Abstract
How to search for a convenient method without a complicated calculation process to predict the physicochemical properties of inorganic crystals through a simple micro-parameter is a greatly important issue in the field of materials science. Herein, this paper presents a new and facile technique for the comprehensive estimation of lattice energy (U), bulk modulus (B), chemical hardness (ƞ), and electronic polarizability (α), just by using a simple mathematic fitting formula with a few structure parameters, such as the systems of rock salt crystals (group I–VII, II–VI) and tetrahedral coordinated crystals (group II–VI, III–V). For the typical binary ANB8-N crystal systems, our present conclusions suggest that a good quantitative correlation between U, B, ƞ, α and chemical bond length (d) is observed, the normal mathematical expression is P = a·db (P represents these physicochemical parameters), constants a and b depend on the type of crystals, and the relevant squares of the correlation coefficient (R2) are larger than 0.9. The results indicate that lattice energy, bulk modulus, and chemical hardness decrease with increases in chemical bond length, but electronic polarizability increases with an increase in chemical bond length. Meanwhile, the new data on the lattice energy, bulk modulus, chemical hardness, and electronic polarizability values of binary ANB8-N crystal systems considered in the present study are calculated via the obtained curve fitting equations without any complex calculation process. We find that there is a very good linear trend in our calculated results along with the values reported in the literature. The present study will be important in solid-state chemistry, which may give researchers useful guidance in searching for relevant data for predicting the properties of new materials or synthetic routes based on a simple mathematic empirical model.
1. Introduction
One of the main aims of theoretical chemistry is to present a useful correlation between chemical concepts, which provides great convenience and important information to researchers for the prediction of molecular properties, such as reactivity and stability of chemical species, and to build a bridge between physics and chemistry in the field of materials science [1,2,3,4,5]. In the past few decades, a considerable number of theoretical calculations in terms of the empirical model have become an essential part of materials research, because of the simplicity allowing a broader class of researchers to understand useful properties in order to help them reduce experimental complexity during the process of exploring the synthetic techniques of novel materials [6,7,8,9,10,11]. In the description of different characteristics of chemical species related to their stability, reactivity, and mechanical and optical-electrical property, popular chemical concepts, such as lattice energy, bulk modulus, chemical hardness, and electronic polarizability are commonly mentioned [12,13,14,15]. It is also worth noting that there is an intrinsic relationship between these concepts based on the other structural parameters, and the detailed description will be discussed in the following section.
The lattice energy of inorganic crystals plays a significant role in the exploration of the existence and stability of materials based on the analysis of thermodynamics [16,17,18,19]. Namely, this energy is considered to be one of most important quantities in the matter of whether new inorganic materials can be synthesized by using designed synthetic routes [16,17,18,19]. Hence, the computation and estimation of lattice energy has attracted great attention in the field of modern materials science. Normally, lattice energy of inorganic crystals can be determined by means of the Born–Fajans–Haber (BFH) thermochemical cycle based on the experimental data, such as standard formation enthalpy, bond dissociation energy, sublimation enthalpy, ionization energy, and electron affinity [12,18,19]. Such an experimental method can provide important original data needed for precise establishment of a theoretical fitting model. Recently, different theoretical models have been proposed for the evaluation of the lattice energy of inorganic crystals [12,16,17,18,19]. By means of the dielectric theory of chemical bond of complex crystals, Zhang’s group presented an empirical method for the estimation of the lattice energy of inorganic ionic crystals [12]. In their subsequent study, a relationship between the lattice energy and bulk modulus of binary inorganic crystals was obtained through introducing the concept of lattice energy density [19]. At the same time, the bulk modulus of binary inorganic crystals was calculated by using the empirical fitting equation, which shows that there is an existing close relationship between lattice energy and the bulk modulus.
The bulk modulus is a macroscopic physical parameter in evaluating a material’s mechanical performance, which has unique and valuable contributions to predict the ability of solids to resist compression deformation within the limits of the elastic regime [13,20]. In other words, materials with a high bulk modulus are often taken as potential superhard materials [1,19]. Meanwhile, the bulk modulus can offer some useful information on the geometry of minerals’ compression, which has been relevant to geophysics and has been used for the interpretation of Earth’s seismic properties [13,21,22]. Hence, extensive relevant studies have been focused on estimating the bulk modulus of crystal materials for either a theoretical basis or experimental technique [13,19]. An accurate determination of bulk modulus requires complicated engineering, involving a careful analysis of elastic parameters, plastic deformation, and even complex experiment measurement processes. In response to this, most researchers tend to choose the computational route to obtain such physical properties of solid materials. Currently, most theoretical calculations of the bulk modulus are performed by using state-of-the-art ab initio techniques [23]. However, these first-principles calculations are relatively complex and require significant effort due to the long computational process and rigorous mathematical formulae involving a series of approximations, which lead to difficulty in constructing relationships among the chemical composition, crystal structure, and intrinsic properties for ordinary researchers. Therefore, it is necessary to search for an effective method to estimate the bulk modulus of different types of crystals from the viewpoint of a simple and convenient operation. Wang et al. presented an empirical model based on the bond valence model in terms of bond length, bond valence, and bond density to predict the bulk modulus of crystal materials [13]. Xue’s group estimated the elastic modulus of different types of crystal materials on the basis of the electronegativities of bonded atoms in the crystallographic frame [24]. It is interesting to note that these studies indicate that the bulk modulus is strongly influenced by the crystal structure.
Chemical hardness has long been used as one of the most useful conceptual constructs of chemistry and physics, which is a significant tool to understand the nature of chemical interactions and to predict the reactivity or stability of chemical species [25,26]. Generally, hardness, as conceived in chemistry, fundamentally offers a measure of resistance towards the deformability of atoms, ions, or molecules, and a polarization degree of electron cloud under a small perturbation generated during the process of chemical reaction [14,25]. According to Sanderson’s electronegativity equalisation principle, Datta derived the geometric mean equation to calculate the chemical hardness of molecules based on the assumption that the chemical hardness is equilibrated globally [27]. Islam et al. presented an algorithm for the evaluation of the hardness of heteronuclear polyatomic molecules, and the obtained hardness data of a set of representative molecules were in good agreement with the corresponding hardness data evaluated by using quantum mechanics [26]. To further offer a practical calculation opportunity for the chemical hardness of atoms and molecules, Kaya et al. proposed a new equation for calculating chemical hardness atoms by using the charges, ionisation energy, and electron affinity of atoms [14]. In addition, chemical hardness is an important parameter that is closely related to lattice energy [18]. Kaya et al. developed a facile technique for the estimation of the lattice energy of inorganic ionic compounds via chemical hardness [18]. Such a method allows for the easy evaluation of the lattice energy of inorganic ionic crystals without the need for ab initio techniques and complex calculations.
