UV-C and UV-C/H₂O-Induced Abiotic Degradation of Films of Commercial PBAT/TPS Blends
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Ultraviolet C Irradiation
2.3. Characterization Methods
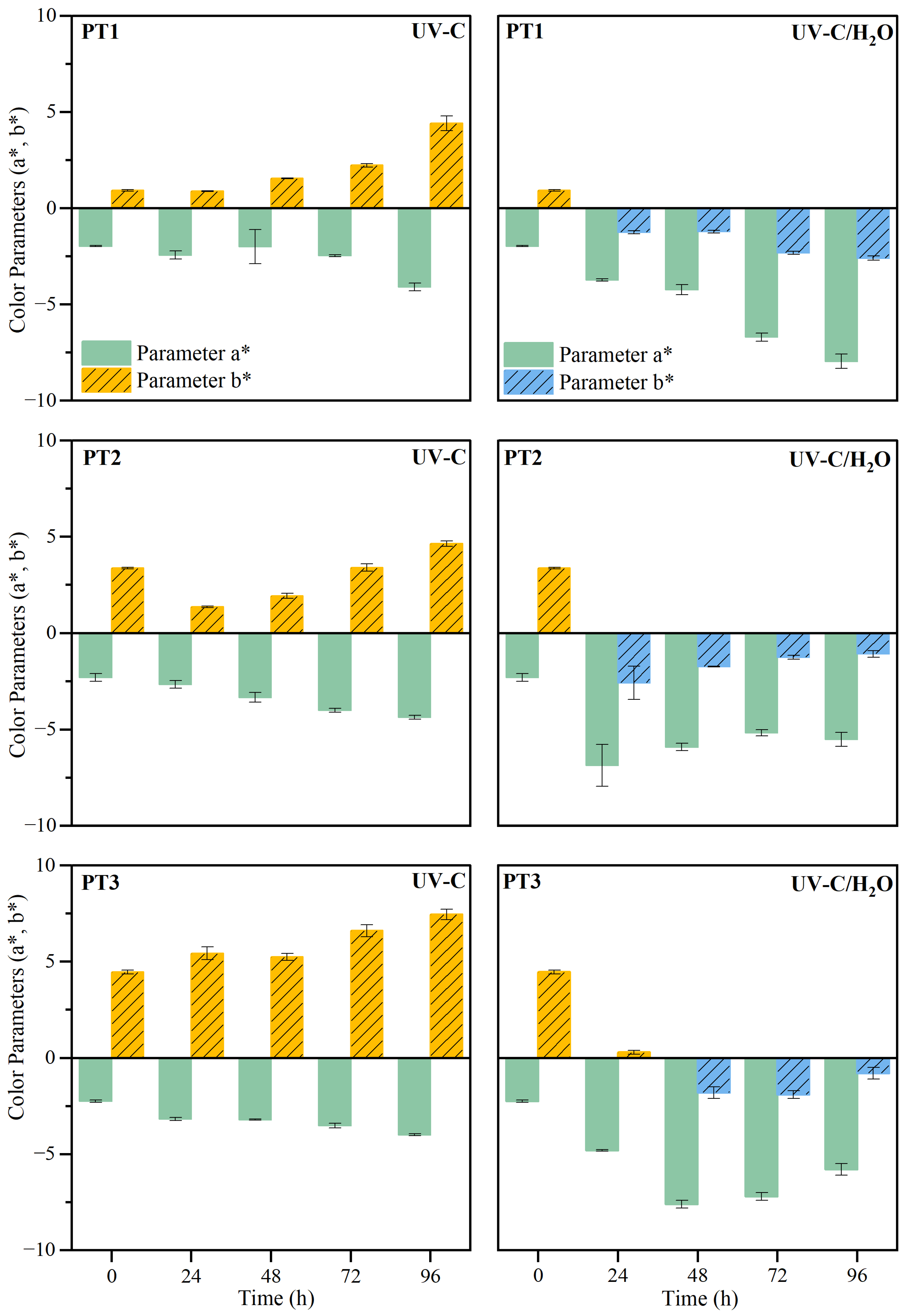
2.3.1. Colorimetry
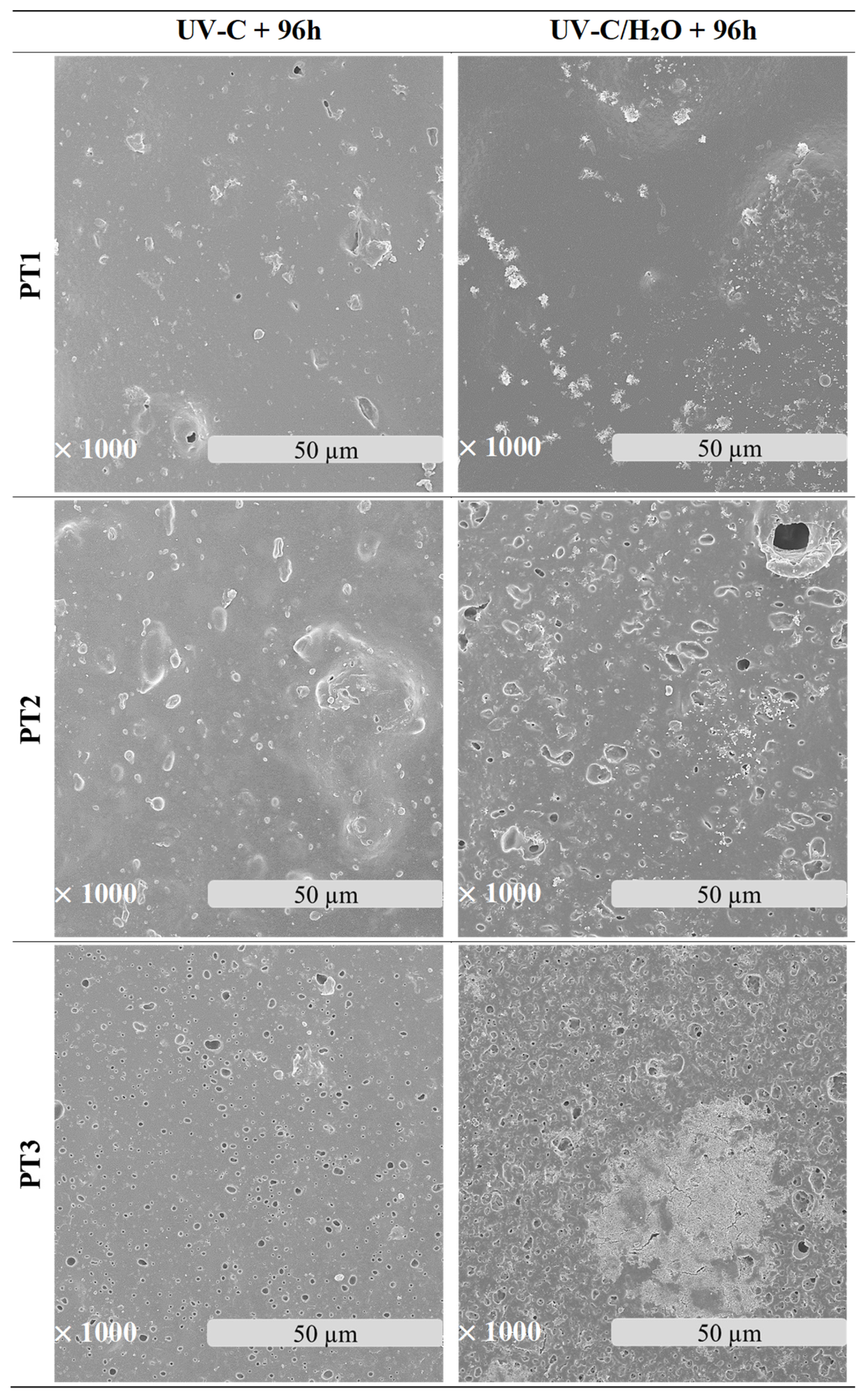
2.3.2. Field-Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy (FE-SEM)
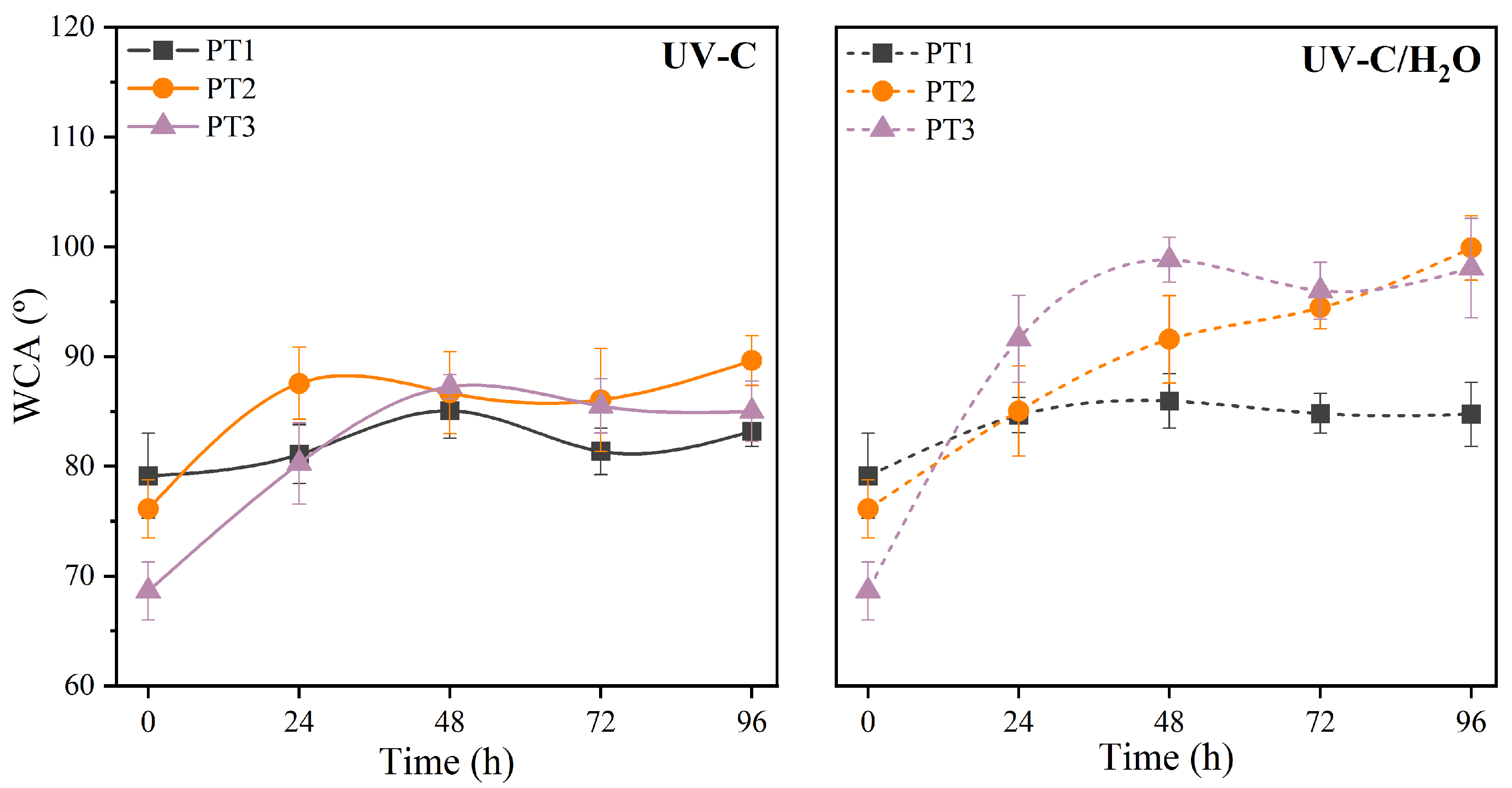
2.3.3. Water Contact Angle (WCA)
2.3.4. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.3.5. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
2.3.6. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.3.7. Gel Permeation Chromatography (GPC)
3. Results and Discussions
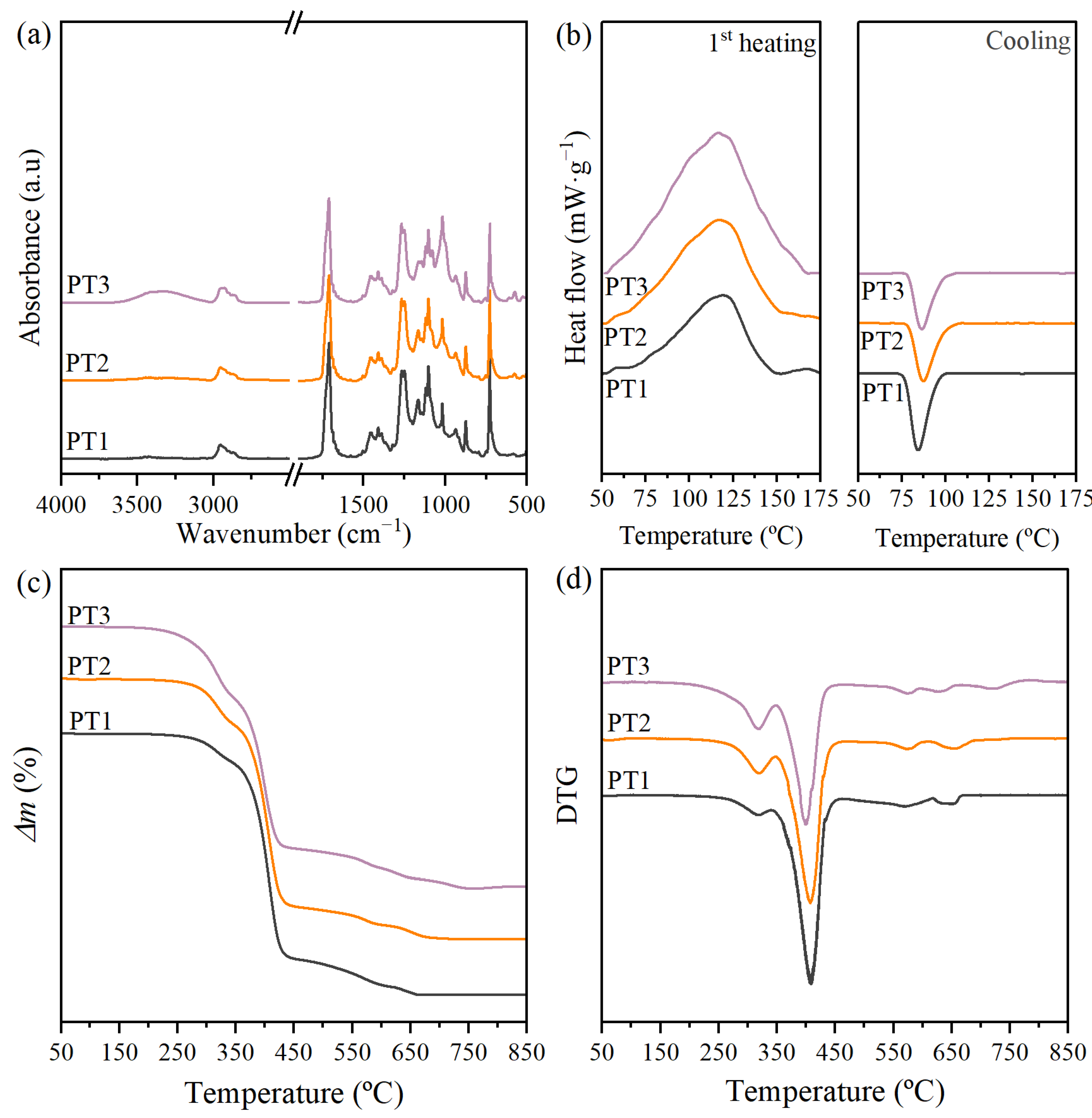
3.1. Initial Physico-Chemical Properties of Films of Commercial PBAT/TPS Blends
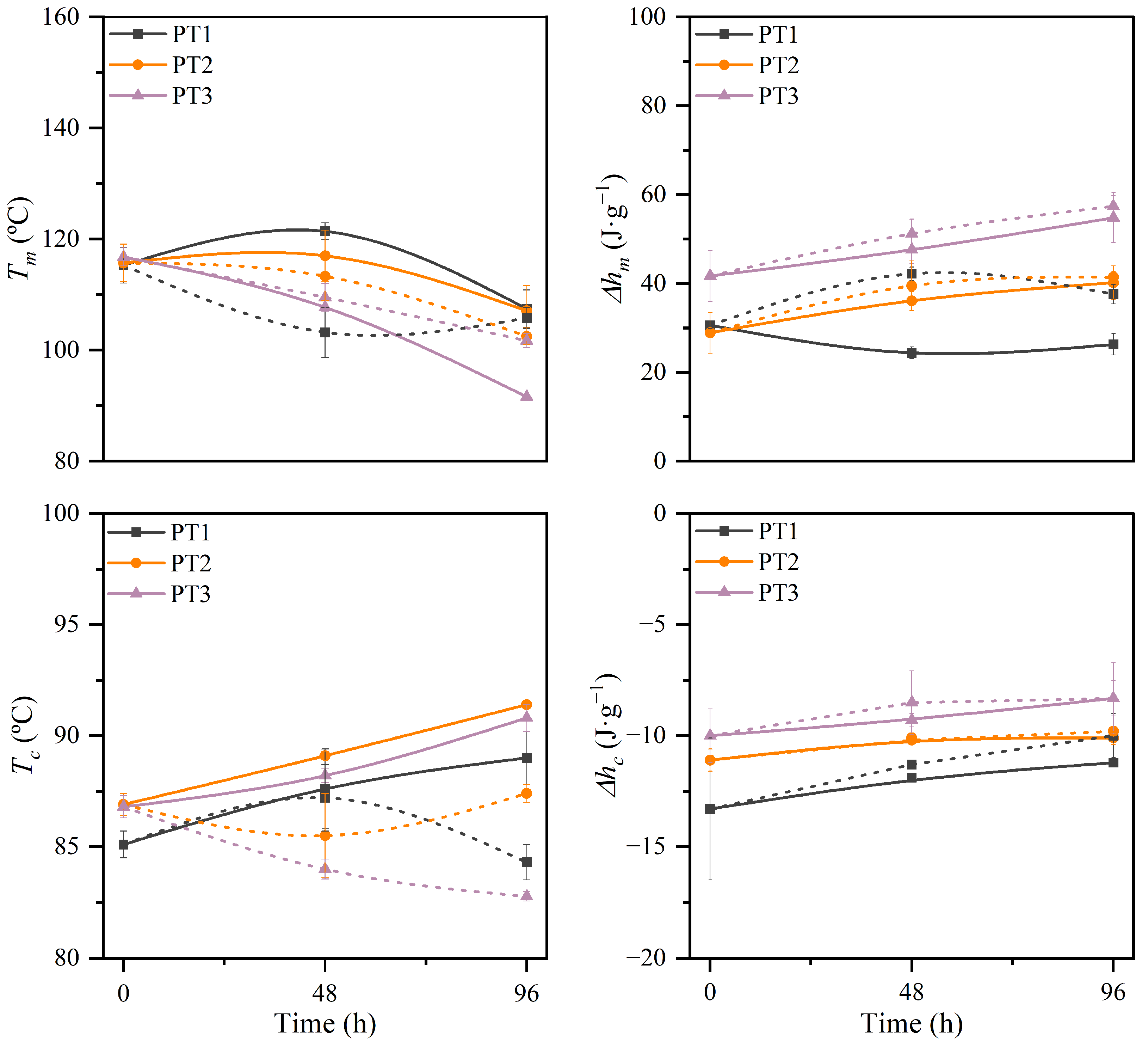
3.2. Consequences of UV-C/H2O-Driven Abiotic Degradation
3.2.1. Macroscopic Changes
3.2.2. Microscopic Morphology and Surface Properties
3.2.3. Chemical Structure
3.2.4. Thermal Properties and Stability
3.2.5. Molar Mass
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- European Bioplastics. EU Policy Manifesto. 2024. Available online: https://www.european-bioplastics.org/european-bioplastics-eu-policy-manifesto/ (accessed on 29 October 2024).
- Plastics Europe. Plastics—The Fast Facts 2023. Available online: https://plasticseurope.org/knowledge-hub/plastics-the-fast-facts-2023/ (accessed on 10 July 2024).
- European Bioplastics. Bioplastics Market Development Update 2023. Available online: https://www.european-bioplastics.org/bioplastics-market-development-update-2023-2/ (accessed on 17 October 2024).
- Silva-López, M.S.; E Alcántara-Quintana, L. The Era of Biomaterials: Smart Implants? ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2023, 6, 2982–2994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westlake, J.R.; Tran, M.W.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Burrows, A.D.; Xie, M. Biodegradable Active Packaging with Controlled Release: Principles, Progress, and Prospects. ACS Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 2, 1166–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikder, A.; Pearce, A.K.; Parkinson, S.J.; Napier, R.; O’reilly, R.K. Recent Trends in Advanced Polymer Materials in Agriculture Related Applications. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2021, 3, 1203–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, T.; Guo, H.; Guo, W.; Liu, W.; Li, W.; Saeb, M.R.; Vatankhah-Varnosfaderani, M.; Sheiko, S.S. Boosting the Strength and Toughness of Polymer Blends via Ligand-Modulated MOFs. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, 2407593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, C.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Gu, Z.; Chen, X.; Kuang, T. Robust and durable biodegradable polymer-based triboelectric nanogenerators enabled by trace amounts of melanin-like nanoparticles. Nano Energy 2025, 135, 110643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dammak, M.; Fourati, Y.; Tarrés, Q.; Delgado-Aguilar, M.; Mutjé, P.; Boufi, S. Blends of PBAT with plasticized starch for packaging applications: Mechanical properties, rheological behaviour and biodegradability. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 144, 112061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kijchavengkul, T.; Auras, R.; Rubino, M.; Ngouajio, M.; Fernandez, R.T. Assessment of aliphatic–aromatic copolyester biodegradable mulch films. Part II: Laboratory simulated conditions. Chemosphere 2008, 71, 1607–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Yan, Y.; Fan, S.; Min, X.; Wang, L.; You, X.; Jia, X.; Waterhouse, G.I.N.; Wang, J.; Xu, J. Prediction Model of Photodegradation for PBAT/PLA Mulch Films: Strategy to Fast Evaluate Service Life. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 9041–9051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kijchavengkul, T.; Auras, R.; Rubino, M.; Ngouajio, M.; Fernandez, R.T. Assessment of aliphatic–aromatic copolyester biodegradable mulch films. Part I: Field study. Chemosphere 2008, 71, 942–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, J.; Xiangbin, Z.; Xianbo, H. An overview on synthesis, properties and applications of poly(butylene-adipate-co-terephthalate)–PBAT. Adv. Ind. Eng. Polym. Res. 2020, 3, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, X.; Wang, W.; Zhang, H.; Dai, Y.; Dong, H.; Hou, H. Effects of high starch content on the physicochemical properties of starch/PBAT nanocomposite films prepared by extrusion blowing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 239, 116231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, M.; Jin, Y.; Han, X.; Sun, J.; Yuan, J.; Tian, H. Biodegradable Poly (Butylene Adipate-Co-Terephthalate) and Thermoplastic Starch Sustainable Blends Modified by Epoxy-Terminated Hyperbranched Polyester with Excellent Mechanical Properties and High Transparency. Starch-Starke 2023, 75, 2200169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.K.; Jung, H.W.; Son, D.; Han, J.H.; Kang, D.; Kang, S.I.; Lee, J.; Shim, J.K. In Situ Reactive Compatibilization of Thermoplastic Starch/Poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) Blends with Robust Water Resistance Performance. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2023, 5, 5445–5453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Guo, P.; Lyu, M.; Wang, B.; Li, C.; Sang, L.; Wei, Z. High Barrier Poly(Glycolic Acid) Modified Poly(Butylene Adipate-co-terephthalate) Blown Films and Accelerated Ultraviolet Degradability Evaluation. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2023, 5, 3457–3467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Z.; Chen, F.; Zhang, H.; Liu, C. High Content of Thermoplastic Starch, Poly(butylenes adipate-co-terephthalate) and Poly(butylene succinate) Ternary Blends with a Good Balance in Strength and Toughness. Polymers 2023, 15, 2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Som, S.; Harnkarnsujarit, N. Antimicrobial biodegradable blown films from PBAT/TPS with Glucono-delta-lactone as acid regulator active packaging. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2024, 46, 101388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNeill, D.C.; Pal, A.K.; Mohanty, A.K.; Misra, M. Injection molding of biodegradable polyester blends filled with mineral and sustainable fillers: Performance evaluation. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2024, 141, e55166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Poyo, C.; Cerisuelo-Ferriols, J.P.; Badia-Valiente, J.D. Influence of Vinyl Acetate-Based and Epoxy-Based Compatibilizers on the Design of TPS/PBAT and TPS/PBAT/PBSA Films. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badia, J.; Gil-Castell, O.; Ribes-Greus, A. Long-term properties and end-of-life of polymers from renewable resources. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2017, 137, 35–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.K.; Mudhoo, A. (Eds.) A Handbook of Applied Biopolymer Technology; Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awasthi, S.K.; Kumar, M.; Kumar, V.; Sarsaiya, S.; Anerao, P.; Ghosh, P.; Singh, L.