Abstract
The influences of the processing parameters on the Mg2FeH6 synthesis yield were studied. Mixtures of magnesium hydride (MgH2) and iron (Fe) were mechanically milled in a planetary ball mill under argon for 0.5-, 1-, 2- and 3-h periods and subsequently sintered at temperatures from 300–500 C under hydrogen. The reaction yield, phase content and hydrogen storage properties of the received materials were investigated. The morphologies of the powders after synthesis were studied by SEM. The synthesis effectiveness map was presented. The obtained results prove that synthesis parameters, such as the milling time and synthesis temperature, greatly influence the reaction yield and material properties and show that extended mechanical milling may not be beneficial to the reaction efficiency.
1. Introduction
The ternary hydride Mg2FeH6 is an attractive material for hydrogen storage, but also receives attention as a heat storage material [1,2,3]. Dimagnesium iron hydride is characterized by a cubic K2PtCl6- type crystal structure [4] with one of the highest volumetric hydrogen densities among all metal hydrides (150 kg/m) and a gravimetric density of 5.4 wt%. Furthermore, the precursors Mg/MgH2 and Fe are relatively inexpensive. The synthesis of Mg2FeH6 is not straightforward because Mg and Fe do not form binary compounds or intermetallic phases. Since the discovery of Mg2NiH4, many attempts have been made to prepare its iron-based analog. Didisheim et al. [4] prepared the Mg2FeH6 hydride by sintering magnesium and iron powders in a stoichiometric ratio of 2:1 (2 Mg-Fe) under a H2 atmosphere (20–120 bar) at 450–520 C. The processing time was long, and the yield was unsatisfactory (50%). A higher yield of 63% was obtained by Raman et al. [5]. In this case, the complex hydride was synthesized by high-energy ball milling of Mg and Fe powders under 10 bar of H2. Additionally, Herrich et al. [6] showed that ternary complex hydrides could be synthesized by reactive milling (RM). The process was based on milling the initial MgH2 and Fe powder mixture in a planetary ball mill under 7 bar of hydrogen. The obtained material had a gravimetric capacity up to 5.2 wt% H2, but the process involved milling under hydrogen pressure for very long periods (up to 80 h). Both Li et al. and Varin et al. [7,8] attempted to synthesize Mg2FeH6 by a process called controlled reactive mechanical alloying. The process consists of two steps. First, pre-milling under an inert atmosphere was applied to a magnesium and iron mixture; then, the resultant powder was milled under hydrogen pressure. Depending on the processing route, these studies managed to synthesize a ternary hydride at a yield of approximately 34% or not at all in the resultant phases. In 2010, we presented results showing the possibility of a very fast and effective synthesis of Mg2FeH6 by ball milling and subsequent sintering under hydrogen pressure. The main finding was that ternary hydride could be formed in the direct reaction between magnesium hydride and iron without prior decomposition of MgH2 [9,10]. Attempts to optimize the process were made to determine the optimum mechanical milling time for the process. We also proved that the magnesium-iron nanocomposite formed during the decomposition of ternary hydride is sufficiently reactive to be easily hydrogenated at temperatures as low as 30 C [11]. We also showed that the synthesis efficiency can be improved to more than 95% for the direct reaction from a MgH2 and Fe mixture using the appropriate processing parameters [12]. The reaction between magnesium hydride and iron was also studied in depth by Puszkiel et al. [13]. The authors carefully described the mechanisms of Mg2FeH6 formation and decomposition and proved that, in the MgH2-MgFe system, synergistic destabilizing effects occur, improving the decomposition and formation reaction rates. Some unconventional synthesis routes were also reported in the literature [14,15,16] such as hot extrusion and cold rolling. Magnesium iron composite made from Mg2FeH6 was even presented as a potential candidate for structural nanocomposite material [17]. In most above-mentioned papers, the chosen parameters were used to conduct the synthesis. To the best of our knowledge, no systematic studies showing the effects of different synthesis conditions (except milling time) on the reaction yield have been conducted until now. In this work, we present new results on the influences of the reaction parameters on the yield of dimagnesium iron hydride manufactured by mechanical milling of magnesium hydride followed by sintering under a high-pressure hydrogen atmosphere. Milling times of 0.5, 1, 2 and 3 h and sintering temperatures of 300, 350, 400, 450 and 500 C for 30 min were applied. The obtained “processing map” shows the processing window where Mg2FeH6 synthesis is most efficient with the chosen method. There is still significant interest in investigation and modeling of the basic physical properties and cyclic behavior of this hydride [18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26]. Furthermore, studies of the influence of different additives and new synthesis routes are still within the scope of work of different teams [27,28,29,30,31,32,33]. Considering that this is one of the most effective methods available for complex hydride manufacturing, this information, provided as a tool for the hydrogen storage research community, will enable a simple, fast and effective synthesis of high-purity magnesium-iron hydride.
2. Materials and Methods
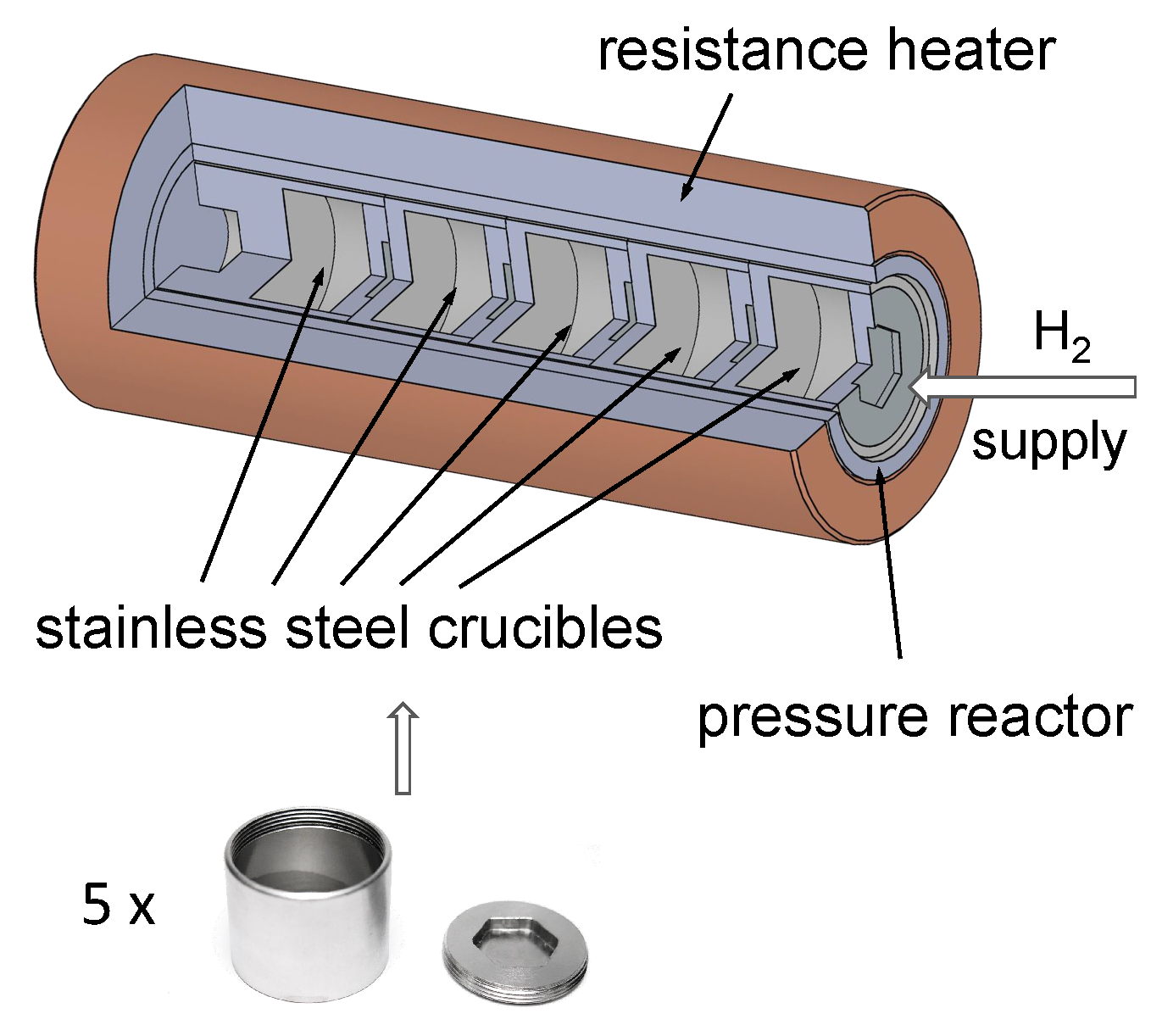
The starting materials, magnesium hydride powder (MgH2, ABCR, declared 98%) and iron powder (Fe, Sigma Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA, 99.7%), were mixed at the stoichiometric molar ratio of 2:1. The mass of the mixture for one batch was 18 g. Each of the four batches was placed in an 80-mL stainless-steel vessel with 30 stainless balls (10 mm in diameter) and subsequently milled in a Fritsch P6 planetary ball mill for 30 min, 1, 2 and 3 h under argon. The milling speed was set to 650 rpm. Milling was performed with 10-min milling/20-min pause cycles. The rotational direction was changed after each cycle. The processing parameters are presented in Table 1. Next, the milled powder samples were placed (without exposure to air) in a custom-made synthesis reactor able to hold up to 5 small stainless-steel crucibles (Figure 1) and capable of heating them to the same temperature.