Electronic polarizability, which governs non-linear optical responses, is one of the most important parameters in the field of electro-optic devices [28,29,30]. Meanwhile, electronic polarizability is also crucial to the study of doping and defect behaviours of functional materials [31]. Dimitrov et al. attempted to calculate the average electronic oxide polarizability of numerous single component oxides based on the linear refractive index and energy gap, and also searched for a suitable relationship between polarizability and the non-linear properties of simple oxide materials [32]. Xue’s group presented a new method for estimating the electronic polarizability of binary and ternary chalcopyrite semiconductors by using electronegativity and the principal quantum number as calculation parameters [33]. Based on a thermodynamic approach, an important link between electronic polarizability and the lattice energy of crystalline silicates has been quantitatively established by Duffy [34], and the value of lattice energy has been estimated by means of the enthalpies of formation. Petrov et al. successfully calculated the lattice energy of complex lanthanide compounds, and their correlations between electronic polarizability and lattice energy have been investigated [35,36,37]. In the previous study, we have searched for a systematic relationship between lattice energy density and electronic polarizability, and the empirical expressions were found for ANB8-N crystal systems, including rock salt (group I–VII, II–VI) and tetrahedral coordinated crystals (group II–VI, III–V) [38]. These empirical methods provide a convenient condition for studying the relationship between lattice energy and electronic polarizability.
Relying upon the commonality of the basic philosophy of the origin and development of the abovementioned physicochemical parameters, more theoretical approaches have been attempted to further explore intrinsic relationships based on the mathematic fitting equation. However, they are too complex to be used by most researchers due to containing many fitting parameters or involving some important theory. Especially, the rationalization of these density functional theory (DFT) calculations often requires a profound understanding of quantum mechanical theory and complex structure parameters. It is, therefore, of scientific and practical interest to develop a simple and suitable method to explore the systematic relationship between lattice energy, bulk modulus, chemical hardness, electronic polarizability, and chemical bond length for binary ANB8-N crystals, and to gain a deeper understanding of these significative physicochemical parameters.
As technologically important materials, binary ANB8-N inorganic crystals have been widely investigated because of their potential applications in modern industry areas, such as microelectronic devices, light-emitting diodes, non-linear optics, catalysts, and superhard materials [39,40,41,42,43]. For example, the BN with zinc blende and orthorhombic structure can be widely used for cutting and polishing tools or scratch-resistant coatings, which have been considered to be promising materials for superhard material in the place of costly diamonds [39]. Group II–VI semiconductors, especially CdTe, have gained a great deal of research interest in optoelectronic devices and catalysts [40,41,42]. On the other hand, second harmonic generation has been observed from nanoarchitecture ZnS under linearly polarized and circularly polarized femtosecond laser excitations due to its remarkably large non-linear optical coefficient [43]. All these applications indicate that an understanding of the relevant chemical and physical parameters for describing their performance in the system of ANB8-N type crystals is crucial to purposely designing new functional materials with tunable intrinsic properties. To search for the link between macro-performance and micro-structure, significant theoretical work has been conducted in this direction for inorganic crystals in recent years [44,45,46,47]. For this purpose, the present work is an attempt to find a mathematic correlation between lattice energy, bulk modulus, chemical hardness, electronic polarizability, and chemical bond length based on the empirical curve fitting model with the use of only a few numerical constants.
To the best of our knowledge, such relations have not yet been well revealed for the comprehensive estimation of multiple physicochemical parameters, just by using a simple mathematical formula with the same one parameter of chemical bond length. In the present paper, the main aim of this study is an attempt to present a systematic relationship between lattice energy, bulk modulus, chemical hardness, electronic polarizability, and chemical bond length in a lot of data analysis on the abovementioned physicochemical parameters from the reported literature. Moreover, the empirical expressions obtained by means of the curve fitting method can be used to calculate the value of lattice energy, bulk modulus, chemical hardness, and electronic polarizability for binary ANB8-N type crystals. The results show that, within the systems studied, the calculated values agree well with the reported data in the previous literature. The present work provides a useful guide for researchers to predict lattice energy, bulk modulus, chemical hardness, and electronic polarizability by means of a simple crystal structure parameter, which are easily understandable and accessible, and thus could give us useful information for designing novel functional materials.
2. Theoretical Method
As was mentioned above, lattice energy is one of the most important quantities in understanding and predicting the structure, character, and behaviour of inorganic solid materials from the point of view of thermodynamics [12]. Recently, an empirical methodology to calculate the lattice energy of inorganic ionic crystals was proposed by Zhang and coworkers based on the dielectric theory of chemical bond [12,19]. In this method, the total lattice energy, Uall, of inorganic crystals with one type of chemical bond can be divided into bond-dependent terms, ionic part Ui and covalent part Uc, as follows:
We suppose that the formula of a simple crystal is AmBn (A and B represent cation and anion, respectively), so then lattice energy Ui and Uc of a binary crystal can be expressed by the following relations:
where ZA and ZB are the valences of A and B ions, respectively; fi and fc are the fractional ionicity and fractional covalency of the chemical bond in crystals. For the binary inorganic crystals, the detailed structural data on the calculation of ionicity and covalency and other chemical bond properties are taken from the literature [48]. The estimated values of lattice energy are in good agreement with the available experimental data. Subsequently, the bulk modulus was calculated by introducing the concept of lattice energy density, Ud, and the mathematic equation is expressed as follows:
In this equation, B represents the bulk modulus, and γ and δ are the empirical parameters, which are relating to the valence and coordination number of the cation [19]. For the rock salt crystals of group I–VII, rock salt crystals of group II–VI, the tetrahedral coordinated crystals of group II–VI, and the tetrahedral coordinated crystals of group III–V, the parameters, γ, are 0.2917, 0.375, 0.5625, and 0.6875, respectively. According to the valence and coordination number of the cation, the value of empirical parameter, δ, is equal to 18/ZANCA for NCA > 4, the values of are equal to 18/ZANCA for the NCA ≤ 4 [19].
It is important to note that chemical hardness is a useful theoretical parameter in many experimental and theoretical studies, and this concept has several important applications in multiple topics including complex stability, chemical reactivity, estimation of formed products in a reaction, and solubility of molecules [14,18]. In order to accurately describe such a parameter, Kaya et al. presented a mathematic equation for the estimation of the chemical hardness of both neutral and charged moleculars according to the hardness equalization principle [14], as follows:
where N represents the total number of atoms in the molecule, q stands for charge of molecule, and ai and bi are parameters based on the ionization energy (I) and electron affinity (A) of atoms, respectively, which can be obtained by using the following mathematical expressions:
Polarizability of inorganic crystals is a basic property of materials and has been studied for a long time, both in experiments and theory in the field of optics and electronics, which is related to many macro and microscopic physicochemical properties, such as dielectric properties, ferroelectricity, optical non-linearity, and chemical stability [15,26,27]. Hence, it is extremely important to quantitatively evaluate the electronic polarizability of crystals. One of the most effective and reasonable methods for calculating electronic polarizability, α, is to apply the Clausius–Mossotti equation based on the concept of dielectric susceptibility, ε, and molar volume, Vm, of substance, and the relevant relation was written as
where the parameter of b is defined as b = 4πNA/3, and N is Avogadro’s number [49]. According to P-V dielectric theory [50,51], the following empirical equation is proposed for the calculation of dielectric constant ε
The corresponding constants A and s′ are collected in Ref. [48].
