Abstract
A stent is a medical device for serving as an internal scaffold to maintain or increase the lumen of a body conduit. Stent placement has become a primary treatment option in coronary artery disease for more than the last two decades. The stenting is also currently used for relieving the symptoms of narrowed lumen of nonvascular organs, such as esophagus, trachea and bronchi, small and large intestines, biliary, and urinary tract. Local delivery of active pharmaceutical agents via the stents can not only enhance healing of certain diseases, but it can also help decrease the potential risk of the stenting procedure to the surrounding tissue. In this review, we focus on reviewing a variety of drug-impregnated stents and local drug delivery systems using the stents.
Keywords:
vascular stent; nonvascular stent; e-PTFE; silicone; polyurethane; paclitaxel; gemcitabine; siRNA 1. Introduction
A stent is a cylindrical medical device usually made of metallic or polymeric wires that could be placed in the blood vessel [,,,,,] and the non-vascular lumen including gastrointestinal, upper respiratory, and urinary tract to alleviate the symptoms caused by the stenosis [,,,,,,,]. Since stenting has been demonstrated to be one of the most successful treatment modality in the interventional medicine, the application range of stenting has been expanding fast. However, the stent placement is not a perfect treatment option, because the stent lumen could be re-obstructed by hyperplasia of the surrounding tissue or invasion of malignant tumor around the stent [,,,,]. The restenosis could also be caused by the stent migration from the original site or mechanical failure of the stent [,,].
The restenosis in the vascular stenting results mainly from intimal hyperplasia, which is a response of a vessel to the vascular injury and endothelial damage caused by the stenting []. A great number of drug delivery methods have been tried to suppress the restenosis, and many types of drug eluting stents (DES) were developed and clinically applied successfully to lower the restenosis rate. Various techniques, including covering of a bare metal stent (BMS) with polymeric membrane or film to prevent invasion of the surrounding tissue through the meshes of the stent and impregnation of the stent with an anti-proliferative drug have been developed to prevent hyperplasia or tumor ingrowth through the mesh of the stent. However, the mesh size of a non-vascular stent is generally much larger than that of a vascular stent, and the drug elution from the stent wires is not enough to suppress the hyperplasia for non-vascular stents, and thus the restenosis of non-vascular stents is much more difficult to control than that of vascular stents [,,].
In this article, we will summarize the coating and covering methods of a stent with polymeric film or membrane, impregnation methods with antiproliferative drugs, and attachment and delivery methods of small interference RNA (siRNA) via the polymeric covering of vascular and non-vascular stents.
2. Antiproliferative Drugs
Although many drugs such as antiplatelet agents, anticoagulants, anti-inflammatory agents, hypolipidemic agents, ACE inhibitors, calcium antagonists and antioxidants were tested, they have failed to reduce restenosis [,]. Thus, it was determined to use antiproliferative drugs in reducing in-stent restenosis because of parallels between tumor growth and in-stent neointimal growth. The most widely applied anti proliferative drugs for control of hyperplasia after stenting are rapamycin (sirolimus), paclitaxel, and gemcitabine (Figure 1).
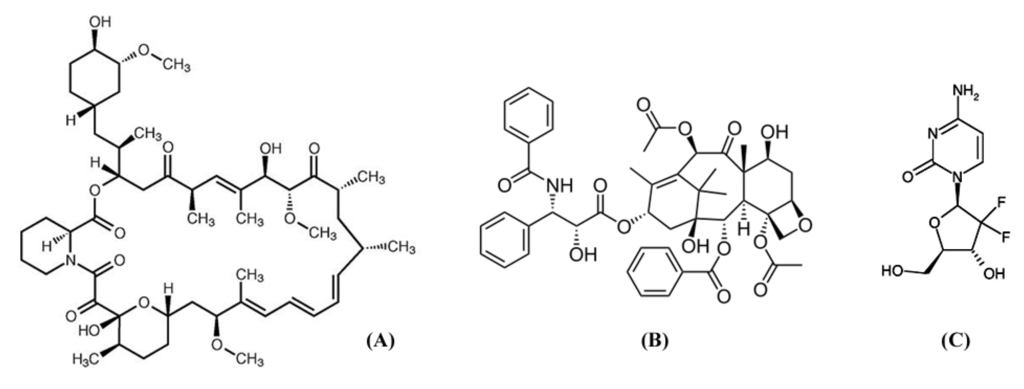
Figure 1.
Chemical structures of antiproliferative drugs: sirolimus (A); paclitaxel (B); and gemcitabine (C).
Favorable results in the studies of drug-eluting stents delivering inhibitors of the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) were observed []. Rapamycin, also known as sirolimus, is a macrolide antibiotic, which is produced naturally during fermentation by Streptomyces hygroscopicus. Rapamycin or sirolimus binds to the intracellular protein FKBP12, inactivate the TOR (target of rapamycin) protein and thus inhibits transition from the G1 phase to the S phase, which exerts an antimigratory and antiproliferative effect on vascular smooth muscle cells [,,]. Therefore, rapamycin or sirolimus blocks proliferation without cell death when it acts in an early phase of the cell cycle. The most prominent member of mTOR inhibitors is sirolimus [].
There are also derivatives of sirolimus such as zotarolimus, everolimus, biolimus A9, novolimus, myolimus, tacrolimus and pimecrolimus. Since these sirolimus analogues were expected to suppress cellular growth as mTOR inhibitors, these drugs have been evaluated. Evelolimus was developed as an immunosuppressive macrolide to prevent rejection in kidney, heart, and lung transplantation. It was shown that evelolimus-eluting stent has also inhibitory effect on proliferation of smooth muscle cells []. Moreover, evelolimus is absorbed by local tissue more rapidly and remains in the cells longer than sirolimus []. In addition, it was found that biolimus A9 resulted in significant reduction of stent thrombosis. Although tacrolimus and pimecrolimus showed sound antirestenotic efficacy in animals, these drugs clearly failed in clinical trials []. Tacrolimus is a macrolide immunosuppressant that has been used for organ transplant patients to prevent the body from rejecting a transplanted organ, and it has shown efficacy against neointimal hyperplasia after stenting in a porcine coronary artery model [].
Paclitaxel, which was initially extracted from the tree Taxus brevifolia, is a cytotoxic drug and inhibits cellular proliferation by suppressing microtubule dynamics []. It produces cytostasis by acting in the transition between G0 and G1 and between G1 and S in low doses, while it leads to cell death by blocking the transition between G2 and M in high doses []. Thus, it is important to find the lowest dose of paclitaxel to inhibit cell response without vascular damage. It was clinically demonstrated that paclitaxel-eluting stent reduced in-stent neointimal hyperplasia [].
Although estradiol-eluting stents showed a beneficial effect on neointimal formation [], a larger study with 502 patients showed that delivery of sirolimus and estradiol from a non polymeric stents did not have a positive effect []. Additionally, although oral corticoids possibly have a moderate effect on neointimal formation [,], corticoid-coated stents did not reveal an anti-proliferative effect [].
Gemcitabine, a deoxycytidine analog that inhibits DNA synthesis, has been reported to have better efficacy than other chemotherapeutic agents in both unresectable pancreatic cancer and bile duct cancer, and thus local delivery of gemcitabine has been tried in in vitro studies as well as in in vivo animal studies [,]. However, clinical application of gemcitabine-eluting stent has yet to be realized.
3. Vascular Drug Eluting Stents
Drug eluting vascular stents are usually modular or slotted-tube configurations that are crimped to a low-profile over a balloon catheter and dilated to the vessel size once positioned across the stenosed vessel, as shown in Figure 2. The drug is coated onto the stent wires and is released after the stent deployment into the arterial wall to control the hyperplasia initiated by the injury of the vessel wall after the stenting. Table 1 shows the materials of commercially available drug eluting stents. Cypher™ stent made of 316L stainless steel wires is coated with sirolimus dissolved in poly(ethylene vinyl acetate) (PEVA)–poly(n-butyl methacrylate) (PBMA) solution. When the drug-polymer coating is applied to the entire stent surface with a standard concentration of 140 μg of sirolimus per cm2 of stent surface area, the sirolimus is expected to be released approximately 80% of the drug within 30 days of stent deployment [].
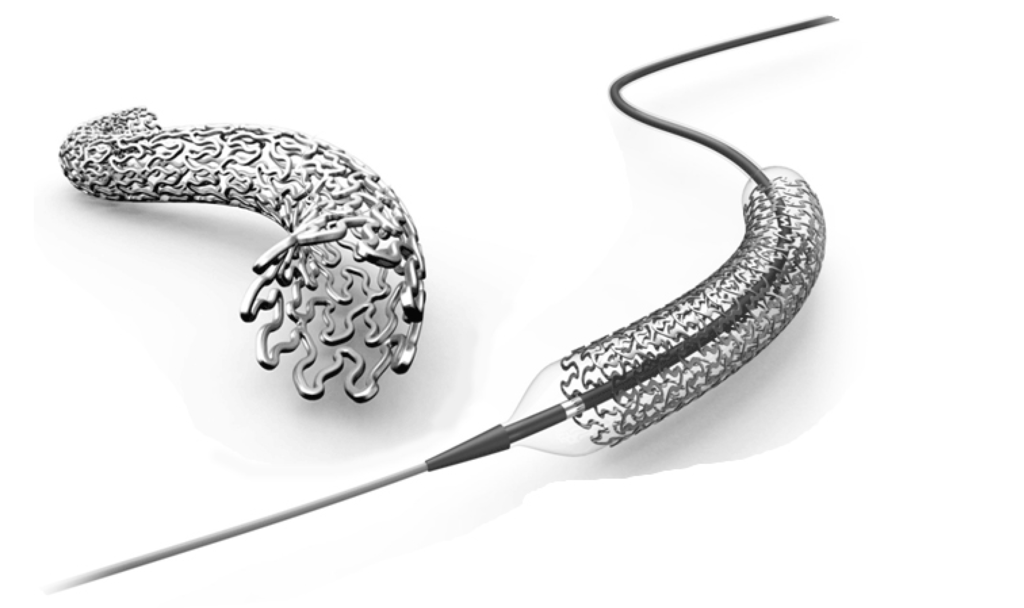

Figure 2.