Table 1.
Parameters of the milling process.
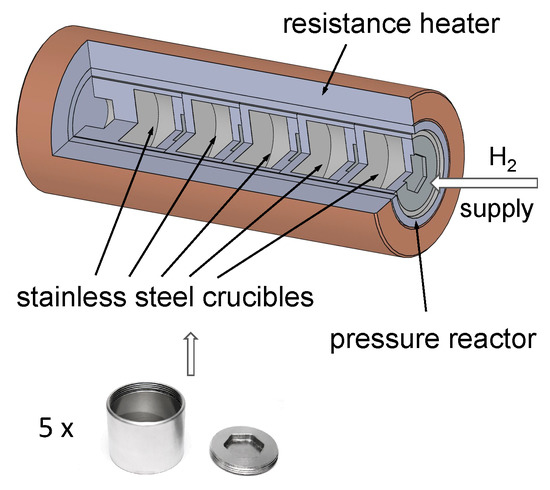
Figure 1.
Custom-made reactor for the synthesis of multiple samples.
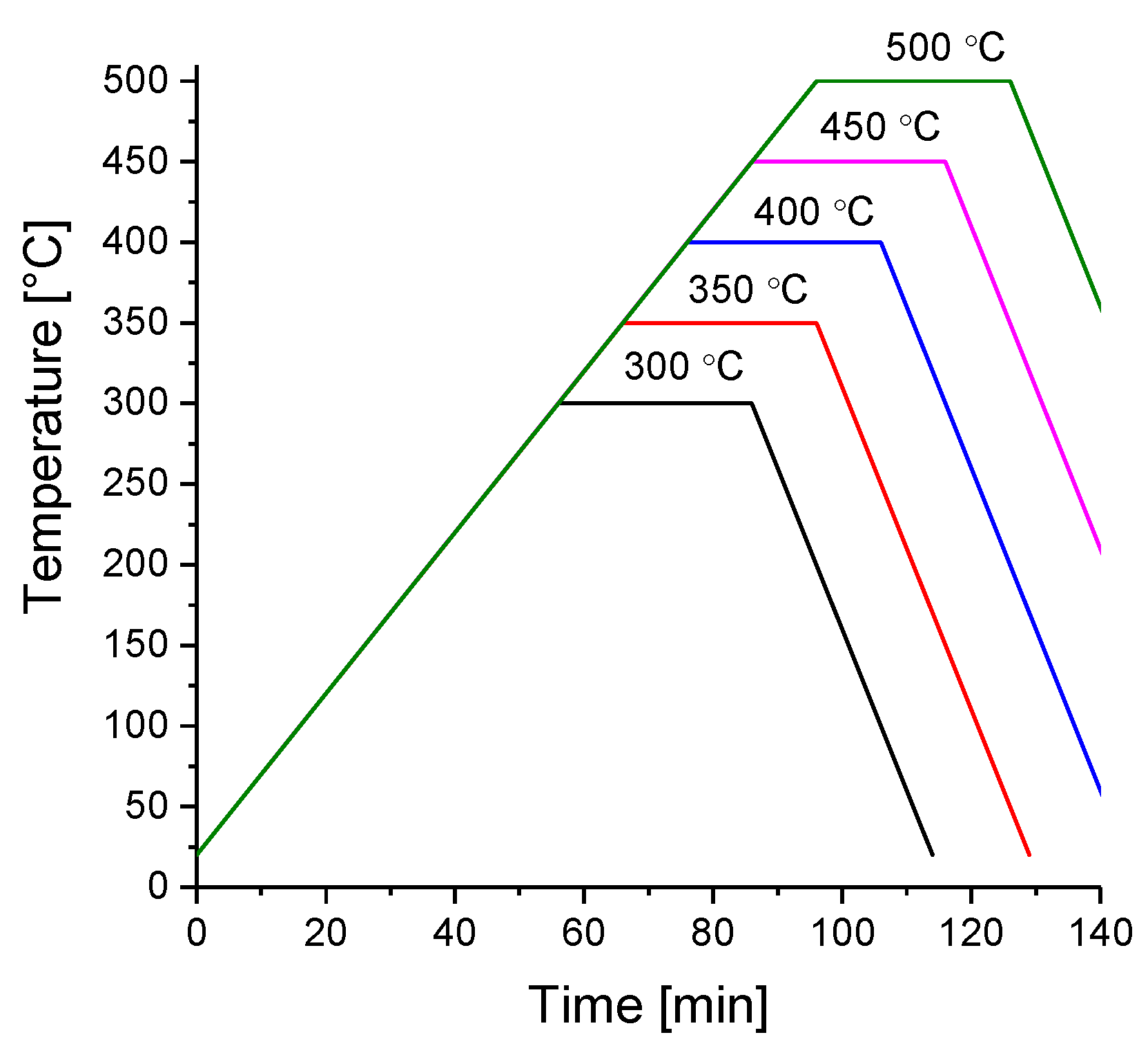
Each set of 4 crucibles (each crucible containing 2.5 g of material milled for different amounts of time) was annealed at 300, 350, 400, 450 and 500 C under an initial hydrogen pressure of 100 bar. The samples were heated according to the theoretical temperature profile shown in Figure 2 with a resistive heater controlled with a proportional integral derivative (PID) temperature controller. The real heating profile was not recorded and may have slightly differed from the theoretical profile in the cooling cycle because the cooling fan could not cool down the reactor according to the programmed profile. All sample handling was performed in an MBraun glovebox under a controlled argon atmosphere with water vapor and oxygen contents lower than 1 ppm.
