Error in Figure
In the original publication, there was a mistake in Figure 1B as published. The immunohistochemistry image of α-SMA in Figure 1b for patient 4 in our article published in Int. J. Cancer [1] was inadvertently reused as the image for patient 3 in Figure 1B of our manuscript published in Cells [2]. The corrected Figure 1 is as appears below. The authors state that the scientific conclusions are unaffected. This correction was approved by the Academic Editor. The original publication has also been updated.
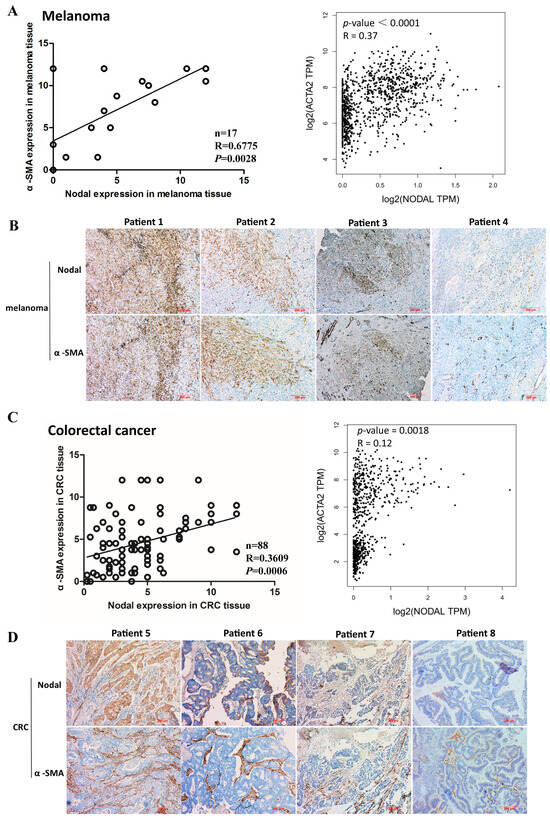
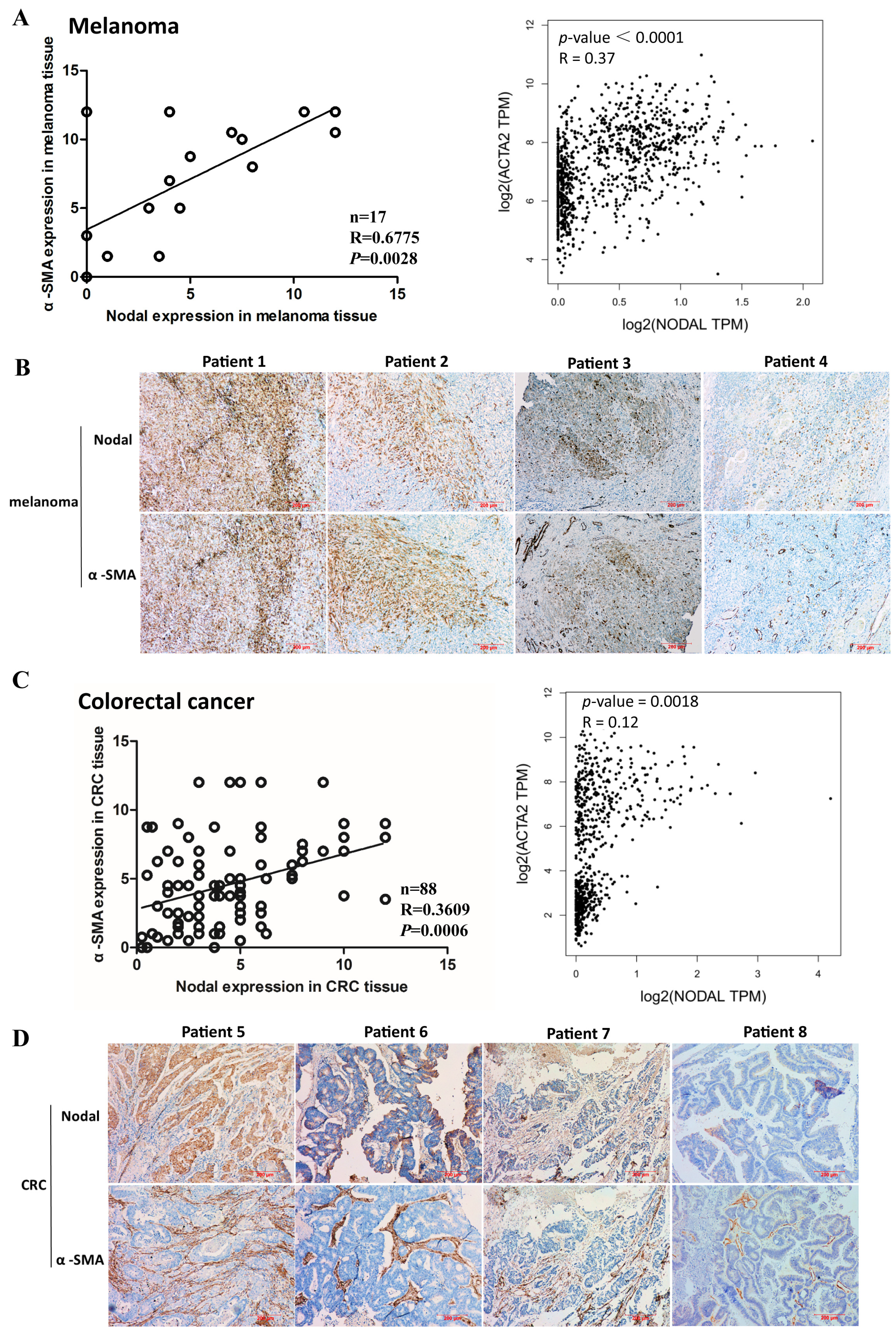
Figure 1.
Correlation of α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) and Nodal expression in human melanoma and colorectal cancer (CRC) tissues. (A) The levels of α-SMA and Nodal expression in human melanoma were detected by immunohistochemistry (IHC) and evaluated (left). Correlation between α-SMA and Nodal mRNA expression in melanoma cancer tissues from the Cancer Genome Atlas Program (TCGA database; right). (B) Representative immunohistochemical images of α-SMA and Nodal expression in human melanoma tissues. (C) The levels of α-SMA and Nodal expression in human CRC were detected by IHC and evaluated (left). Correlation between α-SMA and Nodal mRNA expression in CRC tissues from TCGA database (right). (D) Representative immunohistochemical images of α-SMA and Nodal expression in human CRC tissues.
References
- Li, Z.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, S.; Wang, H.; Du, J. Cancer-associated fibroblasts promote PD-L1 expression in mice cancer cells via secreting CXCL5. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 145, 1946–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, J.; Lu, L.; Wang, H.; Zhang, G.; Wan, G.; Cai, S.; Du, J. Nodal Facilitates Differentiation of Fibroblasts to Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts that Support Tumor Growth in Melanoma and Colorectal Cancer. Cells 2019, 8, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).