser2809, increasing its open probability and sensitivity to cytoplasmic Ca2+ [28,109]. This phosphorylation also causes the dissociation of FKBP12.6, which stabilizes RyR2 in a closed state, thereby facilitating CICR [109].
GLP-1-induced cAMP directly activates Epac2, sensitizing RyR2 and promoting CICR [16,90]. However, the molecular mechanisms by which Epac2 enhances CICR via RyR2 remain unclear.
Through PKA activation, GLP-1 facilitates Ca2+ influx via VGCCs, increasing [Ca2+]i. This activates CaMKII, leading to RyR2 phosphorylation, which enhances their sensitivity to Ca2+ and further facilitates CICR [87].
GLP-1 also increases the formation of cADPR, and the GLP-1-induced Ca2+ increase is inhibited by ryanodine and 8-bromo-cADPR, an inhibitor of cADPR-induced Ca2+ signaling [101].
10. Link Between Glucose Metabolism and Activation of RyRs
The stimulation of β-cells by high glucose leads to diverse changes that are known to modulate the RyRs positively, enhancing CICR. For instance, glucose stimulation leads to an initial uptake of Ca2+ into the ER mediated by SERCA, increasing the filling state of the ER Ca2+ store [110]. Increased ER Ca2+ load increases the likelihood of activation of RyRs [111].
Glucose stimulation increases the concentration of cytoplasmic ATP, which is known to enhance Ca2+-induced activation of RyR2 [35,112]. Increased ATP binds to free Mg2+ ions, effectively reducing the concentration of free Mg2+ in the cytosol [113]. Mg2+ is an inhibitor of RyRs [114]. Therefore, the reduction in free cytosolic Mg2+ is likely to alleviate the Mg2+-mediated inhibition of RyRs. This decreased inhibition could potentially enhance RyR-mediated CICR.
Glycolysis plays a crucial role in insulin secretion. Research has shown that several glycolytic intermediates activate or positively modulate RyR2, with fructose-1,6-diphosphate (FDP) being the most potent [115]. Other active intermediates include glucose-1-phosphate, fructose-6-phosphate, and glucose-6-phosphate. During glucose stimulation, these intermediates likely sensitize RyR2, enhancing CICR.
Glucose stimulation also increases the concentration of arachidonic acid [77] and cADPR [116], which are positive modulators of CICR through RyRs [39]. Glucose metabolism elevates the concentration of long-chain acyl CoA, which can sensitize CICR through RyR2 [117,118].
11. Role of RyR-Mediated CICR in Regulating Somatostatin Secretion from δ-Cells
RyR-mediated CICR plays a crucial role in glucose-stimulated somatostatin secretion from mouse δ-cells. Inhibitors of RyRs, such as ryanodine and dantrolene, suppress this secretion [80,119]. In these cells, Ca2+ entry through VGCCs triggers CICR via RyRs [80,119]. Mouse δ-cells specifically express the RyR3 receptor, but not RyR1 or RyR2 [80]. A tight functional coupling exists between R-type VGCC and RyR3 to mediate CICR in these cells [80]. Notably, human δ-cells differ from their mouse counterparts, predominantly expressing RyR2 with minimal, if any, RyR3.
Vergari et al. described a RyR3-mediated CICR mechanism in δ-cells driven by Na+ [120]. Glucose metabolism and insulin signaling increase Na+ entry into δ-cells, likely via sodium–glucose cotransporters or other Na+-coupled transporters. Elevated [Na+]i activates an intracellular Na+/Ca2+ exchanger (functionally analogous to NCLX) and generates a small initial increase in [Ca2+]i. This Ca2+ signal triggers CICR via RyR3, amplifying the Ca2+ response and stimulating somatostatin secretion [120].
12. Role of RyR-Mediated CICR in Regulating Glucagon Secretion from α-Cells
Glucagon serves as a critical counterregulatory hormone during hypoglycemia. α-cells secrete glucagon maximally when glucose concentrations fall below physiological levels (e.g., 1–3 mM), with low glucose (<4 mM) acting as the primary stimulus. These cells exhibit distinct electrophysiological properties, including low K-ATP channel conductance and Ca2+-dependent electrical activity mediated by L-type VGCCs. Notably, while L-type VGCC inhibitors suppress electrical activity, they do not impair glucagon secretion. In contrast, pharmacological blockade of P/Q-type VGCCs with ω-Agatoxin IVA robustly inhibits low-glucose-induced glucagon release [121].
Further experiments by Acreman et al. demonstrated that glucagon secretion under low-glucose conditions is sensitive to ER Ca2+ store depletion (cyclopiazonic acid) and RyR inhibition (10 μM ryanodine) [121]. Their findings support a model wherein P/Q-type VGCCs, but not L-type VGCCs, are functionally coupled to RyRs. Specifically, Ca2+ influx through P/Q-type channels triggers CICR from RyRs, amplifying Ca2+ signals necessary for glucagon exocytosis. This mechanistic uncoupling between L-type VGCC-driven electrical activity and RyR-mediated CICR highlights a specialized signaling pathway in α-cells, ensuring precise glucagon release during hypoglycemia.
13. Role of RyRs in Mediating Store-Operated Ca2+ Entry (SOCE)
Activation of the RyRs of β-cells triggers Ca2+ entry through some TRP-like channels in the plasma membrane [39,42]. Multiple mechanisms are involved in mediating such Ca2+ entry. One of them is SOCE, which involves the filling state of the ER Ca2+ store, STIM1, Orai1, and some of the TRP channels [122]. β-cells express several TRP channels, some of which are molecular components of SOCE channels [123]. These cells express both RyR1 and RyR2 [54,71]. RyR2 plays an important role in mediating SOCE since deletion of the Ryr2 reduces SOCE [124,125]. In these cells, RyR2 is usually more abundant than RyR1, but some conditions that induce ER stress increase the expression of RyR1 [54]. This leads to leakage of Ca2+ from the ER through RyR1, depletion of the ER Ca2+ store, SOCE and [Ca2+]i oscillation by subthreshold glucose concentrations [54].
RyR activation also triggers Ca2+ entry by a mechanism that is independent of the filing state or the ER [42]. Even when the ER Ca2+ store is emptied, activation of the RyRs triggers Ca2+ entry [42]. RyR activation is required for triggering the Ca2+ entry [124]. It appears that conformational changes in the RyRs facilitate the Ca2+ entry through direct interactions with the SOCE machinery [126]. In this context, it is noteworthy that RyR1 can interact with TRPC3 and trigger Ca2+ entry [127].
Our study shows that activation of RyR2 by several endogenous agonists generated from glucose metabolism activates Ca2+ entry through the TRP-like channels in the plasma membrane and depolarizes the plasma membrane potential to the threshold for the activation of VGCCs [42]. It appears that Ca2+ release through RyR2 activates TRPM5 in the plasma membrane and Na2+ entry through TRPM5 depolarizes the plasma membrane potential [64,128].
14. Role of RyR-Mediated CICR in Regulating Electrical Activity of β-Cells
β-cells stimulated by high concentrations of glucose usually show repetitive depolarizations (slow waves). Superimposed on the plateau of the slow waves are bursts of rapid spikes. After these slow waves, there is a silent repolarization or interval phase. The durations of the slow waves and the interval phases may remain regular (“simple bursting”) or may vary (“complex bursting”). In “complex bursting”, the oscillations in the electrical activities show variable patterns, and several patterns of “complex bursting” have been described [129].
The mechanisms underlying “complex bursting” are not clear, but in a theoretical mathematical modeling study, Zhan et al. introduced RyR2 channels into previously known dynamic models of electrical activity in β-cells [130]. According to their model, the level of activation of RyR2 can regulate the bursting periods. The model predicts that moderate activation of RyR2 can change “simple bursting” to a type of “complex bursting” [130]. Periodic activation of RyR2 and the consequent CICR-mediated amplification of Ca2+ signals contribute to burst termination by activating the Ca2+-activated K+ channels, probably the large-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channels (BK channels). “Complex bursting” is more effective in increasing average [Ca2+]i and insulin secretion [130].
