Abstract
Background: Brain arteriovenous malformations (BAVMs) and cerebral cavernous malformations (CCMs) are rare developmental anomalies of the intracranial vasculature, with an irregular tendency to rupture, and as of yet incompletely deciphered pathophysiology. Because of their variety in location, morphology, and size, as well as unpredictable natural history, they represent a management challenge. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are strands of non-coding RNA of around 20 nucleotides that are able to modulate the expression of target genes by binding completely or partially to their respective complementary sequences. Recent breakthroughs have been made on elucidating their contribution to BAVM and CCM occurrence, growth, and evolution; however, there are still countless gaps in our understanding of the mechanisms involved. Methods: We have searched the Medline (PubMed; PubMed Central) database for pertinent articles on miRNAs and their putative implications in BAVMs and CCMs. To this purpose, we employed various permutations of the terms and idioms: ‘arteriovenous malformation’, ‘AVM’, and ‘BAVM’, or ‘cavernous malformation’, ‘cavernoma’, and ‘cavernous angioma’ on the one hand; and ‘microRNA’, ‘miRNA’, and ‘miR’ on the other. Using cross-reference search; we then investigated additional articles concerning the individual miRNAs identified in other cerebral diseases. Results: Seven miRNAs were discovered to play a role in BAVMs, three of which were downregulated (miR-18a, miR-137, and miR-195*) and four upregulated (miR-7-5p, miR-199a-5p, miR-200b-3p, and let-7b-3p). Similarly, eight miRNAs were identified in CCM in humans and experimental animal models, two being upregulated (miR-27a and mmu-miR-3472a), and six downregulated (miR-125a, miR-361-5p, miR-370-3p, miR-181a-2-3p, miR-95-3p, and let-7b-3p). Conclusions: The following literature review endeavored to address the recent discoveries related to the various implications of miRNAs in the formation and growth of BAVMs and CCMs. Additionally, by presenting other cerebral pathologies correlated with these miRNAs, it aimed to emphasize the potential directions of upcoming research and biological therapies.
1. Introduction
Brain arteriovenous malformations (BAVMs) are predominantly congenital vascular disorders that may arise anywhere inside of the central nervous system [1,2,3,4,5,6]. They are comprised of one or more arterial feeders supplying a vascular nidus, and one or more draining veins. The nidus itself represents the site where arterial blood is shunted directly into the venous system without an interpolating network of capillaries. As a result, the blood flows at a high pressure through these lesions, making them susceptible to hemorrhagic rupture, this being their most common form of presentation. A small number have also been described as appearing later in life after a different cerebral injury (trauma, infection, stroke, tumors etc.), making their pathophysiology and genetic determination all the more intriguing and poorly understood [7,8].
Cerebral cavernous malformations (CCMs), or cavernomas, are vascular lesions that, unlike BAVMs, are generally small and well delineated, with a low blood flow within them [9,10,11,12,13]. Aside from the majority of them being congenital, they have also been observed to appear in patients subjected to radiosurgery [14,15,16]. They are mostly asymptomatic and discovered incidentally on imaging studies; however, they can present via epilepsy or hemorrhagic stroke. The sporadic occurrence of CCMs typically denotes a single isolated lesion possibly linked to a developmental venous anomaly (DVA), whereas the familial variety leads to the formation of multiple lesions spread diffusely within the brain. Familial forms are correlated with an autosomal dominant mutation in any of the three key CCM genes (CCM1/KRIT1, CCM2/OSM, or CCM3/PDCD10) [10]. Both BAVMs and CCMs can be effectively treated via microsurgical resection, ensuring symptomatic control and prevention of any future hemorrhage occurring from these lesions.
MicroRNAs (miRNA or miR) represent short strands of non-coding ribonucleic acid (RNA), approximately 20–22 nucleotides long, with the capacity to regulate the expression of target genes via the complete or partial binding onto their respective complementary sequences [17,18,19,20,21,22]. As a result, they hamper translation while also stimulating mRNA degradation. Currently, there is a shortage of data concerning the multitude of roles miRNAs play in the pathophysiology of AVMs and CCMs. In the following, we will present a summary of the miRNAs discovered to be dysregulated in these vascular pathologies, along with the pathways affected in other.
2. Methods
The purpose of this review is to offer an illustrative synopsis on the recent findings related to miRNAs associated with BAVMs and CCMs. We explored the electronic databases of Medline (PubMed, PubMed Central) by employing various permutations of the terms and idioms: ‘arteriovenous malformation’, ‘AVM’, and ‘BAVM’, or ‘cavernous malformation’, ‘cavernoma’, and ‘cavernous angioma’ on the one hand, and ‘microRNA’, ‘miRNA’, and ‘miR’ on the other. Afterward, using cross-reference search, we then evaluated further articles pertaining to the individual miRNAs found in other cerebral diseases. We have considered both clinical studies on adult human patients and their pathological specimens, regardless of design, as well as experimental studies performed in vitro and in vivo. This non-systematic review may be significant in light of the increasing interest in the effective management and understating of cerebral vascular malformations.
3. microRNAs Involved in Cerebral Vasculogenesis and Angiogenesis
In order to better understand the pathophysiological implications of microRNAs in BAVMs and CCMs, we believe it necessary to first illustrate the mechanisms of normal vasculogenesis and angiogenesis within the brain. In the early embryonic life, the hemangioblasts emerge from the mesoderm as a response to local fibroblast growth factor (FGF) signaling. The surrounding endoderm secrets isoforms of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and the hemangioblasts express VEGFR2 which is essential for their survival and further differentiation. Once hemangioblasts differentiate, they will turn either into hematopoietic cells that will form the blood-islands or into angioblasts that will undergo vasculogenesis. The angioblasts are immature endothelial cells organized in clusters and express both VEGFR1 and VEGFR2. While VEGFR2 is responsible for proliferation, differentiation, and survival, VEGFR1 has opposite effects and supports the formation of the vascular lumen [23], shaping the primitive blood vessels (Figure 1). Research has been conducted on the effects of miRNAs on vasculogenesis by studying mutant variants with loss of function of the Dicer enzyme, an RNase involved in miRNA maturation. Notably, while knockout of VEGFR2 is correlated with the lack of primitive vascular plexi [24], in Dicerex1/2 mice, even if the blood vessels are thin and disorganized, the presence of the vascular bedding suggests that miRNAs are not crucial for vasculogenesis, but for the next phase of vascular development: angiogenesis [25]. Indeed, Dicerex1/2 mice associated lower levels of Tie1 while VEGF, VEGFR1 and VEGFR2 were upregulated, but this is explained by the formation of abnormal blood vessels that favor local hypoxia and respond via VEGF activation accordingly.
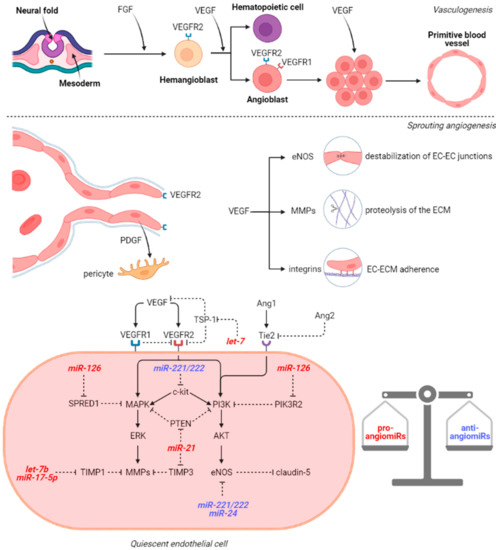
Figure 1.
VEGF signaling pathway in vasculogenesis and angiogenesis. Abbreviations (in alphabetical order): AKT, Protein kinase B; EC, endothelial cell; ECM, endothelial cell membrane; eNOS, nitric oxide synthase; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinases; FGF, fibroblast growth factor; MMPs, metalloproteinases; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; miR, microRNA; PDGF, platelet-derived growth factor; PI3K, Phosphoinositide 3-kinases; PIK3R2, phosphoinositide-3-Kinase Regulatory Subunit 2; PTEN, Phosphatase and tensin homolog; SPRED1, Sprouty Related EVH1 Domain Containing 1; TIMP1/3, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases 1/3; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; VEGFR, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor.
After vasculogenesis, the endothelial cells (ECs) from the primary vascular plexus generate new capillaries by sprouting and non-sprouting angiogenesis. Sprouting angiogenesis is typically seen in brain formation and it is also the prototype for wound healing and tumor angiogenesis whereas non-sprouting angiogenesis involves splitting and fusion of capillaries and mainly occurs in lung development. In physiological sprouting angiogenesis, FGF and VEGF stimulation of the ECs induces the activation of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs): MMP-2 and MMP-9, thus promoting the lysis of the basement membrane and the extracellular matrix (ECM) in the vicinity [26]. VEGF binding to VEGFR also induces endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) phosphorylation which in turn generates nitric oxide. The nitric oxide will further nitrosylate β-catenin which dissociates from VE-cadherin. Normally, the VE-cadherin/β-catenin complex increases the expression of claudin-5 via PI3K/AKT pathway [27]. In this context, VEGF promotes the destabilization of the EC–EC junctions. Therefore, VEGFR2 expressing ECs proliferate and migrate towards the VEGF gradient maintained by the periventricular layer of the neural tube [28]. Moreover, VEGF stimulates the upregulation of integrins (α1β1, α2β1, and αvβ3) which facilitate EC–ECM interactions during the migration. Integrin α5β1 is induced by FGF, IL-8, and TNF-α and potentiate integrin αvβ3-mediated migration [29]. The leading ECs secrete platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) which attracts pericytes and promotes the basement membrane assembly on the migration tract. Not only FGF and VEGF are important in sprouting angiogenesis, but also angiopoietins (Ang1, Ang2, and Ang4) which bind to Tie1 and Tie2 receptors to modulate the response to VEGF. Ang1/Tie2 interaction inhibits the vascular leakage and promotes EC sprouting which is pivotal considering Tie2 knockout mice do not develop brain capillaries and consecutively die in utero [30]. Conversely, in the presence of physiological Ang1 concentrations, Ang2 acts in an opposite manner and leads to vessel destabilization due to the fact that it cannot dissociate the inhibitory Tie1/Tie2 heterodimer, but in the absence of Ang1, Ang2 behaves as a weak agonist of Tie2 [31]. In response to VEGF, Ang2 is released from ECs and orchestrates their plasticity.
