X-ray Structures of Succinimidyl Halobenzoates
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Synthesis and Chemistry
2.2. X-ray Structure Determination
3. Conclusions
4. Experimental Section
4.1. General
4.2. General Synthesis Procedure
4.2.1. Succinimidyl 4-Fluorobenzoate (SFB, 3a)
4.2.2. Succinimidyl 4-Chlorobenzoate (SClB, 3b)
4.2.3. Succinimidyl 4-Bromobenzoate (SBrB, 3c)
4.2.4. Succinimidyl 2-Iodobenzoate (o-SIB, 3d)
4.2.5. Succinimidyl 4-Iodobenzoate (p-SIB, 3e)
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jacobson, O.; Kiesewetter, D.O.; Chen, X. Fluorine-18 Radiochemistry, Labeling Strategies and Synthetic Routes. Bioconjug. Chem. 2015, 26, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wester, H.J.; Schottelius, M. Fluorine-18 Labeling of Peptides and Proteins. In PET Chemistry The Driving Force in Molecular Imaging; Ernest Schering Research Foundation Workshop 61; Schubiger, P.A., Lehmann, L., Friebe, M., Eds.; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 79–112. [Google Scholar]
- Richter, S.; Wuest, F. 18F-Labeled Peptides: The Future Is Bright. Molecules 2014, 19, 20536–20556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olberg, D.E.; Hjuelsten, O.K. Labeling strategies of peptides with 18F for positron emission tomography. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2010, 10, 1669–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okarvi, S.M. Recent progress in fluorine-18 labelled peptide radiopharmaceuticals. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. 2001, 28, 929–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, G.W. The use of activated esters in peptide synthesis. Metabolism 1964, 13, 1026–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalutsky, M.R.; Narula, A.S. A method for the radiohalogenation of proteins resulting in decreased thyroid uptake of radioiodine. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 1987, 38, 1051–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, P.K.; Archer, G.E.; Bigner, D.D.; Zalutsky, M.R. Synthesis of radioiodinated N-succinimidyl iodobenzoate: Optimization for use in antibody labelling. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 1989, 40, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koziorowski, J.; Henssen, C.; Weinreich, R. A new convenient route to radioiodinated N-succinimidyl 3- and 4-iodobenzoate, two reagents for radioiodination of proteins. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 1998, 49, 955–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidyanathan, G.; Zalutsky, M.R. Preparation of N-succinimidyl 3-[*I]iodobenzoate: An agent for the indirect radioiodination of proteins. Nat. Prot. 2006, 1, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glaser, M.; Collingridge, D.R.; Aboagye, E.; Bouchier-Hayes, L.; Brown, D.J.; Hutchinson, O.C.; Martin, S.; Price, P.; Luthra, S.K.; Brady, F. Preparation of [124I]IBA-annexin-V as a potential pet probe for apoptosis. J. Label. Compd. Radiopharm. 2001, 44, S336–S338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourgeois, M.; Guerard, F.; Alliot, C.; Mougin-Degraef, M.; Rajerison, H.; Remaud-Le Saec, P.; Gestin, J.-F.; Davodeau, F.; Cherel, M.; Barbet, J.; et al. Feasibility of the radioastatination of a monoclonal antibody with astatine-211 purified by wet extraction. J. Label. Compd. Radiopharm. 2008, 51, 379–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gifford, A.N.; Kuschel, S.; Shea, C.; Fowler, J.S. Polymer-Supported Organotin Reagent for Prosthetic Group Labeling of Biological Macromolecules with Radioiodine. Bioconjug. Chem. 2011, 22, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajerison, H.; Faye, D.; Roumesy, A.; Louaisil, N.; Boeda, F.; Faivre-Chauvet, A.; Gestin, J.-F.; Legoupy, S. Ionic liquid supported organotin reagents to prepare molecular imaging and therapy agents. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2016, 14, 2121–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlatopolskiy, B.D.; Morgenroth, A.; Urusova, E.A.; Dinger, C.; Kull, T.; Pape, M.; Glatting, G.; Reske, S.N. Towards to hENT1-nucleoside transporter selective imaging agents. Synthesis and in vitro evaluation of the radiolabeled SAENTA analogues. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 5151–5154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossouw, D.D. Radioiodine labelling of a small chemotactic peptide, utilizing two different prosthetic groups: A comparative study. J. Label. Compd. Radiopharm. 2008, 51, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dissoki, S.; Hagooly, A.; Elmachily, S.; Mishani, E. Labeling approaches for the GE11 peptide, an epidermal growth factor receptor biomarker. J. Label. Compd. Radiopharm. 2011, 54, 693–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Byun, Y.; Barinka, C.; Pullambhatla, M.; Bhang, H.