Abstract
Magnesium-based biomaterials have emerged as highly promising candidates in the realm of biomedical engineering due to certain unique properties. However, their widespread application has been limited by a number of challenges, such as insufficient mechanical strength and rapid degradation rates. This study sought to advance the development of high-performance magnesium alloys by examining the microstructural evolution and associated strengthening mechanisms of Mg-Zn alloys modified with varying Nd contents. Comprehensive characterization techniques—including optical microscopy, XRD, and SEM/EDS—were employed to explain the influence of Nd additions on the microstructures. Mechanical performance was assessed through hardness testing, the RFDA method for elastic modulus, and tensile testing. The microstructural analysis of the as-cast Mg-Zn-Nd alloys revealed a complex phase composition comprising dendritic α-Mg, Mg41Nd5, and a Mg3Nd binary phase enriched with rare earth elements. Notably, increasing the Nd content from 0.5% to 5% by weight resulted in a significant enhancement of hardness, reaching 59 HV compared to 42 HV in the base alloy. The tensile strength increased significantly from 62.9 MPa in the Mg-2.5Zn-0.5Nd alloy to 186.8 MPa in the Mg-2.5Zn-5Nd alloy. The elastic modulus values across all investigated alloys remained consistently comparable, which is expected as the elastic modulus is primarily determined by atomic bonding and is not significantly affected by alloying additions. These findings underscore the potential of Nd-alloyed Mg-Zn systems as viable, mechanically robust alternatives for next-generation biodegradable orthopedic implants.
1. Introduction
The exploration of biodegradable materials for biomedical applications has intensified significantly over the past few decades, with magnesium (Mg) alloys emerging at the forefront of research due to their unique combination of biocompatibility, biodegradability, and mechanical properties that closely match those of human cortical bone. As a metallic material capable of naturally dissolving in physiological environments, magnesium presents an exciting alternative to traditional permanent implants such as titanium and stainless steel, which can cause stress shielding and require secondary surgical removal [1,2]. The mechanical properties of magnesium alloys are particularly advantageous for load-bearing biomedical applications. Its Young’s modulus (~45 GPa) is much closer to that of natural bone (~20–30 GPa) than that of titanium alloys (~110 GPa), minimizing the likelihood of stress shielding—a major limitation of permanent metallic implants [3]. Furthermore, Mg’s inherent biodegradability eliminates the need for implant removal surgeries, reducing patient risk and healthcare costs [4]. Although biodegradable magnesium alloys possess several advantages, achieving a balanced combination of high mechanical strength and enhanced corrosion resistance continues to pose a substantial scientific and engineering challenge [5].
Magnesium alloys are mainly grouped into two main categories based on their composition: those without rare earth (RE) elements, known as RE-free alloys, and those that incorporate RE elements. Among the RE-free group, Mg-Al-based and Mg-Zn-based systems are the most prevalent, with AZ (Mg-Al-Zn) and AM (Mg-Al-Mn) series alloys being widely studied and applied [6]. Historically, Mg-Zn alloys have faced challenges related to limited aging hardenability and strength. However, recent findings suggest that introducing neodymium (Nd) can refine the microstructure and significantly enhance their mechanical characteristics [7].
While RE-free alloys dominate current applications, the inclusion of rare earth elements has shown remarkable potential for advancing material performance. Often regarded as essential enhancers in alloy development, RE elements contribute to a variety of improvements, including higher mechanical strength, better resistance to corrosion, and more stable degradation behavior. Additionally, they aid in purifying the melt, refining the solidification structure, reducing deformation-related texture, and enhancing precipitation and diffusion during processing. These benefits highlight the growing importance of RE elements in the ongoing development of high-performance, biodegradable magnesium alloys [8].
Zinc (Zn) plays a vital role as an essential micronutrient, supporting numerous metabolic functions within the human body [9]. In the context of magnesium (Mg) alloy development, Zn has garnered significant attention as a promising alloying element due to its ability to enhance both mechanical strength and corrosion resistance. Numerous studies have consistently shown that incorporating Zn into Mg alloys contributes positively to their structural integrity and degradation behavior [10]. Notably, research by Cai et al. [11] suggests that maintaining Zn content within the range of 1–5% offers an optimal balance, significantly improving corrosion resistance in Mg-Zn systems. Complementary findings by Zhang et al. [12] further highlight Zn’s potential to improve mechanical properties and corrosion performance while maintaining favorable biocompatibility, underscoring its value in the design of next-generation biodegradable materials. Nevertheless, while increasing Zn content beyond 5 wt.%—up to approximately 7 wt.%—can further influence the alloy’s microstructure, it may also promote the formation of secondary phases. These intermetallic compounds, although potentially beneficial in certain contexts, can introduce localized galvanic interactions with the magnesium matrix. Such interactions have been associated with intensified localized corrosion, which may slightly compromise the overall corrosion resistance. However, with careful compositional tuning and microstructural control, these effects can be mitigated, offering valuable insights for optimizing Zn-containing Mg alloys [13,14].
Neodymium (Nd), characterized by its relatively low solid solubility in magnesium (3.6 wt.% at 549 °C) [15], presents a promising rare earth (RE) alloying element. This limited solubility enables the formation of beneficial secondary phase particles even at modest concentrations, effectively enhancing the alloy’s mechanical performance at elevated temperatures [16,17]. Moreover, neodymium (Nd) is considered biocompatible and non-toxic, making the Mg-Nd-Zn alloy system a compelling candidate for the development of bioabsorbable implant materials currently under active investigation [18]. Moreover, the trace addition of Zn to Mg-Nd alloy would further increase its hardness properties [19].
