Association between Metabolic Syndrome and Risk of Hypopharyngeal Cancer: A Nationwide Cohort Study from Korea
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
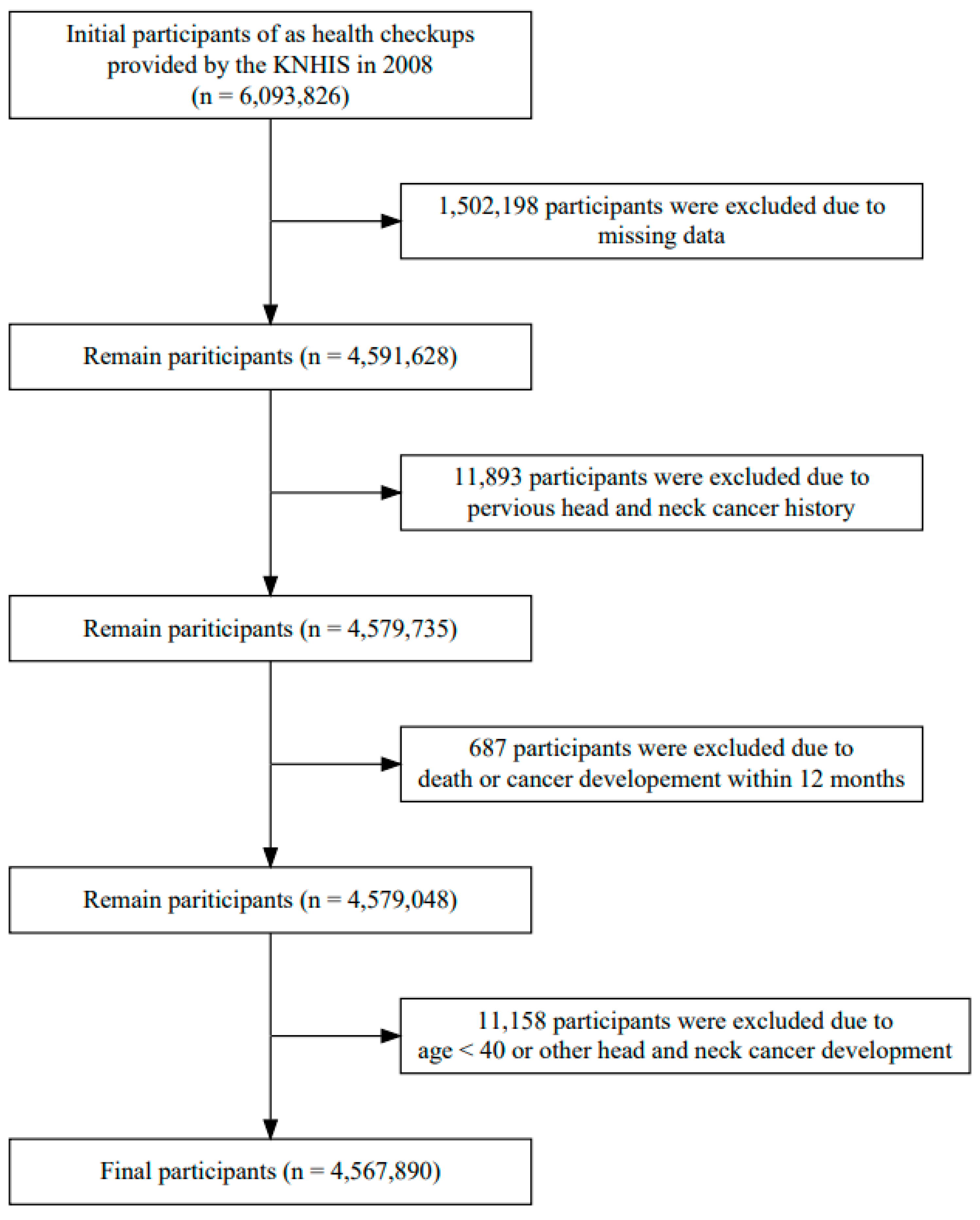
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Source
2.2. Study Population
2.3. Definition of Variables
2.4. Metabolic Syndrome
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
3.2. Effects of Established Risk Factors in Hypopharyngeal Cancer Development
3.3. Metabolic Syndrome and Risk of Hypopharyngeal Cancer
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eckel, H.E.; Bradley, P.J. Natural History of Treated and Untreated Hypopharyngeal Cancer. Adv. Otorhinolaryngol. 2019, 83, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rettig, E.M.; D’Souza, G. Epidemiology of head and neck cancer. Surg. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2015, 24, 379–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, J.D.; Cho, J.H. Trends in Head and Neck Cancer in South Korea Between 1999 and 2012. Clin. Exp. Otorhinolaryngol. 2016, 9, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, J.R.; Connolly, T.M.; Illing, E.A.; Kilgore, M.L.; Locher, J.L.; Carroll, W.R. Survival trends in hypopharyngeal cancer: A population-based review. Laryngoscope 2015, 125, 624–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.G.; Park, B.; Ahn, S.H. Untreated head and neck cancer in Korea: A national cohort study. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2017, 274, 1643–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vageli, D.P.; Doukas, S.G.; Doukas, P.G.; Judson, B.L. Bile reflux and hypopharyngeal cancer (Review). Oncol. Rep. 2021, 46, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, K.; Chiodini, P.; Colao, A.; Lenzi, A.; Giugliano, D. Metabolic syndrome and risk of cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 2402–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.B.; Kim, G.J.; Han, K.D.; Joo, Y.H. Changes in metabolic syndrome status and risk of laryngeal cancer: A nationwide cohort study. