Abstract
Heavy metal contamination in soil poses significant ecological risks, particularly within agricultural and forest ecosystems. This study evaluates the bioaccumulation of heavy metals (Cr, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn, As, Mo, Pb) by the ground beetle Carabus coriaceus Linnaeus, 1758, across contrasting Croatian ecosystems, with a focus on the role of soil pH in shaping metal dynamics. Concentrations in soils (0–30 and 30–60 cm) and beetle tissues were measured using portable X-ray fluorescence (pXRF), which provides total concentrations; inferences on bioavailability were based on soil properties such as pH and organic matter. Orchard soils showed higher Cu (49.9 mg/kg), Mo (10.3 mg/kg), and Ni (32.5 mg/kg), whereas forest soils contained elevated Zn (105.6 mg/kg), Pb (84.5 mg/kg), As (29.7 mg/kg), and Co (16.3 mg/kg). Beetles accumulated up to 481.0 mg/kg Zn at the orchard and 90.0 mg/kg Cu at the forest site. Bioaccumulation factors exceeded 1.0 for Co, Cu, and Zn, with particularly high values for Zn (2.20–5.75) suggesting both site-specific availability and possible physiological regulation. Soil and beetle analyses were complementary rather than equivalent: soils indicated total load, while beetles reflected biologically relevant fractions. C. coriaceus, therefore, represents a sensitive bioindicator, suitable for biodiversity-based soil contamination monitoring.
1. Introduction
Soil is one of the most biologically diverse and functionally complex components of terrestrial ecosystems, providing essential services such as nutrient cycling, water purification, and habitat for a wide array of organisms [1]. However, soil biodiversity and function are increasingly threatened by contamination with heavy metals, a persistent and widespread environmental problem, particularly in areas affected by agriculture, mining, and industrial activities. Metals such as cadmium (Cd), lead (Pb), copper (Cu), chromium (Cr), and zinc (Zn) persist in soils for decades, posing long-term risks to ecosystem integrity, biodiversity, and human health [2].
Agricultural soils are particularly vulnerable to heavy metal accumulation due to phosphate fertilizers, irrigation with contaminated water, pesticide use, and improper waste management [3,4]. Although elements like cobalt (Co), zinc (Zn), and copper (Cu) are essential micronutrients, their excess—largely from agrochemical inputs—can disrupt soil function and enter the food chain, leading to toxicological risks [5,6]. Given the slow regeneration of soil ecosystems, sometimes requiring centuries to recover from degradation, ongoing monitoring is crucial to protect soil health [2].
In Croatia, the Regulation on the Protection of Agricultural Land from Pollution (NN 71/19) defines threshold values for heavy metals based on soil pH, highlighting the legal and environmental necessity of routine soil quality assessment. Table 1 presents these permissible limits, which are pH-dependent, further emphasizing the importance of local soil properties in risk assessment.

Table 1.
Permissible Soil Trace Element Concentrations (mg kg−1) by pH Level According to Croatian Regulation (NN 71/19).
The bioavailability and mobility of metals in soils are strongly influenced by physicochemical factors, particularly pH and organic matter content. In slightly acidic to neutral soils, metals are more soluble and tend to form mobile metal–organic complexes, which increase their availability to organisms [7,8]. By contrast, alkaline soils generally immobilize metals through precipitation or the formation of stable carbonate complexes [9]. High organic matter can also reduce metal bioavailability by binding metal ions to humic substances, which limits their uptake by soil biota [10,11].
To evaluate biologically relevant contamination, the use of soil invertebrates as bioindicators has gained attention. Ground beetles (Coleoptera: Carabidae) are particularly suitable due to their close association with the soil, ecological importance, and capacity to bioaccumulate metals [12,13]. Their functional role in pest regulation and nutrient cycling, combined with their sensitivity to environmental change, makes them ideal organisms for soil quality assessment [14,15]. One of the most widely used indicators for assessing an organism’s capacity to accumulate metals is the bioaccumulation factor, defined as the ratio of metal concentration in organism tissue to that in surrounding soil [16,17].
Carabus coriaceus L. was selected as the focal heavy-metal bioindicator because prior studies identify it as robust in contaminated habitats owing to its large body size, soil-dwelling larvae, slow movement/low dispersal, and predatory linkage to the soil food web—traits that integrate local exposure and favor metal accumulation [18,19,20]. Its wide European distribution supports cross-site comparability and consistent availability, while the ample tissue mass enables multi-element analyses with lower detection limits and sample archiving. Although other ground beetles (e.g., Poecilus, Pseudophonus) have been used to assess metal and pesticide burdens, C. coriaceus offers added value through its greater body size, longer lifespan, and predominantly predatory–detritivore diet (earthworms, slugs, and other soil invertebrates that act as metal pathways), providing a time-integrated signal of contamination; occasional scavenging of plant/detrital material has been reported but does not alter its primary soil-linked exposure route [21,22].
Despite growing interest in soil biodiversity, data on the response of soil macrofauna to contamination remain limited in southeastern Europe. This gap highlights the need for region-specific studies that integrate chemical and biological indicators to support continental-scale monitoring efforts. The integration of ground beetles into soil quality assessments not only reveals contamination risks but also contributes to a broader understanding and monitoring of soil biodiversity. As emphasized in the EU Soil Mission and the proposed Soil Monitoring and Resilience Law, safeguarding and restoring soil biodiversity are central to achieving long-term soil health and resilience across European landscapes [23].
The bioaccumulation factor (BAF) is a commonly used indicator of an organism’s ability to accumulate trace elements from its environment. It is calculated as the ratio of the concentration of a metal in organism tissue to that in surrounding soil [16], with values greater than 1.0 indicating active accumulation [17]. While plants are often the focus of such studies, insects—particularly ground beetles—offer valuable, yet underutilized, insights into biologically active fractions of soil contamination [24,25].
This study is based on the following hypotheses: (1) forest soils in Risnjak National Park contain lower concentrations of heavy metals due to minimal anthropogenic impact; (2) agricultural soils are expected to show higher concentrations of contamination as a result of intensive agrochemical use; (3) both soil and ground beetle analyses are equally effective in detecting heavy metal accumulation; and (4) Carabus coriaceus functions as a reliable bioindicator of soil heavy-metal contamination. Accordingly, the main objectives are to compare heavy metal concentrations in soils from two ecologically distinct habitats (protected forest and agricultural orchard), evaluate the bioindicator potential of Carabus coriaceus using BAFs, and explore how land use intensity influences heavy metal accumulation in soils and beetle tissues.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Sites and Conditions
This study was conducted at two distinct locations in Croatia: a forest ecosystem within Risnjak National Park (45°25′ N, 14°36′ E) and an agricultural ecosystem in an apple orchard near Krapina (46°09′47″ N, 15°52′52″ E). Sampling in Risnjak National Park took place in the Lazac Valley, an area with spruce and fir forests thriving in humid, cold conditions. The park’s climate includes warm summers (avg. 20 °C) and cold, snowy winters [26]. The apple orchard near Krapina in Krapinsko-Zagorska County consists of various apple varieties managed under integrated pest management (IPM). The area has a continental humid climate with warm summers and cold, rainy winters [27].