Previous studies [20,21] have demonstrated that both zinc (Zn) and rare earth (RE) elements play a significant role in shaping the microstructure, phase formation, and mechanical behavior of as-cast Mg-Zn-based alloys. Increasing the Zn content from 0.5 wt.% to 3 wt.% in binary Mg-Zn systems has been shown to significantly refine grain size—from approximately 600–800 μm to 150–200 μm—resulting in an enhancement of tensile strength by over 20%. Although this grain refinement is accompanied by a reduction in ductility up to 30%, strength improvements are notable for structural applications. It is also observed that grain refinement effects tend to plateau beyond 7 wt.% Zn, where further additions primarily lead to the formation of coarser secondary phases rather than additional microstructural refinement [11]. These larger intermetallic particles may increase susceptibility to galvanic corrosion, thereby accelerating the biodegradation process [22]. Consequently, maintaining Zn content within the 2–5 wt.% range appears to offer an optimal balance between mechanical strength and corrosion resistance, particularly for Mg-Zn-based alloys intended for biomedical implant applications [23]. Thus, fixed 2.5 wt.% Zn was used to avoid detrimental effects in current alloys.
Moreover, increasing scientific interest has been devoted to Mg-Zn-Nd alloys due to their advantageous mechanical performance and their suitability for applications in the biomedical field. Wu et al. reported that in extruded Mg-1Zn-xNd (x = 0.5, 1, 2, and 3 wt.%) alloys, tensile strength initially improved with rising Nd content—reaching values between 160 and 240 MPa—before experiencing a slight decline. The predominant secondary phase was identified as Mg12Nd [24]. Similarly, Xu et al. investigated Mg-2Zn-xNd (x = 1, 2, 3, and 4 wt.%) alloys and observed a consistent enhancement in mechanical performance with increasing Nd concentration, with Mg12Nd again emerging as the dominant phase [25]. Complementary studies by Javaid et al. explored the solidification behavior of Mg-4Zn-xNd alloys, revealing the presence of Mg12Zn13, Mg51Zn20, and BCC-MgNdZn phases [26]. Additionally, Gao et al. identified MgZn2 and T2 phases as key intermediates in the Mg-1.84Zn-0.52Nd alloy system [27].
Despite these advancements, investigations specifically addressing the influence of Nd content below 5 wt.% on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg-Zn alloys remain limited. To bridge this gap, the present study focuses on Mg-2.5Zn-xNd alloys (x = 0.5, 2, and 5 wt.%), with the aim of designing a composition that offers a well-balanced combination of strength and structural integrity for advanced engineering and biomedical applications.
2. Materials and Methods
To systematically investigate the impact of various alloying elements and their concentrations on the mechanical properties of magnesium alloys, three series of ternary Mg-based alloys (Mg-2.5Zn and 0.5, 2, 5% wt. Nd) were prepared. Pure magnesium served as the reference material. The alloys were synthesized using high-purity raw materials, including commercial pure Mg (Magnesium Electron, Manchester, UK, 99.94%), Nd (Grirem, Beijing, China, 99.5%), and Zn (99.5%). Each experimental batch comprised 15 kg of material, including magnesium and the designated alloying elements.
The fabrication process was carefully controlled to ensure consistency and homogeneity. Initially, pure magnesium was melted at 750 °C under a protective atmosphere of argon with 2% SF6. Once fully molten, the alloying elements (Zn and Nd) were gradually introduced into the melt. To promote uniform distribution, the mixture was mechanically stirred at 200 rpm for 20 min. The homogenized melt was then poured into a preheated permanent steel mold (1.0044 EU Grade) maintained at 700 °C, with internal dimensions of 70 mm in diameter and 220 mm in height and a wall thickness of 5 mm.
To further improve casting quality, the filled mold was transferred to a tubular furnace and held at 670 °C for 5 min under the same protective gas atmosphere. This holding step facilitated the settling of inclusions. Subsequently, the mold was lowered into cooling water at a controlled rate of 10 mm/s to solidify the alloy under near-ideal conditions. The chemical compositions of the resulting alloys were precisely characterized using spark optical emission spectrometry (Spectrolab M9, Ametek-Spectro, Kleve, Germany), atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS, 240FS AA, Agilent, CA, USA), and X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy (M4 Tornado, Bruker, Bremen, Germany), ensuring reliable and reproducible results and shown Table 1.

Table 1.
Actual chemical compositions of experimental alloys (wt.%).
To ensure comprehensive microstructural analysis, three specimens from each alloy were meticulously prepared for optical microscopy (OM). Samples were embedded in a cold-curing plastic resin and sequentially ground using SiC emery paper up to 2500 grit. Polishing was carried out using a suspension containing 1 μm diamond particles followed by final polishing with 0.25 μm colloidal silica (OPS, 0.05 μm) to achieve a mirror-like finish. The polished surfaces were then etched using a standardized solution composed of 30 mL deionized water, 140 mL ethanol, 7 mL glacial acetic acid, and 8 g picric acid. Optical microstructural characterization was conducted using an Olympus GX53 light microscope (Olympus Corporation, Tokyo, Japan) equipped with a digital imaging system. Grain size was determined by using the linear intercept method at 20× magnification, with a minimum of five test lines applied to each micrograph. The average grain size was calculated in accordance with ASTM E112-13 [28] using AnalysisPro V1.3 software (Olympus Soft Imaging Solution, Tokyo, Japan), ensuring statistical reliability and measurement consistency.