15. The Concept of “Leaky RyRs”
“Leaky RyRs” refer to a dysfunction of RyR channels that release Ca2+ from the ER inappropriately or in an uncontrolled manner. Leaky RyRs allow Ca2+ to escape from the ER into the cytosol. This Ca2+ must then be actively pumped back into the ER by SERCA, an ATP-dependent pump. This cycle of leakage and reuptake of Ca2+ constitutes a futile Ca2+ cycle as it consumes ATP without performing any useful work. Increased ATP consumption can impair cellular energy balance and contribute to pathological outcomes. Leaky RyRs have been linked to clinical disorders like heart failure, muscle weakness, and neurodegenerative diseases [131].
Normally, the binding of FKBP12.6 to RyR2 inhibits RyR2 activity and thereby reduces Ca2+ leak from the ER [132]. Oxidation and S-nitrosylation of RyR2 reduce the binding of FKBP12.6 to RyR2, leading to increased ER Ca2+ leak through the channel. Islets obtained from human diabetes subjects show increased oxidation, increased nitrosylation of RyR2, and decreased binding of FKBP12.6 to RyR2 [96].
Some gain-of-function mutations in the RYR2 gene lead to increased Ca2+ leak through different mechanisms. The RYR2-R2474S and RYR2-N2386I mutations cause leaky RyR2 channels by reducing the binding of FKBP12.6 to RyR2. In knock-in mice that express RYR2-R2474S or RYR2-N2386I, the ER Ca2+ store of the islets is depleted due to Ca2+ leak through RyR2 channels [96]. Glucose-induced insulin release from islets isolated from these mice is reduced, and the mice exhibit impaired glucose tolerance.
Some people who have a genetic predisposition to catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (CPVT) have mutations in the RYR2 gene that lead to leaky RyR2 channels. These patients have impaired glucose tolerance and impaired glucose-induced insulin secretion [96].
16. ER Stress and RyRs
ER stress arises from conditions like increased insulin production demands or glucolipotoxicity, leading to accumulation of misfolded/unfolded proteins. This triggers the unfolded protein response (UPR), an adaptive mechanism that becomes pro-apoptotic under sustained stress. Notably, Ca2+ dysregulation often mediates ER stress, which contributes to β-cell apoptosis in diabetes pathogenesis [133,134].
ER stress reduces luminal Ca2+ stores via RyR-mediated leakage [54,78,135,136]. Both RyR2 activation by misfolded proteins and RyR1 upregulation exacerbate Ca2+ efflux [54,78]. This depletion impairs Ca2+-dependent chaperones, creating a feedforward loop that amplifies UPR and apoptosis. Pharmacological RyR inhibition protects against ER-stress-induced β-cell death, underscoring its pathogenic role [54,78,136].
Paradoxically, while SERCA inhibition exacerbates ER stress via RyR-driven Ca2+ release [136], RyR2 suppression also induces apoptosis through calpain 10 activation [137]. Glucolipotoxicity highlights this bidirectional lethality of RyR modulation, where channel hyperactivity depletes ER Ca2+ stores, while its suppression activates an alternative apoptotic pathway—creating a narrow therapeutic window for RyR-targeted interventions [54].
Lessons learnt from the study of disease models:
- Akita Mice: Mutant proinsulin-induced ER stress causes β-cell apoptosis and diabetes [138]. In these mice, RyR inhibition with ryanodine prevents β-cell apoptosis [78].
- Wolfram syndrome (WSF1 mutation): ER Ca2+ depletion leads to β-cell death, which is inhibited by RyR inhibitors [135]. Mutations in WSF1 are associated with a form of young-onset non-autoimmune diabetes [139].
- THADA mutations: A thyroid adenoma-associated (THADA) protein variant binds RyR2, inducing Ca2+ leakage that impairs insulin secretion and triggers ER stress-mediated apoptosis [140].
17. Role of RyRs in the Pathogenesis of T2DM
The failure of β-cells to compensate for insulin resistance through increased insulin secretion leads to T2DM. This dysfunction involves multiple interconnected processes, including genetic predispositions, metabolic factors, glucolipotoxicity, disrupted signaling, and cellular stresses. Researchers have implicated the RyRs of β-cells and RyR-mediated CICR in the pathogenesis of β-cell defects in T2DM (Figure 2).
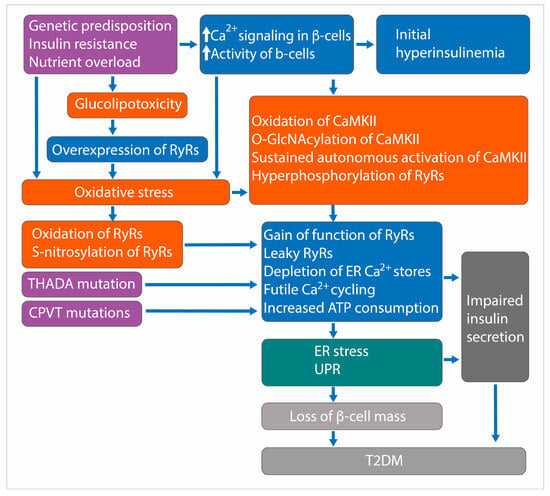
Figure 2.
Schematic of the processes involved in the pathogenesis of T2DM. This figure illustrates the sequence of events leading to impaired insulin secretion and loss of β-cell mass in T2DM. Oxidation, S-nitrosylation, and CaMKII-dependent hyperphosphorylation of RyRs result in leaky RyRs, causing futile Ca2+ cycling, increased ATP consumption, depletion of ER Ca2+ stores, ER stress, and activation of UPR. These processes collectively contribute to impaired insulin secretion and loss of β-cell mass.
17.1. Leaky RyRs and Posttranslational Modifications
RyRs can become leaky due to posttranslational modifications such as phosphorylation, oxidation, and nitrosylation. Oxidation and S-nitrosylation of RyR2 lead to increased Ca2+ leak and impaired insulin secretion in a mouse model of T2DM [96]. Inhibition of Ca2+ leak by the drug S107 shows positive effects on insulin secretion in islets from diabetic patients and murine models of T2DM [96]. Human T2DM islets exhibit increased oxidation and nitrosylation of RyR2, depletion of FKBP12.6, and leaky RyR2 channel.
17.2. CaMKII-Mediated Phosphorylation of RyR2
Before the onset of overt T2DM, β-cells experience prolonged periods of increased activity, leading to frequent prolonged elevations of [Ca2+]i [141]. This results in increased formation of ROS, oxidation of CaMKII [142], and increased O-GlcNAcylation of CaMKII [143], leading to sustained autonomous activation of CaMKII [87]. Activated CaMKII phosphorylates various proteins, including RyR2. CaMKII-mediated phosphorylation of RyR2 is increased in islets from human T2DM donors and mouse models of T2DM [87]. This phosphorylation leads to gain-of-function in the channel, resulting in increased Ca2+ leak from the ER, which can trigger ER stress, and UPR [87].
Studies using RyR2-S2814D knock-in mice, which mimic constitutive phosphorylation of RyR2, show that chronic gain-of-function in RyR2 leads to basal hyperglycemia, impaired GSIS, and glucose intolerance—hallmarks of pre-diabetes and early T2DM [87].