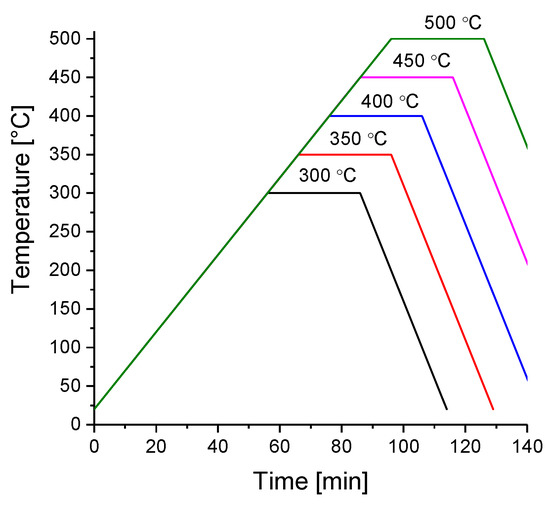
Figure 2.
Programmed temperature profiles of the synthesis process.
The qualitative phase analysis of the obtained materials was carried out using a Rigaku Ultima IV diffractometer operated at 40 kV and 40 mA in the 2-theta of 25–70 using Co K radiation with a characteristic wavelength of = 1.79 Å. Continuous mode with a sampling interval of 0.02 was used with a scanning speed of 1/min. The morphologies of the powders after synthesis were observed using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) operating in backscattered electron (BSE) mode. Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) analysis was performed using a Sensys 3d (Setaram) device working in the horizontal position. Sealed (not gas-tight) aluminum crucibles (170 ) were used. The mass of each sample was lower than 20 mg (15–20 mg). Helium (BIP, Air Product, <10 ppb H2O, O2) was used as a carrier gas with a flow rate of 28 mL/min. The outlet of the DSC instrument was connected to a quadrupole mass spectrometer (Hiden Analytical, Warrington, U.K.) to perform gas analysis. Samples were first purged for 30 min, were then heated from 20–450 C with a constant heating rate of 5 C/min and cooled.
3. Results and Discussion
Two-step syntheses were performed for mixtures after 0.5, 1, 2 and 3 h of milling under argon by annealing them under hydrogen (100 bar) at 300, 350, 400, 450 and 500 C. The yield of each synthesis was calculated by comparing the mass of the closed crucible for the sample before and after synthesis (with 0.01-mg precision). Theoretical hydrogen uptake was estimated according to the predicted reaction on the level of 50 mg per sample. In such a case, using this precision balance should result in the yield estimating error on the level no bigger than 0.05%.
3.1. Phase Composition
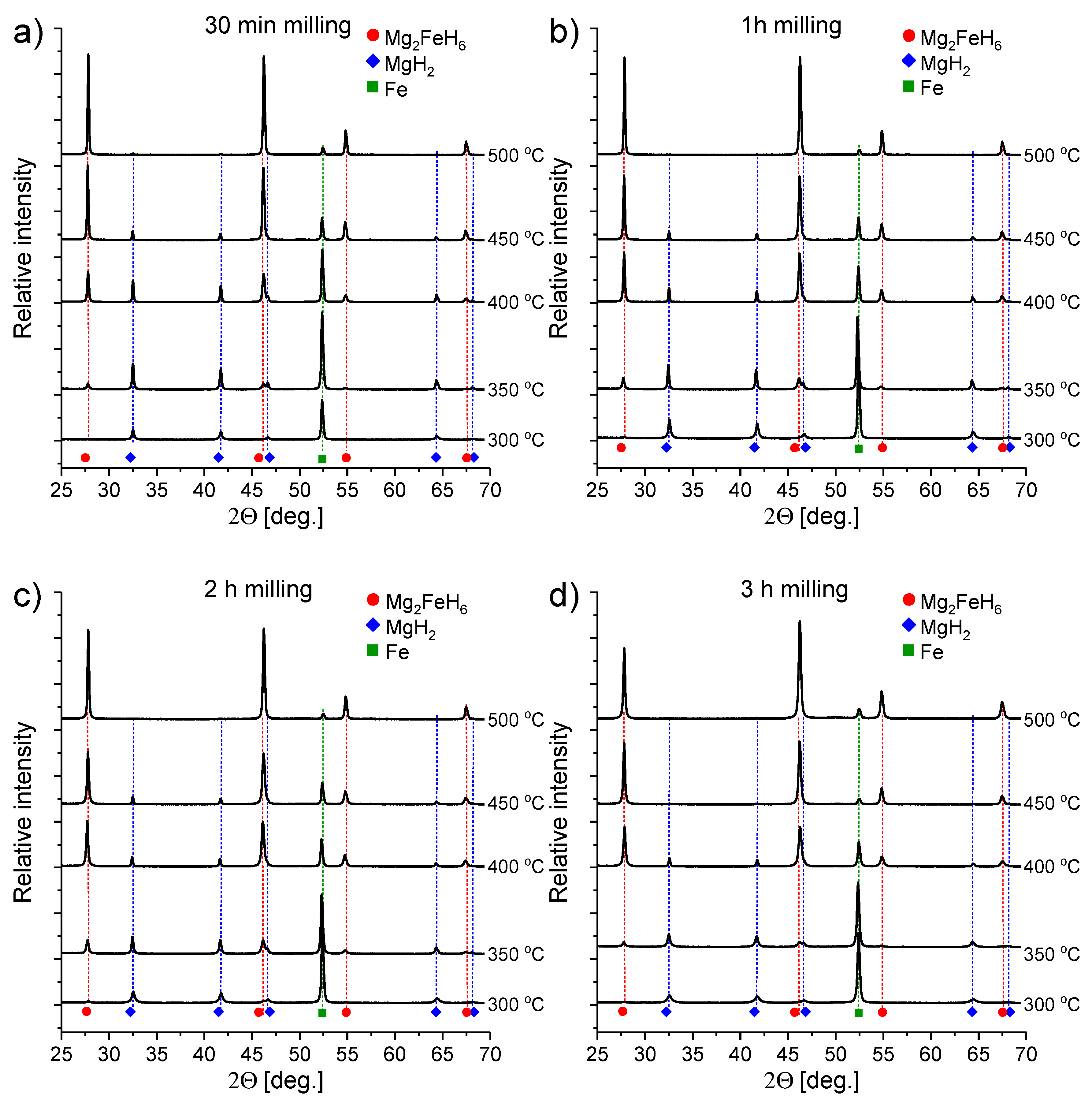
Figure 3 shows the diffraction patterns for the samples synthesized by ball milling under argon for (a) 30 min, (b) 1 h, (c) 2 h and (d) 3 h and sintered under hydrogen pressure at different temperatures (300, 350, 400, 450 and 500 C).
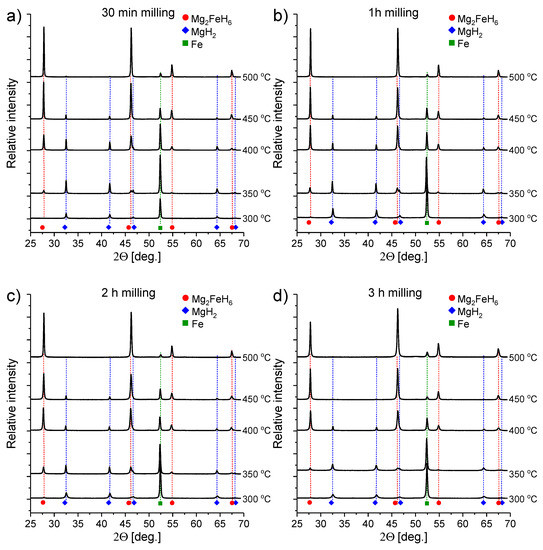
Figure 3.
Diffraction patterns of samples after milling the MgH2+ Fe mixture for (a) 30 min, (b) 1 h, (c) 2 h and (d) 3 h followed by sintering at different temperatures under hydrogen pressure.