In parallel, three additional specimens from each alloy were prepared for scanning electron microscopy (SEM) (TESCAN Group a.s., Brno, Czech Republic). These samples were similarly ground and polished and subsequently coated with a conductive carbon binder (N650 Planocarbon) to minimize charging effects during imaging. High-resolution SEM observations were carried out using a TESCAN VEGA3-SB system (V2023) operated at an acceleration voltage of 15 kV and equipped with energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) (Oxford Instruments, Oxfordshire, UK) for compositional analysis. Additionally, the images of the fractured surfaces after the tensile test were also characterized by SEM.
To identify and characterize the secondary phases present in the alloys, X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis was performed using a Bruker D8 ADVANCE diffractometer (Bruker AXS GmbH, Karlsruhe, Germany) with DIFFRAC.EVA software (V5.2). The instrument utilized Cu Kα radiation (λ = 0.15406 nm) at an operating voltage of 40 kV and current of 40 mA. Diffraction data were collected over a 2θ range of 20° to 75°, with a fine step size of 0.02° and a measurement time of 0.5 s per step, providing high-resolution phase identification. For qualitative analysis, the bulk samples were mechanically ground with SiC abrasive paper from 800 grit to 2500 grit.
Microhardness evaluations were performed using a universal Emcotest microhardness tester (EMCO-Test Prüfmaschinen GmbH, Salzburg, Austria) under a load of 5 kg with a dwell time of 30 s. For each alloy, three specimens were tested, with ten indentations per specimen to ensure statistical reliability and repeatability. The mechanical behavior under tensile loading was assessed using a universal testing machine (Zwick Z050, Zwick GmbH & Co. KG, Ulm, Germany) operating at a controlled strain rate of 0.001 s−1. The tensile specimens were precisely machined with a gauge diameter of 5 mm, a gauge length of 30 mm, and an 8 mm threaded head to ensure consistent alignment and load application as seen in Figure 1. For each alloy composition, mechanical testing was conducted on five specimens to ensure statistical robustness and representativeness of the measured properties.
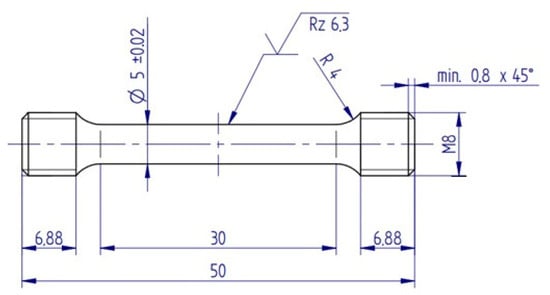
Figure 1.
Dimensions and shape of tensile test sample (unit: mm).
The elastic moduli of the investigated magnesium alloys were evaluated using the impulse excitation technique, facilitated by a IMCE resonant frequency and damping analyzer (IMCE NV, Genk, Belgium), with specimens precisely machined to dimensions of 5 × 10 × 145 mm3, in full compliance with the ASTM E756–05 standard. To enhance the reliability and reproducibility of the data, each specimen was subjected to ten independent measurements, and the averaged values were reported to ensure statistical robustness.
3. Results
3.1. Microstructure Characterizations
Figure 2 displays the optical micrographs of the as-cast Mg-2.5Zn-xNd alloys with varying Nd content. Contrary to the expected grain refinement behavior typically induced by rare earth (RE) elements such as Nd, the micrographs reveal that the average grain size increases with increasing Nd content. This trend is quantitatively confirmed in Table 2, where the grain sizes of the alloys are measured as 153 µm, 167 µm, and 215 µm, respectively.
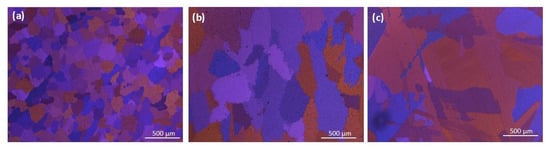
Figure 2.
Optical microstructure of as-cast (a) Mg-2.5Zn-0.5Nd; (b) Mg-2.5Zn-2Nd; and (c) Mg-2.5Zn-5Nd.

Table 2.
Grain sizes of investigated alloys (µm).
Such grain-coarsening behavior after Nd addition is unexpected since numerous studies have demonstrated the grain-refining effect of Nd and other RE elements in Mg alloys through solute drag, increased nucleation sites, and the formation of thermally stable intermetallic compounds [29,30,31]. However, several factors may explain this anomaly. Firstly, the grain refinement efficacy of Nd is known to be highly dependent on its concentration, cooling rate, and interaction with other alloying elements. Javaid et al. [26] reported that excessive Nd content may shift the solidification pathway, leading to the formation of coarse, eutectic intermetallics at grain boundaries that inhibit nucleation rather than promoting it. Furthermore, in diluted Mg-Zn-Nd systems, although both Zn and Nd initially exist in the melt and can contribute to solute drag, their strong affinity leads to the early formation of intermetallic phases such as Mg3Nd, Mg41Nd5, and Mg12Nd during solidification. This reduces their effective availability in the matrix and may thus diminish the overall solute drag effect, particularly at higher Nd concentrations [32].
Moreover, Gavras et al. [33] showed that at higher Nd contents, the grain boundary intermetallics can form as continuous networks, reducing the constitutional undercooling needed for efficient grain refinement. This effect is evident in Figure 2b,c, where coarse, blocky grains dominate the microstructure. In the present study, increased Nd content resulted in grain coarsening, attributed to complex solidification dynamics and the formation of intermetallic phases; nevertheless, mechanical strengthening was achieved predominantly through precipitation hardening mechanisms.
