Abstract
Chitosan is a natural polymer derived from chitin through the deacetylation process. It has emerged as a key ingredient in sustainable wastewater treatment, due to its biodegradability, non-toxicity, and low cost. This biopolymer possesses abundant functional groups, such as -NH2 and -OH, that efficiently interact with pollutants. This review offers a comprehensive evaluation of pollutant separation techniques involving chitosan-based materials, including adsorption, membrane filtration, flocculation, and photocatalysis. It further examines the underlying adsorption mechanisms, emphasizing how pollutants interact with chitosan and its derivatives at the molecular level. Special focus is given to various modifications of chitosan, alongside a comparative assessment of different chitosan-based adsorbents (hydrogels, nanoparticles, nanocomposites, microspheres, nanofibers, etc.), highlighting their performance in removing heavy metals, dyes, and emerging organic pollutants. The reviewed performance of these polymeric materials from 2015–2025 not only gives an insight about the recent advancement but also points the need for the design of high-performing chitosan-based adsorbents with applications in real water matrices.
1. Introduction
Global sustainability means managing the available resources so that they meet the needs of present and future generations. A key component of this goal is ensuring access to safe and potable water. Water scarcity remains a global challenge that threatens the well-being of individuals, communities, and the ecosystem. This shortage of water affects not only households but also businesses, agriculture, and various industries [1,2]. In 2015, the United Nations forwarded specific policy targets, the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Among the 17 SDGs objectives, SDG-06 has a main focus on ensuring universal access to clean water and proper sanitation for everyone in 2030 [3].
Water pollution can arise from natural and human-induced sources. Natural causes include geological processes, climate change, and water–rock interactions [4]. The most common water contamination is through anthropogenic activities (caused by human activities), which include industrial operations, agricultural practices, inappropriate waste disposal, oil spills, and an insufficient sewage system [5]. The most concerning categories of these pollutants are heavy metals, dyes, and emerging organic pollutants (EOPs) [6]. See Figure 1a.
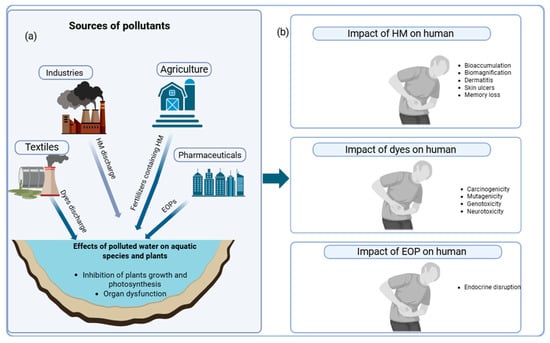
Figure 1.
Effects of pollutants, (a) Sources of different pollutants and their effects on plants and aquatic species (b) Health implications of different pollutants on humans.
Heavy metals are a group of metals or metalloids that are generally toxic. Certain heavy metals, such as zinc, iron, nickel, etc., are essential for plant and animal development, but when concentrations exceed permissible limits, they become hazardous [7]. A few of the most frequent heavy metals that contaminate the environment include mercury, cadmium, arsenic, chromium, nickel, copper, and lead. As shown in Figure 1b, these Heavy metals are responsible for memory loss, tremors, cognitive dysfunction, kidney dysfunction, skin lesions, skin ulcers, dermatitis, and respiratory issues [8,9,10,11].
The primary source of these hazardous metals in surface water is wastewater effluent from traditional wastewater treatment, the sludge from municipal domestic wastewater that contains household products, and solely household waste [12,13,14]. Toxic heavy metals are introduced into river water directly or indirectly, mostly from industrial waste, municipal and urban influences, and the penetration of polluted surface water into the groundwater aquifer system due to soil and land-use patterns [15]. These heavy metals are resistant to decomposition and can pose serious health implications through bioaccumulation and biomagnification [16].
One of the most polluting industries is the textile industry, which produces a major class of pollutants called synthetic dyes. They are, but not limited to, methylene blue, Congo red, and malachite green, etc., and are complex aromatic structures, often recalcitrant and toxic [17,18]. It is estimated that about 7 × 107 tons of synthetic dyes are annually produced globally, with over 10,000 tons of dyes used by textile industries [19], and about 10% of these dyes are lost during processing, which are then released to the environment [20]. Dyes, even at low concentrations, impact the color of the water bodies, inhibit plant growth and photosynthesis, and are carcinogenic [21,22,23,24]. In addition, there are EOPs, which have detrimental impacts on the environment and human health and lack established emission and environmental monitoring standards [25]. EOPs include pharmaceutical and personal care products, endocrine-disrupting compounds, and persistent organic pollutants [26,27]. Some of the effects of dye and EOP exposure in humans are mentioned in Figure 1b.
The implementation of conventional wastewater treatment technology has been in practice for many years. The treatment process aims to eliminate contaminants from water by removing solids, organic matter, nutrients, and chemical pollutants through three separate treatment stages. Primary treatment involves the physical separation of large particles from water, secondary treatment involves the use of aerobic and anaerobic treatment, then the tertiary stage uses coagulation, membrane filtration, reverse osmosis, flocculation methods, etc. [28]. These methods are limited by factors such as high cost, use of specialized equipment, incomplete removal of dyes, and generation of toxic residues, leading to secondary pollution. As a result, there is an interest in more sustainable, efficient, and environmentally friendly solutions. Adsorption has significantly gained attention as a leading alternative, due to its ability to eliminate a wide variety of pollutants, cost effectiveness, and simplicity [29,30].
Adsorption is the process used in wastewater treatment where the pollutants adhere to the surface of the material. Traditional adsorbents (e.g., activated carbon) often face challenges such as high cost, limited reusability, and low selectivity [31]. Natural adsorbents have been utilized in wastewater treatment from cellulosic materials such as grass waste, pomegranate peel, and cellulosic oil palm shell for the effective removal of methylene blue and cupric ions. However, among these diverse arrays of biosorbents, chitosan-based materials have emerged as one of the most promising biopolymers in wastewater treatment [32,33,34,35,36]. Chitosan’s distinctive advantages in water purification stem from its abundant amino and hydroxyl functional groups, which serve to bind strongly with diverse pollutants, including heavy metals and dyes. Additionally, its ability to be chemically and physically modified allows tailoring of properties such as solubility, mechanical stability, and adsorption specificity to suit different treatment needs [37]. According to the retrieval data from the Scopus database (as shown in Figure 2), using the keywords “chitosan AND in AND wastewater AND treatment”, filtering from 2015–2025, 2802 papers, including review articles, research articles, conference papers, etc, have been published, showing the growing interest in studying and utilizing chitosan-based materials in wastewater treatment.
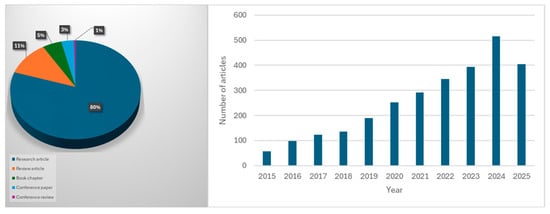
Figure 2.
Number of published articles on “chitosan in wastewater treatment” based on the Scopus database (accessed on 14 July 2025).
Numerous review articles have focused on the general uses of chitosan or chitosan-based materials in wastewater treatment [38,39,40,41,42,43], its preparation and application for solar step generators [44], its application for the removal of pharmaceutical contaminants [45], its application in the removal of antibiotics [46], its modification and application in retardants [47], and also as an alternative to reduce plastic dependency [48]. This review presents a holistic and critical comparison of multiple sustainable and conventional pollutant removal techniques, pollutant–chitosan-based material interaction mechanisms, and advanced modification techniques of chitosan-based materials, highlighting their potential as versatile and eco-friendly alternatives for efficient contaminant removal.
2. Chitosan: Structure, Sources, and Properties
Chitosan is a versatile biopolymer derived from chitin and it is a linear polymer of β-(1→4)2-amino-2-deoxy-d-glucose units (d-glucosamine). The primary sources of chitosan include crustaceans, insects, and fungi. In crustaceans, chitosan is traditionally extracted from the exoskeletons of crabs, shrimp, and lobsters. This method, while common, can be expensive due to the complex extraction processes involved [49]. Insects, including different orders like Lepidoptera and Coleoptera, provide a renewable and abundant source of chitin and chitosan. Additionally, the extraction from insects is gaining attention due to its lower environmental impact and high yield potential [50]. Fungi, filamentous species to be specific, are significant sources of chitosan. Fungal chitosan is noted for its controllable physicochemical properties, making it suitable for diverse applications in food preservation and biomedicine [51].
The conversion of chitin into chitosan through deacetylation is a significant process. As shown in Figure 3, this process involves the removal of acetyl groups from chitin. Deacetylation can be achieved through various methods, including chemical and enzymatic approaches, each affecting the properties of the resulting chitosan. Chemical deacetylation involves the use of a strong base, such as NaOH. Another key parameter that is worth noting is the consideration of the degree of acetylation and chitosan yield, as studies indicate that varying the mass ratio of chitin to NaOH and the reaction time influences the degree of deacetylation and the chitosan yield [52,53]. Enzymatic deacetylation uses chitin deacetylases (CDAs), for the conversion of chitin to chitosan, however, it is less effective than the chemical method, because CDAs remove a limited number of acetyl groups, leading to a low degree of deacetylation, which in turn does not suffice for chitosan production [54]. It is important to note that fully acetylated or deacetylated chitosan chitin does not exist, but a degree of acetylation of 50% and more is considered a chitosan [55].
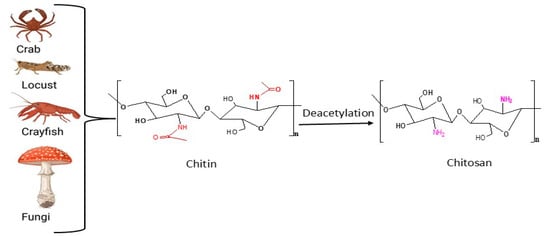
Figure 3.
Sources and deacetylation of chitin to chitosan.
The biodegradability and non-toxicity of chitosan make it a preferred candidate in various fields, including wound dressing and wastewater treatment. The degradation of chitosan occurs through two pathways, enzymatic and chemical degradation. The enzymatic degradability of chitosan is facilitated by enzymes such as lysozymes and chitosanase, which break down the polymer into smaller oligosaccharides and later into glucose and glucosamine. Chemical degradation occurs in acidic or alkaline environments, leading to the hydrolysis of chitosan into smaller fragments [56,57]. Despite the properties chitosan possesses, it has some drawbacks that limit its application in wastewater treatment, such as poor solubility in neutral or alkaline pH, low mechanical strength, and poor thermal stability; therefore, modification becomes crucial to overcome those limitations [58,59].
3. Modifications of Chitosan
Chitosan is rich in amine and hydroxyl groups, and these groups make it easier for this biopolymer to undergo different modifications, allowing the introduction of new functional groups to the structure, increasing the adsorption capacity of chitosan towards pollutants [60].
