Unraveling the Toxicity of a Non-Microcystin-Producing Strain (CCIBt3106) of Microcystis aeruginosa: Ecotoxicological Effects on Aquatic Invertebrates
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Overview of Biomass and Extraction Yields
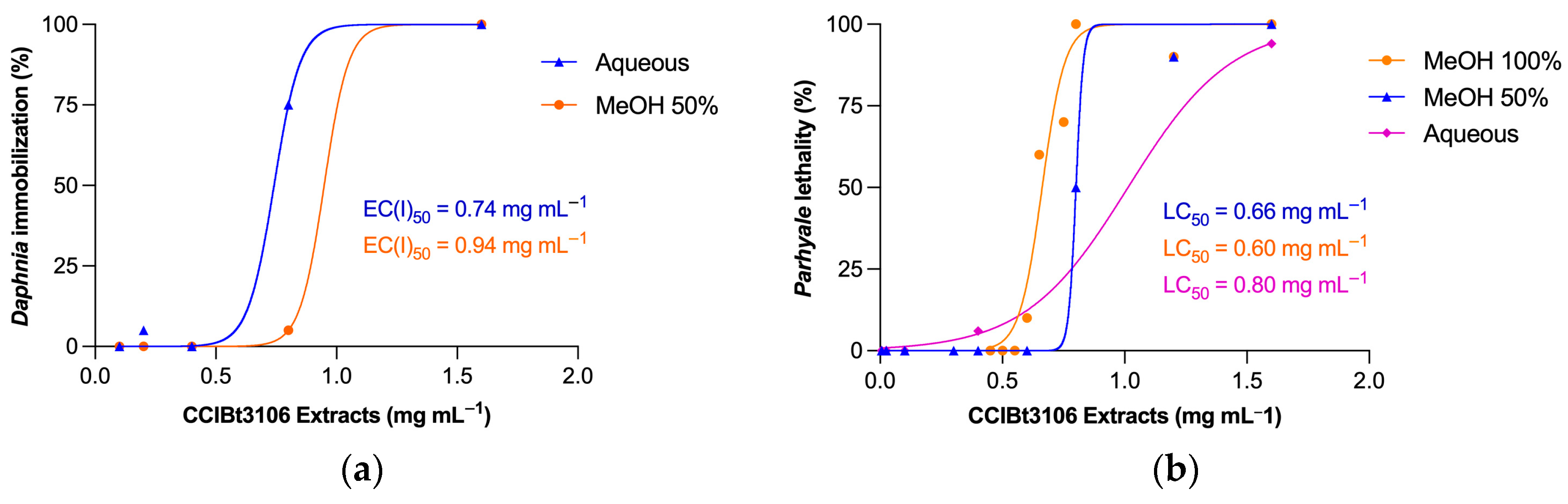
2.2. Extracts’ Toxicity Assessment in Aquatic Microcrustaceans
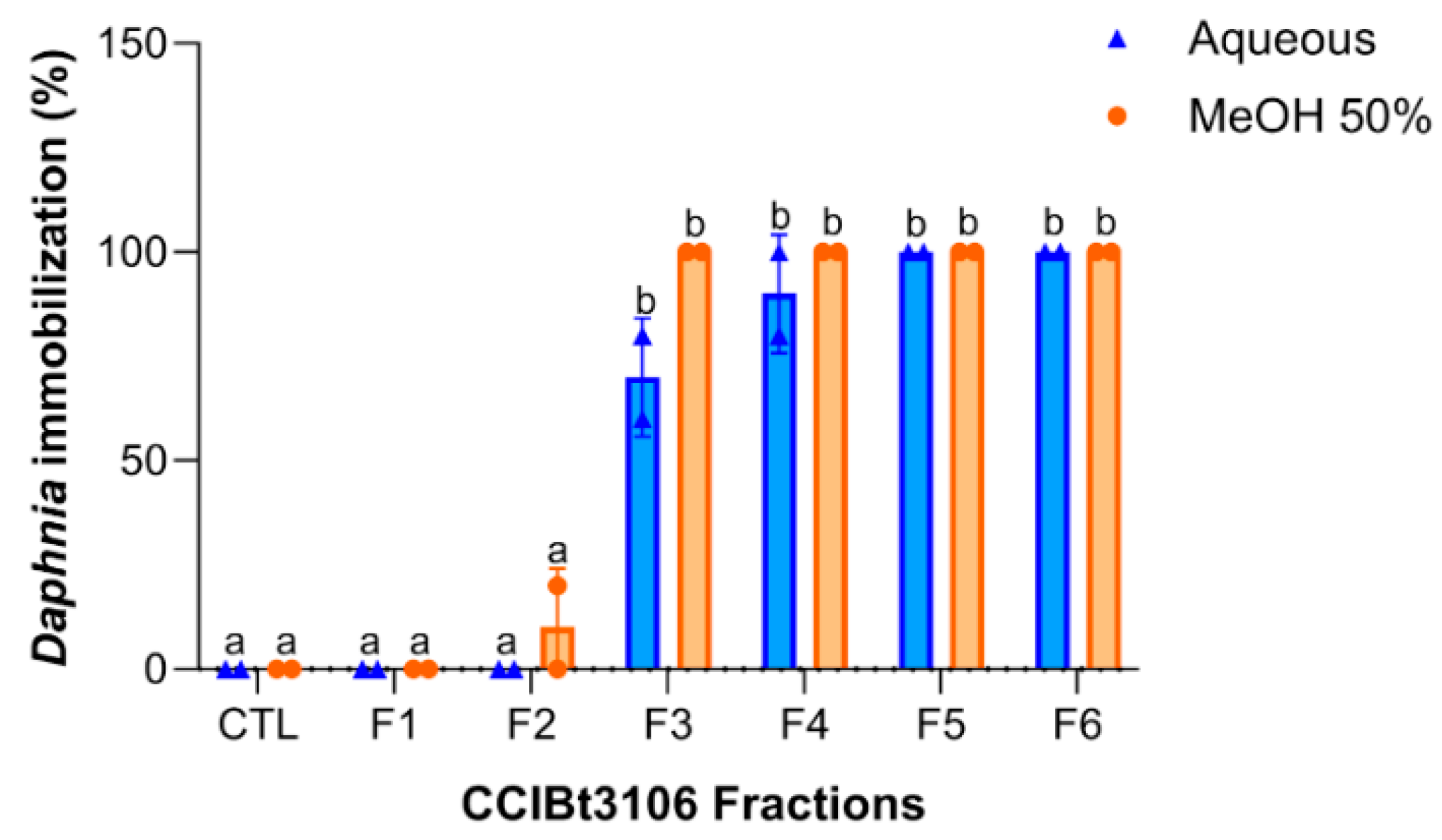
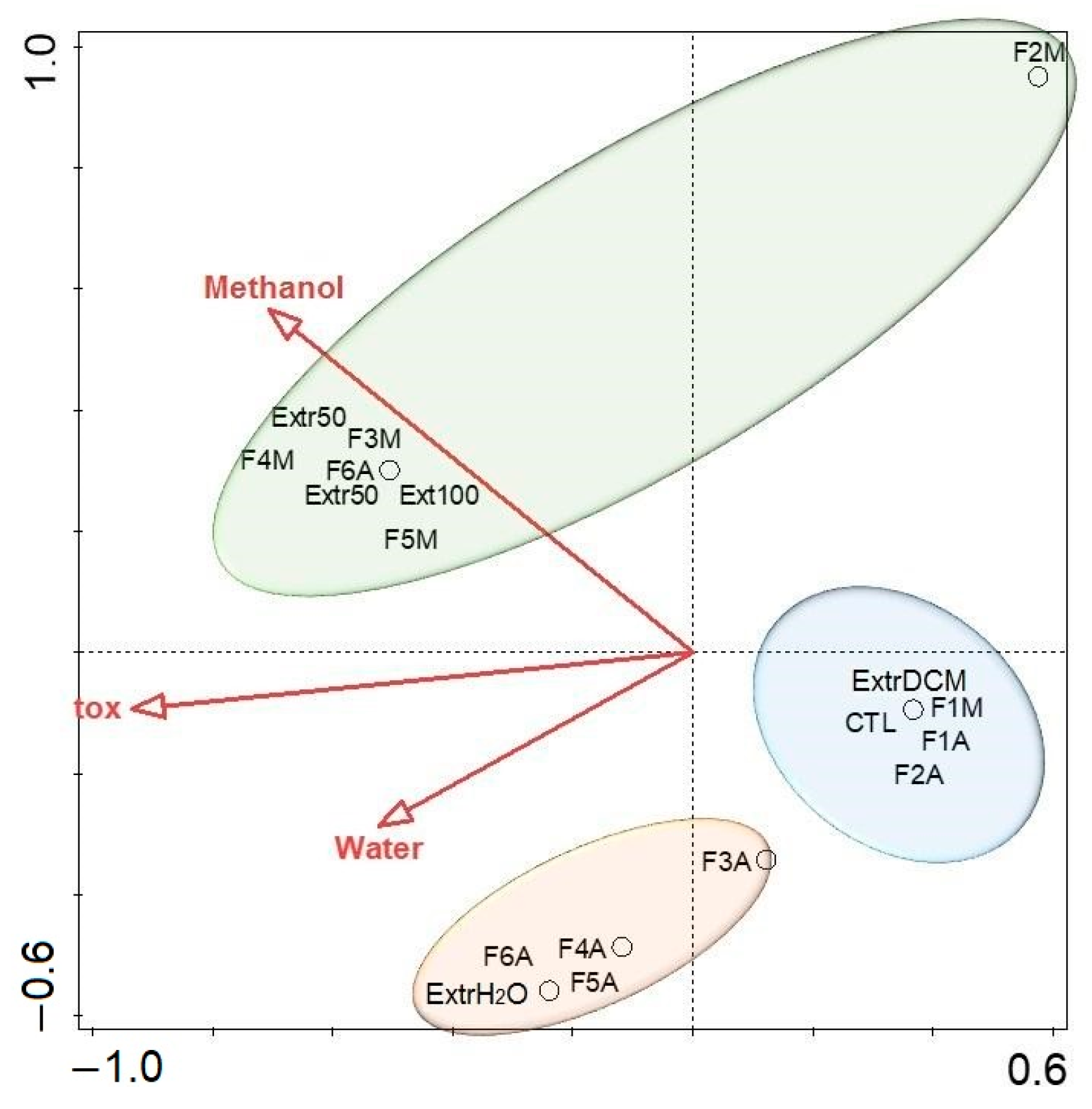
2.3. Fraction Toxicity and Chemical Polarity
2.4. Metabolomic Analysis
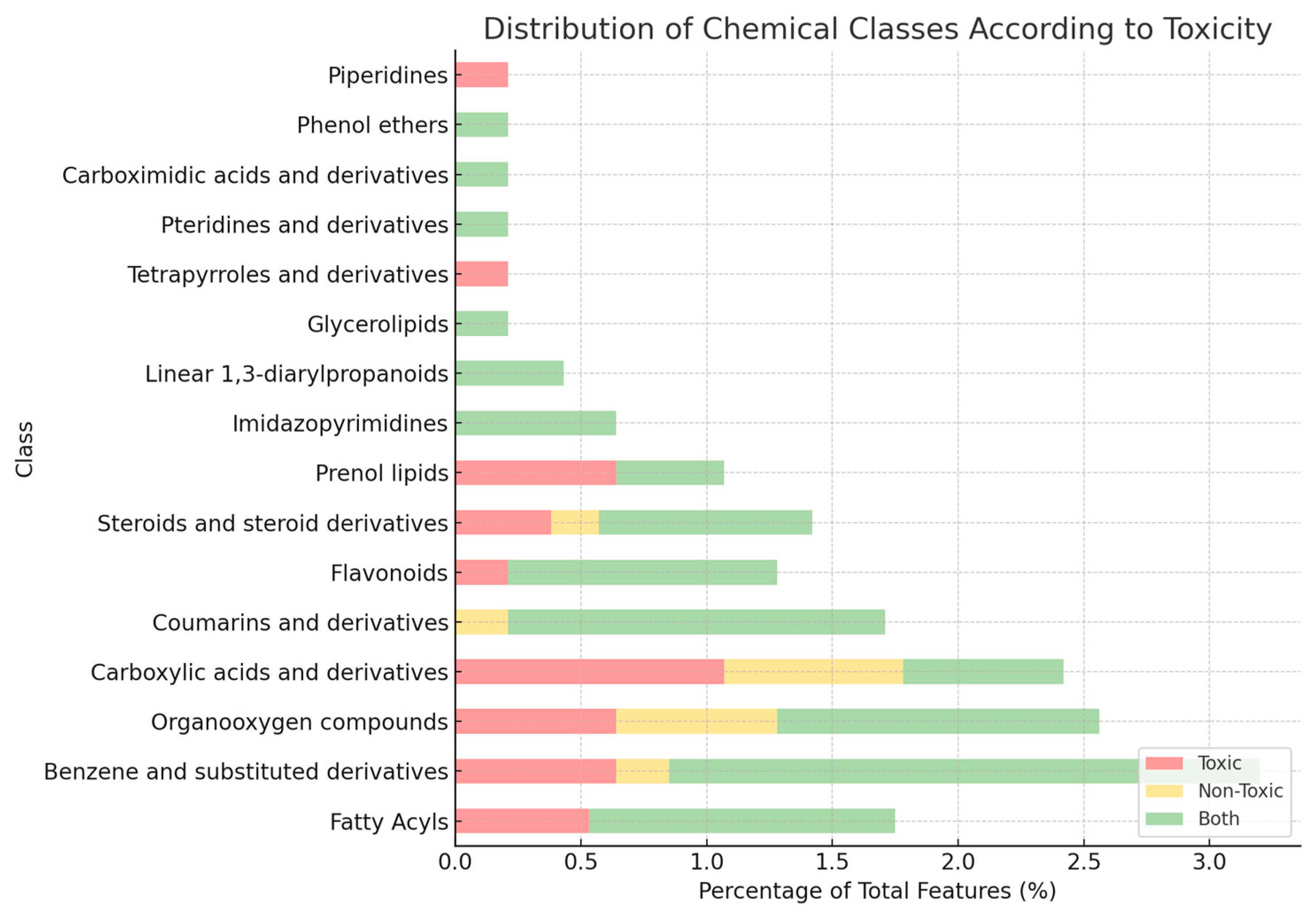
2.4.1. Molecular Networking and Class-Level Diversity
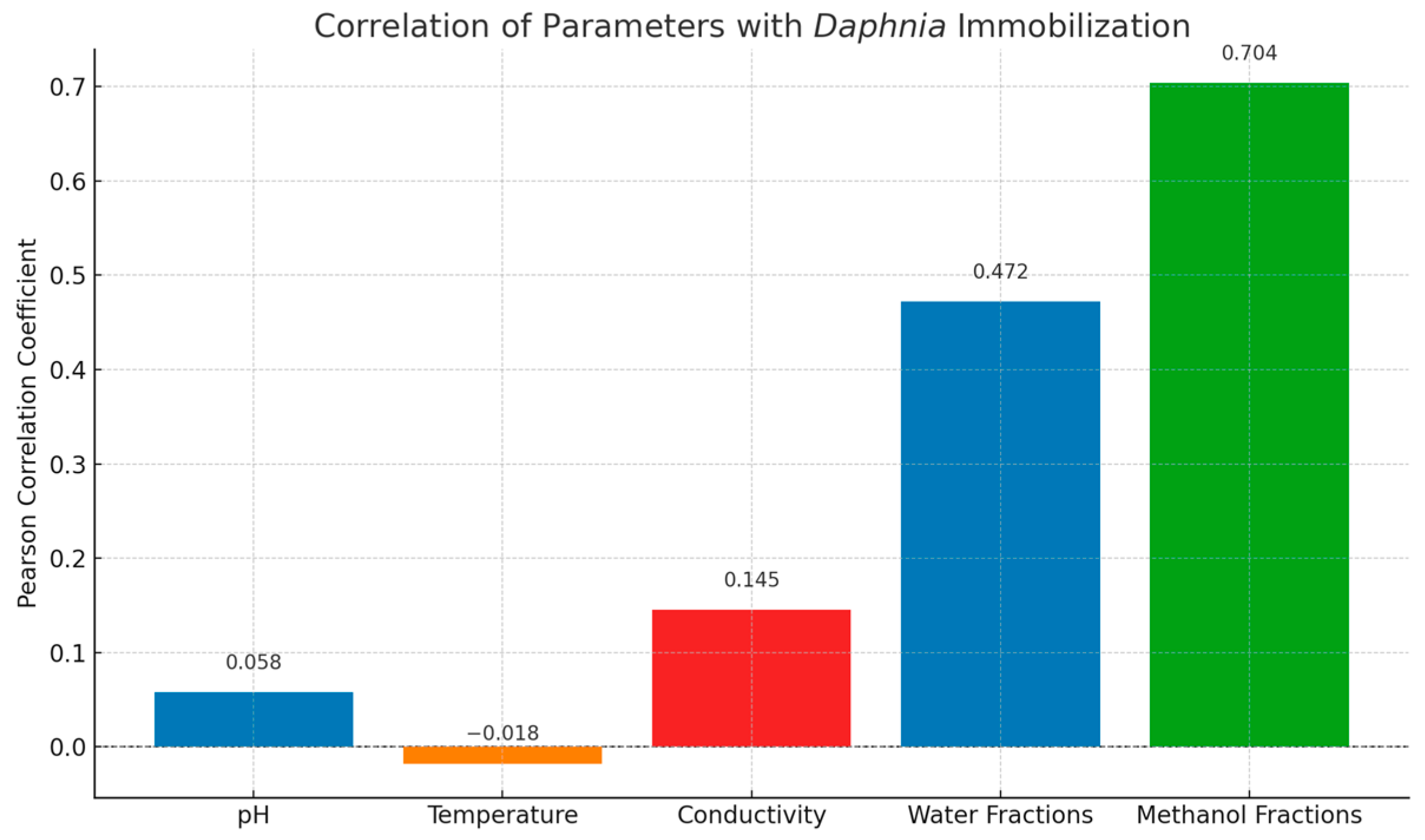
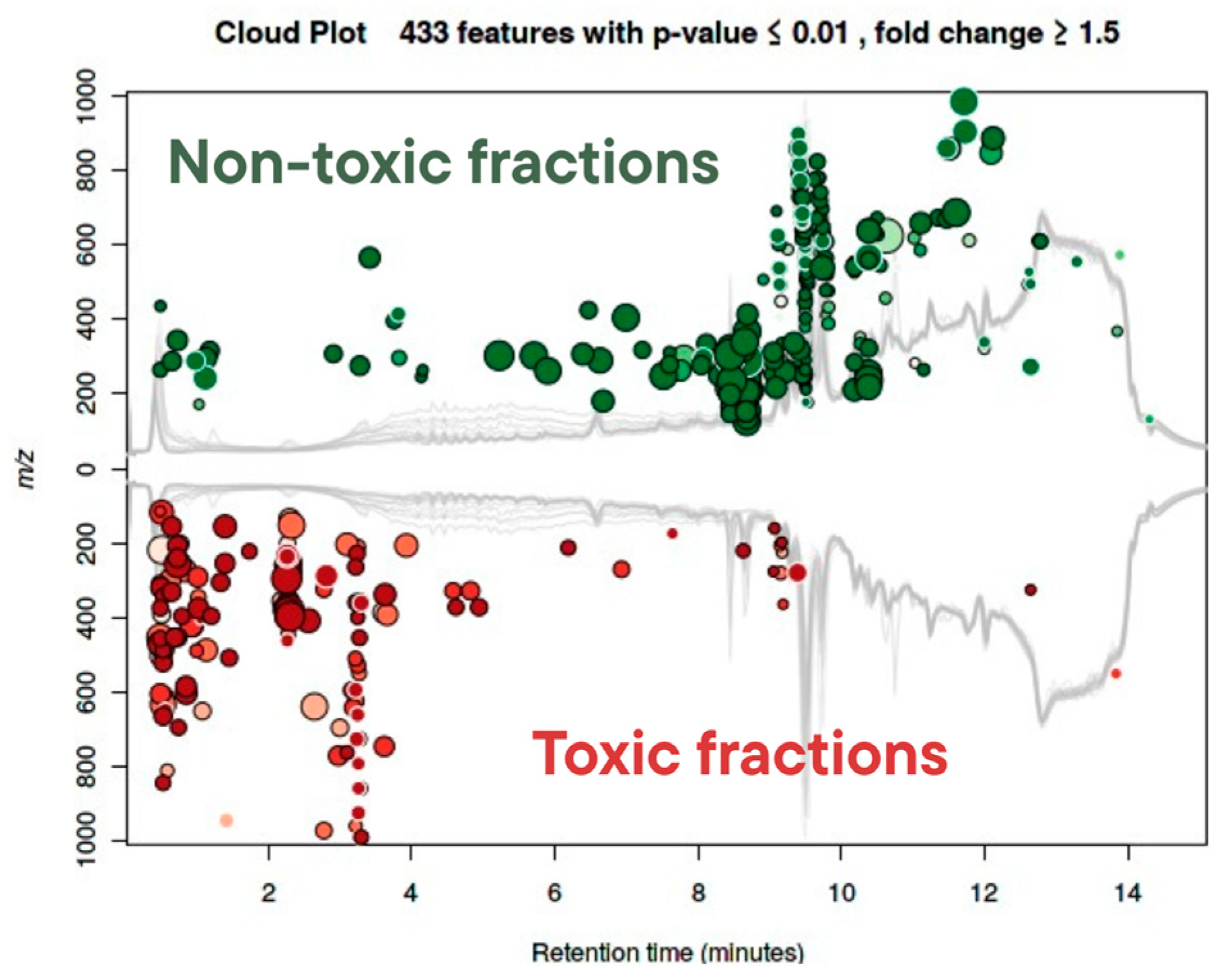
2.4.2. Toxicity-Driven Feature Distribution
2.4.3. Putative Metabolite Annotations and Diagnostic Fragmentation Patterns
2.4.4. Environmental Implications and Chemical Risk
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Microcystis aeruginosa (CCIBt 3106 Strain) Cultivation
4.2. Cell Counting
4.3. Extraction of Cyanobacteria Secondary Metabolites
4.4. Fractioning of the Toxic Extracts
4.5. Acute Toxicity Test with Daphnia similis (Crustacea: Cladocera)
4.6. Acute Toxicity Test with Parhyale hawaiensis (Crustacea: Amphipoda)
4.7. Cytotoxicity Test with Artemia salina (Crustacea: Anostraca)
4.8. Toxicity Statistical Analysis
4.9. LC-MS and Metabolomics Analysis
4.10. Metabolite Identification
4.10.1. Processing of Raw Data
4.10.2. Molecular Networking
4.10.3. Metabolite Annotation
4.11. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ASW | Artificial seawater |
| BOD | Biological oxygen demand |
| CCIBt | Algae, Cyanobacteria, and Fungi Culture Collection of the Botany Institute |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| DMSO | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| EC50/LC50 | Median effective/lethal concentration (50%) |
| EPA | Environmental Protection Agency |
| F1–F6 | Fraction numbers (0–100% IPA gradient) |
| GNPS | Global Natural Products Social Molecular Networking |
| HR-QTOF-MS/MS | High-resolution quadrupole time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometry |
| IPA | Isopropyl alcohol |
| LC-MS/MS | Liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry |
| MeOH | Methanol |
| MCs | Microcystins |
| NMR | Nuclear magnetic resonance |
| RDA | Redundancy analysis |
| RT | Retention time |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| TDI | Tolerable daily intake |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
References
- Kulasooriya, S. Cyanobacteria: Pioneers of Planet Earth. Ceylon J. Sci. Biol. Sci. 2012, 40, 71–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalf, J.S.; Lindsay, J.; Beattie, K.A.; Birmingham, S.; Saker, M.L.; Törökné, A.K.; Codd, G.A. Toxicity of cylindrospermopsin to the brine shrimp Artemia salina: Comparisons with protein synthesis inhibitors and microcystins. Toxicon 2002, 40, 1115–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, I.S.; Zimba, P.V. Cyanobacterial bioactive metabolites—A review of their chemistry and biology. Harmful Algae 2019, 83, 42–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, N.; Hu, C.; Dittmann, E.; Song, L.; Gan, N. The biological functions of microcystins. Water Res. 2024, 262, 122119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harshaw, K.; Fahim, A.; Zi, J.; Chandrasekera, P.C.; Chang, X.; Dixon, B.; MacIsaac, H.J. Non-microcystin extracellular metabolites of Microcystis aeruginosa impair viability and reproductive gene expression in rainbow trout cell lines. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 919, 170747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Z.; Chen, X.; Hu, J.; Chang, X.; Qian, Y. Adverse effects of Microcystis aeruginosa exudates on the filtration, digestion, and reproduction organs of benthic bivalve Corbicula fluminea. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 10934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Xu, J.; MacIsaac, H.J.; McKay, R.M.; Xu, R.; Pei, Y.; Zi, Y.; Li, J.; Qian, Y.; Chang, X. Comparative metabolomic analysis of exudates of microcystin-producing and microcystin-free Microcystis aeruginosa strains. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1075621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacinavicius, F.R.; Geraldes, V.; Crnkovic, C.M.; Delbaje, E.; Fiore, M.F.; Pinto, E. Effect of ultraviolet radiation on the metabolomic profiles of potentially toxic Cyanobacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2021, 97, fiaa243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Chen, C.; Wang, B.; Xie, G.; Wang, B.; Li, X.; Wang, W. Metabolomic Analysis of Both Microcystin-Producing and Microcystin-Free Microcystis aeruginosa Strains in Response to Exogenous Microcystin Exposure. Water 2025, 17, 993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burja, A.M.; Banaigs, B.; Abou-mansour, E.; Burgess, J.G.; Wright, P.C. Marine Cyanobacteria—A prolific source of natural products. Tetrahedron 2001, 57, 9347–9377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, M.B.; Borges, R.M.; Sullivan, P.; Domingues, J.P.B.; da Silva, F.H.S.; Trindade, V.G.S.; Luo, S.; Orjala, J.; Crnkovic, C.M. Chemical diversity of Cyanobacterial natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2024, 42, 6–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrinho, S.; Connaris, H.; Mouncey, N.J.; Goss, R.J.M. Compendium of Metabolomic and Genomic Datasets for Cyanobacteria: Mined the Gap. Water Res. 2024, 256, 121492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, E.M.L. Cyanobacterial peptides beyond microcystins—A review on co-occurrence, toxicity, and challenges for risk assessment. Water Res. 2019, 151, 488–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zi, J.; Barker, J.; Zi, Y.; MacIsaac, H.J.; Zhou, Y.; Harshaw, K.; Chang, X. Assessment of estrogenic potential from exudates of microcystin-producing and non-microcystin-producing Microcystis by metabolomics, machine learning and E-screen assay. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 470, 134170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehjabin, J.J.; Wei, L.; Petitbois, J.G.; Umezawa, T.; Matsuda, F.; Vairappan, C.S.; Morikawa, M.; Okino, T. Biosurfactants from Marine Cyanobacteria Collected in Sabah, Malaysia. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 1925–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.; Garcia, M.; Costa-Rodrigues, J.; Costa, M.S.; Ribeiro, M.J.; Fernandes, M.H.; Barros, P.; Barreiro, A.; Vasconcelos, V.; Martins, R. Exploring bioactive properties of marine Cyanobacteria isolated from the Portuguese coast: High potential as a source of anticancer compounds. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 98–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sticher, O. Natural product isolation. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2008, 25, 517–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kühl, A.M.; Espíndola, E.L.G.; Mantovano, T.; Deosti, S.; Lansac-Tôha, F.A. Toxic tests show the sensitivity of the Daphnia similis (Crustacea, Cladocera) and Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata (Chlorophyceae) to commercial pesticides. An. Acad. Bras. Cienc. 2022, 94, e20201234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fidan, M.; Ayar, A. A toxicity study on Daphnia magna and Artemia salina: Are paper cups safe? Int. J. Sci. Lett. 2023, 5, 330–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.; de Aragão Umbuzeiro, G. Proposal of a chronic toxicity test using the tropical epibenthic amphipod Parhyale hawaiensis. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 194, 115375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USEPA. Recommended Human Health Recreational Ambient Water Quality Criteria or Swimming Advisories for Microcystins and Cylindrospermopsin; EPA 822-R-19-001; U.S. EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Hulot, F.D.; Carmignac, D.; Legendre, S.; Yéprémian, C.; Bernard, C. Effects of microcystin–producing and microcystin–free strains of Planktothrix agardhii on long–term population dynamics of Daphnia magna. Ann. Limnol. 2012, 48, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, H.I.; Jüttner, F. Inter-annual stability of oligopeptide patterns of Planktothrix rubescens blooms and mass mortality of Daphnia in Lake Hallwilersee. Limnologica 2008, 38, 350–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, S.M. Efeitos de Saxitoxinas Produzidas por Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii e de Outras Cianotoxinas Sobre Cladóceros (Branchiopoda); Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Abreu, F.Q.; da Ferrão-Filho, A.S. Effects of an Anatoxin-a(s)-Producing Strain of Anabaena spiroides (Cyanobacteria) on the Survivorship and Somatic Growth of