A laser-cut balloon expandable vascular stent and the delivery set. The stent is crimped onto a tightly-folded balloon catheter for delivery. After correctly positioning the catheter across the stricture, the balloon is inflated with saline to place the stent, and then deflated for removal of the delivery set (courtesy of Genoss, Inc., Suwon, Korea).

Table 1.
Materials for commercial drug eluting stents.
| Product (Manufacturer) | Wire material (Specification) | Coating material | Drug |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cypher™ (Johnson & Johnson, New Brunswick, NJ, USA) | Stainless steel (316L) | Poly(ethylene vinyl acetate) (PEVA)–poly(n-butyl methacrylate) (PBMA) | Sirolimus |
| Taxus Express™ (Boston Scientific, Natick, MA, USA) | Stainless steel (316L) | Poly(styrene-b-isobutylene-b-styrene) (SIBS) | Paclitaxel |
| Nevo™ (Johnson & Johnson, New Brunswick, NJ, USA) | Cobalt–chromium (N/A) | Bioabsorbable poly(d,l-lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA) | Sirolimus |
| Supralimus™ (Sahajanand Medical, Gujarat, India) | Stainless steel (316L) | Bioabsorbable poly(l-lactide) (PLLA)–poly(vinyl-pyrrolidone) (PVP)–PLGA | Sirolimus |
| Endeavor Resolute ZES™ (Medtronic Vascular, Minneapolis, MN, USA) | Cobalt–chromium (MP35N) | Bioabsorbable (BioLinx: C19-PVP-C10) | Zotarolimus |
| BioMatrix™ (Biosensors, Singapore) | Stainless steel (316L) | Bioabsorbable poly(lactic acid) (PLA) | Biolimus A9 |
| EXCEL™ (JW Medical, Weihai, China) | Stainless steel (316L) | Bioabsorbable poly(l-lactic acid) (PLLA) | Sirolimus |
Taxus Express™ is also made of 316L stainless steel and is coated with a formulation of paclitaxel in poly(styrene-b-isobutylene-b-styrene) (SIBS). When the drug-polymer coating was applied to the entire stent surface in single layer with a standard concentration of 100 μg of paclitaxel per cm2 of stent surface area, the release of paclitaxel was shown to be bi-phasic with a 2-day initial burst followed by slow release over the following 10 days []. Both Taxus Express™ and Cypher™ stents are considered as the first generation drug-eluting stent, since the drug-impregnated polymer coatings of the two stents are durable or non-biodegradable. The remaining polymer coatings after drug release are deemed to cause chronic inflammatory response, delayed healing of the arterial wall, and very late stent thrombosis (>1 year). The second generation drug-eluting stents have employed biodegradable or bioabsorbable polymers for drug delivery, and shown prominence in decreasing the very late stent thrombosis [].
Nevo™ stent (Johnson & Johnson) is made of cobalt-chromium that has better mechanical properties than 316L stainless steel, and thus can generate the same radial strength of a stent with thinner stent struts. It has laser-cut microholes loaded with a formulation of sirolimus and a bioabsorbable poly(d,l-lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA). The clinical application of this stent, however, showed inferiority compared to the Taxus Express® stent []. Supralimus™ stent (Sahajanand Medical Technologies, Gujrat, India) delivers sirolimus via bioabsorbable copolymer of poly(l-lactide) PLLA, poly(vinyl-pyrrolidone) (PVP), and poly(d,l-lactide-co-glycolide)(PLGA) []. Endeavor Resolute ZES® stent is coated with a formulation of zotarolimus and a BioLinx polymer, which is a copolymer composed of hydrophilic C19 polymer, polyvinyl pyrrolidone (PVP) and a hydrophobic C10 polymer. This polymer coating was reported to have an extended drug elution due to high biocompatibility and biodurability. The stent has been most promising in terms of rates of adverse clinical events (11.6%), target-lesion revascularization (1.6%) and stent thrombosis (0.0%) at three year follow-up in the RESOLUTE trial []. Biomatrix™ and EXCEL™ stents employed a bioabsorbable poly(lactic acid) as a drug-carrying polymer that biodegrades into lactic acid, carbon dioxide and water in vivo []. In a recent study, Huang et al. incorporated both an anti-proliferative drug (sirolimus) and an anti-thrombotic drug (triflusal) in a biodegradable poly(d,l-lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) coating and showed that the stent coated with these dual drugs has both anti-restenotic and anti-thrombotic effects in an in vivo swine model []. The results suggest that time sequential delivery of multiple drugs could be a right approach to solve the very late stent thrombosis.
4. Non-Vascular Stents
Although conventional stents had been made of stainless steel or cobalt-chrome alloys, the elastic deformation of these conventional stent materials is limited to approx. 1% strain, which is distinctly different elastic deformation behavior from that of the living tissues. In contrast, nitinol alloy, which is intermetallic compound of nickel and titanium, exhibits superelasticity and thus is advantageous to the stent placement in tortuous segments of an internal tract. Shape-memory effect of the nitinol alloy can be useful for compacting a stent inside a delivery system with a small diameter. Thus, nitinol has been utilized increasingly in non-vascular self-expandable stents. Moreover, a nitinol stent can be easily compacted in an ice-water, where the shape memory alloy is in a martensite state, due to the shape memory effect. When the delivery system reaches the stricture and the outer sheath of the delivery system is retracted, the stent expands as the body temperature induces the transformation of nitinol back to an austenite state. Figure 3 shows an example of a biliary self-expanding nitinol stent being placed in the common biliary duct through a flexible endoscope positioned inside a duodenum.
The restenosis in non-vascular stents is usually caused by intimal hyperplasia of the vessel wall or the invasion of the surrounding benign or malignant tissue through the stent mesh []. Effort has been directed toward suppressing the expansion of hyperplasia by covering the stent with polymeric film or membrane. The stent covering material should have a proper mechanical properties such as elasticity to accommodate the expansion required for the stent placed in a tortuous part of the vessel or tract, and toughness that could resist the rigors of compression to make the profile of the stent as small as possible so that it could be loaded into a delivery catheter with smallest diameter []. Minimal profile of the stent and delivery catheter is preferred so that they can be delivered through an endoscope as shown in Figure 3.
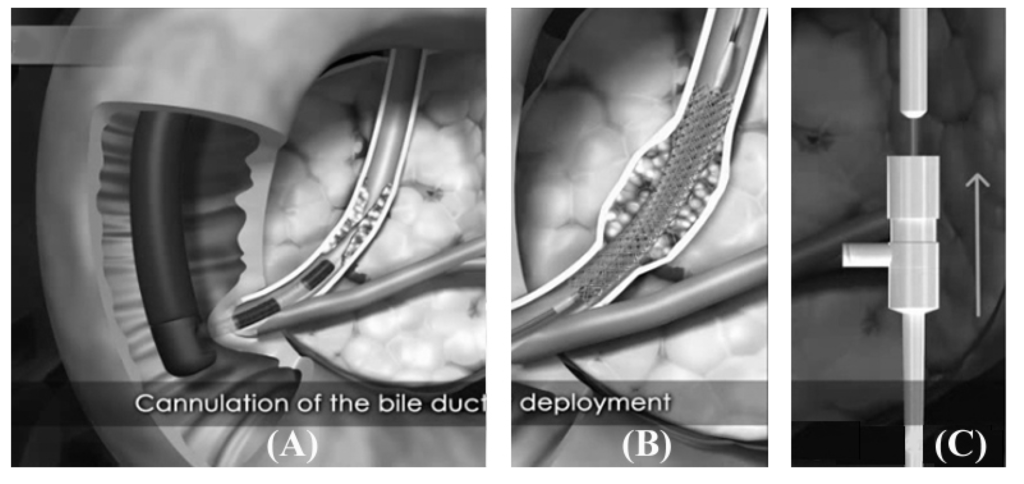
Figure 3.
Endoscopic biliary stent placement. The tip of the endoscope is placed at the duodenal pappila, and the delivery catheter containing the compressed stent is pushed across the stricture (A); The self expandable nitinol stent comes out of the catheter and expands over several days to reopen the obstructed biliary tract (B); To expose the compressed stent inside the catheter, the catheter is pulled back while maintaining the position of the stent with the help of the pusher (C). (Courtesy of S&G Biotech, Seongnam, Korea).
