Abstract
Polystyrene (PS) is an extremely stable polymer with a relatively high molecular weight and a strong hydrophobic character that makes it highly resistant to biodegradation. In this study, PS was subjected to biodegradation tests by Tenebrio Molitor (T. Molitor) and Zophobas Morio (Z. Morio) larvae. Specifically, six different experimental diets were compared: (i) T. Molitor fed with bran; (ii) T. Molitor fed only PS; (iii) T. Molitor fed only PS treated with H2O2; (iv) Z. Morio fed with bran; (v) Z. Morio fed only PS; and (vi) Z. Morio fed only PS treated with H2O2. Therefore, the mass change of the larvae and the survival rate were measured periodically, while the frass collected after 15 and 30 days was analyzed by different analyses, such as spectroscopy (FTIR), spectrometry (molecular weight and polydispersity), thermal analysis (TGA) and microscopy (scanning electron microscopy observations). The obtained results suggest that in the case of T. Molitor larvae, larvae feeding on bran showed the highest survival rate of ~94% at 30 days, while in the case of the Z. Morio larvae, the highest survival rate was exhibited by larvae eating PS-H2O2. Although not strongly pronounced, the Mw and Mn of PS in the frass of both T. Molitor and Z. Morio larvae decreased over 30 days, suggesting PS biodegradation. Finally, the morphological analysis shows that PS samples isolated from the frass of T. Molitor and Z. Morio larvae showed completely different, rough and irregularly carved surface structures, in comparison to PS before biodegradation.
1. Introduction
Plastic products are widely used around the world because of their low cost and ease of production. Presently, over 400 million tons (Mt) of plastics are produced yearly, with exponential growth over the past 50 years, and more than 360 million tons of polymers produced per year are of fossil-based [1]. Specifically, the main products are polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), polyethylene terephthalate (PET), polystyrene (PS) and polyvinyl chloride (PVC), materials that have very attractive characteristics, such as low density, good mechanical impact stability and resistance to chemicals and corrosion, and are commonly used for packaging, construction, automotives, agriculture and electronic devices. The increasing world population has led to increased production and consumption of plastic materials. However, the accumulation of petrol-plastic wastes in the environment has become the focus of worldwide attention because of the environmental problems caused by their improper disposal after use and decommissioning and because the natural degradation of plastics is very sluggish, resulting in the accumulation of plastic waste that poses a serious environmental threat [2,3,4].
The main disposal methods include landfill, incineration, chemical treatment and recycling [5,6]. Landfilling is the process of disposing and accumulating waste in a certain area. It is a traditional method of waste management, which is widely used in many parts of the world. However, major environmental issues like global warming and the increase in soil acid grow as CO2 and other gasses are emitted from landfills. This method destroys soil, affects groundwater and cannot effectively degrade waste plastics. Incineration is the process of burning waste in an incinerator until it is converted to ashes and gas. The process produces a large number of toxic gases, which volatilize into the air and cause harmful effects to public health, biodiversity and ecosystems. Furthermore, the cost of chemical treatment and recycling is high. Hence, these methods are not enough to successfully solve the problem of environmental pollution from plastic products [6,7].
Considering that a lot of plastic waste has not been scientifically or properly treated, through a series of physical and chemical processes, microplastics are formed and dispersed into the environment [3,8]. Furthermore, organisms can interact with plastic waste: several species of vertebrates and invertebrates have been reported to ingest or become entangled in plastic as animals are unable to distinguish food from plastic in the environment, resulting in the ingestion of plastic particles [9,10].
In recent years, several studies have explored the unusual ability of some insects to consume and even biodegrade different types of plastics. While feeding, insects come into contact with a wide range of hydrocarbon polymers in their diet, and the gut of some insects contains microbial symbionts that aid in decomposing these polymers. Recently, various insects, such as mealworms, meal beetles, weevils or wax moths, particularly of the orders Coleoptera and Lepidoptera, were identified as having remarkable abilities to consume and degrade a wide range of synthetic polymers such as polyethylene, polyurethane, polypropylene, polystyrene and polyvinyl chloride into lower-molecular-weight, simple and nontoxic molecules, which are eventually excreted as fecula [11]. Furthermore, the gut microbiota of these organisms, which is involved in the plastic degradation process, has been investigated in recent studies [12,13,14,15].
Moreover, the rate of plastic consumption by these insects is higher than that of bacteria and fungi, isolated from various sources, such as soil, garbage or sewage sludge. These insects mainly include the yellow mealworm (larvae of Tenebrio Molitor), the greater wax moth (larvae of Galleria Mellonella) and the superworm (larvae of Zophobas Morio), among others [5]. The complete life cycle of Lepidopterans and Coleopterans insects consists of four stages: eggs, larvae, pupae and adults; a significant portion of their life is spent in the larval stage. It is worth noting that the length of each stage of the insect life cycle can vary according to several factors, such as temperature, humidity, nutrition and age of the parents. Interestingly, the initial larval and pupal stages of Tenebrio Molitor, also named yellow mealworm larvae for their color, are rich in protein and considered a popular dish in some countries. The larval period varies from 22 to 100 days, while the pupal period lasts about 8 days. Zophobas Morio, a synonym of Zophobas Atratus, is commonly known as a superworm or royal worm, associated with damaged stored foods. Z. Atratus adult beetles look very similar to T. Molitor, but are larger and measure about 2–3 cm in length [12,16]. These larvae can be easily raised on fresh oats, wheat bran or cereals with potatoes, cabbage, carrots or apple.