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0252872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calle, E.E.; Kaaks, R. Overweight, obesity and cancer: Epidemiological evidence and proposed mechanisms. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 579–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicks, D.F.; Bakst, R.; Doucette, J.; Kann, B.H.; Miles, B.; Genden, E.; Misiukiewicz, K.; Posner, M.; Gupta, V. Impact of obesity on outcomes for patients with head and neck cancer. Oral Oncol. 2018, 83, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.S. Introduction: Health of the health care system in Korea. Soc. Work Public Health 2010, 25, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bramer, G.R. International statistical classification of diseases and related health problems. Tenth revision. World Health Stat. Q 1988, 41, 32–36. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. The Asia-Pacific Perspective: Redefining Obesity and Its Treatment. 2000. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/206936/0957708211_eng.pdf (accessed on 7 August 2023).
- Expert Panel on Detection, E.; Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults. Executive Summary of The Third Report of The National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, And Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol In Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III). JAMA 2001, 285, 2486–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, D.P. Cardioprotective effects of light-moderate consumption of alcohol: A review of putative mechanisms. Alcohol Alcohol. 2002, 37, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, K.G.; Zimmet, P.; Shaw, J. Metabolic syndrome—A new world-wide definition. A Consensus Statement from the International Diabetes Federation. Diabet Med. 2006, 23, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howlader, N.; Noone, A.M.; Krapcho, M.; Miller, D.; Bishop, K.; Kosary, C.L.; Yu, M.; Ruhl, J.; Tatalovich, Z.; Mariotto, A.; et al. (Eds.) SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975–2014; National Cancer Institute: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2017. Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2014/ (accessed on 15 November 2016).