Despite the difference in milling time, as expected, high similarities are observed between the samples sintered at the same temperatures. After sintering at 300 C, only a small amount (yield <2%) of dimagnesium iron hydride was observed for the samples milled 2 and 3 h (Figure 3c,d), and only an ~1% yield was observed for the sample milled for 1 h. For the sample milled for 30 min, no magnesium-iron hydride was detected. Only very small peaks, just above the background noise, were noticed for the above-mentioned samples, proving that the synthesis at 300 C, if possible, was not effective. Furthermore, since Mg2FeH6 can be successfully synthesized during the ball milling process of magnesium hydride with iron, such small amounts of ternary hydride could be synthesized in the milling process prior to annealing under hydrogen. The diffraction patterns of powders after milling did not seem to support this theory, as no Mg2FeH6 was observed. However, after ball milling, the peaks are usually very broad with lower intensity, and thus, observing the presence of Mg2FeH6 may be very difficult. Only after heating does the ternary phase become visible. Further observation of the diffractograms after sintering at 300 C shows that the magnesium hydride peaks are typical for those received after mechanical milling; these peaks have low intensity and are broad, indicating that 300 C is neither high enough to release the post-processing stress in the particles, nor high enough to destroy the nanostructure, which is commonly observed for magnesium hydride fabricated with this method. In our previous studies concerning the synthesis of this compound [9,10], when the reaction was traced in situ using synchrotron radiation X-ray diffraction (SRXRD) or pressure changes in a Sieverts apparatus, we observed that the reaction started at approximately 350 C when the mixture was heated at a rate of 5 C/min. However, if the synthesis is thermodynamically possible under the chosen conditions (which is true here), the transformation will occur after a certain time. A low sintering temperature causes slower diffusion and considerably slows the reaction process. Additionally, the use of relatively large quantities of samples for sintering (2.5 g in comparison to the 20–100 mg normally used in the Sieverts apparatus or DSC) may have caused the reaction to proceed more slowly because more time is needed to equilibrate the temperature in the sample (the thermal conductivity of this mixture is in the insulators range rather than metals [34]). For samples sintered at 350 C, strong, but not dominating, peaks of magnesium-iron hydride can be observed. The highest amount of the phase was found for the samples milled for 1 and 2 h (Figure 3b,c) with yields of 12% and 17%, respectively. Again, for samples milled for shorter and longer amounts of time (Figure 3a,c), a lower yield of 6% was observed for both samples. Magnesium hydride peaks remained relatively broad, which may suggest that the nanostructure is still stable at this temperature. The analysis of the diffraction patterns collected for samples sintered under 400 C shows that the ternary hydride is a dominant phase. For only the sample milled for 30 min, the reaction yield was considerably lower at 30%, whereas the yields were greater than 50% for the other samples. Determining whether the nanostructure of the magnesium hydride was still stable was difficult because of the very low MgH2 peak intensity. However, the relatively broad Mg2FeH6 peaks suggest that the formed new hydride may also be nanoconfined. Only traces of the remaining MgH2were present after sintering the composites at 450 C. The yield of the synthesis ranged from 70%–90% and was again highly dependent on the milling time.
All samples sintered at 500 C appeared to be almost fully transformed into Mg2FeH6 with a yield of 90% or higher. Tiny magnesium hydride peaks can be observed only for samples milled for the shortest and, less obviously, for the longest time. This behavior confirms our previous studies illustrating that too long or too short of a milling time may not be beneficial for the synthesis process, and even a high sintering temperature may not be sufficient to allow the full transformation. This behavior is difficult to explain considering that more energy applied during the milling process usually results in a faster reaction between the precursors. In all the cases, we observed residual iron. Initially, we thought that the residual iron resulted from the interaction of iron with the X-rays, which should provide an enhanced diffraction intensity. Later, we discovered that not all magnesium hydride purchased from the manufacturer did had 98% purity. Furthermore, the remaining contamination was not (as declared by the manufacturer) pure magnesium metal, but possibly magnesium hydroxide. In such a case, all calculations performed to prepare stoichiometric mixtures were not correct, and in fact, an excess of iron was added to the magnesium hydride. In such a case, even with ideal conditions, 100% yield was not possible. Because the magnesium hydroxide was likely amorphous and formed on the surface of the magnesium hydride particles, this species was not observed in the XRD patterns, but was visible from the subsequent coupled TG/MS experiments.
3.2. Microstructure
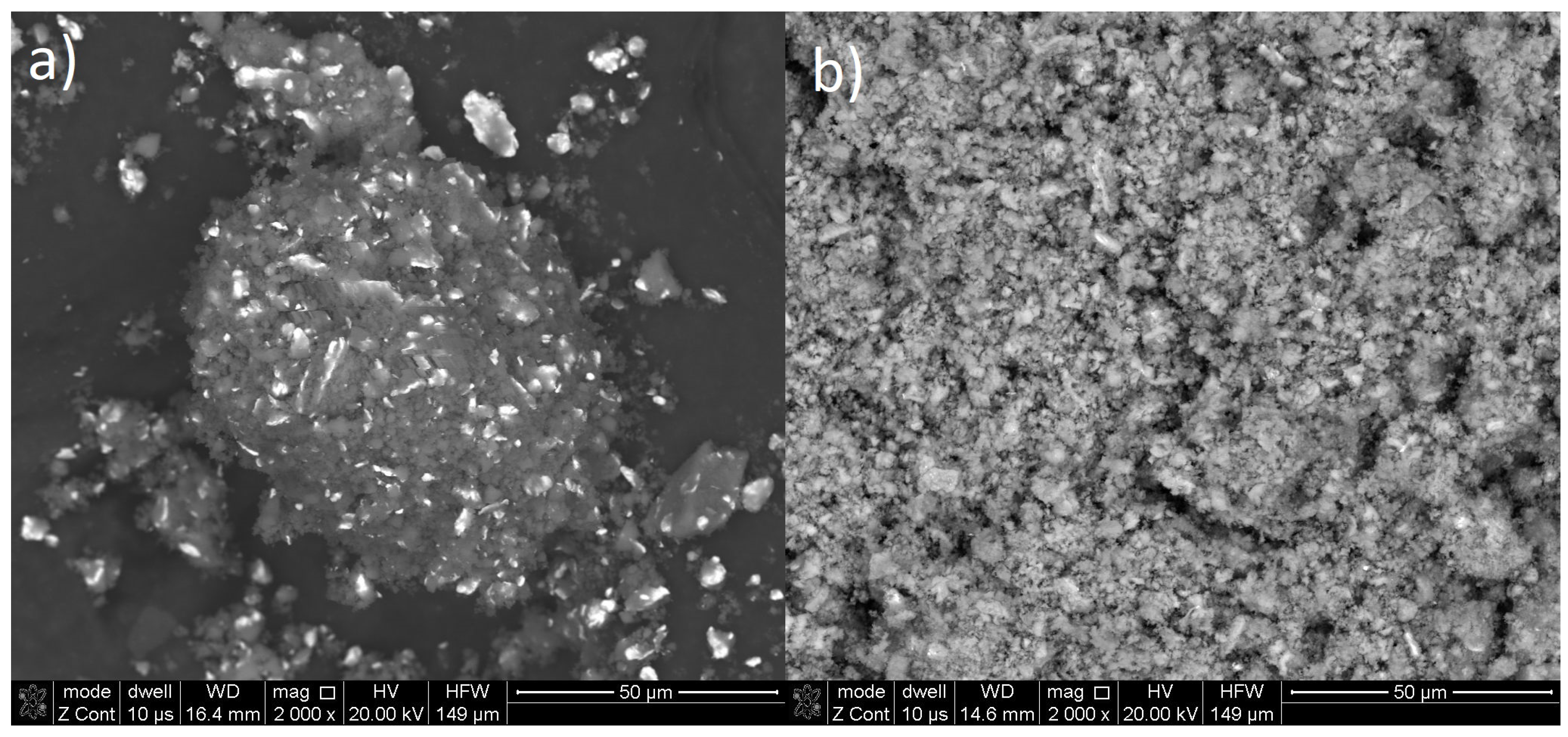
To avoid unnecessary expansion of the paper, all SEM micrographs of the powders after syntheses are shown in the Supplementary Material. The conclusion observed from the BSE images supports the XRD phase analysis data. The samples sintered at 500 C exhibit a homogeneous appearance with not many unreacted iron particles (rare white spots). The exemplary images are shown in Figure 4 and present the samples with lowest and highest yield achieved (30 min of milling, 300 C sintering, and 2 h of milling, 500 C sintering). The difference between those two samples is obvious and proves that evident mass transfer took place only in the case of the later sample, resulting in the homogenous appearance in BSE mode. The sample sintered at 300 C looks just like after ball milling. Due to the form of the investigated samples (powder) and light metal (magnesium) matrix, EDS analysis was not performed, as this measurement would not be reliable and would not provide any useful information. In all cases other than sintering at 500 C, a typical composite structure with unreacted iron and magnesium hydride was observed. Such structures were observed before also by Castro and Gennari [35].