3. Results and Discussion
Firstly, according to the crystal structure type and properties, we calculated lattice energy, U, value based on Equations (1)–(3), which are listed in Table 1, Table 2, Table 3 and Table 4 (column 4). For the same cation in binary ionic crystals, we can see that the lattice energy decreases with an increasing atomic number of anions. Meanwhile, it can be seen that, in general, there is a decreasing trend in the lattice energy along with the chemical bond length. Furthermore, we also calculated the bulk modulus, B, of binary crystals by means of Equation (4). The calculated bulk modulus values of binary crystals are given in Table 1, Table 2, Table 3 and Table 4 (column 6), which have the same trend as lattice energy. On the basis of Equations (5)–(7), we calculated the chemical hardness, ƞ, which are listed in Table 1, Table 2, Table 3 and Table 4 (column 8). The dielectric constant, ε, values obtained from Equation (9) by using the chemical bond length are substituted in Equation (8), and the electronic polarizability, α, values can be evaluated as shown in Table 1, Table 2, Table 3 and Table 4 (column 10). As can be seen from Table 1, Table 2, Table 3 and Table 4, it is obvious that the electronic polarizability trends in binary ANB8-N crystals increases with an increasing chemical bond length for the same cation.

Table 1.
Chemical bond length d, molar volume Vm, lattice energy U, calculated lattice energy Ucal, bulk modulus B and calculated bulk modulus Bcal, chemical hardness η, calculated chemical hardness ηcal, electronic polarizability α, calculated electronic polarizability αcal of rock salt crystals of group I–VII.

Table 2.
Chemical bond length d, molar volume Vm, lattice energy U, calculated lattice energy Ucal, bulk modulus B and calculated bulk modulus Bcal, chemical hardness η, calculated chemical hardness ηcal, electronic polarizability α, calculated electronic polarizability αcal of rock salt crystals of group II–VI.

Table 3.