2.2. Sampling Methods for Soil and Carabid Beetles
Soil sampling was carried out at two depths (0–30 cm and 30–60 cm) using a non-toxic steel hand auger [28]. The 0–30 cm and 30–60 cm depths were selected to capture potential vertical variation in metal distribution, distinguishing between topsoil affected by surface inputs and deeper layers reflecting long-term accumulation or leaching patterns. The sampling procedure was consistent with national soil sampling guidelines (REF) [29]. At each site and depth, one composite soil sample (~1 kg) was prepared by pooling 10 subsamples collected within a 10 × 10 m plot. The topsoil layer was sampled first, followed by the subsoil layer. In total, four composite samples (two depths × two sites) were prepared and analyzed. All analyses were performed in the accredited laboratory of the University of Zagreb, Faculty of Agriculture, Analytical Laboratory of the Department of General Crop Production, Zagreb. Sampling at both sites was conducted on 10 September 2022. The samples were homogenized and stored in polyethylene bags for laboratory analysis.
At each location, three pitfall traps were set to capture ground beetles, following the methods outlined by Greenslade and Spence and Niemelä [30,31].
The traps were spaced 20 m apart to ensure representative sampling. Each trap consisted of a metal cylinder (Ø = 10 cm, h = 20 cm) covered with a metal lid and a plastic cup filled with a 20% saline solution for preservation. Traps were protected from rain and debris. Weekly checks were conducted between 25 August and 23 September 2022. A total of 40 Carabus coriaceus adults, 20 per site, selected from the overall fauna catches were preserved in 70% (v/v) ethanol for subsequent analyses.
2.3. Laboratory Analysis of Soil and Carabid Beetles
The following chemical indicators of soil quality were determined using standardized methods: pH measured in 1 mol/L KCl solution (v/w 1:5) following HRN ISO 10390:2005 [32]; total nitrogen (N, %) determined using HRN ISO 13878:2004 [33]; total sulfur (S, %) determined using ISO 15178:2005 [34]; and humus (%) determined using the Tjurin method (bichromate volumetric method). Total carbon (TC, %) content was determined by dry combustion method (HRN ISO 10694:2004) [35]. Plant-available phosphorus (P2O5, mg/100 g soil) and potassium (K2O, mg/100 g soil) were extracted using ammonium lactate (AL) solution [36]. The detection and quantification of P2O5 were carried out using a spectrophotometer at a wavelength of 620 nm by the colorimetric method. The direct reading of K2O was performed using a flame photometer by the flame emission photometry method.
Prior to laboratory analysis, soil samples were air-dried and sieved through a 2 mm mesh to remove coarse debris and organic matter. The thorax and abdomen of 40 C. coriaceus were dried in a laboratory oven at 105 °C until a constant weight was reached. The dried samples were then ground to a fine powder using a mortar and pestle. Owing to the large body size of C. coriaceus (approximately 0.5–1 g dry tissue per adult), each specimen provided sufficient material for multi-element pXRF analysis, which requires 100–500 mg of tissue.
Both soil and beetle samples were analyzed for heavy metal content using a portable X-ray fluorescence analyzer (pXRF, Olympus Vanta C; Olympus Corp., Tokyo, Japan). The instrument was calibrated using manufacturer-supplied standards and validated with certified reference materials to ensure analytical accuracy. This method enabled the detection of 37 elements, including chromium (Cr), cobalt (Co), nickel (Ni), copper (Cu), zinc (Zn), arsenic (As), molybdenum (Mo), and lead (Pb). The limits of detection ranged from 0.5 to 5 mg/kg depending on the element, indicating the minimum concentration reliably detectable. Concentrations above these thresholds were quantified directly by the instrument and validated against certified reference materials. Four replicate measurements were conducted for each sample. All procedures followed the ISO 13196:2015 [37] standard. Accuracy and precision were assessed using certified reference materials (SRM 2711) and inter-laboratory reference soil samples (ISE 851). The results were deemed satisfactory, with recovery rates within ±5% and relative standard deviations (RSDs) below 5%.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
The concentrations of heavy metals (Cr, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn, As, Mo, Pb) in both soil and Carabus coriaceus specimens were statistically analyzed using SAS software, version 9.1.3 [38] (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA). Analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used to assess significant differences in mean metal concentrations between the two study locations (Risnjak—forest ecosystem and Krapina—agricultural ecosystem). Fisher’s Least Significant Difference (LSD) test was applied post hoc to compare means at a significance level of p = 0.05. The bioaccumulation factor (BAF) was calculated as the ratio of metal concentration in beetle tissue to that in soil (mg/kg beetle tissue ÷ mg/kg soil), using concentrations measured in the 0–30 cm topsoil layer, which is the most ecologically relevant depth for the surface-active species Carabus coriaceus.
2.5. Use of Generative AI
Generative AI was not used in the preparation of this manuscript beyond superficial text editing (e.g., grammar and spelling corrections). No AI tools were used for data analysis, interpretation, or generation of scientific content.
3. Results
3.1. Soil Chemical Properties
According to the Digital Pedological Map of Croatia (2024), the soils at both study sites were classified as rendzina [39]. The basic chemical properties of the studied soils across the two locations (Krapina and Risnjak) and at different soil depths are presented in Table 2.

Table 2.
Variability of basic chemical soil properties at the research sites.
Soil pH ranged from 7.22 to 7.30 in Krapina, categorizing the soil as alkaline [32]. By contrast, pH values in Risnjak ranged from 4.67 to 6.44, indicating acidic to slightly acidic conditions.
The humus content varied considerably, with soils in Krapina classified as low humus (1.0–1.1%), while soils in Risnjak contained significantly higher amounts (up to 9.9%), which classifies them as highly humic. According to Škorić [40], the total nitrogen content (TN) was higher in Risnjak (up to 0.609%), suggesting very fertile soils, whereas soils in Krapina showed moderate nitrogen levels (0.146–0.195%). The total sulfur content (TS) averaged 0.054% in Krapina and 0.072% in Risnjak, with slightly higher values in the surface layers at both sites.