Materials which are widely used in stent covering are expanded polytrafluoroethylene (e-PTFE), silicon, and polyurethane (PU). Expanded PTFE is a porous membrane with about 85% porosity which is made from PTFE resin via paste extrusion followed by heating & stretching. The pore size is in the range of 0.02–40 μm []. Since nonpolarity and nonreactivity of PTFE provide the unique property in suppressing both thromboticity and pseudointimal proliferation when the material is placed in a humane body, PTFE is known as one of the best hemocompatible polymers and thus is useful in stent-graft, which is placed inside an aorta to treat aortic aneurysms and dissections. Since e-PTFE tube with various diameter and thickness are commercially available and the tube is able to be cut to the size of the stent and to be sutured, e-PTFE has been used in a wide range of clinical application including transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS), gastrointestinal stent, coronary stent, renal artery stent, and prostatic (urethral) stent [,,,,,,,,].
Silicones and polysiloxanes are polymers of alternating silicon and oxygen atoms. Silicones have been used in many novel biomedical applications due to their excellent biocompatibility and biodurability as well as unique combination of high temperature stability and low temperature elastomeric properties [,]. Silicones have been applied to medical devices including oxygenators, contact lenses, finger joints, catheters, blood pumps, breast implants, tubing, ophthalmologic implants, drug delivery, and stent covering [,]. It has been reported that silicone is useful in covering vascular [], esophageal [], trachea-bronchial [,], and biliary stents []. Silicone-covered stents are made by dipping or spraying method, which comprises a mixing of two part solutions, evaporation of the solvents, and curing process of the polymer chains.
5. Drug Eluting Non-Vascular Stent
Non-vascular stents are mostly covered with a polymeric membrane or film to prevent ingrowth of surrounding tissue through stent mesh, and drugs for suppression of hyperplastic benign or malignant tissue could be incorporated into the polymeric materials. Unlike the vascular stents, there has not been much interest covering the non-vascular stents in the gastrointestinal tract with bioabsorbable polymer, since permanent polymer covering is preferred in nonvascular stents, where the biodegradation of the stent covering could result in an in-growth of the surrounding benign or malignant tissue and early obstruction of the stent []. Studies on the drug-eluting non-vascular stents are collected in Table 2. A PTFE-covered stent could be impregnated with an anti-proliferative drug, which is co-soluble in a carrier polymer solution. The drug-incorporated carrier polymer fills the micropores of the e-PTFE membrane, and the drug is released when the water-soluble carrier-polymer dissolves slowly [,]. The drugs can also migrate away from the insoluble carrier polymer such as polyurethane via simple diffusion in a rubbery-state polymer []. Incorporation of an anti-proliferative drug into stents covered with silicone is difficult because the stent covering with silicone requires a very harsh organic solvent and vulcanization at an elevated temperature. Thus, silicone is often used as a drug-carrier polymer for PTFE membrane instead [,].

Table 2.
Drug delivery via covered non-vascular stent.
| Covering material | Carrier polymer | Drug | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| PTFE | Polyurethane | Gemcitabine | [] |
| Acetylated pullulan | Gemcitabine | [,] | |
| Silicone | Nitric oxide | [] | |
| Silicone | Abciximab | [] | |
| Polyurethane | None | Paclitaxel | [,,] |
| Gemcitabine | [,] | ||
| IN-1233 | [] |
In contrast to silicone, polyurethane (PU) is soluble in mild organic solvents such as tetrahydrofuran (THF), dimethylacetamide (DMAc), and dimethylformamide (DMF), where a wide variety of drugs could be co-dissolved. Thus, PU has been the most widely used polymer for local drug delivery via stent. Polyurethane films incorporated with paclitaxel (PTX) have been used in suppressing malignant tumor growth around biliary stents as well as benign tissue hyperplasia caused by placement of esophageal and urethral stents [,,,,]. When gemcitabine was incorporated in a polyurethane film, in vitro release behavior and in vivo toxicity of the gemcitabine were studied in an animal model [,,]. IN1233, an activin receptor-like kinase-5 inhibitor, was also incorporated in a stent covered with a polyurethane film and delivered to rabbit esophagus for evaluation of its effect on suppression of neointimal hyperplasia after esophageal stenting []. Polyurethane was also used as a drug-carrying polymer for local delivery of gemcitabine through a PTFE-covered stent [].
A medical grade PU widely used for stent covering is a polycarbonate urethane which is known to be more resistant to the physiological oxidative hydrolysis compared with polyether urethanes []. The polycarbonate urethane is soluble in THF, DMAc, and DMF, and swells in ethanol, methanol, 95% ethanol, acetone, and acetonitrile. It also swells significantly in DMAc-water co-solvent. Table 3 represents the solubility and swelling property data studied in our laboratory for a polycarbonate urethane, [ChronoFlex® AL 85A (AdvanSource Biomaterials Corporation; Wilmington, MA, USA)]. Co-solubility of a drug with PU in a solvent, however, does not guaranty homogeneous distribution of the drug molecules in a stent-covering film, as demonstrated in Figure 4. Although PTX was co-soluble with PU in DMAc, PTX appears to form micro-aggregates as solvent is dried. This suggests that PTX incorporated PU film is composed of free PTX molecules that are released from the PU matrix and micro-aggregates virtually trapped in the PU matrix. This suggestion is supported by the result that the cumulative release of PTX from the PU film did not increase as much as PTX loading into the film and the cumulative percentage of the released PTX from the PU film decreased significantly with the increase in the amount of PTX loading into the film (Figure 5) []. Lee also reported that a similar pattern of release, having extremely small release rate and decrease in cumulative release percentage with increase in drug loading, was found even when a pluronic surfactant was employed for better miscibility of PTX with polyurethane [].

Table 3.
Solubility and swelling properties of a polycarbonate urethane at 25 °C.
| Solvent | Swelling, % | |
|---|---|---|
| Organic | THF DMAc DMF | Soluble Soluble Soluble |
| Ethanol Methanol Acetone Acetonitrile | 38 26 86 30 | |
| Aqueous co-solvent | 95% Ethanol DMAc + H2O (9:1) DMAc + H2O (8:2) DMAc + H2O (7:3) | 13 70 26 6 |
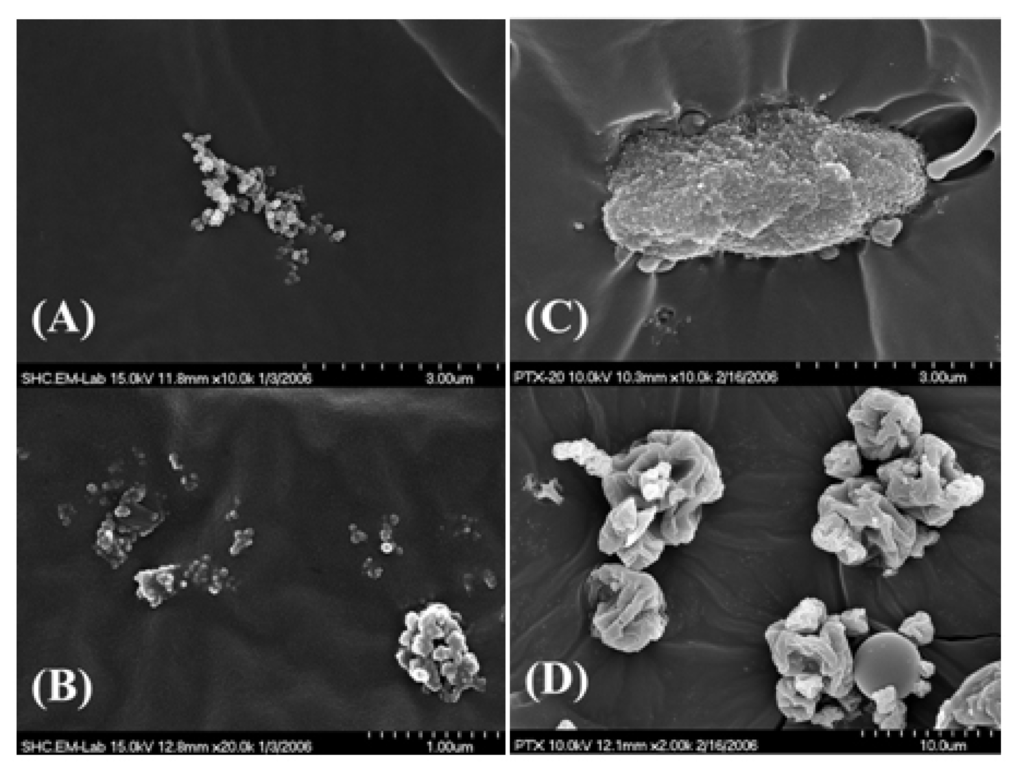

Figure 4.
Scanning electron microscope (SEM) images of micro-aggregates formed in a paclitaxel (PTX)–polyurethane (PU) film on a cut surface (A) and on an air-dried surface (B) from a PTX–PU film with PTX at 5.4 wt %; Larger aggregate was found from a PTX–PU film with PTX wt % at 20% (C); Note that the aggregate morphologies are different from that of original PTX powder (D). (Reprinted with permission from [], Copyright 2010 Springer).