Polystyrene (PS), molecular formula [−CH(C6H5)CH2−]n, commonly known as Styrofoam, accounted for about 5.3% (c.a. 21 Mt/year) of the total plastic consumption in 2022 [17]. Although PS is considered a durable plastic, PS products are often designed for a very short service time and one-time use because of the low cost of this material [18]. It is an extremely stable polymer with a high molecular weight and a strong hydrophobic character, which makes this polymer highly resistant to biodegradation. Several soil invertebrates have also been tested to determine whether they were able to degrade PS, including earthworms, isopods, slugs, millipedes and snails [19].
In this work, the larvae of the yellow mealworm Tenebrio Molitor and superworm Zophobas Morio, two species of Coleopterans Tenebrionidae larvae, were chosen and prepared to carry out the research. Before the tests, the larvae were placed in a polypropylene plastic container and fed their usual food, then expanded PS foam was used as a raw material for the larvae of both species.
The degradation of polystyrene treated with hydrogen peroxide and subjected to microwave irradiation was also studied. The use of microwaves for polymer degradation is an excellent alternative to conventional thermal heating, offering increased reaction rates, reduced reaction times and energy savings. Typically, polymers such as PS have poor dielectric properties and are unable to absorb enough microwave energy to achieve the necessary temperature for degradation. Consequently, in order to increase absorption, it is necessary to use solvents such as hydrogen peroxide that can absorb microwave energy to achieve the required temperature [20,21,22]. The combination of hydrogen peroxide and microwaves may make polystyrene more attractive to eat. In this study, we focused on the chemical–physical characterization of the material and not on the identification of microrganisms that are able to degrade polystyrene. In particular, two species of insect larvae were fed polystyrene (PS) and polystyrene treated with hydrogen peroxide (PS-H2O2) as the sole diet to determine and compare their feeding ability and survival rates; in addition, changes in the product properties of the larvae after feeding PS and PS-H2O2 were analyzed. Six different experimental diets were compared: (i) T. Molitor fed with bran; (ii) T. Molitor fed only PS; (iii) T. Molitor fed only PS treated with H2O2; (iv) Z. Morio fed with bran; (v) Z. Morio fed only PS; and (vi) Z. Morio fed only PS treated with H2O2. The change in the larvae mass and the survival rate were measured periodically. Furthermore, a morphological analysis of frass was performed by scanning electron microscopy (SEM); Mn, Mw and polydispersity index (PDI) were determined by Size-Exclusion Chromatography (SEC); and additional characterization of the residual polymer was obtained using Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA) and Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) to identify chemical modifications resulting from PS digestion. An innovative aspect has been investigated regarding the treatment of PS with H2O2 in order to facilitate PS biodegradation by Tenebrionidae larvae.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test Materials
Tenebrio Molitor (yellow mealworms) and Zophobas Morio (superworms) at the larval stage were purchased from a local supplier (Zoo Service, Palermo, Italy) and ranged in length from 2 to 3 cm and from 4 to 8 cm, respectively. Expanded PS foam waste from electronic equipment boxes was collected and used as a feedstock for the larvae of both species. The number-averaged molecular weight (Mn) and weight-averaged molecular weight (Mw) of PS were 133,174 Da and 236,693 Da, respectively. Hydrogen peroxide (36 volumes 100 mL) was purchased from a local supplier (Sferlazzo Pharmacy, Palermo, Italy). For microwave oxidation, a block of PS was placed in a beaker with hydrogen peroxide H2O2 for 5 min and then microwaved into a commercial microwave oven at 800 Watt for 3 min, which caused the initial breakage of the polystyrene chains.
2.2. Feeding Tests
To compare the PS consumption and biodegradation between the larvae of the two species, six treatments were prepared based on feeding conditions. A group of T. Molitor and Z. Morio larvae (30 as a group) were reared on PS foam (~0.4 g) and PS foam treated with H2O2 (PS H2O2) (~0.4 g) as their exclusive diet in a polypropylene plastic container. As a control, other groups of larvae (30 as a group) were reared on a normal diet of wheat bran and fruits. Prior to the commencement of the feeding experiment, the larvae were subjected to a 48 h starvation period to empty their intestines. All containers were maintained in the climatic chamber under controlled conditions, i.e., 25 ± 1 °C, 60 ± 2% humidity, for a period of 30 days.
2.3. Collection and Characterization of Frass
The mealworms were fed with polystyrene blocks (PS) and polystyrene treated with H2O2 and microwave irradiation (PS-H2O2) as their sole diet for 30 days. Figure 1a shows the difference in length of the Tenebrio Molitor larva before and after its transformation into a pupa. As mealworm pupae are not mobile, removing the dead larvae and pupae from the containers during the experiment was performed to prevent them from being eaten and to protect them from cannibalism by the remaining larvae.
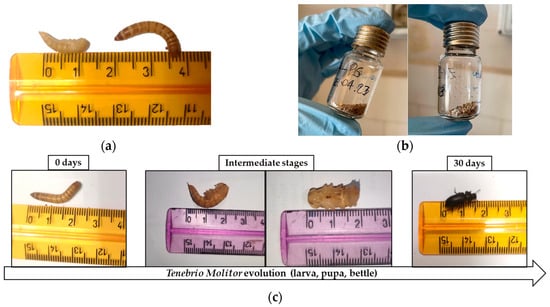
Figure 1.
(a) Length measurement of the pupa and larva of T. Molitor; (b) frass of T. Molitor and Z. Morio larvae collected at the end of the experiment (30 days) after feeding on polystyrene, and (c) T. Molitor evolution from larvae to pupa/beetles for more than ca. 30 days.
