Abstract
An extra-heavy crude oil underground upgrading concept and laboratory experiments are presented which involve the addition of a hydrogen donor (tetralin) to an Orinoco Basin extra-heavy crude oil under steam injection conditions (280–315 °C and residence times of at least 24-h). Three iron-containing nanocatalysts (20 nm, 60 nm and 90 nm) were used and the results showed increases of up to 8° in API gravity, 26% desulfurization and 27% reduction in the asphaltene content of the upgraded product in comparison to the control reaction using inert sand. The iron nanocatalysts were characterized by SEM, XPS, EDAX, and Mössbauer spectroscopy before and after the upgrading reactions. The results indicated the presence of hematite (Fe2O3) as the predominant iron phase. The data showed that the catalysts were deactivating by particle sintering (~20% increase in particle size) and also by carbon deposition. Probable mechanisms of reactions are proposed.
1. Introduction
In general, downhole upgrading processes have several potential benefits in comparison to above-round counterparts: Firstly, enhanced oil recovery can be obtained by accessing more difficult fluids with the potential increase of the volumetric production of wells. Secondly, decreases in the consumption of costly and scarce light and medium crude oils (used as diluents) can be achieved. Reductions in lifting and transportation costs of upgrading crude oil can also be attainable. Finally, there is the potential generation of higher value products with higher API gravities and reduced viscosity, asphaltene, sulfur and heavy-metal contents [1,2,3,4,5,6].
However, there are important technical challenges involved in developing subsurface upgrading processes. Firstly, downhole processes are difficult to monitor under reservoir conditions. Also, each well and reservoir requires individual treatment; thus, increasing the complexity of field operations [1,2,3,4,5,6].
In general, aquathermolysis is the thermal cracking of petroleum oils and hydrocarbons in the presence of water and has been studied for more than 30 years [7,8,9,10,11]. During steam-stimulated production of heavy oils, thermal energy breaks large molecules into smaller ones with the concomitant reduction of oil viscosity [7,8,9,10,11]. The aquathermolysis reaction can be accelerated in the presence of metal catalysts, and has become an important area of research over the last three years. Specifically, several research groups in Mexico [12,13], Japan [14] and China [15,16,17,18,19] have explored this route for the underground upgrading of heavy and extra heavy crude oils under conditions similar to those achieved under steam injection (250–280 °C). Some of the lab results have shown increases of up to 4–5° API with two- to three-fold reduction of viscosity [12,13,14,15].
The catalytic aquathermolysis concept was field tested in the Liaohe Field, China in 2005 [16]. Twenty cyclic steam stimulation wells were treated by adding a dispersed catalyst formulation and hydrogen donors. Increases in the heavy oil production of the wells were obtained with high sulfur removal (86%) and asphaltene removal (28%) in comparison with the original crude oil.
In 2007, Wen et al. [16] reported additional field tests in the same oil field. Steam is injected into vertical wells to pre-heat the oil reservoir. A catalyst solution (Molybdenum Oleate) and the remainder of the steam are then injected into the reservoir (total of 12,500 BBL of steam) with a soak time of 7–10 days. Eight cyclic steam stimulation (CSS) wells were treated by this methodology and in seven wells increases in the heavy crude oil production were obtained [16].
Three metal derived catalysts (water soluble iron with tetralin, oil soluble molybdenum oleate and dispersed aromatic sulfonic iron) were compared and showed slightly higher activity in laboratory vs. field tests with differences in the 10–12% range [15,16,17]. These results show that, indeed, the use of metal catalysts, with and without hydrogen donors has a synergic effect on viscosity reduction of heavy oils, hence the catalytic aquathermolysis and hydrogen addition could be used effectively for steam-stimulated oil recovery.
In 2012, Chen et al. [18] reported the use of an alkyl ester sulfonate copper (0.1–0.3 wt.%), which has not only a catalytic center but also has a potential hydrogen precursor structure. In a field tests at Liaohe Field, steam was injected into a vertical well to pre-heat up the oil reservoir. The catalyst solution and the rest of the steam were then injected into the reservoir (total of 7500 BBL of steam, soaking time six days). Reductions of 85% viscosity and 54% asphaltene content were reported [18]. However, no description of the fate and recycling of the catalyst were reported as well as changes in the API gravity and sulfur contents.
In 2013, Chen et al. [19] studied the catalytic aquathermolysis of iron and copper based p-Toluenesulfonic catalysts for the upgrading of six heavy oils under lab conditions at 200 °C for 24 h. As before, viscosity and asphaltene content reductions were reported. Using H-NMR, SEC and GC-MS, it was proposed that the Cu containing catalyst led to the de-polymerization and cleavage of some bridged bonds of the asphaltenes, whereas the iron counterpart mainly caused the ring-opening of heterocyclic rings and isomerization of side chains.