Figure 3 presents the scanning electron microscopy (SEM) micrographs of as-cast Mg-2.5Zn-xNd (x = 0.5, 2, and 5 wt.%) alloys. As the neodymium content increases, a clear evolution in the morphology and volume fraction of secondary phases is observed. The Mg-2.5Zn-0.5Nd alloy (Figure 3a) reveals a low density of fine, scattered second-phase particles, predominantly along dendrites. In contrast, the Mg-2.5Zn-2Nd alloy (Figure 3b) exhibits an increase in both the size and continuity of these intermetallics. At the highest Nd content, i.e., 5 wt.% (Figure 3c), a dense, interconnected eutectic-like structure emerges, forming a quasi-continuous network of secondary phases.
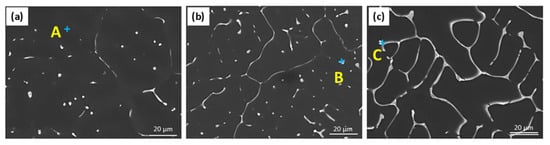
Figure 3.
SEM micrographs of as-cast (a) Mg-2.5Zn-0.5Nd; (b) Mg-2.5Zn-2Nd; and (c) Mg-2.5Zn-5Nd.
Table 3 shows the SEM-EDS results in the investigated alloys. In addition to α-Mg matrix (Figure 3a), these second-phase constituents are identified in the literature as Nd-rich intermetallics, such as Mg41Nd5 (Figure 3b) and Mg3Nd (Figure 3c), which commonly precipitate along the grain/dendrite boundaries in Mg-Zn-Nd alloys [29,31]. The increasing volume fraction of these phases with higher Nd additions is consistent with findings by previous studies [33,34], who reported similar behaviors in Mg-Nd and Mg-Zn-RE alloys.

Table 3.
EDS results in investigated alloys (at%).
Interestingly, despite the increased presence of these intermetallic compounds, their effectiveness in restricting grain growth appears limited. This is evident from the observed grain coarsening trend (see Table 2 and Figure 2), which contrasts with the classical Zener pinning mechanism typically associated with boundary-anchored second phases. One possible explanation lies in the morphology and spatial distribution of the precipitates. As reported in former studies [26,30], coarse and disconnected grain boundary particles—especially when distributed intermittently or forming eutectic clusters—may not exert sufficient pinning force to effectively inhibit boundary migration during solidification and cooling. Moreover, excessive Nd content can modify the solidification path, promoting the early formation of intermetallics that consume Nd before effective boundary pinning can occur. As a result, instead of promoting refinement, high Nd levels can promote constitutional supercooling and lead to the observed coarsening behavior, as supported by thermodynamic modeling and experimental observations in Mg-RE systems [8,32].
Figure 4 presents the X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns of as-cast investigated alloys. In the Mg-2.5Zn-0.5Nd alloy, the diffraction pattern primarily consists of sharp α-Mg peaks, with minimal evidence of secondary phases. With the addition of more Nd, new reflections corresponding to Mg41Nd5 and Mg3Nd phases are detected. In the present study, increased Nd content resulted in grain coarsening, attributed to complex solidification dynamics and the formation of intermetallic phases; nevertheless, mechanical strengthening was achieved predominantly through precipitation hardening mechanisms [26].
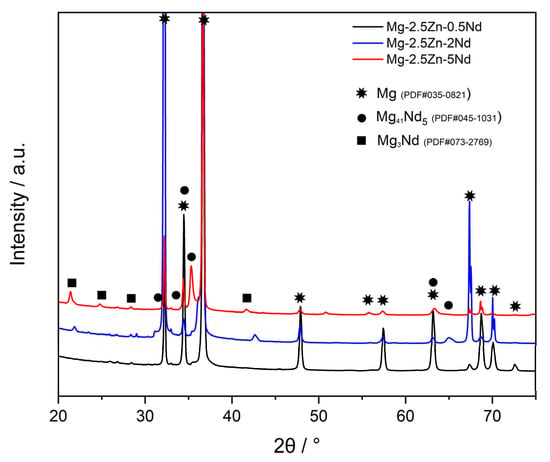
Figure 4.
XRD patterns of the as-cast Mg-2.5Zn-xNd alloys.
3.2. Mechanical Properties
The mechanical properties of the investigated Mg-2.5Zn-xNd (x = 0.5, 2, and 5 wt.%) alloys are summarized in Table 4 and Table 5 and Figure 5 and Figure 6. With the progressive addition of Nd, a significant improvement in both microhardness and yield strength was recorded. The hardness values increased from 42 HV for the 0.5Nd alloy to 59 for the 5Nd alloy (Table 4), demonstrating the strong solid-solution and precipitation strengthening effects induced by Nd addition. This enhancement corresponds closely with the increased volume fraction of intermetallic phases, as observed in the SEM micrographs (Figure 3b,c) and confirmed by the emergence of Mg41Nd5 and Mg3Nd peaks in XRD patterns (Figure 4).

Table 4.
Hardness results of investigated alloys (HV).

Table 5.
Elastic and shear modulus of investigated alloys.
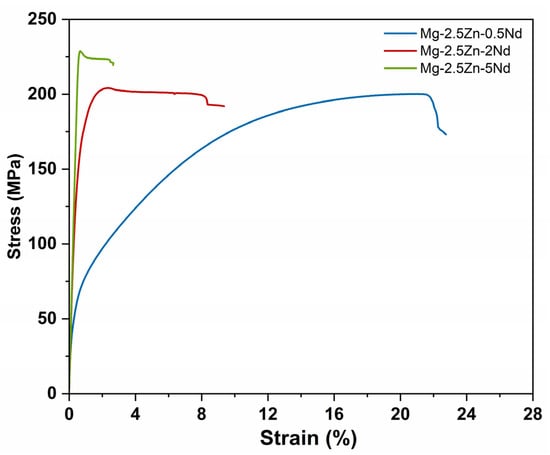
Figure 5.
