Abstract
Within Neotropical pit-vipers, the Mexican/Central-American clade consisting of Atropoides, Cerrophidion, Metlapilcoatlus, and Porthidium is a wide-ranging, morphologically and ecologically diverse group of snakes. Despite their prevalence, little is known of the functional aspects of their venoms. This study aimed to fill the knowledge gap regarding coagulotoxic effects and to examine the potential of different therapeutic approaches. As a general trait, the venoms were shown to be anticoagulant but were underpinned by diverse biochemical actions. Pseudo-procoagulant activity (i.e., thrombin-like), characterized by the direct cleavage of fibrinogen to form weak fibrin clots, was evident for Atropoides picadoi, Cerrophidion tzotzilorum, Metlapilcoatlus mexicanus, M. nummifer, M. occiduus, M. olmec, and Porthidium porrasi. In contrast, other venoms cleaved fibrinogen in a destructive (non-clotting) manner, with C. godmani and C. wilsoni being the most potent. In addition to actions on fibrinogen, clotting enzymes were also inhibited. FXa was only weakly inhibited by most species, but Cerrophidion godmani and C. wilsoni were extremely strong in their inhibitory action. Other clotting enzymes were more widely inhibited by diverse species spanning the full taxonomical range, but in each case, there were species that had these traits notably amplified relatively to the others. C. godmani and C. wilsoni were the most potent amongst those that inhibited the formation of the prothrombinase complex and were also amongst the most potent inhibitors of Factor XIa. While most species displayed only low levels of thrombin inhibition, Porthidium dunni potently inhibited this clotting factor. The regional polyvalent antivenom produced by Instituto Picado Clodomiro was tested and was shown to be effective against the diverse anticoagulant pathophysiological effects. In contrast to the anticoagulant activities of the other species, Porthidium volcanicum was uniquely procoagulant through the activation of Factor VII and Factor XII. This viperid species is the first snake outside of the Oxyuranus/Pseudonaja elapid snake clade to be shown to activate FVII and the first snake venom of any kind to activate FXII. Interestingly, while small-molecule metalloprotease inhibitors prinomastat and marimastat demonstrated the ability to prevent the procoagulant toxicity of P. volcanicum, neither ICP antivenom nor inhibitor DMPS showed this effect. The extreme variation among the snakes here studied underscores how venom is a dynamic trait and how this can shape clinical outcomes and influence evolving treatment strategies.
Key Contribution:
We report the extremely dynamic diversification of coagulotoxicity within this clade of medically important pit-vipers, including Porthidium volcanicum, which uniquely activated coagulation factors VII and XII.
1. Introduction
Snakebite envenomation remains a globally significant issue that continues to be neglected. In Central America, an estimated 5500 venomous snakebites occur each year [1], while 4000 venomous bites are reported in Mexico [2]. However, this is likely a vast underestimation due to data deficiencies, with many rural populations typically not receiving treatment or recording snakebites [3]. The lack of treatment leads to severe local effects and potentially permanent sequalae as a result of envenomation [4,5]. Regardless of data gaps, the existing statistics indicate that in the Americas, pit-vipers are responsible for the vast majority of snakebites [3,5].
Within Neotropical pit-vipers, a clade consists of the morphologically and ecologically distinct genera Atropoides, Cerrophidion, Metlapilcoatlus, and Porthidium. These snakes are found from eastern, southeastern, and southwestern Mexico to western Panama, with only Porthidium extending into northern South America [6]. Atropoides and Metlapilcoatlus, jumping pit-vipers, are heavy-bodied species that occur in tropical and subtropical habitats [6,7]. The montane pit-viper Cerrophidion species are moderately stout, high-altitude specialists, being found between 1300 and 3500 m in elevation [8]. Porthidium species live in low–middle-elevation forests and are typically much more slender than Atropoides, Cerrophidion, and Metlapilcoatlus species [9].
Due to the cryptic nature of these species, very little is known about their natural history, including diet and the functional aspects of their venom. Much of what is known of the venom consists of proteomics investigations, which have revealed that venom composition between species is relatively similar and is typically dominated by metalloproteinases (SVMP), kallikrein-type serine proteases (SVSP), and phospholipases A2 (PLA2s) [10,11,12,13,14,15,16]. However, as these toxin types are multifunctional, such proteomic venom-composition studies do not shed light upon venom activity. Prior work has demonstrated an overall anticoagulant effect for Cerrophidion sasai (formerly considered a Costa Rican population of Cerrophidion godmani before being elevated to full species status), Porthidium nasutum, and Porthidium ophryomegas [13,17]. Nevertheless, these studies have not elucidated the biochemical mechanisms leading to the net anticoagulant state. Similarly, work showing that Metlapilcoatlus venom has a clotting action on plasma does not distinguish between true procoagulant activity (characterized by the activation of endogenous clotting factors leading to well-ordered fibrin clot) and pseudo-procoagulant/”thrombin-like” activity (direct action on fibrin leading to weak, transient fibrin clots) [16,18]. Consequently, the lack of research regarding the functional effects of venom not only limits the evolutionary understanding of the selection pressures acting on these species but also presents a significant knowledge gap in the effective clinical management of snakebite.
As a result of their wide distribution and proximity with humans in forests and agricultural lands, these species are likely to cause a considerable number of bites in the regions in which they occur. For example, Porthidium lansbergii alone is thought to contribute to 20% of snakebites in Colombia [11]. Indeed, Gutiérrez [1] has long emphasized a critical need to characterize the functional aspects of Atropoides, Cerrophidion, Metlapilcoatlus, and Porthidium venoms in order to understand species-specific clinical manifestations of snakebite-envenoming syndromes, which may vary drastically despite the proteomic similarity of the venoms. In addition, bites from coagulotoxic snakes within these regions are typically diagnosed as “bothropic envenomation” [1,19]. This may underestimate the true number of snakebites these species are responsible for due to the misidentification of the offending snakes. Therefore, there is a significant gap regarding the specific venom effects of medically relevant snakes in this clade, including how well the regional antivenoms work against their venoms. In addition, as Bothrops species are unique amongst American pit-vipers as having potent procoagulant toxicity (Factor X activation and prothrombin activation [20]), using “bothropic envenomation” as a catch-all term may obscure extreme coagulotoxicity variations in venom action in non-Bothrops viperid species while obscuring the impact of non-Bothrops species.
Pit-viper-snakebite treatment in Central America typically involves the use of a polyvalent equine antivenom, PoliVal-ICP, made by Instituo Clodomiro Picado in Costa Rica. This antivenom is produced using an immunizing mixture based on equal amounts of venoms of Bothrops asper (Caribbean and Pacific populations), Crotalus simus, and Lachesis stenophrys [21,22]. Testing venoms that are not included in the immunizing mixture reveals the cross-reactivity of the ICP antivenom. Due to the high diversity of species within the region, the degree of cross-reactivity can indicate the efficacy of the antivenom as a successful treatment between species, which is particularly important when the offending snake has not been identified beyond being a viperid species. While limited in scope, prior research into cross-reactivity has yielded positive results, showing strong ability to neutralize venom effects of Central American species A. picadoi, C. sasai, M. mexicanus, P. nasutum, and P. ophryomegas [17,18,22,23], while reports in Mexico have indicated that the two Mexican antivenoms are not effective in neutralizing the lethality of the juvenile and adult venoms of M. nummifer (>24.6 and 33.3 mgAV/mgV) [16].
