Improving Leaf GOGAT Activity After the Post-Silking Period Contributes to High Grain Yield with Reduced Nitrogen in N-Efficient Maize
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Experimental Design and Crop Management
2.3. Sampling and Measurements
2.3.1. Grain Yield, Plant N Uptake Efficiency (NupE), Utilization Efficiency (NutE), and N Harvest Index (NHI)
2.3.2. N Accumulation and Transport to Grain
2.3.3. Metabolizing Enzymes
2.3.4. Gene Relative Expression
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Grain Yield, NutE, NupE, and NHI
3.2. N Accumulation and Distribution
3.3. N Transport from Leaf and Stem to Grain
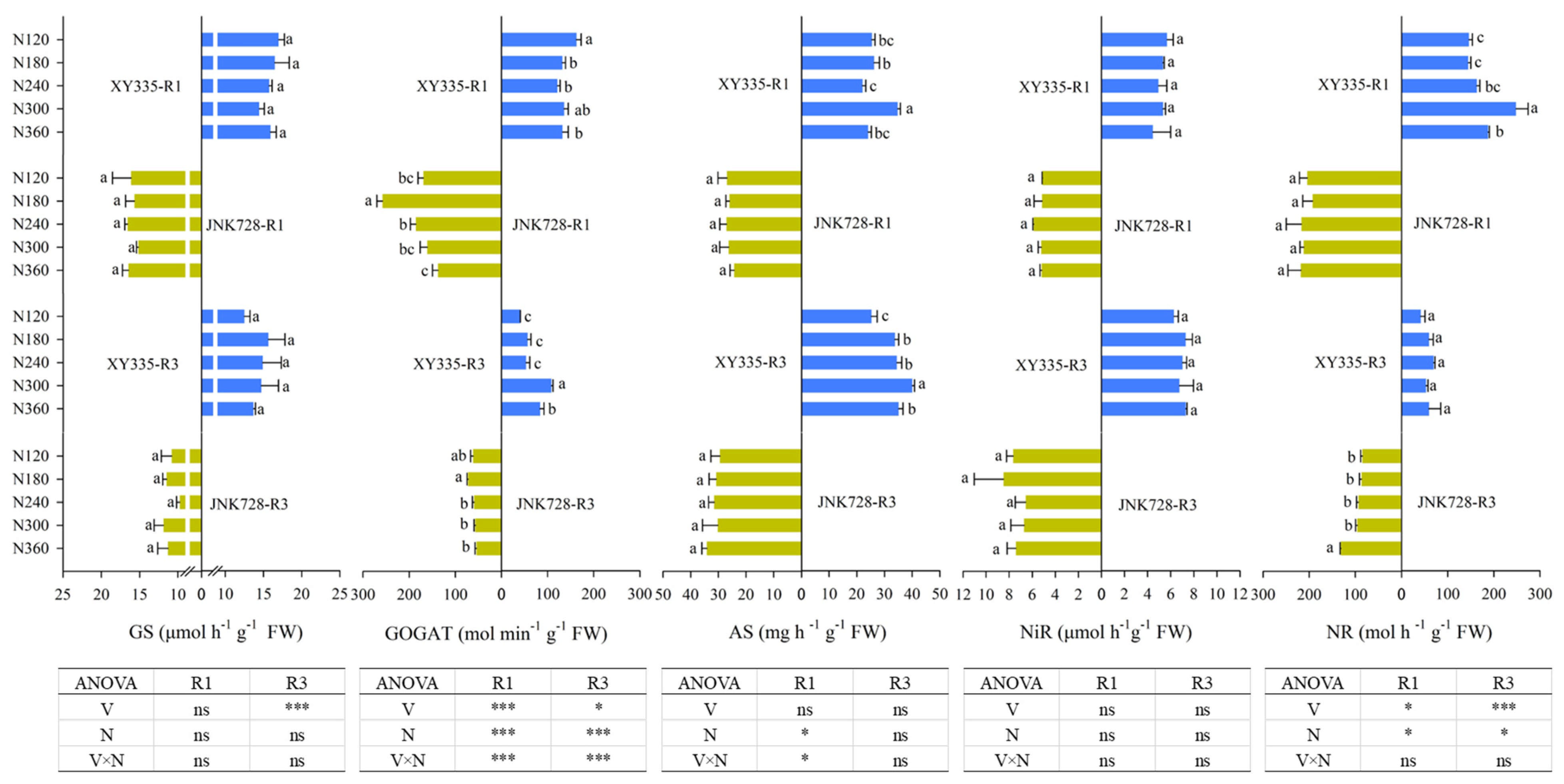
3.4. N Metabolism Enzyme Activities of Leaf
3.5. Relative Expression Levels of Key Genes Encoding Enzymes Related to N Metabolism in Leaves
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peng, Q.; Shen, R.; Li, X.; Ye, T.; Dong, J.; Fu, Y.; Yuan, W. A twenty-year dataset of high-resolution maize distribution in China. Sci. Data 2023, 10, 658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, N.; Meng, Q.; Feng, P.; Qu, Z.; Yu, Y.; Liu, D.L.; Müller, C.; Wang, P. China can be self-sufficient in maize production by 2030 with optimal crop management. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, F.; Wu, Y.; Cui, S.; Wang, X.; Wei, G.; Liu, Q.; Lan, T.; Liu, F.; Zhao, B.; Feng, D.; et al. Effect of chemical fertilizer application on maize production in China over the past 15 years: A meta-analysis. Agronomy 2022, 12, 3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Liu, D.; Liu, M.; Hafeez, M.; Wen, P.; Wang, X.; Wang, R.; Zhang, X.; Li, J. Optimized fertilizer recommendation method for nitrate residue control in a wheat–maize double cropping system in dryland farming. Field Crops Res. 2021, 271, 108258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Pan, X.; Li, J. A 1961–2010 record of fertilizer use, pesticide application and cereal yields: A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2015, 35, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Liu, P.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, X.; Wang, R.; Li, J. Long-term effects of optimized fertilization, tillage and crop rotation on soil fertility, crop yield and economic profit on the Loess Plateau. Eur. J. Agron. 2023, 143, 126731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Guo, S.; Chen, Q.; Chen, F.; Yuan, L.; Mi, G. Use of the stable nitrogen isotope to reveal the source-sink regulation of nitrogen uptake and remobilization during grain filling phase in maize. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, B.; Chen, B.; Zhang, X. Managing Nitrogen to Achieve Sustainable Development Goals in China. 2023, PREPRINT (Version 1) Available at Research Square. Available online: https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-3483975/v1 (accessed on 2 October 2024).
