Fiber Optic Gyro Random Error Suppression Based on Dual Adaptive Kalman Filter
Abstract
1. Introduction
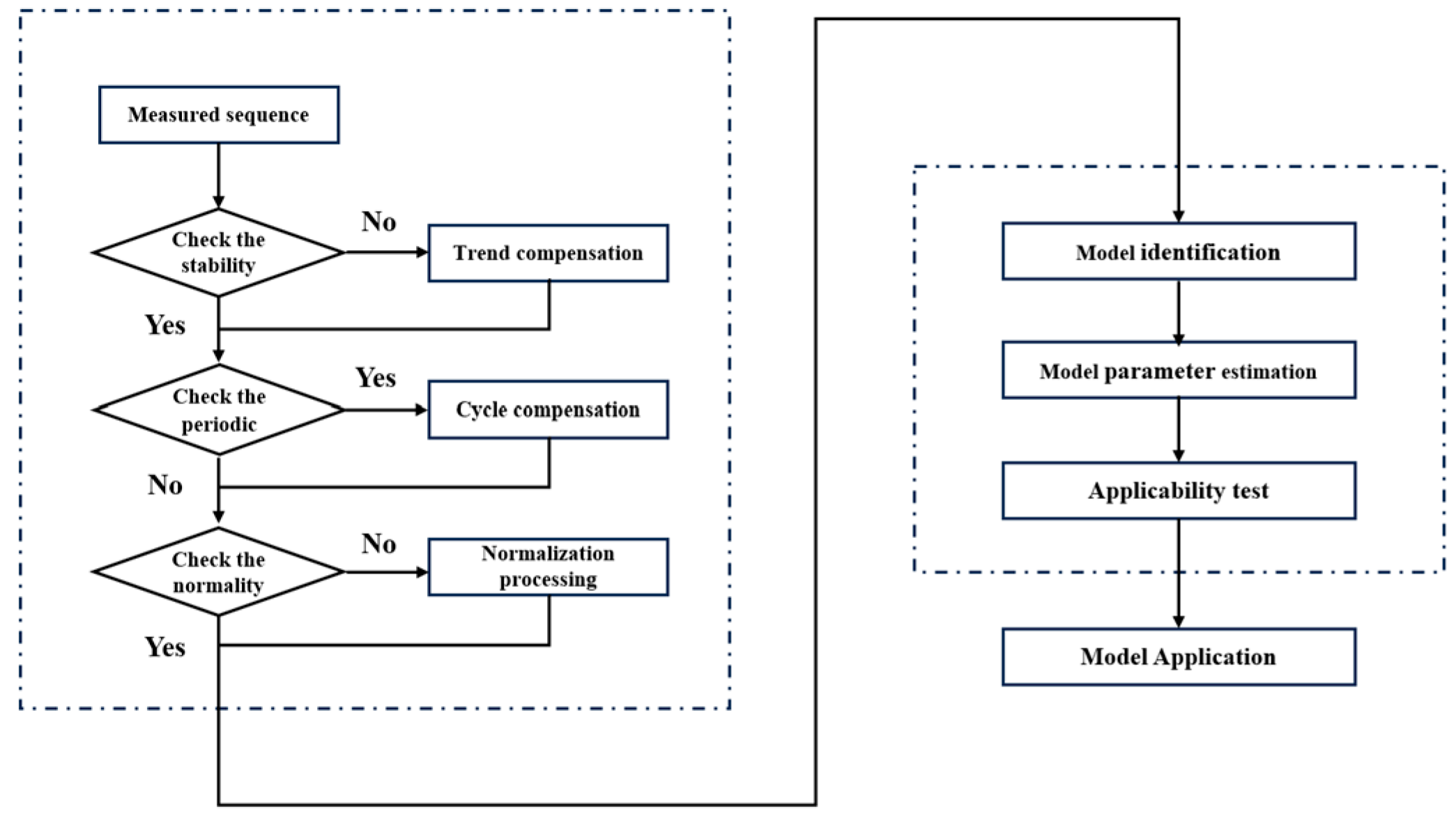
2. A Recursive Dynamic Allan Variance Calculation
2.1. Allan Variance Calculation
2.2. Dynamic Allan Variance Calculation
2.3. A Recursive Dynamic Allan Variance Calculation
3. Design of Kalman Filter Based on ARMA Model
4. An Improved Kalman Filter Based on Dual Adaptive Mechanism
- a.
- Build an AR model based on AIC criteria [29];
- b.
- Setting initial parameters for filtering
- c.
- Updating the adaptive variance weight coefficients
- d.
- Recursively calculate the dynamic Allan variance at time based on Formula (9);
- e.
- One-step prediction of filters
- f.
- Calculating filter remainder
- g.
- Judging the relationship between and . If , proceed to step h. If , then go back to step a to remodel based on the data sequence near the current moment;
- h.
