Assessment of STAT4 Variants and Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Latin Americans and Europeans
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Samples and Study Subjects
2.2. Genotypic Analysis
2.3. Statistical Analysis
2.4. Ethics
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
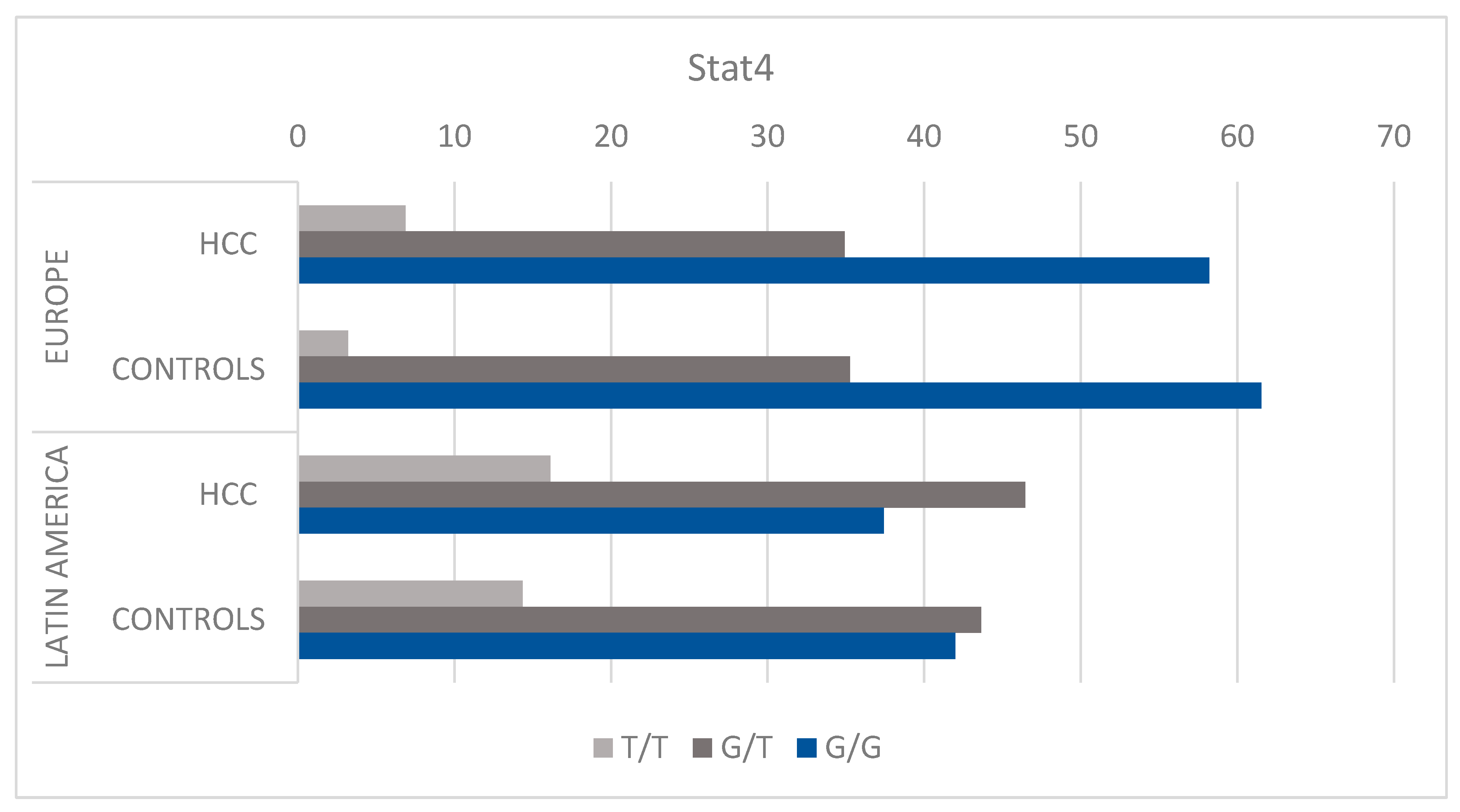
3.2. STAT4 HCC Risk Assessment
3.3. STAT4 HCC Risk Assessment Based on Underlying Liver Disease
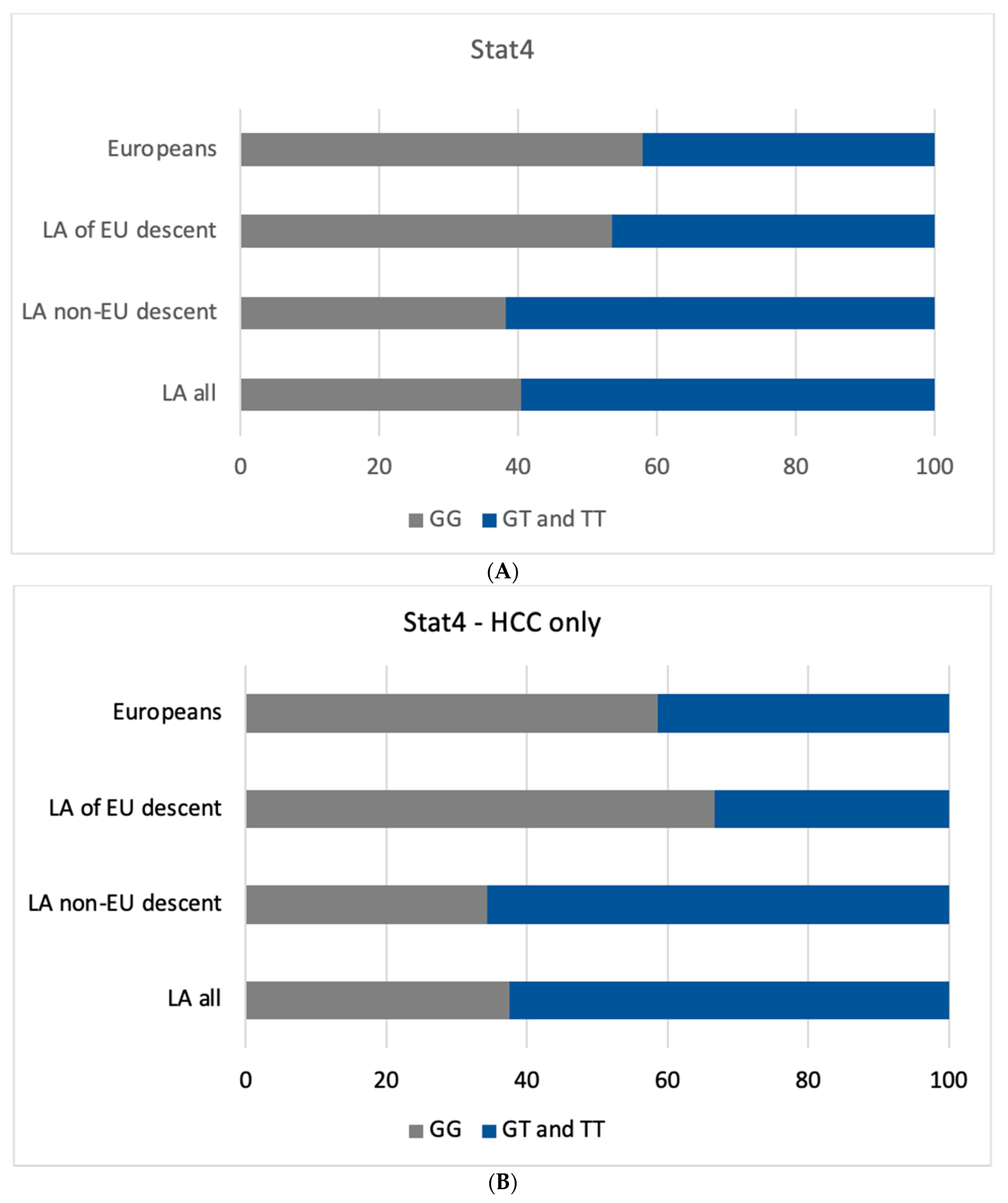
3.4. Effect of Ancestry in HCC Risk Related to STAT4
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hyuna, S.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulik, L.; El-Serag, H.B. Epidemiology and Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 477–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcglynn, K.A.; Petrick, J.L.; El-Serag, H.B. Epidemiology of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Hepatology 2021, 73, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caines, A.; Selim, R.; Salgia, R. The Changing Global Epidemiology of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Clin. Liver Dis. 2020, 24, 535–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, C.; Souza De Oliveira, M.; Cotrim, H.P.; Arrese, M. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Risk Factors in Latin American Populations: Current Scenario and Perspectives. Clin. Liver Dis. 2019, 13, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jose Carrilho, F.; Cerqueira Paranaguá-Vezozzo, D.; Lopes Chagas, A.; Saraiva de Souza Melo Alencar, R.; Gomes da Fonseca, L.; Carrilho, J.; Paulo, S. Epidemiology of Liver Cancer in Latin America: Current and Future Trends. Liver Dis. 2020, 40, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farah, M.; Anugwom, C.; Ferrer, J.D.; Baca, E.L.; Mattos, A.Z.; Possebon, J.P.P.; Arrese, M.; Prieto, J.; Balderramo, D.; Carrera, E.; et al. Changing Epidemiology of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in South America: A Report from the South American Liver Research Network. Ann. Hepatol. 2023, 28, 100876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferlay, J.; LMEMLFCMMLPMZASIBF. Global Cancer Observatory: Cancer Tomorrow. Lyon, France: International Agency for Research on Cancer. Available online: https://gco.iarc.fr/Tomorrow (accessed on 5 December 2022).