Stress strain curves of investigated alloys.
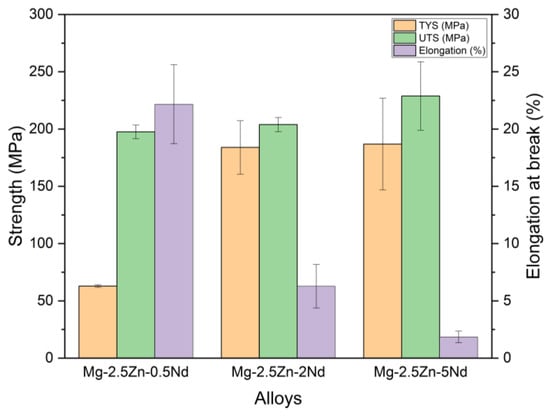
Figure 6.
Mechanical properties of investigated alloys.
The yield strength of magnesium alloys is predominantly governed by the inherent lattice resistance of the magnesium matrix and is further enhanced through synergistic contributions from grain boundary strengthening, dislocation interactions, solid solution effects, and the presence of finely dispersed or precipitated secondary phases. Together, these mechanisms contribute to a robust mechanical performance, making Mg alloys increasingly attractive for advanced structural and biomedical applications [35].
Similarly, the tensile yield strength (TYS) exhibited a remarkable rise from 62.9 MPa (0.5Nd) to 183.9 MPa (2Nd) and 186.8 MPa (5Nd), while ultimate tensile strength (UTS) increased from 197.5 MPa to 228.8 MPa (Figure 5). The relatively minor change in UTS between 2 and 5 wt.% Nd suggests a saturation point beyond which additional Nd does not significantly enhance the tensile response. This plateau effect is attributed to the accumulation and coarsening of second-phase particles (as seen in Figure 2c), which may limit further dislocation strengthening while slightly reducing ductility [33,36].
Indeed, elongation values (Figure 6) dropped sharply from 22.16% for Mg-2.5Zn-0.5Nd to 6.27% and 1.85% for the 2Nd and 5Nd alloys, respectively. This inverse relationship between strength and ductility is commonly observed in Mg-RE alloys and is primarily linked to the brittle nature and morphology of intermetallic phases distributed along the dendrite boundaries [37]. At higher Nd levels, the interconnected eutectic-like network of Mg41Nd5 and Mg3Nd phases promotes crack initiation and propagation, thus compromising formability.
Interestingly, the elastic modulus and shear modulus values remained relatively stable across the compositions, ranging between 43.99 and 45.05 GPa and 16.23–16.67 GPa, respectively (Table 5). This indicates that the stiffness of the alloy system is largely governed by the pure Mg, and the inclusion of rare earth intermetallics does not significantly alter the bulk elastic behavior. Similar trends have been reported in Mg-RE-Zn systems where strength-enhancing precipitates influenced plastic deformation but not the elastic response [38].
The fracture surface morphologies of the Mg-2.5Zn-xNd (x = 0.5, 2, and 5 wt.%) alloys after tensile testing are presented in Figure 7. The Mg-2.5Zn-0.5Nd alloy (Figure 7a) exhibits a dimpled and fibrous structure characteristic of ductile fracture. The presence of elongated microvoids and tearing ridges indicates extensive plastic deformation prior to failure, which is consistent with its high elongation (~23%) observed in the tensile test. In contrast, the Mg-2.5Zn-2Nd alloy (Figure 7b) displays a mixed fracture mode. Although some shallow dimples remain visible, the fracture surface also reveals planar features and parallel tearing lines, indicating reduced ductility and the onset of brittle fracture behavior. The most brittle features are observed in the Mg-2.5Zn-5Nd alloy (Figure 7c), where the fracture surface is dominated by intergranular cleavage and quasi-cleavage facets, with an absence of ductile features such as dimples. This transition correlates with the sharp decrease in elongation to below 2% and the increased presence of hard, brittle intermetallic phases such as Mg41Nd5 and Mg3Nd, which facilitate early crack initiation and propagation along grain boundaries. These observations are consistent with previous reports by Wei et al. [8] and Zhao et al. [34], where increasing rare-earth (RE) content enhanced strength but led to more brittle fracture due to the formation of coarse and continuous intermetallic networks. Overall, the fracture surface analysis supports the mechanical test results and confirms that the microstructural evolution induced by increasing Nd content governs the fracture mode transition from ductile to brittle behavior.

Figure 7.
Fracture surface morphology of the as-cast (a) Mg-2.5Zn-0.5Nd; (b) Mg-2.5Zn-2Nd; and (c) Mg-2.5Zn-5Nd.
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of Nd Alloying on Precipitation Nucleation and Growth
Optical and SEM micrographs revealed a trend of grain coarsening with increasing Nd content—a finding contrary to the widely reported grain-refining effect of rare earth (RE) elements in Mg alloys. This unexpected behavior can be attributed to the formation of coarse, eutectic-like intermetallic phases at grain boundaries and dendrite, which appeared to disrupt the solute drag and Zener pinning mechanisms that typically refine grains.