17.3. Thyroid Adenoma Associated (THADA) and RyR2 Interaction
THADA has been identified as a T2DM-associated gene through genome-wide association studies (GWAS) [140]. The T allele of rs7578597 is considered the risk allele for T2DM [144]. It is strongly associated with T2DM, particularly through maternal inheritance. THADA protein, an ER resident protein, interacts with RyR2, induces Ca2+ leak through RyR2, and reduces ER Ca2+ stores, triggering ER stress and apoptosis. THADA knock-out in mice enhances β-cell function and reduces β-cell apoptosis, protecting against high-fat high-sucrose and streptozotocin-induced hyperglycemia. Importantly, treatment with alnustone, an inhibitor of THADA protein’s function, ameliorates hyperglycemia in obese mice, suggesting that THADA protein could be a potential target for developing T2DM therapies [140].
17.4. RYR2 Mutations and Glucose Intolerance
CPVT patients with RYR2 mutations, including RYR2-R2474S and RYR2-N2386I, have been found to have glucose intolerance [96]. Additionally, a missense variant (p.N2291D) in the RYR2 gene has been identified in individuals with familial T2DM without overt CPVT. The p.N2291D overlaps the RIH (RyR and IP3R homology) domain, indicating that it is crucial for channel function. The p.N2291D variant is in the second mutational hotspot (residues 2246-2534) of the RYR2 protein. Certain missense mutations in the RYR2 gene in this hotspot are associated with complete penetrance for glucose intolerance [145].
17.5. Other Evidence
Deletion of Ryr2 leads to reduced insulin transcript, content, and glucose-induced secretion [103,124]. RyR2 regulates basal cytoplasmic Ca2+ levels and various aspects of Ca2+ signaling, such as SOCE and phospholipase C activity [124]. It also plays a role in regulating IRBIT (IP3R-binding protein released with inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate) levels and activity, which together control insulin production and secretion. Some experiments using an insulin-secreting cell line have shown that glucolipotoxicity increases the expression of RyRs, making cells vulnerable to ER stress [54]. However, it remains unclear whether RYR gene expression is increased in human β-cells at any stage of T2DM.
18. RYRs and GWAS for T2DM
While GWAS have identified numerous loci associated with T2DM and related glycemic traits, they have not consistently identified variants in the RYR genes associated with the disease or its related glycemic traits in large-scale studies [146,147]. For a gene to be identified in GWAS for T2DM, it must have functional polymorphisms that are both common enough in the population and have a sufficient effect size on the disease. RYR gene variants associated with T2DM or related glycemic traits are likely rare.
Traditional GWAS focus on common variants (minor allele frequency ≥ 1%), which may not capture rare, functionally significant variants of RYR genes. The effect size of common RYR variants on T2DM may be small, making them difficult to detect in GWAS with limited sample sizes. Moreover, T2DM is highly polygenic, with many loci contributing small effects, making it challenging to ascertain the contribution of any single gene.
Since GWAS are inadequate for detecting rare variants of RYRs associated with T2DM or related glycemic traits, investigators have used other advanced genetic methods. Whole-exome sequencing has identified an atypical missense variant in the RYR2 gene that co-segregated with T2DM in a family study, associated with glucose intolerance [145].
Family-based association tests using generalized estimating equations (FBAT-GEE) have identified several polymorphisms within the RYR3 gene associated with the risk of T2DM and age at onset of T2DM [148]. This study found three single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) significantly associated with T2DM risk, and two other SNPs significantly associated with age at the onset of T2DM.
19. Conclusions
Despite their relatively low expression levels in islet cells, RyRs play important roles in Ca2+ signaling and hormone secretion. In β-cells, RyRs modulate multiple aspects of Ca2+ signaling and Ca2+-dependent processes, including the amplification of Ca2+ signals via CICR, SOCE, electrical activity, ER stress, UPR, and apoptosis. GLP-1, widely used in diabetes treatment, enhances insulin secretion by promoting RyR-mediated CICR in beta cells. Dysregulation of RyRs, whether through increased phosphorylation or the presence of “leaky” channels, impairs insulin secretion, and certain RyR mutations are linked to impaired glucose tolerance and diabetes.
This review discussed the experimental methods and pharmacological tools used to study RyRs, their complex regulation, and potential reasons for some of the controversies in the field. Further research into the precise roles and regulation of RyRs in islet cells will be essential for understanding their involvement in diabetes pathogenesis and for the development of novel therapeutic strategies.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
Financial support was obtained from the Karolinska Institutet and the Uppsala County Council, Department of Internal Medicine, Uppsala University Hospital. Thanks to Fuad Bahram for the artworks.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| 4-CEP | 4-Chloro-3-ethylphenol |
| 4-CmC | 4-Chloro-m-cresol |
| CaMKII | Ca2+-calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II |
| CICR | Ca2+-induced Ca2+ release |
| CPVT | Catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia |
| cADPR | Cyclic ADP-ribose |
| ER | Endoplasmic reticulum |
| FKBP12.6 | FK506 binding protein 12.6 |
| IP3 | Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate |
| IP3R | Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor |
| IP3R3 | Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor, type 3 |
| MBED9-Methyl-7-bromoeudistomin D | |
| NO | Nitric oxide |
| PDE | Phosphodiesterase |
| PKA | Protein kinase A |
| RyR | Ryanodine receptor |
| RyR1 | Type 1 ryanodine receptor |
| RyR2 | Type 2 ryanodine receptor |
| RyR3 | Type 3 ryanodine receptor |
| T2DM | Type 2 diabetes mellitus |
| THADA | Thyroid adenoma associated |
| UPR | Unfolded protein response |
| VGCC | Voltage-gated Ca2+ channel |
References
- Islam, M.S. Calcium Signaling: From Basic to Bedside. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2020, 1131, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.S. Stimulus-Secretion Coupling in Beta-Cells: From Basic to Bedside. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2020, 1131, 943–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordenskjold, F.; Andersson, B.; Islam, M.S. Expression of the Inositol 1,4,5-Trisphosphate Receptor and the Ryanodine Receptor Ca(2+)-Release Channels in the Beta-Cells and Alpha-Cells of the Human Islets of Langerhans. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2020, 1131, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.; Bradford, P.G.; Laychock, S.G. Characterization of Inositol 1,4,5-Trisphosphate Receptor Isoform mRNA Expression and Regulation in Rat Pancreatic Islets, RINm5F Cells and betaHC9 Cells. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 1998, 21, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ríos, E. Calcium-Induced Release of Calcium in Muscle: 50 Years of Work and the Emerging Consensus. J. Gen. Physiol. 2018, 150, 521–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, G.; Chepurny, O.G.; Rindler, M.J.; Collis, L.; Chepurny, Z.; Li, W.H.; Harbeck, M.; Roe, M.W.; Holz, G.G. A cAMP and Ca2+ Coincidence Detector in Support of Ca2+-Induced Ca2+ Release in Mouse Pancreatic Beta Cells. J. Physiol. 2005, 566, 173–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyachok, O.; Tufveson, G.; Gylfe, E. Ca2+-Induced Ca2+ Release by Activation of Inositol 1,4,5-Trisphosphate Receptors in Primary Pancreatic Beta-Cells. Cell Calcium 2004, 36, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parys, J.B.; De Smedt, H. Inositol 1,4,5-Trisphosphate and Its Receptors. In Calcium Signaling; Islam, M.S., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; Volume 740, pp. 255–279. [Google Scholar]