This study comprised two main aims. The first aim was to characterize the functional effects of Atropoides, Cerrophidion, Metlapilcoatlus, and Porthidium venoms upon the human coagulation cascade. It was hypothesized that such a diverse clade of snakes would incur a variety of venom effects. Secondly, we wanted to test the efficacy of the regionally widely used PoliVal-ICP antivenom against medically significant species, as none of the studied species are included in the antivenom immunizing mixture. The results of this study comprise the most complete assessment of the functional activity of Atropoides, Cerrophidion, Metlapilcoatlus, and Porthidium venoms to date.
2. Results
Initial tests on human plasma revealed that accelerated clotting was evident for Atropoides picadoi, Cerrophidion tzotzilorum, Metlapilcoatlus mexicanus, M. nummifer, M. occiduus, M. olmec, Porthidium porrasi, and P. volcanicum. As simple clotting tests cannot distinguish between clotting due to factor-activation that produces strong, well-ordered fibrin clots (true procoagulant toxicity) or to the direct “thrombin-like” cleavage of fibrinogen to produce weak, aberrant fibrin clots (pseudo-procoagulant toxicity), additional tests were run for the ability to directly clot fibrinogen. All these species except for P. volcanicum were able to directly clot fibrinogen (Figure 1).
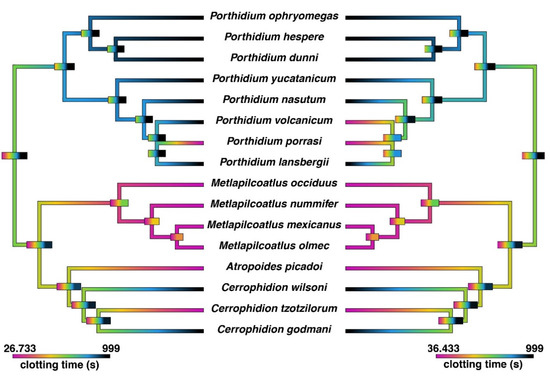
Figure 1.
Ancestral state reconstruction of coagulotoxic venom effects on human fibrinogen (left) and plasma (right). The spontaneous clotting time of human plasma was 358.9 s. Cooler colors represent the inhibition of clotting in plasma (anticoagulant effect) and no clotting of fibrinogen. Warmer colors represent clotting in plasma and fibrinogen. The maximum machine reading time was 999 s. Bars represent 95% confidence intervals for the estimate at each node. The phylogeny used is based upon Alencar et al. [24] and timetree.org. The correlations between fibrinogen clotting and plasma clotting were congruent with direct action upon fibrinogen rather than the activation of clotting factors. However, for P. volcanicum, only plasma was clotted, with no direct action upon fibrinogen, which was suggestive of the activation of one or more clotting factors.
Subsequent thromboelastographic studies provided a distinction between pseudo-procoagulant (weak clots formed by the direct “thrombin-like” action on fibrinogen) and true procoagulant (strong clots formed by the activation of clotting-factor zymogens upstream of fibrinogen) venom activities. Weak clots were confirmed for Atropoides picadoi, Cerrophidion tzotzilorum, Metlapilcoatlus mexicanus, M. nummifer, M. occiduus, M. olmec, and Porthidium porrasi (Figure 2), revealing that these venoms clotted via the pseudo-procoagulant (‘thrombin-like’) pathway. In contrast, strong clots were observed in P. volcanicum, suggestive of a true procoagulant activity.
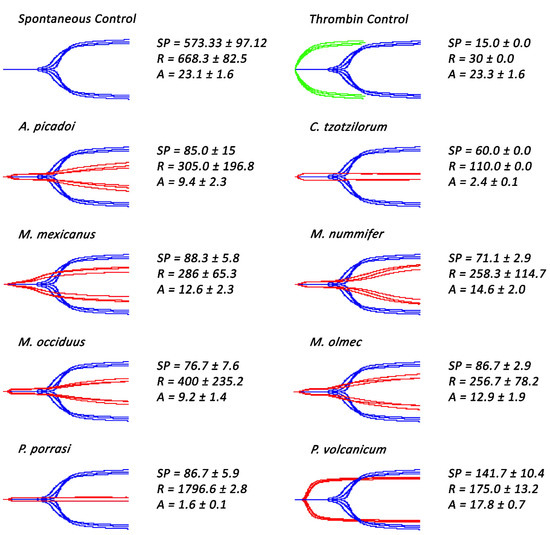
Figure 2.
Thromboelastography traces showing Atropoides/Cerrophidion/Metlapilcoatlus venoms ability to clot human plasma in comparison to the spontaneous control. Samples showed to possess pseudo-procoagulant (Atropoides/Cerrophidion/Metlapilcoatlus) and procoagulant (P. volcanicum) venoms. Blue traces represent spontaneous controls, green traces represent thrombin control, and red traces represent samples incubated with venoms. SP = split point, which is the time taken until the clot began to form (min). R = time to initial clot formation, where formation is 2 mm + (min). A (amplitude) = clot strength (mm). Assays were performed in triplicate (n = 3) with data representing the mean ± SD.
As P. volcanicum was unique in possessing a true procoagulant venom, additional testing was performed to deduce the mechanism responsible for the observed activity. Testing confirmed that P. volcanicum did in fact induce clotting in plasma through factor activation. Indeed, four zymogens were activated, with the differential potency of FVII > FXII >> FXI > FX (Figure 3).
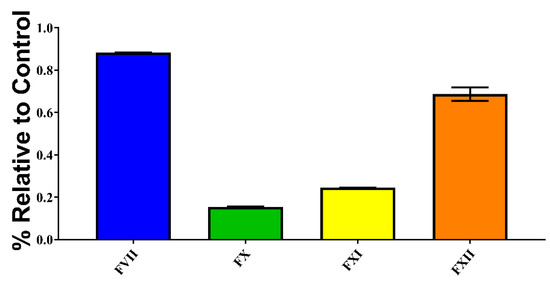
Figure 3.
Factor activation assay showing P. volcanicum’s procoagulant ability to activate FVII, FX, FXI, and FXII. Activation is shown as the relative percentage of zymogen converted to its active form compared with the active-zymogen positive control. Assays were performed in triplicate (n = 3) with data representing the mean ± SD.