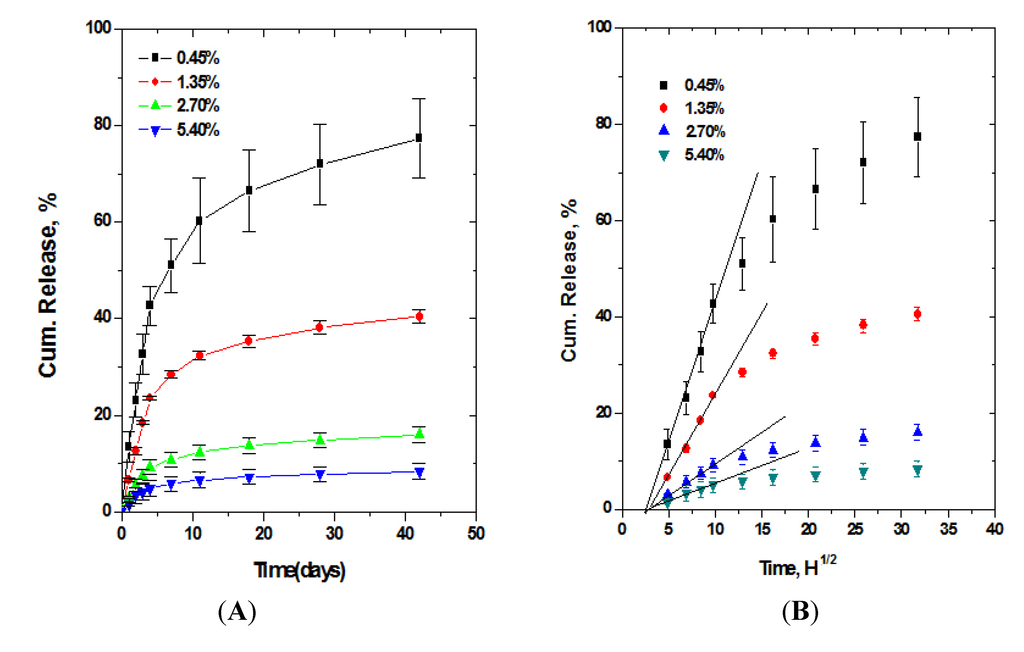
Figure 5.
Cumulative release of PTX from a polyurethane (PU) film. A 12-fold increase in the amount of PTX loading into PU film resulted in only two-fold increase in cumulative amount of PTX released from the PU film (A) and the cumulative percentage release was inversely proportional to the drug loading (B). (Reprinted with permission from [], Copyright 2010 Springer).
It should be noted that PTX release behavior in a durable polymer such as polyurethane and that in a biodegradable polymer, such as PGLA, is quite different in that the drug is released not only via diffusion of the drug molecules, but also by the degradation of the polymer and subsequent water absorption in the case of a drug in a biodegradable polymer matrix []. As for the vascular stents, the antiproliferative drug eluting from the stent targets the smooth muscle cell proliferation in the early stage (several weeks) after stenting, and thus drug elution from a biodegradable polymer is preferred since the drug release could be completed in a month and the release rate could be easily controlled. Both paclitaxel from a PGLA coating and sirolimus from polymer-free stent wires with micro-pores releases the drugs within a month, as shown in Figure 6 and Figure 7 [,]. The drug elution from a non-vascular stent, however, should last for a longer period of time than that from a vascular stent to prevent the stent from a malignant tissue in-growth.
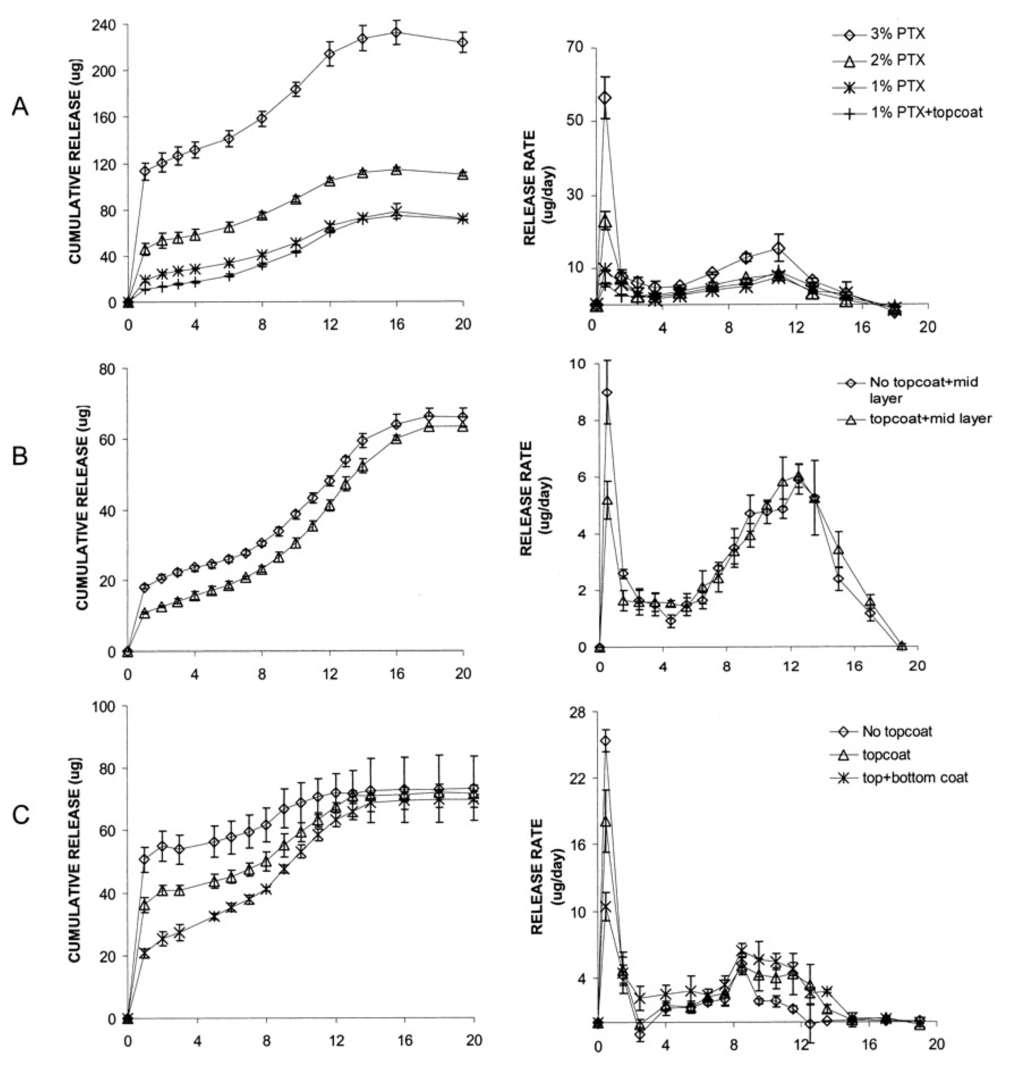
Figure 6.
Paclitaxel release from a PGLA-coated stent. Differing cumulative doses can be released (A) and the release rate is controlled by application of drug-free barrier layers (B,C). (Reprinted with permission from []. Copyright 2003 Wolters Kluwer Health).
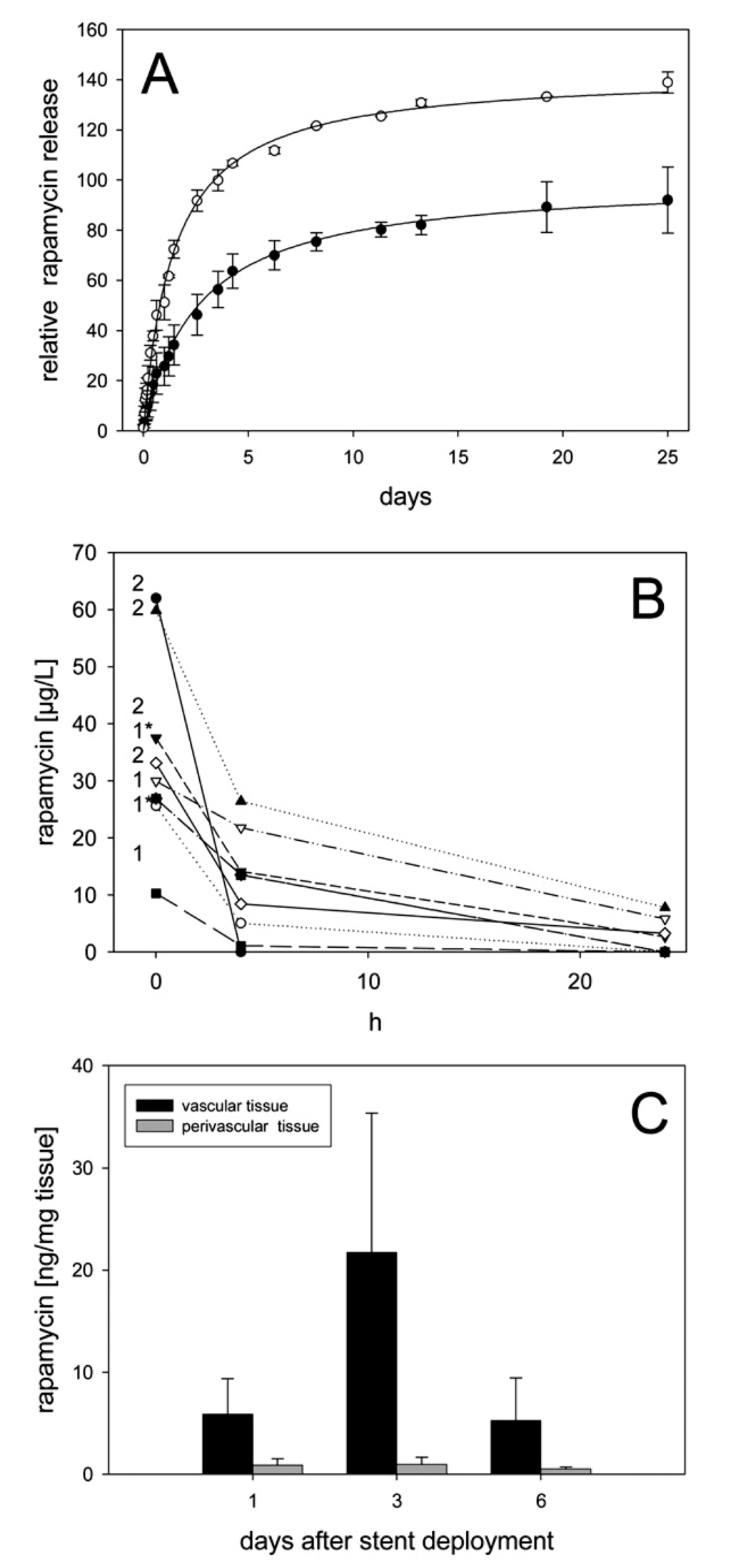
Figure 7.