Total carbon (TC) was generally higher in Krapina (7.06–7.70%) compared to Risnjak (6.75–8.43%), possibly due to differences in parent material and organic matter input. Available potassium (K2O) was more abundant in the surface soil layers at both sites, with the highest concentration recorded in Risnjak (8.43 mg/100 g), followed by Krapina (7.70 mg/100 g).
Available phosphorus (P2O5) concentrations were relatively low, ranging from 2.2 to 3.2 mg/100 g, with slightly higher values in deeper layers in Krapina, while in Risnjak, values remained relatively stable with depth.
3.2. Vertical Distribution of Metal Content in Soil
Table 3 presents the vertical distribution of heavy metals in the soil samples collected at two depths (0–30 cm and 30–60 cm) from Krapina and Risnjak. In Krapina, slight decreases with depth were observed for arsenic (from 23.4 to 22.9 mg/kg) and copper (from 49.9 to 48.4 mg/kg), although these changes were not statistically significant (Pr > 0.05). By contrast, the concentration of nickel increased slightly with depth, from 111.7 to 120.7 mg/kg, but again without statistical significance.

Table 3.
Vertical distribution of metal content in soil based on location and depth.
In Risnjak, a more pronounced vertical distribution of metal concentrations in the soil was observed. Arsenic and cobalt decreased slightly with depth (As: 29.7 to 28.1 mg/kg; Co: 7.0 to 5.1 mg/kg), while lead showed a statistically significant decrease from 84.5 to 67.1 mg/kg (Pr < 0.0002). Although zinc also decreased with depth (Zn: 171.2 to 155.4 mg/kg), the difference was not statistically significant (Pr = 0.10). Other metals showed slight increases or decreases with depth, but these variations were not statistically significant (Pr > 0.05).
3.3. Heavy Metal Content in Soil and Carabid Beetles
Statistically significant differences were observed between the two study locations for most of the examined elements in the topsoil (0–30 cm). Lead (Pb) and zinc (Zn) concentrations were significantly higher in Risnjak soils, while copper (Cu) and molybdenum (Mo) were more abundant in the Krapina orchard soil. Zinc (Zn) exhibited highly significant variation, with concentrations nearly twice as high in Risnjak compared to Krapina (171.2 vs. 83.6 mg/kg). Nickel (Ni) was significantly more concentrated in the Krapina soil (111.7–120.7 mg/kg) compared to Risnjak (62.0–63.7 mg/kg). Arsenic (As) and cobalt (Co) concentrations were also significantly different between sites, with higher values found in Risnjak. Chromium (Cr) content showed no statistically significant difference (Pr > 0.05), although values were slightly higher in the deeper layer (30–60 cm) of the Krapina soil.
The comparison of metal concentrations (mg/kg) measured in soils (0–30 cm and 30–60 cm) and in Carabus coriaceus from the two study sites—Krapina (orchard soil) and Risnjak (forest soil)—is summarized in Table 4. The variability in the heavy metal accumulation in C. coriaceus across the two study locations showed that the concentrations of arsenic (As), cobalt (Co), nickel (Ni), molybdenum (Mo), and lead (Pb) did not differ significantly between sites (Pr > 0.05). A statistically significant difference was found for chromium (Cr) (Pr = 0.0020), with higher concentrations in beetles from Krapina (9.0 mg/kg) than in those from Risnjak (7.5 mg/kg). Copper (Cu) concentrations were significantly higher in Risnjak beetles (90.0 mg/kg) compared to Krapina beetles (59.0 mg/kg), with Pr < 0.05 and LSD = 2.64 mg/kg. By contrast, zinc (Zn) concentrations were higher in beetles from Krapina (481.0 mg/kg vs. 377.0 mg/kg in Risnjak), also representing a statistically significant difference (Pr = 0.01, LSD = 60.1 mg/kg).

Table 4.
Comparison of metal concentrations (mg/kg) measured in soil (at depths 0–30 cm and 30–60 cm) and in carabid beetles (C. coriaceus) from two study sites: Krapina and Risnjak.
3.4. Bioaccumulation Factors in Carabid Beetles
The calculated bioaccumulation factors (BAFs) for C. coriaceus at both study locations are shown in Figure 1. Low BAF values (BAF < 0.25) were recorded for arsenic (As), chromium (Cr), nickel (Ni), and lead (Pb) at both sites, indicating limited accumulation of these metals in beetle tissues relative to their presence in soil. By contrast, BAF values exceeding 1.0 were observed for cobalt (Co), copper (Cu), and zinc (Zn) in beetles from Krapina and for Cu and Mo in beetles from Risnjak. The highest bioaccumulation was recorded for zinc in Krapina (BAF = 5.75), identifying it as the most intensively accumulated element in this location.
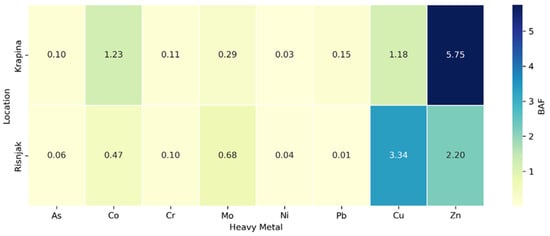
Figure 1.
Bioaccumulation factors (BAFs) of heavy metals in Carabus coriaceus from two ecosystems: Krapina (orchard soil) and Risnjak (forest soil).
4. Discussion
4.1. Soil Chemical Properties and Metal Contamination
According to Bašić [41], rendzina (Leptosol, calcaric, WRB) is a loamy soil with generally favorable physical properties, including a good ratio of pores, excellent water permeability, and favorable air–water relationships. It has a neutral pH (greater than 7) and contains 5–20% humus in rangelands. As identified in this study, the sites were characterized as humus-accumulative with a typical A-C or A-AC-C horizon sequence. In Croatia, rendzina covers a significant area of 420,184 hectares, which is around 7% of the country’s territory. Rendzina soils develop on loose carbonate or silicate–carbonate substrates, such as limestone or marl limestone, which are prone to fragmentation and dissolution. These soils are characterized by a loamy texture and favorable physical properties, but their metal retention capacity varies with pH and organic matter content [42].
