Prognostic Value of Circulating Cytokines in Chemorefractory Colorectal Cancer
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Eligibility Criteria
2.2. Cytokine Analysis
2.3. Study Objective and Statistical Considerations
2.4. Ethical Aspects
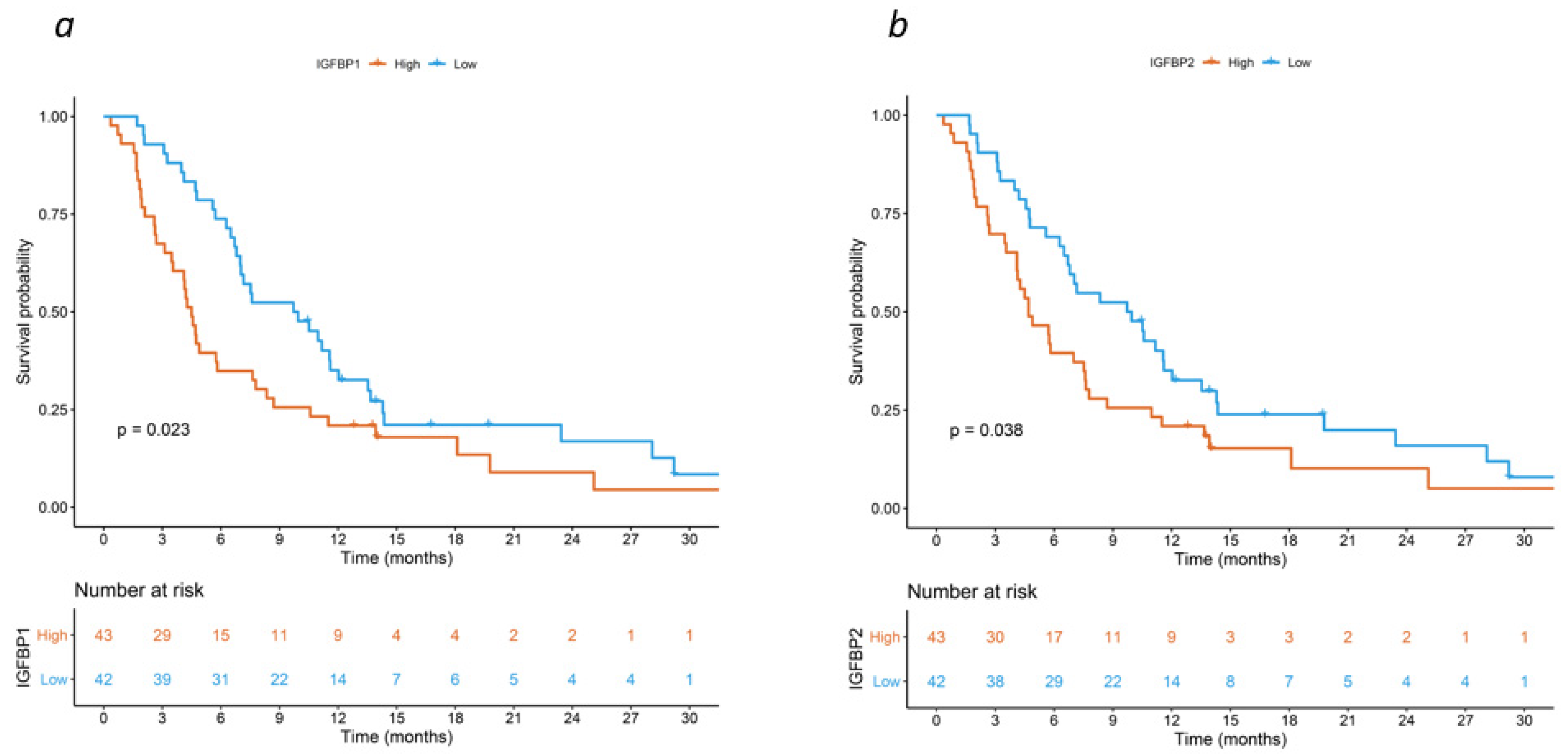
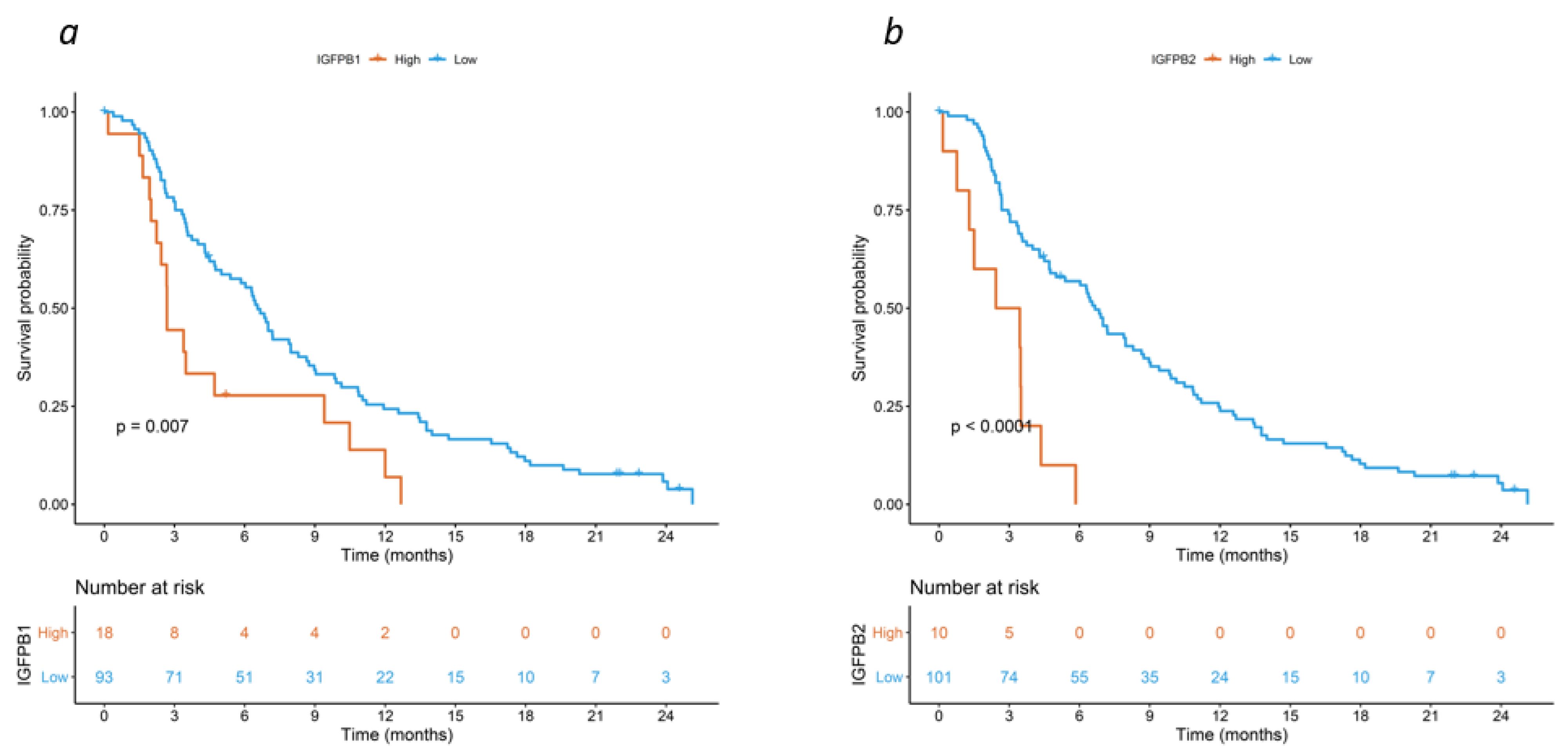
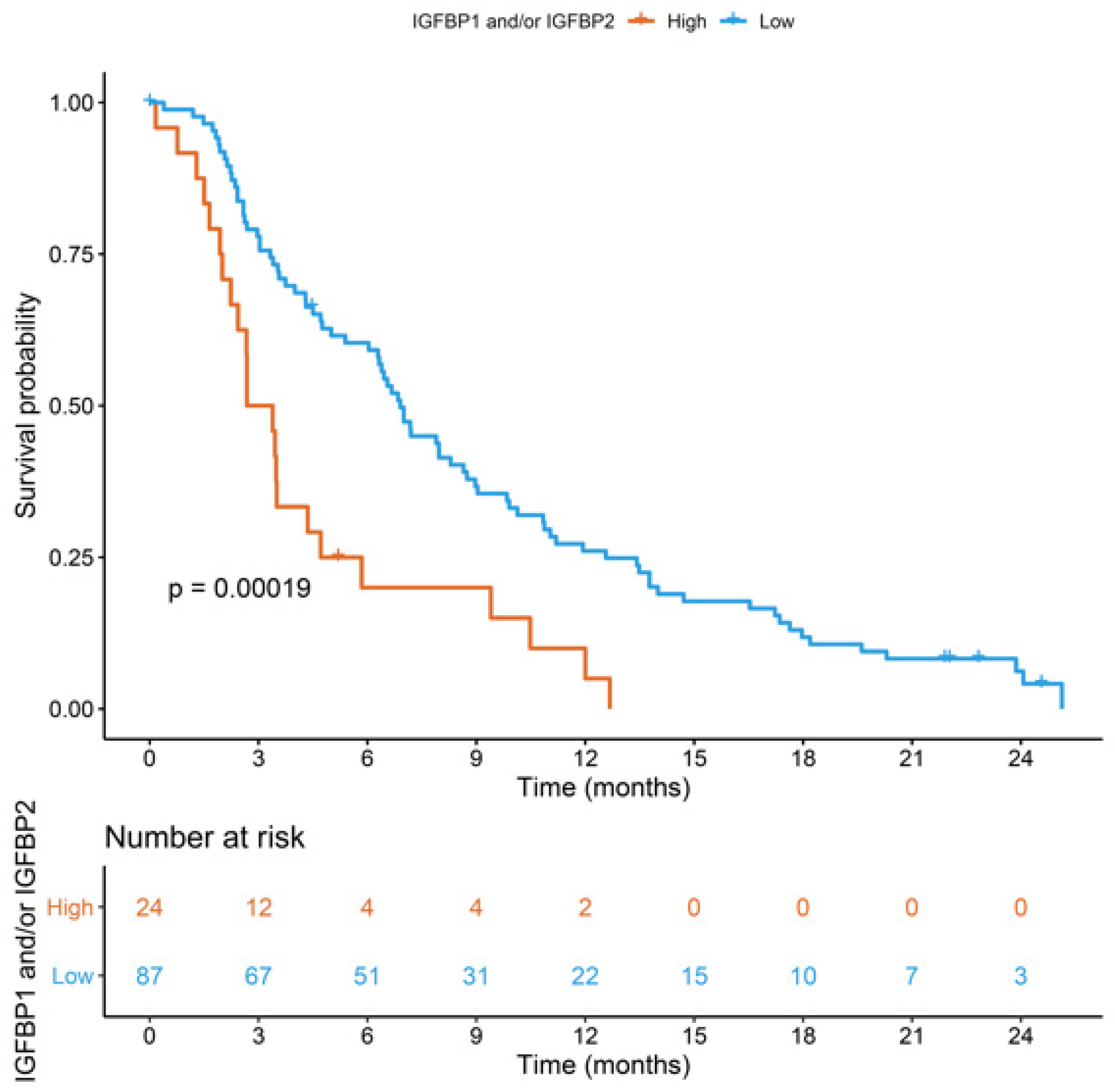
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ALP | alkaline phosphatase |
| CI | confidence intervals |
| CRC | colorectal cancer |
| ECOG | Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group |
| ELISA | enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| FDR | false discovery rate |
| HR | hazard ratio |
| IGFBP-1 | insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 1 |
| IGFBP-2 | insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 2 |
| OD | optical density |
| OS | overall survival |
| PS | performance status |
| SAA | serum amyloid A |
| WB-MATV | whole-body metabolically active tumor volume |
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cremolini, C.; Loupakis, F.; Antoniotti, C.; Lupi, C.; Sensi, E.; Lonardi, S.; Mezi, S.; Tomasello, G.; Ronzoni, M.; Zaniboni, A.; et al. FOLFOXIRI plus bevacizumab versus FOLFIRI plus bevacizumab as first-line treatment of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer: Updated overall survival and molecular subgroup analyses of the open-label, phase 3 TRIBE study. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 1306–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- André, T.; Shiu, K.K.; Kim, T.W.; Jensen, B.V.; Jensen, L.H.; Punt, C.; Smith, D.; Garcia-Carbonero, R.; Benavides, M.; Gibbs, P.; et al. Pembrolizumab in Microsatellite-Instability-High Advanced Colorectal Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2207–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douillard, J.Y.; Oliner, K.S.; Siena, S.; Tabernero, J.; Burkes, R.; Barugel, M.; Humblet, Y.; Bodoky, G.; Cunningham, D.; Jassem, J.; et al. Panitumumab-FOLFOX4 treatment and RAS mutations in colorectal cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 1023–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopetz, S.; Grothey, A.; Yaeger, R.; Van Cutsem, E.; Desai, J.; Yoshino, T.; Wasan, H.; Ciardiello, F.; Loupakis, F.; Hong, Y.S.; et