Pharmaco kinetics of rapamycin-coated microporous stents. (A) HPLC-based cumulative rapamycin release kinetics from single-coated and dual-coated stent; (B) High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC)-measured rapamycin blood levels in 8 pigs receiving either 1 or 2 single-coated rapamycin-eluting microporous stents (number on the left of the diagram); and (C) Maximum tissue levels in the vascular and perivascular wall. (Reprinted with permission from []. Copyright 2005 Wolters Kluwer Health).
The release behavior of another anti-cancer drug gemcitabine from the PU matrix is quite different from that of PTX due to the extreme difference in water solubility between gemcitabine and PTX.PTX is practically insoluble in water, whereas gemcitabine is readily soluble in water and has a solubility of 1.55% [,]. There are two forms of gemcitabine; one is the pure chemical form of gemcitabine (PGEM), and the other is a clinical formulation gemcitabine (GEM). The clinical formulation is actually a gemcitabine hydrochloride and it is further admixed with sodium acetate and mannitol for venous injection. PGEM tends to form more crystals during the drying and solvent evaporation process of the stent covering. An initial burst of clinical gemcitabine, which is estimated from the cumulative absorbance of the drug-releasing medium, increases greatly with gemcitabine wt %, as shown in Figure 8. The initial burst of the drug at 4 h from the PU film incorporated with 10% GEM is only about 10%, but it increases to about 57% for 15% GEM-PU film and to about 75% for 20% drug-loaded GEM-PU film. In addition, when PGEM is used, the drug release is much slower with less initial burst and the initial burst as well as the release rate increases with the increase in GEM wt %. The initial burst is generally attributed to the dissolution of undissolved drug aggregates on the film surface. However, the fact that the micropores were observed in the middle of the GEM–PU film after the drug release demands more explanation (Figure 9). Gemcitabine release behavior and the micropores of the PU matrix after the drug release could be explained by an osmotically controlled drug release mechanism []. The solute concentration inside the PU film should be much higher than that in the physiological condition because of the excipients, mannitol and sodium acetate, as well as the dissociated gemcitabine-HCl. The water penetration into a pure PU matrix is known to be less than 2% [], but the presence of mannitol and sodium acetate as well as gemcitabine-HCl should facilitate water penetration into the PU matrix owing to the osmotic pressure gradient between the inside and outside of the polymer film. The film eventually releases the solutes into the surrounding milieu via the water channels formed inside the film, the rubbery PU chains then rearrange themselves and produce microporous network when the solutes are completely released, as shown in Figure 9. The increase of the initial burst of drug release with the increase in GEM concentration (Figure 8) indicates that the osmotic pressure created by the excipients and imbibed water is the major factor to determine the release rate of gemcitabine from the PU film.
Concluding this section, we emphasize that the paclitaxel release from a stent cover is very slow, whereas the gemcitabine release from a stent cover is very fast. Although there has been a clinical trial of PTX-eluting biliary stent for suppressing malignant tumor around the stent, the previous study failed to show efficacy of PTX-eluting stent, compared to the ordinary stent without PTX []. The safety of gemcitabine-releasing stent has been studied in a canine model, but its clinical application is yet to be tried []. Further study on how to control the drug release rate of these drugs is warranted for clinical success of the stent-based delivery of these anti-proliferative drugs.
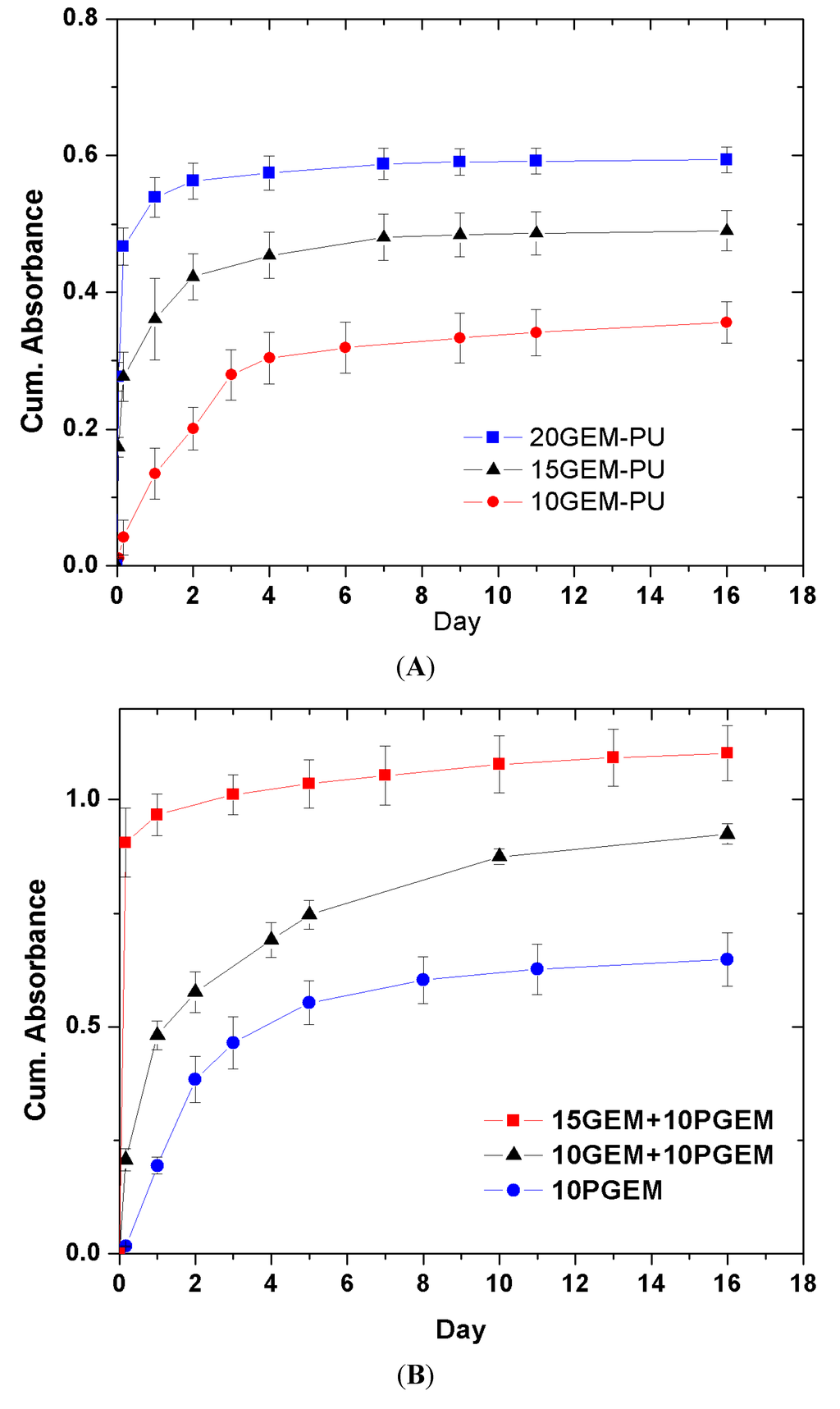
Figure 8.
Gemcitabine release behavior from a polyurethane film. Initial burst increases with drug dose when a clinical formulation of gemcitabine (GEM) is used (A). The initial burst is negligible for pure gemcitabine (PGEM) but it increases when the clinical form GEM is added (B). (Reprinted with permission from []. Copyright 2012 Editions de Sante).