Frass samples were collected from the container after 15 and 30 days of the experiment and Figure 1b shows the difference between Tenebrio Molitor frass and Zophobas Morio frass collected after 30 days.
Figure 1c shows the evolution of T. Molitor from larva to pupa/beetle for more than ca. 30 days, using real images of T. Molitor’s evolution stages. It is important to highlight that after ca. 30 days, all larvae turned into pupae/beetles, and the experimental analysis, concerning the nutritional diet with bran or plastic, was inevitably interrupted.
2.3.1. Weight Variation and Survival Rate
The weight of the larvae was monitored by weighing them every 5 days and ended on day 30. Since not all larvae were the same size, the weight was normalized to the number of individuals and the NW, normalized weight (grams of total larvae/number of larvae), was calculated. The tests were conducted in triplicate.
2.3.2. Size-Exclusion Chromatography (SEC) Analysis
The changes in the molecular weight of the polymer were assessed by SEC. The detection was carried out using a differential refractometer. THF was the mobile phase with a flow rate of 1 mL min−1. Calibration was performed with polystyrene standards (from 20,250 to 470,000 g mol−1). Preparative SEC analyses were performed in THF with Azura GPC Knauer apparatus equipped with four TSKgel Guard Super columns using an RDI 2.1 L differential refractometer. In total, 60 microliters of a polymer solution (3 mg mL−1) were injected and eluted at a flow rate of 1 mL min−1.
2.3.3. Spectroscopy Analysis
A Fourier Transform Infrared Spectrometer (Spectrum One, Perkin Elmer, Shelton, CT, USA) was used to record IR spectra using 16 scans at a resolution of 4 cm−1 in the range 4000–450 cm−1, using air as the background. For KBr pelleting sample preparation, a press was used to produce KBr pellets of the powder. The frass samples were mixed with KBr at a ratio of 1:100 and ground in a mortar and pestle to prepare a homogeneous powder. The mixture was then pressed into a 7 mm pellet using a hydraulic press (Mini Pellet Press, Specac, Orpington, UK).
2.3.4. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
The thermal stability of the entire sample series was confirmed using a TGA 8000 apparatus (Perkin Elmer Milan—Italy). The analyses were performed on the samples with a nitrogen flow of approximately 60 mL/min, with a heating ramp of 10 °C/min, in the temperature range from 50 °C to 600 °C. Data were acquired and analyzed using Pyris Software V. 13.3.3.0032, provided by the manufacturer.
2.3.5. Morphological Analysis
The morphology of the surfaces of PS, PS-H2O2 and frass samples were investigated using a Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM FEI, Ocala, FL, USA, Quanta 200 FEG) equipped with an X-ray energy-dispersive spectrometer (EDS). Prior to examination, samples were placed onto a conductive stub and then gold-sputtered to avoid electrostatic charging effects.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Weight Variation and Survival Rate of T. Molitor and Z. Morio larvae
The weight of the larvae was monitored every 5 days during the test and Figure 2a,b show the normalized weight (NW) of the T. Molitor and Z. Morio larvae over 30 days of testing.
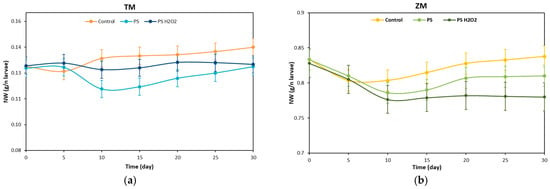
Figure 2.
Weight variation during the time: (a) NW of T. Molitor and (b) NW of Z. Morio fed with bran (control), foam PS and foam PS-H2O2.
The NW of the T. Molitor larvae eating bran slightly decreased during the first 5 days; see Figure 2a. The NW then slowly increased over the further 25 days, reaching a final increment of ~8.5% with respect to the initial NW value. The NW of T. Molitor larvae eating PS remained almost constant during the first 5 days, while it decreased at 10 days (time requested to assess and adapt to the conditions). The NW then increased during the remaining 20 days with a final NW value similar to the initial value. T. Molitor larvae eating PS treated with H2O2 maintained a similar NW value to the initial NW value all over the 30 days, suggesting that larvae ate the PS-H2O2 foams more easily than the untreated ones. These results are in line with the data available in the literature. Peng et al. [23] reported a mass decrease of ~8% for T. Molitor larvae eating PS, while the same authors observed a mass increase of ~14% when feeding the larvae with PS and bran at the same time.
The NW of the Z. Morio larvae eating bran showed a similar trend to that of the T. Molitor ones; see Figure 2b. However, a lower final NW value of ~0.5% was achieved at 30 days. Conversely, the NW of the Z. Morio larvae eating treated and untreated PS foams always decreased during the first 10 days, by ~6%. The NW of larvae eating PS then slightly increased, while that of larvae eating PS-H2O2 remained almost constant. The final NW values of larvae fed with untreated and treated PS were ~2.8% and ~5.8% lower than the initial value (day 0).
The survival rates of the larvae of T. Molitor and Z. Morio eating bran (control), PS foam and PS-H2O2 foam are shown in Figure 3 and summarized in Table 1.
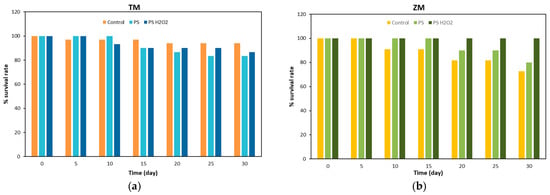
Figure 3.