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Awasthi, M.K. A comprehensive review on recent advancements in biodegradation and sustainable management of biopolymers. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 307, 119600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-Silva, K.; Jordán-Silvestre, A.; Cháfer, A.; Muñoz-Espí, R.; Gil-Castell, O.; Badia, J. Ultrasonic chemo-thermal degradation of commercial poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) (PBAT) and thermoplastic starch (TPS) blends. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2024, 232, 111133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bher, A.; Cho, Y.; Auras, R. Boosting Degradation of Biodegradable Polymers. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2023, 44, 2200769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil-Castell, O.; Badia, J.; Kittikorn, T.; Strömberg, E.; Martínez-Felipe, A.; Ek, M.; Karlsson, S.; Ribes-Greus, A. Hydrothermal ageing of polylactide/sisal biocomposites. Studies of water absorption behaviour and Physico-Chemical performance. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2014, 108, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badia, J.; Santonja-Blasco, L.; Martínez-Felipe, A.; Ribes-Greus, A. Hygrothermal ageing of reprocessed polylactide. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2012, 97, 1881–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badia, J.; Kittikorn, T.; Strömberg, E.; Santonja-Blasco, L.; Martínez-Felipe, A.; Ribes-Greus, A.; Ek, M.; Karlsson, S. Water absorption and hydrothermal performance of PHBV/sisal biocomposites. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2014, 108, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciuffi, B.; Fratini, E.; Rosi, L. Plastic pretreatment: The key for efficient enzymatic and biodegradation processes. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2024, 222, 110698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Možar, K.B.; Miloloža, M.; Martinjak, V.; Cvetnić, M.; Kušić, H.; Bolanča, T.; Grgić, D.K.; Ukić, Š. Potential of Advanced Oxidation as Pretreatment for Microplastics Biodegradation. Separations 2023, 10, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thew, X.E.C.; Lo, S.C.; Ramanan, R.N.; Tey, B.T.; Huy, N.D.; Wei, O.C. Enhancing plastic biodegradation process: Strategies and opportunities. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2024, 44, 477–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bher, A.; Mayekar, P.C.; Auras, R.A.; Schvezov, C.E. Biodegradation of Biodegradable Polymers in Mesophilic Aerobic Environments. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Castell, O.; Badia, J.; Teruel-Juanes, R.; Rodriguez, I.; Meseguer, F.; Ribes-Greus, A. Novel silicon microparticles to improve sunlight stability of raw polypropylene. Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 70, 247–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santonja-Blasco, L.; Rodriguez, I.; Sanchez-Ballester, S.; Badia, J.D.; Meseguer, F.; Ribes-Greus, A. Protection of high-density polyethylene–silicon composites from ultraviolet–visible photodegradation. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134, 45439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasin, N.M.; Akkermans, S.; Van Impe, J.F. Enhancing the biodegradation of (bio)plastic through pretreatments: A critical review. Waste Manag. 