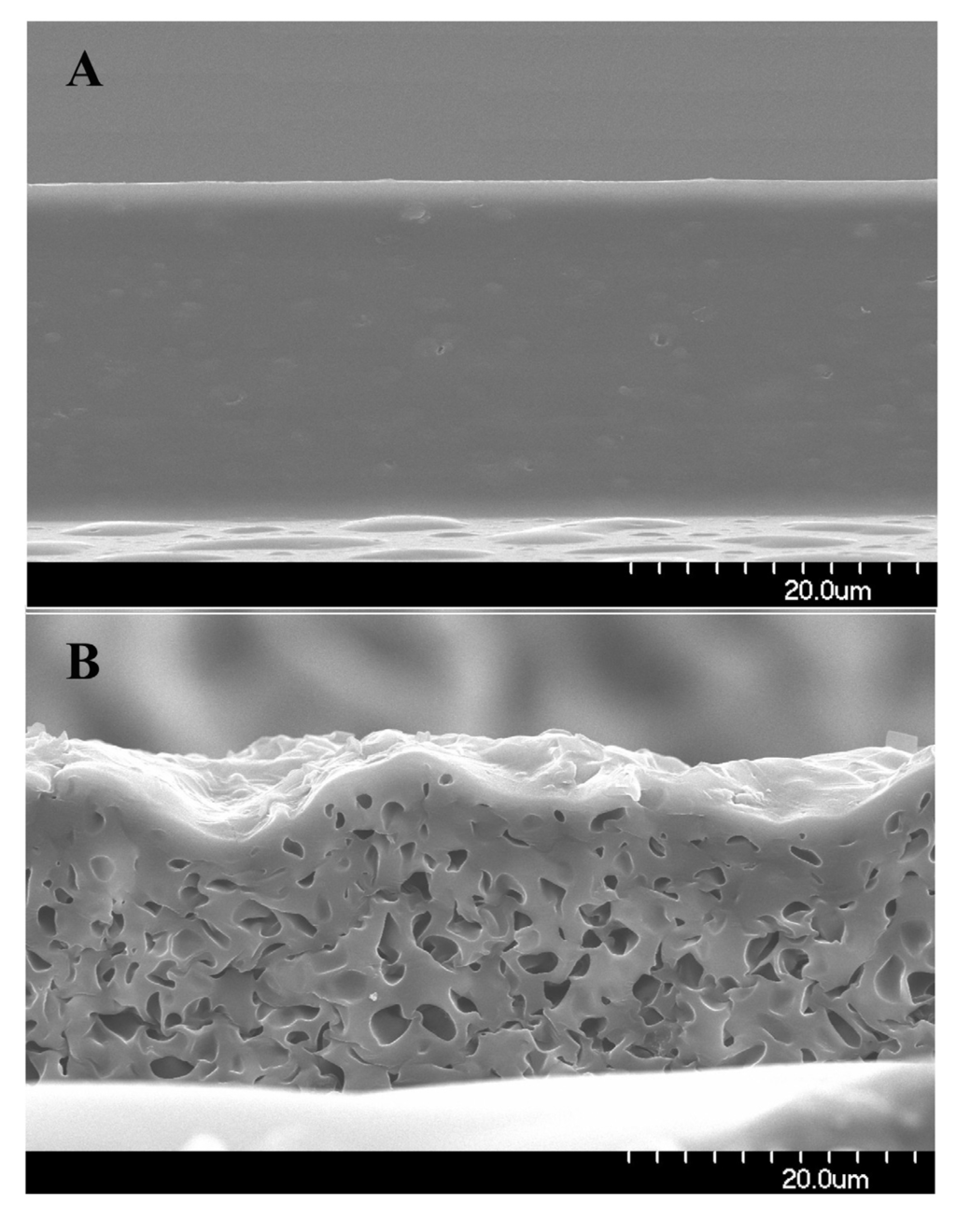
Figure 9.
SEM images of 10GEM-10PGEM–PU film before (A) and after the release of gemcitabine (B) GEM and PGEM denote the clinical form and pure chemical form of gemcitabine, respectively. (Reprinted with permission from []. Copyright 2012 Editions de Sante).
6. Small Interfering RNA Delivery Stent
Since some short interfering RNAs (siRNAs) are known to be effective in suppressing tissue hyperplasia, it is worthwhile to briefly mention the recent studies on local Si-RNA delivery. Small or short interfering RNAs (siRNA) mediate the degradation of complementary mRNA, which results in a specific silencing of gene expression [,]. The use of siRNA-targeting mRNAs that encode for cytokine receptors or adhesion molecules might be useful in minimizing the risks of stenting such as inflammation and excessive proliferation of vascular smooth muscle [,]. SiRNAs can be incorporated into a stent coating to locally deliver siRNAs to the vessel wall. Moreover, immobilization of siRNA on the target surface can enhance the transfer of siRNA by maintaining an elevated concentration of siRNA within the cellular microenviroment, which induces the sustained release of siRNA and facilitates the subsequent cellular internalization.
Various methods to incorporate siRNA into a stent surface were developed based on the fact that siRNA is the negatively charged polymer, and thus can bind to cationic polymers and a cationized surface by Coulombic interactions. It was reported that a cationized pullulan hydrogel-coated metal stents could be loaded with siRNA targeted at MMP2 gene, the coating by a cationized pullulan hydrogel was able to withstand the crimping of the stent on a balloon-catheter and its development and the release of siRNA from the stent was modulated by the presence of the cationic groups of the polymer coating of the stent []. In addition, the negatively charged siRNA can be incorporated into cationic polymers such as poly-l-lysine, poly(ethyleneimine) (PEI), chitosan to form complexes, which facilitates the siRNA uptake by a cell. It was reported that Akt1 siRNA-PEI complexes were immobilized on the hyaluronic acid-coated stent surface and that after treatment of the complexes in the rat VSMC line, the suppression of the Akt1 protein and its downstream signaling proteins regulating cellular proliferation was observed []. Polyelectrolyte multilayers (PEMs) with biodegradable polymers are also useful in the controlled release and stabilization of siRNA-polyelectrolyte complexes. A number of studies have demonstrated that siRNA can be incorporated into PEMs and the PEM cooperated with siRNA induces the release and the uptake of siRNA into cells in vitro. Flessner showed that siRNA embedded as a single layer in PEMs was released and able to silence targeted protein expression in the cancerous cell line HeLa. []. Recently, it was demonstrated that siRNA-chitosan complexes can be incorporated into PEMs consisting of hyaluronic acid and chitosan and that the siRNA-PEI complexes were delivered to cells in vitro and the complexes were transferred into artery walls in ex vivo []. Thus, it is possible that siRNA local delivery via stent can be an effective treatment option for control of both malignant tumors around a nonvascular stent as well as smooth muscle proliferation around a vascular stent. Despite these successes in the animal model, however, clinical application of siRNA-delivering stent has yet to be tried.
7. Conclusions
Stenting is a fast-growing and very successful clinical option for the treatment of both vascular and nonvascular stenoses. Stents can also become an efficient vehicle for local delivery of drugs and genes since drugs and genes could be coated on the stent wires or stent coverings. Clinical drug delivery stents have been successful in the treatment of vascular region by suppressing hyperplasia of smooth muscle cells after coronary stenting, but have yet to show a clinical efficacy on hyperplastic tissue around the stents in the nonvascular region. Further research and technical improvement are required to develop the efficacy and safety of the drug- or gene-eluting stents in the nonvascular conduits.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Yuan, J.G.; Marin, M.L.; Veith, F.J.; Ohki, T.; Sanchez, L.A.; Suggs, W.D.; Lyon, R.T. Endovascular grafts for noninfected aortoiliac anastomotic aneurysms. J. Vasc. Surg. 1997, 26, 210–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonello, L.; Com, O.; Gaubert, J.Y.; Sbraggia, P.; Paganelli, F. Covered stent for closure of symptomatic plexus-like coronary fistula. Int. J. Cardiol. 2006, 109, 408–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitigen, A.; Cevik, C.; Turan, B.; Otahbachi, M. Use of PTFE-covered stent in acute myocardial infarction of aneurysmatic coronary artery. Int. J. Cardiol. 2009, 132, 72–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Z.W.; Hoopes, P.J.; Koutras, P.C.; Ebbighausen, W.H.; Wagner, R.J.; Bettmann, M.A. Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt with an autologous vein-covered Stent: Results in a swine model. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2001, 12, 1333–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, J.V.; Rossbach, M.M.; Cleveland, T.J.; Gaines, P.A.; Beard, J.D. Endovascular stent-graft repair of traumatic carotid artery pseudoaneurysm. Clinic. Radiol. 2002, 57, 308–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeloni, S.; Merli, M.; Salvatori, F.M.; Santis, A.D.; Fanelli, F.; Pepino, D.; Attili, A.F.; Rossi, P.; Riggio, O. Polytetrafluoroethylene-covered stent grafts for TIPS procedure: 1-Year patency and clinical results. J. Hepatol. 2005, 42, 75–76. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.W.; Yang, S.G.; Na, K. Gemcitabine-releasing polymeric films for covered self-expandable metallic stent in treatment of gastrointestinal cancer. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 427, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.; Yang, S.G.; Na, K. An acetylated polysaccharide-PTFE membrane-covered stent for the delivery of gemcitabine for treatment of gastrointestinal cancer and related stenosis. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 3603–3610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, M.J.; Kim, H.; Kim, K.S.; Park, S.; Chung, J.B.; Park, S.W. Safety evaluation of self-expanding metallic biliary stents eluting gemcitabine in a porcine model. J. Gastroen. Hepatol. 2012, 27, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, D.B.; Silvis, S.E.; Ansel, H.J. Management of a tracheoesophageal fistula with a silicone-covered self-expanding metal stent. Gastrointest. Endosc. 1994, 40, 497–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, E.Y.; Shin, J.H.; Song, H.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Shim, T.S.; Kim, D.K. Bronchopleural fistula treated with a silicone-covered bronchial occlusion stent. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2010, 89, 293–296. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.H.; Shin, J.H.; Song, H.Y.; Lee, S.C.; Kim, K.R.; Park, J.H. Use of a retrievable metallic stent internally coated with silicone to treat airway obstruction. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2008, 19, 1208–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, C.J.; Song, H.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Park, H.G.; Kang, H.S.; Ro, J.Y.; Hong, J.H. Temporary placement of a covered, retrievable, barbed stent for the treatment of hormone-induced benign prostatic hyperplasia: Technical feasibility and histologic changes in canine prostates. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2010, 21, 1429–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, H.K.; Song, H.Y.; Yeo, H.J.; Park, J.H.; Kim, J.H.; Park, H.; Kim, C.S. Retrospective comparison of internally and externally covered retrievable stent placement for patients with benign urethral strictures caused by traumatic injury. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2012, 198, W55–W61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastrati, A.; Schömig, A.; Elezi, S.; Schühlen, H.; Dirschinger, J.; Hadamitzky, M.; Wehinger, A.; Hausleiter, J.; Walter, H.; Neumann, F.J. Predictive factors of restenosis after coronary stent placement. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1997, 30, 1428–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.Y.; Do, Y.S.; Han, Y.M.; Sung, K.B.; Choi, E.K.; Sohn, K.H.; Kim, H.R.; Kim, S.H.; Min, Y.I. Covered, expandable esophageal metallic stent tubes: Experiences in 119 patients. Radiology 1994, 193, 689–696. [Google Scholar]