- Judging the relationship between and . If the magnitudes of the values of and are basically the same, continue with step i. If a relatively large error occurs between the values of and , then and then proceed to step i;
- i.
- Estimate noise measurement
- j.
- Filter gain update
- k.
- Optimal estimate
- l.
- Mean square deviation update
- m.
- Calculation process noise
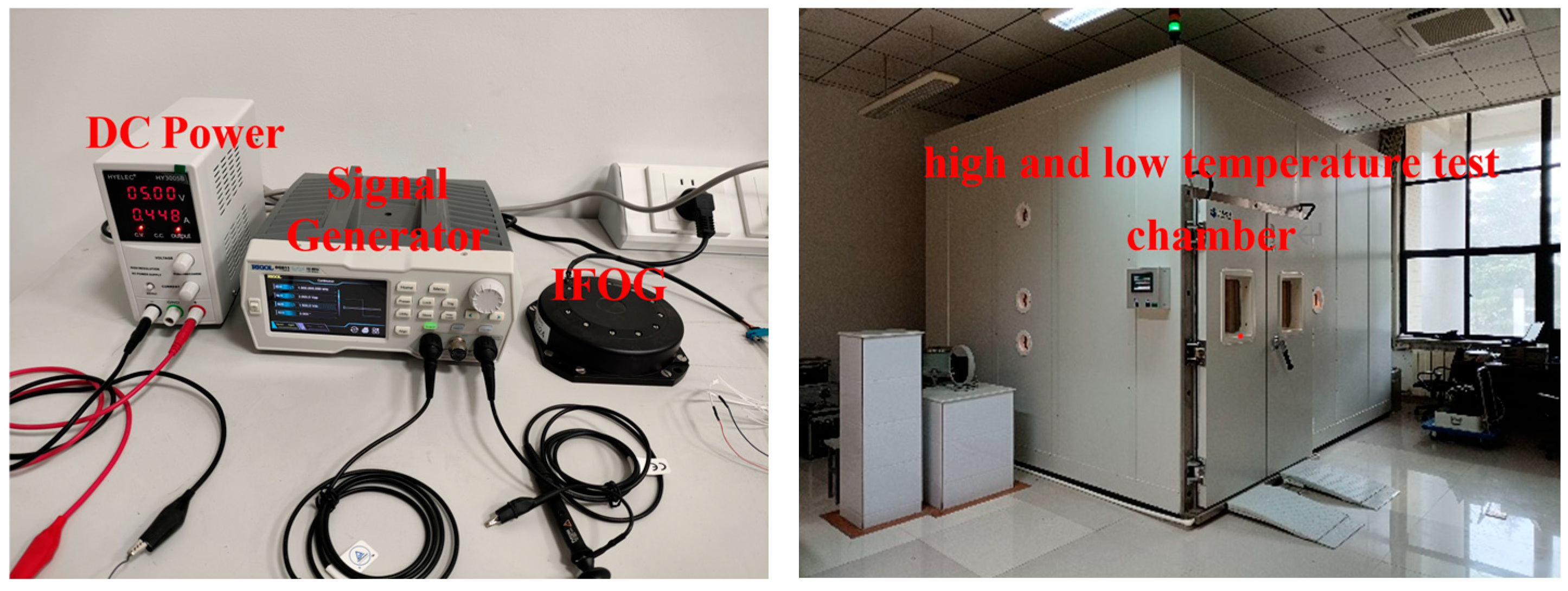
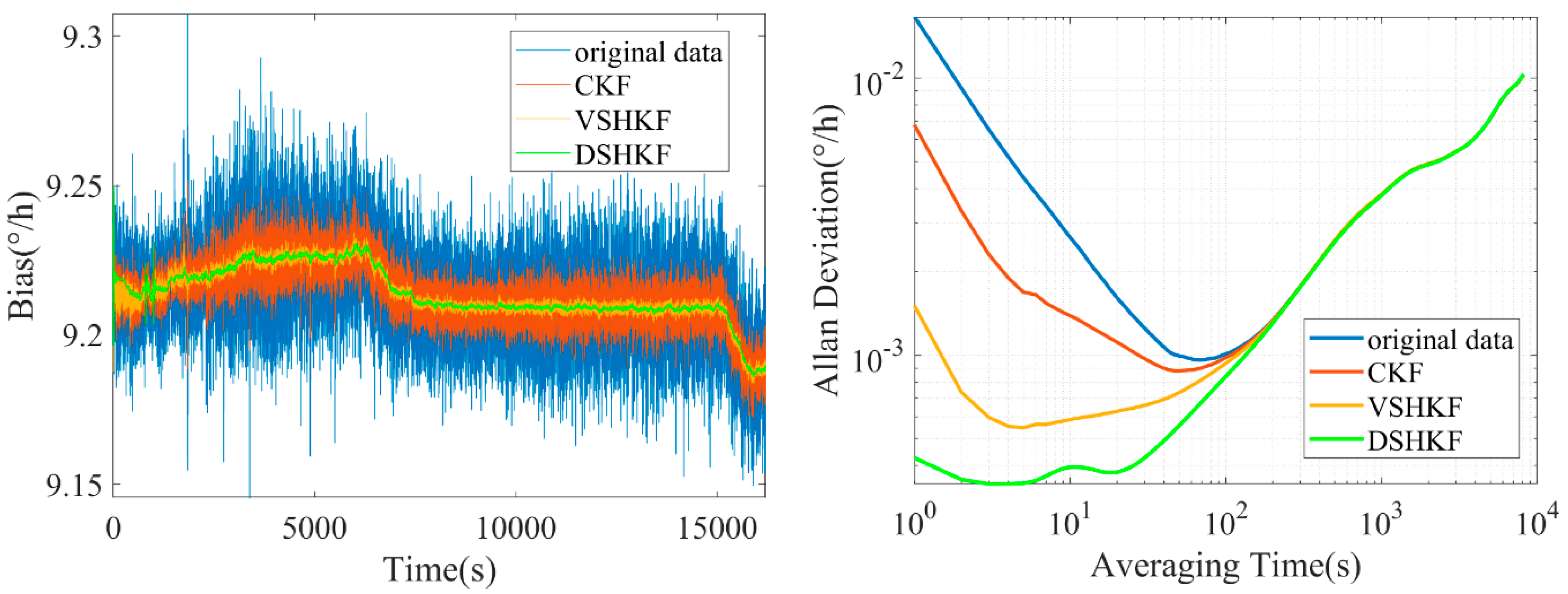
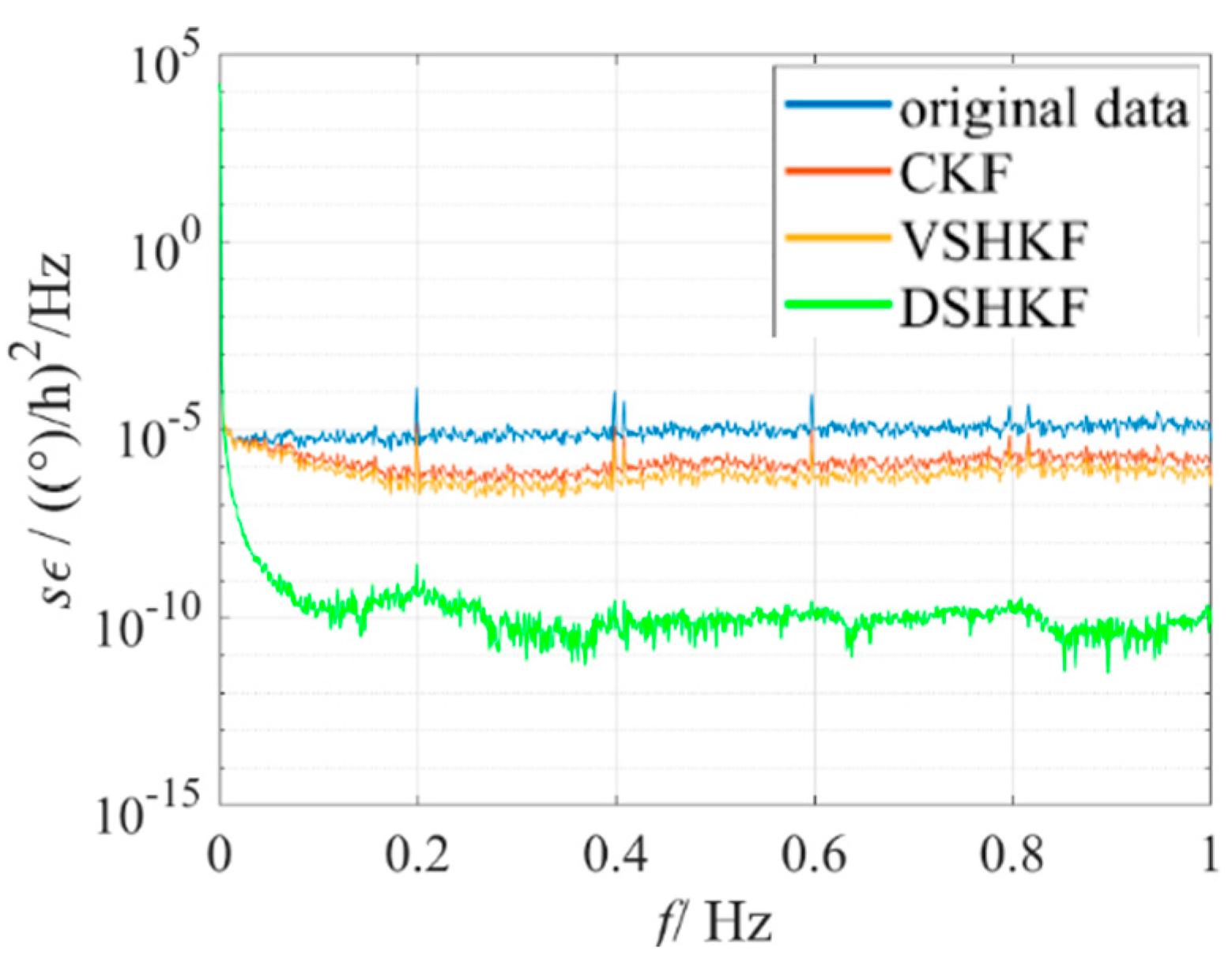
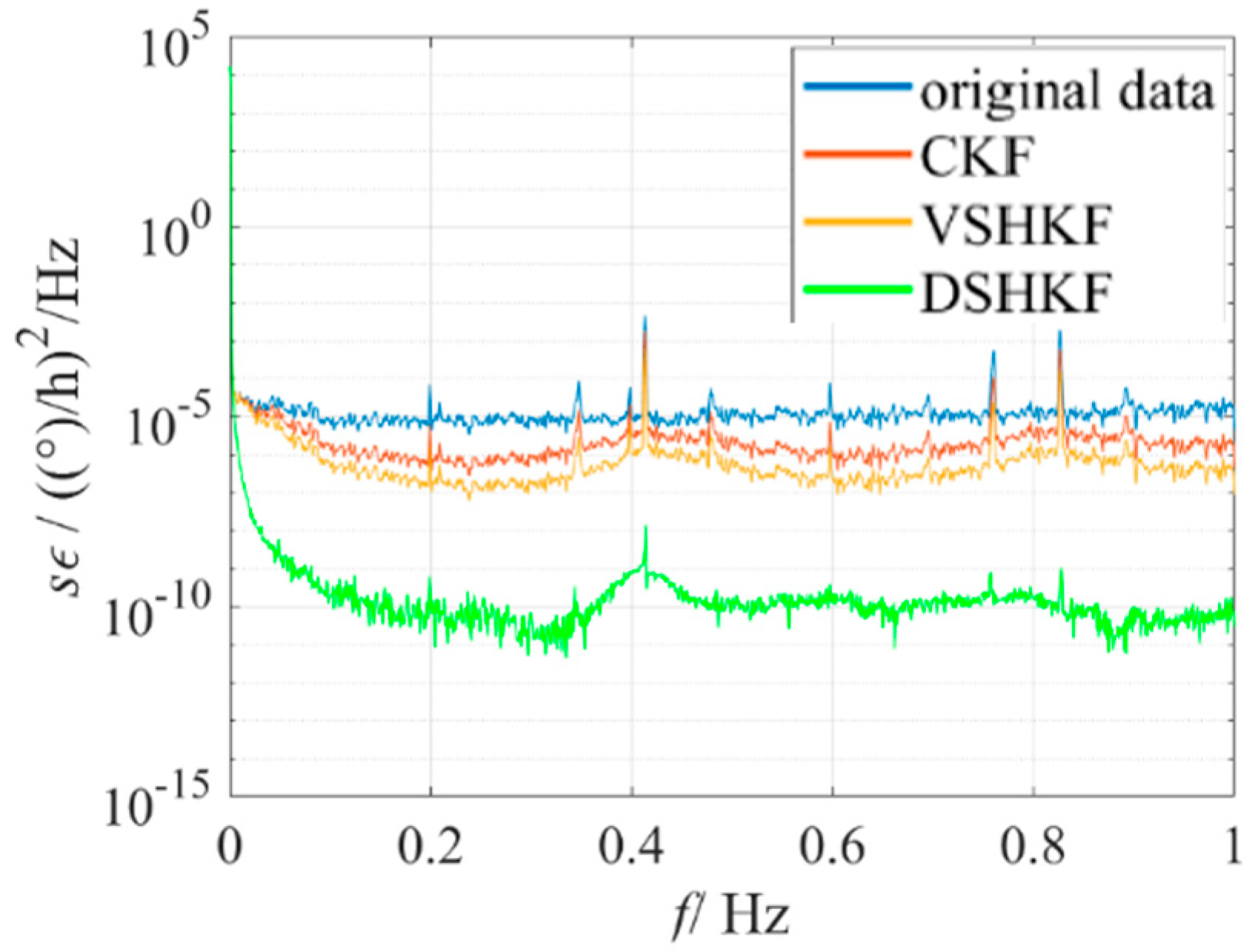
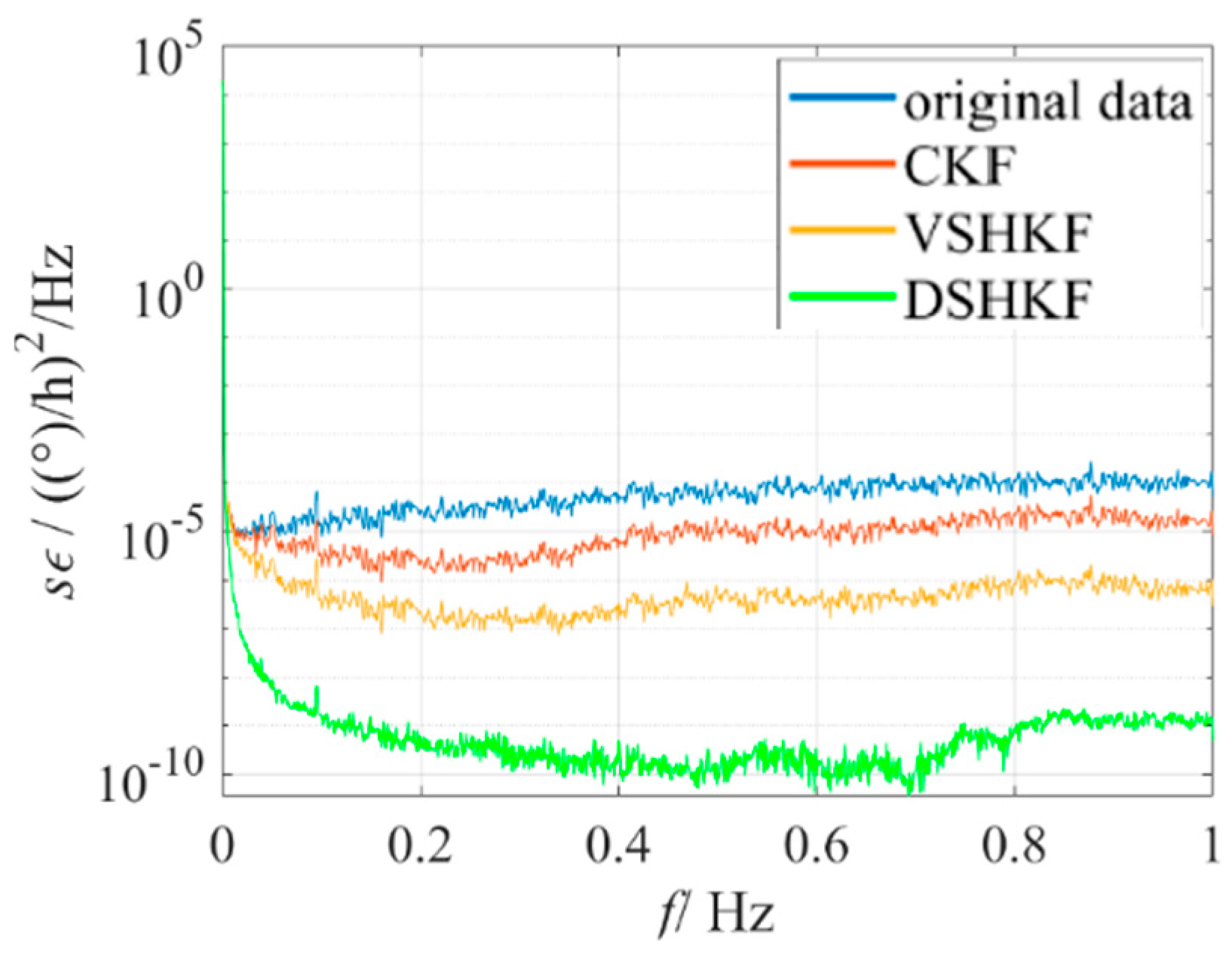
5. Experimental Verification
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lawrence, A. The interferometric fiber-optic gyro. In Modern Inertial Technology (Mechanical Engineering Series); Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1998; pp. 188–207. [Google Scholar]
- Lefèvre, H.C.; Steib, A.; Claire, A.; Sekeriyan, A.; Couderette, A.; Pointel, A.; Viltard, A.; Bonnet, A.; Frénois, A.; Gandoin, A. The fiber optic gyro ‘adventure’ at Photonetics, iXsea and now iXblue. In Optical Waveguide and Laser Sensors; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Han, S.; Luo, S.; Lu, J.; Dong, J. A unified modeling approach of stochastic error in fiber optic gyro and application in ins initial alignment. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 20, 7241–7252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radi, A.; Bakalli, G.; Guerrier, S.; El-Sheimy, N.; Sesay, A.B.; Molinari, R. A multisignal wavelet variance-based framework for inertial sensor stochastic error modeling. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2019, 68, 4924–4936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrier, S.; Molinari, R.; Stebler, Y. Wavelet-based improvements for inertial sensor error modeling. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2016, 65, 2693–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narasimhappa, M.; Sabat, S.L.; Nayak, J. Fiber-optic gyroscope signal denoising using an adaptive robust kalman filter. IEEE Sens. J. 2016, 16, 3711–3718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Xiaosu, X.; Yiting, L.; Tao, Z.; Yao, L. FOG random drift signal denoising based on the improved AR model and modified Sage-Husa adaptive Kalman filter. Sensors 2016, 16, 1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, N.; Yuan, Z.; Pan, X. Adaptive Kalman filter based on random-weighting estimation for denoising the fiber-optic gyroscope drift signal. Appl. Opt. 2019, 58, 9505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu-wen, D.; Hong-wei, H.; Kang-le, W.; Peng-zhan, C. Application of different EMD-based denoising methods for fiber optic gyro. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Communication and Information Processing, New York, NY, USA, 26–29 November 2016; pp. 144–147. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Xu, X.; Zhang, T.; Zhu, Y.; Tong, J. An EMD-MRLS de-noising method for fiber optic gyro signal. Optik 2019, 183, 971–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.B.; Zhang, F. Fiber optic gyro de-noising based on VMD algorithm. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1237, 022183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Yang, Z.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, X.; Liu, C. Application and optimization of wavelet transform filter for north-seeking gyroscope sensor exposed to vibration. Sensors 2019, 19, 3624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, W.; Fang, D.