3.1. Alkylation
Alkylation is one of the most used modifications of chitosan, and this reaction leads to various groups being introduced into the amino sites. For instance, the most widely employed modifications in alkylation are quaternization and Schiff base synthesis. Quaternization modifications primarily convert the primary amino groups into quaternary ammonium salts. Quaternization includes the reaction of the amino group of chitosan and halogenated hydrocarbon, enhancing the positive charge of chitosan, and making it soluble in basic conditions. This positive charge enables chitosan to achieve a strong affinity with anions and enhance chelation [61,62]. For instance, Stepnova et al. [61] synthesized alkylated chitosan with quaternary ammonium groups, which had a removal percentage of more than 90% towards arsenate ions. Quaternized chitosan has been used in wastewater treatment to remove chromium ions, cationic dyes, and anionic dyes [63,64,65].
The first chitosan Schiff base (CSB) was synthesized in 1977 through the reaction of chitosan and different aldehydes. Since then, the CSB synthesis has been used in various applications [66]. This Schiff reaction is a unique type of alkylation reaction. Generally, the amino groups in the chitosan polymer react with aldehyde or ketone to form an imine linkage (−N═CH–R). CSBs have been used in wastewater treatment for the removal of Cd (II) and Fe (III) ions [67], Cu (II) ions [68], Pd (II) ions [69], Cr (II) ions [70], Bismarck Brown and Rhodamine B dye [71], methyl green [72], and methyl orange [73].
3.2. Acylation
Acylation in chitosan modification is the process of introducing the acyl group to the polymer through the reaction with acyl chloride or anhydrides, forming the amide derivatives. This is performed on the amino group or hydroxyl group, being N-acylation on the amine group and O-acylation on the hydroxyl group. O-acylation is similar to esterification. It is worth noting that the acylation reaction of many types of acid anhydrides preferentially occurs on amino sites as opposed to hydroxyl sites, which also increases the reaction selectivity of acylation modification. The diversity of reactants also significantly enhances the concepts of modification [74,75]. Fujita et al. [76] synthesized EDTA-linked chitosan by N-acylation of chitosan with ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) monoanhydride in acidic to slightly basic conditions, which acted as a flocculent to remove almost 100% of Cu (II), using chelation. Besides acylation, some substitution reactions have been shown to possess the pollutant removal property, see Table 1.

Table 1.
Other substitution reactions.
Table 1.
Other substitution reactions.
| Modification | Type of Substitution Reaction | Materials | Introduced Group | Pollutant Removed | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thiolation | Nucleophilic substitution | Thiolated chitosan | Introduction of -SH (thiol) groups | Cu (II) and Cd (II) | [77] |
| Phosphorylation | Nucleophilic substitution or esterification | Phosphorylated chitosan | Introduction of phosphate groups | U (VI) ions | [78] |
| Sulfonation | Electrophilic aromatic/hydroxyl substitution | Chitosan lignosulfonate | Introduction of -SO3H or -SO3− | Congo red, Cr (VI), and Rhodamine B | [79] |
3.3. Crosslinking of Chitosan
Crosslinking is a stabilizing technique, whereby ionic or covalent bonds between polymer chains are formed, forming a bulky 3D polymer structure, with improved thermal and mechanical properties [80]. This means a crosslinking reaction between chitosan and the crosslinking agent leads to crosslinked chitosan. As shown in Figure 4, there are a variety of crosslinking agents that are compatible with chitosan, including, but not limited to, glutaraldehyde, glyoxal, and formaldehyde [81,82,83]. These are aldehyde crosslinking agents. For instance, glutaraldehyde has demonstrated the ability to crosslink the active amino group of chitosan and bind the molecules of chitosan together with covalent bonds. The electrospun and crosslinked chitosan/poly (vinyl alcohol) (PVA) blend nanofiber has an adsorption capacity of 166.34 mg/g towards Pb (II) ions [84]. There are also epoxy-based crosslinking agents which form covalent crosslinks, such as epichlorohydrin and 1,4-butanediol diglycidyl ether (BDDE) [85,86]. To cite an example, epichlorohydrin crosslinked chitosan was found to be effective in the removal of methyl green dye [87].
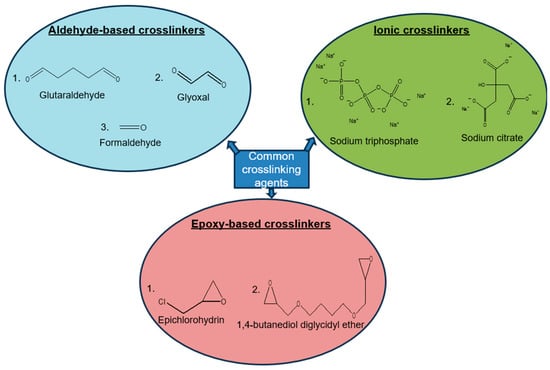
Figure 4.
Crosslinking agents of chitosan.
There are also ionic crosslinking agents of chitosan, which are specifically designed for electrostatic interactions [88]. Babakhani et al. [89] synthesized a novel ion-imprinted crosslinked chitosan with sodium tripolyphosphate, and the polymeric material has a maximum adsorption capacity of 1.05 mmol/g towards Cd (II) ions in aqueous solution [85,86,87].
3.4. Graft Polymerization
Graft copolymerization is an efficient modification process of chitosan. This process involves the reactant’s connection with the functional groups of chitosan, resulting in a polymeric material with dual or merged properties [90]. Graft polymerization can be performed using various monomers such as acrylamide, vinyl acetate, methyl methacrylate, etc. [91]. The grafted chitosan has been reported in many studies to remove Pb (II) ions [92], Cu (II) and Zn (II) ions [93], As (V) ions [94], and methylene blue [95].
3.5. Depolymerization of Chitosan
Depolymerization is a critical process in the modification of chitosan for use in wastewater treatment. This can be chemical, physical, or enzymatic, and it breaks down the long chain of chitosan into low-molecular-weight chitosan (LMWC). Unlike the functional group modifications mentioned above, this process solely alters the molecular weight and chain length.
- (i)
- Chemical depolymerization
Chemical depolymerization includes acidic depolymerization, where glycosidic bonds are broken when chitosan’s amino groups are protonated by acidic conditions, such as acetic acid or HCl. This procedure makes chitosan more soluble and lowers its molecular weight [96]. Alkaline depolymerization of chitosan can also use NaOH, which hydrolyzes its polymer chains. However, because of the severe reaction conditions, this method is not as widely used [96]. Furthermore, oxidative depolymerization breaks the glycosidic bonds in chitosan using ozone (O3), a potent oxidizing agent [97].
- (ii)
- Enzymatic depolymerization
Enzymatic depolymerization employs enzymes such as chitinases and chitosanases, which break down the glycosidic bond in the polymer chain, resulting in low-molecular-weight oligomers or monomers. As shown in Table 2, this method is more friendly than chemical depolymerization [98,99].
- (iii)
- Physical depolymerization
This depolymerization technique uses physical force to break chitosan chains, such as ultrasonic, ultraviolet, gamma-ray, etc. [100,101]. Table 2 is a comparative analysis of these methods.

Table 2.
Comparative analysis of depolymerization methods.
Table 2.
Comparative analysis of depolymerization methods.
| Method | Advantages | Disadvantages | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical depolymerization | Cost-effective, simple, and widely used. | Loss of functional groups such as hydroxyl and amino groups, and environmental concerns due to hazardous byproducts. | [102] |
| Enzymatic depolymerization | Environmentally friendly, mild reaction conditions, and high specificity. | Limited scalability and high costs. | [98,99] |
| Physical depolymerization | Chemical-free, simple, and energy-efficient. | Limited control over depolymerization and high energy input. | [103] |
4. Techniques for Removing Pollutants from Wastewater
There are different techniques that have been used to eliminate pollutants from wastewater, such as flocculation or coagulation, membrane separation, ion exchange, membrane filtration, etc. Each technique offers a distinct advantage in removing different types of pollutants from wastewater.
4.1. Flocculation
Flocculation is the process of removing suspended solids or contaminants from a system. This technique involves two mechanisms, such as charge neutralization and bridging, whereby the chitosan-based material will act as a cationic polyelectrolyte, due to its -NH2 groups, which in turn neutralize the negative charges on suspended particles, causing their aggregation into massive flocs, which can be removed easily from wastewater [104,105]. In the sweep flocculation mechanism, the chitosan-based material forms a network that captures and settles the suspended contaminants [106]. Wei et al. [107] designed a pH-responsive chitosan-based flocculant, which yielded the maximum flocculation capacity of 1.5 g/g towards Reactive Brilliant Red K-2BP (azo dye) and a high dye removal efficiency of approximately 98.5% under optimized conditions. Another extensive study by Sun et al. [108] prepared a novel chitosan-based flocculent, called carboxylated chitosan-graft-poly[acrylamide-2-acrylamido-2-methylpropane sulfonic acid], with chromium and nickel removal rates of 94.6% and 99.4%, respectively.
4.2. Photocatalysis
Photocatalysis is the process that is mostly used in wastewater treatment, which breaks down pollutants under light irradiation. Traditional photocatalysts, such as TiO2 and CdS suffer from a small surface area, high band gap, poor adsorption capacity, and poor carrier life [109,110]. The incorporation of these metal oxides with chitosan enhances catalytic activity by providing more active sites and suppressing electron–hole recombination rates [109,110]. In a study conducted by Nyamiati et al. [111], chitosan-TiO2 membranes demonstrated effective degradation efficiency of 91.89% towards Pb and Cd in batik waste. Additionally, Ali et al. [112], prepared a novel chitosan-encapsulated metal selenide photocatalyst, which degraded Bromothymol Blue dye by 97% within 100 min under optimized conditions. The FeNi3/chitosan/BiOI nanocomposite also showed effective degradation of metronidazole of 100% [113].
4.3. Membrane Filtration
Membrane filtration is a separation technique whereby a semi-permeable membrane is used to remove pollutants from wastewater. Chitosan-based materials have been used to remove pollutants from wastewater with this technique. For instance, Machodi et al. [114] synthesized polyethersulphone/chitosan membranes coated with polyamide, which exhibited significant improvement of 56 to 93 L/m2.hr in pure water flux upon the addition of 1 wt% chitosan. Mn2+, Fe2+, Mg2+, and Ca2+ had rejection percentages of 90.4%, 88.3%, 89.3%, and 75.7%, respectively. Furthermore, in a related study by Bassyouni et al. [115], chitosan nanofiltration membranes fabricated via solvent casting achieved 100% rejection of Direct Blue 78 dye with a permeation flux of 9.3 L/m2.h and maintained antifouling performance over 10 h of continuous filtration.
5. Adsorption Mechanisms of Chitosan-Based Materials
Understanding the adsorption mechanisms of chitosan-based materials is crucial. As mentioned earlier, chitosan has many functional groups that enable it to interact with pollutants through different adsorption mechanisms. Chitosan can be modified to better suit these mechanisms in wastewater treatment. These mechanisms include, but are not limited to, hydrogen bonding, chelation interactions, and electrostatic interactions.
