Silicon Hybridization for the Preparation of Room-Temperature Curing and High-Temperature-Resistant Epoxy Resin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiment
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Preparation of Silica Sol
2.2.2. Preparation of SiO2 Hybrid Epoxy Resin
2.2.3. Process of Curing
2.3. Tests and Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
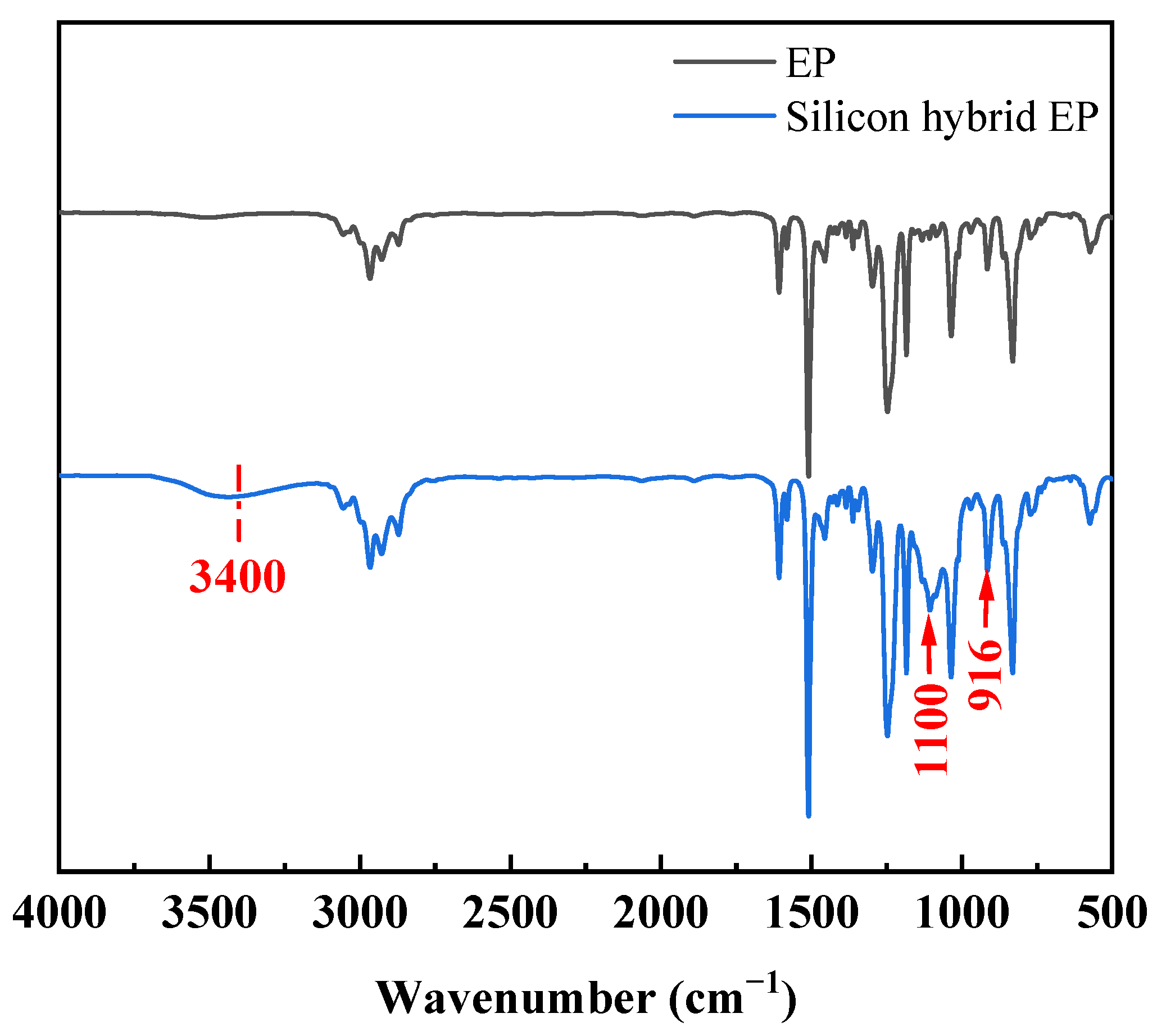
3.1. Structural Analysis
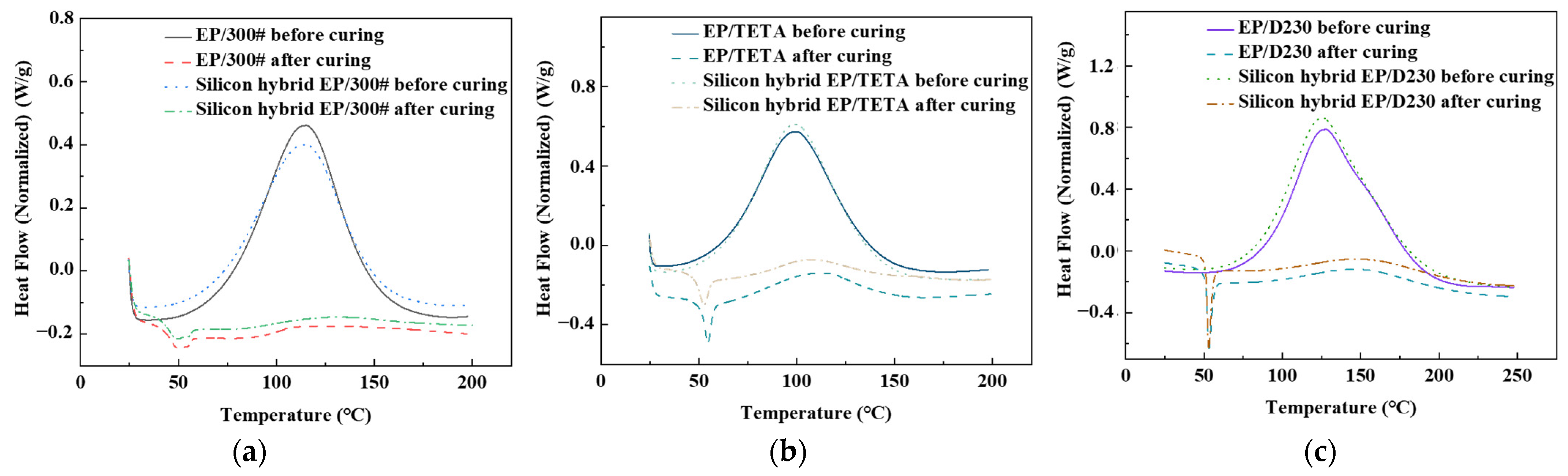
3.2. Curing Reactivity Analysis
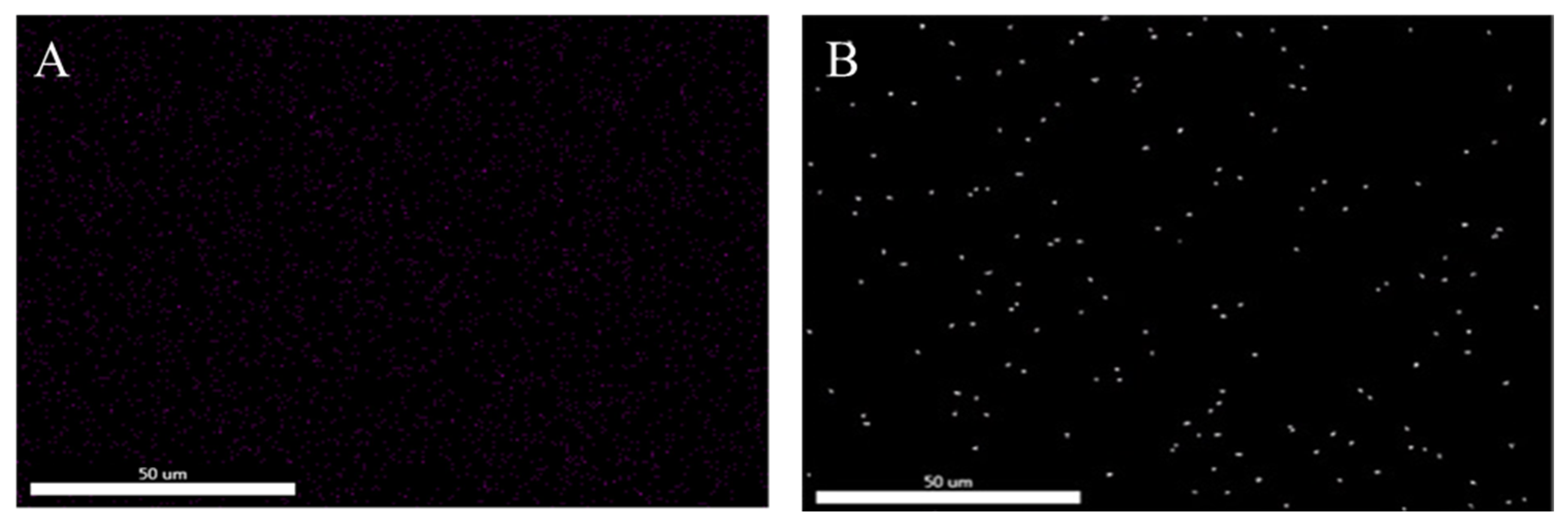
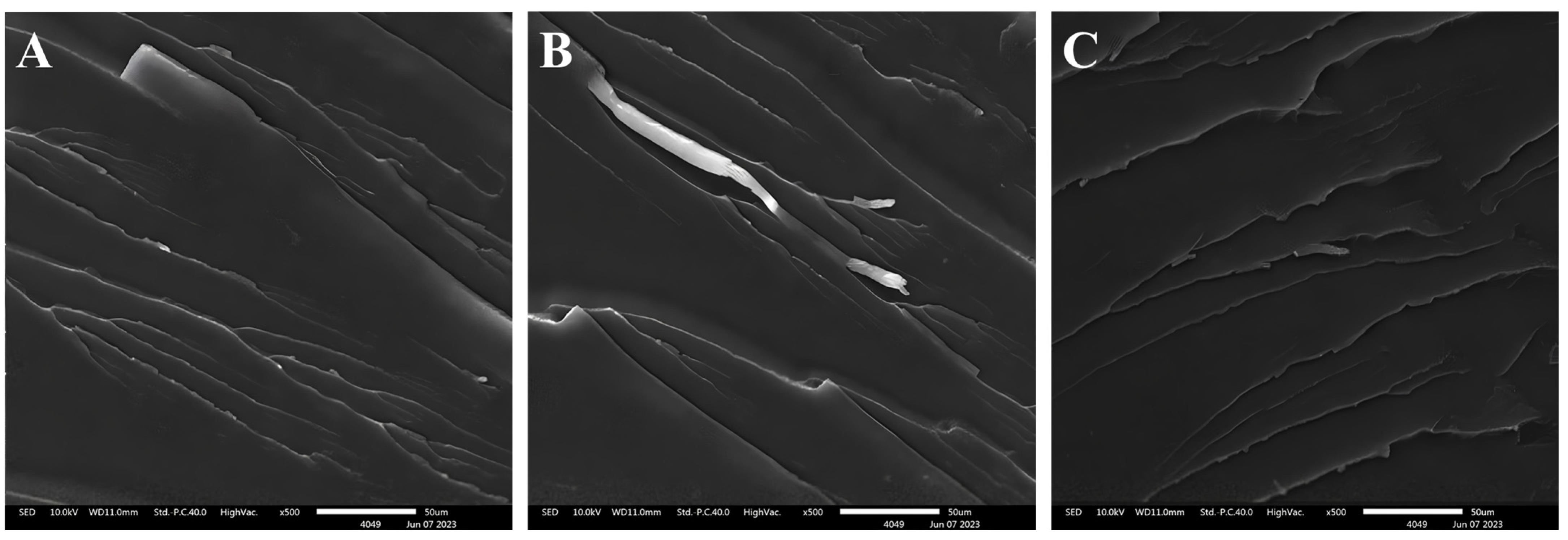
3.3. Bonding Performance Analysis
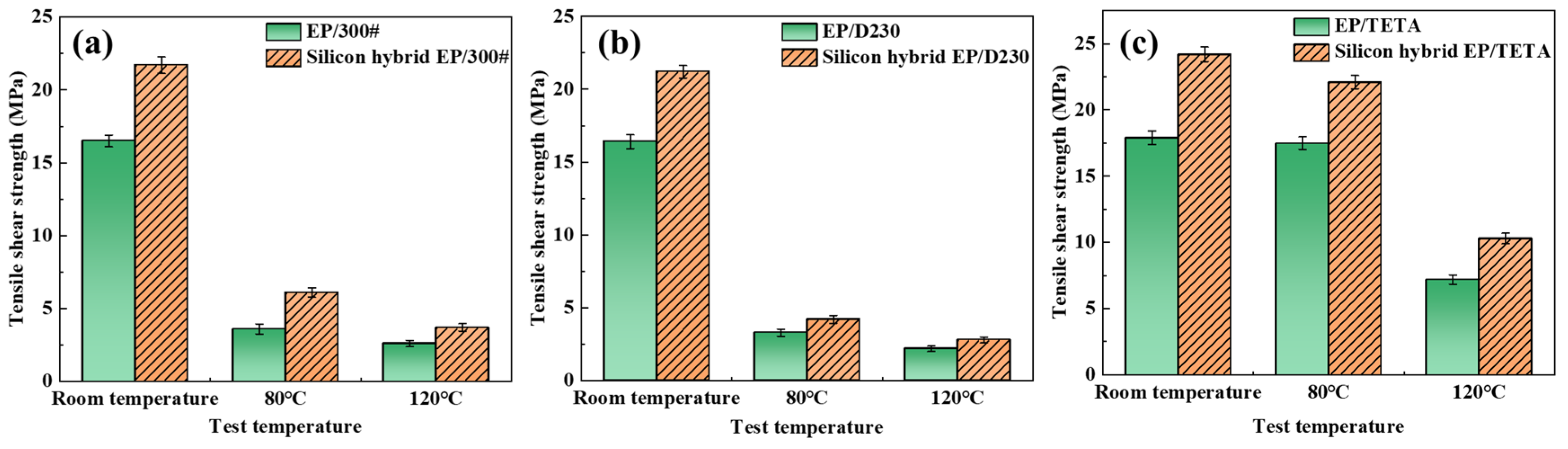
3.3.1. Tensile Shear Strength
3.3.2. Peel Strength
3.4. Heat Resistance Analysis
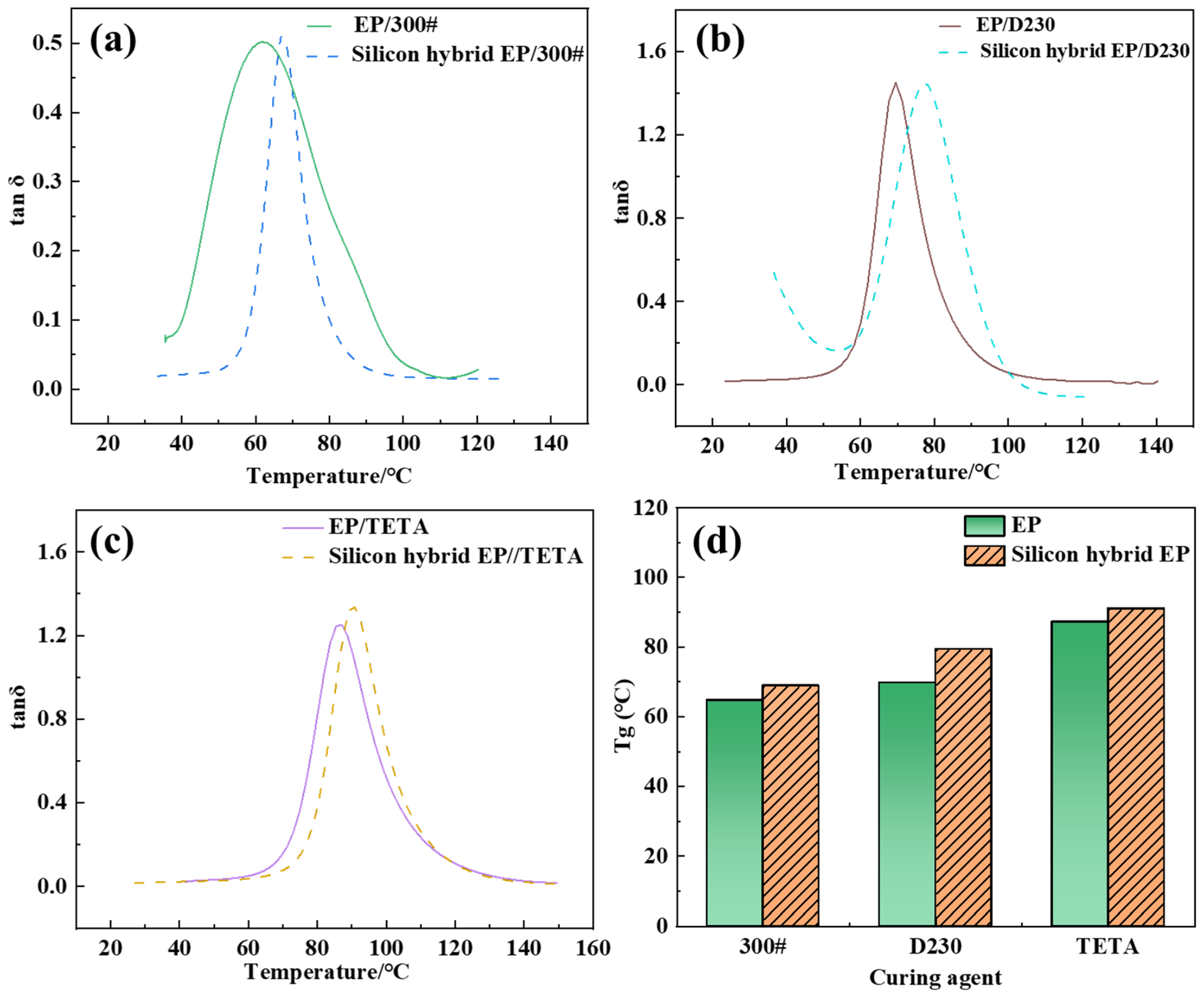
3.4.1. Glass-Transition Temperature
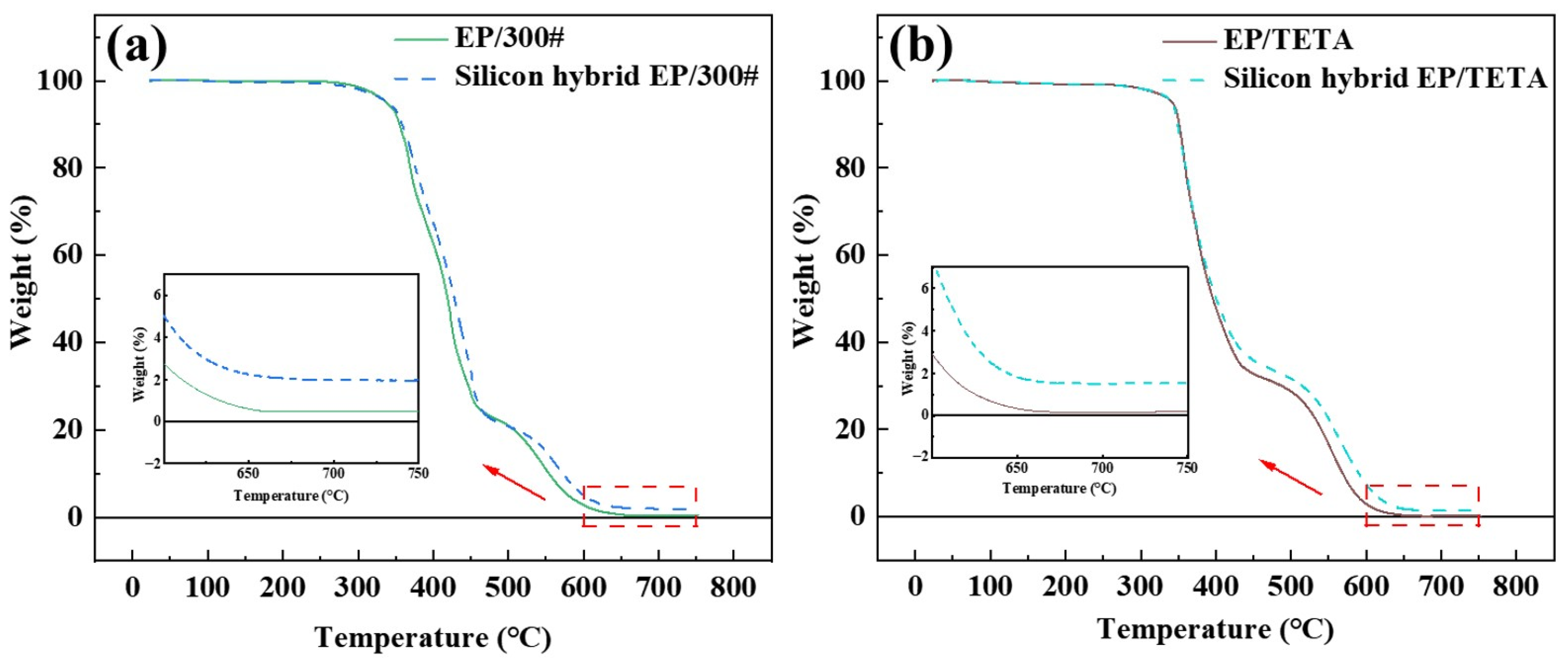
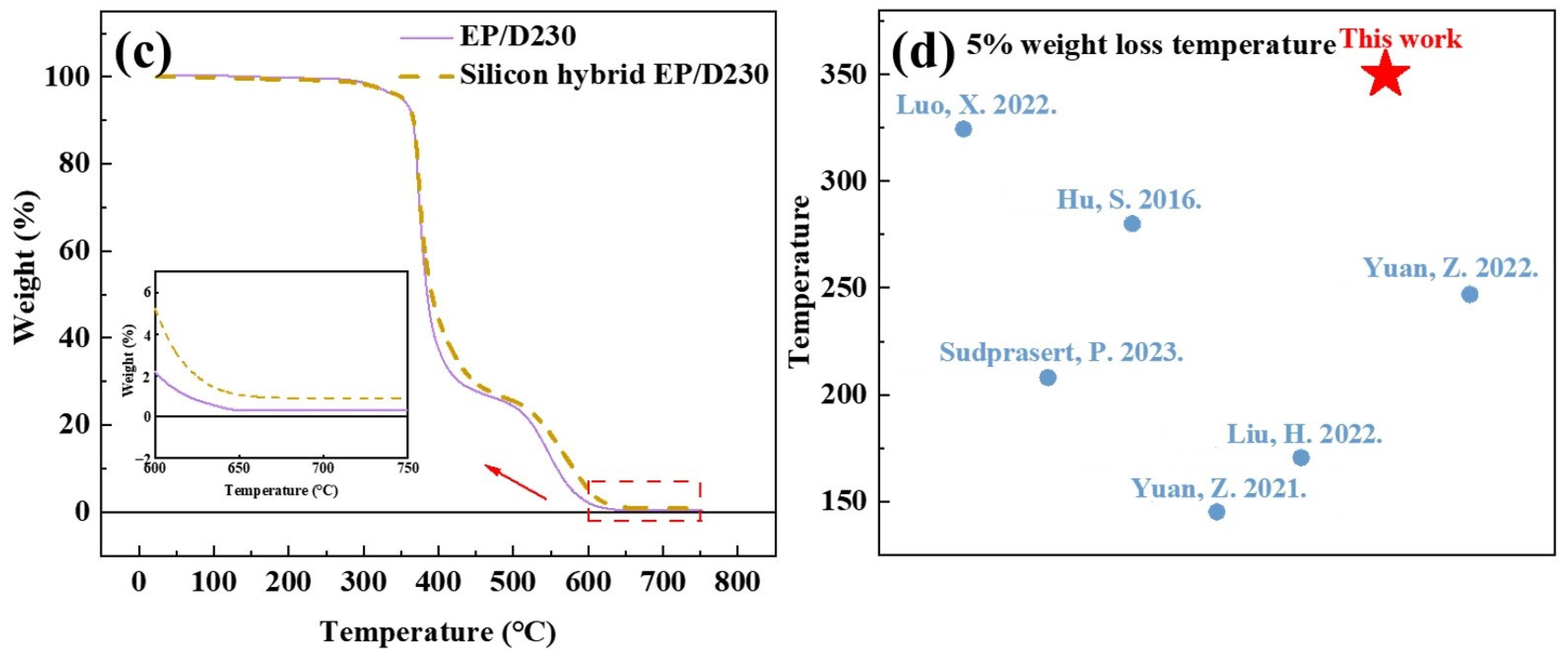
3.4.2. Thermal Weight Loss
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sprenger, S. Epoxy resin composites with surface-modified silicon dioxide nanoparticles: A review. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 130, 1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, F.-L.; Li, X.; Park, S.-J. Synthesis and application of epoxy resins: A review. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 29, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Ren, M.; Chen, K.; Liang, Y.; Lü, Q.-F.; Zhang, T. Synthesis of a novel silicon-containing epoxy resin and its effect on flame retardancy, thermal, and mechanical properties of thermosetting resins. Mater. Today Commun. 2019, 19, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaskaran, P.E.; Subramaniam, T.; Kaliyannan, G.V.; Palaniappan, S.K.; Rathanasamy, R. Green Adhesive for Industrial Applications; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 57–84. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.; Zhang, Q.; Lu, M.; Meng, H.; Qu, Z.; Xu, C.A.; Jiao, E. Synthesis of a novel lignin-based epoxy resin curing agent and study of cure kinetics, thermal, and mechanical properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 138, 50523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Wei, W.; Yang, T.; Zheng, C.; Zheng, C.; Deng, P. Properties of a New Type Heat-Resistant System of Epoxy Resin Cured at Room Temperature. Chin. J. Appl. Chem. 2016, 33, 175. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Liang, H. Synthesis of epoxy resin room temperature fast curing agent. Synth. Resins Plast. 2013, 30, 25. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Z.; Wang, T.; Cai, W.; Pan, Z.; Wang, J.; Derradji, M.; Liu, W. Preparation, dielectric and thermomechanical properties of a novel epoxy resin system cured at room temperature. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2021, 32, 24902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Dayo, A.Q.; Wang, J.; Wang, A.; Lv, D.; Zegaoui, A.; Derradji, M.; Liu, W. Mechanical and thermal properties of a room temperature curing epoxy resin and related hemp fibers reinforced composites using a novel in-situ generated curing agent. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2018, 203, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Liu, M.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, W.; Deng, P.; Zheng, C. Kinetics and thermal properties of epoxy resins containing the ionic liquid [C6mim]FeCl4. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 11407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, D.; Lu, S. Trifunctional Epoxy Resin Curing Agent Compound at Room Temperature and Its Curing Kinetics. J. East China Univ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 41, 477. [Google Scholar]
- Aviation Industries of China. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) Test Method for Curing Degree of Composite Resin Matrices; Aviation Industries of China: Beijing, China, 1998; Volume HB7614-1998. [Google Scholar]