- Song, H.Y.; Park, S.I.; Do, Y.S.; Yoon, H.K.; Sung, K.B.; Sohn, K.H.; Min, Y.I. Expandable metallic stent placement in patients with benign esophageal strictures: Results of long-term follow-up. Radiology 1997, 203, 131–136. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, F.S.; Katsanos, K.; Fotiadis, N.; Gulati, M.; Sabharwal, T.; Adam, A. Management of complications following percutaneous biliary interventions. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2009, 32, S1–S27. [Google Scholar]
- Serruys, P.W.; Foley, D.P.; Jackson, G.; Bonnier, H.; Macaya, C.; Vrolix, M.; Branzi, A.; Shepherd, J.; Suryapranata, H.; de Feyter, P.J.; et al. A randomized placebo-controlled trial of fluvastatin for prevention of restenosis after successful coronary balloon angioplasty; final results of the fluvastatin angiographic restenosis (FLARE) trial. Eur. Heart. J. 1999, 20, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, D.R., Jr.; Savage, M.; LaBlanche, J.M.; Grip, L.; Serruys, P.W.; Fitzgerald, P.; Fischman, D.; Goldberg, S.; Brinker, J.A.; Zeiher, A.M.; et al. Results of prevention of restenosis with tranilast and its outcomes (PRESTO) trial. Circulation 2002, 106, 1243–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stettler, C.; Allemann, S.; Wandel, S.; Kastrati, A.; Morice, M.C.; Schömig, A.; Pfisterer, M.; Stone, G.; Leon, M.; Lezo, J.S.; et al. Drug eluting and bare metal stents in people with and without diabetes: Collaborative network meta-analysis. Br. Med. J. 2008, 337. [Google Scholar]
- Marx, S.O.; Marks, A.R. Bench to bedside the development of rapamycin and its application to stent restenosis. Circulation 2001, 104, 852–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, C.R.; Huie, P.; Billingham, M.E.; Morris, R.E. Rapamycin inhibits arterial intimal thickening caused by both alloimmune and mechanical injury: Its effect on cellular, growth factor, and cytokine response in injured vessels. Transplantation 1993, 55, 1409–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poon, M.; Marx, S.O.; Gallo, R.; Badimon, J.J.; Taubman, M.B.; Marks, A.R. Rapamycin inhibits vascular smooth muscle cell migration. J. Clin. Invest. 1996, 98, 2277–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessely, R.; Schömig, A.; Kastrati, A. Sirolimus and paclitaxel on polymer-based drug-eluting stents: Similar but different. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2006, 47, 708–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, R. Drug-eluting stents and other anti-restenosis devices. Rev. Esp. Cardiol. 2005, 58, 842–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribamar Coata, J.; Abizaid, A.; Feres, F.; Costa, R.; Seixas, A.C.; Maia, F.; Eduardo Sousa, J. EXCELLA first-in-man (FIM) study: Safety and efficacy of novolimus-eluting stent in de novo coronary lesions. EuroIntervention 2008, 4, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ormiston, J.A.; Serruys, P.W.; Regar, E.; Dudek, D.; Thuesen, L.; Webster, M.W.; Garcia-Garcia, H.M.; McGreevy, R.; Veldhof, S. A bioabsorbable everolimus-eluting coronary stent system for patients with single de-novo coronary artery lesions (ABSORB): A prospective open-label trial. Lancet 2008, 371, 899–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamada, N.; Miyata, M.; Eto, H.; Shirasawa, T.; Akasaki, Y.; Nagaki, A.; Tei, C. Tacrolimus-eluting stent inhibits neointimal hyperplasia via calcineurin/NFAT signaling in porcine coronary artery model. Atherosclerosis 2010, 208, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herdeg, C.; Oberhoff, M.; Baumbach, A.; Blattner, A.; Axel, D.I.; Schröder, S.; Heinle, H.; Karsch, K.R. Local paclitaxel delivery for the prevention of restenosis: Biological effects and efficacy in vivo. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2000, 35, 1969–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heldman, A.W.; Cheng, L.; Jenkins, G.M.; Heller, P.F.; Kim, D.W.; Ware, M., Jr.; Nater, C.; Hruban, R.H.; Rezai, B.; Abella, B.S.; et al. Paclitaxel stent coating inhibits neointimal hyperplasia at 4 weeks in a porcine model of coronary restenosis. Circulation 2001, 103, 2289–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abizaid, A.; Albertal, M.; Costa, M.A.; Abizaid, A.S.; Staico, R.; Feres, F.; Sousa, J.E. First human experience with the 17-β-estradiol-eluting stent: The estrogen and stents to eliminate restenosis (EASTER) trial. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2004, 43, 1118–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adriaenssens, T.; Mehilli, J.; Wessely, R.; Ndrepepa, G.; Seyfarth, M.; Wieczorek, A.; Schömig, A. Does addition of estradiol improve the efficacy of a rapamycin-eluting stent? Results of the ISAR-PEACE randomized trial. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2007, 49, 1265–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patti, G.; Pasceri, V.; Carminati, P.; D’Ambrosio, A.; Carcagnì, A.; di Sciascio, G. Effect of dexamethasone-eluting stents on systemic inflammatory response in patients with unstable angina pectoris or recent myocardial infarction undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention. J. Am. Cardiol. 2005, 95, 502–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrero, V.; Ribichini, F.; Rognoni, A.; Marino, P.; Brunelleschi, S.; Vassanelli, C. Comparison of efficacy and safety of lower-dose to higher-dose oral prednisone after percutaneous coronary interventions (the IMPRESS-LD study). Am. J. Cardiol. 2007, 99, 1082–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesarini, G.; Ferrero, V.; Tomai, F.; Paloscia, L.; de Cesare, N.; Tamburino, C.; Ribichini, F. Steroid-eluting stents in patients with acute coronary syndromes. Angiographic results of DESIRE: Dexamethasone-eluting stent Italian registry. J. Invasive Cardiol. 2009, 21, 86–91. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, M.S.; Hong, J.Y.; Park, S. Gemcitabine release behavior of polyurethane matrixes designed for local anti-cancer drug delivery via stent. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2012, 22, 301–306. [Google Scholar]
- Moses, J.W.; Leon, M.B.; Popma, J.J.; Fitzgerald, P.J.; Holmes, D.R.; O’Shaughnessy, C.; Kuntz, R.E. Sirolimus-eluting stents versus standard stents in patients with stenosis in a native coronary artery. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 349, 1315–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, G.W.; Ellis, S.G.; Cox, D.A.; Hermiller, J.; O’Shaughnessy, C.; Mann, J.T. A polymer-based, paclitaxel-eluting stent in patients with coronary artery disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foerst, J.; Vorpahl, M.; Engelhardt, M.; Koehler, T.; Tiroch, K.; Wessely, R. Evolution of coronary stents: From bare-metal stents to fully biodegradable, drug-eluting stents. Comb. Prod. Ther. 2013, 3, 9–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krucoff, M.W.; Kereiakes, D.J.; Petersen, J.L.; Mehran, R.; Hasselblad, V.; Lansky, A.J. A novel bioresorbable polymer paclitaxel-eluting stent for the treatment of single and multivessel coronary disease: Primary results of the COSTAR (cobalt chromium stent with antiproliferative for restenosis) II study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2008, 51, 1543–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dani, S.; Kukreja, N.; Parikh, P.; Joshi, H.; Prajapati, J.; Jain, S.; Thanvi, S.; Shah, B.; Dutta, J.P. Biodegradable-polymer-based, sirolimus-eluting supralimus stent: 6-Month angiographic and 30-month clinical follow-up results from the series I prospective study. Eur. Intervention. 2008, 4, 59–63. [Google Scholar]
- Gutiérrez-Chico, J.L.; van Geuns, R.J.; Regar, E.; Giessen, W.J.; Kelbæk, H.; Saunamäki, K.; Escaned, J.; Gonzalo, N.; Mario, C.; Borgia, F.; et al. Tissue coverage of a hydrophilic polymer-coated zotarolimus-eluting stent vs. a fluoropolymer-coated everolimus-eluting stent at 13-month follow-up: An optical coherence tomography substudy from the resolute all comers trial. Eur. Heart J. 2011, 32, 2454–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Venkatraman, S.S.; Boey, F.Y.; Lahti, E.M.; Umashankar, P.R.; Mohanty, M.; Arumugam, S.; Khanolkar, L.; Vaishnav, S. In vitro and in vivo performance of a dual drug-eluting stent (DDES). Biomaterials 2010, 31, 4382–4391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.Y.; Song, H.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Fan, Y.; Park, S.; Kim, D.K.; Na, H.K. IN-1233–eluting covered metallic stent to prevent hyperplasia: Experimental study in a rabbit esophageal model. Radiology 2013, 267, 396–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Guo, S.; Wang, Z. A type of esophageal stent coating composed of one 5-fluorouracil-containing EVA layer and one drug-free protective layer: In vitro release, permeation and mechanical properties. J. Control. Release 2007, 118, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wikol, M.; Hartmann, B.; Brendle, J.; Crane, M.; Beuscher, U.; Brake, J.; Gore, W.L. Expanded polytetrafluoroethylenemembranes and their applications. Drugs Pharm. Sci. 2008, 174, 619–640. [Google Scholar]