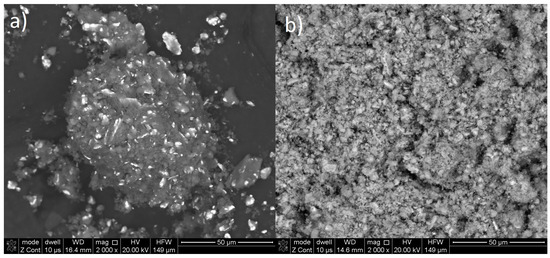
Figure 4.
SEM (backscattered electron (BSE) mode) micrographs of exemplary samples (a) after 30 min of milling and sintering at 300 C and (b) after 2 h of milling and sintering at 500 C.
3.3. Decomposition Properties
DSC analysis of the samples was carried out to observe the temperature range in which hydrogen could be desorbed.
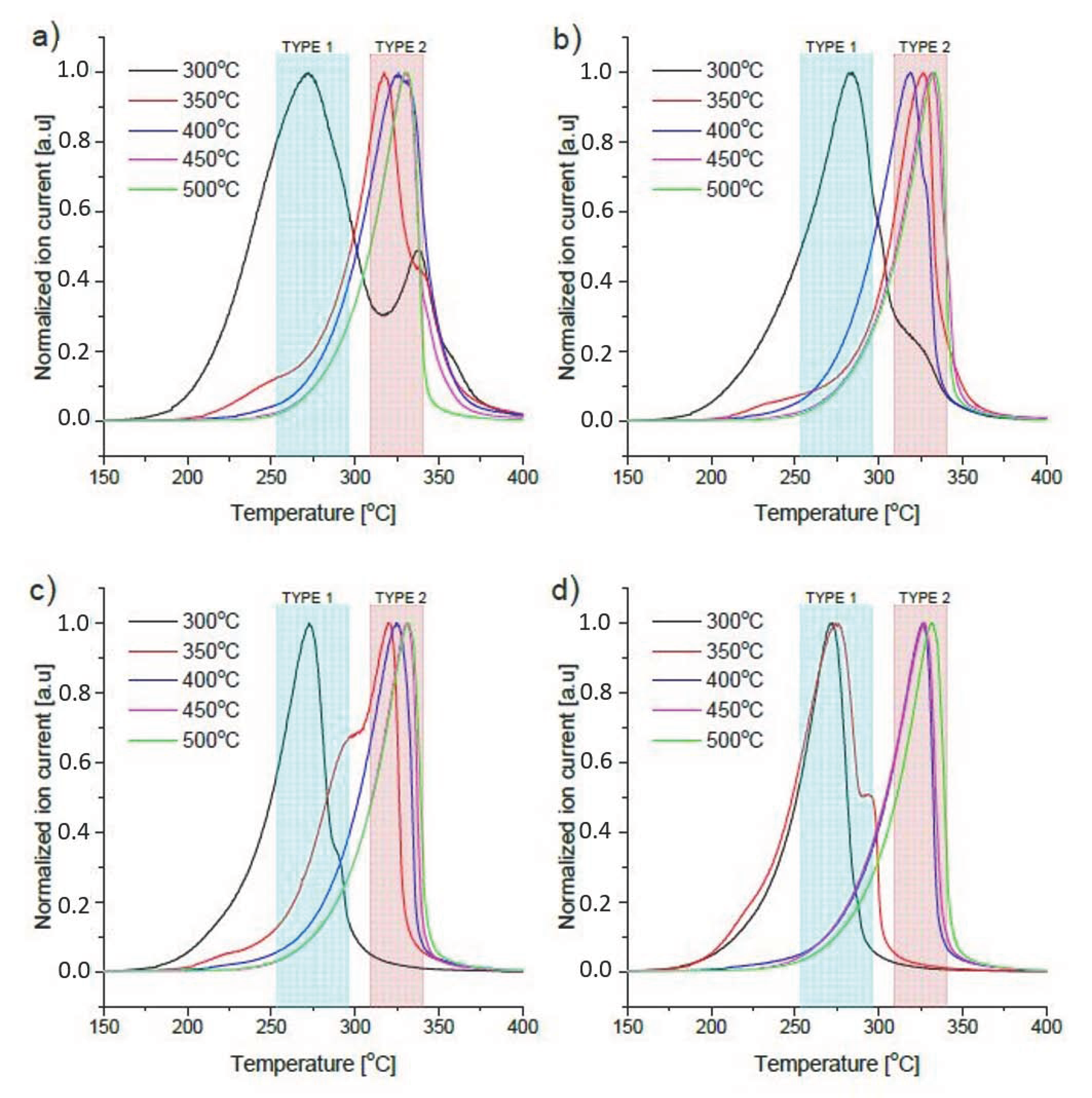
Coupling DSC with a mass spectrometer was necessary to differentiate the thermal effects related to the release of hydrogen from the thermal effects caused by other possible factors. Using this method, the temperature programmed desorption (TPD) spectra of hydrogen were registered and are shown in Figure 5.
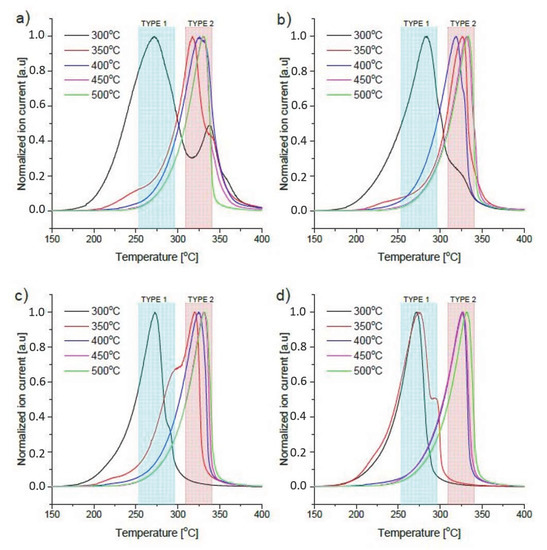
Figure 5.
Thermal desorption spectra (m/z = 2) after milling the MgH2+ Fe mixture for (a) 30 min, (b) 1 h, (c) 2 h and (d) 3 h followed by sintering at different temperatures under hydrogen pressure.
Since DSC and TPD were found to be relatively consistent, only the TPD curves are presented because these spectra contain all the required information and have less background noise and fewer artifacts. Even a short analysis demonstrates that the observed desorption peaks can be divided into two populations. The first peaks have maxima at approximately 270–280 C (marked as Type 1), while the second set has maxima at approximately 325 C (marked as Type 2). In some cases, only a single peak is observed for the sample, while doublets are easily found for others. The explanation for this phenomenon seems to be very simple based on our previous experience with this material. The Type 1 peak, occurring at a lower temperature, is a result of the decomposition of magnesium hydride, milled and very efficiently catalyzed by iron. Iron (as well as other transition metals) is known for its catalytic properties toward magnesium hydride decomposition [36,37,38,39,40].