XRD analysis and SEM-EDS data confirmed the formation of secondary phases such as Mg41Nd5 and Mg3Nd, which increased in volume fraction with higher Nd additions. These intermetallics—while beneficial for precipitation strengthening—appeared to form discontinuous or clustered networks rather than fine, uniformly distributed particles. Previous studies have shown that when such phases localize primarily along grain boundaries, their grain boundary pinning capability becomes less effective, thereby permitting grain growth during solidification [26,39]. Regarding the diffraction intensity, although the volume fraction of intermetallic phases increases with Nd addition, the observed relative peak intensities may decrease due to several contributing factors: (i) preferred orientation effects (texture) of the matrix or phases; (ii) inhomogeneous phase distribution, especially along grain boundaries as observed in SEM; and (iii) limited crystallite size or poor crystallinity of the newly formed intermetallics, which can broaden and weaken their reflections [15].
Furthermore, minor shifts in diffraction peak positions were observed in intermetallic phases with increasing Nd content. These can be attributed to solid solution effects and lattice parameter changes, as Zn atoms can substitute for Mg or Nd sites in ternary Mg-Nd-Zn phases such as Mg3Nd, resulting in detectable lattice distortion. Similar peak shifts due to compositional variation and phase substitution have been reported by Zhang et al. in RE-containing Mg alloys [29]. These microstructural changes further support the formation of non-equilibrium and compositionally complex intermetallics in the as-cast state.
4.2. Strengthening Mechanism
From a mechanical perspective, increasing Nd content significantly enhanced hardness and tensile strength. The Mg-2.5Zn-5Nd alloy showed a 59.5% increase in microhardness and nearly threefold improvement in tensile yield strength compared to the 0.5 wt.% Nd alloy. These results suggest that the solid solution and precipitation strengthening effects of Nd dominate the mechanical behavior, even in the presence of grain coarsening. This observation aligns with previous findings in Mg-Nd-based systems where finely dispersed RE-rich phases contributed to high strength despite less refined grain structures [35,40].
Elongation dropped precipitously as Nd content increased, reaching less than 2% in 5 wt.% Nd alloys. To address the limited ductility observed in the Mg-2.5Zn-2Nd and Mg-2.5Zn-5Nd alloys, the further refinement of their microstructures is essential. This limitation is primarily attributed to the formation of brittle intermetallic phases along dendritic boundaries, which significantly reduce the alloys’ formability. Recent studies have demonstrated that severe plastic deformation (SPD) techniques, such as equal channel angular pressing (ECAP) and high-pressure torsion (HPT), are effective in enhancing ductility through intensive grain refinement and the disruption of continuous second-phase networks, while maintaining or even improving mechanical strength [41,42].
In parallel, thermomechanical processing routes such as hot extrusion have been shown to reduce casting-related porosity, refine grain structures, and improve the alignment and morphology of intermetallic particles. These improvements collectively contribute to enhanced plastic deformation behavior in magnesium alloys [43]. Therefore, such processing strategies present promising pathways for improving the mechanical performance of Mg-Zn-Nd-based systems, particularly for load-bearing bio-medical implant applications where both high strength and adequate ductility are essential.
Interestingly, despite the pronounced microstructural evolution and variation in mechanical strength, the elastic modulus remained relatively constant across all alloy compositions, consistently measured in the range of 44–45 GPa. This stability indicates that stiffness is predominantly governed by the α-Mg matrix, which retains its intrinsic elastic properties regardless of the amount or morphology of RE-rich intermetallic phases. Similar trends have been reported in other Mg-RE-Zn systems, where alloying additions had minimal impact on the elastic modulus due to their limited influence on the primary bonding characteristics of the hexagonal close-packed (HCP) Mg lattice [44].
From a biomedical viewpoint, although the measured modulus values are higher than those of human cortical bone (typically 20–30 GPa), they are significantly lower than those of conventional metallic biomaterials such as Ti-6Al-4V (~110 GPa) and 316 L stainless steel (~200 GPa), which are known to induce stress shielding and subsequent bone resorption [45]. Therefore, the relatively low modulus of magnesium alloys offers a promising compromise, potentially minimizing stress shielding while maintaining sufficient load-bearing capacity. Additional strategies, including porous scaffold design and surface modification, may further tailor the mechanical performance to better match the in vivo biomechanical environment.
5. Conclusions
This study systematically evaluated the effect of neodymium (Nd) content on the microstructure and mechanical properties of as-cast Mg-2.5Zn-xNd alloys for potential biomedical applications. The main conclusions are summarized as follows:
- Grain Size Evolution: Increasing Nd content from 0.5 to 5 wt.% led to a progressive increase in grain size, contradicting the expected grain-refining effect of RE elements. This was attributed to early precipitation of intermetallics that failed to provide sufficient Zener pinning.
- Phase Composition: SEM and XRD analyses confirmed the formation of secondary phases such as Mg41Nd5 and Mg3Nd, with their volume fraction rising in parallel with Nd content. These phases contributed significantly to the alloy’s strengthening behavior.
- Mechanical Strengthening: Both microhardness and yield strength improved notably with higher Nd levels. The Mg-2.5Zn-5Nd alloy exhibited the highest hardness (58 HV) and tensile yield strength (186.8 MPa), underscoring the strengthening effect of Nd-rich intermetallics.
- Ductility Balance: Despite strength gains, elongation dropped sharply to below 2% in the higher Nd-containing alloys, highlighting a brittle fracture mechanism linked to intermetallic phase morphology and distribution.
- Elastic Properties: The elastic modulus and shear modulus remained relatively constant across all compositions, preserving compatibility with the mechanical properties of human bone.