- Simard, E.P.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. International trends in head and neck cancer incidence rates: Differences by country, sex and anatomic site. Oral Oncol. 2014, 50, 387–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blot, W.J.; McLaughlin, J.K.; Winn, D.M.; Austin, D.F.; Greenberg, R.S.; Preston-Martin, S.; Bernstein, L.; Schoenberg, J.B.; Stemhagen, A.; Fraumeni, J.F., Jr. Smoking and drinking in relation to oral and pharyngeal cancer. Cancer Res. 1988, 48, 3282–3287. [Google Scholar]
- Hashibe, M.; Brennan, P.; Benhamou, S.; Castellsague, X.; Chen, C.; Curado, M.P.; Dal Maso, L.; Daudt, A.W.; Fabianova, E.; Fernandez, L.; et al. Alcohol drinking in never users of tobacco, cigarette smoking in never drinkers, and the risk of head and neck cancer: Pooled analysis in the International Head and Neck Cancer Epidemiology Consortium. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2007, 99, 777–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschi, S.; Talamini, R.; Barra, S.; Baron, A.E.; Negri, E.; Bidoli, E.; Serraino, D.; La Vecchia, C. Smoking and drinking in relation to cancers of the oral cavity, pharynx, larynx, and esophagus in northern Italy. Cancer Res. 1990, 50, 6502–6507. [Google Scholar]
- Schlecht, N.F.; Franco, E.L.; Pintos, J.; Kowalski, L.P. Effect of smoking cessation and tobacco type on the risk of cancers of the upper aero-digestive tract in Brazil. Epidemiology 1999, 10, 412–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudet, M.M.; Olshan, A.F.; Chuang, S.C.; Berthiller, J.; Zhang, Z.F.; Lissowska, J.; Zaridze, D.; Winn, D.M.; Wei, Q.; Talamini, R.; et al. Body mass index and risk of head and neck cancer in a pooled analysis of case-control studies in the International Head and Neck Cancer Epidemiology (INHANCE) Consortium. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2010, 39, 1091–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, X.; Nelson, H.H.; Langevin, S.M.; McClean, M.; Marsit, C.J.; Waterboer, T.; Pawlita, M.; Kelsey, K.T.; Michaud, D.S. Obesity and head and neck cancer risk and survival by human papillomavirus serology. Cancer Causes Control 2015, 26, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eytan, D.F.; Blackford, A.L.; Eisele, D.W.; Fakhry, C. Prevalence of Comorbidities among Older Head and Neck Cancer Survivors in the United States. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2019, 160, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, P.; Wang, Y.; Yu, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.J. Type 2 diabetes mellitus and risk of head and neck cancer subtypes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Acta. Diabetol. 2021, 58, 549–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Zhou, L.; He, Q.; Jiang, K.; Yuan, J.; Huang, X. The effect of metabolic syndrome on head and neck cancer incidence risk: A population-based prospective cohort study. Cancer Metab. 2021, 9, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stott-Miller, M.; Chen, C.; Schwartz, S.M. Type II diabetes and metabolic syndrome in relation to head and neck squamous cell carcinoma risk: A SEER-Medicare database study. Cancer Epidemiol. 2013, 37, 428–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, G.W.; Cheong, H.K.; Choi, S.Y.; Lee, Y.C.; Oh, I.H.; Eun, Y.G. Association between oral cavity cancer and metabolic syndrome. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 149, 4005–4013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zucchetto, A.; Taborelli, M.; Bosetti, C.; Montella, M.; La Vecchia, C.; Franchin, G.; Libra, M.; Serraino, D.; Polesel, J. Metabolic disorders and the risk of nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A case-control study in Italy. Eur. J. Cancer Prev. 2018, 27, 180–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.L.; Hsu, M.Y.; Hu, C.C.; Tantoh, D.M.; Lu, W.Y.; Nfor, O.N.; Liaw, Y.P. Association of Age and Sex with Metabolic Syndrome in Taiwanese Adults. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2021, 14, 1403–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellastella, G.; Scappaticcio, L.; Esposito, K.; Giugliano, D.; Maiorino, M.I. Metabolic syndrome and cancer: “The common soil hypothesis”. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2018, 143, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pothiwala, P.; Jain, S.K.; Yaturu, S. Metabolic syndrome and cancer. Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord. 2009, 7, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barb, D.; Williams, C.J.; Neuwirth, A.K.; Mantzoros, C.S. Adiponectin in relation to malignancies: A review of existing basic research and clinical evidence. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 86, 858S–866S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanders, O.; Pathak, S. Hypopharyngeal Cancer; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Auperin, A. Epidemiology of head and neck cancers: An update. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2020, 32, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Cho, Y.J. Socioeconomic status in association with metabolic syndrome and coronary heart disease risk. Korean J. Fam. Med. 2013, 34, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Hypopharyngeal Cancer | Non-Hypopharyngeal Cancer | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | (n = 821) | (n = 4,567,069) | p-Value |
| Follow-up period, years | 9.51 ± 2.66 | 11.16 ± 1.19 | |
| Sex, n (%) | <0.001 | ||
| Male | 765 (93) | 2,469,600 (54) | |
| Female | 56 (7) | 2,097,469 (46) | |
| Age, years | 61.54 ± 8.93 | 53.96 ± 9.32 | <0.001 |
| 40–49 | 78 (9.5) | 1,753,488 (38.4) | |
| 50–59 | 255 (31.1) | 1,619,385 (35.5) | |
| 60–69 | 307 (37.4) | 780,233 (17.1) | |
| 70–79 | 164 (20) | 378,442 (8.3) | |
| 80- | 17 (2.1) | 35,521 (0.8) | |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 22.88 ± 2.86 | 23.98 ± 3.32 | <0.001 |
| <18.5 | 49 (6) | 87,617 (1.9) | |
| 18.5–22.9 | 391 (47.6) | 1,630,303 (35.7) | |
| 23–24.9 | 189 (23) | 1,260,472 (27.6) | |
| ≥25 | 192 (23.4) | 1,588,677 (34.8) | |
| Blood pressure, mmHg | |||
| Systolic | 128.59 ± 16.67 | 124.64 ± 15.63 | <0.001 |
| Diastolic | 79.00 ± 10.49 | 77.63 ± 10.26 | <0.001 |
| Chemistry, mg/dL | |||
| FBG | 101.83 ± 25.67 | 98.69 ± 25.15 | <0.001 |
| TC | 188.36 ± 36.56 | 197.45 ± 36.95 | <0.001 |
| TG | 139.27 ± 89.87 | 139.80 ± 108.34 | 0.8884 |
| HDL | 55.41 ± 16.78 | 55.55 ± 31.89 | 0.9003 |
| LDL | 106.42 ± 35.68 | 119.64 ± 79.48 | <0.001 |
| Hazard Ratio (95% Confidence Interval) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | HPC (n) | Model 1 a | Model 2 b | Model 3 c |
| Sex | ||||
| Male | 765 | 1 | ||
| Female | 56 | 0.075 (0.057–0.098) * | ||
| Age (years) | ||||
| 40–49 | 78 | 1 | ||
| 50–59 | 255 | 3.282 (2.547–4.23) * | ||
| 60–69 | 307 | 7.39 (5.757–9.487) * | ||
| 70–79 | 164 | 7.922 (6.031–10.406) * | ||
| 80- | 17 | 12.742 (7.526–21.573) * | ||
| BMI | ||||
| <18.5 | 49 | 2.473 (1.838–3.328) * | 2.168 (1.61–2.92) * | 2.061 (1.529–2.778) * |
| 18.5–22.9 | 391 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 23–24.9 | 189 | 0.615 (0.517–0.732) * | 0.556 (0.467–0.662) * | 0.579 (0.487–0.69) * |
| ≥25 | 192 | 0.488 (0.411–0.58) * | 0.452 (0.38–0.538) * | 0.474 (0.398–0.564) * |
| Smoking | ||||
| Never smoked | 253 | 1 | 1 | |
| Ex-smoker | 90 | 2.81 (2.295–3.44) * | 1.368 (1.112–1.683) * | |
| Current smoker | 297 | 4 (3.444–4.645) * | 2.268 (1.938–2.655) * | |
| Alcohol | ||||
| None | 227 | 1 | 1 | |
| Mild | 340 | 2.013 (1.739–2.33) * | 1.257 (1.08–1.463) * | |
| Heavy | 73 | 5.121 (4.016–6.528) * | 2.828 (2.205–3.626) * | |