- Akambase, J.A.; Prieto, J.E.; Mattos, A.Z.; Mattos, A.A.; Carrera, E.; Díaz-Ferrer, J.; Gallardo, P.; Curia, A.; Ballerga, E.G.; Tovo, C.V.; et al. Epidemiology and Risk Factors for Histopathologic Characteristics of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in South America. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debes, J.D.; Chan, A.J.; Balderramo, D.; Kikuchi, L.; Gonzalez Ballerga, E.; Prieto, J.E.; Tapias, M.; Idrovo, V.; Davalos, M.B.; Cairo, F.; et al. Hepatocellular Carcinoma in South America: Evaluation of Risk Factors, Demographics and Therapy. Liver Int. 2018, 38, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galle, P.R.; Forner, A.; Llovet, J.M.; Mazzaferro, V.; Piscaglia, F.; Raoul, J.L.; Schirmacher, P.; Vilgrain, V. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 182–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezina, A.; Philips, N.; Bogus, Z.; Erez, N.; Xiao, R.; Fan, R.; Olthoff, K.M.; Reddy, K.R.; Samadder, N.J.; Nielsen, S.M.; et al. Multigene Panel Testing in Individuals With Hepatocellular Carcinoma Identifies Pathogenic Germline Variants. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2021, 5, 988–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shastry, B.S. SNPs: Impact on Gene Function and Phenotype. Methods Mol. Biol. 2009, 578, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.-K.; Sun, J.; Cao, G.; Liu, Y.; Lin, D.; Gao, Y.-Z.; Ren, W.-H.; Long, X.-D.; Zhang, H.; Ma, X.-P.; et al. Genetic Variants in STAT4 and HLA-DQ Genes Confer Risk of Hepatitis B Virus–Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 72–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael Morton, N.; James Simmonds, M.; Monzani, F.; Yu, Y.; Gao, X.; Wang, J. The Association Between STAT4 Rs7574865 Polymorphism and the Susceptibility of Autoimmune Thyroid Disease: A Meta-Analysis. Front. Genet. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Dai, W.Q.; Wang, F.; He, L.; Zhou, Y.Q.; Lu, J.; Xu, X.F.; Guo, C.Y. Association of STAT4 Gene Rs7574865G > T Polymorphism with Ulcerative Colitis Risk: Evidence from 1532 Cases and 3786 Controls. Arch. Med. Sci. 2014, 10, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Ji, G.; Le, X.; Luo, Z.; Wang, C.; Feng, M.; Xu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Lau, W.B.; Lau, B.; et al. An Integrated Analysis Identifies STAT4 as a Key Regulator of Ovarian Cancer Metastasis. Oncogene 2017, 36, 3384–3396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, Y.H.; Hwang, H.J.; Sung, H.J.; Heo, S.H.; Kim, D.S.; Hong, S.H.; Lee, K.H.; Cho, J.Y. Upregulation of Complement Factor H by SOCS-1/3–STAT4 in Lung Cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Sharkawy, R.; George, J.; Eslam, M. Editorial: STAT-4 Polymorphism—A Tool to Personalise Clinical Practice in Chronic HBV Infection. Authors’ Reply. Aliment. Pharmacol. The.r 2018, 48, 769–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Shi, W.; Xin, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhu, X.; Wu, X.; Li, Z.; Li, H.; Liu, Y. Replication of Genome-Wide Association Studies on Hepatocellular Carcinoma Susceptibility Loci in a Chinese Population. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e77315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Chen, H.; Zhou, B.; Yin, J.; Cao, G.; Hou, J.; Jiang, D. The Effects of the Interactions of STAT4 Rs7574865 with HBV Mutations on the Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Mol. Carcinog. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Sharkawy, R.; Thabet, K.; Lampertico, P.; Petta, S.; Mangia, A.; Berg, T.; Metwally, M.; Bayoumi, A.; Boonstra, A.; Brouwer, W.P.; et al. A STAT4 Variant Increases Liver Fibrosis Risk in Caucasian Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 48, 564–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Gao, N.; Yang, L.; Guo, Y.; Fang, Y.; Wang, T.; Xu, C.; Li, G.F.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Stat4 Rs7574865 Polymorphism Promotes the Occurrence and Progression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma via the Stat4/CYP2E1/FGL2 Pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debes, J.D.; Carrera, E.; Mattos, A.Z.; Prieto, J.E.; Boonstra, A. Hepatocellular Carcinoma, a Unique Tumor with a Lack of Biomarkers. Ann. Hepatol. 2019, 18, 786–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debes, J.D.; Boonstra, A.; Balderramo, D.; Mattos, A.Z.; Arrese, M. Hepatobiliary Cancers in South America: Disparity Strikes. Lancet. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 4, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amit Singal, C.G.; Llovet, J.M.; Yarchoan, M.; Mehta, N.; Heimbach, J.K.; Dawson, L.A.; Jou, J.H.; Kulik, L.M.; Agopian, V.G.; Marrero, J.A.; et al. AASLD Practice Guidance on Prevention, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Hepatocellular. Hepatology 2023. ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Francioli, L.C.; Goodrich, J.K.; Collins, R.L.; Wang, Q.; Alföldi, J.; Watts, N.A.; Vittal, C.; Gauthier, L.D.; Poterba, T.; et al. A Genome-Wide Mutational Constraint Map Quantified from Variation in 76,156 Human Genomes. bioRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, X.; Wu, J.; Zhang, W.; Feng, X.; Zhao, L.; Huang, F.; Jiang, C. A New Discovery of STAT4 Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms Associated with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Risk in Chinese Han Population: A Case-Control Study. Biosci. Rep. 2021, 41, BSR20210124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, L.H.; Cheong, H.S.; Namgoong, S.; Kim, J.O.; Kim, J.H.; Park, B.L.; Cho, S.W.; Park, N.H.; Cheong, J.Y.; Koh, I.S.; et al. Replication of Genome-Wide Association Studies on Hepatocellular Carcinoma Susceptibility Loci of STAT4 and HLA-DQ in a Korean Population. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2015, 33, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, A.; Gerlach, F.; van Tong, H.; Hoan, N.X.; Song, L.H.; Toan, N.L.; Bock, C.-T.; Kremsner, P.G.; Velavan, T.P. A Trivial Role of STAT4 Variant in Chronic Hepatitis B Induced Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2013, 18, 257–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.W.; Zheng, H.F.; Cui, Y.; Sun, L.D.; Ye, D.Q.; Hu, Z.; Xu, J.H.; Cai, Z.M.; Huang, W.; Zhao, G.P.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Study in a Chinese Han Population Identifies Nine New Susceptibility Loci for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Nat. Genet 2009, 41, 1234–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remmers, E.F.; Plenge, R.M.; Lee, A.T.; Graham, R.R.; Hom, G.; Behrens, T.W.; de Bakker, P.I.W.; Le, J.M.; Lee, H.-S.; Batliwalla, F.; et al. STAT4 and the Risk of Rheumatoid Arthritis and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Wang, F.; Luo, F. The Role of JAK/STAT Pathway in Fibrotic Diseases: Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liang, L.; Liu, Y.; Luo, Y.; Liang, X.; Luo, D.; Feng, Z.; Dang, Y.; Yang, L.; Chen, G. Clinicopathological Significance of STAT4 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Its Effect on Cell Growth and Apoptosis. Onco. Targets Ther. 2016, 9, 1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Qu, A.; Qu, A. Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 4 in Liver Diseases. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2015, 11, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Chen, J.H.; Qiang, Y.; Wang, D.Z.; Chen, Z. Decreased STAT4 Indicates Poor Prognosis and Enhanced Cell Proliferation in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 3983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wubetu, G.Y.; Utsunomiya, T.; Ishikawa, D.; Yamada, S.; Ikemoto, T.; Morine, Y.; Iwahashi, S.; Saito, Y.; Arakawa, Y.; Imura, S.; et al. High STAT4 Expression Is a Better Prognostic Indicator in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma after Hepatectomy. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2014, 21, 721–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Main Data of the Seventh National Population Census. Available online: http://www.stats.gov.cn/english/PressRelease/202105/t20210510_1817185.html (accessed on 19 February 2023).