Two Daphnia similis Clones. J. Environ. Prot. 2013, 4, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smutná, M.; Babica, P.; Jarque, S.; Hilscherová, K.; Maršálek, B.; Haeba, M.; Bláha, L. Acute, chronic and reproductive toxicity of complex Cyanobacterial blooms in Daphnia magna and the role of microcystins. Toxicon 2014, 79, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schymanski, E.L.; Jeon, J.; Gulde, R.; Fenner, K.; Ruff, M.; Singer, H.P.; Hollender, J. Identifying small molecules via high resolution mass spectrometry: Communicating confidence. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 2097–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, S.; Torres, A.G.; Ribas de Pouplana, L. Inosine in biology and disease. Genes 2021, 12, 600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lifshits, M.; Kovalerchik, D.; Carmeli, S. Microcystbiopterins A-E, five O-methylated biopterin glycosides from two Microcystis spp. bloom biomasses. Phytochemistry 2016, 123, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welker, M.; Maršálek, B.; Šejnohová, L.; von Döhren, H. Detection and identification of oligopeptides in Microcystis (Cyanobacteria) colonies: Toward an understanding of metabolic diversity. Peptides 2006, 27, 2090–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teramoto, K.K.; Dorr, F.; Sanz, M.; Pinto, E. Microginins screening in Cyanobacteria by LC-MS. Quim. Nova 2020, 43, 1385–1392. [Google Scholar]
- Strangman, W.K.; Wright, J.L.C. Microginins 680, 646, and 612—New chlorinated Ahoa-containing peptides from a strain of cultured Microcystis aeruginosa. Tetrahedron Lett. 2016, 57, 1801–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcdonald, K.; Desrochers, N.; Renaud, J.B.; Sumarah, M.W.; Mcmullin, D.R. Metabolomics Reveals Strain-Specific Cyanopeptide Profiles. Toxins 2023, 15, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirenko, L.A. Physiological Fundamentals of Reproduction of the Blue-Green Algae in Reservoirs; Naukova Dumka: Kiev, Ukraine, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, M.; Huang, Z.; Fang, J.; Wang, Z. Diversity, Biosynthesis and Bioactivity of Aeruginosins, a Family of Cyanobacteria-Derived Nonribosomal Linear Tetrapeptides. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacinavicius, F.R.; Pacheco, A.B.F.; Chow, F.; Verissimo da Costa, G.C.; Kalume, D.E.; Rigonato, J.; Schmidt, E.C.; Sant’Anna, C.L. Different ecophysiological and structural strategies of toxic and non-toxic Microcystis aeruginosa (Cyanobacteria) strains assessed under culture conditions. Algal Res. 2019, 41, 101548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.; Qiao, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, L. Flavonoids: Promising anticancer agents. Med. Res. Rev. 2003, 23, 519–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spector, A.A.; Yorek, M.A. Membrane lipid composition and cellular function. J. Lipid Res. 1985, 26, 1015–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality, 4th ed.; World Health Organization (WHO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Gorham, P.R.; McLachlan, J.; Hammer, U.T.; Kim, W.K. Isolation and culture of toxic strains of Anabaena flos-aquae (Lyngb.) de Bréb. SIL Proc. 1922-2010 1964, 15, 796–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biology Working Group. The Enumeration and Identification of Algae; Standing Committee of Analysts: Exeter, UK, 2024; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- McCloud, T.G. High throughput extraction of plant, marine and fungal specimens for preservation of biologically active molecules. Molecules 2010, 15, 4526–4563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Krunic, A.; Chlipala, G.E.; Orjala, J. Microseiramide from the freshwater cyanobacterium Microseira sp. UIC 10445. Phytochem. Lett. 2015, 13, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.S.; Sturdy, M.; Krunic, A.; Kim, H.; Shen, Q.; Swanson, S.M.; Orjala, J. Minutissamides E-L, antiproliferative cyclic lipodecapeptides from the cultured freshwater cyanobacterium cf. Anabaena sp. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2012, 20, 6134–6143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ABNT—Associação Brasileira de Normas Técnicas. Ecotoxicologia Aquática: Toxicidade Aguda—Método de Ensaio com Daphnia spp. (Crustacea, Cladocera); NBR 12713:2016; ABNT: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Artal, M.C.; dos Santos, A.; Henry, T.B.; de Aragão Umbuzeiro, G. Development of an acute toxicity test with the tropical marine amphipod Parhyale hawaiensis. Ecotoxicology 2018, 27, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz, M.; Andreote, A.P.D.; Fiore, M.F.; Dörr, F.A.; Pinto, E. Structural characterization of new peptide variants produced by Cyanobacteria from the Brazilian Atlantic Coastal Forest using liquid chromatography coupled to quadrupole time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometry. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 3892–3919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Carver, J.J.; Phelan, V.V.; Sanchez, L.M.; Garg, N.; Peng, Y.; Nguyen, D.D.; Watrous, J.; Kapono, C.A.; Luzzatto-Knaan, T.; et al. Sharing and community curation of mass spectrometry data with Global Natural Products Social Molecular Networking. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 828–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A Software Environment for Integrated Models. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, M.R.; Pinto, E.; Torres, M.A.; Dörr, F.; Mazur-Marzec, H.; Szubert, K.; Tartaglione, L.; Dell’Aversano, C.; Miles, C.O.; Beach, D.G.; et al. CyanoMetDB, a comprehensive public database of secondary metabolites from cyanobacteria. Water Res. 2020, 196, 117017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dührkop, K.; Fleischauer, M.; Ludwig, M.; Aksenov, A.A.; Melnik, A.V.; Meusel, M.; Dorrestein, P.C.; Rousu, J.; Böcker, S. SIRIUS 4: A rapid tool for turning tandem mass spectra into metabolite structure information. Nat. Methods 2019, 16, 299–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Extracts | Artemia salina | Daphnia similis | Parhyale hawaiensis |
|---|---|---|---|
| EC50/LC50 (95% CI) (µg mL−1) | |||
| Aqueous extract | >1000 | 740 (490–790) | 800 (770–850) |
| MeOH 50% extract | >1000 | 940 (540–1380) | 660 (610–720) |
| MeOH 100% extract | >1000 | >1000 | 600 (490–880) |
| DCM: MeOH 1:1 extract | >1000 | >1000 | >1000 |