al. Encorafenib, Binimetinib, and Cetuximab in BRAF V600E-Mutated Colorectal Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 1632–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sartore-Bianchi, A.; Trusolino, L.; Martino, C.; Bencardino, K.; Lonardi, S.; Bergamo, F.; Zagonel, V.; Leone, F.; Depetris, I.; Martinelli, E.; et al. Dual-targeted therapy with trastuzumab and lapatinib in treatment-refractory, KRAS codon 12/13 wild-type, HER2-positive metastatic colorectal cancer (HERACLES): A proof-of-concept, multicentre, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 738–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drilon, A.; Laetsch, T.W.; Kummar, S.; DuBois, S.G.; Lassen, U.N.; Demetri, G.D.; Nathenson, M.; Doebele, R.C.; Farago, A.F.; Pappo, A.S.; et al. Efficacy of Larotrectinib in TRK Fusion-Positive Cancers in Adults and Children. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 731–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLean, J.; Rho, Y.S.; Kuruba, G.; Mamo, A.; Gilabert, M.; Kavan TPanasci, L.; Melnychuk, D.; Batist, G.; Kavan, P. Clinical Practice Patterns in Chemotherapeutic Treatment Regimens for Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. Clin. Colorectal. Cancer 2016, 15, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlomagno, C.; De Stefano, A.; Rosanova, M.; De Falco, S.; Attademo, L.; Fiore, G.; De Placido, S. Multiple treatment lines and prognosis in metastatic colorectal cancer patients. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2019, 38, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervantes, A.; Adam, R.; Roselló, S.; Arnold, D.; Normanno, N.; Taïeb, J.; Seligmann, J.; De Baere, T.; Osterlund, P.; Yoshino, T.; et al. Metastatic colorectal cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2023, 34, 10–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines®) Colon Cancer Version 2.2023; NCCN: Plymouth Meeting, PA, USA, 2023.