Chemical bond length d, molar volume Vm, lattice energy U, calculated lattice energy Ucal, bulk modulus B and calculated bulk modulus Bcal, chemical hardness η, calculated chemical hardness ηcal, electronic polarizability α, calculated electronic polarizability αcal of tetrahedral coordinated crystals of group II–VI.

Table 4.
Chemical bond length d, molar volume Vm, lattice energy U, calculated lattice energy Ucal, bulk modulus B and calculated bulk modulus Bcal, chemical hardness η, calculated chemical hardness ηcal, electronic polarizability α, calculated electronic polarizability αcal of tetrahedral coordinated crystals of group III–V.
During the last few decades, the extensive theoretical research based on the curve fitting model was devoted to understanding basic structural properties and the relation between the physics and chemistry of solids, which led to great advances in the rational design synthetic route of novel functional materials [4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38]. Although those methods are not supported by present fundamental theory, much important information about materials have been acquired, which has gradually become an essential part of materials research. In particular, the simplicity of these approaches allows a broader class of researchers to calculate useful properties, and often trends become more evident. With the help of the empirical fitting model and relevant chemical theories, chemists can achieve the goal of predicting chemical reactions and design a feasible synthetic route. Hence, numerous attempts have been made to establish links between macroscopic properties of solids and their atomic-scale microparameters.
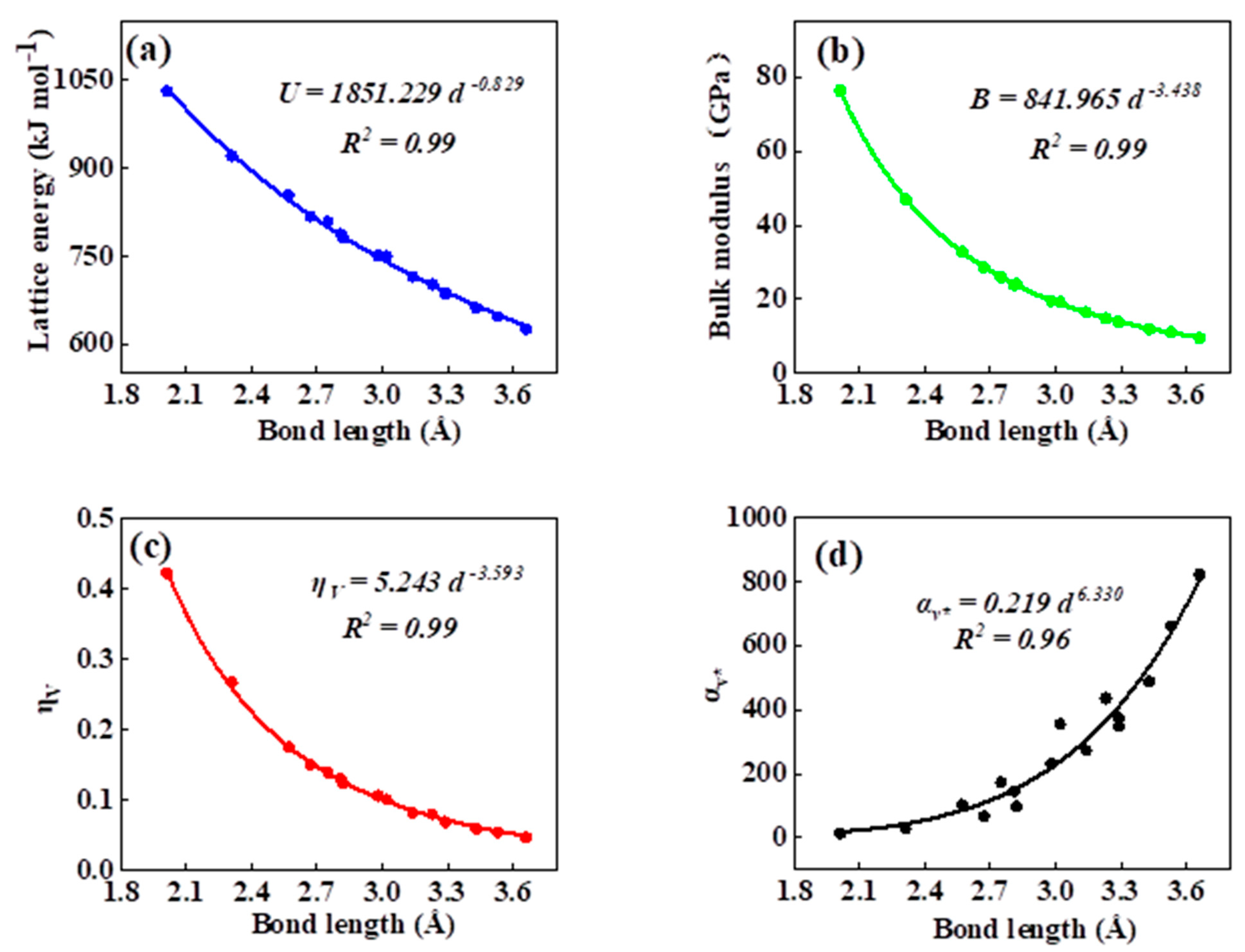
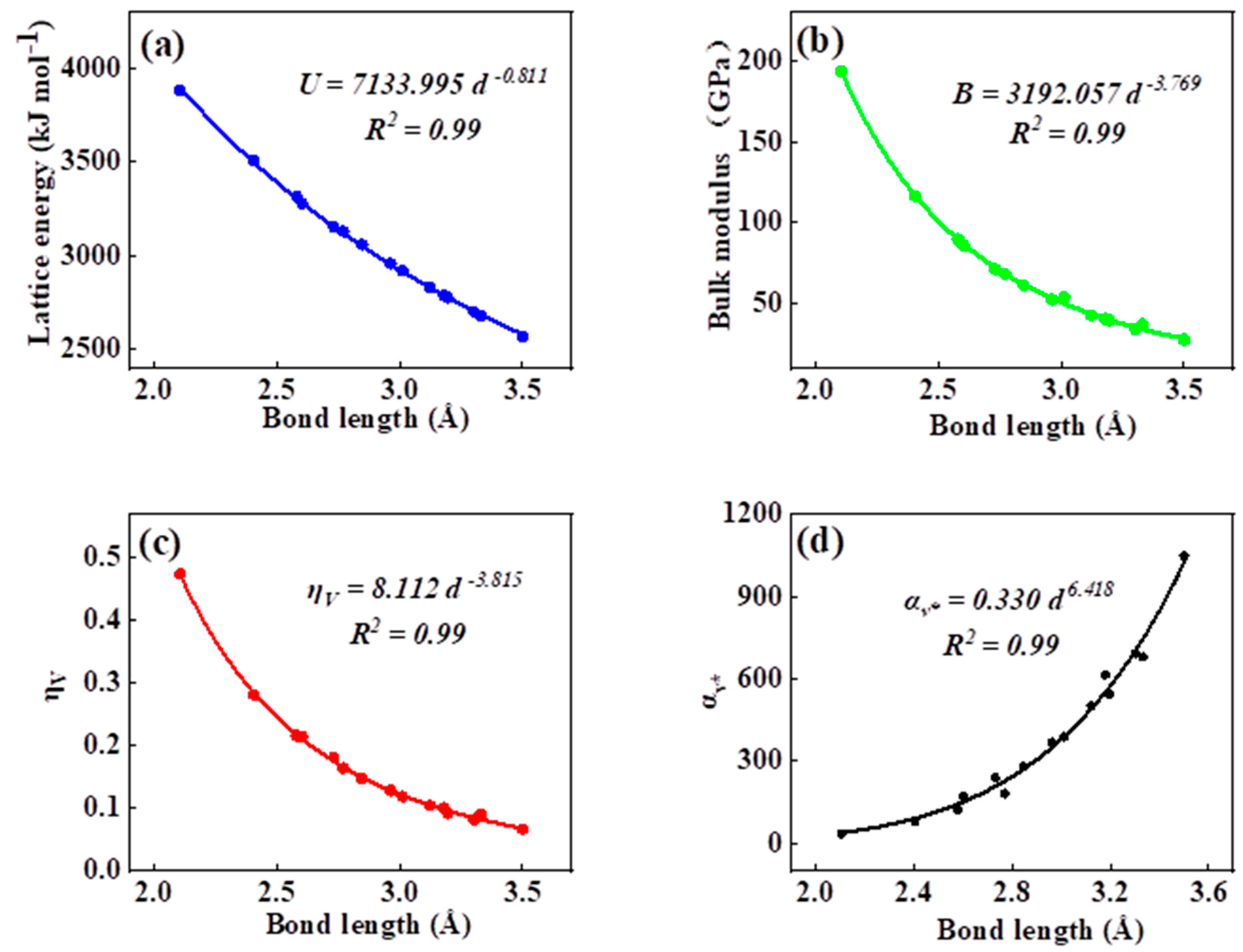
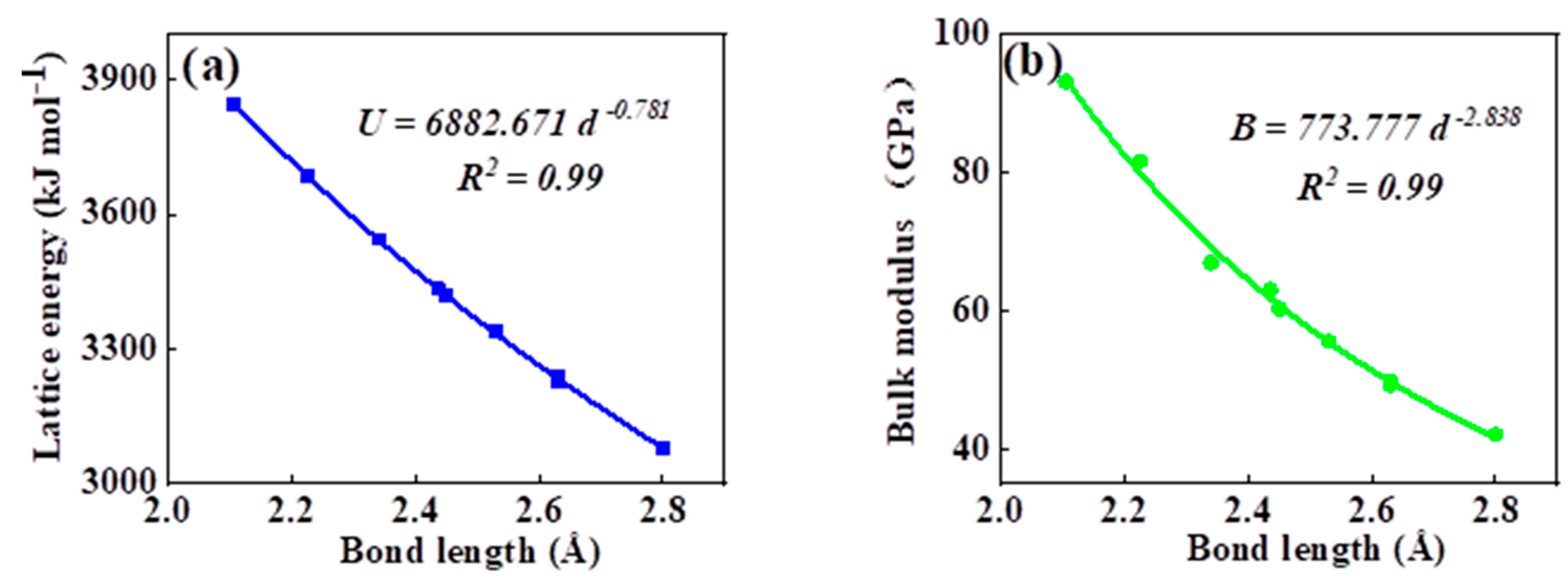
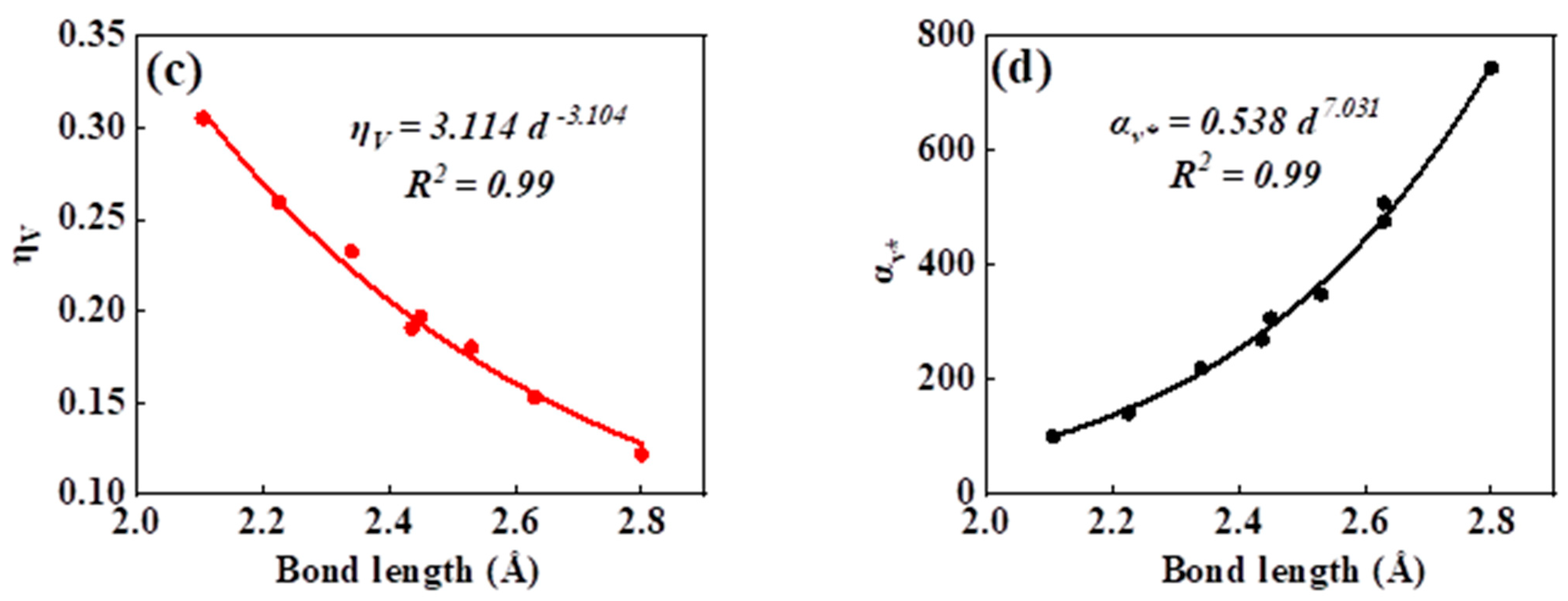
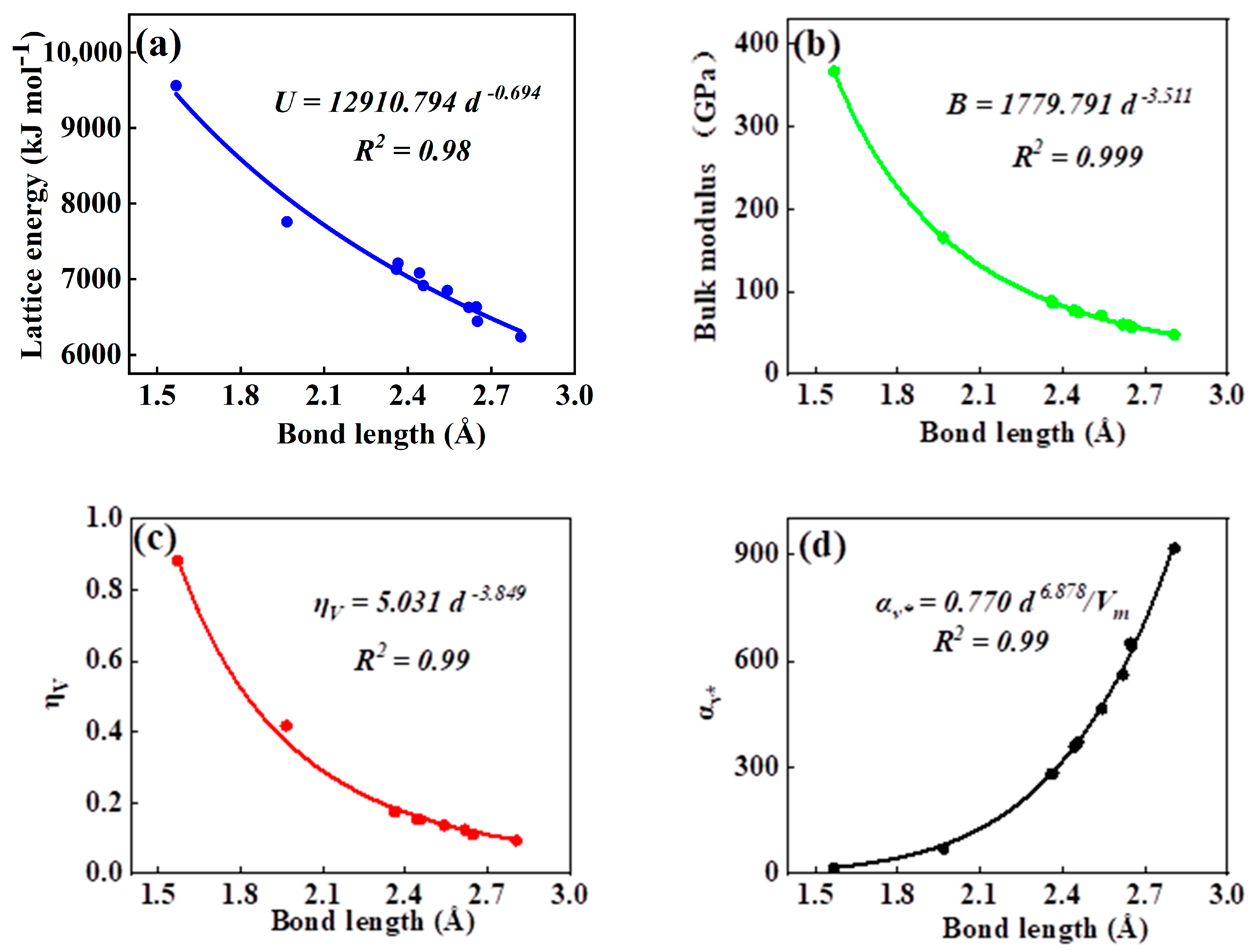
As can be seen in all investigated systems of Table 1, Table 2, Table 3 and Table 4, we can find a general trend in the lattice energy, bulk modulus, chemical hardness, and electronic polarizability with chemical bond length. Therefore, to search for a detailed and precise relation between these physicochemical parameters