| Samples | Mean m/z [M + H]+ (Measured) | Mean RT (min) | Putative Formula | Putative Compound | m/z Error (ppm) | Annotation Level * | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All extracts and fractions | 269.0889 | 1.48 | C10H12N4O5 | Inosine | 1.152037 | 2a | Srinivasan et al. [28]. |
| MeOH 100%, MeOH 50%, DCM:MeOH 1:1, F1–F4 (H2O and MeOH) | 414.1622 | 3.1 | C16H23N5O8 | Microcystbiopterin B or E | −0.700208 | 2b | Lifshits et al. [29]. |
| All extracts and fractions | 591.3587 | 5.02 | C31H50N4O5S | New microginin? | 1.149896 | 2b | Welker et al. [30]. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Almeida, É.C.; Jacinavicius, F.R.; Médice, R.V.; Menezes, R.B.; Passos, L.S.; Anderson, D.; Yoon, J.; Faria, E.D.; Crnkovic, C.M.; Fonseca, A.L.; et al. Unraveling the Toxicity of a Non-Microcystin-Producing Strain (CCIBt3106) of Microcystis aeruginosa: Ecotoxicological Effects on Aquatic Invertebrates. Toxins 2025, 17, 321. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17070321
Almeida ÉC, Jacinavicius FR, Médice RV, Menezes RB, Passos LS, Anderson D, Yoon J, Faria ED, Crnkovic CM, Fonseca AL, et al. Unraveling the Toxicity of a Non-Microcystin-Producing Strain (CCIBt3106) of Microcystis aeruginosa: Ecotoxicological Effects on Aquatic Invertebrates. Toxins. 2025; 17(7):321. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17070321
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlmeida, Éryka Costa, Fernanda Rios Jacinavicius, Rhuana Valdetário Médice, Rafaella Bizo Menezes, Larissa Souza Passos, Dominique Anderson, Jaewon Yoon, Elaine Dias Faria, Camila Manoel Crnkovic, Ana Lúcia Fonseca, and et al. 2025. "Unraveling the Toxicity of a Non-Microcystin-Producing Strain (CCIBt3106) of Microcystis aeruginosa: Ecotoxicological Effects on Aquatic Invertebrates" Toxins 17, no. 7: 321. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17070321
APA StyleAlmeida, É. C., Jacinavicius, F. R., Médice, R. V., Menezes, R. B., Passos, L. S., Anderson, D., Yoon, J., Faria, E. D., Crnkovic, C. M., Fonseca, A. L., Henry, T., & Pinto, E. (2025). Unraveling the Toxicity of a Non-Microcystin-Producing Strain (CCIBt3106) of Microcystis aeruginosa: Ecotoxicological Effects on Aquatic Invertebrates. Toxins, 17(7), 321. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17070321