Anticoagulant venoms were tested for inhibitory action upon several clotting factors (Figure 4). While C. godmani and C. wilsoni were the most potent in inhibiting FIXa, FXa, FXIa, and the prothrombinase complex, other species also showed significant inhibition of these clotting enzymes, including, P. dunni, P. nasutum, P. ophryomegas, P. porrasi, and P. yucatanicum (Figure 4). In contrast, only P. dunni showed evidence of strong thrombin inhibition (Figure 4). All anticoagulant venoms tested also showed fibrinogenolytic activity, cleaving the fibrinogen molecule in a destructive (non-clotting) manner and preventing clotting despite the addition of thrombin (Figure 5).
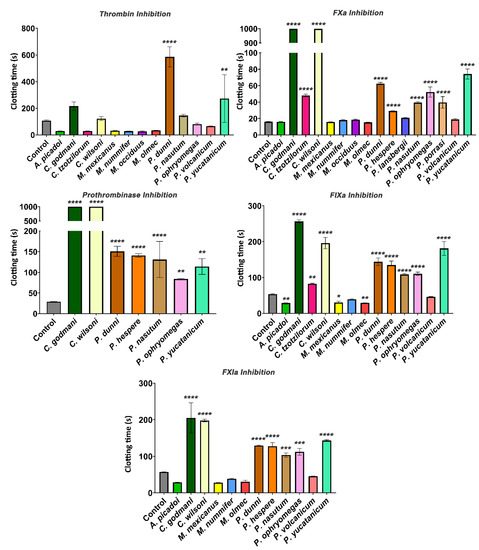
Figure 4.
Coagulation-cascade-factor-inhibition assays showing the inhibitory effects of Cerrophidion godmani, C. wilsoni, P. dunni, P. nasutum, P. ophryomegas, and P. yucatanicum on thrombin, FXa, prothrombinase, FIXa, and FXIa. Venoms that induced clotting could not be used for the prothrombinase inhibition assay as plasma was clotted before machine recording. Assays with venoms missing were due to a lack of stock, and such venoms were unable to be tested. Assays were performed in triplicate (n = 3) with data representing the mean ± SD. Values were statistically analyzed using one-way ANOVAs with a multiple-comparison tests compared with the negative control. Statistical significance from the negative control is indicated by * p < 0.1, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, or **** p < 0.0001.

Figure 5.
Thromboelastography traces showing effects of two Cerrophidion and seven Porthidium species venoms that did not directly clot fibrinogen. A solution of fibrinogen was incubated for 30 min either alone (for the thrombin control) or with venoms, followed by the addition of thrombin. The green trace represents the 30 min fibrinogen incubation for all samples. Blue traces represent samples in which thrombin was added to fibrinogen in the absence of venom. Red traces represent samples in which venoms were incubated with a fibrinogen solution for 30 min, followed by the addition of thrombin. SP = Split point, i.e., the time taken until a clot began to form (min). R = time to initial clot formation, where formation is 2 mm + (min). A (amplitude) = clot strength (mm). Assays were performed in triplicate (n = 3) with data representing the mean ± SD.
Assays investigating the efficacy of the ICP antivenom demonstrated a significant ability to neutralize the fibrinogen-clotting pseudo-procoagulant activity and the enzyme-inhibiting anticoagulant effects of venom (Figure 6 and Figure 7). However, the ICP antivenom showed poor cross-reactivity towards the procoagulant activity of P. volcanicum venom (Figure 8). In contrast, metalloprotease inhibitors prinomastat and marimastat were effective in neutralizing P. volcanicum-venom activity, while SVMP inhibitor 2,3-dimercapto-1-propanesulfonic acid (DMPS) performed poorly by comparison (Figure 8).
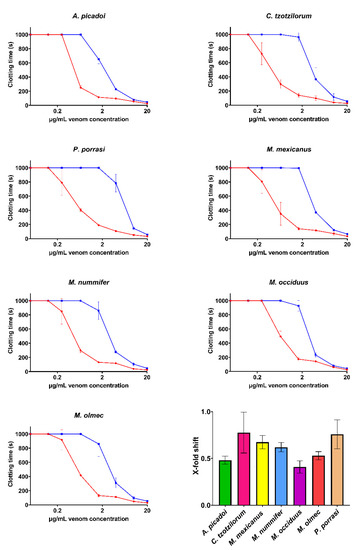
Figure 6.
Concentration–response curves showing the pseudo-procoagulant effects and the relative efficacy of the PoliVal-ICP antivenom. Curves represent the clotting time of both the venom-only assay (red) and the incubation-with-antivenom assay (blue). The bar graph represents the X-fold shift value of each venom when incubated with antivenom. Calculated values represent antivenom neutralization, where 0 is no neutralization and >0 indicates neutralization. Assays were performed in triplicate (n = 3), excluding P. porrasi, which was in duplicate (n = 2) due to a shortage of venom supply. Data represent the mean ± SD. Note: some data points have error bars that are smaller than the size of the symbol.
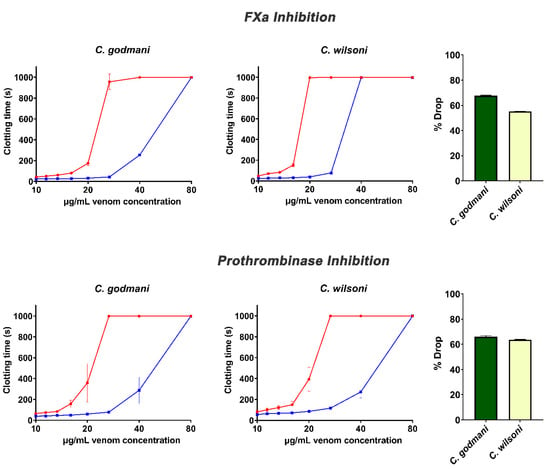
Figure 7.
Concentration–response curves showing the anticoagulant effects of two Cerrophidion venoms and the relative efficacy of the PoliVal-ICP antivenom in neutralizing FXa-inhibition and the inhibition of the prothrombinase complex. Curves represent the venom-only assay (red) and the incubation-with-antivenom assay (blue). Bar graphs indicate the percentage drop-in venom activity of venom incubated with antivenom relative to the assay of venom incubated without antivenom. Assays were performed in triplicate (n = 3) with data representing the mean ± SD. Note: some data points have error bars that are smaller than the size of the symbol.
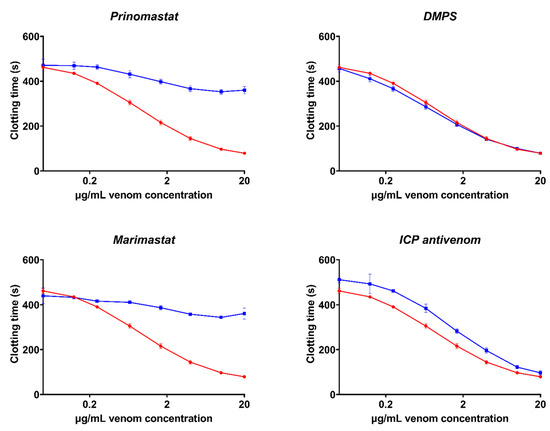
Figure 8.