and the chemical bond length of binary ANB8-N crystals, we plotted the data of the lattice energy, bulk modulus, chemical hardness, and electronic polarizability in Table 1, Table 2, Table 3 and Table 4 as a function of chemical bond length in Figure 1, Figure 2, Figure 3 and Figure 4. Furthermore, for the estimation of chemical hardness and polarizability, we introduced a parameter of molar volume of inorganic materials that can be easily obtained by means of their chemical formulas and densities in their curve fitting assessment. According to pioneering studies on the concept of lattice energy density by Zhang’s group, we defined ηV (ηV = η/Vm) as chemical hardness density [19]. Meanwhile, αv* (αv* = α·Vm) is defined as a product of electronic polarizability and molar volume learned from Qi’s ideas [29]. As can be seen from Figure 1, Figure 2, Figure 3 and Figure 4, it is worth noting that a very good agreement exists between these physicochemical parameters and the chemical bond length of binary ANB8-N crystals, and the correlation coefficient R2 values are larger than 0.9 (most correlation R2 values are 0.99), indicating that least squares fittings and calculations are effective and reliable for the present binary ANB8-N crystal systems. The corresponding trend lines, correlation equations, and the values of squares of correlation coefficient are given in Figure 1, Figure 2, Figure 3 and Figure 4. The normal mathematical expression between the abovementioned parameters and the chemical bond length is P = a·db (P represents these parameters, d is chemical bond length). The detailed data on constant, a and b, are listed in Figure 1, Figure 2, Figure 3 and Figure 4. As can be seen from Figure 1a–c, Figure 2a–c, Figure 3a–c and Figure 4a–c, there is a clear decreasing trend in the lattice energy, bulk modulus, and chemical hardness along with the chemical bond length. However, different trends can be seen in Figure 1d, Figure 2d, Figure 3d and Figure 4d, where we plotted the data on electronic polarizability as a function of chemical bond length for binary ANB8-N crystals.