Survival rate of (a) T. Molitor and (b) Z. Morio larvae fed with bran (control), foam PS and foam PS-H2O2.

Table 1.
Summary of PS biodegradation by T. Molitor and Z. Morio larvae.
In the case of T. Molitor larvae, see Figure 3a, the larvae feeding on bran showed the highest survival rate of ~94% at 30 days. Conversely, the larvae fed PS reported the lowest value of ~83%. The larvae fed with PS-H2O2 foam had a survival rate of ~87%. In the literature, Peng et al. [23] reported survival rates of ~90% for T. Molitor larvae eating PS, while Yang et al. [19] observed values of ~86%. In addition, Yang et al. [19] also measured survival rates of ~85% for larvae eating bran. The different, although similar, survival rates of T. Molitor larvae can be attributed to the genetic differences between mealworm populations around the globe [24].
In the case of the Z. Morio larvae, the highest survival rate was exhibited by larvae eating PS-H2O2. The lowest value of ~73% was found for Z. Morio larvae eating bran, while the larvae fed with PS had a survival rate of ~80%. These results are in contrast with the NW behavior of Z. Morio larvae, indicating that, although the larvae lost weight during the tests, they had a more suitable environment where they lived. The lower survival rates of the Z. Morio larvae with respect to that of the T. Molitor ones were somehow expected. An et al. [3] reported a survival rate of ~70% for PS-foam-eating and normal diet (bran)-eating Zophobas atratus larvae, which belong to the family of Zophobas larvae.
3.2. Size-Exclusion Chromatography (SEC) Analysis
SEC analysis was conducted to characterize the depolymerization and biodegradation of ingested PS [25]. The ponderal molecular weight (Mw), numerical molecular weight (Mn) and polydispersity index (IPD) of frass of T. Molitor and Z. Morio after 15 and 30 days are shown in Figure 4a,b and Figure 4c,d, respectively. The Mw, Mn and IPD of PS and PS-H2O2 foams analyzed at day 0 are also reported.
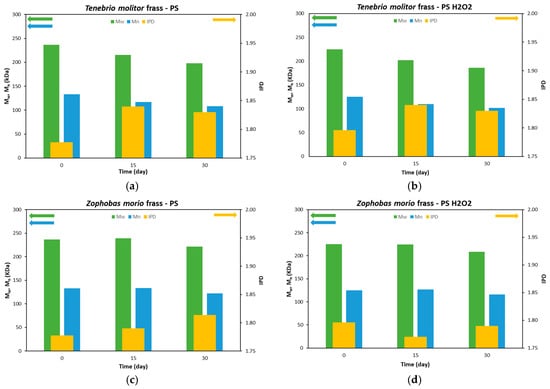
Figure 4.
Data related to the changes in ponderal molecular weight (Mw) (green, left axis), numerical molecular weight (Mn) (blue, left axis) and polydispersity index (IPD) (yellow, right axis) of PS and PS-H2O2 (0 days), and frass of (a,b) TM and (c,d) ZM after 15 and 30 days.
The Mw and Mn of PS frass of T. Molitor larvae decreased over 30 days. Specifically, Mw was 237, 215 and 197.8 kDa at 0, 15 and 30 days, respectively, with a final reduction of 16.4%. Mn values decreased from 133, 117 to 108.4 kDa, again showing a decrease of 18.6%. In the literature, Yang et al. [19] reported similar Mw and Mn percentage reductions. Peng et al. [23] also observed an Mn decrease of ~20%; however, the authors reported an Mw reduction of ~60%. IPD increased in digested samples, as a consequence of the depolymerization and degradation action of the larvae producing lower-molecular-weight fragments [19,26]. PS-H2O2 foams already had lower initial values of Mw and Mn with respect to those of pristine PS ones due to the action of the H2O2, which also caused an increase in the IPD index. Mw and Mn decreased in the frass of T. Molitor larvae eating PS-H2O2 foam due to the action of the larvae’s digestion, showing similar reduction percentages to those of the PS foam case; see Figure 4b.
A lower degradation action was observed in Z. Morio larvae. The Mw and Mn values remained almost constant during the first 15 days in the frass from both PS and PS-H2O2 foams, while a decrease of ~7% was only achieved at 30 days; see Figure 4c,d. The results indicate the superior depolymerization and biodegradation activity of T. Molitor larvae compared to Z. Morio larvae.
3.3. Spectroscopy Analysis
The FTIR spectra of neat PS and PS-H2O2 foams before and after T. Molitor and Z. Morio larvae degradation are shown in Figure 5. Specifically, Figure 5a illustrates the FTIR spectra of neat PS and PS-H2O2 foams; Figure 5b,c refer to the frass collected after 15 and 30 days from T. Molitor and Z. Morio larvae eating PS foams; and Figure 5d,e report the comparison between FTIR spectra of frasses collected at 30 days from T. Molitor and Z. Morio larvae eating PS and PS-H2O2 foams.
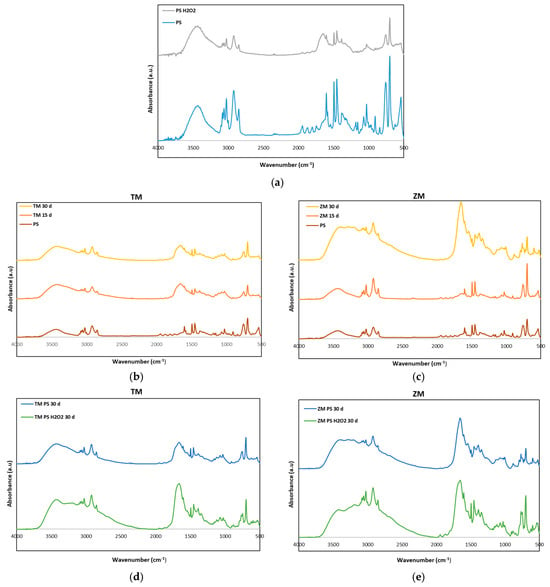
Figure 5.