- Marx, S.O.; Gaburjakova, J.; Gaburjakova, M.; Henrikson, C.; Ondrias, K.; Marks, A.R. Coupled Gating Between Cardiac Calcium Release Channels (Ryanodine Receptors). Circ. Res. 2001, 88, 1151–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezprozvanny, I.; Watras, J.; Ehrlich, B.E. Bell-Shaped Calcium-Response Curves of Ins(1,4,5)P3-Gated and Calcium-Gated Channels from Endoplasmic-Reticulum of Cerebellum. Nature 1991, 351, 751–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fill, M.; Copello, J.A. Ryanodine Receptor Calcium Release Channels. Physiol. Rev. 2002, 82, 893–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Rorsman, P.; Berggren, P.O. Ca(2+)-Induced Ca2+ Release in Insulin-Secreting Cells. FEBS Lett. 1992, 296, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.S. The Ryanodine Receptor Calcium Channel of Beta-Cells: Molecular Regulation and Physiological Significance. Diabetes 2002, 51, 1299–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, K.J.; Cho, D.S.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, B.J.; Lee, K.M.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, D.K.; Kim, S.H.; Park, H.S. Ca2+-Induced Ca2+ Release from Internal Stores in INS-1 Rat Insulinoma Cells. Korean J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2011, 15, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, S.; Nakagaki, I.; Kondo, H.; Hori, S. Involvement of the Ryanodine-Sensitive Ca2+ Store in GLP-1-Induced Ca2+ Oscillations in Insulin-Secreting Hit Cells. Pflug. Arch. 2002, 445, 342–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, G.X.; Chepurny, O.G.; Holz, G.G. cAMP-Regulated Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factor II (Epac2) Mediates Ca2+-Induced Ca2+ Release in INS-1 Pancreatic β-Cells. J. Physiol.-Lond. 2001, 536, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.H.; Lee, B.; Yang, C.; Hsu, W.H. Effects of Caffeine on Intracellular Calcium Release and Calcium Influx in a Clonal Beta-Cell Line RINm5F. Life Sci. 1996, 58, 983–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willmott, N.J.; Galione, A.; Smith, P.A. Nitric-Oxide Induces Intracellular Ca2+ Mobilization and Increases Secretion of Incorporated 5-Hydroxytryptamine in Rat Pancreatic Beta-Cells. FEBS Lett. 1995, 371, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamberucci, A.; Fulceri, R.; Pralong, W.; Bánhegyi, G.; Marcolongo, P.; Watkins, S.L.; Benedetti, A. Caffeine Releases a Glucose-Primed Endoplasmic Reticulum Ca2+ Pool in the Insulin Secreting Cell Line INS-1. FEBS Lett. 1999, 446, 309–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graves, T.K.; Hinkle, P.M. Ca2+-induced Ca2+ Release in the Pancreatic Beta-Cell: Direct Evidence of Endoplasmic Reticulum Ca2+ Release. Endocrinology 2003, 144, 3565–3574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Kindmark, H.; Larsson, O.; Berggren, P.O. Thiol Oxidation by 2,2′-Dithiodipyridine Causes a Reversible Increase in Cytoplasmic Free Ca2+ Concentration in Pancreatic Beta-Cells. Role for Inositol 1,4,5-Trisphosphate-Sensitive Ca2+ Stores. Biochem. J. 1997, 321 Pt 2, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Larsson, O.; Nilsson, T.; Berggren, P.O. Effects of Caffeine on Cytoplasmic Free Ca2+ Concentration in Pancreatic Beta-Cells Are Mediated by Interaction with ATP-Sensitive K+ Channels and L-Type Voltage-Gated Ca2+ Channels but not the Ryanodine Receptor. Biochem. J. 1995, 306 Pt 3, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lund, P.E.; Gylfe, E. Caffeine Inhibits Cytoplasmic Ca2+ Oscillations Induced by by Carbachol and Guanosine 5′-O-(3-Thiotriphosphate) in Hyperpolarized Pancreatic Beta-Cells. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 1994, 349, 503–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutter, G.A.; Theler, J.M.; Li, G.; Wollheim, C.B. Ca2+ Stores in Insulin-Secreting Cells—Lack of Efect of cADP Ribose. Cell Calcium 1994, 16, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Squires, P.E.; Hills, C.E.; Rogers, G.J.; Garland, P.; Farley, S.R.; Morgan, N.G. The Putative Imidazoline Receptor Agonist, Harmane, Promotes Intracellular Calcium Mobilisation in Pancreatic Beta-Cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 501, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herchuelz, A.; Lebrun, P. A Role for Na/Ca Exchange in the Pancreatic B-Cell—Studies with Thapsigargin and Caffeine. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1993, 45, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roe, M.W.; Lancaster, M.E.; Mertz, R.J.; Worley, J.F.; Dukes, I.D. Voltage-Dependent Intracellular Calcium Release from Mouse Islets Stimulated by Glucose. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 9953–9956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Leibiger, I.; Leibiger, B.; Rossi, D.; Sorrentino, V.; Ekstrom, T.J.; Westerblad, H.; Andrade, F.H.; Berggren, P.O. In Situ Activation of the Type 2 Ryanodine Receptor in Pancreatic Beta Cells Requires cAMP-Dependent Phosphorylation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 6145–6150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Bjorklund, A.; Islam, M.S. A TRPM4 Inhibitor 9-Phenanthrol Inhibits Glucose- and Glucagon-Like Peptide 1-Induced Insulin Secretion from Rat Islets of Langerhans. J. Diabetes Res. 2017, 2017, 5131785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulhunty, A.F.; Beard, N.A.; Casarotto, M.G. Recent Advances in Understanding the Ryanodine Receptor Calcium Release Channels and Their Role in Calcium Signalling. F1000Research 2018, 7, F1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutko, J.L.; Airey, J.A.; Welch, W.; Ruest, L. The Pharmacology of Ryanodine and Related Compounds. Pharmacol. Rev. 1997, 49, 53–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanna, B.; Welch, W.; Ruest, L.; Sutko, J.L.; Williams, A.J. Excess Noise in Modified Conductance States Following the Interaction of Ryanoids with Cardiac Ryanodine Receptor Channels. FEBS Lett. 2002, 516, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pessah, I.N.; Zimanyi, I. Characterization of Multiple [3H] Ryanodine Binding Sites on the Ca2+ Release Channel of Sarcoplasmic Reticulum from Skeletal and Cardiac-Muscle: Evidence for a Sequential Mechanism in Ryanodine Action. Mol. Pharmacol. 1991, 39, 679–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postic, S.; Sarikas, S.; Pfabe, J.; Pohorec, V.; Krizancic Bombek, L.; Sluga, N.; Skelin Klemen, M.; Dolensek, J.; Korosak, D.; Stozer, A.; et al. High-Resolution Analysis of the Cytosolic Ca(2+) Events in Beta Cell Collectives In Situ. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, 324, E42–E55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llanos, P.; Contreras-Ferrat, A.; Barrientos, G.; Valencia, M.; Mears, D.; Hidalgo, C. Glucose-Dependent Insulin Secretion in Pancreatic Beta-Cell Islets from Male Rats Requires Ca2+ Release via ROS-Stimulated Ryanodine Receptors. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.D.; Kuang, S.H.; Misler, S.; Polonsky, K.S. Ryanodine Receptors in Human Pancreatic Beta Cells: Localization and Effects on Insulin Secretion. FASEB J. 2004, 18, 878–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, P.A.; Thompson, B.; Liu, C.T.; Bertram, R.; Satin, L.S.; Sherman, A.S. Ca2+Release or Ca2+Entry, That Is the Question: What Governs Ca2+Oscillations in Pancreatic β Cells? Am. J. Physiol.-Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, 324, E477–E487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, M.; Grapengiesser, E. Pancreatic Beta-Cells from Obese-Hyperglycemic Mice are Characterized by Excessive Firing of Cytoplasmic Ca2+ Transients. Endocrine 2001, 15, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolcott, O.O.; Gustafsson, A.J.; Dzabic, M.; Pierro, C.; Tedeschi, P.; Sandgren, J.; Bari, M.R.; Nguyen, K.H.; Bianchi, M.; Rakonjac, M.; et al. Arachidonic Acid Is a Physiological Activator of the Ryanodine Receptor in Pancreatic Beta-Cells. Cell Calcium 2006, 39, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosker, C.; Meur, G.; Taylor, E.J.A.; Taylor, C.W. Functional Ryanodine Receptors in the Plasma Membrane of RINm5F Pancreatic Beta-Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 5186–5194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gromada, J.; Dissing, S.; Bokvist, K.; Renstrom, E.; Frokjaerjensen, J.; Wulff, B.S.; Rorsman, P. Glucagon-Like Peptide I Increases Cytoplasmic Calcium in Insulin-Secreting betaTC3-Cells by Enhancement of Intracellular Calcium Mobilization. Diabetes 1995, 44, 767–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafsson, A.J.; Ingelman-Sundberg, H.; Dzabic, M.; Awasum, J.; Hoa, N.K.; Ostenson, C.G.; Pierro, C.; Tedeschi, P.; Woolcott, O.; Chiounan, S.; et al. Ryanodine Receptor-Operated Activation of TRP-Like Channels Can Trigger Critical Ca2+ Signaling Events in Pancreatic Beta-Cells. FASEB J. 2004, 18, 301–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessah, I.N.; Stambuk, R.A.; Casida, J.E. Ca2+-Activated Ryanodine Binding: Mechanisms of Sensitivity and and Intensity Modulation by Mg2+, Caffeine, and Adenine Nucleotides. Mol. Pharmacol. 1987, 31, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holz, G.G.; Leech, C.A.; Heller, R.S.; Castonguay, M.; Habener, J.F. cAMP-Dependent Mobilization of Intracellular Ca2+ Stores by Activation of Ryanodine Receptors in Pancreatic Beta-Cells. A Ca2+ Signaling System Stimulated by the Insulinotropic Hormone Glucagon-Like Peptide-1-(7-37). J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 14147–14156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Chen, Z.; Yin, W.X.; Miao, L.; Zhou, Z.S.; Ji, G.J. Ryanodine Receptors Are Involved in Nuclear Calcium Oscillation in Primary Pancreatic Beta-Cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 423, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemmens, R.; Larsson, O.; Berggren, P.O.; Islam, M.S. Ca2+-Induced Ca2+ Release from the Endoplasmic Reticulum Amplifies the Ca2+ Signal Mediated by Activation of Voltage-Gated L-Type Ca2+ Channels in Pancreatic Beta-Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 9971–9977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Sylvester, P.L.; Porta, M.; Juettner, V.V.; Lv, Y.Z.; Fleischer, S.; Copello, J.A. Eudistomin D and Penaresin Derivatives as Modulators of Ryanodine Receptor Channels and Sarcoplasmic Reticulum Ca2+ ATPase in Striated Muscle. Mol. Pharmacol. 2014, 85, 564–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruton, J.D.; Lemmens, R.; Shi, C.L.; Persson-Sjögren, S.; Westerblad, H.; Ahmed, M.; Pyne, N.J.; Frame, M.; Furman, B.L.; Islam, M.S. Ryanodine Receptors of Pancreatic-Cells Mediate a Distinct Context-Dependent Signal for Insulin Secretion. FASEB J. 2002, 16, 301–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramson, J.J.; Zable, A.C.; Favero, T.G.; Salama, G. Thimerosal Interacts with the Ca2+ Release Channel Ryanodine Receptor from Skeletal Muscle Sarcoplasmic Reticulum. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 29644–29647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Larsson, O.; Berggren, P.O. Cyclic ADP-ribose in Beta Cells. Science 1993, 262, 584–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blondel, O.; Takeda, J.; Janssen, H.; Seino, S.; Bell, G.I. Sequence and Functional Characterization of a Third Inositol Trisphosphate Receptor Subtype, IP3R-3, Expressed in Pancreatic Islets, Kidney, Gastrointestinal Tract, and Other Tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 11356–11363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.A.; Rossi, A.M.; Riley, A.M.; Potter, B.V.L.; Taylor, C.W. Subtype-Selective Regulation of IP3 Receptors by Thimerosal via Cysteine Residues within the 1P3-Binding Core and Suppressor Domain. Biochem. J. 2013, 451, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Sengupta, C.; Meyer, U.A.; Carafoli, E. Binding of Dantrolene Sodium to Muscle Intracellular Membranes. FEBS Lett. 1980, 117, 37–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, I.X.; Herrmann, A.; Leon, J.; Jeyarajan, S.; Arunagiri, A.; Arvan, P.; Gilon, P.; Satin, L.S. ER Stress Increases Expression of Intracellular Calcium Channel RyR1 to Modify Ca(2+) Homeostasis in Pancreatic Beta Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2023, 299, 105065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janjic, D.; Wollheim, C.B.; Sharp, G.W.G. Selective Inhibition of Glucose-Stimulated Insulin Release by Dantrolene. Am. J. Physiol. 1982, 243, E59–E67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Shim, H.M.; Na, A.Y.; Bae, J.H.; Im, S.S.; Song, D.K. Orexin A Regulates Plasma Insulin and Leptin Levels in a Time-Dependent Manner Following a Glucose Load in Mice. Diabetologia 2015, 58, 1542–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kobayashi, S.; Yano, M.; Suetomi, T.; Ono, M.; Tateishi, H.; Mochizuki, M.; Xu, X.; Uchinoumi, H.; Okuda, S.; Yamamoto, T.; et al. Dantrolene, a Therapeutic Agent for Malignant Hyperthermia, Markedly Improves the Function of Failing Cardiomyocytes by Stabilizing Interdomain Interactions Within the Ryanodine Receptor. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2009, 53, 1993–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaburjakova, J.; Gaburjakova, M. Molecular Aspects Implicated in Dantrolene Selectivity with Respect to Ryanodine Receptor Isoforms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Zucchi, R.; Ronca-Testoni, S.; Ronca, G. Protection of Ischemic Rat Heart by Dantrolene, an Antagonist of the Sarcoplasmic Reticulum Calcium Release Channel. Basic Res. Cardiol. 2000, 95, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takasawa, S.; Kuroki, M.; Nata, K.; Noguchi, N.; Ikeda, T.; Yamauchi, A.; Ota, H.; Itaya-Hironaka, A.; Sakuramoto-Tsuchida, S.; Takahashi, I.; et al. A Novel Ryanodine Receptor Expressed in Pancreatic Islets by Alternative Splicing from Type 2 Ryanodine Receptor Gene. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 397, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansari, N.; Hadi-Alijanvand, H.; Sabbaghian, M.; Kiaei, M.; Khodagholi, F. Interaction of 2-APB, Dantrolene, and TDMT with IP3R and RyR Modulates ER Stress-Induced Programmed Cell Death I and II in Neuron-Like PC12 Cells: An Experimental and Computational Investigation. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2014, 32, 1211–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacMillan, D.; Chalmers, S.; Muir, T.C.; McCarron, J.G. IP3-Mediated Ca2+ Increases do not Involve the Ryanodine Receptor, but Ryanodine Receptor Antagonists Reduce IP3-Mediated Ca2+ Increases in Guinea-Pig Colonic Smooth Muscle Cells. J. Physiol. 