Bubble Melt Electrospinning for Production of Polymer Microfibers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
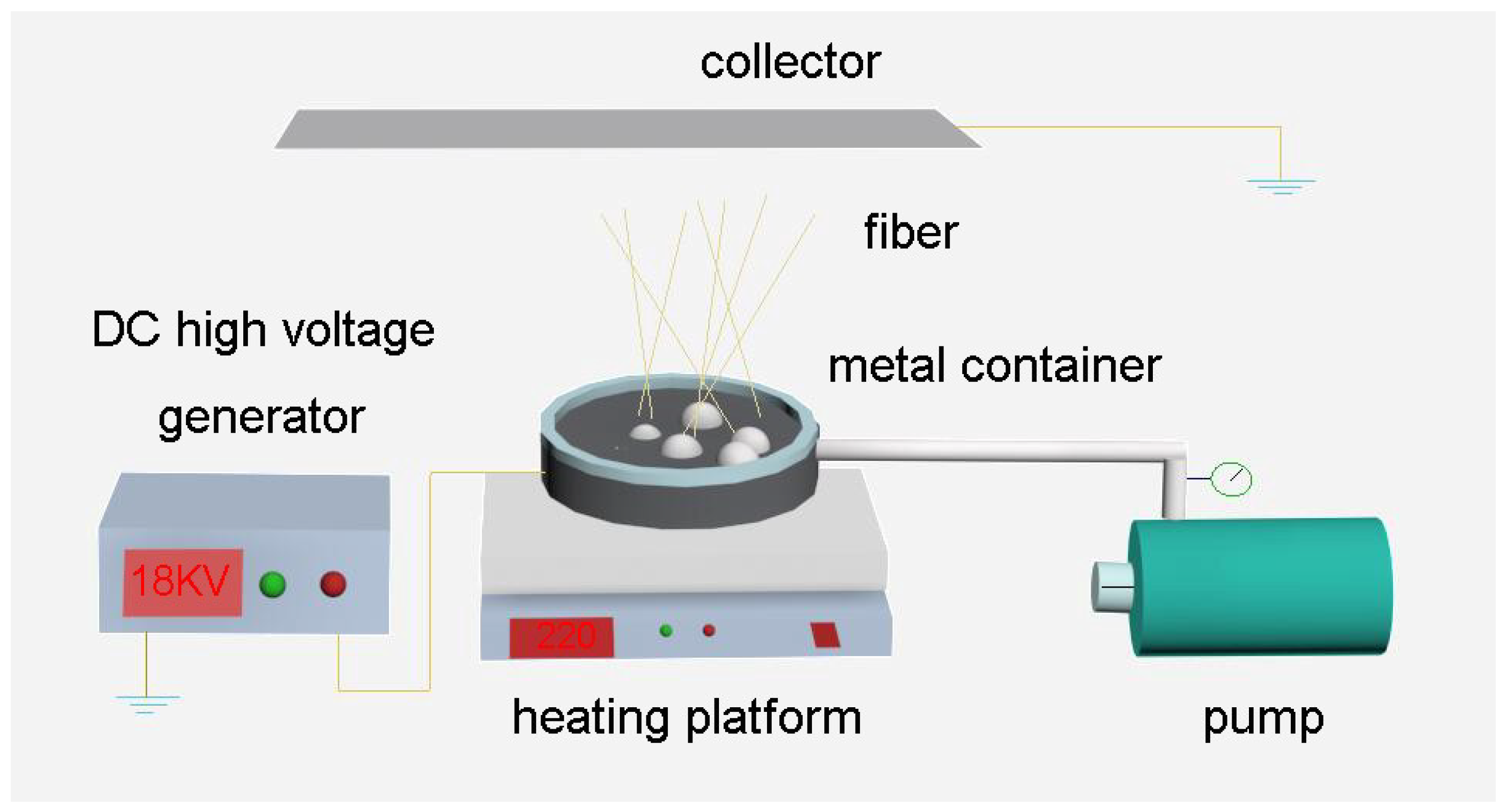
2.2. Melt E-Spinning Setup
2.3. E-Spinning Process
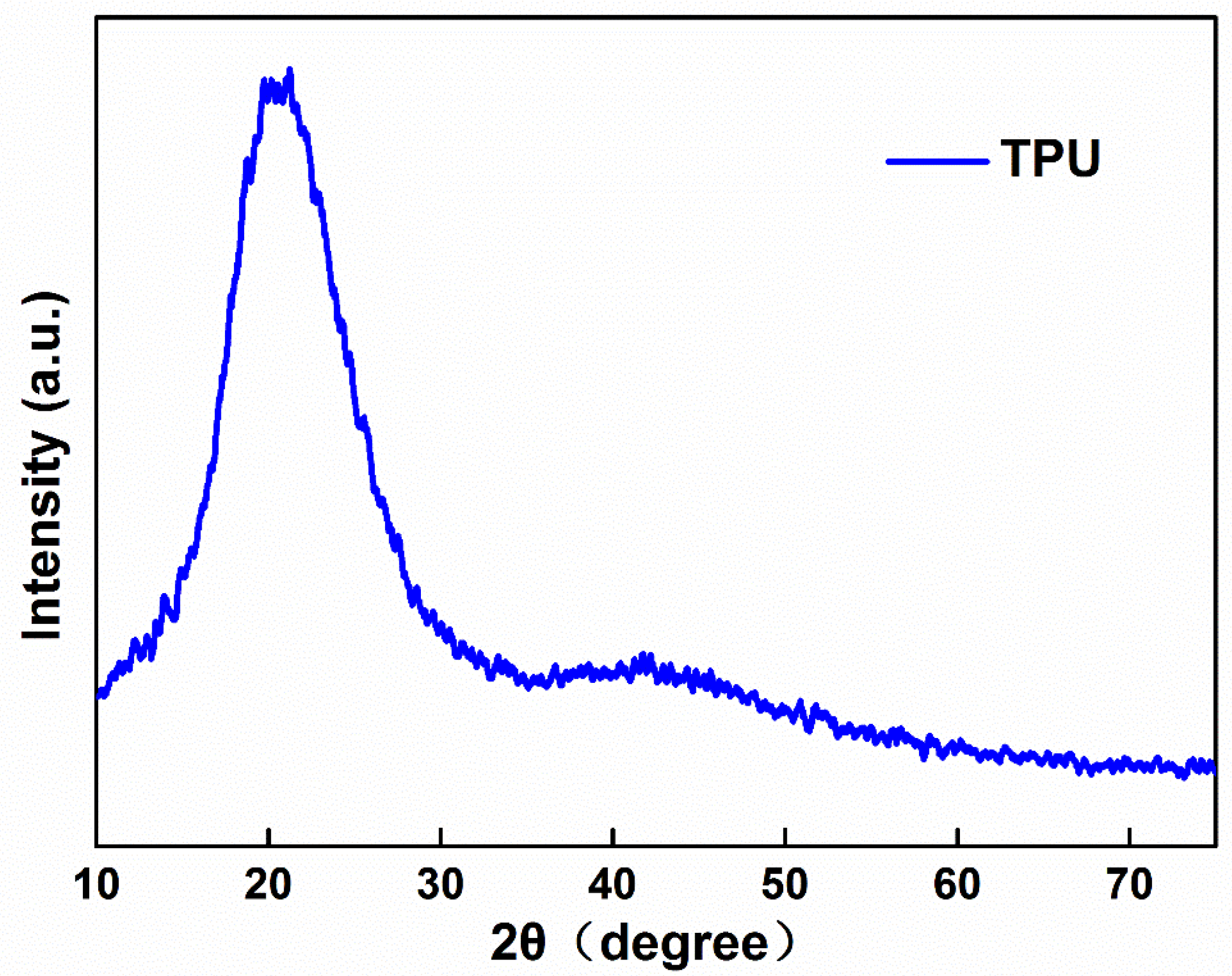
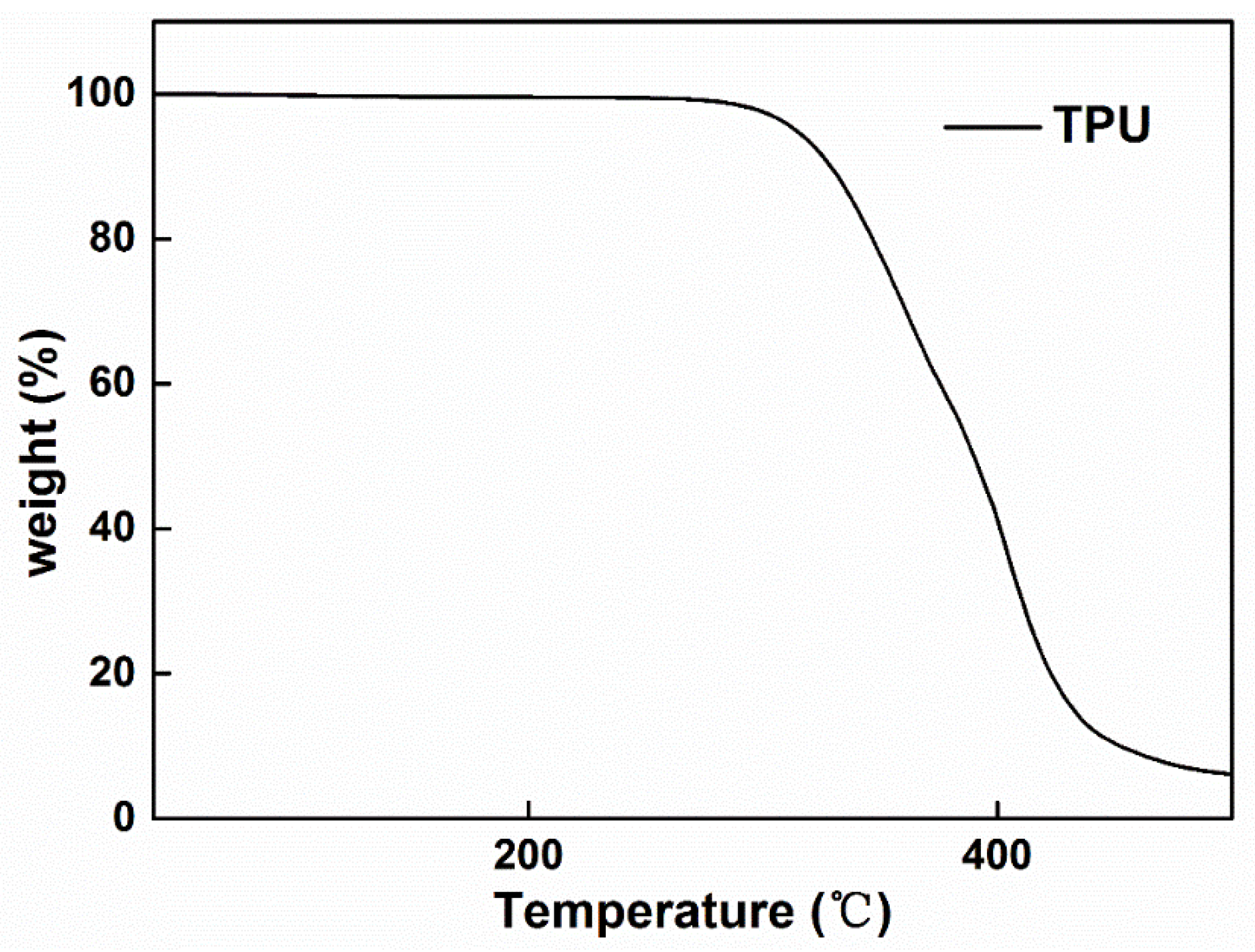
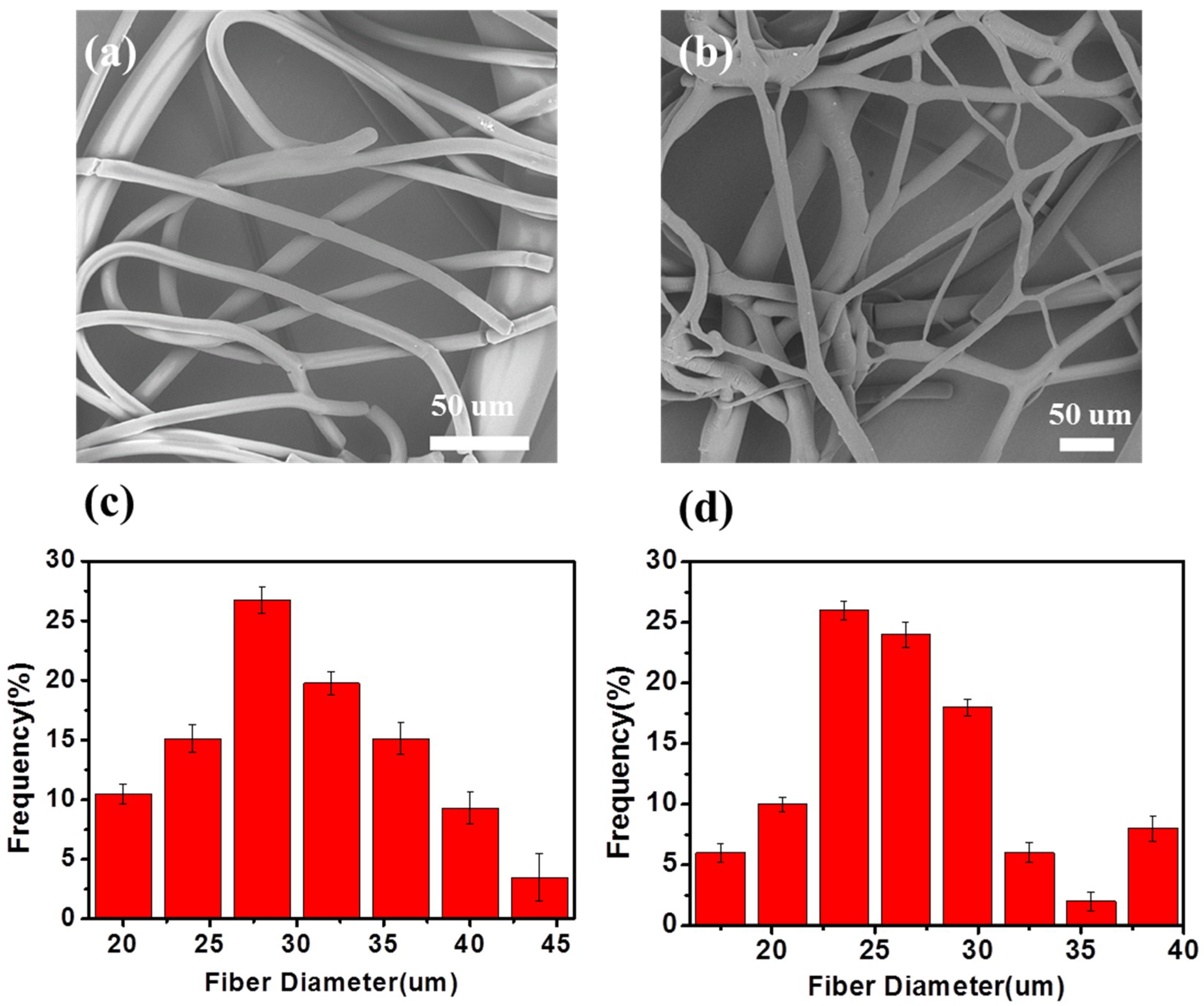
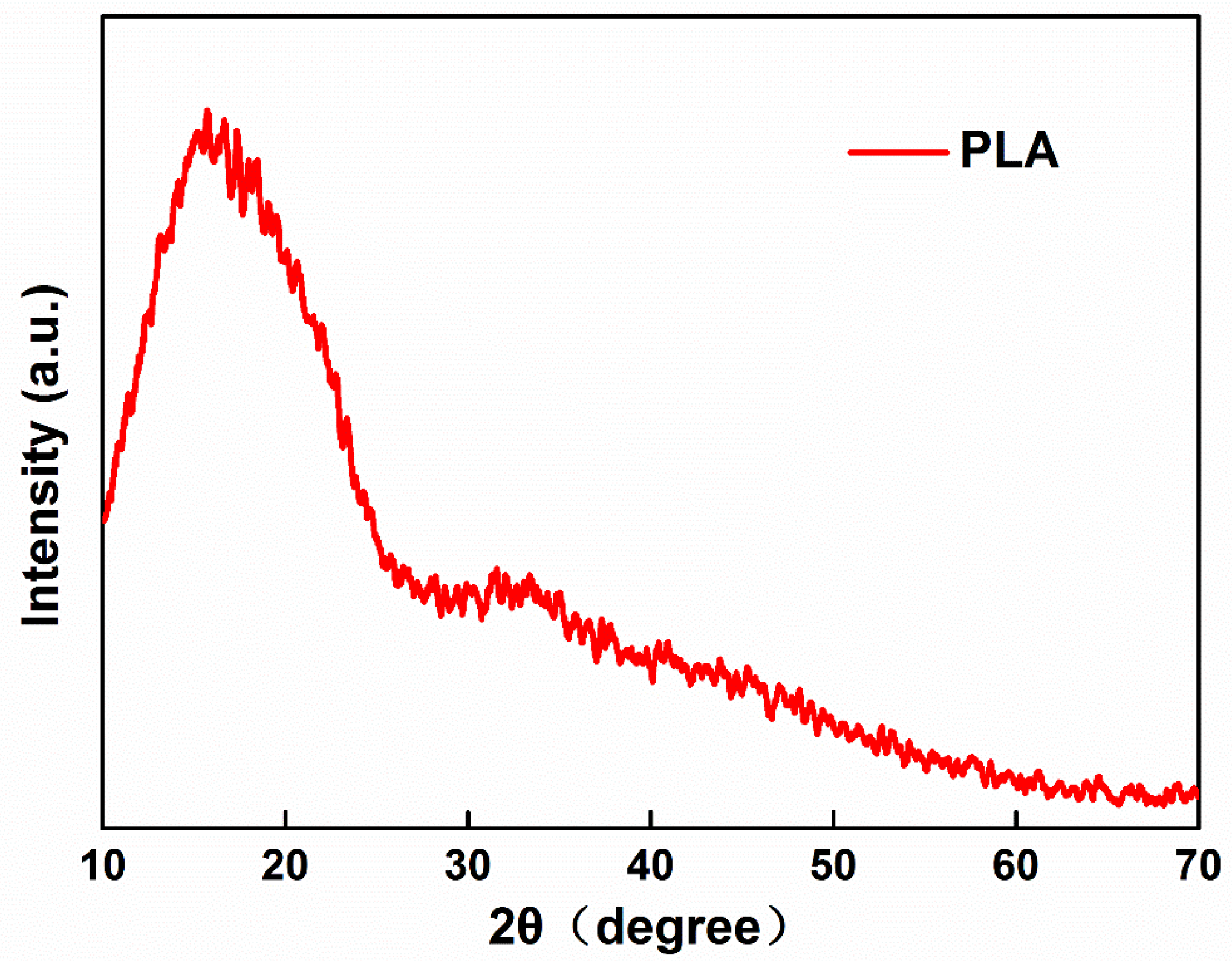
2.4. Characterization
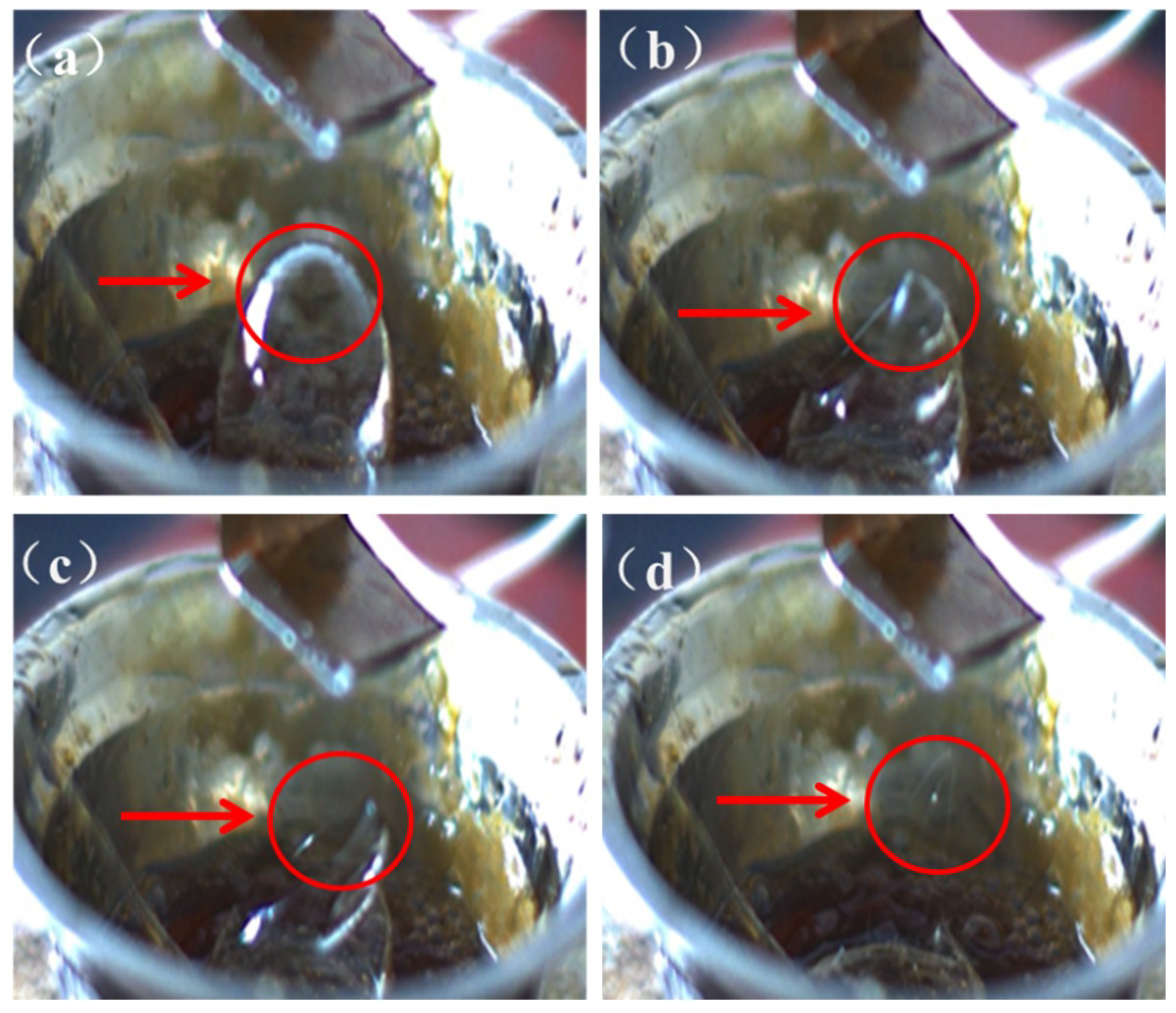
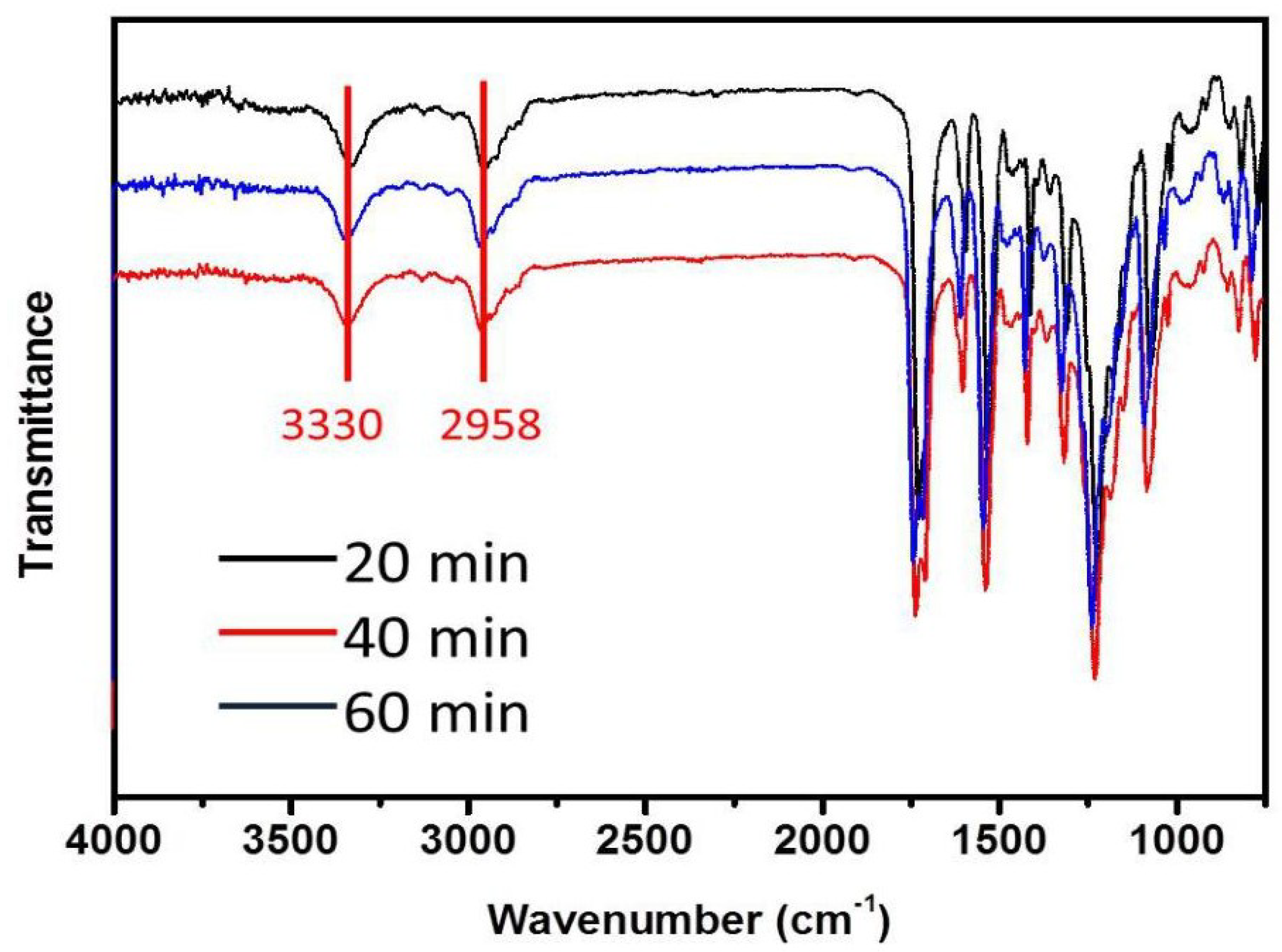
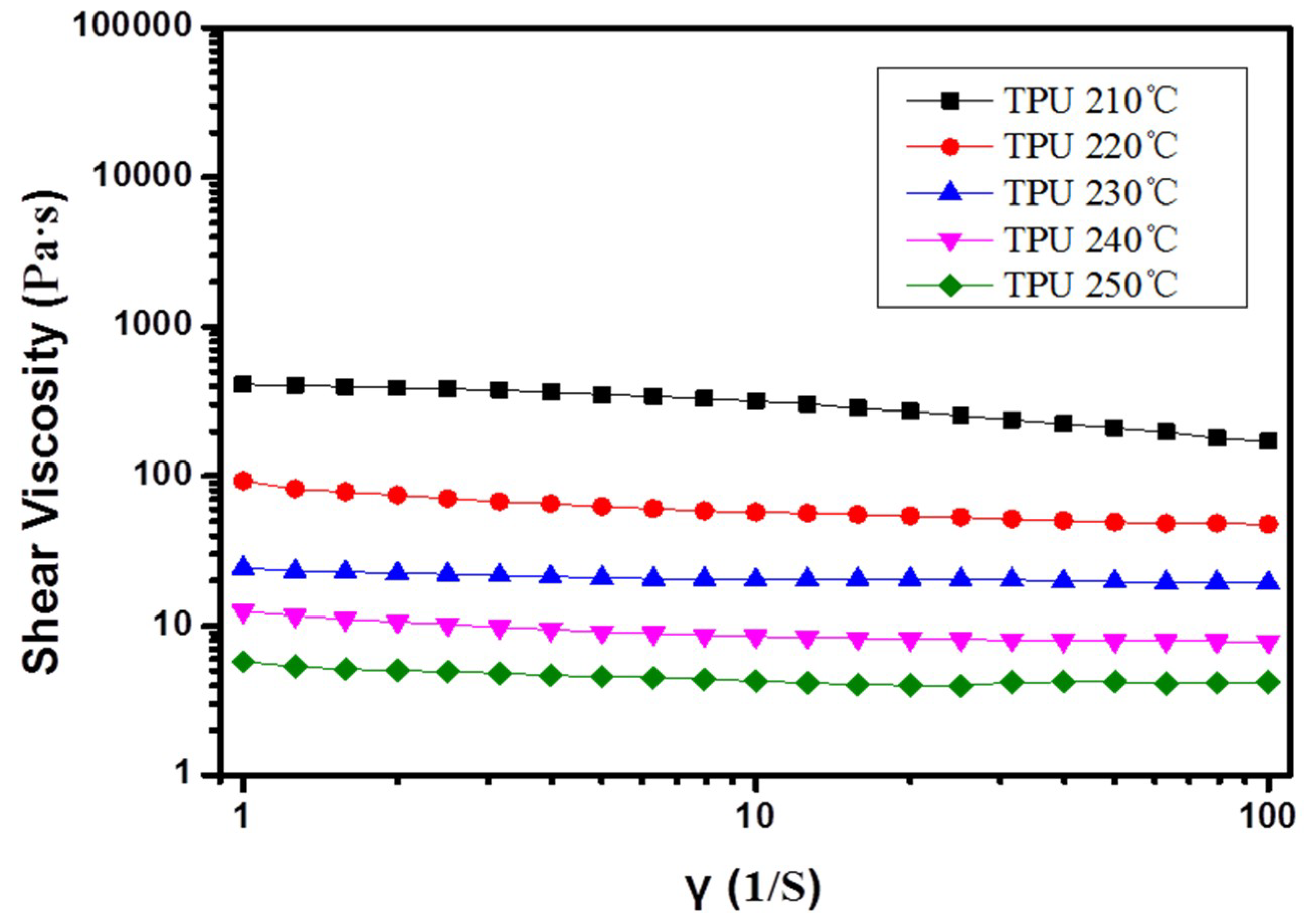
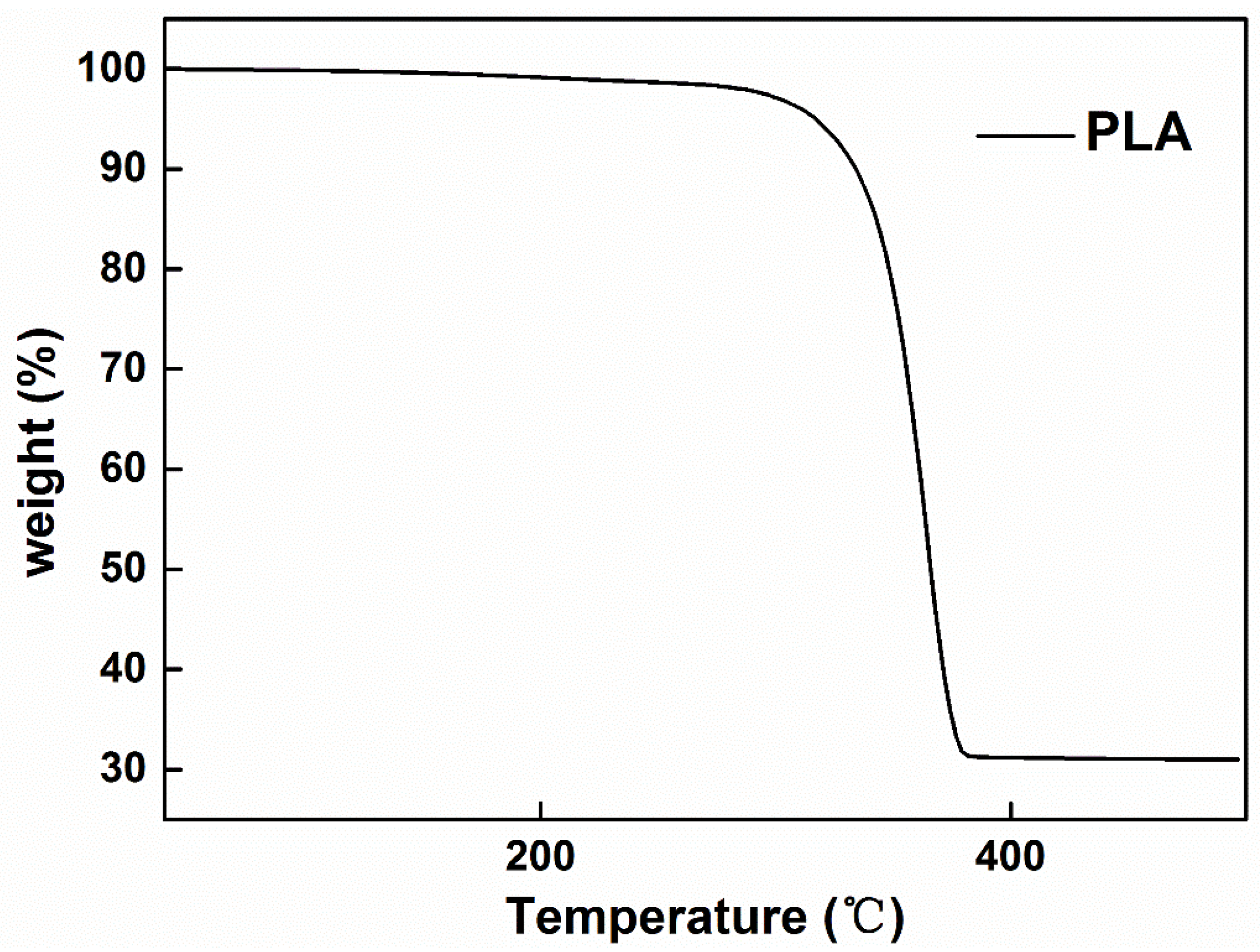
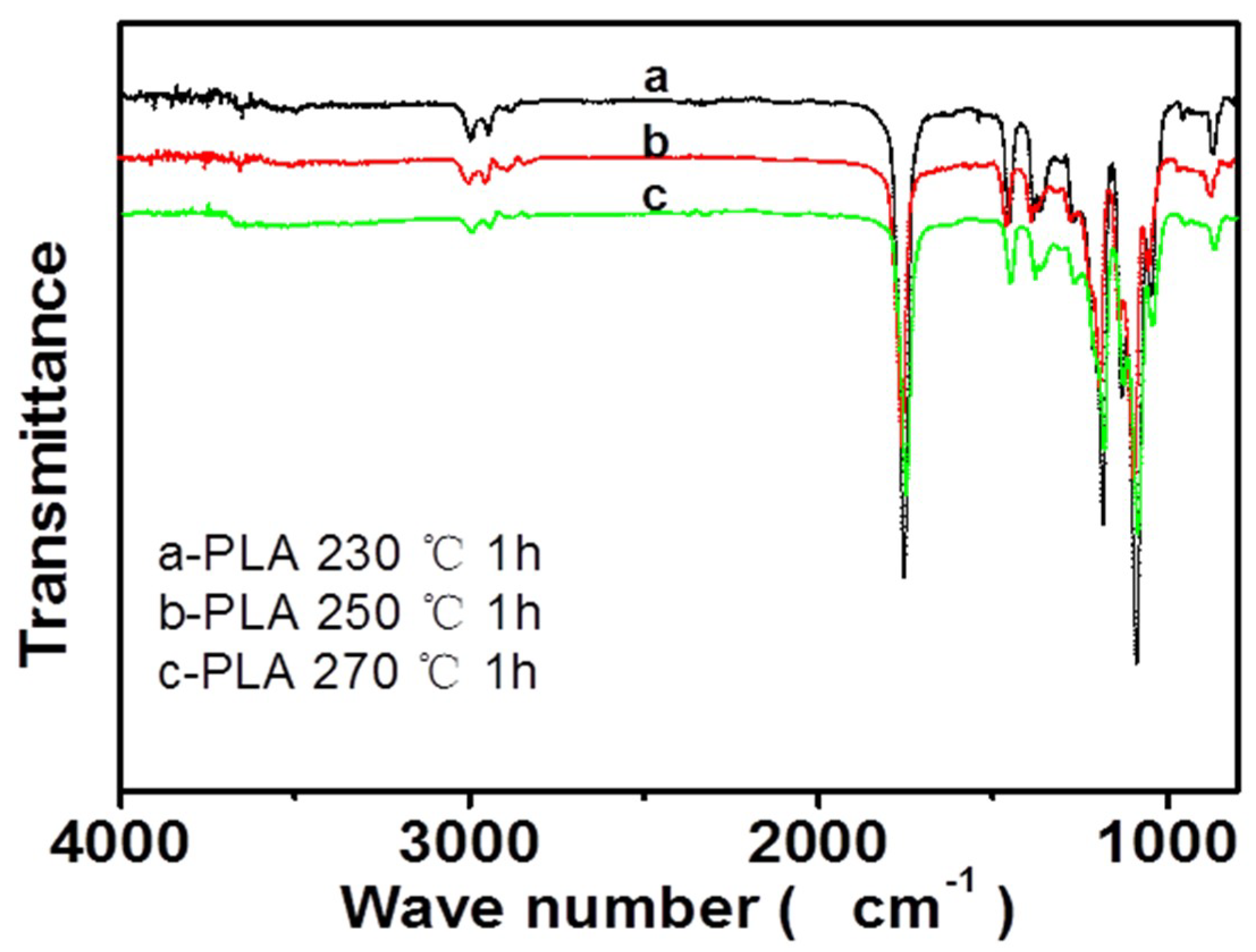
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reneker, D.H.; Chun, I. Nanometre diameter fibres of polymer, produced by electrospinning. Nanotechnology 1996, 7, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norton, C.L. Method of and Apparatus for Producing Fibrous or Filamentary Material. U.S. Patent 2,048,651, 21 July 1936. [Google Scholar]
- Ramakrishna, S.; Fujihara, K.; Teo, W.E.; Yong, T.; Ma, Z.; Ramaseshan, R. Electrospun nanofibers: solving global issues. Mater. Today 2006, 9, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, T.H.; Ishii, D.; Mahara, A.; Murakami, S.; Yamaoka, T.; Sudesh, K.; Samian, R.; Fujita, M.; Maeda, M.; Iwata, T. Scaffolds from electrospun polyhydroxyalkanoate copolymers: fabrication, characterization, bioabsorption and tissue response. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 1307–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munir, M.M.; Nuryantini, A.Y.; Mikrajuddin, A.; Iskandar, F.; Okuyama, K. Preparation of polyacrylonitrile nanofibers with controlled morphology using a constant-current electrospinning system for filter applications. Mater. Sci. Forum 2013, 737, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.H.; Duan, X.P.; Yan, X.; Yu, M.; Ning, X.; Zhao, Y.; Long, Y.Z. Recent advances in melt electrospinning. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 53400–53414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarin, A.L.; Zussman, E. Upward needleless electrospinning of multiple nanofibers. Polymer 2004, 45, 2977–2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, H.; Lin, T.; Wang, X. Needleless electrospinning. I. A comparison of cylinder and disk nozzles. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 114, 3524–3530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; He, J.H. Bubble electrospinning for mass production of nanofibers. Int. J. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2007, 8, 393–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; He, J.; Xu, L.; Yu, J. Bubble-electrospinning for fabricating nanofibers. Polymer 2009, 50, 5846–5850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.H.; Kong, H.Y.; Yang, R.R.; Dou, H.; Faraz, N.; Wang, L.; Feng, C. Review on fiber morphology obtained by bubble electrospinning and blown bubble spinning. Therm. Sci. 2012, 16, 1263–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; He, J.H.; Xu, L.; Yu, J.Y. The principle of bubble electrospinning and its experimental verification. J. Polym. Eng. 2008, 28, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Dong, L.; Fan, J.; Wang, R.; Yu, J.Y. Effect of applied voltage on diameter and morphology of ultrafine fibers in bubble electrospinning. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2011, 120, 592–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; He, J.H.; Yu, J.Y. Bubble-electrospinning: a novel method for making nanofibers. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2008, 96, 012001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ya, L.; Rou-xi, C.; Fu-Juan, L. Comparison between electrospun and Bubbfil-spun Polyether sulfone fibers. Matéria (Rio de Janeiro) 2014, 19, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, S.; Wendorff, J.H.; Greiner, A. Progress in the field of electrospinning for tissue engineering applications. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 3343–3351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, S.; Wendorff, J.H.; Greiner, A. Use of electrospinning technique for biomedical applications. Polymer 2008, 49, 5603–5621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.; Hsiao, B.S.; Chu, B. Functional electrospun nanofibrous scaffolds for biomedical applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2007, 59, 1392–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villarreal-Gómez, L.J.; Cornejo-Bravo, J.M.; Vera-Graziano, R.; Grande, D. Electrospinning as a powerful technique for biomedical applications: a critically selected survey. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2016, 27, 157–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalton, P.D.; Grafahrend, D.; Klinkhammer, K.; Klee, D.; Möller, M. Electrospinning of polymer melts: Phenomenological observations. Polymer 2007, 48, 6823–6833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, N.; Kundu, S.C. Electrospinning: a fascinating fiber fabrication technique. Biotechnol. Adv. 2010, 28, 325–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khorshidi, S.; Solouk, A.; Mirzadeh, H.; Mazinani, S.; Lagaron, J.M.; Sharifi, S.; Ramakrishna, S. A review of key challenges of electrospun scaffolds for tissue-engineering applications. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2016, 10, 715–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larrondo, L.; St John Manley, R. Electrostatic fiber spinning from polymer melts. I. Experimental observations on fiber formation and properties. J. Polym. Sci. Part B 1981, 19, 909–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangkupan, R.; Reneker, D.H. Electrospinning Process of Molten Polypropylene in Vacuum. J. Met. Mater. Miner. 2003, 12, 81–87. [Google Scholar]
- Lyons, J.; Li, C.; Ko, F. Melt-electrospinning part I: processing parameters and geometric properties. Polymer 2004, 45, 7597–7603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhmayev, E.; Cho, D.; Joo, Y.L. Nanofibers from gas-assisted polymer melt electrospinning. Polymer 2010, 51, 4140–4144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, Z.K.; Balogh, A.; Drávavölgyi, G.; Ferguson, J.; Pataki, H.; Vajna, B.; Marosi, G. Solvent-free melt electrospinning for preparation of fast dissolving drug delivery system and comparison with solvent-based electrospun and melt extruded systems. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 102, 508–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Green, T.B.; Joo, Y.L. The thermal effects on electrospinning of polylactic acid melts. Polymer 2006, 47, 7497–7505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, T.D.; Dalton, P.D.; Hutmacher, D.W. Melt electrospinning today: An opportune time for an emerging polymer process. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2016, 56, 116–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochleitner, G.; Jüngst, T.; Brown, T.D.; Hahn, K.; Moseke, C.; Jakob, F.; Dalton, P.D.; Groll, J. Additive manufacturing of scaffolds with sub-micron filaments via melt electrospinning writing. Biofabrication 2015, 7, 035002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muerza-Cascante, M.L.; Haylock, D.; Hutmacher, D.W.; Dalton, P.D. Melt electrospinning and its technologization in tissue engineering. Tissue Eng. Part B 2014, 21, 187–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.Y.; Bubakir, M.M.; Xia, T.; Zhong, X.F.; Ding, Y.M.; Yang, W.M. Mass production of ultra-fine fibre by melt electrospinning method using umbellate spinneret. Mater. Res. Innov. 2014, 18, S4-921–S4-925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Zhang, L.; Sutton, D.; Wang, X.; Lin, T. Needleless melt-electrospinning of polypropylene nanofibres. J. Nanomater. 2012, 2012, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, H.Y.; Salick, M.R.; Jing, X.; Jacques, B.R.; Crone, W.C.; Peng, X.F.; Turng, L.S. Characterization of thermoplastic polyurethane/polylactic acid (TPU/PLA) tissue engineering scaffolds fabricated by microcellular injection molding. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2013, 33, 4767–4776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boubakri, A.; Elleuch, K.; Guermazi, N.; Ayedi, H.F. Investigations on hygrothermal aging of thermoplastic polyurethane material. Mater. Des. 2009, 30, 3958–3965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, C.H.; Lee, M.H.; Kim, Y.D.; Min, B.H.; Kim, J.H. Effect of clay modifiers on the morphology and physical properties of thermoplastic polyurethane/clay nanocomposites. Polymer 2006, 47, 6718–6730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, H.L. Kinetics of thermal degradation of char-forming plastics from thermogravimetry. Application to a phenolic plastic. J. Polym. Sci. Part C 1964, 6, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, P.; Barker, I.A.; Parsons, A.; Thurecht, K.J.; Ahmed, I.; Walker, G.S.; Rudd, C.D.; Irvine, D.J. Influence of compatibilizing