- Bo, Q.; Ma, T.; Wei, X.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.; Tang, A.; Gao, J.; Zhang, J.; Wei, Y.; et al. Improvement of maize post-silking agronomic traits contributes to high grain yield under N-efficient cultivars. Field Crops Res. 2024, 313, 109417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Liu, J.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Z.; Ren, W.; Gong, X.; Wang, L.; Cai, H.; Pan, Q.; Yuan, L.; et al. Breeding for high-yield and nitrogen use efficiency in maize: Lessons from comparison between Chinese and US cultivars. Adv. Agron. 2021, 166, 251–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Davidason, E.A.; Mauzerall, D.L.; Searchinger, T.D.; Dumas, P.; Shen, Y. Managing nitrogen for sustainable development. Nature 2015, 528, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Fang, Z.; Gao, Q.; Ye, Y.; Jia, L.; Yuan, L.; Mi, G.; Zhang, F. Evaluation of the yield and nitrogen use efficiency of the dominant maize hybrids grown in north and Northeast China. Sci. China Life Sci. 2013, 56, 552–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, X.; Ren, Y.; Shi, L.; Dong, X.; Bao, S.; Li, Q. Differences in dry matter production and grain yield of maize (Zea mays L.) cultivars with contrasting nitrogen efficiency. N. Z. J. Crop Hortic. Sci. 2024, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciampitti, I.A.; Murrell, S.T.; Camberato, J.J.; Tuinstra, M.; Xia, Y.; Friedemann, P.; Vyn, T.J. Physiological dynamics of maize nitrogen uptake and partitioning in response to plant density and nitrogen stress factors: II. Reprod. Phase Crop Sci. 2013, 53, 2588–2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liang, Z.; He, X.; Meng, Q.; Hu, Y.; Schmidhalter, U.; Zhang, W.; Zou, C.; Chen, X. Improving grain yield and protein concentration of maize (Zea mays L.) simultaneously by appropriate hybrid selection and nitrogen management. Field Crops Res. 2020, 249, 107754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, X.; Chen, Q.; Chen, F.; Yuan, L.; Mi, G. Within-leaf nitrogen allocation in adaptation to low nitrogen supply in maize during grain-filling stage. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Chen, F.; Chen, Y.; Gao, Q.; Yang, X.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, F.; Mi, G. Modern maize hybrids in Northeast China exhibit increased yield potential and resource use efficiency despite adverse climate change. Glob. Change Biol. 2013, 19, 923–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.L.; Guo, L.G.; Zhou, B.Y.; Tang, X.M.; Chen, C.C.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, S.Y.; Li, C.F.; Xiao, K.; Dong, W.X.; et al. Characterization of low-N responses in maize (Zea mays L.) cultivars with contrasting nitrogen use efficiency in the North China Plain. J. Integr. Agric. 2019, 18, 2141–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Hu, C.; Wang, Y.; Sha, Y.; Hao, Z.; Chen, F.; Yuan, L.; Mi, G. Nitrogen allocation and remobilization contributing to low-nitrogen tolerance in stay-green maize. Field Crops Res. 2021, 263, 108078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, M.; Zhang, M.; Yang, Q.; Han, J.; Wang, X.; Lin, X. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer on photosynthetic characteristics, C4 pathway, and related gene expression of maize varieties with different nitrogen efficiency. Pak. J. Bot. 2024, 56, 1387–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masclaux-Daubresse, C.; Daniel-Vedele, F.; Dechorgnat, J.; Fabien, C.; Laure, G.; Akria, S. Nitrogen uptake, assimilation and remobilization in plants: Challenges for sustainable and productive agriculture. Ann. Bot. 2010, 105, 1141–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forde, B.G.; Lea, P.J. Glutamate in plants: Metabolism, regulation and signaling. J. Exp. Biol. 2007, 58, 2339–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, P.; Cui, Y.; Li, X.; Xiao, K.; Tao, P.; Zhang, Y. Responses of photosynthetic characteristics and enzyme activity of nitrogen metabolism to low nitrogen in maize with different nitrogen tolerance. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2020, 13, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaufichon, L.; Reisdorf-Cren, M.; Rothstein, S.J. Biological functions of asparagine synthetase in plants. Plant Sci. 2010, 179, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prester, T.; Groh, S.; Landbech, M.; Seitz, G. Nitrogen uptake and utilization efficiency of European maize cultivars developed under conditions of low and high nitrogen input. Plant Breed. 2010, 121, 480–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortunato, S.; Nigro, D.; Lasorella, C.; Marcotuli, I.; Gadaleta, A.; de Pinto, M.C. The role of glutamine synthetase (GS) and glutamate synthase (GOGAT) in the Improvement of nitrogen use efficiency in cereals. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cañas, R.A.; Yesbergenova-Cuny, Z.; Belanger, L.; Rouster, J.; Brulé, L.; Gilard, F.; Quilleré, I.; Sallaud, C.; Hire, B. NADH-GOGAT overexpression does not improve maize (Zea mays L.) performance even when pyramiding with NAD-IDH, GDH and GS. Plants 2020, 9, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The, S.V.; Rachel, S.; Mechthild, T. Targeting nitrogen metabolism and transport processes to improve plant nitrogen use efficiency. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 11, 628366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.; Shin, D.; Marmagne, A.; Masclaux-Daubresse, C.; An, G.; Nam, H.G. OsASN1 overexpression in rice increases grain protein content and yield under nitrogen-limiting conditions. Plant Cell Physiol. 2020, 61, 1309–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Han, J.L.; Yang, M.; Yao, D.D.; Zhou, Y.F.; Wang, W.P.; Wu, Z.X.; Yang, Q. Study on Nitrogen uptake, transport and metabolism of different nitrogen-efficient maize varieties. J. Nucl. Agric. Sci. 2020, 34, 2800–2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leff, B.; Ramankutty, N.; Foley, J.A. Geographic distribution of major crops across the world. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2004, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, Q.; Guo, N.; Xian, Q.; Lan, B.; Nangia, V.; Mo, F.; Liu, Y. Polyamines mediate the inhibitory effect of drought stress on nitrogen reallocation and utilization to regulate grain number in wheat. J. Exp. Bot. 2024, 75, 1016–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehman, M.; Yang, M.; Fahad, S.; Saleem, M.H.; Liu, L.; Liu, F.; Deng, G. Morphophysiological traits, antioxidant capacity, and N metabolism in ramie under N fertilizer. Agron. J. 2020, 112, 2988–2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.P.; Cui, Z.L.; Vitousek, P.M.; Cassman, K.G.; Matson, P.A.; Bai, J.S.; Meng, Q.F.; Hou, P.; Yue, S.C.; Volker, R.; et al. Integrated soil-crop system management for food security. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 6399–6404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, T.; Liu, X.; Zhu, Q.; Zeng, M.; Chen, X.; Yang, L.; Shen, J.; Shi, X.; Zhang, F.; deVries, W. Quantifying drivers of soil acidification in three Chinese cropping systems. Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 215, 105230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haegele, J.W.; Cook, K.A.; Nichols, D.M.; Below, F.E. Changes in nitrogen use traits associated with genetic improvement for grain yield of maize hybrids released in different decades. Crop Sci. 2013, 53, 1256–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Sha, Y.; Huang, Y.; Hao, Z.; Guo, W.; Ke, L.; Chen, F.; Yuan, L.; Mi, G. Efficient nitrogen allocation and reallocation into the ear in relation to the superior vascular system in low-nitrogen tolerant maize hybrid. Field Crops Res. 2022, 284, 108580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Ren, Y.; Fu, H.; Li, Z.; Kong, F.; Yuan, J. Cultivar differences in carbon and nitrogen accumulation, balance, and grain yield in maize. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 992041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertin, P.; Gallais, A. Genetic variation for nitrogen use efficiency in a set of recombinant maize inbred lines. I. Agrophysiological Results. Maydica 2000, 45, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.A.; Tollenaar, M. Physiological basis of successful breeding strategies for maize grain yield. Crop Sci. 2007, 47, S202–S215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Camberato, J.J.; Tuinstra, M.R.; Kumudini, S.V.; Vyn, T.J. Genetic improvement in density and nitrogen stress tolerance traits over 38 years of commercial maize hybrid release. Field Crops Res. 2016, 196, 438–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciampitti, I.A.; Vyn, T.J. Physiological perspectives of changes over time in maize yield dependency on nitrogen uptake and associated nitrogen efficiencies: A review. Field Crops Res. 2012, 133, 48–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, C.; Stitt, M. Nitrate Reduction and signalling. In Plant Nitrogen; Lea, P.J., Morot-Gaudry, J.F., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anas, M.; Liao, F.; Verma, K.K.; Sarwar, M.A.; Mahmood, A.; Chen, Z.L.; Li, Q.; Zeng, X.P.