The soil pH results confirm that the Krapina soil is alkaline (pH > 7), while the Risnjak soil ranges from acidic to slightly acidic (pH 4–6), consistent with the classification by Škorić [40]. This variation in pH significantly influences heavy metal mobility and bioavailability. Specifically, metals such as cadmium (Cd), zinc (Zn), and nickel (Ni) tend to be less available in alkaline soils, as they are more likely to form insoluble hydroxides and complexes, thereby reducing their mobility. As observed in this study, the alkaline pH of the Krapina soil may facilitate the formation of stable metal–carbonate complexes, further limiting metal bioavailability. By contrast, in acidic to neutral soils such as those found in Risnjak, metals can form more soluble and bioavailable metal–organic or ionic complexes, which enhance their mobility and potential for uptake by organisms [8,43,44].
The humus content also differed significantly between the two sites: the agricultural soil in Krapina contained only 1%, which indicates low organic matter content, whereas the forest soil in Risnjak contained up to 10%, which classifies it as highly humus-rich [45]. Organic matter plays an important role in the retention and availability of heavy metals. In forest soils, higher organic matter content promotes metal binding through organic ligands, reducing the mobility of metals such as copper (Cu) and lead (Pb) [9,10]. By contrast, in agricultural soils with lower organic matter, metals are more likely to remain in their free ionic forms, which are more mobile and available for uptake by organisms [7].
Despite the contrasting pH levels, both soils are classified as rendzina, an automorphic soil type formed over calcareous parent material, typically characterized by high alkalinity and the presence of calcium carbonate [39].
The higher total nitrogen (TN) and sulfur (TS) concentrations in the Risnjak soils are likely a result of the enhanced nutrient cycling and microbial activity typical of undisturbed forest ecosystems with high organic matter content [10]. By contrast, the lower TN and TS concentrations in Krapina reflect the impact of agricultural practices that reduce organic inputs and disturb soil structure. Total carbon (TC) ranged from 7.06 to 7.70% in Krapina and 6.75 to 8.43% in Risnjak, with higher values in Risnjak at 0–30 cm and slightly higher values in Krapina at 30–60 cm. This may be related to different sources of organic carbon, such as root biomass or fertilization residues, though carbon in forest soils is generally more stable due to continuous litter input [5]. Potassium (K2O) concentrations were higher in Krapina, particularly in the topsoil (18.7 mg/100 g), likely due to fertilization and low soil mobility. In Risnjak, the lower K2O concentrations (11.7 mg/100 g) may result from slower mineralization and natural cycling [46]. Phosphorus (P2O5) concentrations were low at both sites, with slightly higher concentrations in the deeper layers of Krapina (3.2 mg/100 g). In acidic forest soils like those at Risnjak, phosphorus is strongly adsorbed to Fe and Al oxides, which reduces its availability [40,43].
These findings suggest that the forest soils in Risnjak have more favorable chemical characteristics, such as higher organic matter content, better nutrient cycling, and improved retention of essential elements like nitrogen and sulfur. By contrast, the lower organic matter and nutrient levels in Krapina soils are likely associated with agricultural practices such as fertilization, tillage, and soil disturbance, which can degrade soil quality over time [47]. This supports the well-documented observation that intensive agricultural use can lead to the long-term degradation of soil quality.
4.2. Heavy Metal Content in Soils
The metal contamination concentrations varied significantly between the two study sites, particularly in the concentrations of arsenic (As), cobalt (Co), copper (Cu), molybdenum (Mo), and lead (Pb). The acidic forest soil in Risnjak exhibited elevated concentrations of As (29.7 mg/kg) and Pb (84.5 mg/kg), both exceeding the Croatian regulatory limits for acidic soils (Narodne novine 71/2019) [48]. By contrast, the alkaline orchard soil in Krapina had significantly higher concentrations of Cu (49.9 mg/kg) and Mo (10.3 mg/kg), although these remained below the maximum allowable concentrations for alkaline soils (120 mg/kg Cu, 15 mg/kg Mo) [46].
The elevated concentrations of As and Pb in Risnjak may be attributed to natural geological processes, such as the weathering of arsenopyrite and other arsenic-bearing minerals, or to long-range atmospheric deposition from industrial sources [49]. These findings are in line with previous studies reporting that acidic soils enhance the mobility and bioavailability of heavy metals, thereby increasing the likelihood of accumulation in plants and soil invertebrates [50]. The observed arsenic concentrations in particular raise concerns due to their potential ecological and human health risks [51]. In Krapina, the higher Cu and Mo concentrations are likely linked to agricultural inputs, especially the use of copper-based fungicides in orchard management. These observations are consistent with findings from agricultural ecosystems where elevated Cu concentrations are often associated with long-term pesticide and fertilizer application [52]. While the concentrations in Krapina did not exceed regulatory thresholds, continued monitoring is warranted to avoid future accumulation to harmful concentrations.
Comparison with the Croatian Geochemical Atlas [53] shows that the arsenic concentrations at both locations exceeded the national average of 13 mg/kg, underscoring the need for long-term monitoring, particularly in forest soils such as those in Risnjak. Similarly, the lead concentrations in Risnjak (84.5 mg/kg) were more than double the national average of 38 mg/kg, indicating possible localized contamination, likely from past industrial activity or airborne deposition. These findings align with regional studies indicating that forest ecosystems are vulnerable to long-range heavy metal input [42,53].
All the studied metals—As, Co, Cu, Pb, Cr, Ni, and Zn—are generally more mobile and bioavailable under acidic conditions, while in alkaline soils, they tend to form less-soluble complexes with carbonates and phosphates [54]. pXRF provides total concentrations of metals, without distinguishing between fractions that are tightly bound and those potentially available. As such, our references to ‘bioavailability’ are inferential and based primarily on soil properties such as pH and organic matter content, which are well-established determinants of metal solubility and mobility [42,55]. Acidic conditions in particular are known to enhance the release of cationic metals from mineral and organic surfaces, thereby increasing the proportion of the labile pool. Conversely, alkaline conditions and the presence of carbonates promote the formation of insoluble complexes, reducing availability to plants and soil organisms. While these relationships provide a useful interpretive framework, they cannot substitute for the direct measurement of bioavailable fractions. Future studies should, therefore, combine pXRF with extraction-based methods, such as CaCl2, DTPA, or sequential fractionation, to more accurately quantify the pools of metals available to biota. Additionally, the elevated organic matter content in Risnjak may further enhance the retention and accumulation of metals, as organic matter has a high binding affinity for metal ions [10]. Comparing these findings with the Croatian regulation on soil contamination, the maximum permissible levels (MPLs) of metals in soils (NN 71/19) [46] are as follows: for soils with a pH below 5, the maximum allowable concentration of copper is 60 mg/kg, while for soils with a pH above 6, it increases to 120 mg/kg. In our study, the copper concentrations in the Krapina soil were within the permissible limits, while the zinc concentrations exceeded the allowed range for soils with alkaline pH (pH > 6), which is capped at 200 mg/kg in the regulation. The elevated zinc concentrations in Krapina could, therefore, be indicative of localized contamination or a higher bioavailability of the metal, possibly influenced by agricultural practices and soil management [52].