In the previously-mentioned studies, these metals have generally been added in much smaller amounts, so the hydrogen content in the mixture would remain relatively high, and therefore, their effectiveness was found to be much lower. We have also previously shown that magnesium hydride, in nanoparticle form with high iron content, decomposes at as low as 250 C, and decomposition starts just above 100 C [11]. This hypothesis also corresponds well to the phase content of the obtained materials. As we discussed, basing on the XRD data, in all cases after sintering at 300 C, almost no ternary hydride was observed; so magnesium hydride is the only compound that can decompose. In all four figures (Figure 5a–d), we can see that the sample sintered at 300 C decomposes mainly as a Type 1 peak. For each sample except that milled for 3 h, a strong shoulder or even a peak doublet was observed. This is likely due to the sample inhomogeneity after ball milling. Particles of magnesium hydride, which are uniformly and effectively covered with iron, decompose at lower temperatures, while uncatalyzed particles seem to decompose at much higher temperatures. This effect, which cannot be directly proven, appears obvious as the “shoulders” decrease in intensity with increasing milling time, and the sample milled for 3 h is characterized by a single intense decomposition peak (Figure 5d). Furthermore, the nanostructure effect may be causing this phenomenon; this hypothesis is supported by the fact that the sample milled for 3 h, which demonstrates a single peak for desorption, exhibits a strong shoulder after sintering at 350 C, while still possessing a very low amount of ternary hydride. For samples milled less than 3 h, not all of the sample may be nanostructured or refined to result in decomposition at low temperature. Samples sintered at 350 C and higher generally decompose as “Type 2” peaks, which seems to verify the correlation between the nanostructure and decomposition temperature, as in most cases, the synthesis yield is much lower than 90%, while the desorption peaks seem to be relatively uniform with very similar botonset and maximum temperatures.
3.4. Synthesis Efficiency Map and Conclusions
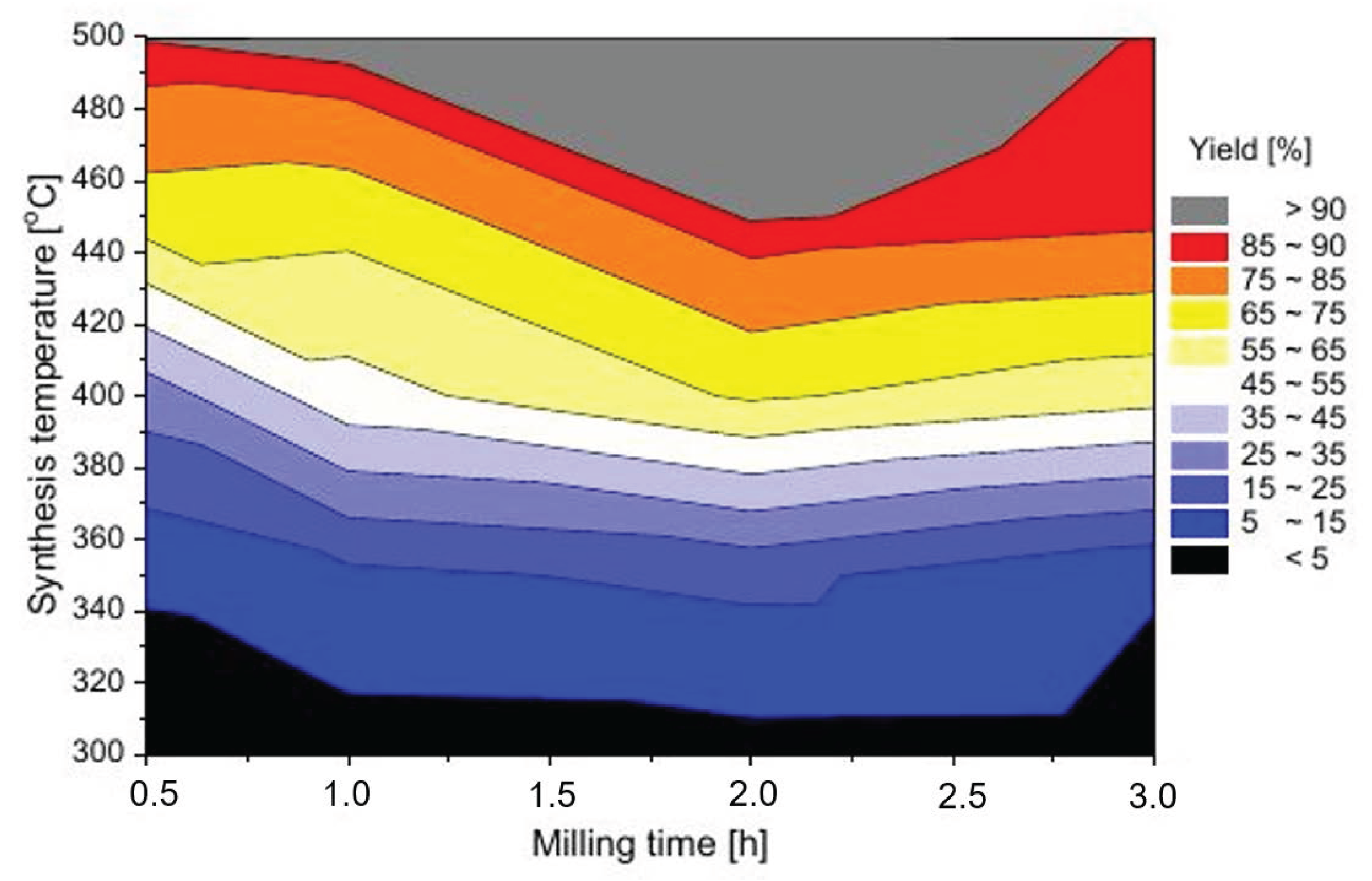
Based on the calculated synthesis yields, an efficiency map was plotted and is shown in Figure 6. The map covers a broad range of the parameters commonly used for the synthesis of ternary hydrides. Shorter milling time may also be within the interest of readers; however, in preliminary experiments, milling for considerably shorter than 30 min results in relatively inhomogeneous mixtures in the experimental setup chosen for this experiment (the vial and ball sizes, as well as the amount of powder). Additionally, considering the processing time (vial loading/unloading), milling for a shorter time does not considerably decrease the total processing time as a whole, and therefore, the yield for shorter times was not considered. The longest time was also experimentally chosen, as a very homogeneous mixture was produced after that length of time, and more importantly, no trace of Mg2FeH6 was seen in the post-milling mixture, which was characteristic of samples milled for longer times. Of course, direct synthesis by ball milling of the ternary hydride is very interesting and sometimes very beneficial. However, without a reactive hydrogen atmosphere, the reaction cannot reach completion, and the yield is insufficient due to a shortage of hydrogen in the reaction. Additionally, introducing another variable, such as the presence of a ternary hydride in the mixture before sintering, might complicate the experiment in such a way that no direct and universal conclusions can be drawn. The map shown in Figure 6 summarizes all the results; however, the visualization of the results is clearer than plotting single or even a series of XRD patterns or TPD curves.
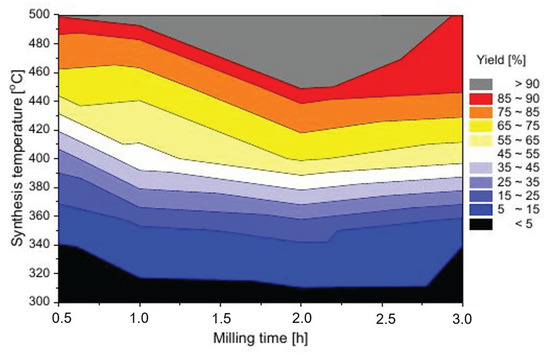
Figure 6.