In our previous publications [3,4,5,6], we reported a concept that involves the addition of a hydrogen donor additive (tetralin or other distillate fractions having at least 40 wt.% naphthenic aromatic compounds) and, in the presence of steam, natural formation (catalyst) and methane (natural gas), leads to extra-heavy crude oil upgrading (from 9 to 14° API) at lab conditions [5,6]. This concept could be coupled to a steam stimulation process with 70–80% hydrogen donor recycled [5,6]. In our previous publication [5], X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) analysis of the natural formation indicated the presence of 0.6 wt.%. of iron as Fe2O3. The use of this compound as catalyst led to further reduction in the viscosity of the upgraded crude oil (from 5500 cP at 60 °C with natural formation to 1300 cP using Fe2O3) [5]. Thus, in this work, three iron-containing nanocatalysts were evaluated and laboratory experiments will be presented that involve the addition of a hydrogen donor additive (tetralin) to an Orinoco Basin extra-heavy crude oil (Hamaca C.) under steam injection conditions (280–315 °C and residence times of at least 24-h.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Upgrading Reaction
The upgrading experiments were carried out under batch conditions with a sand:crude oil:tetralin:water ratio of 10:1:1:1 at 6.2 MPa of CH4 of initial pressure at 280–315 °C for 24 h. Firstly, a control experiment (Table 1, Run 1 with 0 h) was carried out in order to determine the effects of sample handling procedure. As can be seen, product characterization indicates an increase of only 1° API, 5% reduction of sulfur (%HDS) and 9% reduction in asphaltenes. These changes can be attributed to upgrading reactions occurring during the time needed to reach the distillation temperature to separate the tetralin, which was approximately 30–45 min (see Experimental Section)
By increasing reaction time to 24 h (Table 1, Run 2), a product with higher ° API (14.7°) and lower percentages of sulfur (12%) and asphaltenes (13%) was obtained in comparison with the original crude oil. Even though the changes in the product properties were small and sometimes within the experimental error of the techniques used, the results presented in Table 1 indicates a general trend, which allows concluding that effective crude oil upgrading can be achieved in the presence of hydrogen donor (tetralin) at steam injection conditions (315 °C, 24 h) [5]. As mentioned, these results have been reported before in our previous publications [3,4,5,6].
The effect of the tetralin concentration (from 1% to 50% w/w) on the properties of the upgraded crude oils was studied in our previous paper [5]. For example, the viscosity of the product decreased from 9870 to 2900 cP (measured at 60 °C) with the hydrogen donor added up to 50% w/w [5].

Table 1.
Properties of the upgraded crude oil using tetralin under steam injection conditions a. Effect of the presence of iron nanocatalysts.
| Run | Solid (Reaction time) | °API b (±0.5°) | %HDS c (±1%) | % Asphaltenes Reduction d |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | Original Hamaca C. e | 9.1 | - | - |
| 1 | Control Exp.(0 h) f | 10.2 | 5% | 9% |
| 2 | Mineral Formation g | 14.7 | 12% | 13% |
| 3 | Fe-20/SiO2 h | 17.5 | 28% | 31% |
| 4 | Fe-60/SiO2 h | 14.5 | 22% | 19% |
| 5 | Fe-90/SiO2 h | 13.2 | 8.5% | 17.9% |
a Experiments carried out under batch conditions, no stirring, Ratio sand:crude:tetralin:water = 10:1:1:1, 900 psi of CH4 initial pressure, 1600 psi of final pressure at 315 °C for 24 h. Results are the average of at least two different experiments. b API gravity. Numbers in bracket indicate the errors. c Percentage of reduction of sulfur with respect to the original crude oil. Numbers in bracket indicate the errors. d Percentage of reduction asphaltenes with respect to the original crude oil. e Original crude oil before upgrading experiments. f Same experimental conditions, but the tetralin was removed and the products analyzed just as the reactor reached the operating temperature. g Natural mineral formation from the Hamaca reservoir. h 5 wt.%. (nominal) Fe supported on sand (99% SiO2, partially dehydroxylated at 600 °C with a surface area of 10 m2/g).
Next, three iron supported nanocatalysts were prepared by dispersion of commercial 20 nm, 60 nm and 90 nm iron oxide nanoparticles in a natural silica support (see Experimental Section for details). In the presence of iron-containing nanocatalysts, further improvement in the upgraded crude oil properties were obtained (Table 1, Runs 3–5). Maximum increases in the API gravity of up of 17.5° API with percentage of hydrodesulfurization (%HDS) of 28% and removal of asphaltenes of 31% were obtained (Run 3). These results clearly indicate that the presence of a catalyst is necessary to yield upgraded products with higher quality. Consistent with these and previous results, naphthalene was detected in the reaction media as determined by GC-MS analysis [3,4,5,6].
The fact that the removal of sulfur and asphaltenes increase in the presence of iron may indicate that the hydrogen transfer from the tetralin hydrogen donor could be assisted by the metal catalyst as reported in the literature [15,16,17,18,19] and by Sakanishi et al. during coal liquefaction experiments [20]. As reported previously [3,4,5,6], the main sulfur-containing product detected was H2S in the gas formed (lower than 5% w/w) during the upgrading experiments.
The effect of reaction temperature on the viscosity of the upgraded crude oils can be seen in Figure 1. As shown, the results indicate that the order of activity of the iron nanocatalysts is Fe-20/SiO2 > Fe-60/SiO2 > Fe-90/SiO2. It can be proposed that the order of activity is inversely proportional to the catalysts’ initial particle size. Thus, different iron catalysts gave different upgraded crude oils with different properties. Therefore, the catalyst characterization study was carried out, and the results are presented in the next section.