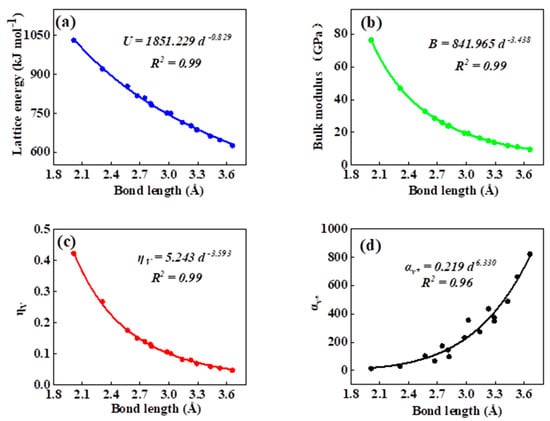
Figure 1.
Plot of correlation between the lattice energy, (a) bulk modulus, (b) chemical hardness density, (c) product of electronic polarizability and molar volume, (d) and chemical bond length of rock salt crystals of group I–VII.
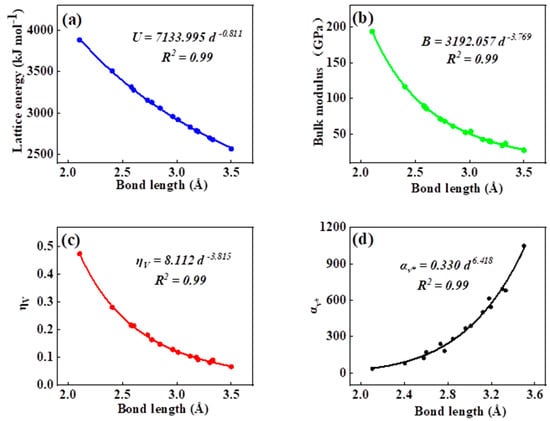
Figure 2.
Plot of correlation between the lattice energy, (a) bulk modulus, (b) chemical hardness density, (c) product of electronic polarizability and molar volume, (d) and chemical bond length of rock salt crystals of group II–VI.
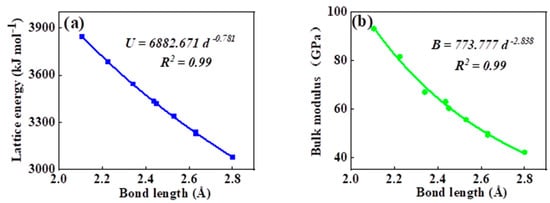
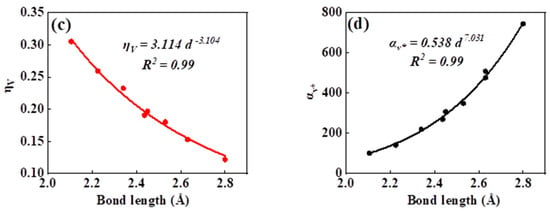
Figure 3.
Plot of correlation between the lattice energy, (a) bulk modulus, (b) chemical hardness density, (c) product of electronic polarizability and molar volume, (d) and chemical bond length of tetrahedral coordinated crystals of group II–VI.
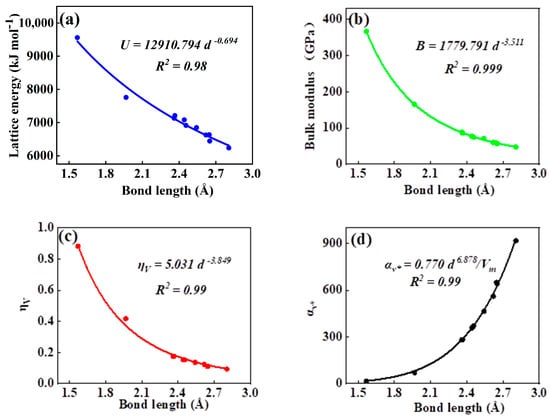
Figure 4.
Plot of correlation between the lattice energy, (a) bulk modulus, (b) chemical hardness density, (c) product of electronic polarizability and molar volume, (d) and chemical bond length of tetrahedral coordinated crystals of group II–VI.
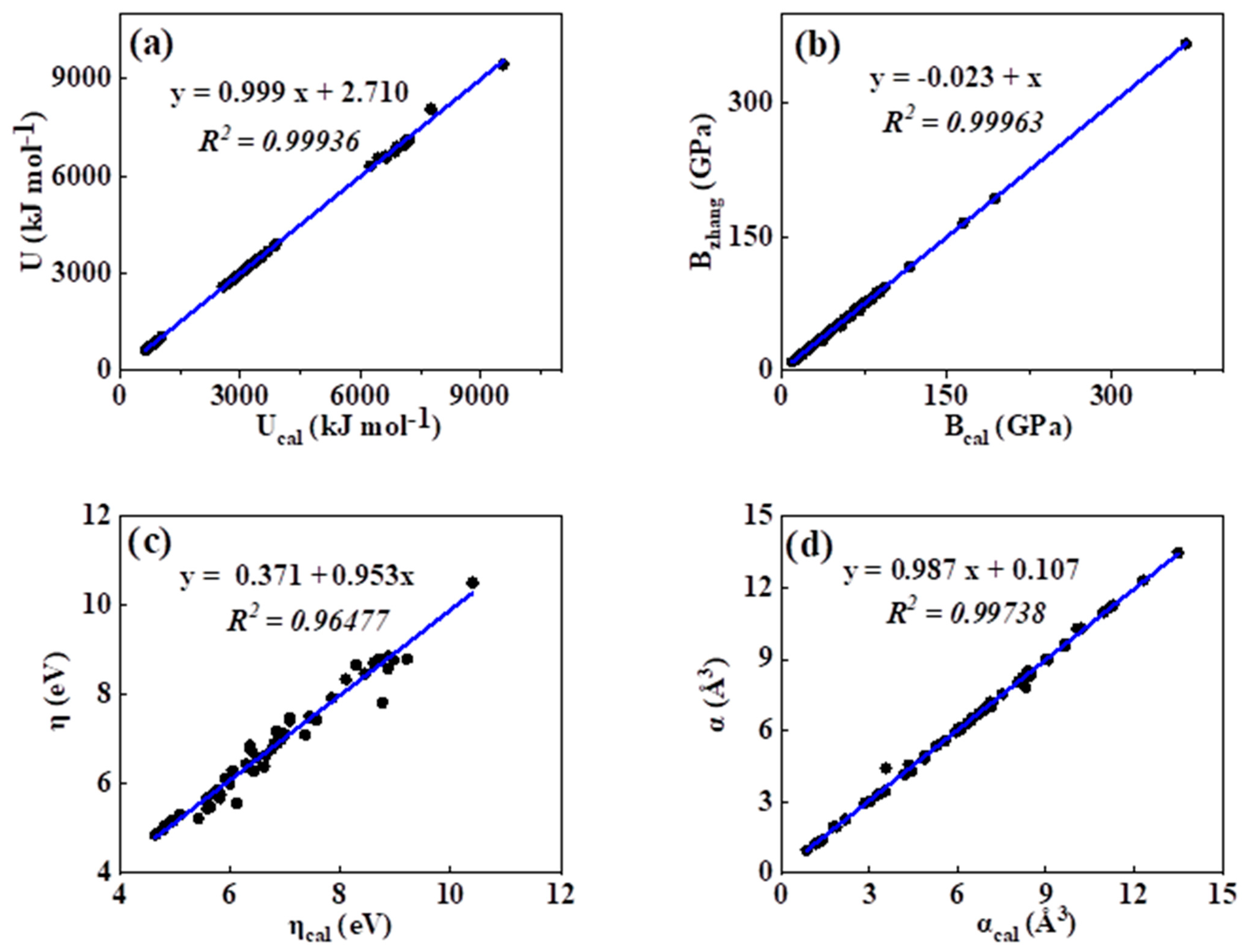
As was mentioned in the introduction, so far, many theoretical methods have been proposed for the estimation of the lattice energy, bulk modulus, chemical hardness, and electronic polarizability of inorganic ionic crystals. In order to show the practical significance of the present curve fitting model, we introduced such a mathematic equation into calculating the lattice energy, bulk modulus, chemical hardness, and electronic polarizability values of binary ANB8-N crystals. The calculated results of lattice energy, bulk modulus, and electronic polarizability of ANB8-N crystals by means of the abovementioned empirical equation P = a·db have been compared with the reported values in the literature, which are plotted and presented in Figure 5a–d. As shown in Figure 5, we can see that a remarkable linear correlation between the estimated values and the corresponding data evaluated in the literature is found (R2 > 0.9). Hence, it is obvious that the calculation of these physicochemical parameters, such as lattice energy, bulk modulus, and electronic polarizability, can be expressed in terms of the chemical bond length of ANB8-N crystals on the basis of empirical fitting relation P = a·db.