Subsequently to the generation of the vascular network, remodeling, pruning and maturation phenomena occur in order to form the functional adult circulatory system. In adult life, angiogenesis is restricted to wound healing, inflammation, and reproduction. In the absence of these triggers, ECs are maintained in a quiescent stage (Figure 1) by the balance between pro-angiogenic (VEGF, FGF, EGF, IFN, MMPs, ANGs) and anti-angiogenic (angioarrestin, angiostatin, IL-12, TSP-1, fibronectin fragment) factors. The network of these stimuli influences the local miRNAome and is also under the control of miRs. Therefore, in physiological conditions, the most abundant miRs in ECs are both pro-angiomiRs (miR-21, miR-126, let-7 family, miR-23, and miR-17-92 cluster) and anti-angiomiRs (miR-221, miR-222, and miR-24) [32].
miR-126 is considered an endothelial-specific miR and acts by downregulation of the putative genes SPRED1, PIK3R2, and VCAM-1. SPRED1 is an inhibitor of MAPK/ERK pathway, which is activated by upstream signals mediated by VEGFR2. VEGFR2 also activates the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway whereas PIK3R2 inhibits PI3K activation. Throughout these mechanisms, miR-126 facilitates the VEGFR2-mediated migration of ECs. The let-7 family also influences the migration by modulation of VEGF signals. For instance, let-7 family members possibly target thrombospondin-1 (TSP-1), an endogenous inhibitor of angiogenesis. TSP-1 blocks the VEGF pathway by several mechanisms including inhibition of VEGFR2 phosphorylation, direct binding to VEGF, and binding to the inactive form of MMP-9 [33]. Dicer and Drosha knockout in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) results in the upregulation of TSP-1, probably by the decrease of let-7 family [34]. Another study revealed that Dicer blockade influences angiogenesis through miR-17-5p and let-7b which reduce tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 1 (TIMP1) expression and consequently MMPs activity [35]. The other two members of the miR-17-92 cluster, namely miR-18a and miR-19a, were also demonstrated to repress proteins containing thrombospondin type 1 repeats (TSR), angiogenesis inhibitors related to TSP-1 [36]. miR-21, a well-known onco-miR, has angiogenic effects by targeting PTEN, an upstream regulator of both MAPK/ERK and PI3K/AKT pathways, and also by enhancing the expression of HIF-1α and VEGF [37]. Another direct target of miR-21 is TIMP3, whose downregulation promotes MMP-2 and MMP-9 secretion [38]. Regarding anti-angiomiRs, miR-221 and miR-222 have relatively similar targets including c-kit, Ets1, Ets2, ZEB2, STAT5a, and eNOS [39]. ECs express both c-kit and its ligand stem cell factor (SCF) and c-kit activates PI3K/AKT, MAPK/ERK, and JAK/STAT pathways. miR-24 inhibits eNOS, GATA2, PAK4, Delta-like ligand 1 (Dll1), and Notch1 which regulates PDGF, VEGF, and the corresponding receptors, determining proliferation and pericytes recruitment [40].
In hypoxic conditions, HIF-1α contributes to the alteration of miRNAs in HUVECs by upregulating miR-210, let-7a, let-7e, miR-103, miR-107, and to a lesser extent miR-150 and miR-328 [41,42]. miR-210 has been shown to directly target Ephrin A3 (EFNA3), modulating the activity of PI3K/AKT pathway. However, miR-328 is an anti-angiomiR whose target CD44 is involved in EC-EC and EC-ECM interactions [43]. Strikingly, let-7a, let-7e, miR-103, and miR-107 have AGO1 as a putative target and by the inhibition of AGO1-RISC complex, they produce a release in mRNAs that are suppressed during normoxia. Consequently, these miRs facilitate the VEGF desuppression in hypoxia (20). Under VEGF stimulation, miR-155, miR-191, miR-21, and some of the miR-17-92 cluster (miR-18a, miR-17-5p, and miR-20a) are overexpressed in ECs, also shifting the balance towards angiogenic factors [44].
4. microRNAs in Brain Arteriovenous Malformations
In the following paragraphs, we review the miRNAs associated with BAVMs, and also discuss the other pathologies these strands have been linked to. Because the involvement of both miR-137 and miR-195* in BAVMs was researched in the same study [20] and because they possess comparable effects in similar pathologies, they are covered within the same subsection.
4.1. miR-7-5p
Despite the fact that little is known of the implications miR-7-5p has in the development of BAVMs, Chen et al. established that it was significantly upregulated in the serum of patients with these malformations [18]. According to them, the Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) signaling pathway is implicated in 15 of the genes targeted by miR-7-5p, among miR-199a-5p and miR-200b-3p. Several studies showed that miR-7-5p is downregulated in the peripheral blood of glioblastoma patients [45], glioma cell lines and human glioma tissue [46,47], or in the microvasculature of these tumors themselves and targeting the RAF1 oncogene [48]. It has also been proven as protective against ischemia-reperfusion injury in in vivo rat models by some [49], and as aggravating by others [50]. A recent study demonstrated that miR-7-5p was decreased in the serum of patients suffering from hemorrhagic stroke [51]. Should the results extrapolated from rats be accurate, this would mean a diminished inhibition the PI3K/AKT pathway, leading to an increase of aquaporin 4 (AQP4) within the brain edema area caused by the hemorrhage. This was thought to aggravate to edema, while the rats receiving intraperitoneal bultylphthalide presented increased miR-7-5p expression and lower severity brain edema. Considering the evidence at hand, it is unclear whether miR-7-5p stimulates or represses angiogenesis within the developing brain or in a budding congenital vascular lesion. Its involvement in BAVMs other than a hypothetical peripheral biomarker remains to be ascertained.
4.2. miR-18a
Brain endothelial cells (BECs) of BAVMs are considered strikingly active, proliferate and migrate faster than normal endothelial cells, and exhibit atypical functions aside from modified expression levels of growth factors modulating angiogenesis [9,22,52]. Increased levels of thrombospondin-1 (TSP-1), an antagonist of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A (VEGF-A) have been discerned within BAVM BECs, as a result of the high levels of “inhibitor of DNA-binding protein A” (Id-1), which represses the transcription of TSP-1 [19,20,53]. With the aim of downregulating this inhibitor, the intensification via transfection of miR-18a, of the miR-17 to miR-92 cluster, might hamper the chaotic and unfettered growth of BAVMs, even following subtotal surgical resection or embolization. Although miR-17, miR-18a, miR-19a, and miR-20a have displayed antiangiogenic and tumor suppressive activity, most notably when considered independently, they have also been connected to oncogenesis and neoplastic angiogenesis [17,54,55]. The majority of members belonging to the miR-17-92 cluster were upregulated in pediatric brain tumors including medulloblastomas, ependymomas, and astrocytomas, with the highest expression being noticed for miR-18a and miR-18b [56]. Based on the study of Miao et al., miR-18a elevated the permeability of the glioma blood–tumor barrier through the runt-related transcription factor 1 (RUNX1) mediated reduction in tight junction related proteins ZO-1, occludin, and claudin-5 [57]. High expression of miR-18a has been observed in glioblastoma tissues and cell lines, with neogenin, a close relative of Deleted in Colorectal Cancer, as its target [58]. By binding with its ligands in healthy tissues, neogenin adjusts a number of physiological roles such as cellular migration, adhesion, and differentiation, tissular morphogenesis, axon guidance, angiogenesis, and even apoptosis, being regarded as a tumor suppressor in several neoplastic lesions [59,60,61,62,63,64]. Nevertheless, high levels of neogenin have been noticed in diffuse intrinsic pontine gliomas, affecting tumor invasion [65]. Its deficiency was also associated with the Moyamoya-like vasculopathy [66], and its depletion in mouse brains was correlated with abnormally permeable blood vessels with a reduced blood flow, disrupted vascular basement membranes, a declined number of pericytes, compromised BEC barrier, and increased BEC proliferation [67]. It is possible that miR-18a influences neogenin expression in BAVMs, however, to the best of our knowledge, this has yet to be investigated. As demonstrated by Marin-Ramos et al., miR-18a reduces VEGF production by downregulating plasminogen activator inhibitor (PAI-1) levels, the expression of bone morphogenetic protein 4 (BMP4), and diminishing hypoxia inducible factor 1α (HIF-1A) levels [68]. Technically, this can be summarized by a diminished activation of Smad1/5 and Notch signaling. The deterrent in HIF-1A expression via miR-18a transpires under the influence of normoxia, which is ordinarily present in BAVMs. Furthermore, miR-18a also lessened the invasiveness of BAVM BECs, associated with a decline in matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) 2 and 9, and ADAM metallopeptidase domain 10 (ADAM10) levels. As Ferreira et al. indicated, the most obvious effects of miR-18a emerged on cells subjected to different arterial shear flow conditions, its signaling significantly lessening the release of VEGF-A and VEGF-D from BECs of BAVMs [19]. This research was also the first to determine that the internalization of miR-18a can be attained even without a transfection reagent (naked microRNA) in untransformed BECs, and not sacrificing its functionality. Therefore, treatment with miR-18a might be successfully performed in patients with BAVMs in the near future, as long as its oncogenic properties do not lead to the development of cerebral tumors.
4.3. miR-137 and miR-195*
As stated by Huang et al., miR-137 and miR-195* within the vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMC) of BAVMs seemingly possess inferior expression rates than normal [20]. The functional role of these two miRNAs is the repression of cellular migration and tube formation, thereby reducing the survival of VSMCs in vitro. There is a likelihood that this mechanism deters anomalous angiogenesis and participates as a safeguard against the development of BAVMs. Nevertheless, inhibitors of miR-137 and miR-195* did not influence the aforementioned processes, inferring a low baseline level of these two miRNAs. Since the smooth muscles of BAVM vascular walls are hypertrophied, it seems likely that VSMCs are concerned, the actual cause of inflammation, angiogenesis and atheromatosis being the signaling interaction between VSMCs and various other cell types. miR-137 is reportedly involved in alleviating ischemic stroke via the lncRNA GAS5/miR-137 signaling pathway [69], by reducing JAK1 and STAT 1 production [70], or by regulating Src-related oncogenic signaling and disabling the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) cascade [71]. Its overexpression has also been associated with schizophrenia in several studies [72,73,74,75,76,77]. Its level is diminished in glioma cells, miR-137 having been shown to suppress cancer cell invasion, proliferation, and ability to metastasize by deterring the self-renewal process of neoplastic cells and stimulating their differentiation [78,79]. It is highly probable that either Rac1 or Cox-2, targets of miR-137, are accountable for these effects in gliomas [80,81], whereas CSE1L behaves similarly in oligodendroglial tumors and is directly inhibited by the miRNA in question [82]. Since it has been observed that the incidence of gliomas is decreased in schizophrenic individuals, miR-137 expression might be, at least in part, responsible [83]. Huang et al. also uncovered that 54 proteins normally inhibited by miR-137 and miR-195* are overexpressed in BAVM VSMCs, subject to specific signaling pathways that use protein kinase B (Akt), p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (p38MAPK), phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K), extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), VEGF, and nuclear factor kappa-light-chain of activated B cells (NFkB), as mediators [20]. Regarding miR-195*, its downregulation leads to an increase of VEGFA in the infarcted brain [84], therefore its dwindled expression in BAVMs seems veritable. It has similarly exhibited a bolstered expression in schizophrenic patients, conducting toward a decreased brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) level and impaired cognitive functions, although this phenomenon has not been as widely studied [85,86]. On the other hand, Alzheimer’s disease (AD) patients with the lower cognitive performances demonstrated a diminished cerebral miR-195* presence, and elevating it rescued AD-related lysosomal irregularities in inducible pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs)-derived brain cells [87]. Furthermore, it has the capacity to lessen the beta-site APP cleaving enzyme 1 (BACE1) protein level and amyloid-β in mouse brains [88], and to limit amyloid-β accumulation, dendritic degeneration, and neuronal death in rats with chronic brain hypoperfusion [89,90], suggesting that it could be a veritable therapeutic agent for AD. miR-195* ameliorated neural apoptosis in rats subjected to ischemic stroke by suppressing the KLF5-mediated activation of the JNK signaling axis [91], while also displaying the potential to block inflammatory processes via NFkB and promote neural stem cell proliferation and migration after stroke [92]. Lastly, it has also shown tumor suppressive effects in malignant meningiomas by inhibiting fatty acid synthase (FASN) [93], as well as stimulating apoptosis and reducing proliferation and migration in gliomas [94,95]. Currently, it is unclear which of the aforementioned pathways and mechanisms affected by miR-137 and miR-195* are directly involved in BAVM pathophysiology.