FTIR spectra of (a) neat PS and PS-H2O2 before the experiments (0 days) and FTIR spectra of (b) frass of TM and (c) frass of ZM for the larvae fed with PS after 15 and 30 days. (d,e) are the comparison of the spectra after 30 days for frass of TM and ZM feeding on PS and PS-H2O2, respectively.
Peaks at 625–970 cm−1 (ring-bending vibration) were visible in all FTIR spectra, although the peak intensity was slightly damped after larvae digestion. The characteristic peaks known to represent the PS benzene ring (1550–1610 cm−1 and 1800–2000 cm−1) were visible in the neat PS samples, while they were considerably dampened in frass, providing evidence of ring cleavage. In addition, evidence of degradation was the appearance of carbonyl groups (1700 cm−1) in frass. The broadening of peaks at 2500–3500 cm−1 in the FTIR of frass was also associated with the hydrogen bond of hydroxyl groups and/or carboxylic acid groups, suggesting a shift from hydrophobic to more hydrophilic surface properties [12].
The frass of T. Molitor larvae showed PS degradation already after 15 days; Figure 5b. Conversely, the frass of Z. Morio larvae after 15 days had the same FTIR spectrum as neat PS foams. The H2O2 treatment already caused a damping effect of peaks at 2500–3500 cm−1, as well as of those at 1550–1610 cm−1 and 1800–2000 cm−1, indicating the degradation of the PS material [20,22]. Treatment of the PS with H2O2 promoted the degradation action of the larvae. A more intense peak at 1700 cm−1 and a wider peak at 2500–3500 cm−1 were, in fact, reported in FTIR spectra of frass collected from larvae eating PS-H2O2 foams with respect to those collected from the PS-eating ones; see Figure 5d.
3.4. Thermogravimetric Analysis
Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) can be considered a valuable tool to compare the changes in the composition and the modification by larvae from pristine foam PS to frass at the end of the test (30 days). As noticeable in Figure 6a,b, the TGA curves of PS and PS-H2O2 showed only one sharp mass loss where more than 95% of the loss occurred between 350 °C and 460 °C, and specifically, the maximum decomposition rate occurred at ca. 420 °C for both PS and PS-H2O2.
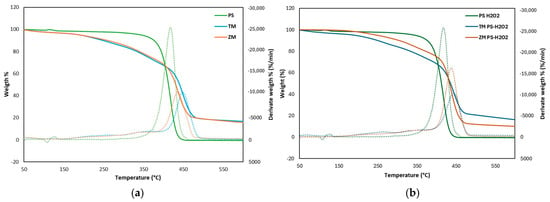
Figure 6.
TGA curve of (a) PS and (b) PS-H2O2 and frass of T. Molitor and Z. Morio larvae after 30 days feeding on foam PS and PS-H2O2. Solid lines represent weight curve (left axis) and dashed lines represent DTG curve (right axis).
In contrast, the frass of T. Molitor fed only PS showed three weight loss stages: stage 1 of 10% at 150–300 °C (max. decomposition rate occurred at 260 °C), stage 2 of 17.5% at 300–395 °C (max. rate at 364 °C) and stage 3 of 43.0% at 395–500 °C (max. rate at 451 °C). When Z. Morio was fed only PS, the frass showed three weight loss stages: stage 1 of 6.1% at 150–260 °C (max. rate at 207 °C), stage 2 of 14.0% at 260–373 °C (max. rate 338 °C) and stage 3 of 44.0% at 373–487 °C (max. rate 434 °C). Similarly, the frass of both T. Molitor and Z. Morio fed PS-H2O2 showed three weight loss stages with maximum decomposition rates very similar to those fed with PS in Figure 6a, although there is a small difference between TM-PS-H2O2 and ZM-PS-H2O2. The frass of TM fed with PS-PS-H2O2 showed the lowest derivative weight, indicating that the PS content in the frass was lower and the degradation efficiency of PS was higher.
According to the literature [5,13,19,23], under the same heating program, the frass of TM or ZM decomposed in more stages than the control. This suggests that the frass contained not only PS but also other components produced during digestion in the insect gut. During stage 3, the weight loss of the frass was less than the control, demonstrating the depletion of PS content in the frass.
3.5. Morphological Analysis
The surface erosion of the plastic by the larvae was evaluated by SEM analysis of the frass. Firstly, the action of H2O2 and microwave irradiation on the PS foam was investigated. Figure 7 shows the SEM images of the original PS samples and those treated with PS-H2O2 at different magnifications, i.e., 150×, 1200× and 20,000×.