-E.C.; Fox, J.J.; Lubkowski, J.; Mease, R.C.; Pomper, M.G. Bioisosterism of urea-based GCPII inhibitors: Synthesis and structure–activity relationship studies. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 392–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Mease, R.C.; Pullambhatla, M.; Lisok, A.; Chen, Y.; Foss, C.A.; Wang, Y.; Shallal, H.; Edelman, H.; Hoye, A.T.; et al. [18F]Fluorobenzoyllysinepentanedioic Acid Carbamates: New Scaffolds for Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Imaging of Prostate-Specific Membrane Antigen (PSMA). J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 206–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Medina, C.; Patel, N.; Robson, M.; Badar, A.; Lythgoe, M.F.; Årstad, E. Evaluation of a 125I-labelled benzazepinone derived voltage-gated sodium channel blocker for imaging with SPECT. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2012, 10, 9474–9480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riss, P.J.; Lu, S.; Telu, S.; Aigbirhio, F.I.; Pike, V.W. CuI-Catalyzed 11C Carboxylation of Boronic Acid Esters: A Rapid and Convenient Entry to 11C-Labeled Carboxylic Acids, Esters, and Amides. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 2698–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yngve, U.; Hedberg, E.; Tolmachev, V.; Långström, B. Synthesis of N-succinimidyl-4-[76Br]bromobenzoate and its use in conjugation to proteins and 5’-modified oligonucleotides. J. Label. Compd. Radiopharm. 1997, 40, 120–121. [Google Scholar]
- Yngve, U.; Hedberg, E.; Lövqvist, A.; Tolmachev, V.; Långström, B. Synthesis of N-Succinimidyl 4-[76Br]Bromobenzoate and its Use in Conjugation Labelling of Macromolecules. Acta Chem. Scand. 1999, 53, 508–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäding, P.; Füchtner, F.; Wüst, F. Module-assisted synthesis of the bifunctional labelling agent N-succinimidyl 4-[18F]fluorobenzoate ([18F]SFB). Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2005, 63, 329–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X. Synthesis of N-succinimidyl 4-[18F]fluorobenzoate ([18F]SFB). In Radiochemical Syntheses, Radiopharmaceuticals for Positron Emission Tomography; Scott, P.J.H., Hockley, B.G., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 81–86. [Google Scholar]
- Carroll, M.; Yan, R.; Aigbirhio, F.; Soloviev, D.; Brichard, L. Single-step synthesis of N-succinimidyl-4-[18F]fluorobenzoate. J. Nucl. Med. 2008, 49, 298. [Google Scholar]