5.1. Electrostatic Interactions
Electrostatic interaction is a prevalent adsorption process utilized by chitosan-based polymers for the removal of persistent heavy metals, dyes, and EOPs from wastewater. This mechanism arises when charged species are separated by a certain distance due to ionization. The repulsive forces among like charges and the attraction force between unlike charges are noted as a key phenomenon [116]. As shown in Figure 5, the amine group in chitosan is protonated at low pH and becomes more cationic, leading to the attraction of anionic dyes, e.g., azo dyes. This interaction between chitosan and anionic pollutants leads to enhanced binding efficiency and significant pollutant removal rates [117].
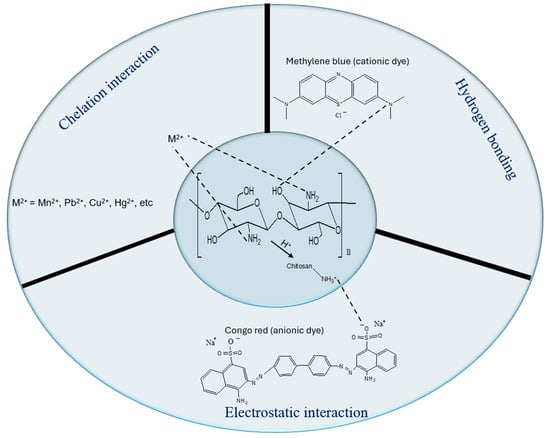
Figure 5.
Common adsorption mechanisms of chitosan-based materials for the elimination of dyes or heavy metals.
5.2. Hydrogen Bonding
Hydrogen bonding is a dipole–dipole interaction between molecules. This dipole–dipole contact arises from the covalent bond between hydrogen and two strongly electronegative atoms, such as nitrogen and oxygen in chitosan-based material. Hydrogen bonding interaction between two atoms with a higher affinity for electrons is necessary for the hydrogen bonding interactions. In this case, the link is stronger than the van der Waals force but weaker than an ionic or covalent bond [118]. For instance, the hydrogen bonding mechanism in chitosan-based materials has been described in the elimination of EOPs (phenols and rotenone) [119,120,121] and dyes [122,123,124]. In a study by Kyomuhimbo et al. [125], the general mechanism for the removal of Bismarck Brown (BB), Orange G (OG), Brilliant Blue G (BBG), and Indigo Carmine (IC) dyes was through hydrogen bonding.
5.3. Chelation Interaction
Chelation is a process in which a molecule, such as a polydentate ligand with two or more donor atoms, binds to a metal ion to form a chelate complex (see Figure 5). In the case of water remediation, chitosan-based materials have been utilized to remove many ions in wastewater, as they contain many amino groups with donor atoms [58]. Enhanced interactions are essential for an effective adsorption process [126]. Conversely, fluctuations in pH may modify the adsorbent’s structure and disrupt the adsorption process [127]. Lyu et al. [128] synthesized chitosan-Mg-Al layered double hydroxide (CS-LDH) and used it to remove Pb (II) ions, with XPS analysis of CS-LDH conducted before and after the removal procedure illustrating the chelation mechanism. There are numerous studies where this mechanism was involved in the elimination of Pb (II), Cu (II), Co (II), and Cd (II) ions [117,129,130,131].
5.4. π–π Interactions
π–π interactions, or stacking, are non-covalent interactions between aromatic rings, and this mechanism is very important in dye removal. However, chitosan lacks an aromatic ring; therefore, to facilitate this mechanism, chitosan must be functionalized with aromatic moieties. Dyes with multiple aromatic rings, such as Methylene Blue and Congo Red, exhibit enhanced π–π interactions due to their extensive π systems. The interaction is further enhanced when the dye molecules are planar, allowing for optimal overlap with the aryl-functionalized chitosan surface [132,133]. The intensity of π–π interactions can be adjusted by using dyes that contain electron-donating groups (e.g., hydroxyl or amino) or electron-withdrawing groups (e.g., sulfonic acid). For instance, protonated chitosan surfaces, where electron-rich regions promote π–π stacking, interact strongly with anionic dyes such as tartrazine [134,135]. This mechanism has been observed in aryl-modified chitosan for the removal of dyes, including Acid Red 88, Reactive Orange 16, and Reactive Blue 221 [136,137,138], as well as in phenol removal [120].
6. Chitosan as an Adsorbent
Chitosan-based materials exist in various forms, depending on how the material was processed to serve as an adsorbent. These forms include films, nanofibers, membranes, hydrogels, nanocomposites, sponges, and nanoparticles. Each adsorbent form has its own unique advantages; however, according to the literature, the most promising chitosan-based material is hydrogel, due to its high water swelling capacity [139]. To evaluate the efficiency of chitosan-based materials, models of adsorption kinetics are used to elucidate the interaction mechanisms between adsorbents and pollutants (mostly pseudo-first-order and pseudo-second-order kinetic models) [140,141], while adsorption isotherms assess both adsorption efficiency and economic feasibility. Commonly applied isotherm models include Langmuir, Freundlich, Redlich–Peterson, and Sips, each reflecting different surface and interaction characteristics [142]. The following sections detail the preparation and application of these chitosan-based adsorbents in wastewater treatment.
6.1. Sponges
Chitosan sponges are mostly created through freeze-drying techniques, which result in a porous structure that enhances adsorption capacity for various pollutants, such as dyes, heavy metals, and EOPs [143], for instance, Xu et al. [144] synthesized xanthate-modified sponge-like chitosan-based adsorbent (CTS-SX) through a facile method, which exhibited excellent adsorption performance for Sr (II) and Cs (I) with maximum adsorption capacities of 76.21 and 133.15 mg/g, respectively.
6.2. Films and Membranes
Chitosan-based films and membranes are mostly prepared by casting and drying a chitosan solution and sometimes modified with crosslinking agents to improve the mechanical strength and stability in acidic conditions [145,146]. These materials are effective in membrane separation processes, notably for nanofiltration and microfiltration, where they help in the removal of heavy metal ions and emulsified oil droplets [145].
6.3. Nanofibers, Nanoparticles, and Nanocomposites
Chitosan nanofibers are produced through electrospinning, which enables them to have a large surface area and high porosity, enhancing adsorption capabilities [143]. Chitosan nanoparticles are pure, or nearly pure, chitosan particles at the nano-range, which can be prepared through ionotropic gelation, microemulsion, emulsification diffusion methods, etc. [147]. Chitosan composites are mostly doped with nanoparticles or other materials (e.g., metal oxides, clay, graphene), to improve the adsorption capacity in wastewater treatment [148].
6.4. Hydrogels
Hydrogels are the most remarkable chitosan-based adsorbents in wastewater treatment because of their three-dimensional network, which can swell and retain large amounts of water. They are synthesized through the crosslinking of chitosan with aldehyde-based crosslinkers (e.g., glutaraldehyde) [148]. Table 3 highlights the recent advancements and use of these materials in water remediation.

Table 3.
Recent studies on the use of chitosan-based adsorbents in wastewater treatment and their adsorption capacities.
Table 3.
Recent studies on the use of chitosan-based adsorbents in wastewater treatment and their adsorption capacities.
| Chitosan-Based Adsorbent | Pollutant | Reusability | pH | Adsorption Capacity (mg/g) | Mechanism Involved | Kinetic Studies | Isotherm Model | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sponges | ||||||||
| ZIF-8@chitosan (ZIF-8@CS) composite sponge | Congo Red | 5 | - | 987.01 | Electrostatic interactions, hydrogen bonding, π–π interactions | PFO | LIM and FIM | [149] |
| PEI-S-CS sponge | Hg (II) | 6 | 1–7 | 1227.15 | Chelation | PSO | LIM | [150] |
| Chitosan/silver cluster-loaded cellulose nanofibril/Cu-ZIF-8 | Cr (VI) | 10 | 2 | 171.20 | Electrostatic interactions, hydrogen bonding | PSO | LIM | [151] |
| Ammonium-modified chitosan composite sponge | Congo Red | 5 | 6 | 1261.64 | Electrostatic interactions, hydrogen bonding | PSO | SIM | [152] |
| Chitosan–alginate sponge | Maranth, Carmine, and Sunset Yellow | 6 | 2 | 94.34, 111.50, and 80.05, respectively | Electrostatic interactions | PSO | LIM | [153] |
| Microspheres | ||||||||
| Porous magnetic chitosan microspheres (PPy@PMCS) | Cr (VI) | 4 | 2 | 330.42 | Chelation | PSO | LIM | [154] |
| Chitosan-based composite microspheres (CP) | Cr (VI) | 4 | 3 | 299.69 | Electrostatic interaction, chelation | PSO | LIM | [155] |
| Chitosan-based composite microspheres (CP) | Eriochrome Black T dye (EBBR) | - | 5 | 317.21 | Electrostatic interactions | PSO | LIM | [155] |
| Nitrilotriacetic acid-modified magnetic chitosan microspheres | Tetracycline (TC) | 5 | 8 | 625.52 | π–π interactions, hydrogen bonding | PSO | FIM | [156] |
| Iron-doped chitosan microspheres | As (III) | 3 | 8 | ≥125 | Electrostatic interaction, chelation | PSO | FIM | [157] |
| Nanoparticles | ||||||||
| Magnetic chitosan nanoparticles | Reactive Red 141 (RR-141), Reactive Yellow 14 (RY-14) | 5 | RR-141: 5.5 RY-14: 5.6 | RR-141.00: 98.8 RY-14: 89.70 | Electrostatic interactions | PSO | FIM | [158] |
| Magnetic Fe3O4-chitosan nanoparticles | Cs (I) | 5 | - | 161.30 | Electrostatic interactions | PSO | LIM | [159] |
| Magnetic thiazole-functionalized chitosan nanoparticles | Cd (II) | 5 | 4 | 200.00 | Ion exchange, chelation | PFO | SIM and LIM | [160] |
| Magnetite-functionalized chitosan nanoparticles grafted with TDP | Cr (VI) | 5 | 4 | 299.00 | Electrostatic interactions, chelation, ion exchange | PFO | SIM and LIM | [161] |
| Magnetic ion-imprinted chitosan nanoparticles (MIIP) | Ni (II) | 15 | 7 | 18.50 | Electrostatic interactions, chelation | PSO | LIM | [162] |
| Nanofibers/membranes | ||||||||
| Electrospun CS/CQDs/PCL nanofiber membrane | Ni (II) | 5 | 6 | 341.80 | Electrostatic interactions, chelation | PSO | LIM | [163] |
| CS-g-PNVCL/ZIF-8 | Phenol | 5 | 3 | 395.80 | π–π interactions, electrostatic interactions | PSO | RPIM | [164] |
| Electrospun CS/PVA nanofiber loaded with Ce-MOF | Malachite Green (MG) | 8 | 5 | 359.20 | Electrostatic interactions, chelation, hydrogen bonding | PSO | LIM | [165] |
| Chitosan-sulfonated polyphenylsulfone nanofibers | Congo Red | 4 | 6.5 | 531.56 | Electrostatic interactions, chelation, hydrogen bonding, hydrophobic interactions | PSO | FIM | [166] |
| Functionalized cellulose/chitosan porous nanofibrous membranes | Cu (II) | 6 | 5 | 121.06 | Electrostatic interactions, chelation | PSO | LIM | [167] |
| Magnetic ion-imprinted electrospun nanofiber membrane | Pb (II) | 7 | 7 | 133.20 | Ion-imprinting, chelation, electrostatic interactions | PSO | LIM | [168] |
| Chitosan/Nylon-6 (CS/N) nanofiber | Cu (II) | 8 | 4 | 240.00 | Electrostatic interactions, chelation | PSO | LIM and FIM | [169] |
| Chitosan–lignin composite cast membrane | MB | 5 | 7 | 241.62 | Hydrogen bonding, electrostatic interaction, van der Waals forces | PFO | LIM | [170] |
| Films | ||||||||
| ZnFe2O4/HEC/chitosan film | Methyl Orange | 5 | 8 | 914.00 | Electrostatic interactions and hydrogen bonding | PSO | LIM | [171] |
| CS/PVP/β-CD/NCC composite film | Cu (II) | 5 | 5 | 148.20 | Electrostatic interactions, hydrogen bonding, ion exchange, surface complexation | PSO | LIM | [172] |
| CMC-chitosan film | Pb (II), Cd (II) | 4 | 5 | Pb (II): 483.00, Cd (II): 123.00 | Complexation, electrostatic interactions | PSO | LIM | [173] |
| Chitosan film | As(V) | 4 | 3 | 15.23 | Ligand exchange, electrostatic interactions | PSO | LIM and FIM | [174] |
| Chitosan film | Diclofenac (DCF) | 10 | 5 | ~10.00 | Electrostatic interactions | PSO | FIM and TIM | [175] |
| Nanocomposites | ||||||||
| Fe3O4–chitosan@bentonite nanocomposite | Congo Red | 8 | 5 | 169.00 | Electrostatic interactions, hydrogen bonding, π–π stacking | PSO | LIM | [176] |