These results stand in contrast to our initial hypothesis that forest soils would contain lower heavy metal concentrations than agricultural soils. Instead, Risnjak forest soils exhibited higher levels of As, Co, Pb, and Zn compared to those at the orchard site. Such a pattern has been observed in other forest ecosystems, where elevated metal loads have been linked to both geogenic background and long-range atmospheric deposition [56,57]. This finding highlights that even protected areas cannot be presumed to be free from contamination and emphasizes the need for continued monitoring of forest soils.
4.3. Heavy Metal Content in Carabus coriaceus
Our results confirm that Carabus coriaceus is capable of accumulating heavy metals in both forest and agricultural ecosystems, reinforcing its suitability as a bioindicator species for soil contamination. The temporal window of sampling (late August–September) coincided with the peak in adult C. coriaceus activity—a period when surface activity and trophic interactions are the most pronounced—according to phenological data indicating that activity begins in late April/early May and peaks in July–August (Alekseev et al., 2021, Turin et al., 2003) [22,58]. This timing enhances the ecological relevance of exposure and bioaccumulation assessment. Like findings on pesticide residues in carabid beetles from Mediterranean agroecosystems [59,60], our findings on C. coriaceus displayed varying concentrations of metal accumulation in this study, which generally reflected soil concentrations.
No statistically significant differences were observed in C. coriaceus tissues for arsenic, cobalt, molybdenum, nickel, or lead between sites, although the soils did differ significantly for these metals in the 0–30 cm layer (Table 4; p ≤ 0.01). This does not indicate greater metal bioavailability under alkaline conditions, which generally reduce metal solubility. Instead, the elevated Zn BAF in Krapina likely reflects site-specific factors, such as legacy agricultural inputs, prey composition, and trophic transfer, or metal speciation, which can maintain a labile Zn pool despite a higher soil pH [5,42,55].
4.4. Comparative Bioaccumulation Studies
The bioaccumulation factors (BAFs) calculated for C. coriaceus provide additional insight into the species’ ability to accumulate heavy metals from soil. BAF values exceeding 1.0 for zinc and copper at both sites suggest that these metals were present in bioavailable forms and efficiently accumulated by beetles. The highest BAF was recorded for zinc in Krapina (5.75), indicating substantial uptake under alkaline soil conditions. Although alkaline soils generally reduce Zn solubility, the very low organic matter content in Krapina (1%) may have limited Zn binding, thereby counteracting the immobilizing effect of high pH. In addition, zinc can occur in exchangeable or weakly complexed forms not fully captured by pH measurements, which could explain its persistence in a labile pool [7,42]. Importantly, as zinc is an essential micronutrient, its uptake and internal concentrations are not solely the result of passive accumulation but can also be subject to physiological regulation. Homeostatic control of Zn has been documented in soil invertebrates, where uptake is maintained even under conditions of reduced environmental availability [61,62]. Such mechanisms may have contributed to the elevated Zn BAF observed in C. coriaceus at the Krapina site.
These results are also consistent with earlier studies identifying carabid beetles as reliable indicators of soil metal contamination due to their ground-dwelling behavior, dietary habits, and bioaccumulation capacity [63]. The inclusion of C. coriaceus in monitoring programs could contribute to more-accurate assessments of soil quality and contamination risk across diverse landscapes.
The lower BAF values for arsenic and lead at both sites suggest the limited mobility and uptake potential of these metals. Nevertheless, their presence raises concerns for long-term ecological risks, as even low-level chronic exposure can adversely affect more sensitive invertebrate species, such as collembolans (springtails) and earthworms, leading to cumulative impacts on soil biodiversity [64,65]. For instance, arsenic contamination has been linked to reduced body size in collembolans, which indicates growth inhibition as an early sign of pollution [66]. Similarly, earthworms Eisenia fetida (Savigny, 1826) have shown adverse responses to arsenic exposure in historically contaminated soils [67].
Further evidence from earthworm studies has shown that bioconcentration is strongly influenced by soil pH, organic matter, and metal persistence [68]. Our findings confirm that differences in soil conditions between sites—particularly pH and land use—play an important role in shaping bioaccumulation patterns in C. coriaceus. These site-specific responses highlight the importance of environmental context when evaluating contamination risk and interpreting bioindicator data.
In this context, the third hypothesis that soil and beetle analyses would be equally effective was not supported by the data. Rather, the two approaches proved to be complementary: soil analyses capture the total metal burden, while beetle data reflect the fraction most relevant to biological uptake and trophic transfer. This underscores the importance of integrating chemical and biological lines of evidence when assessing contamination risk. These findings suggest that heavy metal accumulation in C. coriaceus may have ecological consequences beyond the bioindicator species itself. Elevated BAF values could signal disruptions in trophic interactions, which could potentially reduce the abundance of sensitive soil invertebrates and alter the community structure [69,70]. Similar impacts were documented by Migliorini et al. [70] in contaminated soils, where metal accumulation in arthropods varied with soil conditions and contributed to imbalances in biodiversity. The observed bioaccumulation in C. coriaceus, therefore, not only reflects soil contamination but may also contribute to cascading effects on soil food webs, similarly to patterns reported in other ground beetles and arthropods from polluted habitats [69,70].
The ability of C. coriaceus to accumulate heavy metals corresponds with findings from other ground beetle species, such as those from the genera Poecilus and Pseudophonus, which have demonstrated bioaccumulation of pesticides in Mediterranean vineyards and olive groves managed under integrated pest management [60]. Consistency across taxa and land use types further supports the use of ground beetles as effective bioindicators for monitoring soil contamination and its ecological consequences. These findings contribute to a broader understanding of how metal contamination can influence soil biodiversity through bioaccumulation pathways, especially in regions of Europe where such data remain scarce.