2005, 569, 533–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pian-Smith, M.C.; Wiedenkeller, D.E.; Sharp, G.W. Paradoxical Potentiation of Stimulated Insulin Release by Dantrolene in Rat Pancreatic Islets. Pancreas 1986, 1, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murao, N.; Morikawa, R.; Seino, Y.; Shimomura, K.; Maejima, Y.; Yamada, Y.; Suzuki, A. β-Adrenergic Blockers Increase cAMP and Stimulate Insulin Secretion Through a PKA/RYR2/TRPM5 Pathway in Pancreatic β-Cells In Vitro. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2025, 13, e70092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HerrmannFrank, A.; Richter, M.; Sarkozi, S.; Mohr, U.; LehmannHorn, F. 4-Chloro-m-Cresol, a Potent and Specific Activator of the Skeletal Muscle Ryanodine Receptor. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Gen. Subj. 1996, 1289, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, A.R.; Moe, S.T.; Allen, P.D.; Fessenden, J.D. Structural Determinants of 4-Chloro-m-Cresol Required for Activation of Ryanodine Receptor Type 1. Mol. Pharmacol. 2006, 70, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosoi, E.; Nishizaki, C.; Gallagher, K.L.; Wyre, H.W.; Matsuo, Y.; Sei, Y. Expression of the Ryanodine Receptor Isoforms in Immune Cells. J. Immunol. 2001, 167, 4887–4894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, B.; Chen, G.L.; Daskoulidou, N.; Xu, S.Z. The Ryanodine Receptor Agonist 4-Chloro-3-Ethylphenol Blocks ORAI Store- Operated Channels. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 171, 1250–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerblad, H.; Andrade, F.H.; Islam, M.S. Effects of Ryanodine Receptor Agonist 4-Chloro-m-Cresol on Myoplasmic Free Ca2+ Concentration and Force of Contraction in Mouse Skeletal Muscle. Cell Calcium 1998, 24, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varadi, A.; Rutter, G.A. Dynamic Imaging of Endoplasmic Reticulum Ca2+ Concentration in Insulin-Secreting MIN6 Cells Using Recombinant Targeted Cameleons—Roles of Sarco(endo)plasmic Reticulum Ca2+-ATPase (SERCA)-2 and Ryanodine Receptors. Diabetes 2002, 51, S190–S201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, K.J.; Pinton, P.; Varadi, A.; Tacchetti, C.; Ainscow, E.K.; Pozzan, T.; Rizzuto, R.; Rutter, G.A. Dense Core Secretory Vesicles Revealed as a Dynamic Ca2+ Store in Neuroendocrine Cells with a Vesicle-Associated Membrane Protein Aequorin Chimaera. J. Cell Biol. 2001, 155, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Eu, J.P.; Meissner, G.; Stamler, J.S. Activation of the Cardiac Calcium Release Channel (Ryanodine Receptor) by Poly-S-Nitrosylation. Science 1998, 279, 234–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakada, S.; Ishikawa, T.; Yamamoto, Y.; Kaneko, Y.; Nakayama, K. Constitutive Nitric Oxide Synthases in Rat Pancreatic Islets: Direct Imaging of Glucose-Induced Nitric Oxide Production in β-Cells. Pflug. Arch. 2003, 447, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunemaker, C.S.; Buerk, D.G.; Zhang, M.; Satin, L.S. Glucose-Induced Release of Nitric Oxide from Mouse Pancreatic Islets as Detected with Nitric Oxide-Selective Glass Microelectrodes. Am. J. Physiol.-Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 292, E907–E912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dettbarn, C.; Palade, P. Arachidonic Acid-Induced Ca2+ Release from Isolated Sarcoplasmic Reticulum. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1993, 45, 1301–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muslikhov, E.R.; Sukhanova, I.F.; Avdonin, P.V. Arachidonic Acid Activates Release of Calcium Ions from Reticulum via Ryanodine Receptor Channels in C2C12 Skeletal Myotubes. Biochem.-Mosc. 2014, 79, 435–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, B.A.; Turk, J.; Sherman, W.R.; McDaniel, M.L. Intracellular Ca2+ Mobilization by Arachidonic Acid. Comparison with Myo-Inositol 1,4,5-Trisphosphate in Isolated Pancreatic Islets. J. Biol. Chem. 1986, 261, 3501–3511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, W.R.; Bone, R.N.; Sohn, P.; Syed, F.; Reissaus, C.A.; Mosley, A.L.; Wijeratne, A.B.; True, J.D.; Tong, X.; Kono, T.; et al. Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Alters Ryanodine Receptor Function in the Murine Pancreatic Cell. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 168–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, P.P.; MacQuaide, N.; Louch, W.E. Dyadic Plasticity in Cardiomyocytes. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Bengtsson, M.; Partridge, C.; Salehi, A.; Braun, M.; Cox, R.; Eliasson, L.; Johnson, P.R.; Renstrom, E.; Schneider, T.; et al. R-Type Ca(2+)-Channel-Evoked CICR Regulates Glucose-Induced Somatostatin Secretion. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collier, M.L.; Ji, G.; Wang, Y.X.; Kotlikoff, M.I. Calcium-Induced Calcium Release in Smooth Muscle—Loose Coupling Between the Action Potential and Calcium Release. J. Gen. Physiol. 2000, 115, 653–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, X.; Li, D.Q.; Olofsson, C.S.; Salehi, A.; Surve, V.V.; Caballero, J.; Ivarsson, R.; Lundquist, I.; Pereverzev, A.; Schneider, T.; et al. CaV2.3 Calcium Channels Control Second-Phase Insulin Release. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S. Calcium Signaling in the Islets. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2010, 654, 235–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.; Patel, D.; Zhao, Q.; Peng, R.; Guo, H.; Diwu, Z. A Novel Ca(2+) Indicator for Long-Term Tracking of Intracellular Calcium Flux. Biotechniques 2021, 70, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Q.F.; Dong, Y.M.; Yang, H.; Lou, X.L.; Ding, J.P.; Xu, T. Protein Kinase Activation Increases Insulin Secretion by Sensitizing the Secretory Machinery to Ca2+. J. Gen. Physiol. 2004, 124, 653–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothberg, B.S.; Magleby, K.L. Gating Kinetics of Single Large-Conductance Ca2+-Activated K+ Channels in High Ca2+ Suggest a Two-Tiered Allosteric Gating Mechanism. J. Gen. Physiol. 1999, 114, 93–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixit, S.S.; Wang, T.N.; Manzano, E.J.Q.; Yoo, S.; Lee, J.; Chiang, D.Y.; Ryan, N.; Respress, J.L.; Yechoor, V.K.; Wehrens, X.H.T. Effects of CaMKII-Mediated Phosphorylation of Ryanodine Receptor Type 2 on Islet Calcium Handling, Insulin Secretion, and Glucose Tolerance. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehrens, X.H.; Lehnart, S.E.; Reiken, S.R.; Marks, A.R. Ca2+/Calmodulin-Dependent Protein Kinase II Phosphorylation Regulates the Cardiac Ryanodine Receptor. Circ. Res. 2004, 94, e61–e70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marx, S.O.; Reiken, S.; Hisamatsu, Y.; Jayaraman, T.; Burkhoff, D.; Rosemblit, N.; Marks, A.R. PKA Phosphorylation Dissociates FKBP12.6 from the Calcium Release Channel (Ryanodine Receptor): Defective Regulation in Failing Hearts. Cell 2000, 101, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzhura, I.; Chepurny, O.G.; Kelley, G.G.; Leech, C.A.; Roe, M.W.; Dzhura, E.; Afshari, P.; Malik, S.; Rindler, M.J.; Xu, X.; et al. Epac2-Dependent Mobilization of Intracellular Ca2+ by Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonist Exendin-4 is Disrupted in Beta-Cells of Phospholipase C-Epsilon Knockout Mice. J. Physiol.-Lond. 2010, 588, 4871–4889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hain, J.; Onoue, H.; Mayrleitner, M.; Fleischer, S.; Schindler, H. Phosphorylation Modulates the Function of the Calcium Release Channel of Sarcoplasmic Reticulum from Cardiac Muscle. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 2074–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdivia, H.H.; Kaplan, J.H.; Ellis-Davies, G.C.; Lederer, W.J. Rapid Adaptation of Cardiac Ryanodine Receptors: Modulation by Mg2+ and Phosphorylation. Science 1995, 267, 1997–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, N.; Takasawa, S.; Nata, K.; Tohgo, A.; Kato, I.; Ikehata, F.; Yonekura, H.; Okamoto, H. Cyclic ADP-Ribose Binds to FK506-Binding Protein 12.6 to Release Ca2+ from Islet Microsomes. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 3133–3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Li, Z.Z.; Wei, B.; Yin, W.X.; Xu, T.; Kotlikoff, M.I.; Ji, G.J. FKBP12.6-Knockout Mice Display Hyperinsulinemia and Resistance to High-Fat Diet-Induced Hyperglycemia. FASEB J. 2010, 24, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, N.; Yoshikawa, T.; Ikeda, T.; Takahashi, I.; Shervani, N.J.; Uruno, A.; Yamauchi, A.; Nata, K.; Takasawa, S.; Okamoto, H.; et al. FKBP12.6 Disruption Impairs Glucose-Induced Insulin Secretion. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 371, 735–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santulli, G.; Pagano, G.; Sardu, C.; Xie, W.J.; Reiken, S.; D’Ascia, S.L.; Cannone, M.; Marziliano, N.; Trimarco, B.; Guise, T.A.; et al. Calcium Release Channel RyR2 Regulates Insulin Release and Glucose Homeostasis. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 1968–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meszaros, L.G.; Bak, J.; Chu, A. Cyclic ADP-Ribose as an Endogenous Regulator of the Non-Skeletal Type Ryanodine Receptor Ca2+ Channel. Nature 1993, 364, 76–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venturi, E.; Pitt, S.; Galfre, E.; Sitsapesan, R. From Eggs to Hearts: What Is the Link Between Cyclic ADP-Ribose and Ryanodine Receptors? Cardiovasc. Ther. 2012, 30, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.H.; Sun, W.; Huang, L.H.; Zhu, K.Y.; Pei, F.; Zhu, L.C.; Wang, Q.; Lu, Y.Y.; Zhang, H.M.; Jin, H.W.; et al. Identifying Glyceraldehyde 3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase as a Cyclic Adenosine Diphosphoribose Binding Protein by Photoaffinity Protein-Ligand Labeling Approach. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 156–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, D.L.; Islam, M.S.; Efanov, A.M.; Brown, G.; Kohler, M.; Larsson, O.; Berggren, P.O. Insulin Exocytosis and Glucose-Mediated Increase in Cytoplasmic Free Ca2+ Concentration in the Pancreatic Beta-Cell Are Independent of Cyclic ADP-Ribose. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 19074–19079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.J.; Park, K.H.; Yim, C.Y.; Takasawa, S.; Okamoto, H.; Im, M.J.; Kim, U.H. Generation of Nicotinic Acid Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate and Cyclic ADP-Ribose by Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Evokes Ca2+ Signal That Is Essential for Insulin Secretion in Mouse Pancreatic Islets. Diabetes 2008, 57, 868–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaluri, N.; Modi, S.; Rodríguez, M.L.; Stancáková, A.; Kuusisto, J.; Kokkola, T.; Laakso, M. Simvastatin Impairs Insulin Secretion by Multiple Mechanisms in MIN6 Cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, K.E.; LaVigne, E.K.; Dar, M.S.; Salyer, A.E.; Pratt, E.P.S.; Sample, P.A.; Aryal, U.; Gowher, H.; Hockerman, G.H. RyR2/IRBIT Regulates Insulin Gene Transcript, Insulin Content, and Secretion in the Insulinoma Cell Line INS-1. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 7713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makino, M.; Uchiyama, T.; Oshima, Y.; Daikoku, T.; Yamamoto, Y.; Okamoto, H.; Nakamura, S.; Takasawa, S. Alteration of Splice Type in Type 2 Ryanodine Receptor Causes Impaired Insulin Secretion in Mice. Diabetes 2024, 73, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meloni, A.R.; DeYoung, M.B.; Lowe, C.; Parkes, D.G. GLP-1 Receptor Activated Insulin Secretion from Pancreatic ß-Cells: Mechanism and Glucose Dependence. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2013, 15, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leech, C.A.; Dzhura, I.; Chepurny, O.G.; Kang, G.X.; Schwede, F.; Genieser, H.G.; Holz, G.G. Molecular Physiology of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Insulin Secretagogue Action in Pancreatic Beta Cells. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2011, 107, 236–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuboi, T.; Xavier, G.D.; Holz, G.G.; Jouaville, L.S.; Thomas, A.P.; Rutter, G.A. Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Mobilizes Intracellular Ca2+ and Stimulates Mitochondrial ATP Synthesis in Pancreatic MIN6 Beta-Cells. Biochem. J. 2003, 369, 287–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holz, G.G. Epac: A New cAMP-Binding Protein in Support of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor-Mediated Signal Transduction in the Pancreatic Beta-Cell. Diabetes 2004, 53, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marks, A.R. Calcium Cycling Proteins and Heart Failure: Mechanisms and Therapeutics. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grapengiesser, E.; Gylfe, E.; Hellman, B. Glucose Sensing of Individual Pancreatic Beta-Cells Involves Transitions Between Steady-State and Oscillatory Cytoplasmic CA2+. Cell Calcium 1992, 13, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laver, D.R. Ca2+ Stores Regulate Ryanodine Receptor Ca2+ Release Channels Via Luminal and Cytosolic Ca2+ Sites. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2007, 34, 889–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kermode, H.; Williams, A.J.; Sitsapesan, R. The Interactions of ATP, ADP, and Inorganic Phosphate with the Sheep Cardiac Ryanodine Receptor. Biophys. J. 1998, 74, 1296–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dukes, I.D.; Sreenan, S.; Roe, M.W.; Levisetti, M.; Zhou, Y.P.; Ostrega, D.; Bell, G.I.; Pontoglio, M.; Yaniv, M.; Philipson, L.; et al. Defective Pancreatic β-Cell Glycolytic Signaling in Hepatocyte Nuclear Factor-1α-Deficient Mice. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 24457–24464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laver, D.R. Regulation of the RyR Channel Gating by Ca(2+) and Mg(2+). Biophys. Rev. 2018, 10, 1087–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kermode, H.; Chan, W.M.; Williams, A.J.; Sitsapesan, R. Glycolytic Pathway Intermediates Activate Cardiac Ryanodine Receptors. FEBS Lett. 1998, 431, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takasawa, S.; Akiyama, T.; Nata, K.; Kuroki, M.; Tohgo, A.; Noguchi, N.; Kobayashi, S.; Kato, I.; Katada, T.; Okamoto, H. Cyclic ADP-Ribose and Inositol 1,4,5-Trisphosphate as Alternate Second Messengers for Intracellular Ca2+ Mobilization in Normal and Diabetic Beta-Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 2497–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corkey, B.E.; Deeney, J.T.; Yaney, G.C.; Tornheim, K.; Prentki, M. The Role of Long-Chain Fatty acyl-CoA Esters in β-Cell Signal Transduction. J. Nutr. 2000, 130, 299S–304S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connelly, T.; Ahern, C.; Sukhareva, M.; Coronado, R. Removal of Mg2+ Inhibition of Cardiac Ryanodine Receptor by Palmitoyl Coenzyme A. FEBS Lett. 1994, 352, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denwood, G.; Tarasov, A.; Salehi, A.; Vergari, L.; Ramracheya, R.; Takahashi, H.; Nikolaev, V.O.; Seino, S.; Gribble, F.; Reimann, F.; et al. Glucose Stimulates Somatostatin Secretion in Pancreatic δ-cells by cAMP-Dependent Intracellular Ca2+ Release. J. Gen. Physiol. 2019, 151, 1094–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergari, E.; Denwood, G.; Salehi, A.; Zhang, Q.; Adam, J.; Alrifaiy, A.; Asterholm, I.W.; Benrick, A.; Chibalina, M.V.; Eliasson, L.; et al. Somatostatin Secretion by Na+-Dependent Ca2+-Induced Ca2+ Release in Pancreatic Delta Cells. Nat. Metab. 