2022, 150, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bardi, M.A.; Munhoz, M.M.; Auras, R.A.; Machado, L.D. Assessment of UV exposure and aerobic biodegradation of poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate)/starch blend films coated with radiation-curable print inks containing degradation-promoting additives. Ind. Crops Prod. 2014, 60, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, N.; Bienaime, C.; Belloy, C.; Queneudec, M.; Silvestre, F.; Nava-Saucedo, J.-E. Polymer biodegradation: Mechanisms and estimation techniques—A review. Chemosphere 2008, 73, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kijchavengkul, T.; Auras, R.; Rubino, M.; Alvarado, E.; Montero, J.R.C.; Rosales, J.M. Atmospheric and soil degradation of aliphatic–aromatic polyester films. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2010, 95, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kijchavengkul, T.; Auras, R.; Rubino, M.; Selke, S.; Ngouajio, M.; Fernandez, R.T. Formulation selection of aliphatic aromatic biodegradable polyester film exposed to UV/solar radiation. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2011, 96, 1919–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podzorova, M.V.; Tertyshnaya, Y.V.; Selezneva, L.D.; Popov, A.A. Effect of Environmental Factors on Polylactide–Polybutylene Adipate Terephthalate Composites. Polym. Sci. Ser. D 2024, 17, 516–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Ding, J.; Song, X.; Zheng, L.; Huang, J.; Zou, H.; Wang, Z. Aging of poly (lactic acid)/poly (butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) blends under different conditions: Environmental concerns on biodegradable plastic. Sci. Total. Environ. 2023, 855, 158921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, H.; Echizen, Y.; Nishimura, Y. Enzymatic Degradation of Poly(l-Lactic Acid): Effects of UV Irradiation. J. Polym. Environ. 2006, 14, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattanasuttichonlakul, W.; Sombatsompop, N.; Prapagdee, B. Accelerating biodegradation of PLA using microbial consortium from dairy wastewater sludge combined with PLA-degrading bacterium. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2018, 132, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, H.J.; Kim, M.N. Biodegradation of poly(l-lactide) (PLA) exposed to UV irradiation by a mesophilic bacterium. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2013, 85, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riyajan, S.A.; Poolyarat, N. Cassava starch with ozone amendment and its blend: Fabrication and properties for fruit packaging application. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 201, 116886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podzorova, M.V.; Selezneva, L.D.; Tertyshnaya, Y.V. Photodegradation of composites based on polylactide and polybutylene adipate terephtalate. Russ. Chem. Bull. 2023, 72, 1414–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokhrel, S.; Sigdel, A.; Lach, R.; Slouf, M.; Sirc, J.; Katiyar, V.; Bhattarai, D.R.; Adhikari, R. Starch-based biodegradable film with poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate): Preparation, morphology, thermal and biodegradation properties. J. Macromol. Sci. Part A 2021, 58, 610–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aversa, C.; Barletta, M. Addition of Thermoplastic Starch (TPS) to Binary Blends of Poly(lactic acid) (PLA) with Poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) (PBAT): Extrusion Compounding, Cast Extrusion and Thermoforming of Home Compostable Materials. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. Engl. Ed. 2022, 40, 1269–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO291; Plastics—Standard Atmospheres for Conditioning and Testing. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1997.