- Lamarca, A.; Mendiola, M.; Barriuso, J. Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Exploring the Impact of Ethnicity on Molecular Biology. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2016, 105, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; El-Serag, H.B.; Thrift, A.P. Sex and Race Disparities in the Incidence of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in the United States Examined through Age-Period-Cohort Analysis. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2020, 29, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakeman, P.; Henneman, L.; Bezemer, P.D.; Cornel, M.C.; Kate, L.P. Ten Developing and Optimizing a Decisional Instrument Using Self-Reported Ancestry for Carrier Screening in a Multi-Ethnic Society. Genet. Med. 2006, 8, 502–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhu, R.X.; Seto, W.K.; Lai, C.L.; Yuen, M.F. Epidemiology of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in the Asia-Pacific Region. Gut Liver 2016, 10, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalil, I.; Arshad, M.; Khan, S.; Dasti, J.I. The STAT4 and Not the IFNL3 Variant Is Associated with Hepatitis B Virus Clearance in a Population from the Khyber Pakhtunkhwa Region of Pakistan. Arab J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 21, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, X.; Luo, M.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Yu, X.; Liu, L.; Chen, S. Genetic Variants in STAT4 and Their Interactions with Environmental Factors for the Incidence of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer Biomark. 2021, 32, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Wang, M.; Zhang, Z.; Tang, H.; Zuo, X.; Meng, X.; Xiong, M.; Zhou, F.; Liang, B.; Dai, F.; et al. Replication the Association of 2q32.2-Q32.3 and 14q32.11 with Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Gene 2015, 561, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, M.; Li, J.; Tang, R.; Zhu, P.; Qiu, F.; Wang, C.; Qiu, J.; Wang, L.; Dai, Y.; Xu, P.; et al. Multiple Genetic Variants Associated with Primary Biliary Cirrhosis in a Han Chinese Population. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2015, 48, 316–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiba, Y.; Yamazaki, K.; Nishida, N.; Kawashima, M.; Hitomi, Y.; Nakamura, H.; Komori, A.; Fuyuno, Y.; Takahashi, A.; Kawaguchi, T.; et al. Disease Susceptibility Genes Shared by Primary Biliary Cirrhosis and Crohn’s Disease in the Japanese Population. J. Hum. Genet. 2015, 60, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Li, F.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, H.; Yang, F.; Li, X.; Jiang, X.; Chen, L.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, J. STAT4 Genetic Polymorphism Significantly Affected HBeAg Seroconversion in HBeAg-Positive Chronic Hepatitis B Patients Receiving Peginterferon-α Therapy: A Prospective Cohort Study in China. J. Med. Virol. 2022, 94, 4449–4458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limothai, U.; Chuaypen, N.; Poovorawan, K.; Poovorawan, Y.; Tangkijvanich, P. Genetic Variation in STAT4 Is Associated with Treatment Response to Pegylated Interferon in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B. Asian Pac. J. Allergy Immunol. 2022, 40, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Sun, J.; Zhou, B.; Peng, J.; Xie, Q.; Liang, X.; Fan, R.; Conran, C.; Xu, J.; Ji, Y.; et al. A Missense Variant in Complement Factor B (CFB) Is a Potential Predictor of 24-Week off-Treatment Response to PegIFNα Therapy in Chinese HBeAg-Positive Chronic Hepatitis B Patients. Aliment Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 51, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Sun, J.; Zhou, B.; Xie, Q.; Liang, X.; Fan, R.; Conran, C.; Xu, J.; Ji, Y.; Zhang, X.; et al. Variants in STAT4 Associated with Cure of Chronic HBV Infection in HBeAg-Positive Patients Treated with Pegylated Interferon-Alpha. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 18, 196–204.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.K.; Wu, X.; Qian, J.; Ma, X.P.; Yang, J.; Li, Z.; Wang, R.; Sun, L.; Liu, F.; Zhang, P.; et al. Genetic Variation in STAT4 Predicts Response to Interferon-α Therapy for Hepatitis B e Antigen-Positive Chronic Hepatitis B. Hepatology 2016, 63, 1102–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Peng, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, F.; Sun, Z. STAT4 Genetic Polymorphisms Association with Spontaneous Clearance of Hepatitis B Virus Infection. Immunol. Res. 2015, 62, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.K.; Ma, X.P.; Wu, X.; Peng, L.; Yin, J.; Dan, Y.; Huang, H.X.; Ding, D.L.; Zhang, L.Y.; Shi, Z.; et al. Genetic Variations in STAT4,C2,HLA-DRB1 and HLA-DQ Associated with Risk of Hepatitis B Virus-Related Liver Cirrhosis. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Cai, B.; Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Ying, B.; Tao, C.; Zhao, M.; Ba, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, L. Association of HLA-DP/DQ, STAT4 and IL-28B Variants with HBV Viral Clearance in Tibetans and Uygurs in China. Liver Int. 2015, 35, 886–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, N.A.; Hamdy, N.M.; Gibriel, A.A.; EL Mesallamy, H.O. Investigation of the Relationship between CTLA4 and the Tumor Suppressor RASSF1A and the Possible Mediating Role of STAT4 in a Cohort of Egyptian Patients Infected with Hepatitis C Virus with and without Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Arch. Virol. 2021, 166, 1643–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Trépo, E.; Nahon, P.; Cao, Q.; Moreno, C.; Letouzé, E.; Imbeaud, S.; Gustot, T.; Deviere, J.; Debette, S.; et al. PNPLA3 and TM6SF2 Variants as Risk Factors of Hepatocellular Carcinoma across Various Etiologies and Severity of Underlying Liver Diseases. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 144, 533–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chanthra, N.; Payungporn, S.; Chuaypen, N.; Piratanantatavorn, K.; Pinjaroen, N.; Poovorawan, Y.; Tangkijvanich, P. Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in STAT3 and STAT4 and Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Thai Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2016, 16, 8405–8410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, H.; He, H.; Ojha, S.C.; Sun, C.; Fu, J.; Yan, M.; Deng, C.; Sheng, Y. Association of STAT3 and STAT4 Polymorphisms with Susceptibility to Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection and Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Meta-Analysis. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, 20190783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Liu, G.; Gong, L. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis on the Association between Polymorphisms in Genes of IL-12 Signaling Pathway and Hepatocellular Carcinoma Risk. J. Cancer 2018, 9, 3583–3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Xu, K.; Liu, C.; Chen, J. Meta-Analysis Reveals an Association between Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription-4 Polymorphism and Hepatocellular Carcinoma Risk. Hepatol. Res. 2017, 47, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Su, K.; Tao, J.; Fan, R.; Xu, Y.; Han, H.; Li, L.; Li, M.D. Association of STAT4 Polymorphisms with Hepatitis B Virus Infection and Clearance in Chinese Han Population. Amino Acids 2016, 48, 2589–2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Jiang, K.; Liang, B.; Huang, X. STAT4 Gene Polymorphism and Risk of Chronic Hepatitis B-Induced Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2015, 71, 353–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Cai, B.; Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Tao, C.; Huang, H.; Wang, L. Association of HLA-DP/DQ and STAT4 Polymorphisms with HBV Infection Outcomes and a Mini Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Characteristics | Latin America | European |