2020, 2, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acreman, S.; Ma, J.F.; Denwood, G.; Gao, R.; Tarasov, A.; Rorsman, P.; Zhang, Q. The Endoplasmic Reticulum Plays a Key Role in a-Cell Intracellular Ca 2+ Dynamics and Glucose-Regulated Glucagon Secretion in Mouse Islets. Iscience 2024, 27, 109665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabourin, J.; Allagnat, F. Store-Operated Ca2+ Entry: A Key Component of the Insulin Secretion Machinery. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2016, 57, F35–F39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S. Molecular Regulations and Functions of the Transient Receptor Potential Channels of the Islets of Langerhans and Insulinoma Cells. Cells 2020, 9, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvey, K.E.; Tang, S.Q.; LaVigne, E.K.; Pratt, E.P.S.; Hockerman, G.H. RyR2 Regulates Store-Operated Ca2+ Entry, Phospholipase C Activity, and Electrical Excitability in the Insulinoma Cell Line INS-1. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0285316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, I.R.X.; Ren, J.H.; Vadrevu, S.; Raghavan, M.; Satin, L.S. ER Stress Increases Store-Operated Ca2+ Entry (SOCE) and Augments Basal Insulin Secretion in Pancreatic Beta Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 5685–5700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.S.; Ayon, R.J.; Yuan, J.X.J. Ryanodine Receptor-2: A Necessity for Gating Store-Operated Ca2+ Channels. Cardiovasc. Res. 2016, 111, 13–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kiselyov, K.I.; Shin, D.M.; Wang, Y.M.; Pessah, I.N.; Allen, P.D.; Muallem, S. Gating of Store-Operated Channels by Conformational Coupling To Ryanodine Receptors. Mol. Cell 2000, 6, 421–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, K.; Ma, Z.; Bjorklund, A.; Islam, M.S. Role of Transient Receptor Potential Melastatin-Like Subtype 5 Channel in Insulin Secretion from Rat Beta-Cells. Pancreas 2014, 43, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henquin, J.C.; Meissner, H.P.; Schmeer, W. Cyclic Variations of Glucose-Induced Electrical Activity in Pancreatic B-Cells. Pflugers Arch. 1982, 393, 322–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, X.; Yang, L.; Yi, M.; Jia, Y. RyR Channels and Glucose-Regulated Pancreatic β-Cells. Eur. Biophys. J. Biophys. Lett. 2008, 37, 773–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marks, A.R. Targeting Ryanodine Receptors to Treat Human Diseases. J. Clin. Investig. 2023, 133, e162891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehrens, X.H.; Lehnart, S.E.; Huang, F.; Vest, J.A.; Reiken, S.R.; Mohler, P.J.; Sun, J.; Guatimosim, S.; Song, L.S.; Rosemblit, N.; et al. FKBP12.6 Deficiency and Defective Calcium Release Channel (Ryanodine Receptor) Function Linked to Exercise-Induced Sudden Cardiac Death. Cell 2003, 113, 829–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, J.; Johnson, J.D.; Arvan, P.; Han, J.; Kaufman, R.J. Therapeutic Opportunities for Pancreatic β-Cell ER Stress in Diabetes Mellitus. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2021, 17, 455–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.J.; Lin, C.Y.; Haataja, L.; Gurlo, T.; Butler, A.E.; Rizza, R.A.; Butler, P.C. High Expression Rates of Human Islet Amyloid Polypeptide Induce Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Mediated β-Cell Apoptosis, a Characteristic of Humans with Type 2 but not Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes 2007, 56, 2016–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, T.; Mahadevan, J.; Kanekura, K.; Hara, M.; Lu, S.M.; Urano, F. Calcium Efflux From the Endoplasmic Reticulum Leads to β-Cell Death. Endocrinology 2014, 155, 758–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luciani, D.S.; Gwiazda, K.S.; Yang, T.L.B.; Kalynyak, T.B.; Bychkivska, Y.; Frey, M.H.Z.; Jeffrey, K.D.; Sampaio, A.V.; Underhill, T.M.; Johnson, J.D. Roles of IP3R and RyR Ca2+ Channels in Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and beta-Cell Death. Diabetes 2009, 58, 422–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.D.; Han, Z.Q.; Otani, K.; Ye, H.G.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, H.; Horikawa, Y.; Misler, S.; Bell, G.I.; Polonsky, K.S. RyR2 and Calpain-10 Delineate a Novel Apoptosis Pathway in Pancreatic Islets. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 24794–24802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Takeuchi, T.; Tanaka, S.; Kubo, S.K.; Kayo, T.; Lu, D.H.; Takata, K.; Koizumi, A.; Izumi, T. A Mutation in the Insulin 2 Gene Induces Diabetes with Severe Pancreatic β-Cell Dysfunction in the Mody Mouse. J. Clin. Investig. 1999, 103, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, V.; Boehm, B.O.; Darvasi, A. Identification of a Missense Variant in the WFS1 Gene that Causes a Mild form of Wolfram Syndrome and Is Associated with Risk for Type 2 Diabetes in Ashkenazi Jewish individuals. Diabetologia 2018, 61, 2180–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Q.; Han, S.; Liu, C.C.; Zheng, Y.W.; Li, H.; Gao, F.; Bian, Y.H.; Liu, X.; Liu, H.B.; Hu, S.R.; et al. THADA Inhibition in Mice Protects Against Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus by Improving Pancreatic Beta-Cell Function and Preserving Beta-Cell Mass. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaidya, R.A.; Desai, S.; Moitra, P.; Salis, S.; Agashe, S.; Battalwar, R.; Mehta, A.; Madan, J.; Kalita, S.; Udipi, S.A.; et al. Hyperinsulinemia: An Early Biomarker of Metabolic Dysfunction. Front. Clin. Diabetes Healthc. 2023, 4, 1159664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erickson, J.R.; Joiner, M.L.; Guan, X.; Kutschke, W.; Yang, J.; Oddis, C.V.; Bartlett, R.K.; Lowe, J.S.; O’Donnell, S.E.; Aykin-Burns, N.; et al. A Dynamic Pathway for Calcium-Independent Activation of CaMKII by Methionine Oxidation. Cell 2008, 133, 462–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erickson, J.R.; Pereira, L.; Wang, L.; Han, G.; Ferguson, A.; Dao, K.; Copeland, R.J.; Despa, F.; Hart, G.W.; Ripplinger, C.M.; et al. Diabetic Hyperglycaemia Activates CaMKII and Arrhythmias by O-Linked Glycosylation. Nature 2013, 502, 372–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonis-Bik, A.M.; Nijpels, G.; van Haeften, T.W.; Houwing-Duistermaat, J.J.; Boomsma, D.I.; Reiling, E.; van Hove, E.C.; Diamant, M.; Kramer, M.H.; Heine, R.J.; et al. Gene Variants in the Novel Type 2 Diabetes loci CDC123/CAMK1D, THADA, ADAMTS9, BCL11A, and MTNR1B Affect Different Aspects of Pancreatic Beta-Cell Function. Diabetes 2010, 59, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, V.; Winkelmann, B.R.; Dietrich, J.W.; Boehm, B.O. Whole-Exome Sequencing in Familial Type 2 Diabetes Identifies an Atypical Missense Variant in the RyR2 Gene. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1258982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Spracklen, C.N.; Marenne, G.; Varshney, A.; Corbin, L.J.; Luan, J.; Willems, S.M.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Horikoshi, M. The Trans-Ancestral Genomic Architecture of Glycemic Traits. Nat. Genet. 2021, 53, 840–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downie, C.G.; Dimos, S.F.; Bien, S.A.; Hu, Y.; Darst, B.F.; Polfus, L.M.; Wang, Y.; Wojcik, G.L.; Tao, R.; Raffield, L.M. Multi-Ethnic GWAS and Fine-Mapping of Glycaemic Traits Identify Novel Loci in the PAGE Study. Diabetologia 2022, 65, 477–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, S.; Su, B.B.; Tovar, H.; Mao, C.; Gonzalez, V.; Liu, Y.; Lu, Y.; Wang, K.S.; Xu, C. Polymorphisms Within RYR3 Gene Are Associated With Risk and Age at Onset of Hypertension, Diabetes, and Alzheimer’s Disease. Am. J. Hypertens. 2018, 31, 818–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).