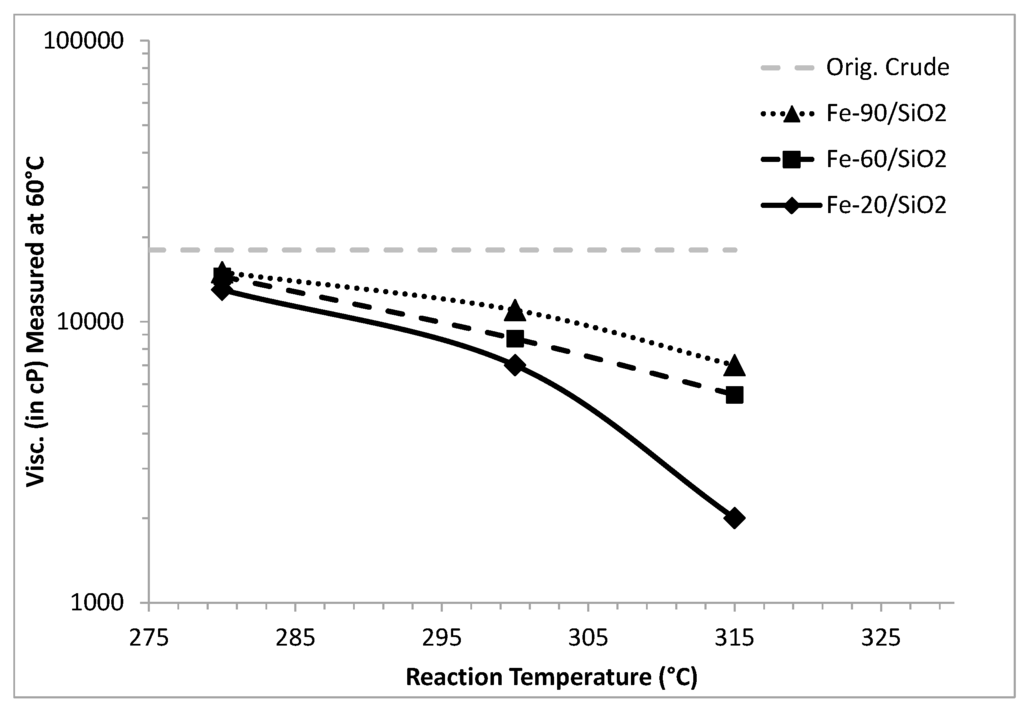
Figure 1.
Viscosity (cP) at 60 °C of the upgraded crude oil using iron-containing catalysts.
2.2. Catalyst Characterization
Firstly, the catalysts were analyzed by Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) and the results are shown in Figure 2. As can be seen, the iron catalyst Fe-20/SiO2 before the upgrading reaction showed a more or less even dispersion with particles of similar size and shapes. The analysis of 100 particles gave a mean average size of 18 nm. On the other hand, TEM analysis of the same catalyst after the upgrading reaction showed an uneven dispersion of the metal with particles of different shapes and sizes. The measurement of 100 particles gave a mean average size of 23 nm giving evidence of a particle sintering under reaction conditions (315 °C, tetralin, water, 24 h).
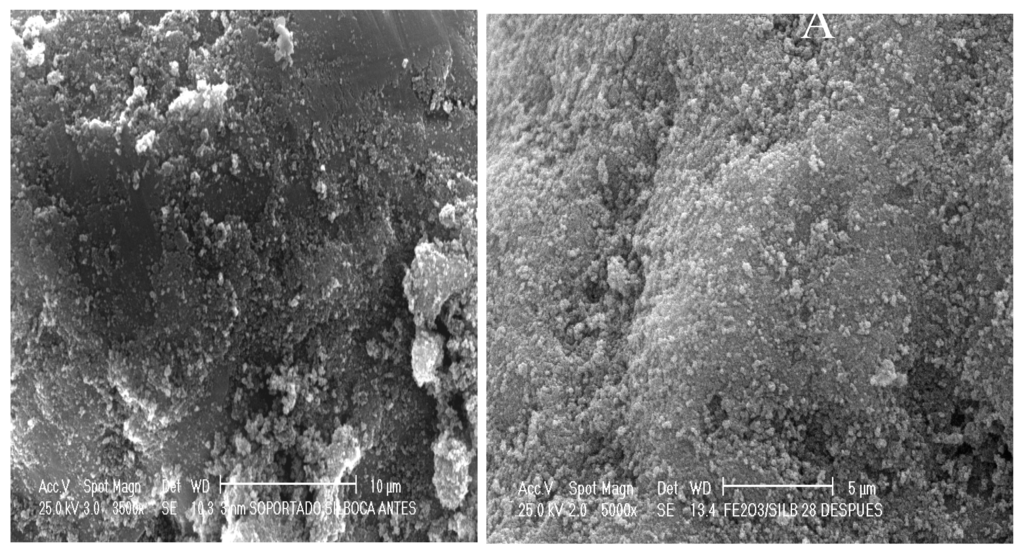
Figure 2.
Scanning Electron Microscopy photographs of the Fe-20/SiO2 catalyst (A) Before the upgrading reaction and (B) After the upgrading reaction (315 °C and 24 h, Tetralin).