- Chun, J.-H.; Pike, V.W. Single-step syntheses of no-carrier-added functionalized [18F]fluoroarenes as labeling synthons from diaryliodonium salts. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2013, 11, 6300–6306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.; Hooker, J.M.; Ritter, T. Nickel-Mediated Oxidative Fluorination for PET with Aqueous [18F] Fluoride. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 17456–17458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vangveravong, S.; Xu, J.; Zeng, C.; Mach, R.H. Synthesis of N-substituted 9-azabicyclo[3.3.1]nonan-3α-yl carbamate analogs as σ2 receptor ligands. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2006, 14, 6988–6997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wu, W.; McNeil, A.J. Detecting a peroxide-based explosive via molecular gelation. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 7310–7312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Blacker, M.; Valliant, J.F. Preparation and Evaluation of Fluorine-18-Labeled Insulin as a Molecular Imaging Probe for Studying Insulin Receptor Expression in Tumors. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 3678–3686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matusiak, N.; Castelli, R.; Tuin, A.W.; Overkleeft, H.S.; Wisastra, R.; Dekker, F.J.; Prly, L.M.; Bischoff, R.P.M.; van Waarde, A.; Dierckx, R.A.J.O.; et al. A dual inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinases and a disintegrin and metalloproteinases. [18F]FB-ML5, as a molecular probe for non-invasive MMP/ADAM-targeted imaging. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2015, 23, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotgiu, G.; Galeotti, M.; Samori, C.; Bongini, A.; Mazzanti, A. Push–Pull Amino Succinimidyl Ester Thiophene-Based Fluorescent Dyes: Synthesis and Optical Characterization. Chem. Eur. J. 2011, 17, 7947–7952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Liu, R.; Xu, Q.; Liang, X. N-Hydroxysuccinimide-promoted Oxidation of Primary Alcohols and Aldehydes to Form Active Esters with Hypervalent(III) Iodine. Chem. Lett. 2006, 35, 566–567. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Yu, Q.-Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, S.; Chen, S.-Y.; Yu, X.-Q. Iodide-catalyzed amide synthesis from alcohols and amines. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 21306–21310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azarian, V.; Gangloff, A.; Seimbille, Y.; Delaloye, S.; Czernin, J.; Phelps, M.E.; Silverman, D.H.S. Synthesis and liposome encapsulation of a novel 18F-conjugate of ω-conotoxin GVIA for the potential imaging of N-type Ca2+ channels in the brain by positron emission tomography. J. Label. Compd. Radiopharm. 2006, 49, 269–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Almeida, A.M.; Andersen, T.L.; Lindhardt, A.T.; de Almeida, M.V.; Skrydstrup, T. General Method for the Preparation of Active Esters by Palladium-Catalyzed Alkoxycarbonylation of Aryl Bromides. J. Org. Chem. 2015, 80, 1920–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barr, A.; Tnta, M.-L.; Alix, F.; Gembus, V.; Papamical, C.; Levacher, V. Palladium-Catalyzed Carbonylation of (Hetero)Aryl, Alkenyl and Allyl Halides by Means of N-Hydroxysuccinimidyl Formate as CO Surrogate. J. Org. Chem. 2015, 80, 6537–6544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinda, M.; Bose, C.; Ghosh, T.; Maity, S. Cross dehydrogenative coupling (CDC) of aldehydes with N-hydroxyimides by visible light photoredox catalysis. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 44928–44932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldrick, G.M. A short history of SHELX. Acta Cryst. 2008, A64, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheldrick, G.M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Cryst. 2015, C71, 3–8. [Google Scholar]
- Sheldrick, G.M. SHELXL 2014/1; University of Göttingen: Göttingen, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Bruker AXS Inc. APEX-II (ver. 2008.1-0), SAINT (ver. 7.51A) and SADABS (ver. 2007/4); Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]

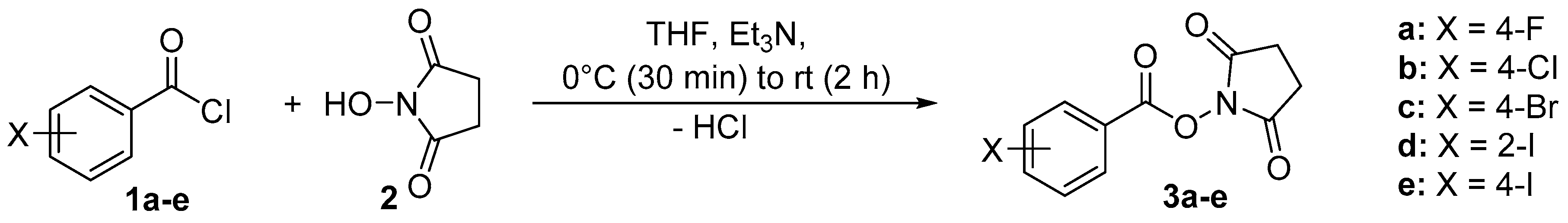
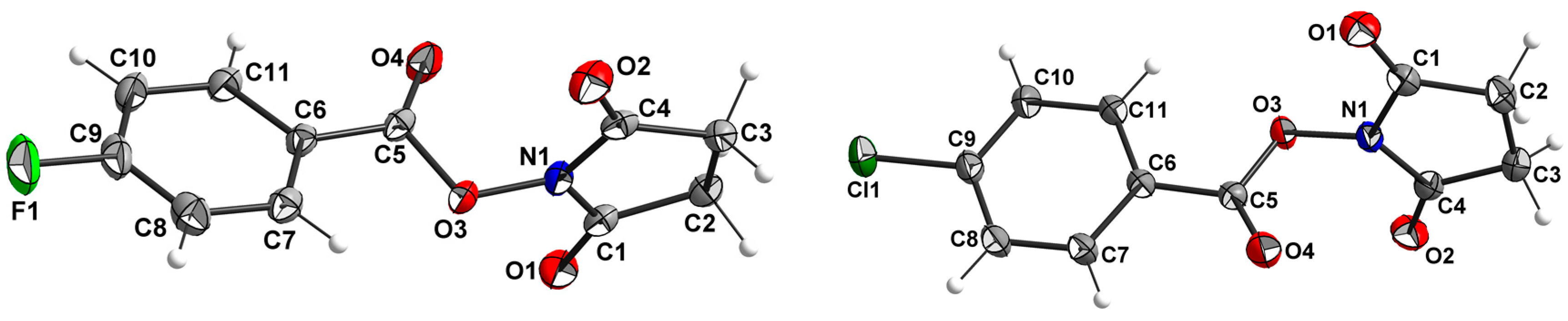

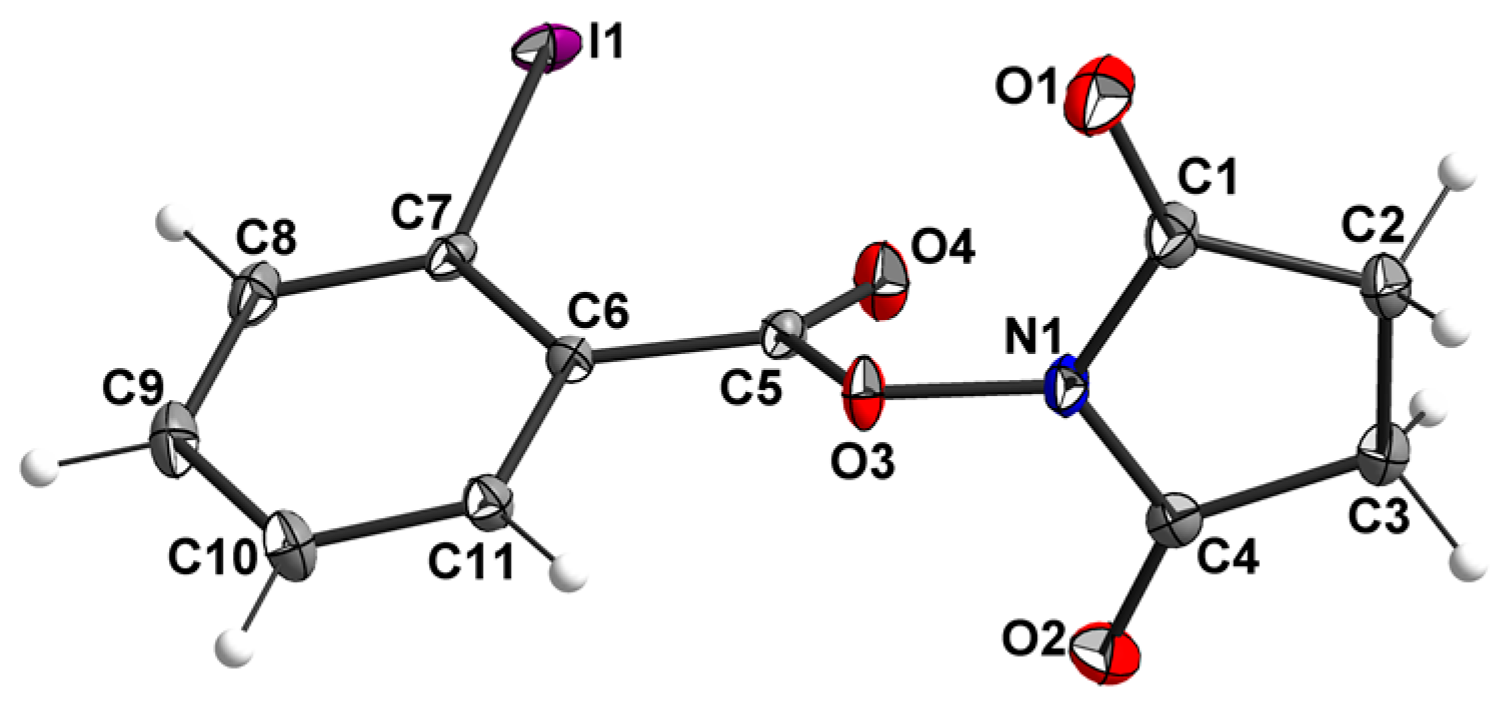
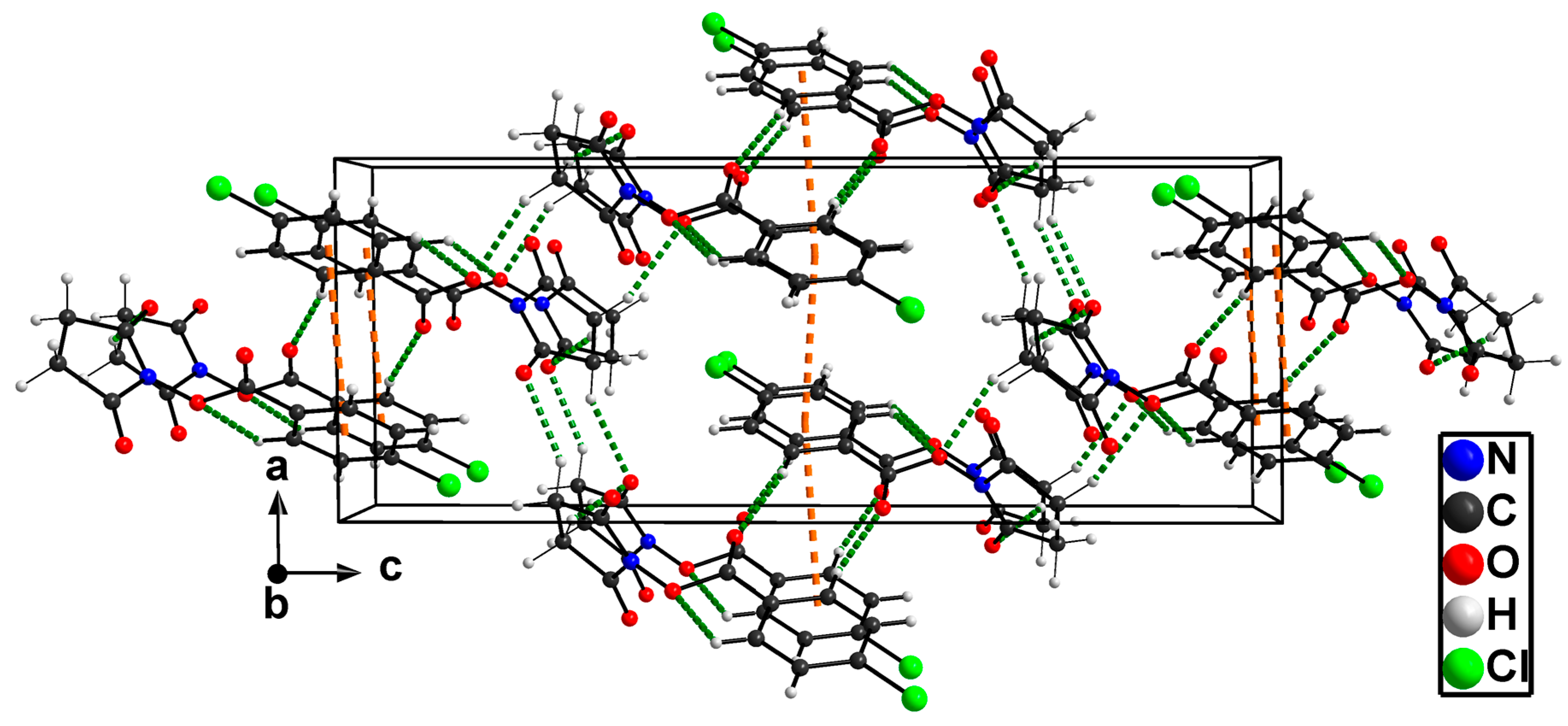
| Parameter | 3a | 3b | 3c | 3d | 3e |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Formula | C11H8FNO4 | C11H8ClNO4 | C11H8BrNO4 | C11H8INO4 | C11H8INO4 |
| Formula weight (g·mol−1) | 237.18 | 253.63 | 298.09 | 345.08 | 345.08 |
| Temperature (K) | 123 | ||||
| Wavelength (Å) | 0.71073 | ||||
| Crystal system | monoclinic | monoclinic | monoclinic | monoclinic | orthorhombic |
| Space group | P21/c | P21/n | P21/n | P21/n | Pbca |
| Unit cell dimensions | |||||
| a (Å) | 11.6331(6) | 8.7157(7) | 8.554(2) | 8.566(3) | 12.1900(3) |