Concentration–response curves showing the procoagulant effect of P. volcanicum venom on plasma and the relative efficacy of three SVMP inhibitors and the PoliVal-ICP antivenom in neutralizing the venom effects. Curves represent the venom-only assay (red) and the incubation-with-inhibitor/antivenom assay (blue). Assays were performed in triplicate (n = 3) with data representing the mean ± SD. Note: some data points have error bars that are smaller than the size of the symbol.
3. Discussion
This study assessed the coagulotoxic effects of sixteen venoms spanning the full ecological, geographical, and taxonomical diversity of the Atropoides/Cerrophidion/Metlapilcoatlus/Porthidiium clade, thereby representing the most complete study to date of venom functional activity within this group of snakes. Many of the species included were shown to possess the ability to directly clot fibrinogen, indicating that their venoms act in a pseudo-procoagulant (‘thrombin-like’) manner (Figure 1). This is a common aspect of pit-viper venom that has been described in many species, whereby the venom cleaves fibrinogen to form weak fibrin clots that are easily broken down, resulting in a net anticoagulant effect [25,26,27,28,29]. Further thromboelastographic testing confirmed this pseudo-procoagulant activity, revealing that the venoms that clotted fibrinogen produced weak clots in human plasma (Figure 2).
The results indicate that the most parsimonious explanation is that the pseudo-procoagulant-venom activity is basal to the Atropoides/Cerrophidion/Metlapilcoatlus clade, with classic anticoagulant activity arising as a secondary evolution on two separate occasions (C. godmani and C. wilsoni) (Figure 1). In contrast, classic anticoagulant activity is basal to the Porthidium genus, with P. porrasi secondarily evolving pseudo-procoagulant-venom activity and P. volcanicum secondarily evolving true procoagulant activity. However, the basal condition of the Atropoides/Cerrophidion/Metlapilcoatlus/Porthidiium clade as a whole remains uncertain and may be either classically anticoagulant or pseudo-procoagulant. Morphologically the basal trait is a slender/moderately built “Porthidium-like” snake, while conversely the extremely robust morphology (epitomized in Metlapilcoatlus nummifer) is a derived trait. If venom condition parallels morphology, this suggests that the basal venom condition is “Porthidium-like” classic anticoagulant venom (destructive cleavage of fibrinogen and inhibition of activated clotting factors). This indicates that the pseudo-procoagulant (‘thrombin-like’) direct actions on fibrinogen is a derived trait within this clade. Investigating the selection pressures leading to these changes in venom phenotype is a rich area for future research.
The unique procoagulant toxicity of P. volcanicum is also a derived state relative to the basal anticoagulant activity. The activity of P. volcanicum, whereby it clotted plasma but not fibrinogen, revealed that this venom activated a clotting factor, a trait which is unique within this clade. We report that the activation of both FVII and FXII is largely responsible for the procoagulant activity observed, with FX and FIX activation contributing but to a lesser degree (Figure 3). While Factor X activation is known for Bothrops venoms [20], it is only known amongst non-Bothrops American pit-viper species from neonate Crotalus culminatus as an ontogenetic trait [28]. The FX activation in C. culminatus thus represents a convergent evolution relative to Bothrops venom. Therefore, FX activation in P. volcanicum represents a third independent evolution of this trait within American pit-vipers. Underscoring the usefulness of this trait in prey capture, FX activation has evolved convergently in diverse Afro-Asian snake lineages such as the Daboia/Macrovipera/Montivipera viperid clade, viperid species Bitis worthingtoni, viperid genus Cerastes, viperid genus Echis, lamprophiid genus Atractaspis, and colubrid genus Rhabdophis [30,31,32,33,34,35,36]. In contrast to FX activation being previously widely known as a convergent trait, Factor VII activation by snake venom has only previously been known for the Australian elapid clade of Oxyuranus + Pseudonaja [37]. As the Australian elapids activate FVII through weaponized form of Factor Xa unique to Australian elapid snake venoms, the ability of P. volcanicum to activate FVII thus represents a convergent evolution of this novel trait. In contrast, no snake venom has previously been described as being able to activate Factor XI or Factor XII, thereby underscoring the evolutionary novelty of P. volcanicum venom.
The activation of clotting factors is well documented among a wide range of viperid snakes and has been shown to be predominantly driven by the SVMP toxin class [20,28,34]. SVMPs have been shown to represent a large proportion of P. volcanicum venom composition [15]. We demonstrated that the clotting ability of P. volcanicum was indeed driven by SVMPs through the effective neutralization of venom activity by SVMP inhibitors prinomastat and marimastat. However, the metalloprotease inhibitor DMPS showed poor neutralization of the procoagulant-venom activity (Figure 8). It should be noted that the positive results for prinomastat and marimastat were from idealized (pre-incubation) in vitro conditions and need to be tested in a more dynamic system. Understanding their potential in a clinical setting requires in vivo corroboration. Conversely, the poor response of DMPS under such idealized conditions is not likely to improve in a more dynamic in vivo assay system.
Our findings also demonstrated that the procoagulant-venom effects of P. volcanicum were not effectively neutralized by the ICP antivenom. As no similar venom is included within the immunizing mixture, it results in poor cross-neutralization of the complex factor activating the effects of P. volcanicum venom. While the ICP antivenom includes a procoagulant phenotype (Bothrops asper), it was unsurprising that the antivenom did not cross-react, as Bothrops antivenoms are well documented as having limited cross-reactivity even among Bothrops species [20,38]. Thus, it would have in fact been surprising if Bothrops antivenom cross-reacted with venom from a distantly related (>20 MYA) species that has independently evolved a novel procoagulant-venom phenotype. While the antivenom displayed slight efficacy in isolation against P. volcanicum, its use in combination with small-molecule inhibitors may improve the therapeutic potential. Indeed, several recent studies have shown the therapeutic synergy between small-molecule inhibitors and antivenom for a range of snake venoms [39,40].
As previously noted, Porthidium species, as well as C. godmani and C. wilsoni, were potently anticoagulant, and all of them exceeded the machine maximum recording time (Figure 1). Further factor inhibition assays revealed that C. godmani and C. wilsoni inhibited Factors IXa, Xa, and XIa, and prothrombinase, as did diverse Porthidium species (Figure 4). Only P. dunni was observed to inhibit thrombin, producing a significant delay in clotting time within the thrombin-inhibition assay (Figure 4). Future work is required to ascertain which toxin types are responsible for inhibiting the clotting factors, with characterized inhibitors of clotting enzymes in viperid-snake venoms such as kunitz peptides, the alpha–beta covalently-linked dimeric-form of lectin toxins, and Group II phospholipase A2 toxins [35,41,42,43].