The characterization of the Fe-60/SiO2 gave similar results with particles sizes of 53 and 61 nm before and after the upgrading reaction (See Figure 3). The differences in particle sizes and, presumably the metal dispersion, between Fe-20/SiO2 (18–23 nm) and Fe-60/SiO2 (53–61 nm) could explain why the first catalyst is more active (higher °API, HDS and removal of asphaltenes) than the second (see Table 1). Similar results were obtained for Fe-90/SiO2 (from 83 nm to 93 nm before and after upgrading reaction).
The characterization by X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) of the iron catalyst Fe-20/SiO2 showed binding energies for the Fe 2p3/2 of 710.6 and 711.3 eV before and after the upgrading experiments, respectively (Table 2). According to the data reported in the literature [21], these bands can be assigned to Fe3+ present in the Fe2O3. Consistent with these results, the O1s bands were found at 530.9 and 532.0 eV, respectively, and were assigned to O2− [21]. Similar results were obtained for the Fe-60/SiO2 and Fe-90/SiO2 catalysts.
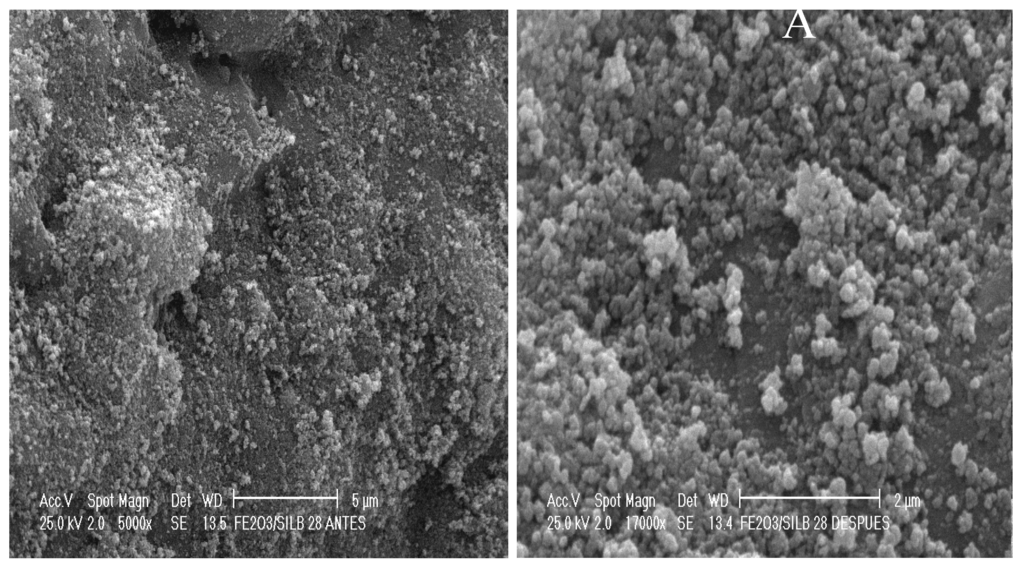
Figure 3.
Scanning Electron Microscopy photographs of the Fe-60/SiO2 catalyst (A) Before the upgrading reaction and (B) After the upgrading reaction (315 °C and 24 h, tetralin).

Table 2.
Characterization by X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) of the iron catalyst Fe-20/SiO2.
| Experiment a | Element Band b | Binding Energy (eV) c | % Atomic d | Fe-Dispersion e |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before Upgrading Reaction | Fe 2p2/3 | 710.6 | 16.27 | 4.54 |
| O 1s | 530 | 25.07 | ||
| C 1s | 284.6 | 55.09 | ||
| Si 2p | 103.1 | 3.58 | ||
| After Upgrading Reaction | Fe 2p2/3 | 711.3 | 6.86 | 1.75 |
| O 1s | 530.5 | 18.27 | ||
| C 1s | 284.6 | 69.18 | ||
| Si 2p | 103 | 5.68 |
a Experiments carried out under batch conditions, no stirring, Ratio sand:crude:tetralin:water = 8:1:1:1, 900 psi of CH4 initial pressure, 1600 psi of final pressure at 315 °C for 24 h. b Element analyzed and XPS band. c Binding energy in eV. d Atomic percentage. e Iron dispersion calculated by dividing Iron atomic percentage into Si atomic percentage.
Also using the XPS data, iron dispersion was estimated by dividing the iron atomic percentage into the silicon atomic percentage. As can be seen in Table 2, Fe dispersion (as determined by Fe/Si atomic percentages) was reduced from 4.54 to 1.75. These results are consistent with the increase in particle size determined by TEM. Similar results were obtained for the Fe-60/SiO2 and Fe-90/SiO2 catalysts.
The characterization of the Fe-20/SiO2 by XRD after the upgrading experiment can be seen in Figure 4. By using the XRD-library of the apparatus, Fe2O3, SiO2, coke, and graphite phases could be detected on the catalyst after the upgrading reactions. These results are consistent with those observed by XPS, in which iron, oxygen, silicon, and carbon were found on the catalyst surfaces.