- Laorenza, Y.; Harnkarnsujarit, N. Surface adhesion and physical properties of modified TPS and PBAT multilayer film. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2024, 44, 101312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.; Nada, A.; Diaa, E.K. Density functional theory and FTIR spectroscopic study of carboxyl group. Indian J. Pure Appl. Phys. 2005, 43, 911–917. [Google Scholar]
- Kijchavengkul, T.; Auras, R.; Rubino, M.; Selke, S.; Ngouajio, M.; Fernandez, R.T. Biodegradation and hydrolysis rate of aliphatic aromatic polyester. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2010, 95, 2641–2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauritzen, J.I.; Hoffman, J.D.; Lauritzen, J.I.; Hoffman, J.D. Formation of Polymer Crystals with Folded Chains from Dilute Solution. J. Chem. Phys. 1959, 31, 1680–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, J.D.; Lauritzen, J.I. Crystallization of bulk polymers with chain folding: Theory of growth of lamellar spherulites. J. Res. Natl. Bur. Stand. Sect. A Phys. Chem. 1961, 65, 297–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, R.; Franco, L.; Rodríguez-Galán, A.; Puiggalí, J. Characterization and degradation behavior of poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate)s. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2002, 40, 4141–4157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kargarzadeh, H.; Galeski, A.; Pawlak, A. PBAT green composites: Effects of kraft lignin particles on the morphological, thermal, crystalline, macro and micromechanical properties. Polymer 2020, 203, 122748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Runt, J.; Miley, D.M.; Zhang, X.; Gallagher, K.P.; McFeaters, K.; Fishburn, J. Crystallization of poly(butylene terephthalate) and its blends with polyarylate. Macromolecules 1992, 25, 1929–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Zhang, F.; Li, C.; Ding, W.; Jin, Y.; Tang, L.; Huang, R. Effect of Starch Plasticization on Morphological, Mechanical, Crystalline, Thermal, and Optical Behavior of Poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate)/Thermoplastic Starch Composite Films. Polymers 2024, 16, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, P.T.T.; Son, N.T.; Van Khoi, N.; Trang, P.T.; Duc, N.T.; Anh, P.N.; Linh, N.N.; Tung, N.T. Poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate)/thermoplastic canna starch (Canna edulis ker.) (PBAT/TPS) blend film—A novel biodegradable material. J. Indian Chem. Soc. 2024, 101, 101245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, S.; Riahi, O.; Said, S.M.; Sabri, M.F.; Rozali, S. Biopolymers From Crop Plants. Ref. Modul. Mater. Sci. Mater. Eng. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhir, M.A.M.; Zubir, S.A.; Mariatti, J.; Teknologi, F.; Kimia, K. Effect of different starch contents on physical, morphological, mechanical, barrier, and biodegradation properties of tapioca starch and poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) blend film. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2023, 34, 717–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garalde, R.A.; Thipmanee, R.; Jariyasakoolroj, P.; Sane, A. The effects of blend ratio and storage time on thermoplastic starch/poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) films. Heliyon 2019, 5, e01251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, X.; Zhang, R.; Wang, W.; Hou, H. Relationship between phase morphologies and mechanical properties of thermoplastic starch/poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) composite films prepared by extrusion blowing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 224, 1356–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Tian, H.; Wang, X.; Yu, J.; Jia, S.; Han, L.; Pan, H.; Zhang, H. Study on thermal, rheological, mechanical, morphological, and barrier properties of poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate)/thermoplastic starch/poly(propylene carbonate) biodegradable blown films. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2023, 148, 1853–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Ju, D.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yang, H.; Zhang, H.; Dong, L. Mechanical properties, hydrophobic properties and thermal stability of the biodegradable poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate)/maleated thermoplastic starch blown films. Fibers Polym. 2016, 17, 1540–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, X.; Han, J.; Chang, L.; Zhao, F.; Zhang, R.; Wang, W.; Hou, H. Effects of starch filling on physicochemical properties, functional activities, and release characteristics of PBAT-based biodegradable active films loaded with tea polyphenols. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 277, 134505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seligra, P.G.; Moura, L.E.; Famá, L.; Druzian, J.I.; Goyanes, S. Influence of incorporation of starch nanoparticles in PBAT/TPS composite films. Polym. Int. 2016, 65, 938–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Zhai, X.; Wang, W.; Zhang, R.; Hou, H.; Lim, L.-T. Material properties and antimicrobial activities of starch/PBAT composite films incorporated with ε-polylysine hydrochloride prepared by extrusion blowing. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2022, 32, 100831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pretsch, E.; Buhlmann, P.; Badertscher, M. Structure Determination of Organic Compounds; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Campos, S.S.; de Oliveira, A.; Moreira, T.F.M.; da Silva, T.B.V.; da Silva, M.V.; Pinto, J.A.; Bilck, A.P.; Gonçalves, O.H.; Fernandes, I.P.; Barreiro, M.-F.; et al. TPCS/PBAT blown extruded films added with curcumin as a technological approach for active packaging materials. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2019, 22, 100424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Yu, L.; Tong, Z.; Chen, L.; Liu, H.; Li, X. Thermal degradation and stability of starch under different processing conditions. Starch-Stärke 2013, 65, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.; Kopitzky, R.; Berrenrath, C. Experimental Determination of Molecular Weight-Dependent Miscibility of PBAT/PLA Blends. Polymers 2021, 13, 3686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwiczak, J.; Dmitruk, A.; Skwarski, M.; Kaczyński, P.; Makuła, P. UV resistance and biodegradation of PLA-based polymeric blends doped with PBS, PBAT, TPS. Int. J. Polym. Anal. Charact. 2023, 28, 366–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wypych, G. ANALYTICAL METHODS IN UV DEGRADATION AND STABILIZATION STUDIES. In Handbook of UV Degradation and Stabilization; Wypych, G., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 439–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wondraczek, H.; Kotiaho, A.; Fardim, P.; Heinze, T. Photoactive polysaccharides. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 83, 1048–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolini, A.C.; Mestres, C.; Raffi, J.; Buléon, A.; Lerner, D.; Colonna, P. Photodegradation of Cassava and Corn Starches. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 675–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiedorowicz, M.; Tomasik, P.; You, S.; Lim, S.-T. Molecular Distribution and Pasting Properties of UV-Irradiated Corn Starches. Starch-Starke 1999, 51, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshoulles, Q.; Le Gall, M.; Benali, S.; Raquez, J.-M.; Dreanno, C.; Arhant, M.; Priour, D.; Cerantola, S.; Stoclet, G.; Le Gac, P. Hydrolytic degradation of biodegradable poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) (PBAT)—Towards an understanding of microplastics fragmentation. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2022, 205, 110122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quispe, M.M.; López, O.V.; Villar, M.A. Oxidative Degradation of Thermoplastic Starch Induced by UV Radiation. J. Renew. Mater. 2019, 7, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taiatele, I.; Bosco, T.C.D.; Faria-Tischer, P.C.S.; Bilck, A.P.; Yamashita, F.; Bertozzi, J.; Michels, R.N.; Mali, S. Abiotic Hydrolysis and Compostability of Blends Based on Cassava Starch and Biodegradable Polymers. J. Polym. Environ. 2019, 27, 2577–2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Liao, Y.; Zou, Z.; Chen, Y.; Jin, M.; Zhu, J.; Abdalkarim, S.Y.H.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, H.-Y. Novel strategy to interpret the degradation behaviors and mechanisms of bio- and non-degradable plastics. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 355, 131757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oelker, J.; Losa, S.N.; Richter, A.; Bracher, A. TROPOMI-Retrieved Underwater Light Attenuation in Three Spectral Regions in the Ultraviolet and Blue. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 787992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, J.D.; Cone, M.T.; Fry, E.S. Ultraviolet (250–550 nm) absorption spectrum of pure water. Appl. Opt. 2016, 55, 7163–7172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalogirou, C.; Höfft, O.; Gödde, A.; Papadimitriou, N.; Pandis, P.K.; Argirusis, C.; Sourkouni, G. Assessing the Time Dependence of AOPs on the Surface Properties of Polylactic Acid. J. Polym. Environ. 2023, 31, 345–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandler, S.R.; Karo, W.; Bonesteel, J.; Pearce, E.M. Polymer Synthesis and Characterization: A Laboratory Manual; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1998; Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/book/9780126182408/polymer-synthesis-and-characterization (accessed on 26 September 2023).