- Corcoran, R.B.; Chabner, B.A. Application of Cell-free DNA Analysis to Cancer Treatment. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 1754–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinarello, C.A. Historical Review of Cytokines. Eur. J. Immunol. 2007, 37 (Suppl. 1), S34–S45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balkwill, F. Cancer and the chemokine network. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 540–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, R.M.; Mortimer, T.O.; O’Neill, K.L. Cytokines: Can Cancer Get the Message? Cancers 2022, 14, 2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camera, S.; Telli, T.A.; Woff, E.; Vandeputte, C.; Kehagias, P.; Guiot, T.; Critchi, G.; Wissam, Y.; Bregni, G.; Trevisi, E.; et al. Prognostic value of the pace of tumor progression as assessed by serial 18F-FDG PET/CT PET/CT scan and liquid biopsy in refractory colorectal cancer: The CORIOLAN trial. Cancers 2020, 12, 2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendlisz, A.; Deleporte, A.; Vandeputte, C.; Charette, N.; Paesmans, M.; Guiot, T.; Garcia, C.; Flamen, P. Regorafenib assessment in refractory advanced colorectal cancer: RegARd-C study protocol. BMJ Open 2015, 5, e007189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- West, N.R.; McCuaig, S.; Franchini, F.; Powrie, F. Emerging cytokine networks in colorectal cancer. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 615–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braumüller, H.; Mauerer, B.; Andris, J.; Berlin, C.; Wieder, T.; Kesselring, R. The Cytokine Network in Colorectal Cancer: Implications for New Treatment Strategies. Cells 2023, 12, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Qi, M.; Hutchinson, M.R.; Yang, G.; Goldys, E.M. Recent advances in cytokine detection by immunosensing. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 79, 810–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiteside, T.L. Cytokines and cytokine measurements in a clinical laboratory. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 1994, 1, 257–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollak, M. The insulin and insulin-like growth factor receptor family in neoplasia: An update. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furstenberger, G.; Senn, H.J. Insulin-like growth factors and cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2002, 3, 298–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, F.; Xu, L.; Khambata-Ford, S. Correlation between Gene Expression of IGF-1R Pathway Markers and Cetuximab Benefit in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 1156–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Ji, Q.; Li, Q. Resistance to anti-EGFR therapies in metastatic colorectal cancer: Underlying mechanisms and reversal strategies. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 40, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigneri, P.G.; Tirrò, E.; Pennisi, M.S.; Massimino, M.; Stella, S.; Romano, C.; Manzella, L. The Insulin/IGF System in Colorectal Cancer Development and Resistance to Therapy. Front. Oncol. 2015, 5, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baxter, R. IGF binding proteins in cancer: Mechanistic and clinical insights. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Firth, S.M.; Baxter, R.C. Cellular actions of the insulin-like growth factor binding proteins. Endocr. Rev. 2002, 23, 824–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Geng, Y.; Lu, W.; Yin, J.; Li, Z.; Huang, L.; Liu, H.; Xu, N. IGFBP2 promotes the EMT of colorectal cancer cells by regulating E-cadherin expression. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2019, 12, 2559–2565. [Google Scholar]
- Hung, C.S.; Huang, C.Y.; Lee, C.H.; Chen, W.Y.; Huang, M.T.; Wei, P.L.; Chang, Y.J. IGFBP2 plays an important role in heat shock protein 27-mediated cancer progression and metastasis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 54978–54992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liou, J.M.; Shun, C.T.; Liang, J.T.; Chiu, H.M.; Chen, M.J.; Chen, C.C.; Wang, H.P.; Wu, M.S.; Lin, J.T. Plasma insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-2 levels as diagnostic and prognostic biomarker of colorectal cancer. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 95, 1717–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Hong, C.Q.; Luo, Y.H.; Wei, L.F.; Luo, Y.; Peng, Y.H.; Xu, Y.W. Prognostic value of IGFBP2 in various cancers: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Med. 2022, 11, 3035–3047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, E.K.; Ma, J.; Pollak, M.N.; Rifai, N.; Fuchs, C.S.; Hankinson, S.E.; Giovannucci, E. A prospective study of C-peptide, insulin-like growth factor-I, insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1, and the risk of colorectal cancer in women. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2005, 14, 850–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenab, M.; Riboli, E.; Cleveland, R.J.; Norat, T.; Rinaldi, S.; Nieters, A.; Biessy, C.; Tjønneland, A.; Olsen, A.; Overvad, K. Serum C-peptide, IGFBP-1 and IGFBP-2 and risk of colon and rectal cancers in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition. Int. J. Cancer 2007, 121, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolpin, B.M.; Meyerhardt, J.A.; Chan, A.T.; Ng, K.; Chan, J.A.; Wu, K.; Pollak, M.N.; Giovannucci, E.L.; Fuchs, C.S. Insulin, the insulin-like growth factor axis, and mortality in patients with nonmetastatic colorectal cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hang, D.; He, X.; Kværner, A.S.; Chan, A.T.; Wu, K.; Ogino, S.; Hu, Z.; Shen, H.; Pollak, M.N.; Giovannucci, E.L.; et al. Plasma Biomarkers of Insulin and the Insulin-like Growth Factor Axis, and Risk of Colorectal Adenoma and Serrated Polyp. JNCI Cancer Spectr. 2019, 3, pkz056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.C.; Ha, Y.J.; Tak, K.H.; Roh, S.A.; Kim, C.W.; Kim, T.W.; Kim, S.K.; Kim, S.Y.; Cho, D.H.; Kim, Y.S. Complex Behavior of ALDH1A1 and IGFBP1 in Liver Metastasis from a Colorectal Cancer. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renehan, A.G.; Jones, J.; Potten, C.S.; Shalet, S.M.; O’Dwyer, S.T. Elevated serum insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-II and IGF binding protein-2 in patients with colorectal cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2000, 83, 1344–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haschemi, R.; Kobelt, D.; Steinwarz, E.; Schlesinger, M.; Stein, U.; Bendas, G. Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Protein-2 (IGFBP2) Is a Key Molecule in the MACC1-Mediated Platelet Communication and Metastasis of Colorectal Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Discovery Cohort (N = 85) | Validation Cohort (N = 111) | |
|---|---|---|
| Age | ||
| Median (IQR) | 64 (13) | 66 (14) |
| Sex | ||
| Male | 48 (56.5%) | 66 (59.5%) |
| Female | 37 (43.5%) | 45 (40.5%) |
| ECOG PS | ||
| 0 | 39 (45.9%) | 51 (45.9%) |
| ≥1 | 46 (54.1%) | 59 (53.2%) |
| Unknown | 1 (0.9%) | |
| Primary tumor location | ||
| Left | 61 (71.8%) | 74 (66.7%) |
| Right | 21 (24.7%) | 20 (18.0%) |