- Melissano, G.; Civilini, E.; Bertoglio, L.; Setacci, F.; Chiesa, R. Endovascular treatment of aortic arch aneurysms. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. 2005, 29, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimono, T.; Kato, N.; Yasuda, F.; Suzuki, T.; Yuasa, U.; Onoda, K.; Yada, I. Transluminal stent-graft placements for the treatments of acute onset and chronic aortic dissections. Circulation 2002, 106, 241–247. [Google Scholar]
- Curtis, J.; Colas, A. Silicone Biomaterials: History and Chemistry. In Biomaterials Science: An Introduction to Materials in Medicine, 2nd ed.; Rutner, B.D., Hoffman, A.S., Schoen, F.J., Lemons, J.E., Eds.; Elsevier Academic Press: Melville, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Curtis, J.; Colas, A. Medical Applications of Silicones. In Biomaterials Science: An Introduction to Materials in Medicine, 2nd ed.; Rutner, B.D., Hoffman, A.S., Schoen, F.J., Lemons, J.E., Eds.; Elsevier Academic Press: Melville, NY, USA, 2004; pp. 697–707. [Google Scholar]
- Hron, P. Hydrophilisation of silicone rubber for medical applications. Polym. Int. 2003, 52, 1531–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashak, A.; Rahimi, A. Silicone polymers in controlled drug delivery systems: A review. Iran. Polym. J. 2009, 18, 279–295. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, D.B.; Axelrad, A.M.; Fleischer, D.E.; Kozarek, R.A.; Silvis, S.E.; Benjamin, S.B.; Freeman, M.L. Silicone-covered wallstent prototypes for palliation of malignant esophageal obstruction and digestive-respiratory fistulas. Gastrointest. Endosc. 1997, 45, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, T.K.; Pollack, J.; Chodash, H.B. Silicone-covered metal stents (An in vitro evaluation for biofilm formation and patency). Dig. Dis. Sci. 1999, 44, 1780–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, B.W.; Jeong, S.; Lee, D.H.; Lee, J.I.; Lee, S.C.; Kang, S.G. The biodurability of covering materials for metallic stents in a bile flow phantom. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2012, 57, 1056–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.G.; Lee, S.C.; Choi, S.H.; Park, S.S.; Jeong, S.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, M. Paclitaxel-polyurethane film for anti-cancer drug delivery: Film characterization and preliminary in vivo study. Macromol. Res. 2010, 18, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, T.H.; Jo, E.A.; Na, K. Development of polymeric coating material for effective drug-elutingstent. Polymer (Korea) 2011, 35, 483–487. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, D.; Narciso, H.; Kamdar, K.; Zhang, P.; Barclay, B.; March, K.L. Stent-based nitric oxide delivery reducing neointimal proliferation in a porcine carotid overstretch injury model. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2005, 28, 60–65. [Google Scholar]
- Fontaine, A.B.; Borsa, J.J.; Passos, S.D.; Hoffer, E.K.; Bloch, R.D.; Starr, F.; So, C. Evaluation of local abciximab delivery from the surface of a polymer-coated covered stent: In vivo canine studies. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2001, 12, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.H.; Song, H.Y.; Cho, C.G.; Yuk, S.H.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, Y.M.; Yoon, C.J.; Kim, T.H.; Suh, J.Y.; He, X. Tissue hyperplasia: Influence of a paclitaxel-eluting covered stent-preliminary study in a canine urethral model. Radiology 2005, 234, 438–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.K. Drug-eluting stent in malignant biliary obstruction. J. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Surg. 2009, 16, 628–632. [Google Scholar]
- Jeon, S.R.; Eun, S.H.; Shim, C.S.; Ryu, C.B.; Kim, J.O.; Cho, J.Y.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, M.S.; Jin, S.Y. Effect of drug-eluting metal stents in benign esophageal stricture: An in vivo animal study. Endoscopy 2009, 41, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lao, L.L.; Venkatraman, S.S. Paclitaxel release from single and double-layered poly(d,l-lactide-co-glycolide)/poly(l-lactide) film for biodegradable coronary stent application. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2008, 87, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein, A.; McClean, D.; Kar, S.; Takizawa, K.; Varghese, K.; Baek, N.; Park, K.; Fishbein, M.C.; Makkar, R.; Litvack, F.; et al. Local drug delivery via a coronary stent with programmable release pharmacokinetics. Circulation 2003, 107, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessely, R.; Hausleiter, J.; Michaelis, C.; Jaschke, B.; Vogeser, M.; Milz, S.; Behnisch, B.; Schratzenstaller, T.; Renke-Gluszko, M.; Stover, M.; et al. Inhibition of neointima formation by a novel drug-eluting stent system that allows for dose-adjustable, multiple, and on-site stent coating. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2005, 25, 748–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamada, H.; Ishihara, K.; Masuoka, N.; Mikuni, K.; Nakajima, N. Enhancement of water-solubility and bioactivity of paclitaxel using modified cyclodextrins. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2006, 102, 369–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, B.P.; Thakur, N.; Jain, N.P.; Banweer, J.; Jain, S. Osmotically controlled drug delivery system with associated drugs. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 13, 571–588. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, I.; Smith, N.; Jones, E.; Finch, D.S.; Cameron, R.E. Analysis and evaluation of a biomedical polycarbonate urethane tested in an in vitro study and an ovine arthroplasty model. Part I: Materials selection and evaluation. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, T.J.; Lee, S.S.; Yun, S.C.; Park, D.H.; Seo, D.W.; Lee, S.K.; Kim, M.H. Paclitaxel-eluting covered metal stents versus covered metal stents for distal malignant biliary obstruction: A prospective comparative pilot study. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2011, 73, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fire, A.; Xu, S.; Montgomery, M.K.; Kostas, S.A.; Driver, S.E.; Mello, C.C. Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 1998, 391, 806–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorsett, Y.; Tuschl, T. SiRNAs: Applications in functional genomics and potential as therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Drug. Discov. 2004, 3, 318–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, T.M. Illuminating the silence: Understanding the structure and function of small RNAs. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San Juan, A.; Bala, M.; Hlawaty, H.; Portes, P.; Vranckx, R.; Feldman, L.J.; Letourneur, D. Development of a functionalized polymer for stent coating in the arterial delivery of small interfering RNA. Biomacromolecules 2009, 10, 3074–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, H.L.; Bae, I.H.; Lim, K.S.; Song, I.T.; Lee, H.; Muthiah, M.; Namgung, R.; Kim, W.J.; Kim, D.G.; Ahn, Y.; et al. Suppression of post-angioplasty restenosis with an Akt1 siRNA-embeddedcoronary stent in a rabbit model. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 8548–8556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrova, M.; Affolter, C.; Meyer, F.; Nguyen, I.; Richard, D.G.; Schuster, C.; Bartenschlager, R.; Voegel, J.C.; Ogier, J.; Baumert, T.F. Sustained delivery of siRNAs targeting viral infection by cell-degradable multilayered polyelectrolyte films. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2008, 105, 16320–16325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flessner, R.M.; Jewell, C.M.; Anderson, D.G.; Lynn, D.M. Degradable polyelectrolyte multilayers that promote the release of siRNA. Langmuir 2011, 27, 7868–7876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossfeld, S.; Nolte, A.; Hartmann, H.; Recke, M.; Schaller, M.; Walker, T.; Kjems, J.; Schlosshauer, B.; Stoll, D.; Wendel, H.P.; et al. Bioactive coronary stent coating based on layer-by-layer technology for siRNA release. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 6741–6752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).