| Hazard Ratio (95% Confidence Interval) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | HPC (n) | Model 1 a | Model 2 b | Model 3 c |
| MS † | ||||
| No | 612 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Yes | 209 | 0.906 (0.774–1.06) | 0.853 (0.729–0.999) * | 0.829 (0.708–0.971) * |
| WC † | ||||
| Low | 659 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| High | 162 | 1.125 (0.948–1.337) | 0.678 (0.57–0.805) * | 0.82 (0.711–0.945) * |
| TC | ||||
| Low | 519 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| High | 302 | 0.701 (0.608–0.808) * | 0.826 (0.716–0.953) * | 0.819 (0.706–0.949) * |
| TG † | ||||
| Low | 557 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| High | 264 | 1.003 (0.866–1.161) | 0.883 (0.763–1.023) | 0.829 (0.703–0.978) * |
| HDL † | ||||
| Low | 693 | 1.612 (1.335–1.947) * | 1.082 (0.894–1.308) | 1.072 (0.886–1.298) |
| High | 128 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| LDL | ||||
| Low | 361 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| High | 460 | 0.545 (0.475–0.625) * | 0.675 (0.588–0.775) * | 0.697 (0.607–0.801) * |
| HTN, Raised BP † | ||||
| No | 330 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Yes | 491 | 1.489 (1.295–1.712) * | 0.98 (0.851–1.13) | 0.977 (0.848–1.127) |
| DM, Raised FBG † | ||||
| No | 459 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Yes | 362 | 1.518 (1.322–1.742) * | 1.094 (0.953–1.256) | 1.08 (0.941–1.241) |
| Hazard Ratio (95% Confidence Interval) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Male | Female | |
| MS components | |||
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 1–2 | 1.054 (0.86–1.292) | 1.16 (0.932–1.443) | 0.511 (0.274–0.952) * |
| ≥3 | 0.866 (0.688–1.089) | 0.992 (0.777–1.265) | 0.295 (0.132–0.66) * |
| MS | |||
| No | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Yes | 0.829 (0.708–0.971) * | 0.878 (0.746–1.033) | 0.488 (0.248–0.961) * |
| WC | |||
| Low | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| High | 0.82 (0.711–0.945) * | 0.693 (0.582–0.826) * | 0.558 (0.2–1.555) |
| TG | |||
| Low | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| High | 0.829 (0.703–0.978) * | 0.83 (0.713–0.967) * | 0.883 (0.479–1.627) |
| HDL | |||
| Low | 1.072 (0.886–1.298) | 1.064 (0.868–1.303) | 1.006 (0.572–1.771) |
| High | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| HTN | |||
| No | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Yes | 0.977 (0.848–1.127) | 1.035 (0.892–1.2) | 0.522 (0.294–0.924) * |
| DM | |||
| No | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Yes | 1.08 (0.941–1.241) | 1.118 (0.969–1.29) | 0.686 (0.367–1.282) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, J.W.; Cheong, H.-K.; Kim, S.I.; Lee, M.K.; Lee, Y.C.; Oh, I.-H.; Eun, Y.-G. Association between Metabolic Syndrome and Risk of Hypopharyngeal Cancer: A Nationwide Cohort Study from Korea. Cancers 2023, 15, 4454. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15184454
Kang JW, Cheong H-K, Kim SI, Lee MK, Lee YC, Oh I-H, Eun Y-G. Association between Metabolic Syndrome and Risk of Hypopharyngeal Cancer: A Nationwide Cohort Study from Korea. Cancers. 2023; 15(18):4454. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15184454
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Jeong Wook, Hyeon-Kyoung Cheong, Su Il Kim, Min Kyeong Lee, Young Chan Lee, In-Hwan Oh, and Young-Gyu Eun. 2023. "Association between Metabolic Syndrome and Risk of Hypopharyngeal Cancer: A Nationwide Cohort Study from Korea" Cancers 15, no. 18: 4454. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15184454
APA StyleKang, J. W., Cheong, H.-K., Kim, S. I., Lee, M. K., Lee, Y. C., Oh, I.-H., & Eun, Y.-G. (2023). Association between Metabolic Syndrome and Risk of Hypopharyngeal Cancer: A Nationwide Cohort Study from Korea. Cancers, 15(18), 4454. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15184454