Although this study did not directly measure physiological or behavioral endpoints, existing work demonstrates that chronic metal exposure can significantly affect locomotor activity, respiratory efficiency, morphology, and energy metabolism in ground beetles. For example, Lagisz [71] documented morphological changes in Pterostichus oblongopunctatus near zinc and lead smelters, while Stone et al. [72] reported increased mortality risk under combined metal and environmental stressors. Furthermore, Bednarska et al. [73] observed altered locomotor activity and respiration rates in P. oblongopunctatus exposed to elevated nickel, particularly under suboptimal thermal conditions. These findings suggest that metal accumulation in C. coriaceus could have substantial sub-lethal consequences, warranting further research that integrates chemical, physiological, and behavioral assessments.
Integrative Perspective on Soil–Beetle Interactions
When considered together, the element-specific patterns provide a more integrated view of soil–beetle interactions. Copper was more concentrated in the Krapina soils, largely due to agricultural inputs, yet accumulated more strongly in the Risnjak beetles, highlighting the influence of acidic conditions on bioavailability. Zinc displayed the opposite pattern: despite alkaline soils in Krapina, beetles exhibited an exceptionally high BAF, likely driven by low organic matter, the potential occurrence of labile Zn forms, and the homeostatic regulation of this essential micronutrient [42,61,62]. By contrast, arsenic and lead reached high concentrations in the Risnjak soils but were not mirrored in the beetle tissues, which reflects their limited trophic transfer and strong binding to soil constituents [66,67]. Taken together, these findings demonstrate that soil analyses capture the total contamination load, while beetle data reveal the biologically relevant fraction. This complementary perspective underscores the value of integrating chemical and biological indicators to achieve a more comprehensive assessment of heavy metal contamination and its ecological implications.
5. Conclusions
This study demonstrates that soil type and land use significantly influence the distribution, mobility, and bioavailability of heavy metals, with implications for ecosystem functioning and potential plant stress. The ground beetle Carabus coriaceus exhibited site-specific accumulation patterns, particularly for zinc, copper, and chromium, which confirm its sensitivity to environmental metal exposure and its value as a bioindicator species.
By combining soil chemistry with bioaccumulation data, this study highlights that total metal concentrations alone cannot capture the biologically relevant fraction available for trophic transfer. Our results emphasize the need for integrated monitoring approaches that unite chemical and biological indicators to provide a more ecologically meaningful assessment of soil contamination.
Furthermore, the exceptionally high zinc bioaccumulation factor at the Krapina site underlines the importance of site-specific conditions and potential physiological regulation, warranting further investigation. Future studies should also incorporate extraction-based measures of bioavailability and assess sub-lethal endpoints in beetles, such as locomotor activity and energy metabolism, to deepen our understanding of the ecological consequences of heavy metal exposure.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.L., F.R., I.P.Ž., and A.B.; Data curation, I.P.Ž. and M.F.; Formal analysis, H.V.G., D.L., A.P., I.P.Ž., and M.F.; Investigation, H.V.G., A.P., F.R., A.B., I.P.Ž., and M.F.; Methodology, H.V.G., D.L., A.B., M.F., and I.P.Ž.; Project administration, I.P.Ž.; Resources, M.F., Supervision, I.P.Ž.; Validation, A.B.; Visualization, H.V.G. and M.F.; Writing—original draft, H.V.G., F.R., and I.P.Ž.; Writing—review and editing, D.L., I.P.Ž., and A.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
All data supporting the findings of this study are included within the article.
Acknowledgments
During the preparation of this manuscript, the author(s) used OpenAI 2025 for the purposes of language editing. The authors have reviewed and edited the output and take full responsibility for the content of this publication.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- FAO. State of Knowledge of Soil Biodiversity: Status, Challenges and Potentialities; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2020; Available online: https://www.fao.org/documents/card/en/c/cb1928en (accessed on 13 August 2025).
- Su, C.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, W. A review on heavy metal contamination in the soil worldwide: Situation, impact and remediation techniques. Environ. Skept. Crit. 2014, 3, 24–38. [Google Scholar]
- Satarug, S.; Baker, J.R.; Urbenjapol, S.; Haswell-Elkins, M.; Reilly, P.E.; Williams, D.J.; Moore, M.R. A global perspective on cadmium pollution and toxicity in non-occupationally exposed population. Toxicol. Lett. 2003, 137, 65–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, R.S. Heavy metal pollutants and chemical ecology: Exploring new frontiers. J. Chem. Ecol. 2010, 36, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alloway, B.J. Heavy Metals in Soils: Trace Metals and Metalloids in Soils and Their Bioavailability, 3rd ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rascio, N.; Navari-Izzo, F. Heavy metal hyperaccumulating plants: How and why do they do it? And what makes them so interesting? Plant Sci. 2011, 180, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauvé, S.; Norvell, W.A.; McBride, M.; Hendershot, W. Speciation and complexation of cadmium in extracted soil solutions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, R.Y.; Yoon, J.K.; Kim, T.S.; Yang, J.E.; Owens, G.; Kim, K.R. Bioavailability of heavy metals in soils: Definitions and practical implementation—A critical review. Environ. Geochem. Health 2015, 37, 1041–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michael, A. Heavy Metals in Soil: A Review. Chem. Eng. Process Tech. 2023, 8, 1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linehan, D.J. Organic matter and trace metals in soils. In Soil Organic Matter and Biological Activity; Vaughan, D., Malcolm, R.E., Eds.; Developments in Plant and Soil Sciences; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1985; Volume 16, pp. 217–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nederlof, M.M.; Van Riemsdijk, W.H.; De Haan, F.A.M. Effect of pH on the Bioavailability of Metals in Soils. In Integrated Soil and Sediment Research: A Basis for Proper Protection; Eijsackers, H.J.P., Hamers, T., Eds.; Soil & Environment; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1993; Volume 1, pp. 715–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemelä, J.; Kotze, J.; Ashworth, A.; Brandmayr, P.; Desender, K.; New, T.R.; Penev, L.; Samways, M.J.; Spence, J. The search for common anthropogenic impacts on biodiversity: A global network. J. Insect Conserv. 2000, 4, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindqvist, L.; Block, M.; Tjalve, H. Distribution and excretion of Cd, Hg, methyl-Hg and ZS in the predatory beetle Pterostichus niger (Coleoptera: Carabidae). Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1995, 14, 1195–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lövei, G.L.; Sunderland, K.D. Ecology and behavior of ground beetles (Coleoptera: Carabidae). Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1996, 41, 231–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGeoch, M.A. The selection, testing and application of terrestrial insects as bioindicators. Biol. Rev. 1998, 73, 181–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakovljević, T.; Radojčić Redovniković, I.; Cvjetko, M.; Bukovac, I.; Sedak, M.; Đokić, M.; Bilandžić, N. The potential of poplar (Populus nigra var. italica) in the phytoremediation of cadmium. Šum. List 2015, 139, 231–232. Available online: https://hrcak.srce.hr/141896 (accessed on 13 August 2025).