Mg2FeH6 synthesis efficiency map.
The map clearly shows that the reaction efficiency depends on both the sintering temperature of the powders and the milling time. However, the dependence is very unintuitive. Normally, one would assume that milling for a longer time would improve the homogenization of the mixture, which would lower the diffusion distances and introduce many vacancies and more stress to the particles. The mixture would no longer exist in an equilibrium state, which would enhance the synthesis kinetics, and the synthesis would start at a lower temperature. However, this is not the case. We clearly see (and have observed this in previous experiments) that a specific optimum time can be found for which the reaction can occur at a lower temperature with a higher yield. The direct result of this observation is that milling for too short or too long is not favorable for the reaction and that a higher temperature is required to obtain the same effect. For the chosen geometry of the milling setup, we found that 2 h is a near-optimal time when considering times between 30 min and 3 h. Based on our previous experience with mechanical synthesis [41], this specific time is likely optimal only for that chosen setup. Changing the vial filling factor, ball size, cylinder size or rotational speed of the cylinder may influence the optimal time. The observation we made is relatively clear. However, the reason for this behavior remains unclear. An understanding of the typical kinetics and material characteristics would lead to the conclusion mentioned above in which a longer milling time should enhance the reaction to achieve a more efficient synthesis. However, the problem may not derive from the reaction kinetics, but may be a problem with the properties of the material after milling. It is possible that the material milled for a longer time exhibits a distinctly lower heat conductivity than the one milled for a shorter time. Therefore, samples with a relatively high volume sintered for a relatively short time may not be able to fully transform, not due to the slow reaction kinetics, but due to the lack of temperature equilibration over the sample volume. Measuring the thermal properties may be crucial to solving this puzzle. In our laboratory, we prepared and tested a laboratory setup for measuring the effective thermal conductivity of the hydrides [34] by an oscillating heating method. We proved that the hydride powders possess a thermal conductivity in the range of insulators. However, the problem is that, due to the specific configuration of the experimental setup, there is no possibility of loading the powders under inert atmosphere and that several grams (5–10 g) of powder are required to perform the measurement. Since all manufactured powders are strongly pyrophoric and tend to heat up and burst into flames when exposed to air, we were unable to perform the measurements. This experiment will be conducted in the future if modifications to the apparatus are possible. The only option to confirm this hypothesis is to create an experiment with several longer sintering times, which, with a large number of samples, may be very time consuming. Other hypothesis of lowering the yield of the reaction may be the magnesium oxide formation due to oxygen uptake during milling (diffusion through sealing, “breathing” during milling/pause cycles). For now, the observation remains without a confirmed explanation. The influence of the sintering temperature is much more intuitive. For all the samples, the following statement is true: a higher sintering temperature results in a higher reaction yield. Additionally, for a sintering temperature of 500 C, all the samples were transformed to the ternary hydride with a very high (>90%) yield.
4. Summary
The experimental work performed and presented in this paper resulted in the following conclusions:
- A two-step Mg2FeH6 synthesis method based on high-energy milling and sintering under high temperature and hydrogen pressure was more efficient compared to conventional routes, resulting in a yield up to 97%.
- Both the milling time and sintering temperature of the precursor powders had a decisive influence on the Mg2FeH6 synthesis efficiency.
- Increasing the milling time of the powders up to a certain length improves the process yield. For the experimental setup used, the highest reaction yield was found with a milling time of 2 h.
- Increasing the sintering temperature improves the process efficiency.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available at http://www.mdpi.com/2073-4352/8/2/94/s1.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the Polish Ministry of Science and Higher Education, Ministry of Science and Higher Education-Project Iuventus PLUS IP2012 007272 (the reactor that was used was constructed within the project) and also by The National Center for Research and Development LIDER/482/L-6/14/NCBR/2015 (precise measurements of reaction yield).
Author Contributions
Marek Polanski designed the custom research equipment, planned the experiment and contributed to writing the manuscript, Katarzyna Witek conducted the synthesis, performed XRD analysis and contributed to writing the manuscript. Magdalena Karpowicz performed DSC/TPD experiments and contributed to writing the paper. Krzysztof Karczewski performed SEM observations.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The founding sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; nor in the decision to publish the results.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| DOAJ | Directory of open access journals |
| TLA | Three letter acronym |
| LD | linear dichroism |
References
- Bogdanovic, B.; Reiser, A.; Schlichte, K.; Spliethoff, B.; Tesche, B. Thermodynamics and dynamics of the Mg-Fe-H system and its potential for thermochemical thermal energy storage. J. Alloys Compd. 2002, 345, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbanczyk, R.; Peinecke, K.; Peil, S.; Felderhoff, M. Development of a heat storage demonstration unit on the basis of Mg2FeH6 as heat storage material and molten salt as heat transfer media. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2017, 42, 13818–13826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Entremont, A.; Corgnale, C.; Sulic, M.; Hardy, B.; Zidan, R.; Motyka, T. Modeling of a thermal energy storage system based on coupled metal hydrides (magnesium iron-sodium alanate) for concentrating solar power plants. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2017, 42, 22518–22529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didisheim, J.J.; Zolliker, P.; Yvon, K.; Fischer, P.; Schefer, J.; Gubelmann, M.; Williams, A.F. Dimagnesium iron(II) hydride, Mg2FeH6, containing octahedral FeH64- anions. Inorg. Chem. 1984, 23, 1953–1957. [Google Scholar]
- Raman, S.S.S.; Davidson, D.J.; Bobet, J.L.; Srivastava, O.N. Investigations on the synthesis, structural and microstructural characterizations of Mg-based K2PtCl6 type (Mg2FeH6) hydrogen storage material prepared by mechanical alloying. J. Alloys Compd. 2002, 333, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrich, M.; Ismail, N.; Handstein, A.; Pratt, A.; Gutfleisch, O. Synthesis and decomposition of Mg2FeH6 prepared by reactive milling. Mater. Sci. Eng. B Solid State Mater. Adv. Technol. 2004, 108, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.L.; Varin, R.A.; Morozova, O.; Khomenko, T. Controlled mechano-chemical synthesis of nanostructured ternary complex hydride Mg2FeH6 under low-energy impact mode with and without pre-milling. J. Alloys Compd. 2004, 384, 231–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varin, R.A.; Li, S.; Calka, A.; Wexler, D. Formation and environmental stability of nanocrystalline and amorphous hydrides in the 2Mg-Fe mixture processed by controlled reactive mechanical alloying (CRMA). J. Alloys Compd. 2004, 373, 270–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polanski, M.; Płociński, T.; Kunce, I.; Bystrzycki, J. Dynamic synthesis of ternary Mg2FeH6. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2010, 35, 1257–1266. [Google Scholar]