Venom from C. godmani, C. wilsoni, and several Porthidium species were shown to cleave fibrinogen, contributing to the net anticoagulant effect by depleting the levels of normal, intact fibrinogen usable for fibrin-clot formation (Figure 5). While this is a well-characterized pathophysiological action of venom kallikrein-type serine proteases, the sites of action on fibrinogen are highly variable, with some isoforms being characterized as only cleaving the alpha or beta chain and others as cleaving both [26,27,29,44,45,46,47]. While previous research into the fibrinogenolytic activity of these species has shown A. picadoi, P. nasutum, and P. ophryomegas venoms to cleave the alpha chain of fibrinogen, leaving the beta and gamma chains unaffected, the alpha-chain cleavage sites have not been determined [48]. For the other species in this study, the specific fibrinogen chains (and sites cleaved within the chain) in which these venoms acted upon remains unknown. Thus, these species warrant further investigation to identify the fibrinogen chain(s) targeted by the venom, including the specific cleavage sites within a particular fibrinogen chain.
Due to the medical significance of bites from these species, the efficacy of the ICP polyvalent regional antivenom was tested on the pseudo-procoagulant (“thrombin-like”) venoms and the anticoagulant C. godmani and C. wilsoni. The results show the strong neutralization of the pseudo-procoagulant- and enzyme-inhibiting effects of the various venoms, further highlighted by the X-fold shift (Figure 6) and percentage drop (Figure 7). This indicated that the ICP antivenom had a high level of cross-reactivity for species across this diverse group of snakes, despite none of the genera having been used in the immunizing mixture. Our data support the growing body of knowledge surrounding the ICP antivenom’s ability to neutralize venoms from the diverse American pit-vipers [17,21,22]. The efficacy of the ICP polyvalent antivenom on the thrombin inhibiting activity of P. dunni was unable to be tested due to venom shortage, and as the pathophysiological target for the remaining Porthidium species is unknown, these venoms were not included in the antivenom assays.
In this study, the limited venom supplies restricted antivenom testing to only a single regional product. The ICP antivenom was chosen due to the very wide geographical range of this clade of snakes, which span from Mexico to Central America. The ICP polyvalent product is made with an immunizing mixture containing venoms of Bothrops, Crotalus, and Lachesis species, while the Mexican bivalent antivenoms are made only using Bothrops and Crotalus. Thus, the immunologically more complex ICP antivenom was chosen for testing. Future work, however, should investigate the ability of the Mexican bivalent antivenoms to neutralize the snake venoms. Such tests should include the Mexican trivalent antivenom, which, similar to ICP, contains Bothrops, Crotalus, and Lachesis in the immunizing mixture (and thus is predicted to have a neutralization potential similar to that of ICP) but is a product exported to South America, while the bivalent antivenoms are those primarily used in Mexican hospitals. Due to the more restricted immunological profile, the Mexican bivalent antivenoms may have more limited cross-reactivity, but this must be experimentally determined.
4. Conclusions
This study identified a wide variation in coagulotoxic effects in the clade comprising genera Atropoides, Cerrophidion, Metlapilcoatlus, and Porthidium. The extreme variation in bioactivity was in stark contrast to previous proteomics studies that reported highly similar venoms across the clade. This underscores that proteomics profiles are poor indicators of pathophysiological actions. The most novel finding we reported was the unique factor activation of FVII and FXII as being the major driver of the clotting of plasma by P. volcanicum venom. The inhibition of FXa was identified to be largely responsible for the anticoagulant properties of C. godmani and C. wilsoni, while thrombin inhibition was the case for P. dunni. In addition, fibrinogenolytic activity was reported in diverse classically anticoagulant venoms. We observed the effective neutralization of anticoagulant- and pseudo-procoagulant-venom effects when incubated with the ICP antivenom. Metalloprotease inhibitors prinomastat and marimastat were highly effective in neutralizing the procoagulant-venom effects of P. volcanicum, while the ICP antivenom and SVMP inhibitor DMPS were not seen to be effective against this activity. Overall, this work supports previous studies, while further adding to the growing body of knowledge surrounding Atropoides, Cerrophidion, Metlapilcoatlus, and Porthidium venoms and representing the most complete study of their venom functional activity to date. This research study provides a useful platform to uncover specific pathophysiological targets producing venom effects and a means to identify and modernize therapeutic approaches. An important caveat is that the work presented in this study was performed in vitro and should be corroborated by in vivo studies prior to clinical recommendations for use.
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Venoms, Plasma, and Reagents
All venom work was conducted under University of Queensland Animal Ethics Approval 2021/AE000075 and UQ Biosafety Committee Approval # IBC/134B/SBS/2015. Human-plasma work was performed under University of Queensland Biosafety Approval #IBC134BSBS2015 and Human Ethics Approval #2016000256. Australian Red Cross (44 Musk Street, Kelvin Grove, QLD 4059, Australia) supplied human platelet-poor plasma (3.2% citrated) under research approval #16- 04QLD-10.
Venom was extracted from sixteen species included within this study: Atropoides picadoi (Costa Rica), Cerrophidion godmani (Mexico), Cerrophidion tzotzilorum (San Cristobal, Mexico), Cerrophidion wilsoni (Honduras), Metlapilcoatlus mexicanus (Chiapas, Mexico), Metlapilcoatlus nummifer (Veracruz, Mexico), Metlapilcoatlus occiduus (Mapastepec, Chiapas, Mexico), Metlapilcoatlus olmec (Soteapan, Veracruz, Mexico), Porthidium dunni (Oaxaca, Mexico), Porthidium lansbergii (Colombia), Porthidium nasutum (San Luis de Poitosi, Mexico), Porthidium hespere (Mexico), Porthidium ophryomegas (Costa rica), Porthidium porrasi (Costa Rica), Porthidium volcanicum (Costa Rica), and Porthidium yucatanicum (Solidaridad, Quintana Roo, Mexico).
Lyophilized venom was reconstituted in deionized water and then centrifuged (4 °C, 10 min, 14,000 RCF). A working stock of 1 mg/mL and 4 mg/mL for anticoagulant testing was made with 50% double deionized water (DDH2O) and 50% glycerol mix to prevent freezing at −20 °C, where it was stored until use to preserve enzymatic activity. Concentrations of the working stock were determined using nanodrop at 280 nm wavelength.
All plasma was stored at −80 °C until use. Reagents used were: Kaolin (Stago catalog # 00597), phospholipid (Stago catalog # 00597), calcium (Stago catalog # 00367), Owren–Koller (OK) buffer (Stago catalog # 00360), factor Xa (Stago catalog # 00311), and thrombin (Stago catalog # 00611).