| Unknown | 3 (3.5%) | 17 (15.3%) |
| RAS/BRAF status | ||
| RAS/BRAF mutated | 42 (49.4%) | 71 (64.0%) |
| RAS/BRAF wild-type | 35 (41.2%) | 38 (34.2%) |
| Unknown | 8 (9.4%) | 2 (1.8%) |
| N of metastatic sites | ||
| 1 | 15 (17.6%) | 14 (12.6%) |
| ≥2 | 70 (82.4%) | 97 (87.4%) |
| Liver metastasis | ||
| Present | 58 (68.2%) | 82 (73.9%) |
| Absent | 27 (31.8%) | 29 (26.1%) |
| Peritoneal metastasis | ||
| Present | 22 (25.9%) | 21 (18.9%) |
| Absent | 63 (74.1%) | 90 (81.1%) |
| Baseline ALP (UI/L) | ||
| Median (IQR) | 140 (137) | 168 (203) |
| Baseline CEA (μg/L) | ||
| Median (IQR) | 73.8 (417) | 132 (286) |
| Time from diagnosis to blood sampling (months) | ||
| Median (IQR) | 31.3 (38) | 36.3 (35) |
| N of prior lines of systemic therapy | ||
| Median (IQR) | 2 (1) | 2 (1) |
| Systemic therapy after blood sampling | ||
| Yes | 64 (75.3%) | 111 (100%) |
| No | 21 (24.7%) | 0 (0%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Assaf, I.; Fimereli, D.; Anthoine, G.; Fazio, R.; Daprà, V.; Audisio, A.; Bardiaux, A.; Telli, T.A.; Vanhooren, M.; Saude-Conde, R.; et al. Prognostic Value of Circulating Cytokines in Chemorefractory Colorectal Cancer. Cancers 2023, 15, 5823. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15245823
Assaf I, Fimereli D, Anthoine G, Fazio R, Daprà V, Audisio A, Bardiaux A, Telli TA, Vanhooren M, Saude-Conde R, et al. Prognostic Value of Circulating Cytokines in Chemorefractory Colorectal Cancer. Cancers. 2023; 15(24):5823. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15245823
Chicago/Turabian StyleAssaf, Irene, Danai Fimereli, Geraldine Anthoine, Roberta Fazio, Valentina Daprà, Alessandro Audisio, Alina Bardiaux, Tugba Akin Telli, Michele Vanhooren, Rita Saude-Conde, and et al. 2023. "Prognostic Value of Circulating Cytokines in Chemorefractory Colorectal Cancer" Cancers 15, no. 24: 5823. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15245823
APA StyleAssaf, I., Fimereli, D., Anthoine, G., Fazio, R., Daprà, V., Audisio, A., Bardiaux, A., Telli, T. A., Vanhooren, M., Saude-Conde, R., Bregni, G., Hendlisz, A., & Sclafani, F. (2023). Prognostic Value of Circulating Cytokines in Chemorefractory Colorectal Cancer. Cancers, 15(24), 5823. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15245823