- Polanski, M.; Nielsen, T.K.; Cerenius, Y.; Bystrzycki, J.; Jensen, T.R. Synthesis and decomposition mechanisms of Mg2FeH6 studied by in-situ synchrotron X-ray diffraction and high-pressure DSC. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2010, 35, 3578–3582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polanski, M.; Bystrzycki, J.; Varin, R.A.; Plocinski, T. Rapid hydrogenation at 30 °C of magnesium (Mg) and iron (Fe) nanocomposite obtained through a decomposition of Mg2FeH6 precursor. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2011, 36, 1059–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polanski, M.; Witek, K.; Nielsen, T.K.; Jaroszewicz, L.; Bystrzycki, J. The influence of the milling time on the yield of Mg2FeH6 from a two-step synthesis conducted in a custom-made reactor. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2013, 38, 2785–2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puszkiel, J.; Gennari, F.; Larochette, P.A.; Karimi, F.; Pistidda, C.; Gosalawit-Utke, R.; Jepsen, J.; Jensen, T.R.; Gundlach, C.; von Colbe, J.B.; et al. Sorption behavior of the MgH2-Mg2FeH6 hydride storage system synthesized by mechanical milling followed by sintering. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2013, 38, 14618–14630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lima, G.F.; Garroni, S.; Baró, M.D.; Suriñach, S.; Kiminami, C.S.; Botta, W.J.; Peres, M.M.; Jorge Junior, A.M. 2Mg-Fe alloys processed by hot-extrusion: Influence of processing temperature and the presence of MgO and MgH2 on hydrogenation sorption properties. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, S460–S463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, G.F.; Triques, M.R.M.; Kiminami, C.S.; Botta, W.J.; Jorge, A.M. Hydrogen storage properties of 2Mg-Fe after the combined processes of hot extrusion and cold rolling. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 586, S409–S412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lima Andreani, G.F.; Miglioli, M.M.; Triques, M.R.M.; Roche, V.; Kiminami, C.S.; Botta, W.J.; Jorge, A.M. Hydrogen storage properties of 2Mg-Fe mixtures processed by hot extrusion at different temperatures. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2017, 42, 11493–11500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorsse, S.; Prakasam, M.; Couillaud, S.; Bouaziz, O.; Bobet, J.L.; Bellanger, P. Light iron and hard magnesium nanocomposites. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 651, 987–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaïdi, W.; Bonnet, J.P.; Zhang, J.; Cuevas, F.; Latroche, M.; Couillaud, S.; Bobet, J.L.; Sougrati, M.T.; Jumas, J.C.; Aymard, L. Reactivity of complex hydrides Mg2FeH6, Mg2CoH5 and Mg2NiH4 with lithium ion: Far from equilibrium electrochemically driven conversion reactions. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2013, 38, 4798–4808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Retuerto, M.; Alonso, J.A.; Martínez, R.; Jiménez-Villacorta, F.; Sánchez-Benítez, J.; Fernández-Díaz, M.T.; Garcia-Ramos, C.A.; Ruskov, T. Neutron Powder Diffraction, X-ray absorption and Mössbauer spectroscopy on Mg2FeH6. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2015, 40, 9306–9313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, A.L.; Dietzel, S.; Li, H.W.; Akiba, E.; Bergemann, N.; Pistidda, C.; Klassen, T.; Dornheim, M. Synthesis of Mg2FeD6 under low pressure conditions for Mg2FeH6 hydrogen storage studies. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2017, 42, 11422–11428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farina, L.; Brutti, S.; Trequattrini, F.; Palumbo, O.; Gatto, S.; Reale, P.; Silvestri, L.; Panero, S.; Paolone, A. An extensive study of the Mg Fe H material obtained by reactive ball milling of MgH2 and Fe in a molar ratio 3:1. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2017, 42, 22333–22341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, J.; Fritzche, H.; Asselli, A.A.C.; Huot, J. In-situ neutron diffraction investigation of Mg2FeH6 dehydrogenation. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2017, 42, 3087–3096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puszkiel, J.A.; Larochette, P.A.; Gennari, F.C. Thermodynamic and kinetic studies of Mg-Fe-H after mechanical milling followed by sintering. J. Alloys Compd. 2008, 463, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puszkiel, J.A.; Larochette, P.A.; Gennari, F.C. Thermodynamic-kinetic characterization of the synthesized Mg2FeH6-MgH2 hydrides mixture. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2008, 33, 3555–3560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puszkiel, J.A.; Larochette, P.A.; Baruj, A.; Meyer, G.; Gennari, F.C. Hydrogen cycling properties of xMg-Fe materials (x: 2, 3 and 15) produced by reactive ball milling. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2016, 41, 1688–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ul Haq, B.; Kanoun, M.B.; Ahmed, R.; Bououdina, M.; Goumri-Said, S. Hybrid functional calculations of potential hydrogen storage material: Complex dimagnesium iron hydride. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2014, 39, 9709–9717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Xiao, X.; Han, L.; Li, Y.; Li, S.; Ge, H.; Wang, Q.; Chen, L. Hydrogen storage performance of 5LiBH4 + Mg2FeH6 composite system. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2012, 37, 6733–6740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmi, H.W.; McGrady, G.S.; Newhouse, R.; Rönnebro, E. Mg2FeH6-LiBH4 and Mg2FeH6-LiNH2 composite materials for hydrogen storage. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2012, 37, 6694–6699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosselin, C.; Deledda, S.; Hauback, B.C.; Huot, J. Effect of synthesis route on the hydrogen storage properties of 2MgH2-Fe compound doped with LiBH4. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 645, S304–S307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zou, J.; Zeng, X.; Ding, W. Hydrogen storage in Mg2Fe(Ni)H6 nanowires synthesized from coarse-grained Mg and nano sized γ-Fe(Ni) precursors. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2016, 41, 14795–14806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lima Andreani, G.F.; Triques, M.R.M.; Kiminami, C.S.; Botta, W.J.; Roche, V.; Jorge, A.M. Characterization of hydrogen storage properties of Mg-Fe-CNT composites prepared by ball milling, hot-extrusion and severe plastic deformation methods. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2016, 41, 23092–23098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.C.; Xiao, X.Z.; Shao, J.; Liu, L.X.; Qin, T.; Chen, L.X. Effects of Ti-based additives on Mg2FeH6 dehydrogenation properties. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China 2016, 26, 791–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadonougbo, J.O.; Jung, J.Y.; Suh, J.Y.; Lee, Y.S.; Shim, J.H.; Cho, Y.W. Low temperature formation of Mg2FeH6 by hydrogenation of ball-milled nano-crystalline powder mixture of Mg and Fe. Mater. Des. 2017, 135, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panas, A.J.; Fikus, B.; Płatek, P.; Kunce, I.; Witek, K.; Kuziora, P.; Olejarczyk, A.; Dyjak, S.; Michalska-Domańska, M.; Jaroszewicz, L.; et al. Pressurised-cell test stand with oscillating heating for investigation heat transfer phenomena in metal hydride beds. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2016, 41, 16974–16983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, F.J.; Gennari, F.C. Effect of the nature of the starting materials on the formation of Mg2FeH6. J. Alloys Compd. 2004, 375, 292–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, G.; Huot, J.; Boily, S.; Van Neste, A.; Schulz, R. Catalytic effect of transition metals on hydrogen sorption in nanocrystalline ball milled MgH2-Tm (Tm = Ti, V, Mn, Fe and Ni) systems. J. Alloys Compd. 1999, 292, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahi, R.R.; Tiwari, A.P.; Shaz, M.A.; Srivastava, O.N. Studies on de/rehydrogenation characteristics of nanocrystalline MgH2 co-catalyzed with Ti, Fe and Ni. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2013, 38, 2778–2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gennari, F.C.; Castro, F.J.; Andrade Gamboa, J.J. Synthesis of Mg2FeH6 by reactive mechanical alloying: Formation and decomposition properties. J. Alloys Compd. 2002, 339, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puszkiel, J.A.; Larochette, R.A.; Gennari, F.C. Hydrogen storage properties of Mg(x)Fe (x: 2, 3 and 15) compounds produced by reactive ball milling. J. Power Sources 2009, 186, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asselli, A.A.C.; Leiva, D.R.; Jorge, A.M.; Ishikawa, T.T.; Botta, W.J. Synthesis and hydrogen sorption properties of Mg2FeH6-MgH0 nanocomposite prepared by reactive milling. J. Alloys Compd. 2012, 536, S250–S254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuziora, P.; Wyszyńska, M.; Polanski, M.; Bystrzycki, J. Why the ball to powder ratio (BPR) is insufficient for describing the mechanical ball milling process. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2014, 39, 9883–9887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).