- Mao, R.; Lang, M.; Yu, X.; Wu, R.; Yang, X.; Guo, X. Aging mechanism of microplastics with UV irradiation and its effects on the adsorption of heavy metals. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 393, 122515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botta, L.; Titone, V.; Teresi, R.; Scarlata, M.C.; Re, G.L.; La Mantia, F.P.; Lopresti, F. Biocomposite PBAT/lignin blown films with enhanced photo-stability. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 217, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, X.; Lin, J.; Meng, Y.; Liu, Y.; He, C. Hydrothermal aging behavior of poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) mulch: Influence of the hydrolysis resistance based on the different filling materials. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2024, 302, 1911–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncalves Bardi, M.A.; Leite Munhoz, M.D.; Oliveira, H.A.; Auras, R.; Machado, L.D. Behavior of UV-cured print inks on LDPE and PBAT/TPS blend substrates during curing, postcuring, and accelerated degradation. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131, 41116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badía, J.; Vilaplana, F.; Karlsson, S.; Ribes-Greus, A. Thermal analysis as a quality tool for assessing the influence of thermo-mechanical degradation on recycled poly(ethylene terephthalate). Polym. Test. 2009, 28, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toda, A. Spherulitic Growth in Crystalline Polymers. In Encyclopedia of Polymers and Composites; Palsule, S., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, M.H.; Gil-Castell, O.; Cea, J.; Carrasco, J.C.; Ribes-Greus, A. Degradation of Plasticised Poly(lactide) Composites with Nanofibrillated Cellulose in Different Hydrothermal Environments. J. Polym. Environ. 2023, 31, 2055–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodard, L.N.; Grunlan, M.A. Hydrolytic Degradation and Erosion of Polyester Biomaterials. ACS Macro Lett. 2018, 7, 976–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayekar, P.C.; Limsukon, W.; Bher, A.; Auras, R. Breaking It Down: How Thermoplastic Starch Enhances Poly(lactic acid) Biodegradation in Compost─A Comparative Analysis of Reactive Blends. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 9729–9737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, H.; Tsukamoto, N.; Arakawa, Y. Facile control of the surface property and hydrolytic degradation of poly(l-lactide) materials by coating poly(l-lactide)-based triblock copolymers with hydrophilic or hydrophobic block. Mater. Adv. 2022, 3, 7053–7060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