4.4. miR-199a-5p
The miRNA in question has exhibited diverse behaviors within different systems and diseases [96]. Two loci of the human genome are tasked with its encoding, namely miR-199a-1 found in chromosome 19, and miR-199a-2 in chromosome 1 respectively, both of them producing the exact same miRNAs (miR-199a-5p and miR-199a-3p). The discrepant methylation of these two loci was observed to result in differential expression levels in gliomas and testicular germ cell tumors, with overexpression in the former and downregulation in the latter [96]. Aside from gliomas, an upregulation of miR-199a-5p has also been observed in cerebral metastases of colorectal cancer [97]. Nevertheless, in the research performed by Wang et al., it was illustrated that microRNA-199a-5p repressed glioma progression, invasion, and migration in vitro by directly targeting magnesium transporter 1 (MAGT1) [98], whereas according to Zhang et al. the same effect was obtained by targeting the membrane-associated ring-CH-type finger 8 (MARCH8) [99]. In glioblastomas, the upregulation of miR-199a-5p by circPVT1 silencing hindered viability, and migration, while also positively influencing apoptosis [100]. Considering the divergent functions of miR-199a-5p concerning brain tumors, it is possible that multiple pathways with opposing effects are also involved in BAVMs. Zhong et al. found increased miR-199a-5p expression in vitro an in vivo mouse models subjected to brain ischemia via MCA occlusion, as opposed to the long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) ANRIL, which was downregulated [101]. They established that either ANRIL overexpression or miR-199a-5p repression could offer a protective effect against cells against cellular ischemic injury via the CAV-1 mediated MEK/ERK pathway, which is directly targeted by miR-199a-5p. Contrariwise, the results by Li et al. suggested that miR-199a-5p itself was protective against cerebral ischemic injury in rats reducing discoidin domain receptor 1 (DDR1) expression [102]. Another study showed that the upregulation of this microRNA helped protect against the ischemia/reperfusion-induced injury in the spinal cord of rats by silencing the ECE1 gene, subsequently constraining caspase-9, Bcl-2, p-JNK, and p-ERK production [103]. As such, the exact role this microRNA plays in triggering or protecting neural cells from ischemia is uncertain. Additionally, miR-199a-5p is known to suppress cellular proliferation and promote apoptosis in hemangiomas by way of HIF-1A signaling [21]. It is also apparent that its inhibition via the lcnRNA H19 escalates the angiogenic potency of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) concomitantly while increasing VEGF-A expression [104]. As reported by Chen et al., miR-199a-5p was consistently upregulated in the serum of BAVM patients, acting via the VEGF pathway [18]. This miRNA can also be utilized as a biomarker for brain AVMs, along with miR-7-5p and miR-200b-3p. In agreement with the findings of Heuslein et al., miR-199a-5p acted as a strong regulator of arteriogenesis, as well as a putative target in the management of peripheral arterial disease [105]. In this study, it suppressed the expression of pro-arteriogenic genes and the in vitro adhesion of monocytes onto endothelial cells, whereas in vivo its overexpression affected both perfusion and arteriogenesis in the limbs of mice. It remains to be demonstrated whether miR-199a-5p has a singular and consistent role in BAVM pathophysiology, or whether it has multiple and possibly conflicting implications.
4.5. miR-200b-3p
An upregulation of miR-200a-3p noticed in the peripheral blood could explain certain features of BAVM pathophysiology, especially in individuals with degenerative alterations of the intrinsic vessels [18]. Zhang et al. showed that miR-200b-3p was also upregulated in neonatal rat brains in the early stage following hypoxia-ischemic injury, and that its inhibition led to a diminished neuronal apoptotic rate [106]. Medulloblastomas exhibit differential expression of miR-200b-3p according to age, with adults presenting an overexpression compared to pediatric patients [107]. Furthermore, miR-200b-3p among other miRNAs was upregulated in patients with brain metastatic gastric adenocarcinomas when compared to patients with this cancer but without cerebral metastases [108]. ZEB2, also referred to as Smad-interacting protein 1 (SIP1) and a known suppressor of the cell-to-cell adhesion molecule E-cadherin [109], was established as the primary target of miR-200b-3p, presenting significant downregulation. According to Li et al., the same mechanism is available for gliomas [110]. Glioma tissues and human glioma cell lines were shown to also have a diminished expression of miR-200b-3p, whereas its increase led to E-cadherin upsurge, declined mesenchymal markers, and a dwindled neoplastic cellular proliferation, migration, and invasion in vitro [111]. The target of this miRNA was identified as extracellular-regulated protein kinase 5 (ERK5). In vivo, miR-200b-3p also demonstrated its suppressive influence on tumor expansion. Hu et al. revealed that miR-200b also regulates the production of lactate dehydrogenase A in gliomas [112], while a recent metanalysis concluded that miRNA-200 expression level might be negatively correlated with the WHO glioma grade of gliomas [113]. The difference of miR-200b-3p expression between gliomas and BAVMs might insinuate that the neoplastic vessels arising in former arise via a different signaling cascade than the ones that constitute the latter. Mouse brains with folate deficiency presented a reduction in miR-200b-3p, alongside miR-106a-5p and miR-339-5p, eliciting a stimulation of the Amyloid Precursor Protein (APP) gene and the subsequent accumulation of amyloid-β [114]. It was suggested that transfection with miR200b/c might inhibit amyloid-β secretion and consecutive cognitive impairment by improving insulin signaling [115]. This could potentially explain one of the pathophysiological mechanisms of AD. Analogously, the brains of mice infected with prions had a lessening in the majority of microRNAs belonging to the miR-200 cluster, including miR-200b-3p, as well as an increase of several of the miRNAs deregulated in AD [116]. The neuroprotector thymosin beta 4 showed promise in mouse models subjected to severe traumatic brain injury, raising the serum levels of both miR-200a-3p and miR-200b-3p [117]. Interestingly, miR-200b-3p and miR-200c-3p have been identified as indicators of cytopathic inflammation produced by cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection [118]. Nonetheless, the means through which this miRNA contributes to the pathophysiology of BAVMs remain ambiguous.
4.6. let-7b-3p
As indicated by Chen et al., increased serum levels of let-7b-3p have been observed in BAVM patients’ serum, although its mechanism is as of yet unclear [18]. Contrarywise, it was significantly downregulated in the serum of individuals with CCMs, as determined in a recent genome-wide association study (GWAS) [119]. In this study, it was determined that let-7b-3p targeted 981 genes, out of which endoglin (ENG), Hes family bHLH transcription factor 1 (HES1), HIF-1A, MAPK1, mindbomb E3 ubiquitin protein ligase 1 (MIB1), occludin (OCLN), programmed cell death 10 (PDCD10), and tight junction protein 1 (TJP1) were relevant to CCM formation. As such, it may be utilized in the future as a prospective diagnostic marker, or even as an angiogenic inhibitor, should its function be fully elucidated. let-7b-3p is particularly downregulated in seizures, along with several other miRNAs [120,121], and is hypothesized to act as a key regulator of various pathways correlated to mesial temporal lobe epilepsy [122], possibly being also implicated in the epileptic manifestation of BAVMs. This assumption demands validation in an upcoming research. After induced middle cerebral artery ischemic stroke in rats, Li et al. ascertained that let-7b-3p had a low expression in both blood and penumbra brain tissue, whereas another microRNA, namely miR-223-3p, had an increased level both in serum and ischemic penumbra [123]. Moreover, let-7b-3p is believed to possess a tumor repressing ability in gliomas, its decreased expression being correlated to a poorer prognosis in patients with these lesions via a disturbed suppression of inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa-B kinase subunit epsilon (IKBKE), E2F2, and the oncogenes KRAS, HMGA2 and MYC [124,125,126]. Findings such as these may highlight that BAVMs and CCMs have distinct pathological cascades that potentially converge at a crossroad, the only difference being the over- or underexpression of a certain microRNA such as let-7b-3p. Finally, the amplified amount of let-7b-3p in patients BAVMs could be the result of the increased blood flow within the affected areas of the brain, based on the observation that its serum levels were diminished after infarct [123]. As CCMs do not possess such a high intralesional flow as BAVMs, and also incorporate areas of reactive gliosis and microhemorrhages, a local response mimicking cerebral ischemia may be the reason this miRNA is downregulated in cavernoma patients. A synopsis of the miRNAs presented, can be found in Table 1, as well as their relative expression levels. Figure 2 shows the currently known pathways of BAVM development wherein miRNAs are involved.

Table 1.
Location, Expression and Putative Targets of Identified microRNAs in Brain Arteriovenous Malformations.
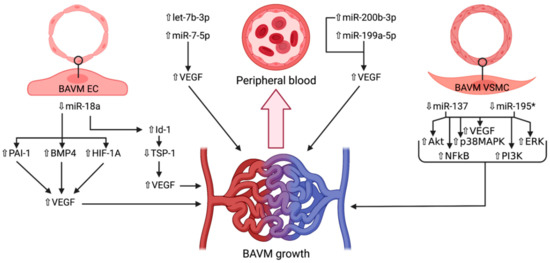
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of the microRNAs and their respective expression levels, putative targets and pathways involved in the development of brain arteriovenous malformations. The microRNAs are divided according to the location wherein they were identified: brain endothelial cells, vascular smooth muscle cells, or peripheral blood. An upward pointing transparent arrow signifies upregulation; a downward pointing transparent arrow denotes downregulation. Abbreviations (in alphabetical order): Akt, protein kinase B; BAVM, brain arteriovenous malformation; BMP4, bone morphogenetic protein; EC, endothelial cell; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; HIF-1A; hypoxia inducible factor 1α; Id-1, inhibitor of DNA-binding protein A; miR, microRNA; NFkB, nuclear factor kappa-light-chain of activated B cells; p38MAPK, p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase; PAI-1, plasminogen activator inhibitor 1; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase; TSP-1, thrombospondin 1; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; VSMC, vascular smooth muscle cell.
5. microRNAs in Cerebral Cavernous Malformations
Below, the miRNAs linked to CCMs are discussed, along with other illnesses possibly influenced by them. miR-27a, miR-125a, and mmu-miR-3472a have been individually studied in several other diseases, as well as in association with other similar acting microRNAs. The genome-wide association study performed by Kar et al. disclosed 52 dysregulated miRNAs in brainstem CCM patients compared to controls, 10 of which were upregulated and 42 downregulated [119]. A more stringent statistical analysis narrowed down five miRNAs (let-7b-5p, miR-361-5p, miR-370-3p, miR-181a-2-3p, and miR-95-3p) as the most significant for CCM, which are discussed ulteriorly in this section, apart the previously reviewed let-7b-5p.