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.R. Fate of nitrogen in agriculture and environment: Agronomic, eco-physiological and molecular approaches to improve nitrogen use efficiency. Biol. Res. 2020, 53, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirel, B.; Andrieu, B.; Valadier, M.H.; Renard, S.; Quillere, I.; Chelle, M.; Pommel, B.; Fournier, C.; Drouet, J.L. Physiology of maize II: Identification of physiological markers representative of the nitrogen status of maize (Zea mays) leaves during grain filling. Physiol. Plant. 2005, 124, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, I.C.; Brears, T.; Knight, T.J.; Clark, A.; Coruzzi, G. Overexpression of cytosolic glutamine synthetase Relation to nitrogen, light, and photorespiration. Plant Physiol. 2002, 129, 1170–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kichey, T.; Heumez, E.; Pocholle, P.; Pageau, K.; Vanacker, H.; Dubois, F.; Le Gouis, J.; Hirel, B. Combined agronomic and physiological aspects of nitrogen management in wheat (Triticum aestivum L). Dynamic and integrated views highlighting the central role for the enzyme glutamine synthetase. New Phytol. 2006, 169, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, J.; Pou de Crescenzo, M.A.; Sene, O.; Hirel, B. Does lowering glutamine synthetase activity in nodules modify nitrogen metabolism and growth of Lotus japonicus? Plant Physiol. 2003, 133, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Tomar, R.S.; Kumar, K.; Kumar, B.; Rakshit, S.; Singh, I. Morpho-physiological and biochemical characterization of maize genotypes under nitrogen stress conditions. Indian J. Genet. Plant Breed. 2021, 81, 255–265. [Google Scholar]







| Gene Names | Serial Number | Primer | Product Fragment Size/bp |
|---|---|---|---|
| AS1 | GRMZM2G074589 | AATCAGAGCAAGTACCCCAATG | 230 |
| CCTCAACACCCCAGGCAGAA | |||
| AS2 | GRMZM2G093175 | GGAAGGATTGAGAAGTGGGTG | 215 |
| TTGGTGGTCGGAGTGTTGTG | |||
| AS3 | GRMZM2G053669 | ACGGATGAGATGATGAACAACG | 113 |
| CCGAGTCCTGAGGGAAGAGC | |||
| GOGAT1 | GRMZM2G085078 | AGGTTCACTCAAGGTTCTCC | 262 |
| CGTGCTGTCATCCTGTCATA | |||
| GOGAT2 | GRMZM2G375064 | TGCCCCACGATGATGACCGA | 228 |
| CGCTGCTTTGCCCAAGTCCG | |||
| GADPH | GRMZM2G04680 | TGGGCCTACTGGTCTTACTACTGA | 135 |
| ACATACCCACGCTTCAGATCCT |
| Variety | NupE (kg·kg−1) | NutE (kg·kg−1) | NHI (%) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | |
| N120 | ||||||||||||
| XY335 | 1.35 a | 1.40 a | 1.76 a | 1.57 a | 63.59 a | 62.78 a | 55.70 a | 56.39 a | 60.11 a | 52.60 a | 44.80 a | 45.95 a |
| JNK728 | 1.19 a | 1.39 a | 1.81 a | 1.56 a | 61.35 a | 61.84 a | 56.03 a | 56.05 a | 61.43 a | 54.48 a | 48.70 a | 48.34 a |
| N180 | ||||||||||||
| XY335 | 1.16 a | 1.25 b | 1.54 b | 0.97 b | 47.38 a | 49.68 a | 45.17 a | 63.30 a | 58.99 b | 55.09 b | 48.32 b | 68.19 b |
| JNK728 | 1.08 a | 1.37 a | 1.71 a | 1.12 a | 50.07 a | 47.48 a | 44.63 a | 58.68 a | 75.26 a | 63.22 a | 57.77 a | 75.49 a |