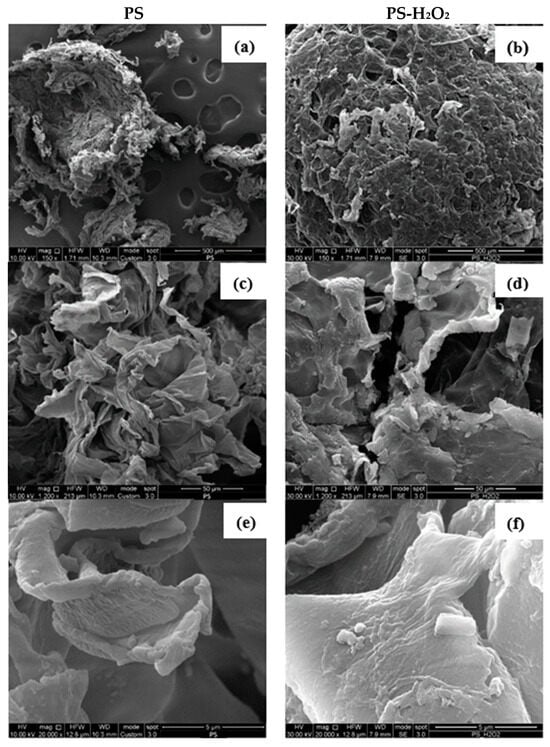

Figure 7.
SEM observations at different magnifications, i.e., 150×, 1200× and 20,000×, of PS (a,c,e) and PS-H2O2 (b,d,f) frass samples, respectively.
A small sphere of PS foam can be seen in Figure 7a, which probably imploded due to the high vacuum pressure applied during the gold sputter process. At a higher magnification, in Figure 7c,e, the smooth surfaces of the PS material can be clearly seen, as typically reported in the literature [24]. Similar structures and smooth surfaces can also be observed in the PS-H2O2 samples; Figure 7b,d,f. This indicates that the action of H2O2 did not affect the surface of the PS foam. Based on this result, only the SEM images of the frond collected after 15 and 30 days from T. Molitor and Z. Morio larvae that fed on PS foam will be discussed below.
Figure 8a,c,e are the SEM images of T. Molitor frass after 15 days, while Figure 8b,d,f refer to the SEM images of T. Molitor frass after 30 days. PS samples isolated from the frass of T. Molitor larvae showed completely different, rough and irregularly carved surface structures from the PS foam; see Figure 7.
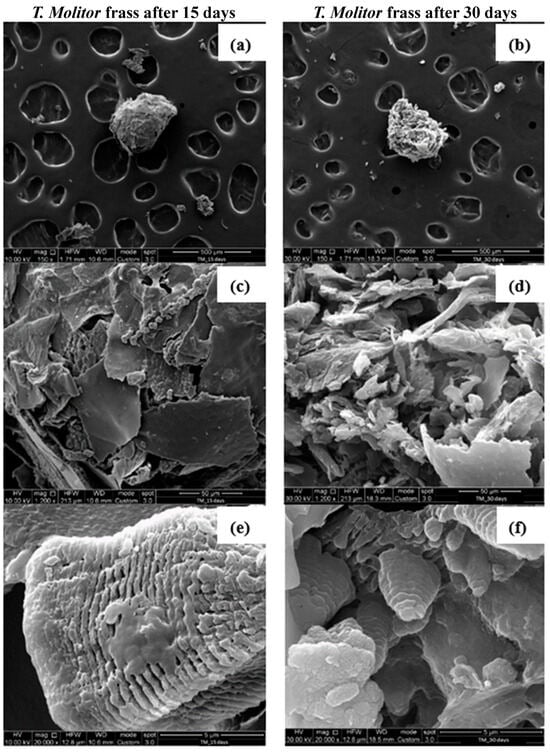
Figure 8.
SEM observations at different magnifications of T. Molitor frass after 15 (a,c,e) and 30 days (b,d,f) of PS foam feeding.
PS flakes can be observed at a magnification of 1200×, Figure 8c,d. In addition, pores can be identified at a magnification of 20,000× on the PS surface, Figure 8e,f, demonstrating the degradation action of the larvae. Surface alterations in the plastics are characteristic of the aging processes occurring under the influence of microorganisms present in the intestines of insects or, more specifically, the enzymes secreted by them. The folding of the previously smooth surface of the polymer and the formation of pitting were observed during the biodegradation of the polymers [24].
SEM observations of frasses collected from Z. Morio larvae after 15 and 30 days are shown in Figure 9.
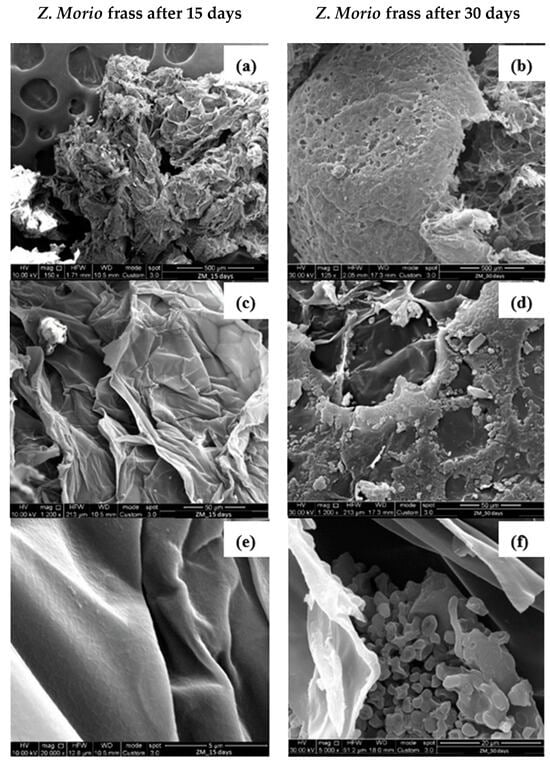

Figure 9.
SEM observations at different magnifications of Z. Morio frass after 15 (a,c,e) and 30 days (b,d,f) of PS foam feeding.