agent molecular structure on the mechanical properties of phosphate glass fiber-reinforced PLA composites. J. Polym. Sci. Part A 2010, 48, 3082–3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.-M.; Wang, X.-X.; Yu, S.-X.; Zhao, Y.-T.; Yan, X.; Zheng, J.; Yu, M.; Yan, S.-Y.; Long, Y.-Z. Bubble Melt Electrospinning for Production of Polymer Microfibers. Polymers 2018, 10, 1246. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10111246
Li Y-M, Wang X-X, Yu S-X, Zhao Y-T, Yan X, Zheng J, Yu M, Yan S-Y, Long Y-Z. Bubble Melt Electrospinning for Production of Polymer Microfibers. Polymers. 2018; 10(11):1246. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10111246
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Ye-Ming, Xiao-Xiong Wang, Shu-Xin Yu, Ying-Tao Zhao, Xu Yan, Jie Zheng, Miao Yu, Shi-Ying Yan, and Yun-Ze Long. 2018. "Bubble Melt Electrospinning for Production of Polymer Microfibers" Polymers 10, no. 11: 1246. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10111246
APA StyleLi, Y.-M., Wang, X.-X., Yu, S.-X., Zhao, Y.-T., Yan, X., Zheng, J., Yu, M., Yan, S.-Y., & Long, Y.-Z. (2018). Bubble Melt Electrospinning for Production of Polymer Microfibers. Polymers, 10(11), 1246. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10111246