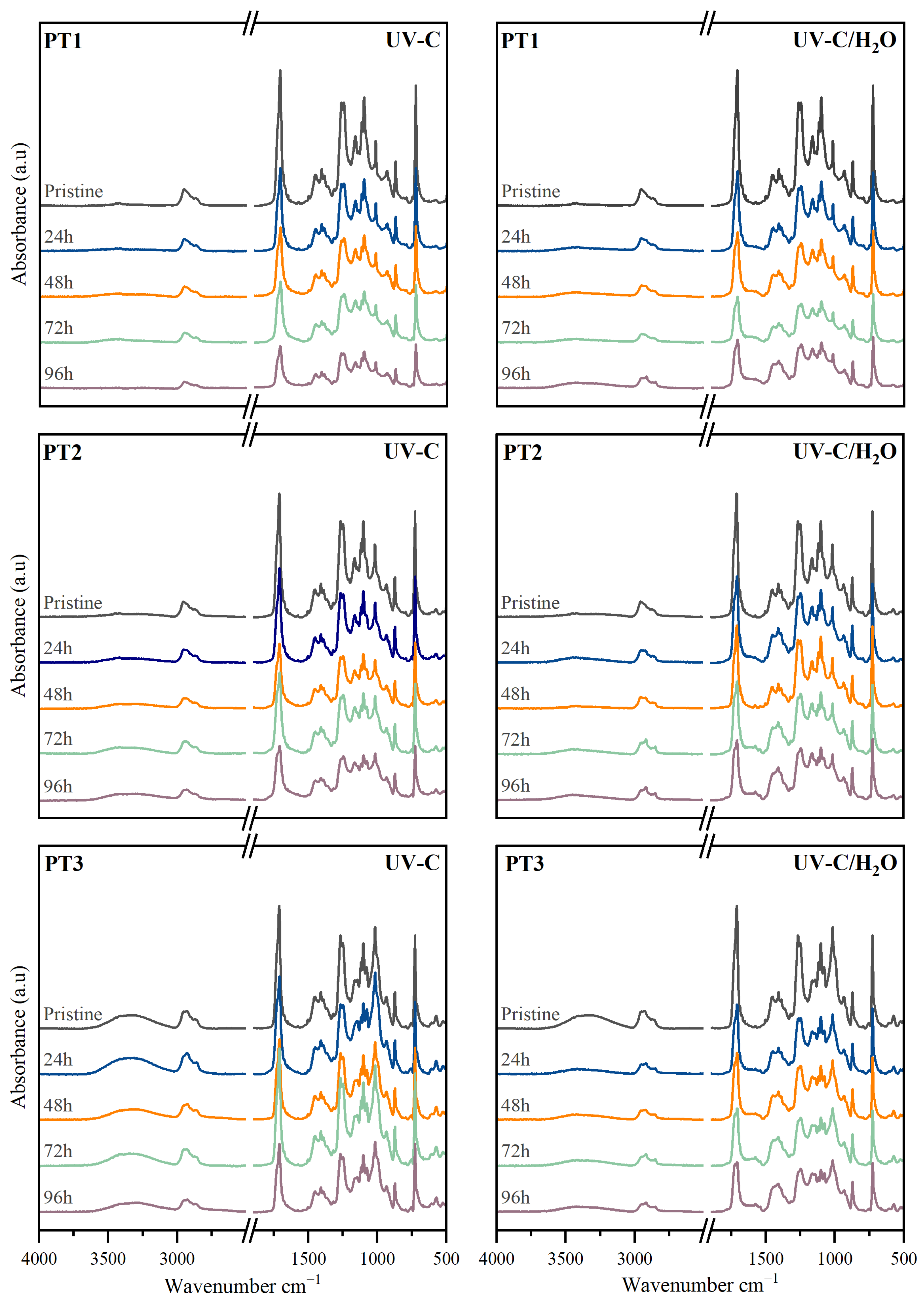
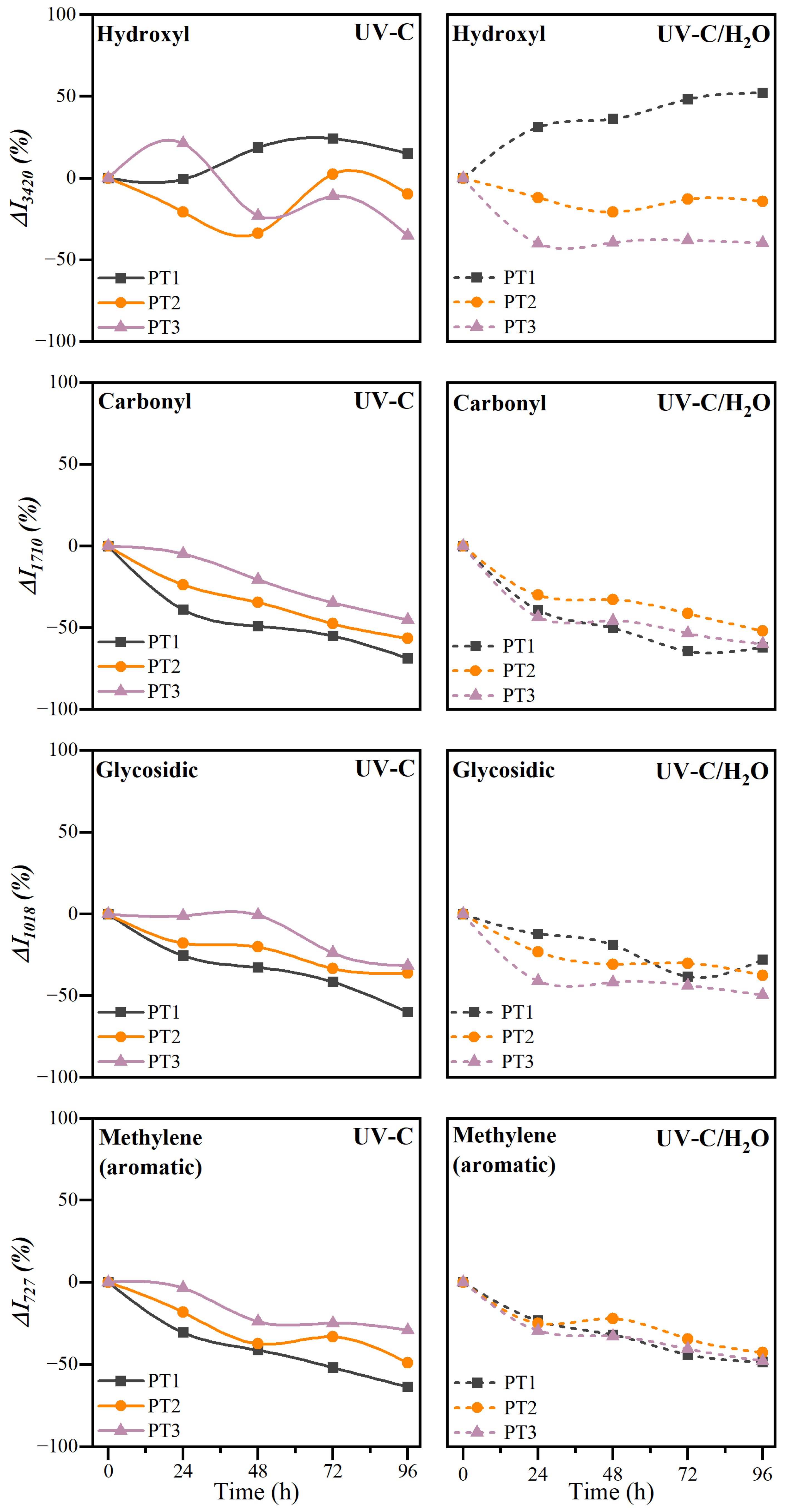
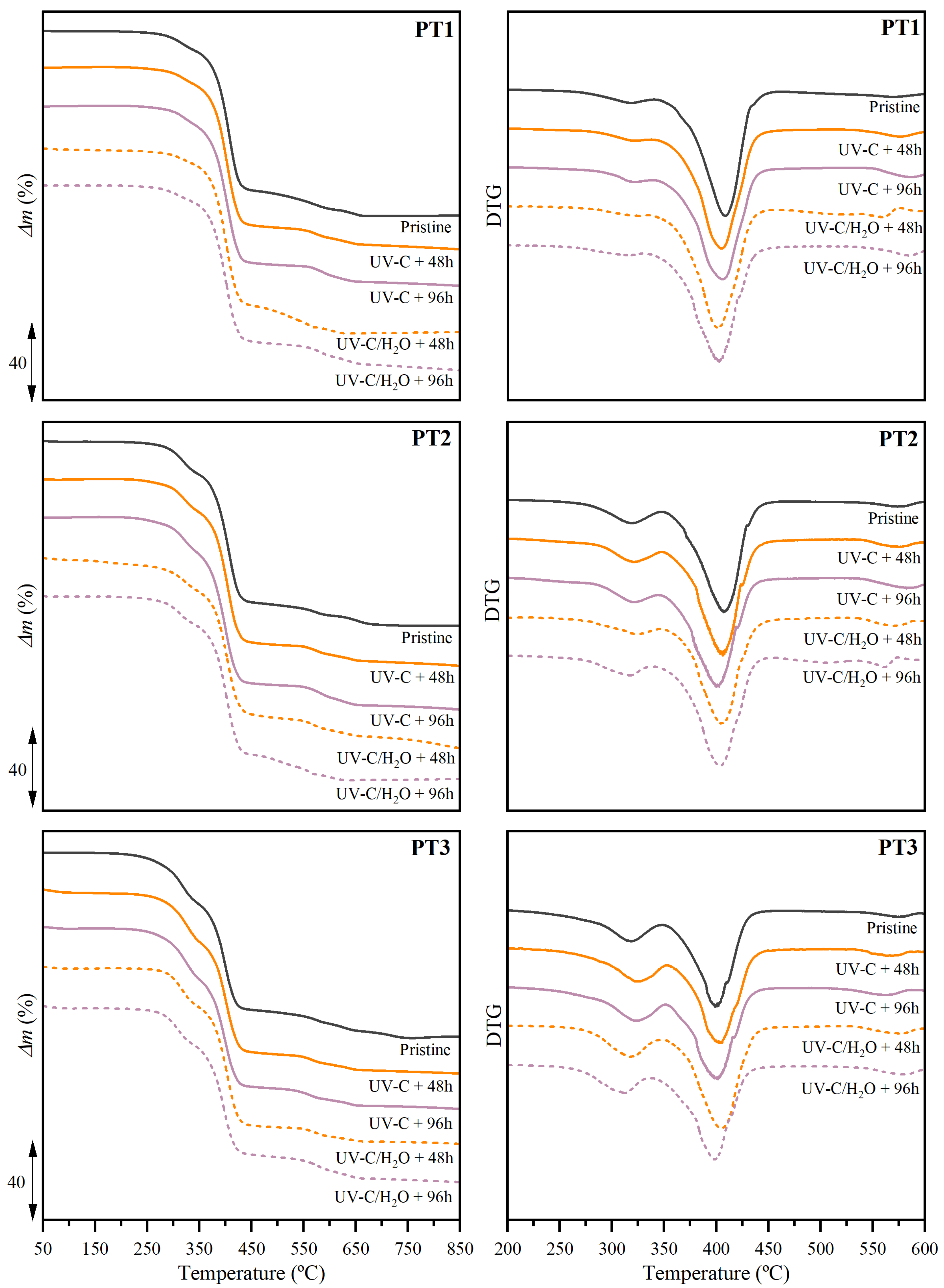
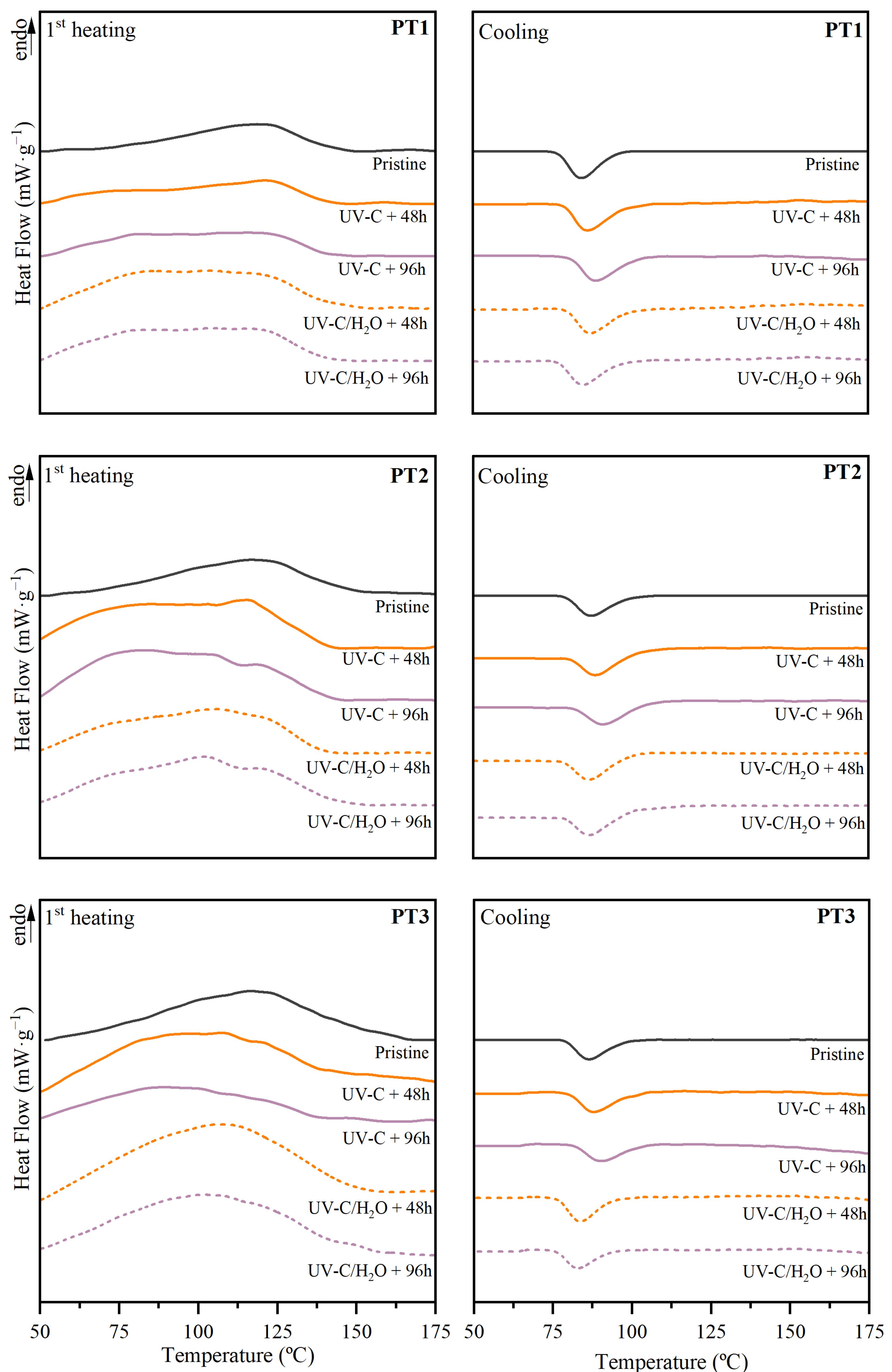
| Polymers | Valorization Strategy | Suggested Parameters | Key Indicators | Biodegradation Environment | Observation Reported | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLA | UV irradiation + enzymatic degradation catalyzed with Proteinase K | UV-A light (λ: 300–700 nm) I: 25.5 mW·cm−2 T: 45 °C RH: 65% t: 60 h | Reduction of Mn | Culture media T: 37 °C t: 10–60 h pH: 8–8.6 | Accelerated depolymerization after 60 h of irradiation | [43] |
| PLA | UV irradiation + Stenotrophomonas maltophilia LB 2–3 | UV-C light (λ: 185–245 nm) I: 6.41 × 10−3–3.22 mW·cm−2 t: 24 h | Reduction of Mn, contact angle and mechanical properties | Compost T: 37 °C t: 24 h | Biodegradability increased after 8 h of UV-C irradiation but became more resistant with longer exposure times | [45] |
| Commercial PLA cups | UV irradiation + bioaugmentation + dairy wastewater sludge (Pseudomonas geniculata WS3) | UV-A-B-C light (λ: 340, 310 and 254 nm) t: 150 min T: room temperature | Significant reduction of Mn after 2 h of irradiation | Soil T: 58 ± 2 °C RH: 40% pH: 4.3–7.9 Air flow: 25 mL·min−1 | Enhanced PLA biodegradation with UV irradiation, along with the addition of dairy wastewater sludge and P. geniculate WS3 | [44] |
| Cassava Starch | Ozone treatment + blending (PVA/NR) + biodegradation | T: 50 °C t: 50 min pH: 7 Ozone gas concentration: 20 mg L−1 | Decreased crystallinity and swelling ratio in toluene and aqueous medium | Soil T: 27–28 °C RH: 85% pH: 7 | Biodegradation improved with increasing Modified CS content (100% in 30 days with ≥ 15% MCS) | [46] |
| PBAT | UV irradiation + biodegradation | UV-A light (λ: 320–400 nm) t: 336 h I: 1.40 W·m−2·nm−1 | Higher opacity and yellowish colour, decrease in TS and ε, higher brittleness, increase in E, reduction in Mw, crosslinking | Compost t: 45 days | Photodegradation enhanced mineralization, only in the first stages, before crosslinking occurred after advanced irradiation | [10] |
| PT1 | PT2 | PT3 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thickness (µm) | 172 ± 20 | 155 ± 10 | 123 ± 10 | |