- Wang, Q.; Chen, M.; Shan, G.; Chen, P.; Cui, S.; Yi, S.; Zhu, L. Bioaccumulation and biomagnification of emerging bisphenol analogues in aquatic organisms from Taihu Lake, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 598, 814–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forsythe, T.G. Feeding and locomotory functions in relation to body form in five species of ground beetle (Coleoptera: Carabidae). J. Zool. 1991, 223, 233–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talarico, F.; Brandmayr, P.; Giulianini, P.G.; Ietto, F.; Naccarato, A.; Perrotta, E.; Tagarelli, A.; Giglio, A. Effects of metal pol-lution on survival and physiological responses in Carabus (Chaetocarabus) lefebvrei (Coleoptera, Carabidae). Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2014, 61, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purchart, L.; Kula, E. Content of heavy metals in bodies of field ground beetles (Coleoptera, Carabidae) with respect to selected ecological factors. Pol. J. Ecol. 2007, 55, 305–314. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/285700351 (accessed on 13 August 2025).
- Thiele, H.U. Carabid Beetles in Their Environments: A Study on Habitat Selection by Adaptations in Physiology and Behaviour; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Turin, H.; Penev, L.; Casale, A. The Genus Carabus in Europe: A Synthesis; Pensoft Publishers: Sofia, Bulgaria, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Mission Soil: Caring for Soil Is Caring for Life—Implementation Plan; Directorate-General for Research and Innovation: Brussels, Belgium, 2021; Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/info/files/mission-soil-implementation-plan_en (accessed on 2 April 2025).
- Lagisz, M.; Laskowski, R. Evidence for between-generation effects in carabids exposed to heavy metals pollution. Ecotoxicology 2008, 17, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, E.; Harangi, S.; Baranyai, E.; Braun, M.; Fábián, I.; Mizser, S.; Tóthmérész, B. Distribution of toxic elements between biotic and abiotic components of terrestrial ecosystem along an urbanization gradient: Soil, leaf litter and ground beetles. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 60, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NP Risnjak. Prirodna Obilježja; NP Risnjak: Crni Lug, Croatia, 2023; Available online: https://www.np-risnjak.hr/prirodna-obiljezja-parka/ (accessed on 30 March 2025).
- Krapina-Zagorje County. Official Website of Krapina-Zagorje County; Krapina-Zagorje County: Krapina, Croatia, 2022; Available online: https://zagorje.croatia.hr/en-gb (accessed on 2 May 2023).
- Eijkelkamp. Soil Augers—Product Information and User Manual; Eijkelkamp Soil & Water: Giesbeek, The Netherlands, 2009; Available online: https://www.eijkelkamp.com (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- Ministarstvo Poljoprivrede. Uzimanje Uzoraka tla za Provođenje Obvezne Analize tla. Savjetodavna Služba. 2 September 2025. Available online: https://savjetodavna.mps.hr/2025/09/02/uzimanje-uzoraka-tla-za-provodenje-obvezne-analize-tla/ (accessed on 5 September 2025).
- Greenslade, P.J.M. Pitfall trapping as a method for studying populations of Carabidae (Coleoptera). J. Anim. Ecol. 1964, 33, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spence, J.R.; Niemelä, J.K. Sampling carabid assemblages with pitfall traps: The madness and the method. Can. Entomol. 1994, 126, 881–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HRN ISO 10390:2005; Soil Quality—Determination of pH. Croatian Standards Institute: Zagreb, Croatia, 2005. Available online: https://repozitorij.hzn.hr/norm/HRN+ISO+10390%3A2005 (accessed on 12 June 2025).
- HRN ISO 13878:2004; Soil Quality—Determination of Total Nitrogen Content by Dry Combustion (Elemental Analysis). Croatian Standards Institute: Zagreb, Croatia, 2004. Available online: https://repozitorij.hzn.hr/norm/HRN+ISO+13878%3A2004 (accessed on 12 June 2025).
- ISO 15178:2005; Soil Quality—Determination of Total Sulfur by Dry Combustion. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2005.
- HRN ISO 10694:2004; Soil Quality—Determination of Organic and Total Carbon After Dry Combustion (Elementary Analysis). Croatian Standards Institute: Zagreb, Croatia, 2004. Available online: https://repozitorij.hzn.hr/norm/HRN+ISO+10694%3A2004 (accessed on 12 June 2025).
- Egner, H.; Riehm, H.; Domingo, W.R. Untersuchungen über die chemische Bodenanalyse als Grundlage für die Beurteilung des Nährstoffzustandes der Böden. K. Lantbrukshögskolans Ann. 1960, 26, 199–215. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 13196:2015; Soil Quality—Screening of Soil Polluted with Potentially Toxic Elements—Method Using X-Ray Fluorescence Spectrometry (XRF). International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015.
- SAS Institute. SAS/STAT® 9.1.3 User’s Guide; SAS Institute Inc.: Cary, NC, USA, 2004; Available online: http://support.sas.com/documentation/onlinedoc/91pdf/index_913.html (accessed on 15 November 2024).
- Digital Pedological Map of Croatia. 2021. Available online: http://pedologija.com.hr/iBaza/DPK-Hr_2021/index.html#6/45.527/14.677 (accessed on 1 April 2025). (In Croatian).
- Škorić, A. Priručnik za Pedološka Istraživanja; Sveučilište u Zagrebu, Fakultet Poljoprivrednih Znanosti: Zagreb, Croatia, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Bašić, F. Pedologija; Školska Knjiga: Zagreb, Croatia, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kabata-Pendias, A.; Mukherjee, A.B. Trace Elements from Soil to Human; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauvé, S.; Martínez, C.E.; McBride, M.; Hendershot, W. Adsorption of Free Lead (Pb2+) by Pedogenic Oxides, Ferrihydrite, and Leaf Compost. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2000, 64, 595–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmsen, J. Measuring bioavailability: From a scientific approach to standard methods. J. Environ. Qual. 2007, 36, 1420–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrvatska agencija za poljoprivredu i hranu (HAPIH). Vodič za optimizaciju gospodarenja tlom i prilagodbu agroekosustava i ag-rotehničkih mjera klimatskim promjenama; HAPIH: Osijek, Croatia, 2023; Available online: https://www.hapih.hr/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/Agroekoteh-Vodic.pdf (accessed on 13 June 2025).