5.1. miR-27a
In the study by Li et al., miR-27a was noticed to be increased in BECs isolated from in vivo mouse model brains harboring early CCM lesions and in cultured BECs displaying either CCM1 or CCM2 depletion [127]. miR-27a acts as an inhibitor of vascular endothelial (VE)-cadherin, and therefore presumably results in a severe disruption of BEC junctional integrity bordering the cavernomas. Additionally, miR-27a operates downstream of Krüppel-like factor (KLF) 2 and 4, whose exaggerated expression are recognized as causative of CCM development independent of VE-cadherin [119,127,128,129]. Knockdown of either KLF2 or KLF4 via small interfering RNA (siRNA) partially decreased miR-27a up-regulation within cultured BECs depleted of CCM2, whereas the simultaneous inhibition of KLF2 and KLF4 completely negated the up-regulation of miR-27a in these cells [127]. This suggests the existence of a regulatory pathway through which the loss of one of the three CCM genes stimulates KLF2/4, resulting in increased miR-27a, which in turn might diminish VE-cadherin expression. miR-27a-3p downregulation in rats was also linked to the upsurge of mitogen-activated protein kinase 4 (MAP2K4) production, resulting in a suppression of hippocampal neuronal apoptosis in epilepsy, both in vivo and in vitro [130]. On the other hand, the intraventricular delivery of a miR-27a-3p mimic in rats suffering from collagenase-induced intracerebral hemorrhage induced a mitigation of brain edema, microvascular leakage, and leukocyte infiltration, as well as an inhibition of neuronal apoptosis and microglia activation within the perihematomal zone by suppressing the overexpression of aquaporin-11 in BECs [131]. Similarly, the induced overexpression of miR-27a in rat brains before traumatic brain injury markedly diminished the neurological deficits and cerebral injury, particularly repressing autophagic activation after trauma occurred [132]. Based on the findings of Sun et al., this happened due to the direct targeting of the Forkhead box O3a (FoxO3a) protein expression and its subsequent suppression. A comparable research performed on mice showed that the administration of mimics of miR-27a along with miR-23a considerably reduced the activation of proapoptotic Bcl-2 family constituents Bax, Noxa, and Puma, lessened the severity of cortical lesion volume and hippocampal neural cell loss, and also undermined markers of caspase-dependent and -independent apoptosis after traumatic brain injury [133]. In the study by Raoof et al., one of the three miRNAs uncovered with biomarker potential in temporal lobe epilepsy in adult patients was miR-27a-3p, the other two being miR-328-3p and miR-654-3p [134]. It may be possible that glycine receptor alpha 2 (GLRA2), with a heightened intracerebral expression and linked to epilepsy is the pathway through which miR-27a-3p operates, an aspect that may also be extrapolated to CCM-induced seizures. Transfection of human BEC lines with miR-27a-3p and miR-222-3p led to a decrease in phosphodiesterase 3 (PDE3) expression, representing a potential link to signaling pathways pertinent to cerebrovascular integrity and healing capacity [135]. According to Tripathi et al., the increased levels of mir-27a was associated with the blockage of oligodendrocyte precursor cell proliferation and differentiation, as well as deficient myelination and remyelination via Wnt-β-catenin signaling disruption [136]. This evidence might suggest a dual role of miR-27a-3p, being both neuroprotective and neurodestructive, according to the targeted pathway. More studies need to be performed on patients harboring CCMs in order to validate these proposed mechanisms and clinical implications.
5.2. miR-125a
miR-125a is essential to the formation of the BEC barrier and is decreased in the affected brains of mice with the deletion of either CCM1 or CCM2 genes [127]. The downregulation of miR-125a has also been observed in children with epilepsy, despite the fact that no connection could be established between this miRNA and the inflammatory cytokines IFN-γ and TNF-α [137]. In rats, miR-125a was decreased in the blood of all models presenting seizures triggered by ischemia, hemorrhage, or kainite toxicity [138], as well as within the hippocampus after pentylenetetrazol-induced epilepsy [139]. In humans, mir-125a-5p has already been identified as a potential biomarker for ischemic stroke [140]. Furthermore, the overexpression of miR-125a-5p resulted in a reduction of seizures and lessened hippocampal inflammation via the suppression of its target gene, calmodulin-dependent protein kinase IV (CAMK4) [139]. Pan et al. showed that microvesicles carrying miR-125a-5p fostered the proliferation, migration, the ability to form tubes of transfected microvessel BECs, improved their apoptotic rate [141], while an earlier study discovered the role of this microRNA in protecting BECs from the injurious effects of oxidized low-density lipoproteins such as, senescence, decrease of nitric oxide (NO), and upsurge of reactive oxygen species (ROS) [142]. It is therefore likely that this microRNA plays a distinctive role in CCM patients presenting with epilepsy, or it could hypothetically act as a biomarker in identifying the cases liable to develop CCM-stimulated seizures.
5.3. mmu-miR-3472a
Koskimäki et al. determined that mmu-miR-3472a presented a differential expression in the serum of mice with or without the loss of the Ccm3/Pdcd10 gene [143]. More interestingly, they discovered that mmu-miR-3472a has cullin associated and neddylation dissociated 2 (CAND2) as the putative target, which was often dysregulated in the transcriptomes of all three models researched (acute, chronic, and control). Also in this study, CAND2, which encodes TIP120b, a muscle-specific TATA-binding protein that is crucial in the process of myogenesis [143,144,145], was downregulated within in vitro BECs, though upregulated within the in vivo neurovascular units (NVUs) of acute and chronic models [143]. CAND2 is associated with the signaling pathway of cullins [146], also coordinating the activity of the Skp, Cullin, and F-box containing complex (SCF complex). Moreover, cullins are known to control the levels of VEGF2R on the surface of vascular endothelial cells via mRNA expression [147], as well as modulate the function of the endothelial barrier through the expression of vascular endothelial (VE)-cadherin, a key constituent of endothelial cell-to-cell adherens junctions. [148]. These factors imply a potential role of CAND2 and mmu-miR-3472a in the development of CCMs. Nevertheless, further research needs to be conducted in order to establish a pathophysiological relationship.
5.4. miR-361-5p
This microRNA was observed as downregulated in the brainstem cavernomas included in the recent GWAS, with possible functional significance [119]. miR-361-5p has been established as a VEGF modulator in coronary artery disease [149], is implicated in the functionality of the blood–brain barrier including the formation of adherens junctions, lymphocyte adhesion to endothelial cells, and the integrity of the extracellular matrix [150], as well as an overexpressed serum biomarker in patients with acute myocardial infarction, ischemic stroke, and pulmonary embolism [151]. In patients with multiple sclerosis, its overexpression has also been correlated with decreased disease severity, suggesting a neuroprotective effect [150]. Among other miRNAs, miR-361-5p behaved as a crucial modulator of X-linked and autosomal genes of intellectual disability [152]. Because of these multiple involvements, miR-361-5p may represent a valid therapeutic target or biomarker for CCMs, although more research on its exact mechanisms is needed.
5.5. miR-370-3p
Regarding brainstem CCMs, miR-370-3p might also present biological or pathophysiological importance for patients harboring lesions at this level by targeting the gene Neurofibromatosis type 1 [119]. Lulli et al. have shown that miR-370-3p expression is markedly downregulated in gliomas when compared to normal brain tissue and neural stem cells [153]. The recovery of miR-370-3p expression in glioblastoma stem-like cells considerably reduced their proliferation, migration, and clonogenic abilities both in vitro, and in vivo models. Amid the genes negatively influenced by the normalized expression of miR-370-3p, EMT-inducer high-mobility group AT-hook 2 (HMGA2), HIF-1A, and the lncRNAs Nuclear Enriched Abundant Transcript (NEAT)1 were ascertained. Additionally, miR-370-3p directly targets the 3′ untranslated region of β-catenin mRNA, consequently inhibiting the expression of the canonical Wnt cascade downstream oncogenes cyclin D1 and c-myc in human gliomas, as well as induces cell cycle arrest within these malignant cells [154]. Moreover, the miR-370-3p-Wnt7a axis modulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition in glioma cells in vitro as well as in vivo, and knockdown of the lncRNA CTBP1-AS2 hindered this process along with proliferation and migration [155]. This translates into a marked repressive effect on glioma cell proliferation by miR-370-3p overexpression or rescue. In an in vivo study, high levels of miR-370-3p were obtained in both brains and serum of mice with sepsis-associated encephalopathy (SAE), though not in sepsis alone or uremia, advocating a specificity towards this type of cerebral lesion [156]. It was hypothesized that TNF-α was responsible for vulnerating neurons to apoptosis in SAE at least partly through miR-370-3p induction. Another possible implication of miR-370-3p could be in primary progressive multiple sclerosis, wherein patients demonstrated significantly dysregulated serum levels of several microRNAs compared to controls, including this one [157]. Whether miR-370-3p downregulation also impacts the formation of CCMs by interfering with inflammatory processes within the brain remains to be validated.
5.6. miR-181a-2-3p
Aside from the downregulation in CCM patients [119], low levels of miR-181a-2-3p, which targets FOXP2, have been linked to a poorer prognosis in patients with glioblastoma, although the exact acting mechanism of FOXP2 in these malignant tumors remains unclear [158]. miR-181a-2-3p is also downregulated under hypoxic conditions in glioblastoma cell lines in vitro [159] and has displayed a statistically significant differential expression between grade III and grade IV glioma cells, with an inferior level within the latter [160]. However, we could not find any additional information correlating this miRNA to other cerebrovascular malformations.
5.7. miR-95-3p
Little is known of the implications miR-95-3p has in pathologies of the brain outside its discovered downregulation in CCM patients recruited in the GWAS by Kar and associates [119]. In an earlier research, it had been shown that miR-95-3p levels were positively correlated to glioma grade, and that a reduction in this microRNA elicited a similar response regarding the ability of glioma cells to proliferate and invade, but enhanced apoptosis [161]. An RNA-binding protein, CUGBP- and ETR-3-like family 2 (CELF2), was incriminated as the presumable target of miR-95-3p, being a likely tumor suppressor. Conversely, the overexpression of miR-95-3p caused a decrease in invasiveness, proliferation, and clonogenicity of metastatic lung adenocarcinoma within the brain by inhibiting oncogene cyclin D1 expression, and as a result prolonging metastasis-free survival [162]. Future studies may shed a light on whether miR-95-3p possesses a pathophysiological role in CCM development, or if its downregulation in this type of lesion was merely incidental. Table 2 summarizes the miRNAs discovered in CCMs, time of discovery, relative expression levels, and possible implications, and Figure 3 illustrates the current findings regarding their signaling pathways and putative targets.

Table 2.
Location, Expression and Putative Targets of Identified microRNAs in Cerebral Cavernous Malformations.
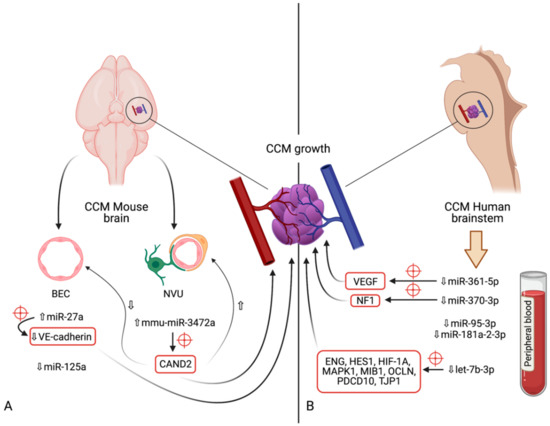
Figure 3.
Diagram indicating the microRNAs and their respective expression levels, putative targets (marked by red crosshairs) and pathways involved in the development of cerebral cavernous malformations. The microRNAs are divided according to the model in which their expression was determined: (A)—mouse models (in vivo); (B)—human brainstem (according to the genome-wide association study by Kar et al. [97]). An upward pointing transparent arrow signifies upregulation; a downward pointing transparent arrow denotes downregulation. Abbreviations (in alphabetical order): BEC, brain endothelial cell; CAND2, cullin associated and neddylation dissociated 2; CCM, cerebral cavernous malformation; ENG, endoglin; HES1, Hes family bHLH transcription factor 1; HIF-1A; hypoxia inducible factor 1α; HMGA2, high-mobility group AT-hook 2; MAPK1, mitogen-activated protein kinase 1; MIB1, mindbomb E3 ubiquitin protein ligase 1; miR, microRNA; NVU, neurovascular unit; OCLN, occludin; PDCD10, programmed cell death 10; TJP1, tight junction protein 1; VE-cadherin, vascular endothelial cadherin.