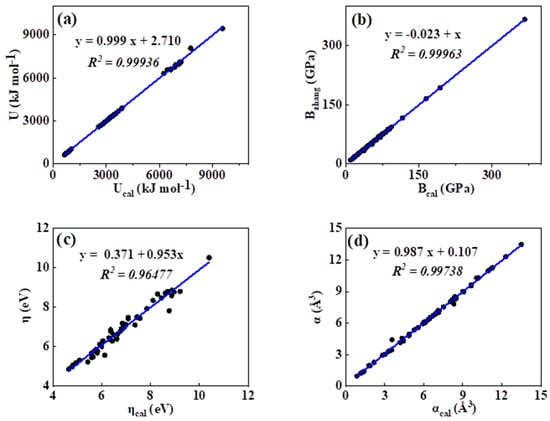
Figure 5.
Plot of correlation between the present calculated values and the date reported in the literature. (a) lattice energy, (b) bulk modulus, (c) chemical hardness, (d) electronic polarizability).
4. Conclusions
In summary, the purpose of the present paper is to propose a facile method for the comprehensive estimation of the lattice energy, bulk modulus, electronic polarizability, and chemical hardness of inorganic crystals based on simple structure parameters for exploring the intrinsic relationships between the structure and property of solid matters. This new method demonstrates that there is a good mathematical relationship between the lattice energy, bulk modulus, electronic polarizability, chemical hardness, and chemical bond length of binary ANB8-N crystals. The normal mathematical expression between these physicochemical parameters and chemical bond length is P = a·db; a and b depend on the type of crystals and the relevant squares of the correlation coefficient R2 have been given to measure the effectiveness of the least squares fitting. The new data on lattice energy, bulk modulus, and electronic polarizability were calculated by using empirical equations. The calculated results are in good agreement with the values reported in the previous literature. It is clear from the obtained results that the present method allows for easy evaluation of the lattice energy, bulk modulus, electronic polarizability, and chemical hardness of binary ANB8-N crystals using a mathematic fitting model without the need for ab initio calculations and complex structure parameters. Finally, it should be noted that further studies about the correlation among lattice energy, bulk modulus, electronic polarizability, and chemical bond length are still necessary for complex crystals. Furthermore, we will search for other physicochemical parameters that are closely related to chemical bond length.
Author Contributions
Conceptualisation, X.W. and X.Z.; methodology, X.W. and X.Z.; investigation, X.W. and X.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, X.W. and X.Z.; writing—review and editing, X.W. and X.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Doctoral Scientific Research Foundation of Inner Mongolia Minzu University (Project No: BS422), Project of Undergraduate Innovation and Entrepreneurship of Inner Mongolia Minzu University (Project No: 202210136007), the Foundation of Basic Scientific Research of Inner Mongolia Minzu University (Project No: GYKY22121), and the Foundation of Liaoning Key Laboratory of Chemical Additive Synthesis and Separation (Project No: ZJNK2008).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
X.Z. deeply thanks the West Light Foundation’s Visiting Scholar Research Program.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Li, K.Y.; Wang, X.T.; Zhang, F.F.; Xue, D.F. Electronegativity identification of novel superhard materials. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 100, 235504–235507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robert, G.P.; Yang, W.T. Density functional approach to the frontier-electron theory of chemical reactivity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1984, 106, 4049–4050. [Google Scholar]
- Carlos, C.; Paul, A.; Frank, D.; David, J.T.; Paul, G. Should negative electron affinities be used for evaluating the chemical hardness? Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 2285–2293. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.Y.; Wang, X.L.; Lin, H.; Wang, Z.Q. Electronic polarizability and optical basicity of lanthanide oxides. Phys. B 2007, 392, 132–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatsu, T.; Dimitrov, V.; Tasheva, T.; Honma, T. A review: A new insight for electronic polarizability and chemical bond strength in Bi2O3-based glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2020, 550, 120365–120380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, D.F.; Zuo, S.; Ratajczak, H. Electronegativity and structural characteristics of lanthanides. Phys. B 2004, 352, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.Y.; Wang, X.L. Physicochemical parameters of oxyfluoride glasses using the average electronegativity. Phys. Chem. Glasses Eur. J. Glass Sci. Technol. B 2009, 50, 332–334. [Google Scholar]
- Verma, A.S. An empirical model for bulk modulus and cohesive energy of rocksalt-, zincblende and chalcopyrite-structured solids. Phys. Status Solidi B 2009, 246, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatsu, T.; Honma, T.; Tasheva, T.; Dimitrov, V. Structural role of Nb2O5 in glass-forming ability, electronic polarizability and nanocrystallization in glasses: A review. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2022, 581, 121414–121433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuleshova, L.N.; Hofmann, D.W.M.; Boese, R. Lattice energy calculation-a quick tool for screening of cocrystals and estimation of relative solubility. Case of flavonoids. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2013, 564, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Song, Z.K.; Wang, Y.; Li, L.X. Effect of ion substitution for Nd3+ based on structural characteristic on the microwave dielectric properties of NdNbO4 ceramic system. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2014, 97, 976–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.T.; Zhang, S.Y.; Wu, Z.J. Lattice energy estimation for inorganic ionic crystals. Inorg. Chem. 2003, 42, 2465–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, W.M.; Fu, Z.Y. A simple bulk modulus model for crystal materials based on the bond valence model. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 22177–22189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, S.; Kaya, C. A new equation for calculation of chemical hardness of groups and molecules. Mol. Phys. 2015, 113, 1311–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.Y.; Wang, X.L.; Lin, H.; Wang, Z.Q. Correlation among electronic polarizability, optical basicity and interaction parameter of Bi2O3–B2O3 glasses. Phys. B 2007, 390, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Prasad, G.M.; Chandra, D. Lattice energy and electronic polarizability of binary tetrahedral semiconductors. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 1997, 58, 463–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.S.; Sharma, D. Lattice energy of zinc blende (AIIIBV and AIIBVI) solids. Phys. Stat. Sol. 2008, 245, 678–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, S.; Kaya, C. A simple method for the calculation of lattice energies of inorganic ionic crystals based on the chemical hardness. Inorg. Chem. 2015, 54, 8207–8213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.Y.; Li, H.L.; Li, H.Y.; Zhou, S.H.; Cao, X.Q. Calculation of the bulk modulus of simple and complex crystals with the chemical bond method. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 1304–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, M.L. Calculation of bulk moduli of diamond and zinc-blende solids. Phys. Rev. B 1985, 32, 7988–7991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinle-Neumann, G.; Stixrude, L.; Cohen, R.E.; Gulseren, O. Elasticity of iron at the temperature of the earth’s inner core. Nature 2001, 413, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laio, A.; Bernard, S.; Chiarotti, G.L.; Scandolo, S.; Tosatti, E. Physics of iron at earth’s core conditions. Science 2000, 287, 1027–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.X. Elastic and electronic properties of TcB2 and superhard ReB2: First-principles calculations. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 91, 101904–101906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.Y.; Xue, D.F. Empirical calculations of elastic moduli of crystal materials. Phys. Scr. 2010, 139, 14072–14076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, N.; Ghosh, D.C. Spectroscopic evaluation of the global hardness of the atoms. Mol. Phys. 2011, 109, 1533–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, N.; Ghosh, D.C. A new algorithm for the evaluation of the global hardness of polyatomic molecules. Mol. Phys. 2011, 109, 917–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, D. Geometric mean principle for hardness eualization: A corollary of Sanderson’s geometric mean principle of electronegativity equalization. J. Phys. Chem. 1986, 90, 4216–4217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkhoshkhany, N.; Marzouk, S.; El-Sherbiny, M.; Ibrahim, H.; Burtan-Gwizdala, B.; Alqahtani, M.S.; Hussien, K.I.; Reben, M.; Yousef, E.S. Investigation of structural, physical, and attenuation parameters of glass: TeO2-Bi2O3-B2O3-TiO2-RE2O3 (RE: La, Ce, Sm, Er, and Yb), and applications thereof. Materials 2022, 15, 5393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Ning, G.L.; Sun, T.Z. Relationships between molar polarizability, molar volume and density of binary silicate, borate and phosphate glasses. Phys. Chem. Glasses Eur. J. Glass Sci. Technol. B 2007, 48, 354–356. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, J.; Xue, D.F.; Ning, G.L. Relationship between the third order nonlinear optical susceptibility and the density of the binary borate glasses. Phys. Chem. Glasses 2004, 45, 361–362. [Google Scholar]
- Kumari, C.R.T.; Al Otaibi, A.; Kamaraj, T.; Nageshwari, M.; Mathubala, G.; Manikandan, A.; Caroline, M.L.; Sudha, S.; Kashmery, H.A.; Madhu, P.; et al. A brief study on optical and mechanical properties of an organic material: Urea glutaric acid (2/1)-a third order nonlinear optical single crystal. Crystals 2021, 11, 1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrov, V.; Sakka, S. Electronic oxide polarizability and optical basicity of simple oxides. J. Appl. Phys. 1996, 79, 1736–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.Y.; Xue, D.F. Electronegativity estimation of electronic polarizabilities of semiconductors. Mater. Res. Bull. 2010, 45, 288–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, J.A. Lattice energies of crystalline silicates and electronic polarizability. Phys. Chem. Glasses 2005, 46, 257–261. [Google Scholar]
- Petrov, D.; Angelov, B. Lattice energies and polarizability volumes of lanthanide monoaluminates. Phys. B 2012, 407, 3394–3397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrov, D. Lattice enthalpies of lanthanide orthoferrites LnFeO3. Acta Chim. Slov. 2015, 62, 716–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrov, D. Lattice enthalpies and magnetic loops in lanthanide iron garnets, Ln3Fe5O12. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2015, 87, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.Y.; Wang, X.L.; Lin, H.; Wang, Z.Q. Relationships between lattice energy and electronic polarizability of ANB8-N crystals. Opt. Commun. 2010, 283, 1668–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.G.; Lu, M.C.; Zhu, L.; Zhu, L.L.; Li, Y.D.; Zhang, M.; Li, Q. Orthorhombic BN: A novel superhard sp3 boron nitride allotrope. Phys. Lett. A 2014, 378, 741–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zon; Thainoi, S.; Kiravittaya, S.; Nuntawong, N.; Sopitpan, S.; Kanjanachuchai, S.; Ratanathammaphan, S.; Panyakeow, S. Direct growth of InSb nanowires on CdTe (001) substrates by molecular beam epitaxy. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2022, 285, 115958–115964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.H.; Lin, S.; Yang, D.; Yang, X.T.; Lei, Y.S.; Zhang, J.Q.; Wu, L.L.; Yang, Y.Q. Preparation and performance optimization of CdTe-based betavoltaic transducer devices. Opt. Mater. 2022, 133, 113018–113026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.C.; Jo, H.G. The effect of Te-doping and heat treatment on the structural properties of CdTe absorber layer for CdS/CdTe solar cell. Opt. Mater. 2022, 134, 113061–113066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Wang, H.; Zhou, X.F.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Duan, J.A. Second harmonic generation in zinc sulfide by femtosecond laser irradiation. Opt. Laser Technol. 2020, 127, 106145–106150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.L.; Zhou, S.H.; Zhang, S.Y. The relationship between the thermal expansions and structures of ABO4 oxides. J. Solid State Chem. 2007, 180, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.S.; Bhardwaj, S.R. Correlation between ionic charge and ground-state properties in rocksalt and zinc blende structured solids. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2006, 18, 8603–8612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, R.R.; Rama Gopal, K.; Narasimhulu, K.; Siva Sankara Reddy, L.; Raghavendra Kumar, K.; Balakrishnaiah, G.; Ravi Kumar, M. Interrelationship between structural, optical, electronic and elastic properties of materials. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 473, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, A.K. Relationship between lattice energy and an ionic ratio in II-VI and III-V semiconductors. Phys. Stat. Sol. 1998, 209, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.Y. Chemical Bond Theory of Complex Structure Crystals on Dielectric Description and Application; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Iwadate, Y.; Fukushima, K. Electronic polarizability of a fluoride ion estimated by refractive indexes and molar volumes of molten eutectic LiF-NaF-KF. J. Chem. Phys. 1955, 14, 6300–6302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philips, J.C.; Vechten, J.A.V. Dielectric classification of crystal structures, ionization potentials, and band structures. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1969, 22, 705–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philips, J.C. Ionicity of the chemical bond in crystals. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1970, 42, 317–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).