To definitively determine the active phase on the surface, the Fe-20/SiO2 catalyst was analyzed by Mössbauer Spectroscopy after the upgrading experiment (Figure 5). As can be seen, a typical spectrum of the hematite (Fe2O3) is found, which confirmed the presence of such phase on the surface of the Fe-20/SiO2 catalyst after the upgrading experiment (315 °C, 24 h).
Finally, to verify the presence of a carbonaceous phase found by XPS and XRD, a TGA analysis was carried out and an average of 2.8% w/w of loss in mass was observed after heating the used catalyst in oxygen atmosphere at 325 °C for 4 h. Similar behavior was observed with the Fe-60/SiO2 catalyst. These results indicate that not only the catalysts were deactivating by particle sintering, but also by carbon deposition.
2.3. Mechanistic Considerations
In order to gain mechanistic information for the upgrading reactions, 1H-NMR analyes were carried out on the upgraded crude oil and the results are shown in Table 3. For the products of the three iron-supported, nanocatalysts increases (15.1–15.9%) in the amount of α-hydrogen bonded to aromatic rings were observed in comparison to those observed for the control run (14.8%) and for the crude oil (14.7%).
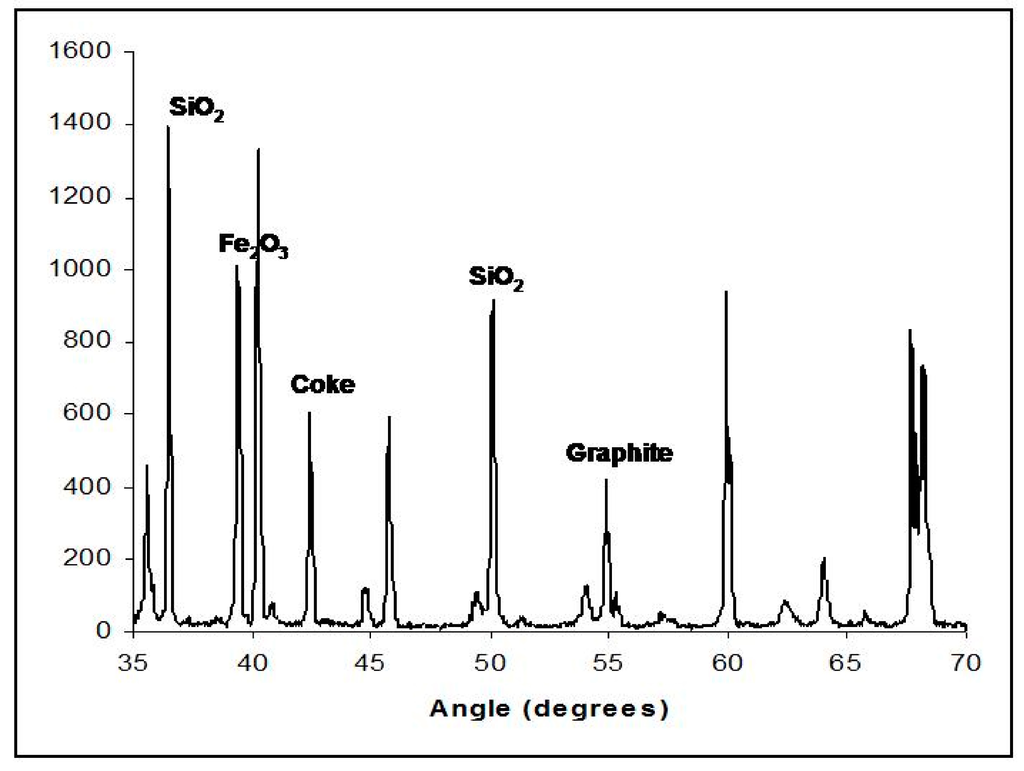
Figure 4.
X-Ray Diffraction Analysis of the Fe-20/SiO2 catalyst after the upgrading reaction (315 °C and 24 h, tetralin).
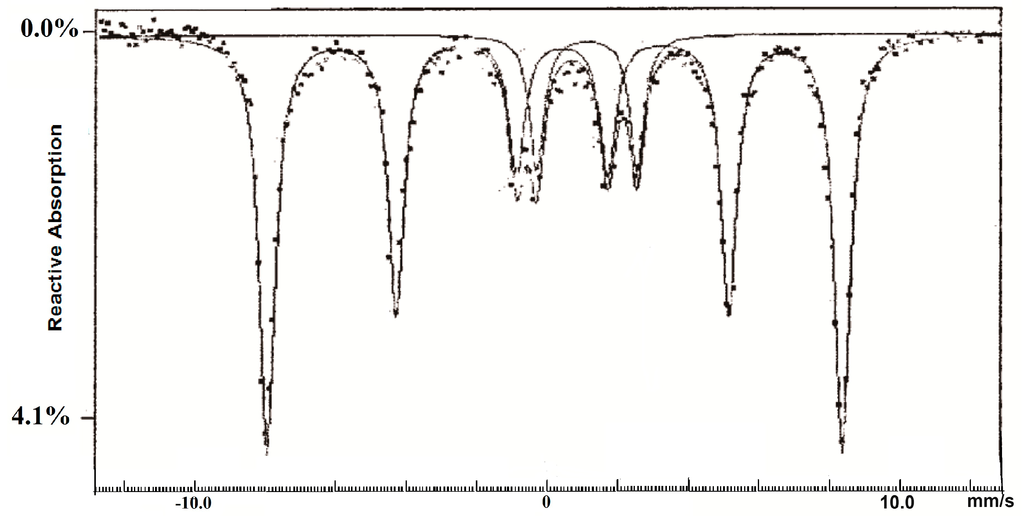
Figure 5.
