Error in Figure
In the original publication [1], there was a mistake in Figures 5F and 6A as published. One of the images in Figure 4F was inadvertently duplicated in Figure 5F during our figure preparation process. A similar error was also noted between Figure 6A,D. The corrected Figure 5 and Figure 6 appear below. The authors state that the scientific conclusions are unaffected. This correction was approved by the Academic Editor. The original publication has also been updated.
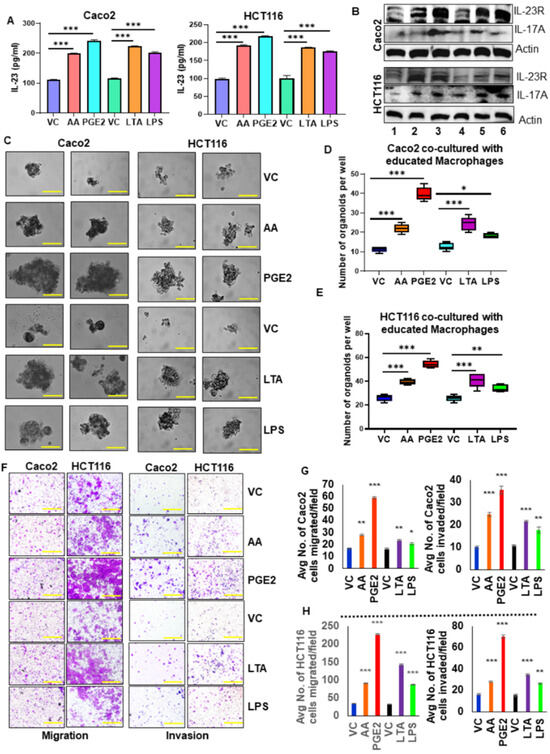
Figure 5.
IL-23 production by macrophages enhances colon tumor cell aggressiveness. (A) The level of IL-23 in the spent media of the co-culture system (Caco2/HCT116 + educated macrophages with AA/PGE2/LTA/LPS) was measured using ELISA. (B) The expression of IL-23R, IL-17A were analyzed in Caco2 and HCT116 cells co-cultured with educated macrophages compared to uneducated macrophages. Lane1-Vehicle control, Lane2-AA, Lane3- PGE2, Lane4- Vehicle control, Lane5- LTA, Lane6- LPS. β-actin was used as a protein loading control. (C) Co-culture of educated macrophages with tumor cells increased the self-renewal ability of cancer cells compared with uneducated macrophages co-culture system (Magnification 40×). (D,E) Quantification of organoids formed by tumor cells co-cultured with educated macrophages compared to uneducated macrophages. (F) Migration and invasion assay showed that tumor cells co-cultured with educated macrophages increased migration and invasion compared to uneducated macrophages (Magnification 10×). (G,H) Quantification of the number of migrated and invaded cells. All experiments were performed a minimum of three times. Bars denote standard deviation (SD). * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, and *** p < 0.001 were considered statistically significant.
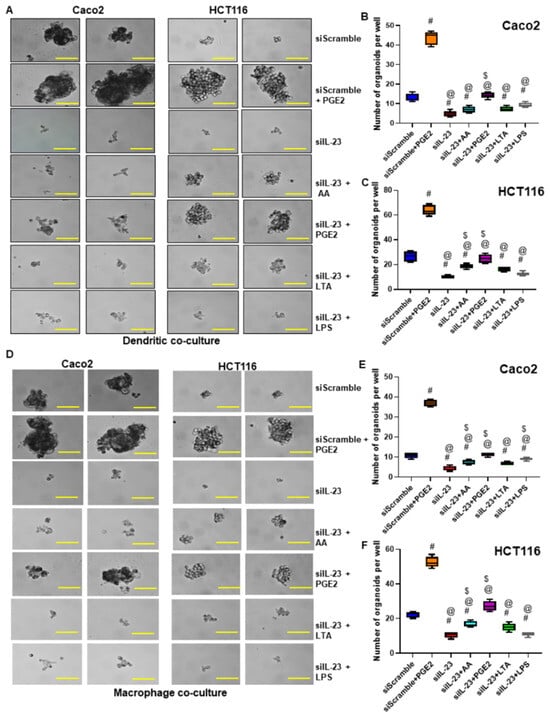
Figure 6.
Inhibition of IL-23 in DCs and macrophages reduced colon tumor cell self-renewal. (A,D) Effect of siRNA knockdown of IL-23 in educated DCs and macrophages on the self-renewal ability of co-cultured Caco2 and HCT116 cells compared to scramble siRNA and scramble siRNA + PGE2 stimulated immune cells (Magnification 40×). (B,C,E,F) Quantification of organoids formed per well by tumor cells co-cultured with siIL-23 treated and educated DCs and macrophages compared to scramble siRNA treated and uneducated macrophages. #-compared with siScramble; @-compared with siScramble + PGE2; $-compared with siIL-23. All experiments were performed a minimum of three times. Bars denote standard deviation (SD).
Reference
- Panneerselvam, J.; Madka, V.; Rai, R.; Morris, K.T.; Houchen, C.W.; Chandrakesan, P.; Rao, C.V. Inflammatory Mediators and Gut Microbial Toxins Drive Colon Tumorigenesis by IL-23 Dependent Mechanism. Cancers 2021, 13, 5159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).