| Macroscopic appearance |  |  |  | |
| Color parameters | L* | 85.7 ± 0.0 | 88.4 ± 0.3 | 82.1 ± 1.9 |
| a* | −2.0 ± 0.0 | −2.4 ± 0.2 | −2.3 ± 0.1 | |
| b* | 0.9 ± 0.0 | 3.4 ± 0.0 | 4.46 ± 0.1 | |
| Microscopic surface | 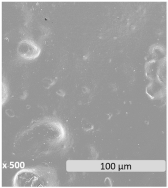 | 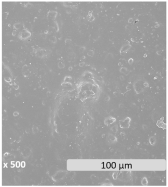 | 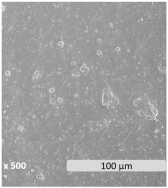 | |
| WCA (°) | 79.1 ± 3.9 | 76.1 ± 2.7 | 68.6 ± 2.6 | |
| Tm (°C) | 121.4 ± 0.9 | 121.6 ± 3.4 | 119.9 ± 4.5 | |
| Td TPS (°C) | 317.8 ± 0.2 | 317.4 ± 0.6 | 320.0 ± 1.5 | |
| Td PBAT (°C) | 405.9 ± 4.5 | 403.9 ± 4.7 | 401.0 ± 2.3 | |
| Mn (g·mol−1) | 55,830 | 58,430 | 62,820 | |
| Mw (g·mol−1) | 113,450 | 119,750 | 118,610 | |
| PDI | 2.03 | 2.05 | 1.89 | |
| t (h) | Mn (g·mol−1) | ΔMn (%) | Mw (g·mol−1) | ΔMw (%) | PDI | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PT1 | - | 0 | 55,830 | - | 113,450 | - | 2.03 |
| UV-C | 96 | 40,830 | −26.9 | 87,410 | −23.0 | 2.14 | |
| UV-C/H2O | 96 | 51,980 | −6.9 | 111,080 | −2.1 | 2.14 | |
| PT2 | - | 0 | 58,430 | - | 115,750 | - | 1.98 |
| UV-C | 96 | 38,910 | −33.4 | 87,520 | −24.4 | 2.25 | |
| UV-C/H2O | 96 | 50,570 | −13.5 | 116,990 | 1.1 | 2.31 | |
| PT3 | - | 0 | 62,790 | - | 115,370 | - | 1.84 |
| UV-C | 96 | 40,940 | −34.8 | 96,370 | −16.5 | 2.35 | |
| UV-C/H2O | 96 | 47,490 | −24.4 | 100,650 | −12.8 | 2.12 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gutiérrez-Silva, K.; Capezza, A.J.; Gil-Castell, O.; Badia-Valiente, J.D. UV-C and UV-C/H₂O-Induced Abiotic Degradation of Films of Commercial PBAT/TPS Blends. Polymers 2025, 17, 1173. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17091173
Gutiérrez-Silva K, Capezza AJ, Gil-Castell O, Badia-Valiente JD. UV-C and UV-C/H₂O-Induced Abiotic Degradation of Films of Commercial PBAT/TPS Blends. Polymers. 2025; 17(9):1173. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17091173
Chicago/Turabian StyleGutiérrez-Silva, K., Antonio J. Capezza, O. Gil-Castell, and J. D. Badia-Valiente. 2025. "UV-C and UV-C/H₂O-Induced Abiotic Degradation of Films of Commercial PBAT/TPS Blends" Polymers 17, no. 9: 1173. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17091173
APA StyleGutiérrez-Silva, K., Capezza, A. J., Gil-Castell, O., & Badia-Valiente, J. D. (2025). UV-C and UV-C/H₂O-Induced Abiotic Degradation of Films of Commercial PBAT/TPS Blends. Polymers, 17(9), 1173. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17091173