- Keeney, D.R.; Nelson, D.W. Nitrogen—Inorganic Forms. In Methods of Soil Analysis. Part 2. Chemical and Microbiological Properties, 2nd ed.; Page, A.L., Ed.; Agronomy Monograph No. 9; ASA–SSSA: Madison, WI, USA, 1982; pp. 643–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinović, J. Tla u Hrvatskoj: Monografija—Završni Izvještaj Prve Inventarizacije Tala; Državna Uprava za Zaštitu Prirode i Okoliša & Pokret Prijatelja Prirode “Lijepa Naša”: Zagreb, Croatia, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Narodne Novine 71/2019. Pravilnik o Zaštiti Poljoprivrednog Zemljišta od Onečišćenja. Ministarstvo Poljoprivrede Republike Hrvatske. Available online: https://narodne-novine.nn.hr/clanci/sluzbeni/2019_07_71_1501.html (accessed on 13 August 2025).
- Nriagu, J.O.; Pacyna, J.M. Quantitative assessment of worldwide contamination of air, water and soils by trace metals. Nature 1988, 333, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fazal, M.A.; Kawachi, T.; Ichion, E. Validity of the Latest Research Findings on Causes of Groundwater Arsenic Contamination in Bangladesh. Water Int. 2001, 26, 380–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Springer, O.; Springer, D. Otrovani Modrozeleni Planet: Priručnik iz Ekologije, Ekotoksikologije i Zaštite Prirode i Okoliša; Meridijani: Zagreb, Croatia, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Grant, A. Pollution Tolerant Species and Communities: Intriguing Toys or Invaluable Monitoring Tools? Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2002, 8, 955–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halamić, J.; Miko, S. Geokemijski Atlas Republike Hrvatske; Hrvatski Geološki Institut: Zagreb, Croatia, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Adamczyk-Szabela, D.; Wolf, W.M. The Impact of Soil pH on Heavy Metals Uptake and Photosynthesis Efficiency in Melissa officinalis, Taraxacum officinalis, Ocimum basilicum. Molecules 2022, 27, 4671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporale, A.G.; Violante, A. Chemical Processes Affecting the Mobility of Heavy Metals and Metalloids in Soil Environments. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2016, 2, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindberg, S.E.; Turner, R.R.; Lovett, G.M.; Richter, D.D.; Johnson, D.W. Atmospheric deposition and canopy interactions of major ions in forests: A review. Science 1982, 215, 1609–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovmand, M.F.; Kemp, K.; Kystol, J.; Johnsen, I.; Riis-Nielsen, T.; Pacyna, J.M. Atmospheric heavy metal deposition accumulated in rural forest soils of Southern Scandinavia. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 155, 537–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alekseev, S.; Ruchin, A.; Semishin, G. Seasonal Dynamics of Carabus coriaceus Linnaeus, 1758 “Coleoptera, Carabidae” Activity in the Areal’s Eastern Part. Entomol. Appl. Sci. Lett. 2021, 8, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viric Gasparic, H.; Lemic, D.; Bazok, R. Neonicotinoid residues in earthworms and ground beetles under intensive sugar beet production: Preliminary study in Croatia. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šerić Jelaska, M.; Jelić, B.; Anđelić Dmitrović, B.; Kos, T. Bioaccumulation of pesticides in carabid beetles in a vineyard and olive grove under integrated pest management. Eur. J. Entomol. 2024, 121, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spurgeon, D.J.; Hopkin, S.P. Effects of metal-contaminated soils on the growth, sexual development, and early cocoon production of Eisenia fetida, with particular reference to zinc. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 1996, 35, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Gestel, C.A.M.; Van Dis, W.A. The influence of soil characteristics on the toxicity of four chemicals to the earthworm Eisenia fetida andrei (Oligochaeta). Biol. Fertil. Soils 1988, 6, 262–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rainio, J.; Niemelä, J. Ground beetles (Coleoptera: Carabidae) as bioindicators. Biodivers. Conserv. 2003, 12, 487–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vries, W.; Römkens, P.F.; Schütze, G. Critical Soil Concentrations of Cadmium, Lead, and Mercury in View of Health Effects on Humans and Animals. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2007, 191, 91–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karczewska, A.; Gruss, I.; Szopka, K.; Dradrach, A.; Twardowski, J.; Twardowska, K. Arsenic Toxicity to Earthworms in Soils of Historical as Mining Sites: An Assessment Based on Various Endpoints and Chemical Extractions. Environ. Geochem. Health 2023, 45, 6713–6726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruss, I.; Lallaouna, R.; Twardowski, J.; Magiera-Dulewicz, J.; Twardowska, K. Collembola Growth in Heavy Metal-Contaminated Soils. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 27998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, J.; Cheng, J.; Zhu, Y.; Geng, J.; Wang, X.; Feng, X.; Hou, H. A New Method for Ecological Risk Assessment of Combined Contaminated Soil. Toxics 2023, 11, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, T.; Kimmel, S.; Hoeger, S.; Lemic, D.; Bazok, R.; Viric Gasparic, H. Plant protection products in agricultural fields—Residues in earthworms and assessment of potentially toxic effects to the environment. J. Cent. Eur. Agric. 2022, 23, 604–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijver, M.; Jager, T.; Posthuma, L.; Peijnenburg, W. Metal uptake from soils and soil-sediment mixtures by larvae of Tenebrio molitor (L.) (Coleoptera). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2003, 54, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migliorini, M.; Pigino, G.; Bianchi, N.; Bernini, F.; Leonzio, C. The effects of heavy metal contamination on the soil arthropod community of a shooting range. Environ. Pollut. 2004, 129, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagisz, M. Changes in Morphology of the Ground Beetle Pterostichus oblongopunctatus F. (Coleoptera; Carabidae) from Vicinities of a Zinc- and Lead Smelter. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2008, 27, 1744–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, D.; Jepson, P.; Kramarz, P.; Laskowski, R. Time to Death Response in Carabid Beetles Exposed to Multiple Stressors along a Gradient of Heavy Metal Pollution. Environ. Pollut. 2001, 113, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bednarska, A.J.; Gerhardt, A.; Laskowski, R. Locomotor Activity and Respiration Rate of the Ground Beetle Pterostichus oblongopunctatus (Coleoptera: Carabidae) Exposed to Elevated Nickel Concentration at Different Temperatures: Novel Application of Multispecies Freshwater Biomonitor®. Ecotoxicology 2010, 19, 864–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).