| Fe3O4@CS-CGSB | Pb (II), Cd (II) | 5 | 7 | Pb: 394.3, Cd: 390.99 | Electrostatic interactions and chelation | PSO | FIM | [177] |
| Crosslinked alginate–rice husk–GO–chitosan nanocomposite | Pb (II) | 5 | 6.5 | 295.50 | Electrostatic interactions, ion exchange, chelation | PSO | FIM | [178] |
| GO–chitosan nanocomposite | Cr (VI), Ni (II) | 4 | Cr (VI): 5 Ni (II): 8 | Cr: 1.01 Ni: 1.34 | Electrostatic interactions, hydrogen bonding | PSO | Cr (VI): FIM Ni (II): LIM | [179] |
| CS–GO nanocomposite | Rotenone | 3 | 1 | 92.59 | Hydrogen bonding, π–π interactions | PFO | LIM | [121] |
| Fe3O4/chitosan/ZIF-8 nanocomposite | Phenol | - | 9.91 | 6.44 | Hydrogen bonding, π–π interactions | PSO | LIM | [120] |
| Hydrogels | ||||||||
| Glucan/chitosan hydrogel | Cu (II), Co (II) | - | 7 | Cu (II): 342.00, Co (II): 232.00 | Ion exchange, electrostatic interactions | PSO | LIM | [141] |
| Chitosan-based hydrogels | 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid | 5 | Neutral (7) | 75.29 | Monolayer formation and multisite interactions | PSO | LIM | [180] |
| Sodium alginate/sodium lignosulfonate/carboxylated chitosan/polyethyleneimine composite hydrogels | Anionic (AD) and cationic dyes (CD) | 5 | - | AD > 550 CD > 1900 | Electrostatic interactions, π–π interactions | PSO | LIM | [135] |
| Carboxymethyl chitosan/sodium alginate hydrogels | Cd (II), Cr (III) | - | - | Cd (II): 314.60 Cr (III): 289.10 | Electrostatic interactions, ion exchange | PSO | LIM | [181] |
| Chitosan-based hydrogel | Tetracycline | 4 | 8 | 541.30 | Electrostatic interactions, hydrogen bonding | PSO | LIM | [121] |
| Acrolein-crosslinked chitosan hydrogel | Acid Blue 93 (AB93) | 12 | - | 1839.00 | Hydrogen bonding, electrostatic interactions | PSO | LIM | [182] |
| Amine-thiourea modified magnetic chitosan hydrogel | Ce (III) | 5 | 6 | 156 | Chelation, electrostatic interactions | PSO | LIM | [183] |
| XMPC hydrogel | Cu (II) | 5 | 5–6 | 185 | Chelation, electrostatic interactions | PSO | LIM | [184] |
Pseudo First Order (PFO), Pseudo Second Order (PSO), Langmuir Isotherm Model (LIM), Freundlich Isotherm Model (FIM), Sips Isotherm Model (SIM), Redlich–Peterson Isotherm (RPIM), and Temkin Isotherm Model (TIM).
7. Conclusions, Future Work, and Recommendations
Chitosan-based adsorbents have emerged as one of the most promising materials in wastewater remediation, as demonstrated across various studies reviewed in this work from 2015–2025. The versatility of chitosan is brought about by its modifiable structure through various methods, which tailor its selectivity and affinity towards specific contaminants such as dyes, heavy metals, and emerging organic pollutants. Sponges have high capacities and rapid uptake from their high porosity, although they have lower mechanical stability. Films and membranes have a continuous filtration due to their superior strength. Nanofibers provide fast adsorption from a large surface area, and magnetic microspheres/nanoparticles enable easy recovery and reuse. These differences reflect how their form of structure affects their performance and application suitability. Among the reviewed chitosan-based adsorbents, hydrogels stand out as the most effective due to their 3D structure and high swelling capacities, leading to more adsorption sites. Most kinetic studies favor the pseudo-second-order model, indicating chemisorption as the main removal mechanism on the reviewed chitosan-based adsorbents, while Langmuir and Freundlich isotherms best describe monolayer and heterogeneous surface adsorption, respectively.
Despite this significant improvement in the utilization of chitosan-based materials in wastewater treatment, some challenges need to be considered before these materials can be used in large-scale water purification systems. (i) The issue of the decrease in adsorption capacity of these materials in a few cycles. (ii) There are few studies that test chitosan-based adsorbent materials in fixed-bed or membrane–adsorption hybrid systems to move closer to industrial application, so integration into a continuous system rather than closed system should be carried out. (iii) These adsorbent materials are tested in controlled laboratories, not in real wastewater matrices, where there can be competitive ions or organic matter interference. So, to bridge this gap, new chitosan-based adsorbents that preserve structural integrity across multiple cycles should be designed; furthermore, there should be an expansion of performance testing to real wastewater matrices.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.D., M.A.S. and P.P.M.; methodology, A.D. and M.A.S.; resources, A.D.; data curation, A.D. and M.A.S.; writing—original draft preparation, A.D.; writing—review and editing, A.D., M.A.S., P.P.M. and M.E.M.; visualization, A.D.; supervision, M.A.S., P.P.M. and M.E.M.; project administration, M.A.S.; funding acquisition, A.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by the National Research Foundation (Sasol Foundation), grant numbers PMDS240613227379.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the University of the Free State (Department of Chemistry) and the University of Johannesburg (Department of Metallurgical Engineering) for providing a conducive research environment, as well as the NRF (Sasol Foundation) for financial support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Mishra, B.K.; Kumar, P.; Saraswat, C.; Chakraborty, S.; Gautam, A. Water security in a changing environment: Concept, challenges and solutions. Water 2021, 13, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollmer, D.; Harrison, I.J. H2O ≠ CO2: Framing and responding to the global water crisis. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 011005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsani, S.; Koundouri, P.; Akinsete, E. Resource management and sustainable development: A review of the European water policies in accordance with the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals. Environ. Sci. Policy 2020, 114, 570–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, N.; Syakir Ishak, M.I.; Bhawani, S.A.; Umar, K. Various natural and anthropogenic factors responsible for water quality degradation: A review. Water 2021, 13, 2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babuji, P.; Thirumalaisamy, S.; Duraisamy, K.; Periyasamy, G. Human Health Risks due to Exposure to Water Pollution: A Review. Water 2023, 15, 2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tufail, M.A.; Iltaf, J.; Zaheer, T.; Tariq, L.; Amir, M.B.; Fatima, R.; Asbat, A.; Kabeer, T.; Fahad, M.; Naeem, H.; et al. Recent advances in bioremediation of heavy metals and persistent organic pollutants: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 850, 157961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vardhan, K.H.; Kumar, P.S.; Panda, R.C. A review on heavy metal pollution, toxicity and remedial measures: Current trends and future perspectives. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 290, 111197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordberg, G.; Jin, T.; Wu, X.; Lu, J.; Chen, L.; Liang, Y.; Lei, L.; Hong, F.; Bergdahl, I.A.; Nordberg, M. Kidney dysfunction and cadmium exposure—Factors influencing dose–response relationships. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2012, 26, 197–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, S.; Dhar, S.; Sudarshan, M.; Chakraborty, A.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Bhattacharjee, P. Investigating the synergistic role of heavy metals in Arsenic-induced skin lesions in West Bengal, India. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2023, 75, 127103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamoli, A.; Karn, S.K. The Effects of Mercury Exposure on Neurological and Cognitive Dysfunction in Human: A Review. In Mercury Toxicity Mitigation: Sustainable Nexus Approach; Kumar, N., Ed.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 117–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, C.B.; Costa, M. Chapter 24—Nickel. In Handbook on the Toxicology of Metals, 5th ed.; Nordberg, G.F., Costa, M., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; pp. 615–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, D.; Singh, M.P. 10—Heavy metal contamination in water and its possible sources. In Heavy Metals in the Environment; Kumar, V., Sharma, A., Cerdà, A., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Wei, C.; Ke, X.; Pan, J.; Wei, G.; Chen, Y.; Wei, C.; Li, F.; Preis, S. Nationwide review of heavy metals in municipal sludge wastewater treatment plants in China: Sources, composition, accumulation and risk assessment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 437, 129267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakare, B.F.; Adeyinka, G.C. Evaluating the Potential Health Risks of Selected Heavy Metals across Four Wastewater Treatment Water Works in Durban, South Africa. Toxics 2022, 10, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahabudin, M.M.; Musa, S. Occurrence of Surface Water Contaminations: An Overview. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 140, 012058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Ahmed, G.; Vedika, S.; Kumar, P.; Chaturvedi, S.K.; Rai, S.N.; Vamanu, E.; Kumar, A.; Sharma, D.; Kumar, A. Toxic heavy metal ions contamination in water and their sustainable reduction by eco-friendly methods: Isotherms, thermodynamics and kinetics study. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 7595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haleem, A.; Ullah, M.; Rehman Sur Shah, A.; Farooq, M.; Saeed, T.; Ullah, I.; Li, H. In-Depth Photocatalytic Degradation Mechanism of the Extensively Used Dyes Malachite Green, Methylene Blue, Congo Red, and Rhodamine B via Covalent Organic Framework-Based Photocatalysts. Water 2024, 16, 1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oladoye, P.O.; Ajiboye, T.O.; Omotola, E.O.; Oyewola, O.J. Methylene blue dye: Toxicity and potential elimination technology from wastewater. Results Eng. 2022, 16, 100678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandanshive, V.; Kadam, S.; Rane, N.; Jeon, B.-H.; Jadhav, J.; Govindwar, S. In situ textile wastewater treatment in high rate transpiration system furrows planted with aquatic macrophytes and floating phytobeds. Chemosphere 2020, 252, 126513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benkhaya, S.; M’rabet, S.; El Harfi, A. A review on classifications, recent synthesis and applications of textile dyes. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2020, 115, 107891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, A.; Chopra, L. Dye Waste: A significant environmental hazard. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 48, 1310–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Tohamy, R.; Ali, S.S.; Li, F.; Okasha, K.M.; Mahmoud, Y.A.-G.; Elsamahy, T.; Jiao, H.; Fu, Y.; Sun, J. A critical review on the treatment of dye-containing wastewater: Ecotoxicological and health concerns of textile dyes and possible remediation approaches for environmental safety. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 231, 113160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, R.; Zahid, M.; Govindwar, S.; Khandare, R.; Vyavahare, G.; Gurav, R.; Desai, N.; Pandit, S.; Jadhav, J. Constructed wetland: A promising technology for the treatment of hazardous textile dyes and effluent. In Development in Wastewater Treatment Research and Processes: Removal of Emerging Contaminants from Wastewater Through Bio-Nanotechnology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 173–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preethi, P.S.; Vickram, S.; Das, R.; Hariharan, N.M.; Rameshpathy, M.; Subbaiya, R.; Karmegam, N.; Kim, W.; Govarthanan, M. Bioprospecting of novel peroxidase from Streptomyces coelicolor strain SPR7 for carcinogenic azo dyes decolorization. Chemosphere 2023, 310, 136836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Sang, W.; Lu, W.; Zhang, W.; Zhan, C.; Jia, D. Recent Advances of Emerging Organic Pollutants Degradation in Environment by Non-Thermal Plasma Technology: A Review. Water 2022, 14, 1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, H.A.; Ahmad, S.; Cui, Q.; Wang, Z.; Wei, H.; Chen, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, M.; Khan, S. The environmental distribution and removal of emerging pollutants, highlighting the importance of using microbes as a potential degrader: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 809, 151926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Zhang Sgen Chang, C.C. Emerging pollutants—Part II: Treatment. Water Environ. Res. 2020, 92, 1603–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younas, F.; Mustafa, A.; Farooqi, Z.U.R.; Wang, X.; Younas, S.; Mohy-Ud-din, W.; Hameed, M.A.; Abrar, M.M.; Maitlo, A.A.; Abro, A.A. Current and emerging adsorbent technologies for wastewater treatment: Trends, limitations, and environmental implications. Water 2021, 13, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshta, B.E.; Yu, H.; Wang, L. MIL series-based MOFs as effective adsorbents for removing hazardous organic pollutants from water. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 322, 124301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Yao, Y.; Li, X.; Lu, J.; Zhou, J.; Huang, Z. Comparison of heavy metal removals from aqueous solutions by chemical precipitation and characteristics of precipitates. J. Water Process Eng. 2018, 26, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qader, I.N.; Ibrahim, B.M.; Fakhre, N.A.; Sharef, H.Y. Adsorption of Heavy Metals from Wastewater by Starch, Cellulose, Chitin, Chitosan and Lignin Biological Macro Molecule: Review Article. Hacet. J. Biol. Chem. 2025, 53, 127–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Dai, T.; He, X.; Chen, M.; Liu, C.; Liang, R.; Chen, J. Preparation of pectin/poly(m-phenylenediamine) microsphere and its application for Pb2+ removal. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 260, 117811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z.; Lu, J.; Ding, J.; Fan, F.; Sun, X.; Li, P.; Fang, Y.; Hu, Q. Novel green chitosan-pectin gel beads for the removal of Cu(II), Cd(II), Hg(II) and Pb(II) from aqueous solution. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 176, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mudugamuwa Arachchige, M.P.; Mu, T.; Ma, M. Effect of high hydrostatic pressure-assisted pectinase modification on the Pb2+ adsorption capacity of pectin isolated from sweet potato residue. Chemosphere 2021, 262, 128102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaurasiya, A.; Poorn Prakash, P.; Ravi, S.; Amar, N.; Tripathi, N.P. Synthesis and characterization of pectin-xanthate and their application in heavy metal and lignin enriched paper industry wastewater treatment. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2023, 58, 3026–3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, A.; Mishra, S. Exploring the potential of waste biomass-derived pectin and its functionalized derivatives for water treatment. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 275, 133613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhuang, S. Removal of various pollutants from water and wastewater by modified chitosan adsorbents. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 47, 2331–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, J.; Dewan, M.; Ghosh, A.; Ray, S.S.; Orasugh, J.T.; Lahiri, B.; Chattopadhyay, D.; Adhikari, A. Chitosan-based adsorbents for remediation of toxic dyes from wastewater: A review on adsorption mechanism, reusability, machine learning based modeling and future perspectives. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 311, 143388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tafraout, F.; Isaad, J. Recent research landscape on chitosan-mineral-based composites for wastewater treatment: A comprehensive bibliometric analysis (2014–2024). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2025, 32, 11815–11837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Silva Bruckmann, F.; Gonçalves, J.O.; Silva, L.F.O.; Oliveira, M.L.S.; Dotto, G.L.; Rhoden, C.R.B. Chitosan-based adsorbents for wastewater treatment: A comprehensive review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 309, 143173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Hu, C.; Jiang, R.; Xiao, M.; Fu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, K. Sustainable chitosan-based adsorbents for phosphorus recovery and removal from wastewater: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 313, 144160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Crini, G.; Lichtfouse, E.; Wilson, L.D.; Picos-Corrales, L.A.; Balasubramanian, P.; Li, F. Chitosan-based materials for emerging contaminants removal: Bibliometric analysis, research progress, and directions. J. Water Process Eng. 2025, 71, 107327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, M.A.; Tripathi, A.; Raj, A.; Gauba, P.; Bhatt, E. Chitosan: A Novel Approach and Sustainable Way to Remove Contaminants and Treat Wastewater. Starch/Staerke 2025, 77, e202400171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.; Wang, Y.; Teng, Y.; Qu, Y.; Huang, D.; Qiang, X. A novel chitosan/Chinese ink composite aerogels: Preparation and application for solar steam generators. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2025, 711, 136322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinarvand, H.; Moradi, O. Sustainable Approaches for Pharmaceutical Pollutant Removal: Advances in Chitosan-Based Nanocomposite Adsorbents. ChemistrySelect 2025, 10, e202405962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.; Sharma, G.; Wang, T.; Kumar, A.; Dhiman, P.; Verma, Y.; Bhaskaralingam, A.; García-Peñas, A. Graphene oxide/chitosan hydrogels for removal of antibiotics. Environ. Technol. 2025, 46, 3391–3421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Ye, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, T.; Jiang, S.; Han, X. Functionalization of chitosan and its application in flame retardants: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 295, 139615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darmenbayeva, A.; Zhussipnazarova, G.; Rajasekharan, R.; Massalimova, B.; Zharlykapova, R.; Nurlybayeva, A.; Mukazhanova, Z.; Aubakirova, G.; Begenova, B.; Manapova, S.; et al. Applications and Advantages of Cellulose–Chitosan Biocomposites: Sustainable Alternatives for Reducing Plastic Dependency. Polymers 2025, 17, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thirugnanasambandan, T.; Gopinath, S.C.B. Laboratory to industrial scale synthesis of chitosan-based nanomaterials: A review. Process Biochem. 2023, 130, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, Z.; Kuzhir, P.; Godeau, G. Update on Chitin and Chitosan from Insects: Sources, Production, Characterization, and Biomedical Applications. Biomimetics 2024, 9, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huq, T.; Khan, A.; Brown, D.; Dhayagude, N.; He, Z.; Ni, Y. Sources, production and commercial applications of fungal chitosan: A review. J. Bioresour. Bioprod. 2022, 7, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mashhadani, M.H.; Adil, H.; Naser, H.G.; Ibraheem, H.; Jwad, R.S.; Alshareef, S.A.; Hasan, A.A.; Ghosh, S.; Hamzah, H.A.; Yousif, E. Organic Modification of Chitosan: An Overview. Baghdad J. Biochem. Appl. Biol. Sci. 2024, 5, 72–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, N.H.; Rajaratinam, H.; Nurul, A.A. Chitosan from Marine Biowaste: Current and Future Applications in Tissue Engineering. In Sustainable Material for Biomedical Engineering Application; Wan Kamarul Zaman, W.S., Abdullah, N.A., Eds.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2023; pp. 87–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmsen, R.A.G.; Tuveng, T.R.; Antonsen, S.G.; Eijsink, V.G.H.; Sørlie, M. Can we make Chitosan by Enzymatic Deacetylation of Chitin. Molecules 2019, 24, 3862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozma, M.; Acharya, B.; Bissessur, R. Chitin, Chitosan, and Nanochitin: Extraction, Synthesis, and Applications. Polymers 2022, 14, 3989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizeq, B.; Younes, N.; Rasool, K.; Nasrallah, G.K. Synthesis, Bioapplications, and Toxicity Evaluation of Chitosan-Based Nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Araby, A.; Janati, W.; Ullah, R.; Ercisli, S.; Errachidi, F. Chitosan, chitosan derivatives, and chitosan-based nanocomposites: Eco-friendly materials for advanced applications (a review). Front. Chem. 2024, 11, 1327426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, C.-Y.; Ajaj, Y.; Mahmoud, Z.H.; Ghadir, G.K.; Alani, Z.K.; Hussein, M.M.; Hussein, S.A.; Karim, M.M.; Al-Khalidi, A.; Abbas, J.K. Adsorption of heavy metal ions use chitosan/graphene nanocomposites: A review study. Results Chem. 2024, 7, 101332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranaz, I.; Alcántara, A.R.; Civera, M.C.; Arias, C.; Elorza, B.; Caballero, A.H.; Acosta, N. Chitosan: An overview of its properties and applications. Polymers 2021, 13, 3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merzendorfer, H. Chitosan Derivatives and Grafted Adjuncts with Unique Properties. In Extracellular Sugar-Based Biopolymers Matrices; Cohen, E., Merzendorfer, H., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 95–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepnova, E.A.; Tikhonov, V.E.; Babushkina, T.A.; Klimova, T.P.; Vorontsov, E.V.; Babak, V.G.; Lopatin, S.A.; Yamskov, I.A. New approach to the quaternization of chitosan and its amphiphilic derivatives. Eur. Polym. J. 2007, 43, 2414–2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guinesi, L.S.; Cavalheiro, É.T.G. Influence of some reactional parameters on the substitution degree of biopolymeric Schiff bases prepared from chitosan and salicylaldehyde. Carbohydr. Polym. 2006, 65, 557–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, C.; Zhang, R.; Bai, F.; Lu, P.; Liang, X. Removal of chromium (VI) from aqueous solutions using quaternized chitosan microspheres. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2017, 25, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narita, Y.; Sakti, S.C.W.; Akemoto, Y.; Tanaka, S. Ultra-rapid removal of cationic organic dyes by novel single- and double-stranded DNA immobilized on quaternary ammonium magnetic chitosan. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.-Y.; Li, W.; Du, N.; Lu, H.-Q.; Meng, L.-D.; Huang, K.-Y.; Li, K. Preparation of quaternary ammonium magnetic chitosan microspheres and their application for Congo red adsorption. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 297, 119995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, S.; Yamaguchi, R.; Matsuda, N.; Miura, O.; Kondo, Y. Chitosan-aldehyde gel A novel polysaccharide gel produced from chitosan and aldehydes. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1977, 41, 1547–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Wang, G.; Liu, F.; Zhao, Y. Removal of Cd(II) Ions from Wastewater by Compounding an O-Xanthogenated Chitosan Schiff Base and Fe(III) Ions. Macromol. Res. 2019, 27, 982–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, R.K.; Mohamed, F.; Gaber, E.O.Z.; Abdel-Gawad, O.F. Insights into the Synergistic Removal of Copper(II), Cadmium(II), and Chromium(III) Ions Using Modified Chitosan Based on Schiff Bases-g-poly(acrylonitrile). ACS Omega 2022, 7, 42012–42026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmanifar, E.; Shiri, F.; Shahraki, S.; Karimi, P. Experimental design for removal of lead ions from water samples using an engineered novel chitosan functionalized Schiff-base adsorbent. Chem. Eng. Commun. 2023, 210, 2022–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olugbemi, S.A.; Amoniyan, O.A. Assessment of the Adsorption Potential of Synthesized Chitosan-Pyrrole-2-Carboxaldehyde Schiff Base for Cr2+ and Pb2+ Ions from Dumpsite Leachate. Eur. J. Adv. Chem. Res. 2023, 4, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawariya, V.; De, S.; Dutta, J. Synthesis and characterization of citric acid-modified chitosan Schiff base with enhanced antibacterial properties for the elimination of Bismarck Brown R and Rhodamine B dyes from wastewater. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 264, 130664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanati, M.; Dehno Khalaji, A.; Mokhtari, A.; Keyvanfard, M. Fast removal of methyl green from aqueous solution by adsorption onto new modified chitosan Schiff base. Prog. Chem. Biochem. Res. 2020, 2021, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalifa, R.E.; Aboulhadeed, S.; Ahmed, H.M.; Omer, A.M.; Tamer, T.M.; Mohy-Eldin, M.S. Fabrication of a novel chitosan Schiff bases hydrogel derivatives for the removal of anionic dyes from wastewater. Desalination Water Treat. 2021, 244, 263–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Wang, J. Radiation-induced modification of chitosan and applications for water and wastewater treatment. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 467, 142924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, S.; Zhang, M.; Chung, B.G.; Kim, S.K. The N-acylation of chitosan fibre and the N-deacetylation of chitin fibre and chitin–cellulose blended fibre at a solid state. Carbohydr. Polym. 2000, 41, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, S.; Sakairi, N. Water soluble EDTA-linked chitosan as a zwitterionic flocculant for pH sensitive removal of Cu(II) ion. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 10385–10392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, S.K.; Bolan, N.; Lombi, E.; Skinner, W. Synthesis and Characterization of Thiolated Chitosan Beads for Removal of Cu(II) and Cd(II) from Wastewater. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2013, 224, 1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morsy, A.M.A. Adsorptive removal of uranium ions from liquid waste solutions by phosphorylated chitosan. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2015, 4, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, F.; Geng, J.; Li, M.; Chang, J.; Cui, Y. Synthesis of Chitosan–Ignosulfonate Composite as an Adsorbent for Dyes and Metal Ions Removal from Wastewater. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 21421–21430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, J.; Sharma, K.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, V. 3—Ionotropic cross-linking methods for different types of biopolymeric hydrogels. In Ionotropic Cross-Linking of Biopolymers; Nayak, A.K., Hasnain, M.S., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024; pp. 63–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medellín-Castillo, N.A.; Isaacs-Páez, E.D.; Rodríguez-Méndez, I.; González-García, R.; Labrada-Delgado, G.J.; Aragón-Piña, A.; García-Arreola, M. Formaldehyde and tripolyphosphate crosslinked chitosan hydrogels: Synthesis, characterization and modeling. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 183, 2293–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khapre, M.A.; Pandey, S.; Jugade, R.M. Glutaraldehyde-cross-linked chitosan–alginate composite for organic dyes removal from aqueous solutions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 190, 862–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczmarek-Szczepańska, B.; Mazur, O.; Michalska-Sionkowska, M.; Łukowicz, K.; Osyczka, A.M. The preparation and characterization of chitosan-based hydrogels cross-linked by glyoxal. Materials 2021, 14, 2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosli, N.; Yahya, W.Z.N.; Wirzal, M.D.H. Crosslinked chitosan/poly(vinyl alcohol) nanofibers functionalized by ionic liquid for heavy metal ions removal. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 195, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumont, V.C.; Isadora, C.C.; Vanessa, B.A.; Marcos Ade, S.; Anderson, J.F.; Sandhra, M.C.; Mansur, A.A.P.; Mansur, H.S. Nanohydroxyapatite reinforced chitosan and carboxymethyl-chitosan biocomposites chemically crosslinked with epichlorohydrin for potential bone tissue repair. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2022, 71, 740–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas-Osorio, Z.; González Castillo, E.I.; Mutlu, N.; Vidomanová, E.; Michálek, M.; Galusek, D.; Boccaccini, A.R. Tailorable mechanical and degradation properties of KCl-reticulated and BDDE-crosslinked PCL/chitosan/κ-carrageenan electrospun fibers for biomedical applications: Effect of the crosslinking-reticulation synergy. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 265, 130647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bashandeh, Z.; Khalaji, A.D. Effective Removal of Methyl Green from Aqueous Solution Using Epichlorohydrine Cross-Linked Chitosan. Adv. J. Chem. Sect. A 2021, 4, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Liu, L.; Chen, H.; Wei, Y.; Dai, L.; Liu, J.; Yuan, F.; Mao, L.; Chen, F.; Gao, Y. Impact of different crosslinking agents on functional properties of curcumin-loaded gliadin-chitosan composite nanoparticles. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 112, 106258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babakhani, A.; Sartaj, M. Synthesis, characterization, and performance evaluation of ion-imprinted crosslinked chitosan (with sodium tripolyphosphate) for cadmium biosorption. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Xu, P.; Liu, Q.; Xue, J. Graft-copolymerization of methylacrylic acid onto hydroxypropyl chitosan. Polym. Bull. 2002, 49, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubair, N.A.; Moawia, R.M.; Nasef, M.M.; Hubbe, M.; Zakeri, M. A Critical Review on Natural Fibers Modifications by Graft Copolymerization for Wastewater Treatment. J. Polym. Environ. 2022, 30, 1199–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moja, T.N.; Bunekar, N.; Mishra, S.B.; Tsai, T.-Y.; Hwang, S.S.; Mishra, A.K. Melt processing of polypropylene-grafted-maleic anhydride/Chitosan polymer blend functionalized with montmorillonite for the removal of lead ions from aqueous solutions. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moridi, H.; Talebi, M.; Jafarnezhad, B.; Mousavi, S.E.; Abbasizadeh, S. The role of chitosan grafted copolymer/zeolite Schiff base nanofiber in adsorption of copper and zinc cations from aqueous media. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 278, 135003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabris, M.A.; Rezania, S.; Rafieizonooz, M.; Khankhaje, E.; Devanesan, S.; AlSalhi, M.S.; Aljaafreh, M.J.; Shadravan, A. Chitosan magnetic graphene grafted polyaniline doped with cobalt oxide for removal of Arsenic(V) from water. Environ. Res. 2022, 207, 112209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshahrani, H.; Abdulhameed, A.S.; Khan, M.K.A.; Al Omari, R.H.; Algburi, S. Functionalization of chitosan/alumina nanoparticles with carboxylic groups using phthalic anhydride for adsorption of methylene blue dye via response surface methodology. Polym. Bull. 2025, 82, 87–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Hu, W. Preparation, characterization and application in environmental protection of low-molecular-weight chitosan: A review. Sustain. Environ. Res. 2024, 34, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatullayeva, S.; Tagiyev, D.; Zeynalov, N.; Mammadova, S.; Aliyeva, E. Recent advances of chitosan-based polymers in biomedical applications and environmental protection. J. Polym. Res. 2022, 29, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safina, V.R.; Melentiev, A.I.; Galimzianova, N.F.; Gilvanova, E.A.; Kuzmina LYu Lopatin, S.A.; Varlamov, V.P.; Baymiev, A.H.; Aktuganov, G.E. Efficiency of Chitosan Depolymerization by Microbial Chitinases and Chitosanases with Respect to the Antimicrobial Activity of Generated Chitooligomers. Appl. Biochem. Microbiol. 2021, 57, 626–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Águila-Almanza, E.; Salgado-Delgado, R.; Vargas-Galarza, Z.; García-Hernández, E.; Hernández-Cocoletzi, H. Enzymatic Depolimerization of Chitosan for the Preparation of Functional Membranes. J. Chem. 2019, 2019, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pankaj, S.K.; Shi, H.; Keener, K.M. A review of novel physical and chemical decontamination technologies for aflatoxin in food. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 71, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandit, A.; Indurkar, A.; Deshpande, C.; Jain, R.; Dandekar, P. A systematic review of physical techniques for chitosan degradation. Carbohydr. Polym. Technol. Appl. 2021, 2, 100033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Jbour, N.D.; Beg, M.D.H.; Gimbun, J. Acid Hydrolysis of Chitosan to Oligomers Using Hydrochloric Acid. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2019, 42, 1741–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, H.J.; Vieceli, M.; Alves, C.; de Muñiz, G.I.B.; Oliveira, C.L.P.; Feroldi, M.; Arantes, M.K. Chitosan Depolymerization and Nanochitosan Production Using a Single Physical Procedure. J. Polym. Environ. 2018, 26, 3913–3923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtfouse, E.; Morin-Crini, N.; Fourmentin, M.; Zemmouri, H.; Nascimento IOdo, C.; Queiroz, L.M.; Tadza, M.Y.M.; Picos-Corrales, L.A.; Pei, H.; Wilson, L.D.; et al. Chitosan for direct bioflocculation of wastewater. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2019, 17, 1603–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macêdo, M.d.O.C.; de Macêdo, H.R.A.; Araujo, A.L.C. Chitosan as a Strategy in the Treatment of Effluent. Res. Soc. Dev. 2022, 11, e22111636819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picos-Corrales, L.A.; Sarmiento-Sánchez, J.I.; Ruelas-Leyva, J.P.; Crini, G.; Hermosillo-Ochoa, E.; Gutierrez-Montes, J.A. Environment-Friendly Approach toward the Treatment of Raw Agricultural Wastewater and River Water via Flocculation Using Chitosan and Bean Straw Flour as Bioflocculants. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 3943–3951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, T.; Wu, L.; Yu, F.; Lv, Y.; Chen, L.; Shi, Y.; Dai, B. pH-responsive chitosan-based flocculant for precise dye flocculation control and the recycling of textile dyeing effluents. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 39334–39340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Chen, A.; Pan, S.Y.; Sun, W.; Zhu, C.; Shah, K.J.; Zheng, H. Novel chitosan-based flocculants for chromium and nickle removal in wastewater via integrated chelation and flocculation. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 248, 109241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirajudheen, P.; Vigneshwaran, S.; Karthikeyan, P.; Nabeena, C.P.; Meenakshi, S. Technological Advancement in Photocatalytic Degradation of Dyes Using Metal-Doped Biopolymeric Composites—Present and Future Perspectives. In Nanomaterials and Nanocomposites for Environmental Remediation; Singh, S.P., Rathinam, K., Gupta, T., Agarwal, A.K., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 205–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotito, S.; Cignolo, D.; Gubitosa, J.; Barucca, G.; Mengucci, P.; Striccoli, M.; Palumbo, F.; Cosma, P.; Fini, P.; Murgolo, S.; et al. Nanoengineering of Chitosan Sponges Via Atomic Layer Deposition of ZnO for Water Remediation Technologies. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 12, 2400831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyamiati, R.D.; Timotius, D.; Rahmawati, S.; Carissavila, C.; Amalia, N. Effect of Chitosan-TiO2 Membrane Performance for the Degradation of Batik Waste with a Photocatalytic Hybrid System. Eksergi 2024, 21, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, N.; Farhan, M.; Malik, S.; Khan, A.; Ali, S.; Kianat, S.; Ghazal, S.; Salim, B.; Al Balushi, R.A.; Al-Hinaai, M.M.; et al. Robust regenerable metal-selenide-chitosan photocatalyst for the effective removal of Bromothymol Blue (BB) from wastewater. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 281, 136419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arghavan, F.S.; Al-Musawi, T.J.; Rumman, G.A.; Pelalak, R.; Khataee, A.; Khataee, A.; Nasseh, N.; Nasseh, N. Photocatalytic performance of a nickel ferrite/chitosan/bismuth(III) oxyiodide nanocomposite for metronidazole degradation under simulated sunlight illumination. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machodi, M.J.; Daramola, M.O. Synthesis and performance evaluation of PES/chitosan membranes coated with polyamide for acid mine drainage treatment. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassyouni, M.; Eteba, A.; ElZahar, M.M.H.; Elshikhiby Mohamed, Z. Utilization of Biodegradable Nanofiltration Membrane for Efficient Removal of Anionic Textile Dye. Egypt. J. Chem. 2024, 67, 987–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponnuchamy, M.; Kapoor, A.; Senthil Kumar, P.; Vo, D.-V.N.; Balakrishnan, A.; Mariam Jacob, M.; Sivaraman, P. Sustainable adsorbents for the removal of pesticides from water: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 2425–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, M.; Ahmad, W.; Park, J.-H.; Vlaskin, M.S.; Vaya, D.; Kim, H. One-step functionalization of chitosan using EDTA: Kinetics and isotherms modeling for multiple heavy metals adsorption and their mechanism. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 49, 102989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnan, A.; Appunni, S.; Chinthala, M.; Jacob, M.M.; Vo, D.-V.N.; Reddy, S.S.; Kunnel, E.S.; Ponnuchamy, M. Chitosan-based beads as sustainable adsorbents for wastewater remediation: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2023, 21, 1881–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muda, M.S.; Kamari, A.; Bakar, S.A.; Yusoff, S.N.M.; Fatimah, I.; Phillip, E.; Din, S.M. Chitosan-graphene oxide nanocomposites as water-solubilising agents for rotenone pesticide. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 318, 114066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshvardoostchokami, M.; Majidi, M.; Zamani, A.; Liu, B. Adsorption of phenol on environmentally friendly Fe3O4/ chitosan/ zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 nanocomposite: Optimization by experimental design methodology. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 323, 115064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Ren, T.; Lei, Z.; Huang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Xu, D.; Wan, C.; Guo, X.; Wu, Y. Non-toxic chitosan-based hydrogel with strong adsorption and sensitive detection abilities for tetracycline. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 427, 131738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, T.; Naeem, A.; Din, I.U.; Farooq, M.; Khan, I.W.; Hamayun, M.; Hamayun, M.; Malik, T. Synthesis of chitosan composite of metal-organic framework for the adsorption of dyes; kinetic and thermodynamic approach. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 427, 127902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, W.; Bai, Z.; Zhu, Y. Fast removal of Co(ii) from aqueous solution using porous carboxymethyl chitosan beads and its adsorption mechanism. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 13370–13387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rathinam, K.; Singh, S.P.; Arnusch, C.J.; Kasher, R. An environmentally-friendly chitosan-lysozyme biocomposite for the effective removal of dyes and heavy metals from aqueous solutions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 199, 506–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyomuhimbo, H.D.; McHunu, W.; Arnold, M.; Feleni, U.; Haneklaus, N.; Brink, H.G. Synthesis and Dye Adsorption Dynamics of Chitosan–Polyvinylpolypyrrolidone (PVPP) Composite. Polymers 2024, 16, 2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, M.M.; Ponnuchamy, M.; Kapoor, A.; Sivaraman, P. Adsorptive decontamination of organophosphate pesticide chlorpyrifos from aqueous systems using bagasse-derived biochar alginate beads: Thermodynamic, equilibrium, and kinetic studies. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2022, 186, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Chen, N.; Feng, C.; Zhang, Z. Adsorption for phosphate by crosslinked/non-crosslinked-chitosan-Fe(III) complex sorbents: Characteristic and mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 353, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, F.; Yu, H.; Hou, T.; Yan, L.; Zhang, X.; Du, B. Efficient and fast removal of Pb2+ and Cd2+ from an aqueous solution using a chitosan/Mg-Al-layered double hydroxide nanocomposite. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 539, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, D.; Molla, M.d.T.H.; Bashar, M.d.A.; Islam, M.d.S.; Ahsan, M.d.S. Chitosan-based nano-sorbents: Synthesis, surface modification, characterisation and application in Cd (II), Co (II), Cu (II) and Pb (II) ions removal from wastewater. Dent. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.C.; Shan, C.; Liu, Y.; Sun, H.; Yao, B.; Gong, G.; Jin, X.; Wang, S. Characterization and Mechanistic Study of Heavy Metal Adsorption by Facile Synthesized Magnetic Xanthate-Modified Chitosan/Polyacrylic Acid Hydrogels. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 11123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Gao, J.; Jia, L.; Wang, S.; Ning, P. Green synthesis of a novel functionalized chitosan adsorbent for Cu(II) adsorption from aqueous solution. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 29, 989–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.-L.; Zaoui, A.; Sekkal, W. Adsorption efficiency of highly methylene blue dye concentrations with multilayer chitosan-modified clays for a precise nanofiltration performance of polluted water. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 57, 104651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, X.; Zhao, S.; Jing, Z.; Jin, Y.; Pi, X.; Du, Q.; Chen, L.; Li, Y.; Chen, B. High-efficient removal of anionic dye from aqueous solution using metal-organic frameworks@chitosan aerogel rich in benzene structure. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 256, 128433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khnifira, M.; Boumya, W.; Attarki, J.; Mahsoune, A.; Abdennouri, M.; Sadiq, M.; Kaya, S.; Barka, N. Elucidating the adsorption mechanisms of anionic dyes on chitosan (110) surface in aqueous medium by quantum chemical and molecular dynamics. Mater. Today Commun. 2022, 33, 104488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Dai, K.; Xiang, H.; Kou, J.; Guo, H.; Ying, H.; Wu, J. High adsorption capacities for dyes by a pH-responsive sodium alginate/sodium lignosulfonate/carboxylated chitosan/polyethyleneimine adsorbent. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 278, 135005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, C.-W.; Wu, M.-T.; Lin, C.-L.; Li, J.-W.; Huang, C.-Y.; Soong, Y.-C.; Lee, J.C.-M.; Lee Sanchez, W.A.; Lin, H.-Y. Adsorption Performance for Reactive Blue 221 Dye of β-Chitosan/Polyamine Functionalized Graphene Oxide Hybrid Adsorbent with High Acid–Alkali Resistance Stability in Different Acid–Alkaline Environments. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulhameed, A.S.; Wu, R.; Musa, S.A.; Agha, H.M.; Alothman, Z.; Jawad, A.H.; Algburi, S. Bisphenol-A-diglycidyl ether modified chitosan/nano-SiO2 via hydrothermal process: A statistical modeling and adsorption mechanism for reactive orange 16 dye removal. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 256, 128267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Abdulhameed, A.S.; Jawad, A.H.; Kong, Y.; Li, H.; Alothman, Z.; Wilson, L.D.; Algburi, S. Development of the chitosan/nanosilica with arene functionalization via hydrothermal synthesis for acid red 88 dye removal: A comparative study for optimized adsorption. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 252, 126342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelu, M.; Musuc, A.M.; Popa, M.; Calderon Moreno, J.M. Chitosan Hydrogels for Water Purification Applications. Gels 2023, 9, 664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norouzi, S.; Heidari, M.; Alipour, V.; Rahmanian, O.; Fazlzadeh, M.; Mohammadi-moghadam, F.; Nourmoradi, H.; Goudarzi, B.; Dindarloo, K. Preparation, characterization and Cr(VI) adsorption evaluation of NaOH-activated carbon produced from Date Press Cake; an agro-industrial waste. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 258, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Wang, X.; Wang, G.; Hao, C.; Li, X.; Li, T. Adsorption performance of a polysaccharide composite hydrogel based on crosslinked glucan/chitosan for heavy metal ions. Compos. B Eng. 2019, 169, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, T.; Artifon, S.E.S.; Cesco, C.T.; Vilela, P.B.; Becegato, V.A.; Paulino, A.T. Chitosan-based hydrogels for the sorption of metals and dyes in water: Isothermal, kinetic, and thermodynamic evaluations. Colloid. Polym. Sci. 2021, 299, 649–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, H.; Taheriyoun, M. Mapping chitosan potentials for treating antibiotics in aquaculture wastewater. Planet. Sustain. 2024, 2, 61–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Huiyu, T.; Jianbo, C.; Lifeng, W.; Kai, W.; Wang, J. Efficient adsorption of Cs(I) and Sr(II) ions from solution by xanthate modified sponge-like chitosan. Nucl. Eng. Des. 2025, 437, 114031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y. Application of chitosan-based materials in wastewater treatment. Highlights Sci. Eng. Technol. 2023, 69, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, J.O.; Strieder, M.M.; Silva, L.F.; dos Reis, G.S.; Dotto, G.L. Advanced technologies in water treatment: Chitosan and its modifications as effective agents in the adsorption of contaminants. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 270, 132307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divya, K.; Jisha, M.S. Chitosan nanoparticles preparation and applications. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2018, 16, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, T.U.; Roy, H.; Shoronika, A.Z.; Fariha, A.; Hasan, M.; Islam, M.d.S.; Marwani, H.M.; Islam, A.; Hasan, M.M.; Alsukaibi, M.R. Sustainable toxic dye removal and degradation from wastewater using novel chitosan-modified TiO2 and ZnO nanocomposites. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 388, 122764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Ma, Y.; Yang, W.; Chen, C.; Li, M.; Lin, D.; Pan, Q. Reusable ZIF-8@chitosan sponge for the efficient and selective removal of congo red. New J. Chem. 2020, 44, 15459–15466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, H.; Feng, Q.; Xue, B.; Li, M.; Xu, B.; Li, Y. The static and dynamic adsorptive performance of a nitrogen and sulfur functionalized 3D chitosan sponge for mercury and its machine learning evaluation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2025, 348, 122866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Qi, X.; Ma, Q.; Guo, X.; Wu, Y. Spherical sponge-inspired design of chitosan/silver cluster-loaded cellulose nanofibrils/Cu-ZIF-8 gel beads for efficient removal of Cr(VI). Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 499, 155767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, K.; Fan, Y.; Xing, G.; Zhai, M.; Sheng, J.; Song, Y. Rapid and convenient synthesis of “green” ammonium-modified chitosan composite sponge with the existence of ascorbic acid for highly efficient removal of Congo red (CR). Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 324, 121444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Z.; Peng, R.; Gao, D.; Lin, J.; Zeng, J.; Li, Z.; Ke, F.; Xia, Z.; Wang, D. Chitosan-alginate sponge with multiple cross-linking networks for adsorption of anionic dyes: Preparation, property evaluation, mechanism exploration, and application. J. Chromatogr. A 2024, 1713, 464507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, P.; Xu, J.; Shi, H.; Du, F.; Du, H.; Li, G. Simultaneous Cr(VI) reduction and Cr(III) sequestration in a wide pH range by using magnetic chitosan-based biopolymer. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 127398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Zhou, X.; Xie, H.; Wang, X.; Yang, L.; Wang, H.; Hao, C. Chitosan-based composite microspheres for treatment of hexavalent chromium and EBBR from aqueous solution. Chemosphere 2022, 305, 135486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.; Huang, Y.; He, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, H.; Hu, Y. Adsorption of tetracycline antibiotics by nitrilotriacetic acid modified magnetic chitosan-based microspheres from aqueous solutions. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 24, 101895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Wang, L.; Jiang, S.; Cui, L.; Wu, G. Iron-doped chitosan microsphere for As(III) adsorption in aqueous solution: Kinetic, isotherm and thermodynamic studies. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 36, 1102–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaafari, J.; Barzanouni, H.; Mazloomi, S.; Amir Abadi Farahani, N.; Sharafi, K.; Soleimani, P.; Haghighat, G.A. Effective adsorptive removal of reactive dyes by magnetic chitosan nanoparticles: Kinetic, isothermal studies and response surface methodology. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 344–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, T.; Yin, L.; Xie, Y.; Ji, Y. Efficiently remove of Cs(I) by metals hexacyanoferrate modified magnetic Fe3O4-chitosan nanoparticles. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2020, 746, 137293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamza, M.F.; Abdel-Rahman, A.A.H.; Negm, A.S.; Hamad, D.M.; Khalafalla, M.S.; Fouda, A.; Wei, Y.; Amer, H.H.; Alotaibi, S.H.; Goda, A.E.-S. Grafting of Thiazole Derivative on Chitosan Magnetite Nanoparticles for Cadmium Removal—Application for Groundwater Treatment. Polymers 2022, 14, 1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamza, M.F.; Wei, Y.; Althumayri, K.; Fouda, A.; Hamad, N.A. Synthesis and Characterization of Functionalized Chitosan Nanoparticles with Pyrimidine Derivative for Enhancing Ion Sorption and Application for Removal of Contaminants. Materials 2022, 15, 4676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ma, X.; Peng, J. Highly selective removal and recovery of Ni(II) from aqueous solution using magnetic ion-imprinted chitosan nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 271, 118435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elamin, N.Y.; Elamin, M.R.; Alhussain, H.; Alotaibi, M.T.; Alluhaybi, A.A.; El-Bindary, A.A. Electrospun nanofibers of polycaprolactone loaded with chitosan/carbon quantum dots composite for adsorptive removal of Cd(II) ions from wastewater: Adsorption, kinetics, thermodynamics, and BOX Behnken design. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 308, 142680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahmani, E.; Koushkbaghi, S.; Darabi, M.; ZabihiSahebi, A.; Askari, A.; Irani, M. Fabrication of novel chitosan-g-PNVCL/ZIF-8 composite nanofibers for adsorption of Cr(VI), As(V) and phenol in a single and ternary systems. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 224, 115148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alatawi, R.A.S. Electrospun nanofiber chitosan/polyvinyl alcohol loaded with metal organic framework nanofiber for efficient adsorption and removal of industrial dyes from waste water: Adsorption isotherm, kinetic, thermodynamic, and optimization via Box-Behnken design. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 299, 140086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, J.; Ali, F.A.A.; Shukla, A.K.; Haider, S.; Riaz, U.; Alhoshan, M. Crosslinked Chitosan-Sulfonated Polyphenylsulfone Electrospun Nanofibers: A Highly Water-Stable and Versatile Adsorbent for Organic Dye Removal. Fibers Polym. 2024, 25, 3307–3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, R.; Zhang, K.; Qin, Y.; Xie, L.; Chai, X.; Zhang, L.; Du, G.; Ge, S.; Rezakazemi, M.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Amine-functionalized UiO-66 incorporated electrospun cellulose/chitosan porous nanofibrous membranes for removing copper ions. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 480, 148077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.H.; Tang, D.Y.; Xiang, Y.L.; Chen, X.; Lin, J.; Zhou, Q.H. Magnetic ion-imprinted polyacrylonitrile-chitosan electro-spun nanofibrous membrane as recyclable adsorbent with selective heavy metal removal and antibacterial fouling in water treatment. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 241, 124620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakoria, A.; Sinha-Ray, S.; Sinha-Ray, S. Industrially scalable Chitosan/Nylon-6 (CS/N) nanofiber-based reusable adsorbent for efficient removal of heavy metal from water. Polymer 2021, 213, 123333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vedula, S.S.; Yadav, G.D. Wastewater treatment containing methylene blue dye as pollutant using adsorption by chitosan lignin membrane: Development of membrane, characterization and kinetics of adsorption. J. Indian Chem. Soc. 2022, 99, 100263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelaziz, M.M.; Abdelaziz, M.A.; Omer, N.; Jame, R.; Alamri, E.S.; Mohamed, E.L.I.; Eledum, H.; Alhuwaiti, A.M.; Al-Balawi, R.S.; Al-Qarni, G. Cost-effective zinc ferrite-functionalized hydroxyethyl cellulose/chitosan film for efficient removal of methyl orange dye from aqueous solutions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 307, 142232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.Q.; Hao, H.Y.; Wang, X.; Shao, Z. Chitosan-based composite film adsorbents reinforced with nanocellulose for removal of Cu(II) ion from wastewater: Preparation, characterization, and adsorption mechanism. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 213, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yaseen, M.; Tong, Z.; Chen, N.; Shi, H. Carboxymethylcellulose-chitosan film modified magnetic alkaline Ca-bentonite for the efficient removal of Pb(II) and Cd(II) from aqueous solution. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 30312–30322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloster, G.A.; Valiente, M.; Marcovich, N.E.; Mosiewicki, M.A. Adsorption of arsenic onto films based on chitosan and chitosan/nano-iron oxide. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 165, 1286–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzi, V.; Romanazzi, F.; Gubitosa, J.; Fini, P.; Romita, R.; Agostiano, A.; Petrella, A.; Cosma, P. Chitosan film as eco-friendly and recyclable bio-adsorbent to remove/recover diclofenac, ketoprofen, and their mixture from wastewater. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhammad, H.; Tuzen, M.; Siddiqui, A.; Umar, A.R. Effective adsorption of Congo red azo dye from different water and wastewater by using porous Fe3O4-bentonite@chitosan nanocomposite: A multivariate optimization. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 310, 143439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saberi-Zare, M.; Bodaghifard, M.A. A Schiff base-functionalized chitosan magnetic bio-nanocomposite for efficient removal of Pb (II) and Cd (II) ions from aqueous solutions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 296, 139794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassar, A.A.; Mubarak, M.F.; El-Sawaf, A.K.; Zayed, M.A.; Hemdan, M. Efficient lead ion removal from aqueous solutions for wastewater treatment using a novel cross-linked alginate-rice husk ash-graphene oxide-chitosan nanocomposite. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 284, 137983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elumalai, N.S.; Jaisankar, S.M.; Kumaran, C. Utilization of Graphene Oxide-Chitosan Nanocomposite for the Removal of Heavy Metals: Kinetics, Isotherm, and Error Analysis. Water Conserv. Sci. Eng. 2024, 9, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, T.; Becegato, V.A.; Paulino, A.T. Equilibrium Isotherms, Kinetics, and Thermodynamics of the Adsorption of 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic Acid to Chitosan-Based Hydrogels. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2021, 232, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arafa, E.G.; Mahmoud, R.; GadelHak, Y.; Gawad, O.F.A. Design, preparation, and performance of different adsorbents based on carboxymethyl chitosan/sodium alginate hydrogel beads for selective adsorption of Cadmium (II) and Chromium (III) metal ions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 273, 132809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.-F.; Tang, J.; Tan, Y.; Lei, H.; Li, Y.; Huang, P.; Li, Y. Efficient removal and recycle of acid blue 93 dye from aqueous solution by acrolein crosslinked chitosan hydrogel. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 632, 127825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Chen, J.; Sun, H.; Qian, P.; Wang, D.; Zhuang, W.; Dong, L. Enhancing Adsorption Performance of Ce(III) by Amine-Thiourea and Aniline-Modified Magnetic Chitosan Nanocomposites. Langmuir 2024, 40, 23398–23405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; Yang, A.; Zhu, Q.; Sun, H.; Sun, P.; Yao, B.; Zang, Y.; Du, X.; Dong, L. Xanthate-Modified Magnetic Fe3O4@SiO2-Based Polyvinyl Alcohol/Chitosan Composite Material for Efficient Removal of Heavy Metal Ions from Water. Polymers 2022, 14, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).