- 621st Research Institute of the People’s Republic of China. Test Method for Tensile Shear Strength of Metal Bonded Joints; 621st Research Institute of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 1981; Volume HB5164-1981. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Aerospace Industry of the People’s Republic of China. Structural Bonded Aluminum Alloy Phosphoric acid Anodizing Process Specification; Ministry of Aerospace Industry of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 1991; Volume HB/Z197-1991. [Google Scholar]
- Commission for Science, Technology and Industry for National Defense of the People’s Republic of China. Test Method for Adhesive 90° Peel Strength (Metal to Metal); Commission for Science, Technology and Industry for National Defense of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 1988; Volume GJB446-1988. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Jia, Y.; Ma, W.; Li, P.; Qu, Y. Preparation of silicon dioxide/epoxy composites with interpenetrating network structure and research on their dielectric properties. Mater. Rep. 2024, 38, 22080082. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, H.; Ge, J.; Cheng, S.; Han, H.; Cui, S. Synthesis and characterization of titania/MQ silicone resin hybrid nanocomposite via sol–gel process. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2011, 59, 635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Jia, Y.; Ma, W.; Sun, P. Curing Reaction Kinetics and Properties of Epoxy Terminated Silicon Oxide/Epoxy Resin/Bismaleimides. Polym. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 37, 34. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, W.; Zuo, J. Mechanical, thermal and electrical properties of epoxy modified with a reactive hydroxyl-terminated polystyrene-butadiene liquid rubber. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2013, 32, 1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Sun, Q.; Jia, J.; Yao, L.; Peng, Z. Thermal and Electrical Properties of Room Temperature Cured Epoxy Resin Modified by Hydroxyl-terminated Liquid Nitrile Butadiene Rubber. Proc. CSEE 2020, 40, 3368. [Google Scholar]
- Ponyrko, S.; Kobera, L.; Brus, J.; Matějka, L. Epoxy-silica hybrids by nonaqueous sol–gel process. Polymer 2013, 54, 6271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, G.; Li, K.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, R.; Tang, H.; Tang, C. Effect of Aminosilane Coupling Agent-Modified Nano-SiO2 Particles on Thermodynamic Properties of Epoxy Resin Composites. Processes 2021, 9, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Li, Y.; Sun, Z.; Wang, G.; Xin, J. Preparation and research of epoxy modified by carboxyl-terminated polybutylene adipate at room temperature. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 20471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wei, L.; Gao, F.; Tang, L.; Li, L.; Sun, Z.; Liu, Y.; Dong, P. Performance Research and Formulation Optimization of High-Performance Local Insulation Spray Coating Materials. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudprasert, P.; Kariya, S.; Ogino, K.; Chirachanchai, S.; Kanehashi, S. Synthesis and characterization of novel bio-based epoxy polymers derived from natural phenolic compound. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2023, 140, e53450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Al Hassan, M.; Wang, Z.-C.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Derradji, M.; Liu, W. Curing behavior, mechanical and thermal properties of epoxy-CeO2 nanocomposites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2022, 139, 51529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.A.; Abdus Samad, U.; Alam, M.; Anis, A.; Al-Zahrani, S.M. Enhancement in Nanomechanical, Thermal, and Abrasion Properties of SiO2 Nanoparticle-Modified Epoxy Coatings. Coatings 2020, 10, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
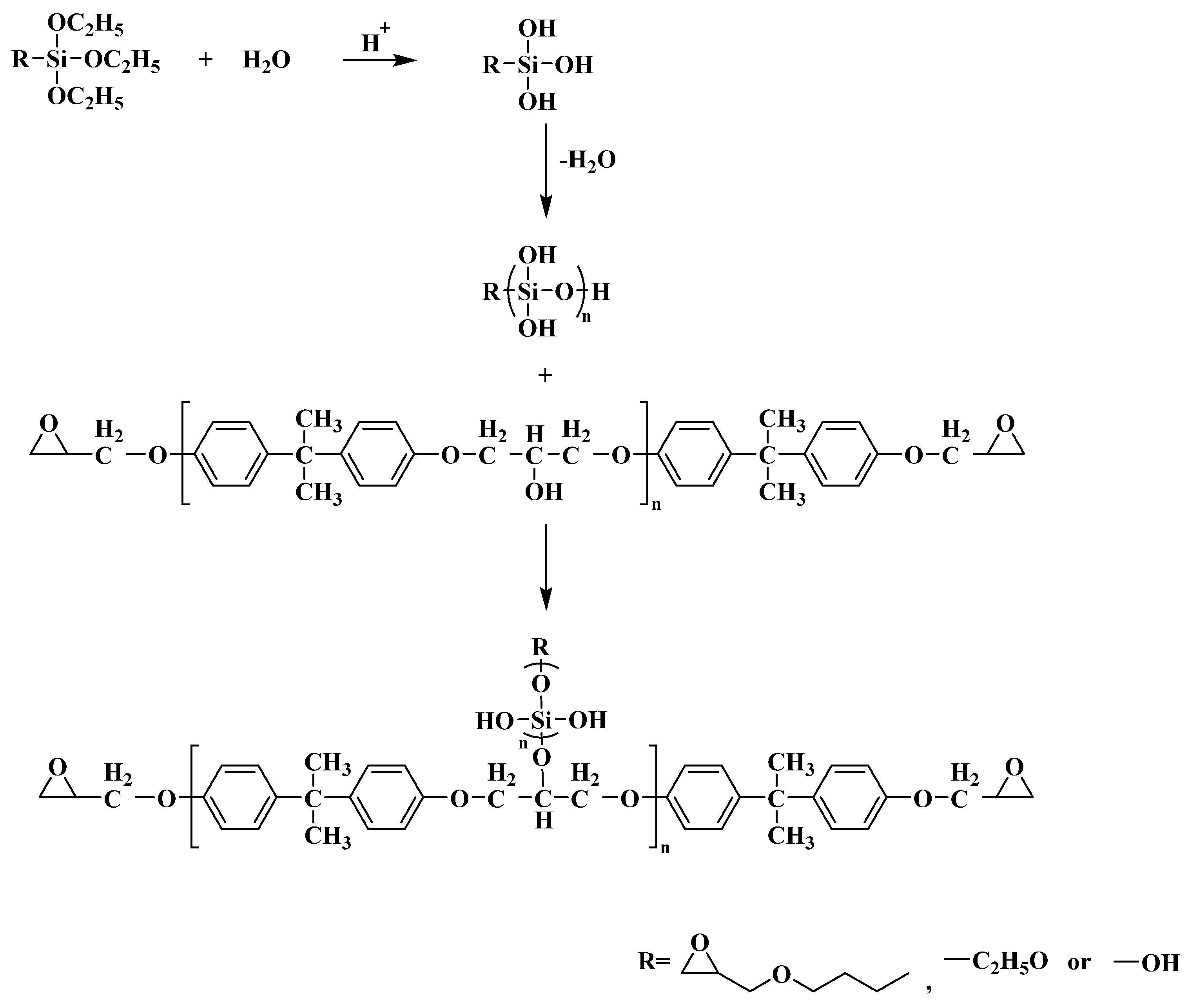

| Key Parameters | EP/300# | Silicon Hybrid EP/300# | EP/D230 | Silicon Hybrid EP/D230 | EP/TETA | Silicon Hybrid EP/TETA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Curing degree at room temperature | 80.4 | 85.2 | 81.9 | 86.7 | 51.6 | 67.7 |
| Shear strength at room temperature | 16.5 | 21.7 | 16.4 | 21.2 | 17.9 | 24.2 |
| Shear strength at 80 °C | 3.6 | 6.1 | 3.3 | 4.2 | 17.5 | 22.1 |
| Shear strength at 120 °C | 2.6 | 3.7 | 2.2 | 2.8 | 7.2 | 10.3 |
| Weight loss rate at 400 °C | 37.38 | 33.75 | 62.47 | 55.53 | 52.11 | 47.21 |
| Resin/Curing Agent | EP/300# | Silicon Hybrid EP/300# | EP/D230 | Silicon Hybrid EP/D230 | EP/TETA | Silicon Hybrid EP/TETA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Curing degree/% | 80.4 | 85.2 | 81.9 | 86.7 | 51.6 | 67.7 |
| Initial curing temperature/°C | 65.3 | 61.9 | 73.4 | 68.3 | 58.6 | 54.1 |
| Resin/Curing Agent | 5% Weight Loss Temperature (°C) | Weight Loss Rate at 400 °C (%) |
|---|---|---|
| EP/300# | 337.88 | 37.38 |
| Silicon hybrid EP/300# | 338.48 | 33.75 |
| EP/D230 | 351.12 | 62.47 |
| Silicon hybrid EP/D230 | 352.87 | 55.53 |
| EP/TETA | 341.98 | 52.11 |