| N240 | ||||||||||||
| XY335 | 0.90 a | 0.99 a | 1.23 a | 1.21 a | 47.20 a | 45.97 a | 43.18 a | 41.82 a | 63.75 a | 55.47 a | 50.45 a | 48.76 a |
| JNK728 | 0.90 a | 0.96 a | 1.25 a | 1.11 a | 44.24 a | 43.29 a | 40.96 a | 39.24 a | 65.39 a | 56.51 a | 51.96 a | 49.65 a |
| N300 | ||||||||||||
| XY335 | 0.78 a | 0.87 a | 1.06 a | 1.01 a | 47.37 a | 47.42 a | 43.65 a | 41.62 a | 72.81 a | 63.04 a | 57.75 a | 54.29 a |
| JNK728 | 0.62 b | 0.68 b | 0.93 b | 0.81 b | 48.11 a | 46.70 a | 42.00 a | 41.69 a | 66.17 b | 58.23 a | 50.67 b | 48.75 b |
| N360 | ||||||||||||
| XY335 | 0.52 a | 0.47 a | 0.61 a | 0.57 a | 59.12 a | 57.16 a | 59.37 a | 52.63 a | 58.57 a | 51.74 a | 52.41 a | 46.12 a |
| JNK728 | 0.41 b | 0.46 a | 0.57 a | 0.51 a | 54.99 a | 59.53 a | 56.76 a | 55.40 a | 53.87 a | 52.51 a | 48.51 a | 47.18 a |
| ANOVA | ||||||||||||
| V | *** | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns |
| N | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | ns | *** |
| V×N | ns | *** | *** | *** | ns | ns | ns | ns | * | *** | ns | ns |
| Genes | R1 | R3 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N120 | N180 | N240 | N300 | N360 | N120 | N180 | N240 | N300 | N360 | |
| XY335 | ||||||||||
| AS1 | 0.62 c | 0.51 d | 0.51 d | 1.65 a | 0.93 b | 0.26 d | 0.58 b | 0.44 c | 0.84 a | 0.55 b |
| AS2 | 1.24 b | 1.70 a | 0.82 c | 0.98 c | 1.17 b | 0.80 b | 0.79 b | 0.78 b | 0.93 a | 0.63 c |
| AS3 | 1.09 c | 1.49 a | 1.44 a | 1.23 b | 1.44 a | 0.98 cd | 0.95 d | 1.00 c | 1.48 a | 1.17 b |
| JNK728 | ||||||||||
| GOGAT1 | 0.65 d | 0.73 d | 0.86 c | 1.38 a | 1.03 b | 2.21 a | 1.32 c | 1.84 b | 1.47 c | 1.70 b |
| GOGAT2 | 0.66 b | 1.01 a | 0.91 c | 0.70 d | 1.18 d | 4.04 b | 4.65 a | 3.82 b | 2.51 c | 1.43 d |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, M.; Liu, W.; Li, X.; Lin, X. Improving Leaf GOGAT Activity After the Post-Silking Period Contributes to High Grain Yield with Reduced Nitrogen in N-Efficient Maize. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1379. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15061379
Li H, Wang Y, Wang J, Zhang M, Liu W, Li X, Lin X. Improving Leaf GOGAT Activity After the Post-Silking Period Contributes to High Grain Yield with Reduced Nitrogen in N-Efficient Maize. Agronomy. 2025; 15(6):1379. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15061379
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Haoyu, Yanbing Wang, Jian Wang, Meng Zhang, Wenbo Liu, Xiangling Li, and Xiaohu Lin. 2025. "Improving Leaf GOGAT Activity After the Post-Silking Period Contributes to High Grain Yield with Reduced Nitrogen in N-Efficient Maize" Agronomy 15, no. 6: 1379. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15061379
APA StyleLi, H., Wang, Y., Wang, J., Zhang, M., Liu, W., Li, X., & Lin, X. (2025). Improving Leaf GOGAT Activity After the Post-Silking Period Contributes to High Grain Yield with Reduced Nitrogen in N-Efficient Maize. Agronomy, 15(6), 1379. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15061379