In conclusion, Nd addition to Mg-2.5Zn alloys offers a viable strategy for enhancing strength and hardness in biodegradable implant materials. However, optimal compositions—such as Mg-2.5Zn-2Nd—must balance strength with ductility to ensure safe and reliable performance in biomedical applications.
Funding
Faruk Mert was supported by the Scientific and Technological Research Council of Türkiye (TÜBİTAK) 2219 International Postdoctoral Research Fellowship Program for Turkish Citizens (1059B192301716). The APC was funded by Helmholtz-Zentrum Hereon.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the author on request.
Acknowledgments
The author would like to thank Gert Wiese and Daniel Strerath for their technical assistance. The author would like to thank Norbert Hort and Regine Willumeit-Römer for hosting him as a post-doctoral researcher in Helmholtz-Zentrum Hereon.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Faruk Mert was employed by the company Helmholtz-Zentrum Hereon GmbH. The author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Sharma, S.; Saxena, K.; Malik, V.R.; Mohammed, K.A.; Prakash, C.; Buddhi, D.; Dixit, S. Significance of alloying elements on the mechanical characteristics of Mg-based materials for biomedical applications. Crystals 2022, 12, 1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.B.; Bai, J.; Xue, F.; Zeng, R.C.; Wang, G.M.; Chu, P.K.; Chu, C.L. Smart self-healing coatings on biomedical magnesium alloys: A review. Smart Mater. Manuf. 2023, 1, 100022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Blawert, C.; Zheludkevich, M. The corrosion performance and mechanical properties of Mg-Zn based alloys—A review. Corros. Mater. Degrad. 2020, 1, 92–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Zhao, Y.; An, Z.; Cheng, M.; Wang, Q.; Cheng, T.; Zhang, X. Enhanced antibacterial properties, biocompatibility, and corrosion resistance of degradable Mg-Nd-Zn-Zr alloy. Biomaterials 2015, 53, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.J.; Chen, C.; Liu, M.; Chang, C.; Yan, X.C.; Dai, Y.L. Improved corrosion resistance of magnesium alloy prepared by selective laser melting through T4 heat treatment for biomedical applications. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 27, 813–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Zhang, H.; Qi, X.; Wang, J.; Jin, P.; Zeng, X. Twin recrystallization mechanisms in a high strain rate compressed Mg-Zn alloy. J. Magnes. Alloy. 2021, 9, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.Z.; Zha, M.; Wang, S.Q.; Wang, S.C.; Wang, C.; Jia, H.L.; Wang, H.Y. Alloying design and microstructural control strategies towards developing Mg alloys with enhanced ductility. J. Magnes. Alloy. 2022, 10, 1191–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Ren, L.; Le, Q.; Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhang, X.; Cao, J.; Liao, Q.; Wang, T. Mg-xNd-Zn-Zr alloys prepared by in-situ reduction: Study of microstructure, corrosion behavior, and mechanical properties. Mater. Today Commun. 2025, 42, 111277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapiero, H.; Tew, K.D. Trace elements in human physiology and pathology: Zinc and metallothioneins. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2003, 57, 399–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Hu, Y.; Yuan, K.; Qiao, Y. Review of the effect of surface coating modification on magnesium alloy biocompatibility. Materials 2022, 15, 3291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Lei, T.; Li, N.; Feng, F. Effects of Zn on microstructure, mechanical properties and corrosion behavior of Mg–Zn alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2012, 32, 2570–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, C.; Li, J.; Song, Y.; Xie, C.; Tao, H.; Zhang, Y.; He, Y.; Jiang, Y.; et al. Research on an Mg–Zn alloy as a degradable biomaterial. Acta Biomater. 2009, 6, 626–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; Blawert, C.; Yang, H.; Wiese, B.; Feyerabend, F.; Bohlen, J.; Mei, D.; Deng, M.; Campos, M.S.; Scharnagl, N.; et al. Microstructure-corrosion behaviour relationship of micro-alloyed Mg-0.5Zn alloy with the addition of Ca, Sr, Ag, In and Cu. Mater. Des. 2020, 195, 108980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Blawert, C.; Feyerabend, F.; Bohlen, J.; Campos, M.S.; Gavras, S.; Wiese, B.; Mei, D.; Deng, M.; Yang, H.; et al. Time-sequential corrosion behaviour observation of micro-alloyed Mg-0.5Zn-0.2Ca alloy via a quasi-in situ approach. Corros. Sci. 2019, 158, 108096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rokhlin, L.L. Magnesium Alloys Containing Rare Earth Metals, 1st ed.; Crc Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003; pp. 20–50. [Google Scholar]
- Penghuai, F.; Liming, P.; Haiyan, J.; Jianwei, C.; Chunquan, Z. Effects of heat treatments on the microstructures and mechanical properties of Mg–3Nd–0.2Zn–0.4Zr (wt.%) alloy. Mat. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 486, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Chen, R.; Ke, W. Microstructure and mechanical properties of a sand-cast Mg–Nd–Zn alloy. Mat. Des. 2014, 58, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, H.; Wang, W.; Huang, H.; Pei, J.; Qu, H.; Yuan, G.; Li, Y. The degradation and transport mechanism of a Mg-Nd-Zn-Zr stent in rabbit common carotid artery: A 20-month study. Acta Biomater. 2018, 69, 372–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, R.; Bettles, C.; Muddle, B.C.; Nie, J.F. Precipitation Hardening in Mg-3 wt%Nd(-Zn) Casting Alloys. Mat. Sci. Forum 2003, 419, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.; Hu, Z.; Sheng, L.; Xu, D.; Zheng, Y.; Xi, T. Influence of Zn content on microstructure and tensile properties of Mg–Zn–Y–Nd alloy. Acta Met. Sin. (Engl. Lett.) 2018, 31, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koç, E.; Kannan, M.; Ünal, M.; Candan, E. Influence of zinc on the microstructure, mechanical properties and in vitro corrosion behavior of magnesium–zinc binary alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 648, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.; Hu, Z.; Wang, J.; Sheng, L.; Zhao, H.; Zheng, Y.; Xi, T. Effect of extrusion process on the mechanical and in vitro degradation performance of a biomedical Mg-Zn-Y-Nd alloy. Bioact. Mater. 