Mössbauer spectrum of Fe-20/SiO2 catalyst after the upgrading experiment (315 °C, 24 h) with the continuous line representing the result of a computer adjustment including, IS (Isomer Shift), FWHM and QS (quadrupole splitting).

Table 3.
Protons distributions for upgraded Hamaca crude oils measured by 1H NMR a. Effect of the Presence of Iron Nanocatalysts.
| Run | Solid (Reaction time) | Harom b | Haliph c | Hα d | Hβ e | Hγ f |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | Original Hamaca C. e | 5.1 | 94.1 | 14.7 | 56.2 | 24.0 |
| 1 | Control Exp.(0 h) f | 5.6 | 94.4 | 14.8 | 55.2 | 24.4 |
| 2 | Mineral Formation g | 6.9 | 93.1 | 14.9 | 53.8 | 24.4 |
| 3 | Fe-20/SiO2 h | 7.6 | 92.4 | 15.4 | 52.1 | 24.9 |
| 4 | Fe-60/SiO2 h | 7.4 | 92.6 | 15.1 | 52.9 | 24.6 |
| 5 | Fe-90/SiO2 h | 6.8 | 93.2 | 14.9 | 54.0 | 24.3 |
a The reactions were carried out as described in Table 1. Errors are expressed in terms of the standard deviations (±0.2%). b Harom: percentages of hydrogen bonded to aromatic carbons. c Haliph: percentages of hydrogen bonded to aliphatic carbons. d Hα: percentages of hydrogen bonded to aliphatic carbons in α position to an aromatic ring. e Hβ: percentages of hydrogen bonded to aliphatic carbons in β position to an aromatic ring. f Hγ: percentages of hydrogen bonded to aliphatic carbons in γ or more position to an aromatic ring. f Same experimental conditions but the tetralin was removed and the products analyzed just as the reactor reached the operating temperature. g Natural mineral formation from the Hamaca reservoir. h 5% wt. (nominal) Fe supported on natural silica (99% SiO2, partially dehydroxylated at 600 °C with a surface area of 10 m2/g).
Furthermore, increases in aromatization occurred for all the upgrading reactions as shown by the increase in the percentages of aromatic protons from 5.1% in the original crude to 6.8–7.6% for runs 3–5. One plausible explanation could be metal catalyzed incorporation of the methyl groups to the crude oil molecules followed by thermal or catalytic aromatization of the naphthenic compounds, as shown in Equation (1) [22].
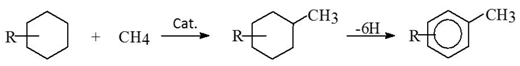
Egiebor and Gray found methyl- and dimethyl-substituted products by GC analysis of the donor solvent (tetralin), which was attributed to direct alkylation by reaction with methane during iron catalyzed coal liquefaction [23]. Also, similar results were obtained previously for extra-heavy crude oil upgrading under higher temperature (380–420 °C) thermal [24] and catalytic conditions (Mo-containing catalyst) [22]. The incorporation of methyl groups, coming from methane, into the crude oil molecules was confirmed by isotopic carbon distribution measurements (13C/12C) using 13CH4 as a source of hydrogen [22]. However, the addition of methane during the upgrading reaction is very small estimated value (0.01% w/w) and alternative explanations can be suggested as well. [22].
Additionally, an alternative explanation for the changes in protons distribution can be suggested. Depending on the substituents on cycloalkyl rings in the original oil, conversion of a naphthenic aromatic compounds such as 1-methyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthalene to the corresponding aromatic analog (1-methyl naphthalene) leads to increases in both the percentages of aromatic protons and α-hydrogen bonded to aromatic rings. Also, this type of reaction reduces β-hydrogen bonded to aromatics as observed in Table 3.
The higher percentages of HDS obtained from the three iron supported nanocatalysts in comparison with the control and sand experiments (runs 1 and 2, Table 1) can also be explained by the generation of hydrogen as shown in Equation (1). Other alternate mechanisms can be proposed, such as a direct addition of methyl radicals to aromatic moieties. Further studies are required to address these important questions.
3. Experimental Section
The extra-heavy crude oil from the Orinoco Belt (Hamaca C.) used showed the following properties: 9.1° API Gravity, 22.0% asphaltenes (heptanes), 14.2% Carbon Conradson, viscosity (80 °C) = 1810 cP, 500 °C + residue = 71%, 7500 ppm nitrogen, 3.75% sulfur, 450 ppm of vanadium and 102 ppm of nickel and initial boiling point of 201 °C at 1 atm).