6. Limitations
Currently, there are significant gaps in our understanding of the roles miRNAs play in the development of intracranial vascular malformations, and the associations described in our review may at times be vague or conjectural. This major limitation is most likely the result of the rarity of these lesions, as well as the definitive and curative nature of the principal treatment methods available, especially surgical removal. As such, a more exhaustive research into the molecular, genetic, and epigenetic mechanisms implicated in their pathophysiology might not seem as attractive as those of incurable and malignant cerebral diseases, where findings in this field may become groundbreaking game changers. However, we are hopeful that the information provided herein would eventually serve as a steppingstone or a solid basis for upcoming research that may provide associations between BAVMs or CCMs and various other brain pathologies. There is a likelihood that by unfolding the roles of miRNAs and their targets will help us in better understanding these malformations and their process of evolution. Should the functions of miRNAs be elucidated, it may also be possible to soon prevent or hinder the development of BAVMs or CCMs, and thus avoid possible life-threatening complications such as severe intracranial hemorrhage, or at least alleviate the complexity of the neurosurgical procedure.
7. Conclusions
Both BAVMs and CCMs are the product of multifarious molecular and genetic factors, with hemodynamic, structural, and degenerative alterations supplying a crucial contribution. However, because of their rarity, studies on the genetic and epigenetic factors involved in the occurrence of these lesions may not seem as appealing or critical as other more frequent cerebral pathologies. As such, our grasp on the miRNAs and affected signaling pathways involved is as of yet lacking, and sometimes based on conjecture. This review aimed to be a succinct and up-to-date summary on our current understanding of the roles of miRNAs and their potential as therapeutic targets or diagnostic biomarkers for BAVMs and CCMs. Despite the fact that many of the mechanisms described in other cerebral pathologies may not be actively involved in the development of intracranial vascular malformations, there is a possibility that at least some common links are present, which can provide valid treatment options in the future. Lastly, while surgery remains the definitive curative therapy for both BAVMs and CCMs, miRNA-targeted therapy may provide an adjuvant management strategy that could assist in neurological recovery after stroke, or hinder vascular malformation growth, thereby lessening the difficulty of the neurosurgical act.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, I.A.F.; A.B. (Andrei Buruiana); T.L.T. and S.S.; methodology, T.L.T. and I.A.F.; formal analysis, I.A.F.; A.B. (Andrei Buruiana) and T.L.T.; investigation, S.S. and T.L.T.; resources, I.A.F.; data curation, I.A.F.; writing—original draft preparation, I.A.F. and T.L.T.—review and editing, A.B. (Adrian Balasa), S.S., I.S.F. and I.B.-N.; visualization, I.A.F. and A.B. (Andrei Buruiana); supervision, A.B. (Adrian Balasa) and I.B.-N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
No funding was received for the preparation of this manuscript.
Acknowledgments
Figures were created using BioRender.com (accessed on 21 April 2021).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors have no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| BAVM | brain arteriovenous malformation |
| CCM | cerebral cavernous malformation |
| miRNA | microRNA |
References
- Abecassis, I.; Xu, D.; Batjer, H.; Al, E. Natural history of brain arteriovenous malformations: A systematic review. Neurosurg Focus. 2014, 37, E7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ion, G.; Chiriac, A.; Dobrin, N.; Poeată, I. Multimodality treatment of brain arteriovenous malformation. Case report. Rom. Neurosurg. 2016, 30, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalb, S.; Gross, B.A.; Nakaji, P. Vascular Malformations (Arteriovenous Malformations and Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas). In Principles of Neurological Surgery, 4th ed.; Ellenbogen, R.G., Sekhar, L.N., Kitchen, N.D., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; Volume 20, pp. 313–324. [Google Scholar]
- Florian, I.S.; Barițchii, A.; Trifoi, S.V. Arterio-venous Mallformations. In Tratat de Chirurgie, 2nd ed.; Popescu, I., Ciuce, C., Eds.; Editura Academiei Române: București, Romania, 2014; Volume VI, pp. 402–410. (In Romanian) [Google Scholar]
- Florian, I.S.; Perju-Dumbravă, L. Therapeutic Options in Hemorrhagic Strokes; Editura Medicală Universitară, Iuliu Hațieganu: Cluj-Napoca, Romania, 2007; pp. 331–346. (In Romanian) [Google Scholar]
- Shetty, R.; Kato, Y.; Watabe, T.; Oguri, D. Unruptured Arteriovenous Malformations of Brain An overview. Rom. Neurosurg. 2010, 17, 34–45. [Google Scholar]
- Florian, I.; Beni, L.; Moisoiu, V.; Timis, T.; Florian, I.; Balașa, A.; Berindan-Neagoe, I. ‘De Novo’ Brain AVMs—Hypotheses for Development and a Systematic Review of Reported Cases. Medicina 2021, 57, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.; Koh, E.J.; Lee, E.J.; Cheon, J.-E.; Kim, S.-K. An acquired cerebral arteriovenous malformation after brain abscess treatment: Case report and a review of the literature. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2021, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertalanffy, H.; Florian, I.A.; Timiș, T.L. Cavernous Malformations of the Pineal Region: Overview, Management, and Controversies. In Pineal Region Lesions; Florian, I.S., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhri, O.; Chen, R.P.; Bulsara, K. Cavernous Malformations of the Brain and Spinal Cord, 4th ed.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iliescu, B.F.; Poeata, I. Cerebral Cavernomas. In Tratat de Chirurgie, 2nd ed.; Popescu, I., Ciuce, C., Eds.; Editura Academiei Române: București, Romania, 2014; Volume VI, pp. 411–414. (In Romanian) [Google Scholar]
- Bozinov, O.; Hatano, T.; Sarnthein, J.; Burkhardt, J.-K.; Bertalanffy, H. Current clinical management of brainstem cavernomas. Swiss Med. Wkly. 2010, 140, w13120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akers, A.; Salman, R.A.-S.; Awad, I.A.; Dahlem, K.; Flemming, K.; Hart, B.; Kim, H.; Jusue-Torres, I.; Kondziolka, D.; Lee, C.; et al. Synopsis of Guidelines for the Clinical Management of Cerebral Cavernous Malformations: Consensus Recommendations Based on Systematic Literature Review by the Angioma Alliance Scientific Advisory Board Clinical Experts Panel. Neurosurgery 2017, 80, 665–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Winkler, E.; Rutledge, C.; Ward, M.; Tihan, T.; Sneed, P.K.; Barbaro, N.; Garcia, P.; McDermott, M.; Chang, E.F. Radiation-induced Cavernous Malformation as a Late Sequelae of Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Epilepsy. Cureus 2018, 10, e2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, S. Cavernous malformation induced by stereotactic radiosurgery: A report and literature review. Neurol. India 2018, 66, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Huang, B.; Liang, R. Radiation-induced cavernous malformation after stereotactic radiosurgery for cavernous sinus meningioma: A case report. BMC Neurol. 2020, 20, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araldi, E.; Suárez, Y. MicroRNAs as regulators of endothelial cell functions in cardiometabolic diseases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2016, 1861, 2094–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Li, Z.; Shi, Y.; Huang, G.; Chen, L.; Tan, H.; Wang, Z.; Yin, C.; Hu, J. Deep Sequencing of Small RNAs in Blood of Patients with Brain Arteriovenous Malformations. World Neurosurg. 2018, 115, e570–e579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, R.; Santos, T.; Amar, A.; Tahara, S.M.; Chen, T.C.; Giannotta, S.L.; Hofman, F.M. MicroRNA-18a improves human cerebral arteriovenous malformation endothelial cell function. Stroke 2014, 45, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Song, J.; Qu, M.; Wang, Y.; An, Q.; Song, Y.; Yan, W.; Wang, B.; Wang, X.; Zhang, S.; et al. MicroRNA-137 and -195* inhibit vasculogenesis in brain arteriovenous malformations. Ann. Neurol. 2017, 82, 371–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Dai, Y.-X.; Wang, S.-Q.; Qiu, M.-K.; Quan, Z.-W.; Liu, Y.-B.; Ou, J.-M. miR-199a-5p inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis in hemangioma cells through targeting HIF1A. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2018, 31, 0394632017749357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zammar, S.G.; El Tecle, N.E.; El Ahmadieh, T.Y.; McClendon, J.; Comair, Y.G.; Bendok, B.R. A Biological Approach to Treating Brain Arteriovenous Malformations. Neurosurgery 2014, 74, N15–N17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, G.-H.; Rossant, J.; Gertsenstein, M.; Breitman, M.L. Role of the Flt-1 receptor tyrosine kinase in regulating the assembly of vascular endothelium. Nature 1995, 376, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalaby, F.; Rossant, J.; Yamaguchi, T.P.; Gertsenstein, M.; Wu, X.-F.; Breitman, M.L.; Schuh, A.C. Failure of blood-island formation and vasculogenesis in Flk-1-deficient mice. Nature 1995, 376, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.J.; Yang, D.D.; Na, S.; Sandusky, G.E.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, G. Dicer Is Required for Embryonic Angiogenesis during Mouse Development. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 9330–9335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, K.A. Angiogenesis. In Encyclopedia of Cell Biology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 102–116. Available online: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/B9780123944474400192 (accessed on 30 April 2021).