The SEM images of PS samples collected from the frass of the Z. Morio larvae after 15 days, Figure 9a,c,e, showed a very similar structure with respect to that of the PS one, Figure 7. This indicates that Z. Morio larvae did not interact with the PS material during the first 15 days of the tests, as also discussed in Section 3.1, Section 3.2, Section 3.3 and Section 3.4.
PS degradation can be noticed only after 30 days, namely, PS shreds and holes can be observed Figure 9b,d,f. However, comparing Figure 8b and Figure 9b, it can always be observed that large pieces of PS materials are still found in the frass of Z. Morio larvae, confirming the lower degradation action of the Z. Morio larvae compared to T. Molitor larvae. Interestingly, traces of microorganisms were observed in the frass of Z. Morio larvae as shown in Figure 10.

Figure 10.
(a,b) SEM observation at different magnifications of organic matter in the frass of Z. Morio larvae after 15 days fed with PS foam.
Spherical cocci bacteria are observed. The presence of cocci bacteria is in accordance with evidence reported by Yang et al. [27]. The authors attributed the ability of the Z. Morio larvae to depolymerize PS to the presence of microbiota, such as the cocci, in their gut. Cocci bacteria were also found in frass after 30 days of tests, here omitted for the sake of brevity.
4. Conclusions
In this work, the biodegradation of PS by T. Molitor and Z. Morio has been investigated, also considering the treatment of PS with H2O2 in order to facilitate PS degradation. As discussed before, six different experimental diets were compared: (i) T. Molitor fed with bran; (ii) T. Molitor fed only PS; (iii) T. Molitor fed only PS treated with H2O2; (iv) Z. Morio fed with bran; (v) Z. Morio fed only PS; and (vi) Z. Morio fed only PS treated with H2O2. The change in the larvae mass and the survival rate were monitored periodically and the obtained results suggest that both T. Molitor and Z. Morio larvae are able to biodegrade the PS and their mass changes and survival rate are similar to those of larvae fed with bran. The analysis of T. Molitor and Z. Morio frass after 15 and 30 days shows a slightly decreased PS molecular weight and an increase in polydispersity, suggesting a reduction in PS chain weight and length. Further, the data coming from FTIR analysis support this thesis, highlighting the changes in PS compositions after digestion.
Therefore, all these results highlight the ability of both larvae to survive using plastic as feed rather than bran.
Therefore, the identification and knowledge of the enzymes involved could open a new window for the controlled degradation and depolymerization of polymers formulated by polyaddition.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.P. and N.T.D.; methodology, R.P. and N.T.D.; validation, G.B., E.A.D.L. and N.T.D.; formal analysis, E.A.D.L., G.B. and G.C.; investigation, E.A.D.L., R.P., G.B. and N.T.D.; resources, N.T.D.; data curation, E.A.D.L., G.B. and G.C.; writing—original draft preparation, E.A.D.L., G.B. and N.T.D.; writing—review and editing, N.T.D.; supervision, N.T.D.; funding acquisition, E.A.D.L. and N.T.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work has been financially supported by MUR—Italy (Ministry of University and Research of Italy)—in the field of “Next Generation EU”—PNRR M4–C2 -investimento 1.1; Fondo per il Programma Nazionale di Ricerca e Progetti di Rilevante Interesse Nazionale (PRIN)—PRIN 2022 cod. 20229BHA75 dal titolo “FUnctional Technology Unlocking Recycling and VALorization of Personal Protective Equipment production scrap and waste” (FUTUREVAL-PPE). CUP B53D23005690006. The APC was funded by E.A. Di Liberto and N.Tz. Dintcheva.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethical review and approval were waived for this study, as the use of invertebrate animals, like insects, for laboratory experiments does not require the approval of bioethics committees and is not subject to procedures in accordance with Directive 2010/63/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council of 22 September 2010 on the protection of animals used for scientific purposes, amended by Regulation (EU) 2019/1010 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 5 June 2019.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Plastic Europe. Plastics—The Fast Facts 2023. 2023. Available online: https://plasticseurope.org/knowledge-hub/plastics-the-fast-facts-2023/ (accessed on 20 February 2024).