| Silicon hybrid EP/TETA | 343.01 | 47.21 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rong, L.; Su, J.; Li, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhang, D.; Zhu, J.; Li, X.; Zhao, Y.; Mi, C.; Kong, X.; et al. Silicon Hybridization for the Preparation of Room-Temperature Curing and High-Temperature-Resistant Epoxy Resin. Polymers 2024, 16, 634. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16050634
Rong L, Su J, Li Z, Liu X, Zhang D, Zhu J, Li X, Zhao Y, Mi C, Kong X, et al. Silicon Hybridization for the Preparation of Room-Temperature Curing and High-Temperature-Resistant Epoxy Resin. Polymers. 2024; 16(5):634. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16050634
Chicago/Turabian StyleRong, Liping, Jiaqi Su, Zhiguo Li, Xiaohui Liu, Dayong Zhang, Jinhua Zhu, Xin Li, Ying Zhao, Changhong Mi, Xianzhi Kong, and et al. 2024. "Silicon Hybridization for the Preparation of Room-Temperature Curing and High-Temperature-Resistant Epoxy Resin" Polymers 16, no. 5: 634. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16050634
APA StyleRong, L., Su, J., Li, Z., Liu, X., Zhang, D., Zhu, J., Li, X., Zhao, Y., Mi, C., Kong, X., & Wang, G. (2024). Silicon Hybridization for the Preparation of Room-Temperature Curing and High-Temperature-Resistant Epoxy Resin. Polymers, 16(5), 634. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16050634