The iron catalysts were prepared by dispersing commercial nanoparticles Fe2O3 in methanol and mixing the resulting solution under inert atmosphere with naturally occurring sand from Yaracuy State, Venezuela (99% SiO2, partially dehydroxylated at 600 °C with a superficial area of 10 m2/g). After stirring for four h, the methanol was removed at 50 °C under vacuum, and the percentage of iron was 5 wt.% (nominal) for all the catalysts studied. The 20 nm (Fe-20/SiO2) and 60 nm (Fe-60/SiO2) Fe2O3 nanoparticles (nominal) were purchased from Nantek and the 90 nm (Fe-90/SiO2) analog from Fildrech Science.
The upgrading reaction system as well as the experimental procedure are described elsewhere5. In a typical experiment, the reactor was loaded with extra-heavy crude oil sands (with or without the nanocatalyst and 10% w/w of crude oil), water, and tetralin (Aldrich used as received) at a weight ratio of 10:1:1, respectively. In all the experiments, the catalyst:crude oil ratio was 2:1.The reactor was heated at 5 °C/min to 260–280 °C, generating a final pressure of approximately 1600 psi for 24 h (900 psi initial methane pressure). After completing the experiment, water and tetralin were separated from the oil sands by vacuum distillation at 300°C and residual tetralin was less than 0.05% as revealed by H-NMR of the distillated residue. The reactor was then cooled to room temperature and oil was removed from sand by solvent extraction with dichloromethane. Crude oil and water mass balances were in the 93–99% w/w range with gas yields lower than 5% w/w. Coke yields were below the detection limit of our technique (1% w/w). Percentages of recovery of tetralin were in the 92–105% range due to distillation of light fractions from the upgraded crude oils. All upgrading results are the average of at least two determinations.
Due to the small volume of samples analyzed, the percentages of sulfur removal (%HDS) and of asphaltene reduction (Table 1) were calculated using Equations 2 and 3:
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) analyzes were carried out in an ISI equipment model SS-40 coupled with an EDAX X-ray analyzer model 9100. The particle sizes were the average of 100 measurements. The samples were covered with gold to improve contrast. X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopic (XPS) experiments were carried out using a Leybold-Heraeus Surface Analysis System, which was operated with an aluminum anode (1486.6 eV). Pass energy was set at a constant value of 50 eV. The instrument sensitivity factors used for scaling the photoelectron peak areas were calculated using the method reported by Leon and Carrazza [25]. The Mössbauer spectroscopy was carried out at room temperature, with a constant acceleration spectrometer (Wissel), in the triangular symmetric mode for the velocity. The source was a 57Co in Rhodium with a nuclear electronic acquisition system made by Oxford Tennelec.
4. Conclusions
Orinoco Belt crude oil (Hamaca C) can be upgraded (increases up to 8° API, 26% HDS, 27% reduction in the asphaltene content, etc.) in the presence of hydrogen donors (tetralin) and silica supported iron nanocatalysts under steam injection conditions (280–315 °C and 1600 psi).
The characterization of the catalysts by TEM, XPS, EDAX, and Mössbauer spectroscopy before and after the upgrading reactions indicates the presence of hematite (Fe2O3) as the most probable active species. The results indicated that the catalysts were deactivating by particle sintering (~20% increase in particle size), but also by carbon deposition.
For three iron-supported nanocatalysts, increases in the amount of α-hydrogen bonded to aromatic rings were observed. Furthermore, increases in aromatization occurred for all the upgrading reactions as shown by the increase in the percentages of aromatic protons.
Acknowledgments
To the late Fernando Gonzalez, for their technical assistant for the Mossbauer experiments and for all the things he taught us.
Author Contributions
Cesar Ovalles contributed to the experimental design and the article writing and revising. Victor Rivero and Arelys Salazar contributed to the catalyst characterization and evaluation.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest
References
- Weisman, J.G.; Kessler, R.V. Downhole heavy crude oil hydroprocessing. Appl. Catal. 1996, 140, 1–16, and references therein. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissman, J.G.; Kessler, R.V.; Sawicki, R.A.; Belgrave, J.D.M.; Laureshen, C.J.; Metha, S.A.; Moore, R.G.; Ursenbach, M.G. Down-Hole Catalytic Upgrading of Heavy Crude Oil. Energy Fuels 1996, 10, 883–889, and references therein. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallejos, C.; Vasquez, T.; Ovalles, C. Process for the downhole upgrading of extra heavy crude oil. U.S. Patent 5,891,829, April 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Ovalles, C.; Vallejos, C.; Vásquez, T.; Martinis, J.; Peréz-Peréz, A.; Cotte, E.; Castellanos, L.; Rodríguez, H. Extra-Heavy Crude Oil Downhole Upgrading Process using Hydrogen Donors under Steam Injection Conditions. In Proceedings of SPE International Thermal Operations and Heavy Oil Symposium, Margarita, Venezuela, 12–14 March 2001.