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H. DAVAR method for random noise signal process of FOG based on optimal window. In AIP Conference Proceedings; AIP Publishing LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Song, J.; Shi, Z.; Wang, L.; Wang, H. Random error analysis of MEMS gyroscope based on an improved DAVAR algorithm. Micromachines 2018, 9, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, C.; Gao, S.; Wang, T.; Lin, T.; Lin, X. Application of fast dynamic Allan variance for the characterization of FOGs-based measurement while drilling. Sensors 2016, 16, 2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Q. Analysis of vibration noise on the fiber-optic gyroscope. In Data Analytics for Drilling Engineering: Theory, Algorithms, Experiments, Software; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 115–137. [Google Scholar]
- Riley, W.J. Handbook of Frequency Stability Analysis. NIST Special Publication. 2007. Available online: https://tsapps.nist.gov/publication/get_pdf.cfm?pub_id=50505 (accessed on 21 January 2025).
- El-Sheimy, N.; Hou, H.; Niu, X. Analysis and modeling of inertial sensors using Allan variance. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2007, 57, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, D.W.; Barnes, J.A. A modified Allan variance with increased oscillator characterization ability. In Proceedings of the 35th Annual Frequency Control Symposium, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 27–29 May 1981; Volume 5. [Google Scholar]
- Galleani, L. The dynamic Allan variance II: A fast computational algorithm. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2009, 57, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galleani, L.; Tavella, P. The dynamic Allan variance V: Recent advances in dynamic stability analysis. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2015, 63, 624–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, B. ARMA Model Identification; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Bustos, O.H.; Yohai, V.J. Robust estimates for ARMA models. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1986, 81, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappas, S.S.; Ekonomou, L. Electricity demand loads modeling using AutoRegressive Moving Average (ARMA) models. Energy 2008, 33, 1353–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrieze, S.I. Model selection and psychological theory: A discussion of the differences between the Akaike information criterion (AIC) and the Bayesian information criterion (BIC). Psychol. Methods 2012, 17, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Liu, F.; Liu, C.; Zhang, P. Modified Sage-Husa adaptive Kalman filter-based SINS/DVL integrated navigation system for AUV. J. Sens. 2021, 2021, 9992041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narasimhappa, M.; Mahindrakar, A.; Guizilini, V.; Terra, M.; Sabat, S. MEMS-based IMU drift minimization: Sage Husa adaptive robust Kalman filtering. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 20, 250–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, H. Frequency-scanning interferometry for dynamic measurement using adaptive Sage-Husa Kalman filter. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2023, 165, 107545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arndt, D. Akaike’s Information Criterion; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2001. [Google Scholar]


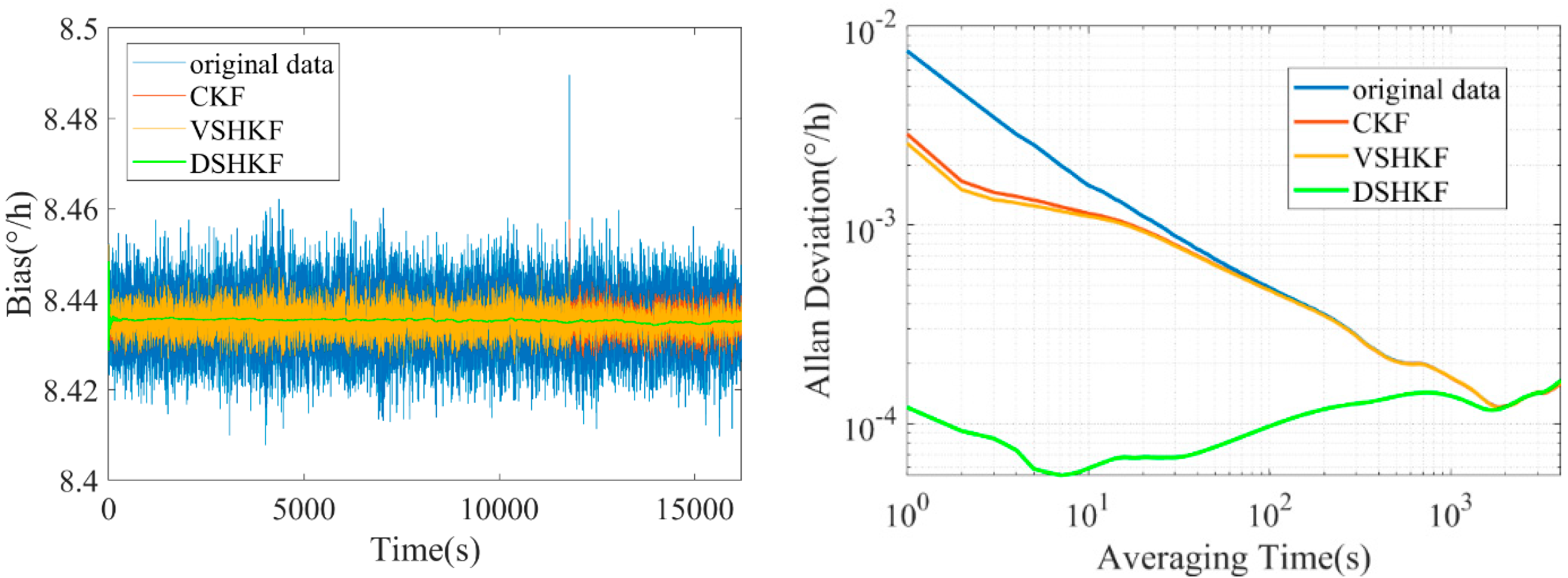
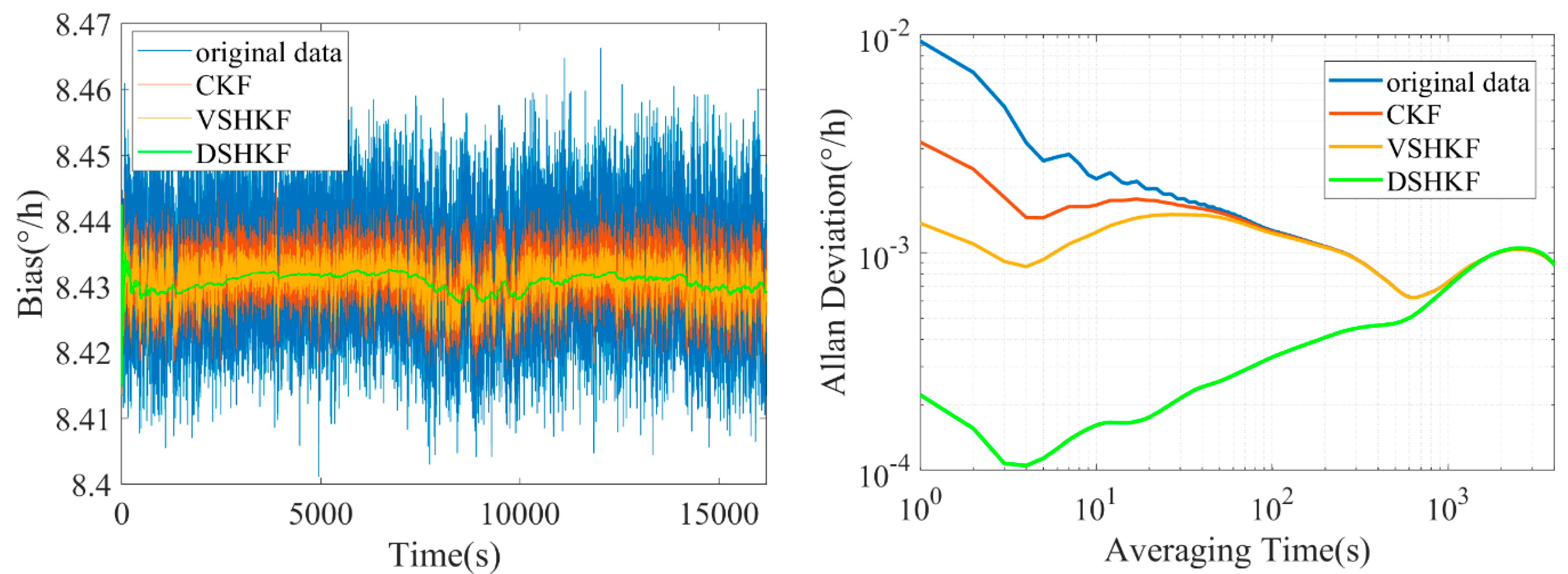
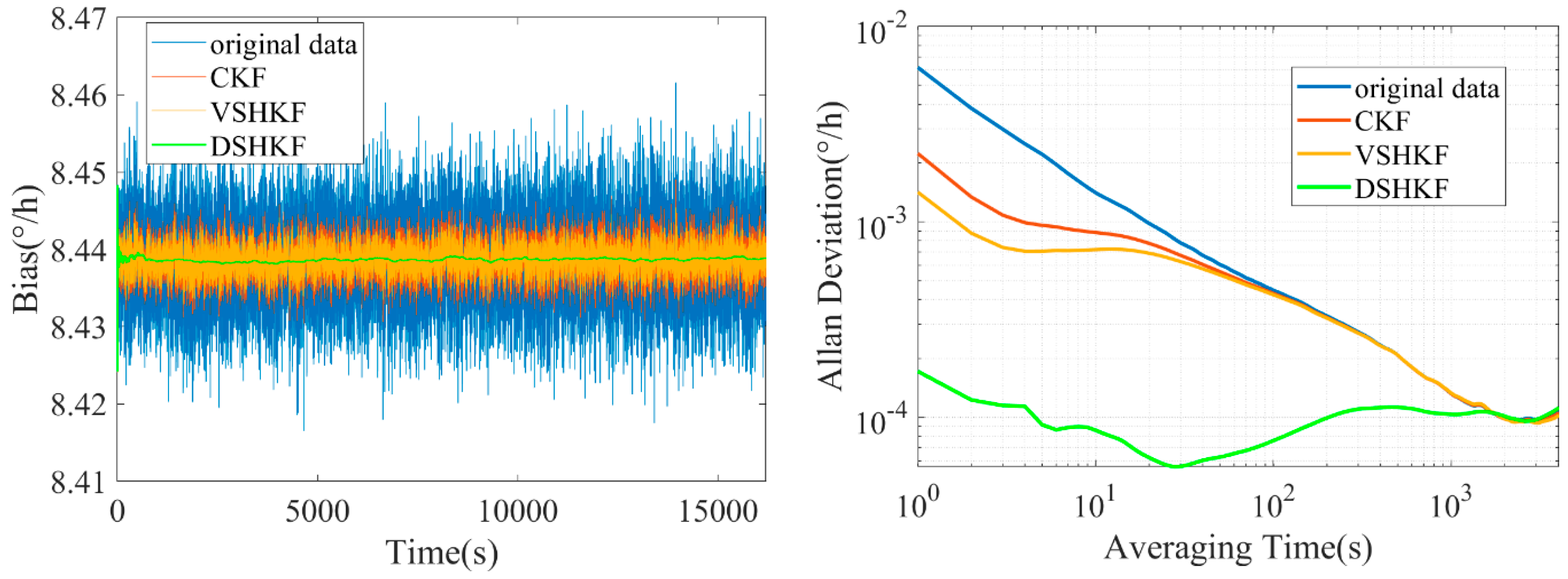

| Model Class | Model Coefficient | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IFOG-A | ARIMA(2,1,0) | −0.8833 | −0.3729 | ||
| IFOG-B | ARIMA(3,1,0) | −0.7750 | −0.5631 | −0.3534 | |
| IFOG-C | ARIMA(4,1,0) | −0.9486 | −0.7320 | −0.4756 | −0.2171 |
| IFOG-A | IFOG-B | IFOG-C | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Original data | |||
| After CKF | |||
| After VSHKF | |||
| After DSHKF |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, H.; Liang, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, J.; Tian, L. Fiber Optic Gyro Random Error Suppression Based on Dual Adaptive Kalman Filter. Micromachines 2025, 16, 884. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16080884
Li H, Liang Z, Zhou Z, Zhang Z, Zhao J, Tian L. Fiber Optic Gyro Random Error Suppression Based on Dual Adaptive Kalman Filter. Micromachines. 2025; 16(8):884. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16080884
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Hongcai, Zhe Liang, Zhaofa Zhou, Zhili Zhang, Junyang Zhao, and Longjie Tian. 2025. "Fiber Optic Gyro Random Error Suppression Based on Dual Adaptive Kalman Filter" Micromachines 16, no. 8: 884. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16080884
APA StyleLi, H., Liang, Z., Zhou, Z., Zhang, Z., Zhao, J., & Tian, L. (2025). Fiber Optic Gyro Random Error Suppression Based on Dual Adaptive Kalman Filter. Micromachines, 16(8), 884. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16080884