- Beghetto, V.; Gatto, V.; Samiolo, R.; Scolaro, C.; Brahimi, S.; Facchin, M.; Visco, A. Plastics Today: Key Challenges and EU Strategies towards Carbon Neutrality: A Review. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 334, 122102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, R.; Liu, C.; Wang, J.; Jia, P. Recent Advances in Degradation of Polymer Plastics by Insects Inhabiting Microorganisms. Polymers 2023, 15, 1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Bartolo, A.; Infurna, G.; Dintcheva, N.T. A Review of Bioplastics and Their Adoption in the Circular Economy. Polymers 2021, 13, 1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Su, T.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Z. Biodegradation of Polystyrene by Tenebrio molitor, Galleria mellonella, and Zophobas atratus Larvae and Comparison of Their Degradation Effects. Polymers 2021, 13, 3539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahnawaz, M.; Sangale, M.K.; Ade, A.B. Plastic Waste Disposal and Reuse of Plastic Waste. In Bioremediation Technology for Plastic Waste; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 21–30. ISBN 9789811374913. [Google Scholar]
- Alqattaf, A. Plastic Waste Management: Global Facts, Challenges and Solutions. In Proceedings of the 2020 Second International Sustainability and Resilience Conference: Technology and Innovation in Building Designs (51154), Sakheer, Bahrain, 11–12 November 2020; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira-Filipe, D.A.; Paço, A.; Duarte, A.C.; Rocha-Santos, T.; Patrício Silva, A.L. Are Biobased Plastics Green Alternatives?—A Critical Review. IJERPH 2021, 18, 7729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enyoh, C.E.; Shafea, L.; Verla, A.W.; Verla, E.N.; Qingyue, W.; Chowdhury, T.; Paredes, M. Microplastics Exposure Routes and Toxicity Studies to Ecosystems: An Overview. Environ. Anal. Health Toxicol. 2020, 35, e2020004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.; Dong, Y.; Nadir, S.; Schaefer, D.A.; Mortimer, P.E.; Xu, J.; Ye, L.; Gui, H.; Wanasinghe, D.N.; Dossa, G.G.O.; et al. Valorizing Plastic Waste by Insect Consumption. Circ. Agric. Syst. 2021, 1, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, B.; Das, A. The Ability of Insects to Degrade Complex Synthetic Polymers. In Arthropods—New Advances and Perspectives; Shields, V.D.C., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2023; ISBN 978-1-80355-612-3. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.-S.; Brandon, A.M.; Andrew Flanagan, J.C.; Yang, J.; Ning, D.; Cai, S.-Y.; Fan, H.-Q.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Ren, J.; Benbow, E.; et al. Biodegradation of Polystyrene Wastes in Yellow Mealworms (Larvae of Tenebrio molitor Linnaeus): Factors Affecting Biodegradation Rates and the Ability of Polystyrene-Fed Larvae to Complete Their Life Cycle. Chemosphere 2018, 191, 979–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, Y.; Li, Y.; Lu, B.; Liu, Q.; Yang, S.-S.; Liu, B.; Ren, N.; Wu, W.-M.; Xing, D. Response of the Yellow Mealworm (Tenebrio Molitor) Gut Microbiome to Diet Shifts during Polystyrene and Polyethylene Biodegradation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 126222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Prabhu, A.; Aroney, S.T.N.; Rinke, C. Insights into Plastic Biodegradation: Community Composition and Functional Capabilities of the Superworm (Zophobas morio) Microbiome in Styrofoam Feeding Trials. Microb. Genom. 2022, 8, 000842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.R.; Lee, H.M.; Yu, H.C.; Jeon, E.; Lee, S.; Li, J.; Kim, D.-H. Biodegradation of Polystyrene by Pseudomonas sp. Isolated from the Gut of Superworms (Larvae of Zophobas atratus). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 6987–6996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pivato, A.F.; Miranda, G.M.; Prichula, J.; Lima, J.E.A.; Ligabue, R.A.; Seixas, A.; Trentin, D.S. Hydrocarbon-Based Plastics: Progress and Perspectives on Consumption and Biodegradation by Insect Larvae. Chemosphere 2022, 293, 133600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plastic Europe Plastics—The Facts 2022. Available online: https://plasticseurope.org/knowledge-hub/plastics-the-facts-2022/ (accessed on 20 February 2024).
- Farrelly, T.A.; Shaw, I.C. Polystyrene as Hazardous Household Waste. In Household Hazardous Waste Management; Mmereki, D., Ed.; InTech: Berlin, Germany, 2017; ISBN 978-953-51-2909-7. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Yang, J.; Wu, W.-M.; Zhao, J.; Song, Y.; Gao, L.; Yang, R.; Jiang, L. Biodegradation and Mineralization of Polystyrene by Plastic-Eating Mealworms: Part 1. Chemical and Physical Characterization and Isotopic Tests. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 12080–12086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achilias, D.S. Polymer Degradation Under Microwave Irradiation. In Microwave-Assisted Polymer Synthesis; Hoogenboom, R., Schubert, U.S., Wiesbrock, F., Eds.; Advances in Polymer Science; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; Volume 274, pp. 309–346. ISBN 978-3-319-42239-8. [Google Scholar]
- Chandrasekaran, S.; Ramanathan, S.; Basak, T. Microwave Material Processing—A Review. AIChE J. 2012, 58, 330–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calles-Arriaga, C.A.; López-Hernández, J.; Hernández-Ordoñez, M.; Echavarría-Solís, R.A.; Ovando-Medina, V.M. Thermal Characterization of Microwave Assisted Foaming of Expandable Polystyrene. Ing. Investig. Y Tecnol. 2016, 17, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Peng, B.-Y.; Su, Y.; Chen, Z.; Chen, J.; Zhou, X.; Benbow, M.E.; Criddle, C.S.; Wu, W.-M.; Zhang, Y. Biodegradation of Polystyrene by Dark (Tenebrio Obscurus) and Yellow (Tenebrio Molitor) Mealworms (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 5256–5265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulak, P.; Proc, K.; Pytlak, A.; Puszka, A.; Gawdzik, B.; Bieganowski, A. Biodegradation of Different Types of Plastics by Tenebrio molitor Insect. Polymers 2021, 13, 3508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puglisi, C.; Samperi, F.; Carroccio, S.; Montaudo, G. Analysis of Poly(Bisphenol A Carbonate) by Size Exclusion Chromatography/Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization. 2. Self-Association Due to Phenol End Groups. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 1999, 13, 2268–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Natale, M.V.; Carroccio, S.C.; Dattilo, S.; Cocca, M.; Nicosia, A.; Torri, M.; Bennici, C.D.; Musco, M.; Masullo, T.; Russo, S.; et al. Polymer Aging Affects the Bioavailability of Microplastics-Associated Contaminants in Sea Urchin Embryos. Chemosphere 2022, 309, 136720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, J.; Xia, M. Biodegradation and Mineralization of Polystyrene by Plastic-Eating Superworms Zophobas atratus. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 708, 135233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).