|---|---|---|
| HCC (n = 344) | n = 155 | n = 189 |
| Age [median (IQR)] years | 68 (62–73) | 67 (61–71) |
| Male, n (%) | 99 (64%) | 145 (77%) |
| Cause of Liver disease, n (%) | ||
| Hep. B virus (HBV) | 6 (4) | 21 (11) |
| Hep. C virus (HCV) | 23 (15) | 23 (12) |
| MASLD/MASH | 71 (46) | 36 (19) |
| Alcohol | 38 (25) | 66 (35) |
| Autoimmune | 4 (3) | 5 (3) |
| Other | 3 (2) | 33 (17) |
| None | 10 (6) | 4 (2) |
| Cirrhosis (n =716) | n = 454 | n = 262 |
| Age [median (IQR)] years | 63 (57–69) | 58 (46–66) |
| Male, n (%) | 220 (48%) | 167 (64%) |
| Cause of Liver disease, n (%) | ||
| Hep. B virus (HBV) | 16 (4) | 80 (31) |
| Hep. C virus (HCV) | 40 (9) | 76 (29) |
| MASLD/MASH | 267 (59) | 43 (16) |
| Alcohol | 67 (15) | 18 (7) |
| Autoimmune | 25 (6) | 21 (8) |
| Other | 36 (8) | 23 (9) |
| None | 3 (1) | 0 |
| Disease | OR | CI 95% | p | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LA | EU | LA | EU | LA | EU | |
| MASLD/MASH | 0.778 | 1 | 0.431–1.382 | 0.440–2.589 | 0.414 | 1 |
| AIH | 2.066 | 0.5 | 0.252–17.927 | 0.064–3.906 | 0.592 | 0.597 |
| ALCOHOL | 0.578 | 1.688 | 0.257–1.299 | 0.577–4.939 | 0.223 | 0.413 |
| HBV | 0.4 | 0.813 | 0.036–4.411 | 0.310–2.138 | 0.623 | 0.805 |
| HCV | 1.143 | 1.364 | 0.376–3.472 | 0.516–3.602 | 1 | 0.631 |
| Latin Americans | OR [95 CI] | p Value |
|---|---|---|
| GG vs. TT | 0.85 [0.48, 1.52] | 0.58 |
| GG vs. (GT and TT) | 0.85 [0.58, 1.25] | 0.46 |
| (GG and GT) vs. TT | 0.92 [0.55, 1.56] | 0.8 |
| Europeans | ||
| GG vs. TT | 0.81 [0.34, 1.93] | 0.67 |
| GG vs. (GT and TT) | 1.01 [0.68, 1.5] | 1 |
| (GG and GT) vs. TT | 0.79 [0.34, 1.87] | 0.56 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ayoub, A.; Anugwom, C.M.; Prieto, J.; Balderramo, D.; Ferrer, J.D.; Mattos, A.Z.; Arrese, M.; Carrera, E.; Groothuismink, Z.M.A.; Oliveira, J.; et al. Assessment of STAT4 Variants and Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Latin Americans and Europeans. Cancers 2023, 15, 4530. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15184530
Ayoub A, Anugwom CM, Prieto J, Balderramo D, Ferrer JD, Mattos AZ, Arrese M, Carrera E, Groothuismink ZMA, Oliveira J, et al. Assessment of STAT4 Variants and Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Latin Americans and Europeans. Cancers. 2023; 15(18):4530. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15184530
Chicago/Turabian StyleAyoub, Alan, Chimaobi M. Anugwom, Jhon Prieto, Domingo Balderramo, Javier Diaz Ferrer, Angelo Z. Mattos, Marco Arrese, Enrique Carrera, Zwier M. A. Groothuismink, Jeffrey Oliveira, and et al. 2023. "Assessment of STAT4 Variants and Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Latin Americans and Europeans" Cancers 15, no. 18: 4530. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15184530
APA StyleAyoub, A., Anugwom, C. M., Prieto, J., Balderramo, D., Ferrer, J. D., Mattos, A. Z., Arrese, M., Carrera, E., Groothuismink, Z. M. A., Oliveira, J., Boonstra, A., & Debes, J. D. (2023). Assessment of STAT4 Variants and Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Latin Americans and Europeans. Cancers, 15(18), 4530. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15184530