5.2. Coagulation Assays
Coagulation assays were carried out using the Stago STA-R max hemostasis analyzer robot, using assays previously validated by Venom Evolution Lab [31,49]. Pooled human plasma was thawed and warmed to 37 °C in a water bath before being placed into the machine. For testing, venom stocks were manually diluted to 1:10 using Owren–Keller (OK) buffer to obtain 0.1 mg/mL solution before being added to the machine. A series of venom dilutions were automatically carried out by the machine (μg/mL: 0.05, 0.125, 0.25, 0.66, 1.66, 4, 10, and 20). For the 1:1 dilution, 50 µL of the 0.1 µg/mL working stock was then added to 50 µL of calcium, 50 µL of phospholipid, and 25 µL of OK buffer, followed by a 120 s incubation. The robot then added 75 µL of plasma, and the time until clot formation was immediately and automatically measured. If a clot did not formed in 999 s during the assays, the machine automatically stopped, as this was the maximum recording time. The negative control in this study replaced venom with a mix of 50% OK buffer and 50% glycerol; this was used to record healthy plasma spontaneous clotting times.
Venoms that displayed strong coagulotoxic effects were tested against the PoliVal-ICP (Instituto Clodomiro Picado; Costa Rica) antivenom at 50 mg/mL concentration. To identify the target which anticoagulant venoms were acting upon, specific factors were incubated with the venom. Antivenom tests were subsequently performed on assays that showed significant results. The specific-factor-inhibition assays are detailed in Table 1.

Table 1.
Coagulation-assay protocols.
To test for SVMP activity on plasma, eight-point dilution curves were run on P. volcanicum venom, where proteinase inhibitors DMPS, prinomastat, and marimastat replaced OK buffer as reagents. Prinomastat and marimastat were solubilized in DMSO, followed by dilution to a 10 mM concentration using DDH2O. To dilute the concentration to 2 mM, the inhibitor aliquots were thawed and pooled to a 900 μL total volume diluted into 3600 μL of OK buffer. DMPS was solubilized in DMSO and diluted in DDH2O to a 20 mM concentration.
5.3. Thromboelastography (TEG)
TEG was used to determine the strength and elasticity of the clots formed by the venoms. For anticoagulant venoms, the fibrinogen-destructive properties were also tested. Experiments were performed using methods previously validated by Venom Evolution Lab [26,34,44]. The following assay conditions were run: 7 µL of venom was added to 72 µL of CaCl2, 72 µL of phospholipid, 20 µL of Owren-Keller buffer followed by 189 µL of plasma or fibrinogen and then run immediately for 30 min to leave appropriate time for clot formation. For venoms that produced no clots, assays were completed with an additional step by adding 7 µL of thrombin followed by a further 30 min to determine if fibrinogen had been destroyed by the venom to prevent clotting.
5.4. Clotting-Factor Activation
Fluoroskan Ascent™ (Thermo Scientific, Vantaa, Finland) was used to determine the activation of clotting factors FVII, FX, FXI, and FXII. Volumes of 10 μL of phospholipid, 10 μL of venom, and 10 μL of zymogen were manually pipetted, followed by the automated pipetting of 70 μL of a mixture of buffer (5 mM CaCl2, 150 mM NaCl, and 50 mM Tris-HCl at pH 7.3) and Fluorogenic Peptide Substrate (ES011 substrate Boc-Val-Pro-Arg-AMC; Boc: t-Butyloxycarbonyl; 7-Amino-4-methyl coumarin) into each experimental well of a 384-well plate. Activated factors were used in place of zymogens as positive controls. The zymogen was also replaced in the venom control wells by 10 μL of Fluoroskan buffer to determine the activity of the venom directly upon the substrate. Fluorescence generated by the cleaving of the substrate was automatically recorded by the machine. The results were obtained by subtracting blank values from reactions, followed by the subtraction of venom without zymogen from venom with zymogen.
5.5. Statistics
All assays were performed in triplicate, and the data were analyzed using GraphPad prism 9.0 software. Eight-point dilution curves were shown in logarithmic form for ease of viewing. For comparison of the antivenoms ability to neutralize venom activity, the area under the curve (AUC) was calculated for both venom curves and venom + antivenom curves. Subsequently, an X-fold shift and percentage drop was calculated using the following formula:
where a value of 0 equals no neutralization. A phylogenetic analysis was performed to determine ancestral states. The phylogenetic tree used was based upon Alencar, Quental, Grazziotin, Alfaro, Martins, Venzon, and Zaher [24] and was imported into R using the APE package to analyze the evolutionary patterns across genera.
All data used for statistical material can be found in the Supplementary Material.
Supplementary Materials
The following is available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/toxins14080511/s1, Supplementary File S1, all raw data.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.J. and B.G.F.; data curation, L.J.; formal analysis, L.J. and B.G.F.; investigation, L.J.; methodology, L.J., N.J.Y. and B.G.F.; visualization, L.J. and B.G.F.; resources, E.N.-C., A.G.-M., M.R.L., R.C., N.F., B.G.F.; writing—original draft preparation, L.J.; writing—review and editing, L.J., N.J.Y., E.N.-C., A.G.-M., M.R.L., R.C., N.F., B.G.F.; supervision, B.G.F.; project administration and funding acquisition, B.G.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
B.G.F. was funded by Australian Research Council Discovery Project DP190100304 and L.J. was the recipient of a Ph.D. Scholarship from the University of Queensland. M.R.L. and R.C. have shares and salary support from Ophirex, Inc., a Public Benefit Corporation and are funded in part by US Defense Health Agency contract W81XWH19C0082.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Work was undertaken with the following University of Queensland institutional review board approvals: the Human Ethics Committee #2016000256, the Biosafety Committee #IBC134BSBS2015, and the Animal Ethics Committee 2021/AE000075 (15 March 2021).