2020, 5, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asadollahi, M.; Gerashi, E.; Alizadeh, R.; Mahmudi, R. Effect of Zn content and processing route on the microstructure, mechanical properties, and biodegradation of Mg–Zn alloys. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 21, 4473–4489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Yan, Z.; Zhou, T.; Chen, L. Microstructure and mechanical properties of expanded Mg-Zn-Nd alloys. J. Shenyang Univ. Technol. 2008, 35, 433–436. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.; Teng, X.; Ge, X. Effect of Nd content and heat treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg-Zn-Nd alloy. Mater. Sci. Forum 2017, 898, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javaid, A.; Hadadzadeh, A.; Czerwinski, F. Solidification behavior of dilute Mg-Zn-Nd alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 782, 132–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Yang, K.; Tan, L. Improvement of mechanical property and corrosion resistance of Mg-Zn-Nd alloy by bidirection drawing. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 81, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM, E112-96; Standard Test Methods for Determining Average Grain Size. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2004.
- Zhang, Z.; Kim, J.; Pu, H.; Zhou, S.; Hu, Y.; Dong, Z.; Huang, G.; Jiang, B. Achieving high strength in ZK60-based Mg alloy with a low RE content through numerous precipitates. J. Alloys Compd. 2025, 1023, 180118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Zhang, X.; Tang, C.; Deng, Y.; Liu, Z.; Yang, L. Microstructures and mechanical properties of the Mg–8Gd–4Y–Nd–Zn–3Si alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 571, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Guan, J.; Xu, Y. Microstructure, mechanical properties and damping capacity of heat-treated Mg–Zn–Y–Nd–Zr alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 609, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhao, S.; Li, J.; Feng, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, Z.; Guo, E. Precipitation behavior and mechanical properties of Mg-Nd-Sm-Zn-Zr alloy. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 28, 3385–3395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavras, S.; Buzolin, R.H.; Subroto, T.; Stark, A.; Tolnai, D. The effect of Zn content on the mechanical properties of Mg-4Nd-xZn alloys. Materials 2018, 11, 1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Wen, M.; Wang, J.; Xu, D.; Zheng, Y.; Sheng, L. Regulating microstructure and mechanical properties of the as-cast Mg-4Zn-0.5Y-0.5Nd alloy by heat treatment. J. Alloys Compd. 2025, 1010, 177232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Guan, K.; Yang, Q.; Niu, X.; Zhang, D.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Tang, Z.; Meng, J. Effects of 0.5 wt% Ce addition on microstructures and mechanical properties of a wrought Mg−8Gd−1.2Zn−0.5Zr alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 763, 120–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, X.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, D.; Meng, F.; Chen, C.; You, Z.; Zhang, J.; Lv, S.; Meng, J. Microstructures and mechanical properties of a newly developed high-pressure die casting Mg-Zn-RE alloy. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 53, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, X.; Ding, W. Effect of Nd and Y addition on microstructure and mechanical properties of as-cast Mg–Zn–Zr alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2007, 427, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, J.; Zhong, Z.; Kainer, K.; Hort, N. Effects of Gadolinium and Neodymium Addition on Young’s Modulus of Magnesium-Based Binary Alloys. In Magnesium Technology 2017; Solanki, K., Orlov, D., Singh, A., Neelameggham, N., Eds.; Springer, International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easton, M.; Davidson, C.; StJohn, D. Grain morphology of as-cast wrought aluminium alloys. Mater. Trans. 2011, 52, 842–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J. Effects of precipitate shape and orientation on dispersion strengthening in magnesium alloys. Scr. Mater. 2003, 48, 1009–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryla, K.; Horky, J. Magnesium Alloys Processed by Severe Plastic Deformation (SPD) for Biomedical Applications: An Overview. Mater. Trans. 2023, 64, 1709–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzadeh, H. Grain refinement of magnesium alloys by dynamic recrystallization (DRX): A review. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 25, 7050–7077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Yang, G.; Xiao, L.; Kan, Z.; Guo, J.; Li, Q.; Jie, W. Effects of the extrusion parameters on microstructure, texture and room temperature mechanical properties of extruded Mg–2.49Nd–1.82Gd–0.2Zn–0.2Zr alloy. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2025, 32, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbarzadeh, F.Z.; Sarraf, M.; Ghomi, E.R.; Kumar, V.V.; Salehi, M.; Ramakrishna, S.; Bae, S. A state-of-the-art review on recent advances in the fabrication and characteristics of magnesium-based alloys in biomedical applications. J. Magnes. Alloys 2024, 12, 2569–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Saijilafu, N.; Wu, X.; Wu, K.; Chen, J.; Tan, L.; Witte, F.; Yang, H.; Mantovani, D.; Zhou, H.; et al. Biodegradable Mg-based alloys: Biological implications and restorative opportunities. Int. Mater. Rev. 2023, 68, 365–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).