- Ovalles, C.; Vallejos, C.; Vasquez, T.; Rojas, I.; Ehrman, U.; Benitez, J.L.; Martinez, R. Downhole Upgrading of Extra-Heavy Crude Oil Using Hydrogen Donor and Methane under Steam Injection Conditions. J. Pet. Sci. Tech. 2003, 21, 255–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovalles, C.; Rengel-Unda, P.; Bruzual, J.; Salazar, A. Upgrading of Extra-Heavy Crude Using Hydrogen Donor under Steam Injection Conditions. Characterization by Pyrolysis GC-MS of the Asphaltenes and Effects of a Radical Initiator. Am. Chem. Soc. Div. Fuel. Chem. 2003, 48, 59–60. [Google Scholar]
- Hyne, J.B.; Clark, P.D.; Clarke, R.A.; Koo, J.; Greidanus, J.W.; Tyrer, J.D.; Verona, D. Aquathermolysis of Heavy Oils. Rev. Tech. INTEVEP 1982, 2, 87–94. [Google Scholar]
- Viloria, A.; Parisi, S.; Martinez, E.; Gineika, A.; Sanchez, V. Efectos de la inyección de vapor sobre la calidad de un crudo extrapesado de la F.P.O. Rev. Tech. INTEVEP 1985, 5, 69–72. [Google Scholar]
- Siskin, M.; Brons, G.; Katritzky, A.R.; Balasubramanian, M. Aqueous Organic Chemistry. 1. Aquathermolysis: Comparison with Thermolysis in the Reactivity of Aliphatic Compounds. Energy Fuels 1990, 4, 475–482, and references therein. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas, O.R.; Campos, R.E.; Borges, L.G. Experimental Evaluation of Transition Metal Solutions as Additives in Steam Recovery Processes. In Presented at 63th Annual Symposium of SPE, Houston, TX, USA, 2–5 October 1988.
- Reynolds, J.G.; Thorsness, C.B. Mild Upgrading of Midway Sunset Crude Oil from The San Joaquin Valley of California by Aqueous Pyrolysis-Catalysis and Modeling. In Presented at 213th ACS National Meeting, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 April 1997.
- Nares, H.R.; Schacht-Hernandez, P.; Ramirez-Garnica, M.A.; Cabrera-Reyes, M.C.; Noe-Valencia, L. Heavy-Crude-Oil Upgrading with transition Metals. In Presented at the SPE Latin America and Caribbean Petroleum Engineering Conference, Buenos Aires, Argentina, 15–18 April 2007.
- Maity, S.K.; Ancheyta, J.; Marroquin, G. Catalytic Aquathermolysis Used for Viscosity Reduction of Heavy Oils: A Review. Energy Fuels 2010, 24, 2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fumoto, E.; Sato, S.; Takanohashi, T. Oxidative Cracking of Oil Sand Bitumen with Iron Oxide Catalyst in a Steam Atmosphere. In Proceedings of 11th International Conference of Petroleum Phase behavior and Fouling, Petrophase, Jersey, NJ, USA, 13–17 June 2010.
- Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; He, J.; Li, P.; Yang, C. Viscosity Reduction of Heavy Oil through Catalytic Aquathermolysis at relatively Low Temperature. In Presented at 11th International Conference of Petroleum Phase behavior and Fouling, Petrophase, Jersey, NJ, USA, 13–17 June 2010.
- Wen, S.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y. A Study on Catalytic Aquathermolysis of Heavfy Crude Oil during steam Stimulation. In Presented at 2007 SPE International Symposium Oilfield Chemistry, Houston, TX, USA, 28 February–2 March 2007.
- Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wu, C.; Xia, F. Laboratory Experiments and Field Tests of an Amphiphilic Metallic Chelate for Catalytic Aquathermolysis of Heavy Oil. Energy Fuels 2008, 22, 1502–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, K.; Chen, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, X.; Li, J. Laboratory Experiments and Field Test of a Difunctional Catalyst for Catalytic Aquathermolysis of Heavy Oil. Energy Fuels 2012, 26, 1152–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, K.; Chen, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, X.; Li, J. Influences on the Aquathermolysis of Heavy Oil Catalyzed by Two Different Catalytic Ions: Cu2+ and Fe3+. Energy Fuels 2013, 27, 2555–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakanishi, K.; Taniguchi, H.; Hasuo, H.-u.; Mochida, I. Iron-Based Catalysts Supported on Carbon Nanoparticles of Hollow Structure for Coal Liquefaction. Eng. Chem. Res. 1997, 36, 306–309, and references therein. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, C.D.; Riggs, W.M.; Davis, L.E.; Moulder, J.F.; Muilenberg, G.E. Handbook of X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy; Perkin-Elmer Corporation Physical Electronics Division: Eden Prairie, MN, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Ovalles, C.; Filgueiras, E.; Morales, A.; Rojas, I.; de Jesus, J.C.; Berrios, I. Use of Dispersed Molybdenum Catalyst and Mechanistic Studies for Upgrading Extra-Heavy Crude Oil Using Methane as Source of Hydrogen. Energy Fuels 1998, 12, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egiebor, N.O.; Gray, M.R. Evidence for methane activation during coal pyrolysis and liquefaction. Fuel 1990, 69, 1276–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovalles, C.; Hamana, A.; Rojas, I.; Bolivar, R. Upgrading of Extra-Heavy Crude Oil by Direct Use of Methane in the Presence of Water. Deuterium Labeled Experiments and Mechanistic Consideration. Fuel 1995, 74, 1162–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leon, V.; Carrazza, J. X- ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) sensitivity factors. A general and simple approach. Rev. Tech. INTEVEP 1989, 9, 81–88. [Google Scholar]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).