Data Availability Statement
All raw data is available in supplementary material.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Gutiérrez, J.M. Current challenges for confronting the public health problem of snakebite envenoming in Central America. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 20, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Neri-Castro, E.; Bénard-Valle, M.; de León, J.L.; Boyer, L.; Alagón, A. Envenomations by Reptiles in Mexico. In Handbook of Venoms and Toxins of Reptiles; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2021; pp. 529–542. [Google Scholar]
- Gutiérrez, J. Snakebite envenomation in Central America. In Handbook of Venoms and Toxins of Reptiles; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009; pp. 491–507. [Google Scholar]
- Boyer, L.; Alagón, A.; Fry, B.G.; Jackson, T.N.W.; Sunagar, K.; Chippaux, J.P. Signs, Symptoms and Treatment of Envenomation. In Venomous Reptiles and Their Toxins: Evolution, Pathophysiology and Biodiscovery; Fry, B.G., Ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 32–60. [Google Scholar]
- Mackessy, S.P. Handbook of Venoms and Toxins of Reptiles; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, J.A.; Lamar, W.W.; Brodie, E.D. The Venomous Reptiles of the Western Hemisphere; Comstock Publishing Associates: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2004; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, J. A new generic name for jumping pitvipers (Serpentes: Viperidae). Rev. Latinoam. Herpetol. 2019, 2, 52–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadin, R.C.; Townsend, J.H.; Castoe, T.A.; Campbell, J.A. Cryptic diversity in disjunct populations of Middle American Montane Pitvipers: A systematic reassessment of Cerrophidion godmani. Zool. Scr. 2012, 41, 455–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castoe, T.A.; Sasa, M.M.; Parkinson, C.L. Modeling nucleotide evolution at the mesoscale: The phylogeny of the Neotropical pitvipers of the Porthidium group (Viperidae: Crotalinae). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2005, 37, 881–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angulo, Y.; Escolano, J.; Lomonte, B.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Sanz, L.; Calvete, J.J. Snake venomics of Central American pitvipers: Clues for rationalizing the distinct envenomation profiles of Atropoides nummifer and Atropoides picadoi. J. Proteome Res. 2008, 7, 708–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Charris, E.; Montealegre-Sanchez, L.; Solano-Redondo, L.; Mora-Obando, D.; Camacho, E.; Castro-Herrera, F.; Fierro-Pérez, L.; Lomonte, B. Proteomic and functional analyses of the venom of Porthidium lansbergii lansbergii (Lansberg’s hognose viper) from the Atlantic Department of Colombia. J. Proteom. 2015, 114, 287–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomonte, B.; Fernández, J.; Sanz, L.; Angulo, Y.; Sasa, M.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Calvete, J.J. Venomous snakes of Costa Rica: Biological and medical implications of their venom proteomic profiles analyzed through the strategy of snake venomics. J. Proteom. 2014, 105, 323–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomonte, B.; Rey-Suárez, P.; Tsai, W.-C.; Angulo, Y.; Sasa, M.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Calvete, J.J. Snake venomics of the pit vipers Porthidium nasutum, Porthidium ophryomegas, and Cerrophidion godmani from Costa Rica: Toxicological and taxonomical insights. J. Proteom. 2012, 75, 1675–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez, R.; Bonilla, F.; Sasa, M.; Dwyer, Q.; Fernández, J.; Lomonte, B. Proteomic profiling, functional characterization, and immunoneutralization of the venom of Porthidium porrasi, a pitviper endemic to Costa Rica. Acta Trop. 2019, 193, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Campos, M.; Sanz, L.; Bonilla, F.; Sasa, M.; Lomonte, B.; Zaruma-Torres, F.; Terán, M.; Fernández, J.; Calvete, J.J.; Caldeira, C.A. Venomics of the poorly studied hognosed pitvipers Porthidium arcosae and Porthidium volcanicum. J. Proteom. 2021, 249, 104379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Osorio, B.; Lomonte, B.; Bénard-Valle, M.; de León, J.L.; Román-Domínguez, L.; Mejía-Domínguez, N.R.; Lara-Hernández, F.; Alagón, A.; Neri-Castro, E. Ontogenetic changes in the venom of Metlapilcoatlus nummifer, the mexican jumping viper. Toxicon 2020, 184, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Tsai, W.-C.; Pla, D.; Solano, G.; Lomonte, B.; Sanz, L.; Angulo, Y.; Calvete, J.J. Preclinical assessment of a polyspecific antivenom against the venoms of Cerrophidion sasai, Porthidium nasutum and Porthidium ophryomegas: Insights from combined antivenomics and neutralization assays. Toxicon 2013, 64, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antúnez, J.; Fernández, J.; Lomonte, B.; Angulo, Y.; Sanz, L.; Pérez, A.; Calvete, J.J.; Gutiérrez, J.M. Antivenomics of Atropoides mexicanus and Atropoides picadoi snake venoms: Relationship to the neutralization of toxic and enzymatic activities. J. Venom Res. 2010, 1, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Otero, R.; Gutiérrez, J.; Beatriz Mesa, M.; Duque, E.; Rodríguez, O.; Luis Arango, J.; Gómez, F.; Toro, A.; Cano, F.; María Rodríguez, L.; et al. Complications of Bothrops, Porthidium, and Bothriechis snakebites in Colombia. A clinical and epidemiological study of 39 cases attended in a university hospital. Toxicon 2002, 40, 1107–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, L.F.; Zdenek, C.N.; Dobson, J.S.; Op den Brouw, B.; Coimbra, F.C.; Gillett, A.; Del-Rei, T.H.; Chalkidis, H.d.M.; Sant’Anna, S.; Teixeira-da-Rocha, M.M.; et al. Coagulotoxicity of Bothrops (lancehead pit-vipers) venoms from Brazil: Differential biochemistry and antivenom efficacy resulting from prey-driven venom variation. Toxins 2018, 10, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Angulo, Y.; Estrada, R.; Gutiérrez, J. Clinical and laboratory alterations in horses during immunization with snake venoms for the production of polyvalent (Crotalinae) antivenom. Toxicon 1997, 35, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Lomonte, B.; Sanz, L.; Calvete, J.J.; Pla, D. Immunological profile of antivenoms: Preclinical analysis of the efficacy of a polyspecific antivenom through antivenomics and neutralization assays. J. Proteom. 2014, 105, 340–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorge, R.J.B.; Monteiro, H.S.; Gonçalves-Machado, L.; Guarnieri, M.C.; Ximenes, R.M.; Borges-Nojosa, D.M.; Karla, P.d.O.; Zingali, R.B.; Corrêa-Netto, C.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; et al. Venomics and antivenomics of Bothrops erythromelas from five geographic populations within the Caatinga ecoregion of northeastern Brazil. J. Proteom. 2015, 114, 93–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alencar, L.R.; Quental, T.B.; Grazziotin, F.G.; Alfaro, M.L.; Martins, M.; Venzon, M.; Zaher, H. Diversification in vipers: Phylogenetic relationships, time of divergence and shifts in speciation rates. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2016, 105, 50–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourke, L.A.; Youngman, N.J.; Zdenek, C.N.; Op den Brouw, B.; Violette, A.; Fourmy, R.; Fry, B.G. Trimeresurus albolabris snakebite treatment implications arising from ontogenetic venom comparisons of anticoagulant function, and antivenom efficacy. Toxicol. Lett. 2020, 327, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debono, J.; Bos, M.H.; Nouwens, A.; Ge, L.; Frank, N.; Kwok, H.F.; Fry, B.G. Habu coagulotoxicity: Clinical implications of the functional diversification of Protobothrops snake venoms upon blood clotting factors. Toxicol. Vitr. 2019, 55, 62–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Debono, J.; Bos, M.H.; Coimbra, F.; Ge, L.; Frank, N.; Kwok, H.F.; Fry, B.G. Basal but divergent: Clinical implications of differential coagulotoxicity in a clade of Asian vipers. Toxicol. Vitr. 2019, 58, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seneci, L.; Zdenek, C.N.; Rodrigues, C.F.; Chowdhury, A.; Neri-Castro, E.; Bénard-Valle, M.; Alagón, A.; Fry, B. A Clot Twist: Potent Coagulotoxicity Found in Mexican Neotropical Rattlesnakes. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seneci, L.; Zdenek, C.N.; Bourke, L.A.; Cochran, C.; Sánchez, E.E.; Neri-Castro, E.; Bénard-Valle, M.; Alagón, A.; Frank, N.; Fry, B.G. A symphony of destruction: Dynamic differential fibrinogenolytic toxicity by rattlesnake (Crotalus and Sistrurus) venoms. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2021, 245, 109034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, A.; Zdenek, C.N.; Lewin, M.R.; Carter, R.; Jagar, T.; Ostanek, E.; Harjen, H.; Aldridge, M.; Soria, R.; Haw, G.; et al. Venom-induced blood disturbances by palearctic viperid snakes, and their relative neutralization by antivenoms and enzyme-inhibitors. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oulion, B.; Dobson, J.S.; Zdenek, C.N.; Arbuckle, K.; Lister, C.; Coimbra, F.C.; Op den Brouw, B.; Debono, J.; Rogalski, A.; Violette, A.; et al. Factor X activating Atractaspis snake venoms and the relative coagulotoxicity neutralising efficacy of African antivenoms. Toxicol. Lett. 2018, 288, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamada, D.; Sekiya, F.; Morita, T. Prothrombin and factor X activator activities in the venoms of Viperidae snakes. Toxicon 1997, 35, 1581–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iddon, D.; Theakston, R. Biological properties of the venom of the red-necked keel-back snake (Rhabdophis subminiatus). Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 1986, 80, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youngman, N.J.; Debono, J.; Dobson, J.S.; Zdenek, C.N.; Harris, R.J.; Coimbra, F.C.; Naude, A.; Coster, K.; Sundman, E.; Braun, R.; et al. Venomous landmines: Clinical implications of extreme coagulotoxic diversification and differential neutralization by antivenom of venoms within the viperid snake genus Bitis. Toxins 2019, 11, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, B.; Dashevsky, D.; Rokyta, D.; Ghezellou, P.; Fathinia, B.; Shi, Q.; Richardson, M.K.; Fry, B.G. Dynamic genetic differentiation drives the widespread structural and functional convergent evolution of snake venom proteinaceous toxins. BMC Biol. 2022, 20, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, A.; Zdenek, C.N.; Dobson, J.S.; Bourke, L.A.; Soria, R.; Fry, B.G. Clinical implications of differential procoagulant toxicity of the Palearctic viperid genus Macrovipera, and the relative neutralization efficacy of antivenoms and enzyme inhibitors. Toxicol. Lett. 2021, 340, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cipriani, V.; Debono, J.; Goldenberg, J.; Jackson, T.N.; Arbuckle, K.; Dobson, J.; Koludarov, I.; Li, B.; Hay, C.; Dunstan, N.; et al. Correlation between ontogenetic dietary shifts and venom variation in Australian brown snakes (Pseudonaja). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2017, 197, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bourke, L.A.; Zdenek, C.N.; Neri-Castro, E.; Bénard-Valle, M.; Alagón, A.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Sanchez, E.F.; Aldridge, M.; Fry, B.G. Pan-American lancehead pit-vipers: Coagulotoxic venom effects and antivenom neutralisation of Bothrops asper and B. atrox geographical variants. Toxins 2021, 13, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva-Carvalho, R.; Gaspar, M.Z.; Quadros, L.H.; Lobo, L.G.; Rogério, L.M.; Santos, N.T.; Zerbinatti, M.C.; Santarém, C.L.; Silva, E.O.; Gerez, J.R.; et al. In vivo treatment with varespladib, a phospholipase A2 inhibitor, prevents the peripheral neurotoxicity and systemic disorders induced by Micrurus corallinus (coral snake) venom in rats. Toxicol. Lett. 2021, 356, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Souza, J.; Oliveira, I.C.; Yoshida, E.H.; Cantuaria, N.M.; Cogo, J.C.; Torres-Bonilla, K.A.; Hyslop, S.; Junior, N.J.S.; Floriano, R.S.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; et al. Effect of the phospholipase A2 inhibitor Varespladib, and its synergism with crotalic antivenom, on the neuromuscular blockade induced by Crotalus durissus terrificus venom (with and without crotamine) in mouse neuromuscular preparations. Toxicon 2022, 214, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eng, W.; Fry, B.; Sunagar, K.; Takacs, Z.; Jackson, T.; Guddat, L. Kunitz peptides. In Venomous Reptiles and Their Toxins: Evolution, Pathophysiology and Biodiscovery; Fry, B.G., Ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2015; pp. 281–290. [Google Scholar]
- Arlinghaus, F.; Fry, B.; Sunagar, K.; Jackson, T.; Eble, J.; Reeks, T.; Clemetson, K. Lectin proteins. Venomous Reptiles & Their Toxins: Evolution, Pathophysiology & Biodiscovery. In Venomous Reptiles and Their Toxins: Evolution, Pathophysiology and Biodiscovery; Fry, B., Ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2015; pp. 299–3311. [Google Scholar]
- Sunagar, K.; Jackson, T.; Reeks, T.; Fry, B. Group I phospholipase A2 Enzymes; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Coimbra, F.C.; Dobson, J.; Zdenek, C.N.; Op den Brouw, B.; Hamilton, B.; Debono, J.; Masci, P.; Frank, N.; Ge, L.; Kwok, H.F.; et al. Does size matter? Venom proteomic and functional comparison between night adder species (Viperidae: Causus) with short and long venom glands. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2018, 211, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debono, J.; Bos, M.H.; Do, M.S.; Fry, B.G. Clinical implications of coagulotoxic variations in Mamushi (Viperidae: Gloydius) snake venoms. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2019, 225, 108567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debono, J.; Bos, M.H.; Frank, N.; Fry, B. Clinical implications of differential antivenom efficacy in neutralising coagulotoxicity produced by venoms from species within the arboreal viperid snake genus Trimeresurus. Toxicol. Lett. 2019, 316, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobson, J.; Yang, D.C.; Op den Brouw, B.; Cochran, C.; Huynh, T.; Kurrupu, S.; Sánchez, E.E.; Massey, D.J.; Baumann, K.; Jackson, T.N.; et al. Rattling the border wall: Pathophysiological implications of functional and proteomic venom variation between Mexican and US subspecies of the desert rattlesnake Crotalus scutulatus. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2018, 205, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gené, J.; Roy, A.; Rojas, G.; Gutiérrez, J.; Cerdas, L. Comparative study on coagulant, defibrinating, fibrinolytic and fibrinogenolytic activities of Costa Rican crotaline snake venoms and their neutralization by a polyvalent antivenom. Toxicon 1989, 27, 841–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zdenek, C.N.; Youngman, N.J.; Hay, C.; Dobson, J.; Dunstan, N.; Allen, L.; Milanovic, L.; Fry, B.G. Anticoagulant activity of black snake (Elapidae: Pseudechis) venoms: Mechanisms, potency, and antivenom efficacy. Toxicol. Lett. 2020, 330, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).