- Taddei, A.; Giampietro, C.; Conti, A.; Orsenigo, F.; Breviario, F.; Pirazzoli, V.; Potente, M.; Daly, C.; Dimmeler, S.; Dejana, E. Endothelial adherens junctions control tight junctions by VE-cadherin-mediated upregulation of claudin-5. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 10, 923–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogan, K.A.; Ambler, C.A.; Chapman, D.; Bautch, V.L. The neural tube patterns vessels developmentally using the VEGF signaling pathway. Development 2004, 131, 1503–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rundhaug, J.E. Matrix metalloproteinases and angiogenesis. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2005, 9, 267–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T.N.; Tozawa, Y.; Deutsch, U.; Wolburg-Buchholz, K.; Fujiwara, Y.; Gendron-Maguire, M.; Gridley, T.; Wolburg, H.; Risau, W.; Qin, Y. Distinct roles of the receptor tyrosine kinases Tie-1 and Tie-2 in blood vessel formation. Nature 1995, 376, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seegar, T.C.; Eller, B.; Tzvetkova-Robev, D.; Kolev, M.V.; Henderson, S.C.; Nikolov, D.B.; Barton, W.A. Tie1-Tie2 Interactions Mediate Functional Differences between Angiopoietin Ligands. Mol. Cell 2010, 37, 643–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Olson, E.N. AngiomiRs-Key regulators of angiogenesis. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2009, 19, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawler, P.; Lawler, J. Molecular Basis for the Regulation of Angiogenesis by Thrombospondin-1 and -2. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2012, 2, a006627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuehbacher, A.; Urbich, C.; Zeiher, A.M.; Dimmeler, S. Role of Dicer and Drosha for Endothelial MicroRNA Expression and Angiogenesis. Circ. Res. 2007, 101, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otsuka, M.; Zheng, M.; Hayashi, M.; Lee, J.D.; Yoshino, O.; Lin, S.; Han, J. Impaired microRNA processing causes corpus luteum insufficiency and infertility in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 1944–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dews, M.; Homayouni, A.; Yu, D.; Murphy, D.; Sevignani, C.; Wentzel, E.; Furth, E.E.; Lee, W.M.; Enders, G.H.; Mendell, J.T.; et al. Augmentation of tumor angiogenesis by a Myc-activated microRNA cluster. Nat. Genet. 2006, 38, 1060–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.-Z.; Li, C.; Chen, Q.; Jing, Y.; Carpenter, R.; Jiang, Y.; Kung, H.-F.; Lai, L.; Jiang, B.-H. MiR-21 Induced Angiogenesis through AKT and ERK Activation and HIF-1α Expression. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19139. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Ni, S.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, T.; Wu, T.; Yin, X.; Lang, Y.; Lu, H. The Angiogenic Effect of microRNA-21 Targeting TIMP3 through the Regulation of MMP2 and MMP9. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0149537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chistiakov, D.A.; Sobenin, I.A.; Orekhov, A.N.; Bobryshev, Y.V. Human miR-221/222 in Physiological and Atherosclerotic Vascular Remodeling. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 354517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchetti, M.; Meloni, M.; Anwar, M.; Al-Haj-Zen, A.; Sala-Newby, G.; Slater, S.; Ford, K.; Caporali, A.; Emanueli, C. MicroRNA-24-3p Targets Notch and Other Vascular Morphogens to Regulate Post-ischemic Microvascular Responses in Limb Muscles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fasanaro, P.; D’Alessandra, Y.; Di Stefano, V.; Melchionna, R.; Romani, S.; Pompilio, G.; Capogrossi, M.C.; Martelli, F. MicroRNA-210 Modulates Endothelial Cell Response to Hypoxia and Inhibits the Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Ligand Ephrin-A3. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 15878–15883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Lai, T.-C.; Jan, Y.-H.; Lin, F.-M.; Wang, W.-C.; Xiao, H.; Wang, Y.-T.; Sun, W.; Cui, X.; Li, Y.-S.; et al. Hypoxia-responsive miRNAs target argonaute 1 to promote angiogenesis. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 1057–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyapalan, Z.; Deng, Z.; Shatseva, T.; Fang, L.; He, C.; Yang, B.B. Expression of CD44 3′-untranslated region regulates endogenous microRNA functions in tumorigenesis and angiogenesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 3026–3041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez, Y.; Fernández-Hernando, C.; Yu, J.; Gerber, S.A.; Harrison, K.D.; Pober, J.S.; Iruela-Arispe, M.L.; Merkenschlager, M.; Sessa, W.C. Dicer-dependent endothelial microRNAs are necessary for postnatal angiogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 14082–14087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Li, Y.; Han, C.; Wang, X.; She, L.; Zhang, H. miRNA microarray reveals specific expression in the peripheral blood of glioblastoma patients. Int. J. Oncol. 2014, 45, 746–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Huang, M.; Cai, Y.; Yang, Y.; Sun, X.; Ke, Y. Circ-U2AF1 promotes human glioma via derepressing neuro-oncological ventral antigen 2 by sponging hsa-miR-7-5p. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 9144–9155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Niu, W.; Mu, M.; Hu, S.; Niu, C. Long non-coding RNA LPP-AS2 promotes glioma tumorigenesis via miR-7-5p/EGFR/PI3K/AKT/c-MYC feedback loop. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 39, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Li, L.; Xu, Z.; Bi, B.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.Y. MiR-7-5p is frequently downregulated in glioblastoma microvasculature and inhibits vascular endothelial cell proliferation by targeting RAF1. Tumor Biol. 2014, 35, 10177–10184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Nie, B.; Liu, L.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, M.; Mei, Y. Curcumin Prevents Brain Damage and Cognitive Dysfunction During Ischemic-reperfusion Through the Regulation of miR-7-5p. Curr. Neurovascular Res. 2020, 16, 441–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, B. MiR-7-5p Enhances Cerebral Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury by Degrading sirt1 mRNA. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2020, 76, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Deng, S.; Lei, Q.; He, Q.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Nie, J.; Lu, W. miR-7-5p Affects Brain Edema After Intracerebral Hemorrhage and Its Possible Mechanism. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 598020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Xu, H.; Qin, Z.; Zhang, J.; Yang, X.; Xu, F. Increased Expression of Angiogenic Factors in Cultured Human Brain Arteriovenous Malformation Endothelial Cells. Cell Biophys. 2014, 70, 443–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangel-Castilla, L.; Russin, J.J.; Martinez-Del-Campo, E.; Soriano-Baron, H.; Spetzler, R.F.; Nakaji, P. Molecular and cellular biology of cerebral arteriovenous malformations: A review of current concepts and future trends in treatment. Neurosurg. Focus 2014, 37, E1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolenda, T.; Guglas, K.; Kopczyńska, M.; Sobocińska, J.; Teresiak, A.; Bliźniak, R.; Lamperska, K. Good or not good: Role of miR-18a in cancer biology. Rep. Pract. Oncol. Radiother. 2020, 25, 808–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Wang, M.; Deng, D. c-Fos/microRNA-18a feedback loop modulates the tumor growth via HMBOX1 in human gliomas. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 107, 1705–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruszka, R.; Zakrzewski, K.; Liberski, P.P.; Zakrzewska, M. mRNA and miRNA Expression Analyses of the MYC/E2F/miR-17-92 Network in the Most Common Pediatric Brain Tumors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.-S.; Zhao, Y.-Y.; Zhao, L.-N.; Wang, P.; Liu, Y.-H.; Ma, J.; Xue, Y.-X. MiR-18a increased the permeability of BTB via RUNX1 mediated down-regulation of ZO-1, occludin and claudin-5. Cell. Signal. 2015, 27, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Wang, P.; Zhao, W.; Yao, Y.; Liu, X.; Ma, J.; Xue, Y.; Liu, Y. MiR-18a regulates the proliferation, migration and invasion of human glioblastoma cell by targeting neogenin. Exp. Cell Res. 2014, 324, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, N.H.; Key, B. Neogenin: One receptor, many functions. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2007, 39, 874–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, S.J.; Bradford, D.; Cooper, H.M. Neogenin: A multi-functional receptor regulating diverse developmental processes. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2007, 39, 1569–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vries, M.; Cooper, H.M. Emerging roles for neogenin and its ligands in CNS development. J. Neurochem. 2008, 106, 1483–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, S.P.; De Wever, O.; Bruyneel, E.; Rooney, R.J.; Gespach, C. Opposing roles of netrin-1 and the dependence receptor DCC in cancer cell invasion, tumor growth and metastasis. Oncogene 2007, 26, 5615–5625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tian, Y.; Li, Z.; Zheng, Z.; Zhu, L. miR-92 regulates the proliferation, migration, invasion and apoptosis of glioma cells by targeting neogenin. Open Med. 2020, 15, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Li, Y.; Wan, X.; Kayira, T.M.; Cao, R.; Ju, X.; Zhu, X.; Zhao, G. Down-Regulation of Neogenin Accelerated Glioma Progression through Promoter Methylation and Its Overexpression in SHG-44 Induced Apoptosis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e38074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sesen, J.; Driscoll, J.; Shah, N.; Moses-Gardner, A.; Luiselli, G.; Alexandrescu, S.; Zurakowski, D.; Baxter, P.A.; Su, J.M.; Fehnel, K.P.; et al. Neogenin is highly expressed in diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma and influences tumor invasion. Brain Res. 2021, 1762, 147348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, X.; Yao, L.-L.; Pan, J.-X.; Zhang, J.-S.; Mei, L.; Wang, Y.-G.; Xiong, W.-C. Linking cortical astrocytic neogenin deficiency to the development of Moyamoya disease–like vasculopathy. Neurobiol. Dis. 2021, 154, 105339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.-L.; Hu, J.-X.; Li, Q.; Lee, D.; Ren, X.; Zhang, J.-S.; Sun, D.; Zhang, H.-S.; Wang, Y.-G.; Mei, L.; et al. Astrocytic neogenin/netrin-1 pathway promotes blood vessel homeostasis and function in mouse cortex. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 6490–6509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marín-Ramos, N.I.; Thein, T.Z.; Ghaghada, K.B.; Chen, T.C.; Giannotta, S.L.; Hofman, F.M. miR-18a Inhibits BMP4 and HIF-1α Normalizing Brain Arteriovenous Malformations. Circ. Res. 2020, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Cai, Q.; Lin, S.; Chen, B.; Jia, B.; Ye, R.; Weygant, N.; Chu, J.; Peng, J. Qingda granule exerts neuroprotective effects against ischemia/reperfusion-induced cerebral injury via lncRNA GAS5/miR-137 signaling pathway. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2021, 18, 1687–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Ge, D.; Su, Z.; Qi, B. miR-137 alleviates focal cerebral ischemic injury in rats by regulating JAK1/STAT1 signaling pathway. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2020, 39, 816–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, R.; Wu, B.; Fu, C.; Guo, K. miR-137 prevents inflammatory response, oxidative stress, neuronal injury and cognitive impairment via blockade of Src-mediated MAPK signaling pathway in ischemic stroke. Aging 2020, 12, 10873–10895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacheco, A.; Berger, R.; Freedman, R.; Law, A.J. A VNTR Regulates miR-137 Expression Through Novel Alternative Splicing and Contributes to Risk for Schizophrenia. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arakawa, Y.; Yokoyama, K.; Tasaki, S.; Kato, J.; Nakashima, K.; Takeyama, M.; Nakatani, A.; Suzuki, M. Transgenic mice overexpressing miR-137 in the brain show schizophrenia-associated behavioral deficits and transcriptome profiles. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0220389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandratsenka, H.; Nestsiarovich, A.; Goloenko, I.; Danilenko, N.; Makarevich, A.; Obyedkov, V.; Davydenko, O.; Waszkiewicz, N. Association of MIR137 With Symptom Severity and Cognitive Functioning in Belarusian Schizophrenia Patients. Front. Psychiatry 2018, 9, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Shang, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, T.; Nie, F.; Song, X.; Zhao, H.; Zhu, C.; Zhang, R.; Hao, D. Identification of miR-22-3p, miR-92a-3p, and miR-137 in peripheral blood as biomarker for schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res. 2018, 265, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudesh, R.; Thalamuthu, A.; John, S.; Thara, R.; Mowry, B.; Munirajan, A.K. Replication of GWAS identified miR-137 and its target gene polymorphisms in Schizophrenia of South Indian population and meta-analysis with Psychiatric Genomics Consortium. Schizophr. Res. 2018, 199, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, K.; Crowley, J.J. A comprehensive review of the genetic and biological evidence supports a role for MicroRNA-137 in the etiology of schizophrenia. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 2018, 177, 242–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bier, A.; Giladi, N.; Kronfeld, N.; Lee, H.K.; Cazacu, S.; Finniss, S.; Xiang, C.; Poisson, L.; Decarvalho, A.C.; Slavin, S.; et al. MicroRNA-137 is downregulated in glioblastoma and inhibits the stemness of glioma stem cells by targeting RTVP-1. Oncotarget 2013, 4, 665–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, M.-L.; Hsieh, T.-H.; Ng, K.-H.; Tsai, Y.-N.; Tsai, C.-F.; Chao, M.-E.; Liu, D.-J.; Chu, S.-S.; Chen, W.; Liu, Y.-R.; et al. Downregulation of miR-137 and miR-6500-3p promotes cell proliferation in pediatric high-grade gliomas. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 19723–19737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, G.; Cao, Y.; Shi, L.; Sun, L.; Wang, Y.; Chen, C.; Wan, Z.; Fu, L.; You, Y. Overexpressed miRNA-137 Inhibits Human Glioma Cells Growth by Targeting Rac1. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 2013, 28, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Yan, W.; Han, L.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Feng, Y.; et al. miR-137 is frequently down-regulated in glioblastoma and is a negative regulator of Cox-2. Eur. J. Cancer 2012, 48, 3104–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.K.-W.; Yang, L.; Pang, J.C.-S.; Chan, A.K.-Y.; Zhou, L.; Mao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Lau, K.-M.; Poon, W.S.; Shi, Z.; et al. MIR-137 Suppresses Growth and Invasion, is Downregulated in Oligodendroglial Tumors and Targets CSE1L. Brain Pathol. 2012, 23, 426–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Mi, Y.; Guo, N.; Xu, H.; Jiang, P.; Zhang, R.; Xu, L. Glioma in Schizophrenia: Is the Risk Higher or Lower? Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.-J.; Zhang, H.-F.; Su, J.-Y. Downregulation of microRNA-195 promotes angiogenesis induced by cerebral infarction via targeting VEGFA. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 5434–5440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.; Feng, W.; Li, Y.; Huang, J.; Chen, S.; Cui, Y.; Tian, B.; Tan, S.; Wang, Z.; Yao, S.; et al. The microRNA-195-BDNF pathway and cognitive deficits in schizophrenia patients with minimal antipsychotic medication exposure. Transl. Psychiatry 2021, 11, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Bao, C.; Lv, Q.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Y.; Lang, X.; Li, Z.; Yi, Z. Sex difference in cognitive impairment in drug-free schizophrenia: Association with miR-195 levels. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2020, 119, 104748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Huang, M.; Guo, L.; Zhu, L.; Hou, J.; Zhang, L.; Pero, A.; Ng, S.; El Gaamouch, F.; Elder, G.; et al. MicroRNA-195 rescues ApoE4-induced cognitive deficits and lysosomal defects in Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis. Mol. Psychiatry 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.-C.; Wang, L.-M.; Wang, M.; Song, B.; Tan, S.; Teng, J.-F.; Duan, D.-X. MicroRNA-195 downregulates Alzheimer’s disease amyloid-β production by targeting BACE1. Brain Res. Bull. 2012, 88, 596–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, J.; Sun, L.-H.; Che, H.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, T.-Z.; Wu, W.-C.; Su, X.-L.; Chen, X.; Yang, G.; Li, K.; et al. MicroRNA-195 Protects Against Dementia Induced by Chronic Brain Hypoperfusion via Its Anti-Amyloidogenic Effect in Rats. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 3989–4001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Jiang, X.-M.; Zhao, L.-J.; Sun, L.-L.; Yan, M.-L.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, S.; Duan, M.-J.; Zhao, H.-M.; Li, W.-R.; et al. MicroRNA-195 prevents dendritic degeneration and neuron death in rats following chronic brain hypoperfusion. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, L.; Zhang, W.; Shi, S.; Peng, Y.; Wang, D.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J. microRNA-195 attenuates neuronal apoptosis in rats with ischemic stroke through inhibiting KLF5-mediated activation of the JNK signaling pathway. Mol. Med. 2020, 26, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.-Y.; Wang, Y.-S.; Hsu, P.-Y.; Chen, C.-Y.; Liao, Y.-C.; Juo, S.-H.H. miR-195 Has a Potential to Treat Ischemic and Hemorrhagic Stroke through Neurovascular Protection and Neurogenesis. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2019, 13, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, L.-R.; Li, D.; Weng, J.-C.; Li, C.-B.; Wang, L.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, J.-T. MicroRNA-195 Functions as a Tumor Suppressor by Directly Targeting Fatty Acid Synthase in Malignant Meningioma. World Neurosurg. 2020, 136, e355–e364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Tian, Y.; An, S.; Yang, D. Effects of microRNA-195 on the Prognosis of Glioma Patients and the Proliferation and Apoptosis of Human Glioma Cells. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2020, 26, 753–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.-P.; Zhang, N.-N.; Ren, X.-Q.; He, J.; Li, Y. miR-103/miR-195/miR-15b Regulate SALL4 and Inhibit Proliferation and Migration in Glioma. Molecules 2018, 23, 2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.; Cheung, H.H.; Lee, T.L.; Lu, G.; Poon, W.S.; Chan, W.Y. Molecular Mechanisms of Regulation and Action of microRNA-199a in Testicular Germ Cell Tumor and Glioblastomas. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e83980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Gu, X.-D.; Fang, Y.; Xiang, J.; Chen, Z. microRNA expression profiles in human colorectal cancers with brain metastases. Oncol. Lett. 2012, 3, 346–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, D.; Luo, C.; Zhang, B.; Sun, X. microRNA-199a-5p suppresses glioma progression by inhibiting MAGT1. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 15248–15254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Chen, Q.; Zhu, J.-W.; Liu, Z.-F. MicroRNA-199a-5p regulates glioma progression via targeting MARCH8. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 7482–7487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, G.; Yang, F.; Xu, D.; Liu, W. Silencing hsa_circ_PVT1 (circPVT1) suppresses the growth and metastasis of glioblastoma multiforme cells by up-regulation of miR-199a-5p. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2020, 48, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, W.; Li, Y.-C.; Huang, Q.-Y.; Tang, X.-Q. lncRNA ANRIL Ameliorates Oxygen and Glucose Deprivation (OGD) Induced Injury in Neuron Cells via miR-199a-5p/CAV-1 Axis. Neurochem. Res. 2020, 45, 772–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Luan, L.; Liu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Lan, X.; Li, Z.; Liu, W. MiRNA-199a-5p Protects Against Cerebral Ischemic Injury by Down-Regulating DDR1 in Rats. World Neurosurg. 2019, 131, e486–e494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, N.; Fang, B.; Lv, H.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, F.; Wang, Z.; Ma, H. Upregulation of miR-199a-5p Protects Spinal Cord Against Ischemia/Reperfusion-Induced Injury via Downregulation of ECE1 in Rat. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 38, 1293–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, J.; Wang, L.; Wu, Q.; Zheng, G.; Long, H.; Wu, H.; Zhou, C.; Guo, T.; Zhong, T.; Wang, L.; et al. Long noncoding RNA H19 upregulates vascular endothelial growth factor A to enhance mesenchymal stem cells survival and angiogenic capacity by inhibiting miR-199a-5p. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2018, 9, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heuslein, J.L.; Gorick, C.M.; McDonnell, S.P.; Song, J.; Annex, B.H.; Price, R.J. Exposure of Endothelium to Biomimetic Flow Waveforms Yields Identification of miR-199a-5p as a Potent Regulator of Arteriogenesis. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2018, 12, 829–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Yang, L.; Meng, L.; Cui, H. Inhibition of miR-200b-3p alleviates hypoxia-ischemic brain damage via targeting Slit2 in neonatal rats. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 523, 931–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visani, M.; Marucci, G.; De Biase, D.; Giangaspero, F.; Buttarelli, F.R.; Brandes, A.A.; Franceschi, E.; Acquaviva, G.; Ciarrocchi, A.; Rhoden, K.J.; et al. miR-196B-5P and miR-200B-3P Are Differentially Expressed in Medulloblastomas of Adults and Children. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minn, Y.-K.; Lee, D.; Hyung, W.; Kim, J.; Choi, J.; Yang, S.-H.; Song, H.; Lim, B.; Kim, S.H. MicroRNA-200 family members and ZEB2 are associated with brain metastasis in gastric adenocarcinoma. Int. J. Oncol. 2014, 45, 2403–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comijn, J.; Berx, G.; Vermassen, P.; Verschueren, K.; van Grunsven, L.; Bruyneel, E.; Mareel, M.; Huylebroeck, D.; van Roy, F. The Two-Handed E Box Binding Zinc Finger Protein SIP1 Downregulates E-Cadherin and Induces Invasion. Mol. Cell 2001, 7, 1267–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yuan, J.; Yuan, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Z.; Weng, L.; Liu, J. MicroRNA-200b inhibits the growth and metastasis of glioma cells via targeting ZEB2. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 48, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Cui, H.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, L. MicroRNA-200b-3p suppresses epithelial-mesenchymal transition and inhibits tumor growth of glioma through down-regulation of ERK5. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 478, 1158–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.; Jiang, Q.; Luo, D.; Zhao, L.; Fu, X.; Chen, Y.; Song, X.; Li, L.; Zhao, H.; He, Y.; et al. miR-200b is a key regulator of tumor progression and metabolism targeting lactate dehydrogenase A in human malignant glioma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 48423–48431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, X.; Gong, S.; Yan, T.; Yang, Y. MicroRNA-200b expression level is negatively associated with pathological grading in human gliomas. Cancer Manag. Res. 2018, 10, 2825–2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Tian, T.; Qin, S.; Li, W.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Gao, Y.; Huang, G. Folic acid deficiency enhances abeta accumulation in APP/PS1 mice brain and decreases amyloid-associated miRNAs expression. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2015, 26, 1502–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higaki, S.; Muramatsu, M.; Matsuda, A.; Matsumoto, K.; Satoh, J.-I.; Michikawa, M.; Niida, S. Defensive effect of microRNA-200b/c against amyloid-beta peptide-induced toxicity in Alzheimer’s disease models. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0196929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boese, A.S.; Saba, R.; Campbell, K.; Majer, A.; Medina, S.; Burton, L.; Booth, T.F.; Chong, P.; Westmacott, G.R.; Dutta, S.M.; et al. MicroRNA abundance is altered in synaptoneurosomes during prion disease. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2016, 71, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osei, J.; Kelly, W.; Toffolo, K.; Donahue, K.; Levy, B.; Bard, J.; Wang, J.; Levy, E.; Nowak, N.; Poulsen, D. Thymosin beta 4 induces significant changes in the plasma miRNA profile following severe traumatic brain injury in the rat lateral fluid percussion injury model. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2018, 18, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.H.; Lim, B.J.; Ferreira, V.H.; Min, S.Y.; Hong, Y.-M.; Jo, J.-H.; Han, S.H. Expression of human miR-200b-3p and -200c-3p in cytomegalovirus-infected tissues. Biosci. Rep. 2018, 38, BSR20180961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kar, S.; Bali, K.K.; Baisantry, A.; Geffers, R.; Samii, A.; Bertalanffy, H. Genome-Wide Sequencing Reveals MicroRNAs Downregulated in Cerebral Cavernous Malformations. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 61, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsharafi, W.A.; Xiao, B.; Abuhamed, M.M.; Luo, Z. miRNAs: Biological and clinical determinants in epilepsy. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2015, 8, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, P.K.; Roncon, P.; Lukasiuk, K.; Gorter, J.A.; Aronica, E.; Pitkänen, A.; Petretto, E.; Johnson, M.R.; Simonato, M. Meta-Analysis of MicroRNAs Dysregulated in the Hippocampal Dentate Gyrus of Animal Models of Epilepsy. Eneuro 2017, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mills, J.D.; van Vliet, E.; Chen, B.J.; Janitz, M.; Anink, J.J.; Baayen, J.C.; Idema, S.; Devore, S.; Friedman, D.; Diehl, B.; et al. Coding and non-coding transcriptome of mesial temporal lobe epilepsy: Critical role of small non-coding RNAs. Neurobiol. Dis. 2020, 134, 104612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Chen, L.; Zhou, X.; Li, J.; Liu, J. miRNA-223-3p and let-7b-3p as potential blood biomarkers associated with the ischemic penumbra in rats. Acta Neurobiol. Exp. 2019, 79, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Hao, S.; Ye, M.; Zhang, A.; Nan, Y.; Wang, G.; Jia, Z.; Yuan, T.; Guo, L.; Pu, P.; et al. MicroRNAs let-7b/i suppress human glioma cell invasion and migration by targeting IKBKE directly. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 458, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, N.; Zhang, D.; Wan, C.; Zhao, S.; Kong, Y.; Yuan, L. Let-7b inhibits the malignant behavior of glioma cells and glioma stem-like cells via downregulation of E2F2. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 72, 733–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakrzewska, M.; Gruszka, R.; Stawiski, K.; Fendler, W.; Kordacka, J.; Grajkowska, W.; Daszkiewicz, P.; Liberski, P.P.; Zakrzewski, K. Expression-based decision tree model reveals distinct microRNA expression pattern in pediatric neuronal and mixed neuronal-glial tumors. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhao, Y.; Choi, J.; Ting, K.K.; Coleman, P.; Chen, J.; Cogger, V.C.; Wan, L.; Shi, Z.; Moller, T.; et al. Targeting miR-27a/VE-cadherin interactions rescues cerebral cavernous malformations in mice. PLoS Biol. 2020, 18, e3000734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Tang, A.T.; Wong, W.-Y.; Bamezai, S.; Goddard, L.M.; Shenkar, R.; Zhou, S.; Yang, J.; Wright, A.C.; Foley, M.; et al. Cerebral cavernous malformations arise from endothelial gain of MEKK3–KLF2/4 signalling. Nature 2016, 532, 122–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuttano, R.; Rudini, N.; Bravi, L.; Corada, M.; Giampietro, C.; Papa, E.; Morini, M.F.; Maddaluno, L.; Baeyens, N.; Adams, R.H.; et al. KLF 4 is a key determinant in the development and progression of cerebral cavernous malformations. EMBO Mol. Med. 2016, 8, 6–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Zhou, N.; Yang, P.; Deng, L.; Liu, G. MicroRNA-27a-3p Downregulation Inhibits Inflammatory Response and Hippocampal Neuronal Cell Apoptosis by Upregulating Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase 4 (MAP2K4) Expression in Epilepsy: In Vivo and In Vitro Studies. Med. Sci. Monit. 2019, 25, 8499–8508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, T.; Jin, F.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, J.; Tang, L.; Wang, Y.; Liebeskind, D.S.; Scalzo, F.; He, Z. miR-27a-3p protects against blood–brain barrier disruption and brain injury after intracerebral hemorrhage by targeting endothelial aquaporin-11. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 20041–20050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Zhao, M.; Wang, Y.; Liu, A.; Lv, M.; Li, Y.; Yang, X.; Wu, Z. Neuroprotective effects of miR-27a against traumatic brain injury via suppressing FoxO3a-mediated neuronal autophagy. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 482, 1141–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabirzhanov, B.; Zhao, Z.; Stoica, B.A.; Loane, D.J.; Wu, J.; Borroto, C.; Dorsey, S.G.; Faden, A.I. Downregulation of miR-23a and miR-27a following Experimental Traumatic Brain Injury Induces Neuronal Cell Death through Activation of Proapoptotic Bcl-2 Proteins. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 10055–10071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raoof, R.; Bauer, S.; El Naggar, H.; Connolly, N.; Brennan, G.P.; Brindley, E.; Hill, T.; McArdle, H.; Spain, E.; Forster, R.J.; et al. Dual-center, dual-platform microRNA profiling identifies potential plasma biomarkers of adult temporal lobe epilepsy. EBioMedicine 2018, 38, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasmeen, S.; Kaur, S.; Mirza, A.H.; Brodin, B.; Pociot, F.; Kruuse, C. miRNA-27a-3p and miRNA-222-3p as Novel Modulators of Phosphodiesterase 3a (PDE3A) in Cerebral Microvascular Endothelial Cells. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 5304–5314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathi, A.; Volsko, C.; Garcia, J.P.; Agirre, E.; Allan, K.C.; Tesar, P.; Trapp, B.D.; Castelo-Branco, G.; Sim, F.J.; Dutta, R. Oligodendrocyte Intrinsic miR-27a Controls Myelination and Remyelination. Cell Rep. 2019, 29, 904–919.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel, R.H.; Kholoussi, N.M.; Eissa, E.; El Nady, H.G.; Fayed, D.B.; Abdelkawy, R.F.M. MicroRNAs as Immune Regulators of Inflammation in Children with Epilepsy. Int. J. Mol. Cell Med. 2020, 9, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.-Z.; Tian, Y.; Ander, B.P.; Xu, H.; Stamova, B.S.; Zhan, X.; Turner, R.; Jickling, G.; Sharp, F.R. Brain and blood microRNA expression profiling of ischemic stroke, intracerebral hemorrhage, and kainate seizures. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2010, 30, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, L.; Yan, G.; Zhang, W.; Huan, Z.; Li, J. MiR-125a-5p Alleviates Dysfunction and Inflammation of Pentylenetetrazol- induced Epilepsy Through Targeting Calmodulin-dependent Protein Kinase IV (CAMK4). Curr. Neurovascular Res. 2019, 16, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiedt, S.; Prestel, M.; Malik, R.; Schieferdecker, N.; Duering, M.; Kautzky, V.; Stoycheva, I.; Böck, J.; Northoff, B.; Klein, M.; et al. RNA-Seq Identifies Circulating miR-125a-5p, miR-125b-5p, and miR-143-3p as Potential Biomarkers for Acute Ischemic Stroke. Circ. Res. 2017, 121, 970–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Q.; Ma, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zheng, J.; Du, D.; Liao, X.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Bihl, J.; et al. Microvesicles-mediated communication between endothelial cells modulates, endothelial survival, and angiogenic function via transferring of miR-125a-5p. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 3160–3172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Q.; Liao, X.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, B.; Lazartigues, E.; Yang, Y.; Ma, X. MicroRNA-125a-5p alleviates the deleterious effects of ox-LDL on multiple functions of human brain microvessel endothelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2017, 312, C119–C130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koskimäki, J.; Zhang, D.; Li, Y.; Saadat, L.; Moore, T.; Lightle, R.; Polster, S.; Carrión-Penagos, J.; Lyne, S.B.; Zeineddine, H.A.; et al. Transcriptome clarifies mechanisms of lesion genesis versus progression in models of Ccm3 cerebral cavernous malformations. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2019, 7, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, T.; Song, J.; Xu, M.; Lv, L.; Liu, C.; Shen, J.; Huang, Y. NEURL rs6584555 and CAND2 rs4642101 contribute to postoperative atrial fibrillation: A prospective study among Chinese population. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 42617–42624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiraishi, S.; Zhou, C.; Aoki, T.; Sato, N.; Chiba, T.; Tanaka, K.; Yoshida, S.; Nabeshima, Y.; Nabeshima, Y.-I.; Tamura, T.-A. TBP-interacting Protein 120B (TIP120B)/Cullin-associated and Neddylation-dissociated 2 (CAND2) Inhibits SCF-dependent Ubiquitination of Myogenin and Accelerates Myogenic Differentiation. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 9017–9028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldenberg, S.J.; Cascio, T.C.; Shumway, S.D.; Garbutt, K.C.; Liu, J.; Xiong, Y.; Zheng, N. Structure of the Cand1-Cul1-Roc1 Complex Reveals Regulatory Mechanisms for the Assembly of the Multisubunit Cullin-Dependent Ubiquitin Ligases. Cell 2004, 119, 517–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakaue, T.; Sakakibara, I.; Uesugi, T.; Fujisaki, A.; Nakashiro, K.-I.; Hamakawa, H.; Kubota, E.; Joh, T.; Imai, Y.; Izutani, H.; et al. The CUL3-SPOP-DAXX axis is a novel regulator of VEGFR2 expression in vascular endothelial cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaue, T.; Fujisaki, A.; Nakayama, H.; Maekawa, M.; Hiyoshi, H.; Kubota, E.; Joh, T.; Izutani, H.; Higashiyama, S. Neddylated Cullin 3 is required for vascular endothelial-cadherin-mediated endothelial barrier function. Cancer Sci. 2017, 108, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.-W.; Lo, H.-H.; Chiu, Y.-L.; Chang, S.-J.; Huang, P.-H.; Liao, K.-H.; Tasi, C.-F.; Wu, C.-H.; Tsai, T.-N.; Cheng, C.-C.; et al. Dysregulated miR-361-5p/VEGF Axis in the Plasma and Endothelial Progenitor Cells of Patients with Coronary Artery Disease. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemond, C.C.; Healy, B.C.; Tauhid, S.; Mazzola, M.A.; Quintana, F.J.; Gandhi, R.; Weiner, H.L.; Bakshi, R. MRI phenotypes in MS. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2019, 6, e530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Long, G.; Zhao, C.; Li, H.; Chaugai, S.; Wang, Y.; Chen, C.; Wang, D.W. Atherosclerosis-Related Circulating miRNAs as Novel and Sensitive Predictors for Acute Myocardial Infarction. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, T.F.; Piergiorge, R.M.; Dos Santos, J.M.; Gusmao, J.; Pimentel, M.; Santos-Rebouças, C.B. Network Profiling of Brain-Expressed X-Chromosomal MicroRNA Genes Implicates Shared Key MicroRNAs in Intellectual Disability. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2019, 67, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lulli, V.; Buccarelli, M.; Ilari, R.; Castellani, G.; De Dominicis, C.; Di Giamberardino, A.; D′alessandris, Q.G.; Giannetti, S.; Martini, M.; Stumpo, V.; et al. Mir-370-3p Impairs Glioblastoma Stem-Like Cell Malignancy Regulating a Complex Interplay between HMGA2/HIF1A and the Oncogenic Long Non-Coding RNA (lncRNA) NEAT1. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Z.; Wu, T.; Li, Y.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Liu, B.; Chen, Q.; Tian, D. MicroRNA-370-3p inhibits human glioma cell proliferation and induces cell cycle arrest by directly targeting β-catenin. Brain Res. 2016, 1644, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zong, J.; Zhao, C. lncRNA CTBP1-AS2 promotes proliferation and migration of glioma by modulating miR-370-3p–Wnt7a-mediated epithelial–mesenchymal transition. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2020, 98, 661–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visitchanakun, P.; Tangtanatakul, P.; Trithiphen, O.; Soonthornchai, W.; Wongphoom, J.; Tachaboon, S.; Srisawat, N.; Leelahavanichkul, A. Plasma miR-370-3P as a Biomarker of Sepsis-Associated Encephalopathy, the Transcriptomic Profiling Analysis of Microrna-Arrays from Mouse Brains. Shock 2019, 54, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimkhani, S.; Vafaee, F.; Young, P.E.; Hur, S.S.J.; Hawke, S.; Devenney, E.; Beadnall, H.; Barnett, M.H.; Suter, C.M.; Buckland, M.E. Exosomal microRNA signatures in multiple sclerosis reflect disease status. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plata-Bello, J.; Fariña-Jerónimo, H.; Betancor, I.; Salido, E. High Expression of FOXP2 Is Associated with Worse Prognosis in Glioblastoma. World Neurosurg. 2021, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RahulAgrawal, R.; Pandey, P.; Jha, P.; Dwivedi, V.; Sarkar, C.; Kulshreshtha, R. Hypoxic signature of microRNAs in glioblastoma: Insights from small RNA deep sequencing. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piwecka, M.; Rolle, K.; Belter, A.; Barciszewska, A.M.; Żywicki, M.; Michalak, M.; Nowak, S.; Naskręt-Barciszewska, M.Z.; Barciszewski, J. Comprehensive analysis of microRNA expression profile in malignant glioma tissues. Mol. Oncol. 2015, 9, 1324–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, B.; Jiao, B.-H.; Fan, F.-S.; Lu, S.-K.; Song, J.; Guo, C.-Y.; Yang, J.-K.; Yang, L. Downregulation of miR-95-3p inhibits proliferation, and invasion promoting apoptosis of glioma cells by targeting CELF2. Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 47, 1025–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, S.J.; Lee, H.W.; Kim, H.R.; Song, H.J.; Lee, D.H.; Lee, H.; Shin, C.H.; Joung, J.-G.; Kim, D.-H.; Joo, K.M.; et al. Overexpression of microRNA-95-3p suppresses brain metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma through downregulation of cyclin D1. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 20434–20448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).