| b (Å) | 5.4971(3) | 5.7238(5) | 5.800(1) | 5.817(2) | 8.5246(2) |
| c (Å) | 17.041(1) | 22.598(2) | 22.844(6) | 23.374(8) | 22.0618(6) |
| β (°) | 103.992(2) | 90.470(4) | 92.20(1) | 93.27(2) | 90.00 |
| Volume (Å3) | 1057.4(1) | 1127.3(2) | 1132.5(5) | 1162.8(7) | 2292.6(1) |
| Z | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 8 |
| Density (calcd.) (g·cm−3) | 1.490 | 1.494 | 1.748 | 1.971 | 2.000 |
| Absorpt. coeff. (mm−1) | 0.12 | 0.34 | 3.64 | 2.76 | 2.76 |
| F(000) | 488 | 520 | 592 | 664 | 1328 |
| Crystal size (mm3) | 0.05 × 0.05 × 0.01 | 0.22 × 0.11 × 0.06 | 0.62 × 0.40 × 0.21 | 0.15 × 0.15 × 0.10 | |
| Refinement method | Full matrix—least-squares | ||||
| Data/restraints/param. | 2373/0/155 | 5553/0/154 | 9377/0/155 | 10986/0/155 | 4166/0/155 |
| Measured reflections | 19468 | 25796 | 67515 | 100672 | 38241 |
| 2 θmax (°) | 27.3 | 36.6 | 45.4 | 47.9 | 33.1 |
| Rint | 0.124 | 0.042 | 0.106 | 0.034 | 0.063 |
| GoF on F2 | 1.11 | 1.05 | 1.05 | 1.13 | 1.16 |
| R1 [I > 2σ(I)] | 0.054 | 0.044 | 0.050 | 0.030 | 0.025 |
| wR2 (all data) | 0.133 | 0.128 | 0.144 | 0.067 | 0.064 |
| Larg. diff. peak/hole (e·Å3) | 0.28/−0.22 | 0.64/−0.66 | 1.88/−1.65 | 2.82/−2.34 | 0.76/−1.49 |
| Distance or Angle | 3a | 3b | 3c | 3d | 3e |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C=O carbonyl [Å] | 1.189(3) | 1.187(1) | 1.191(1) | 1.196(2) | 1.195(1) |
| C–O carbonyl [Å] | 1.389(2) | 1.392(1) | 1.398(1) | 1.395(2) | 1.400(1) |
| C=O succin. (av.) [Å] | 1.200 | 1.206 | 1.209 | 1.202 | 1.208 |
| C–Hal [Å] | 1.356(3) | 1.737(1) | 1.893(1) | 2.094(1) | 2.095(1) |
| ∢ mean plane [°] (halobenzoyl/succinimidyl residues) | 76.2 | 72.9 | 70.7 | 80.5 | 71.6 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mamat, C.; Weiß, D.H.; Köckerling, M. X-ray Structures of Succinimidyl Halobenzoates. Crystals 2017, 7, 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst7030090
Mamat C, Weiß DH, Köckerling M. X-ray Structures of Succinimidyl Halobenzoates. Crystals. 2017; 7(3):90. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst7030090
Chicago/Turabian StyleMamat, Constantin, Daniel Holger Weiß, and Martin Köckerling. 2017. "X-ray Structures of Succinimidyl Halobenzoates" Crystals 7, no. 3: 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst7030090
APA StyleMamat, C., Weiß, D. H., & Köckerling, M. (2017). X-ray Structures of Succinimidyl Halobenzoates. Crystals, 7(3), 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst7030090








