Ultrasonographic Considerations for Safe and Efficient Botulinum Neurotoxin Injection in Masseteric Hypertrophy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
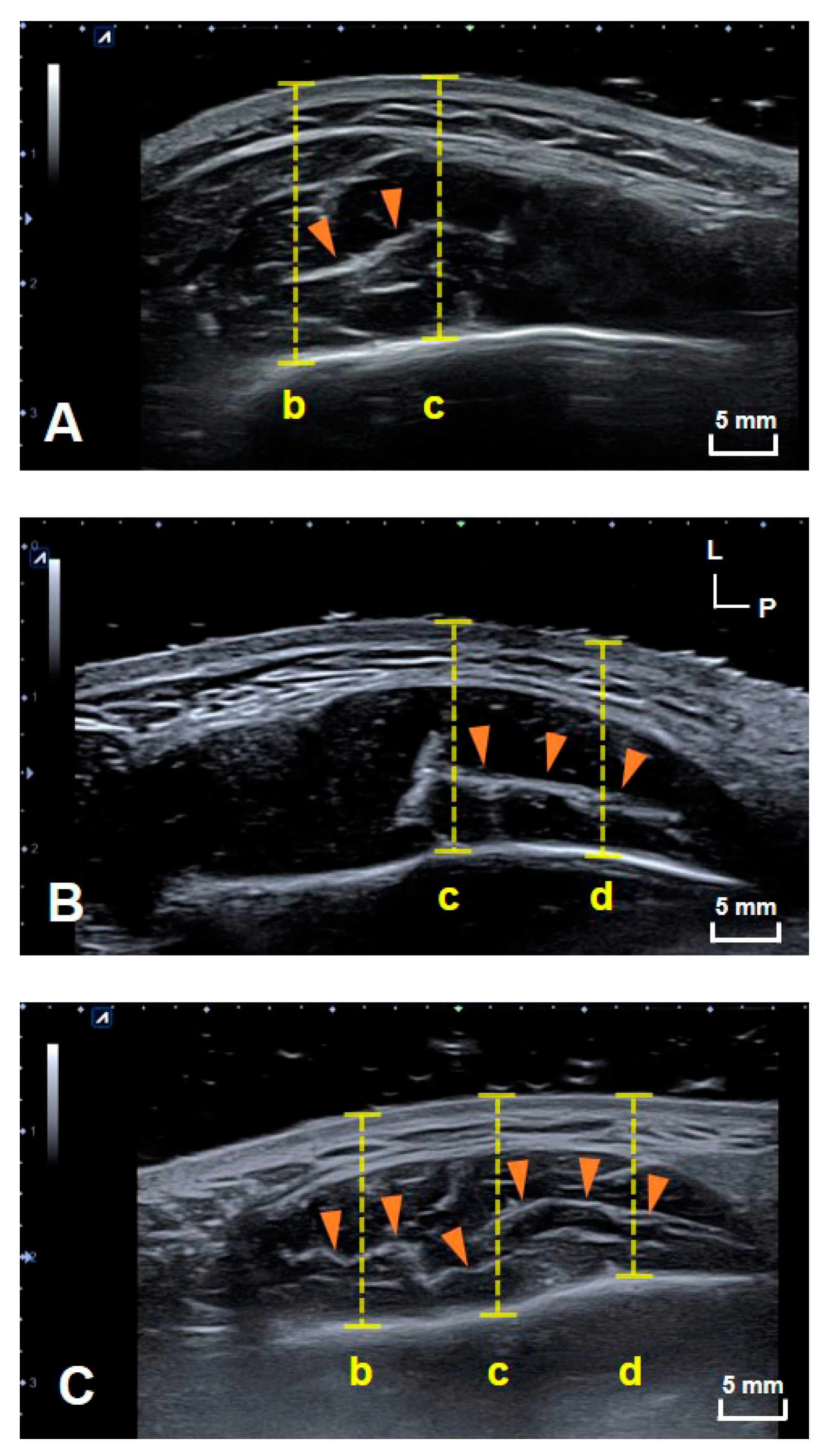
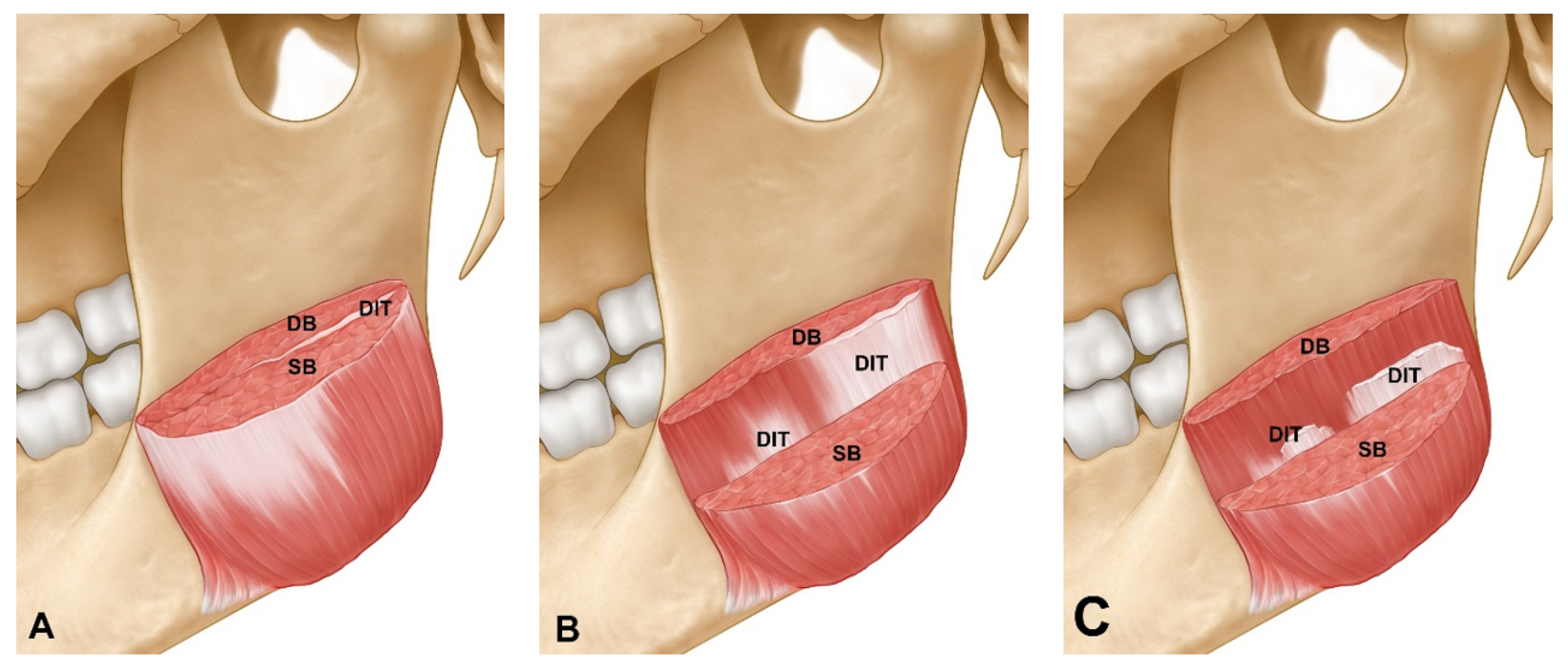
2.1. Types of DIT in Healthy Young Subjects
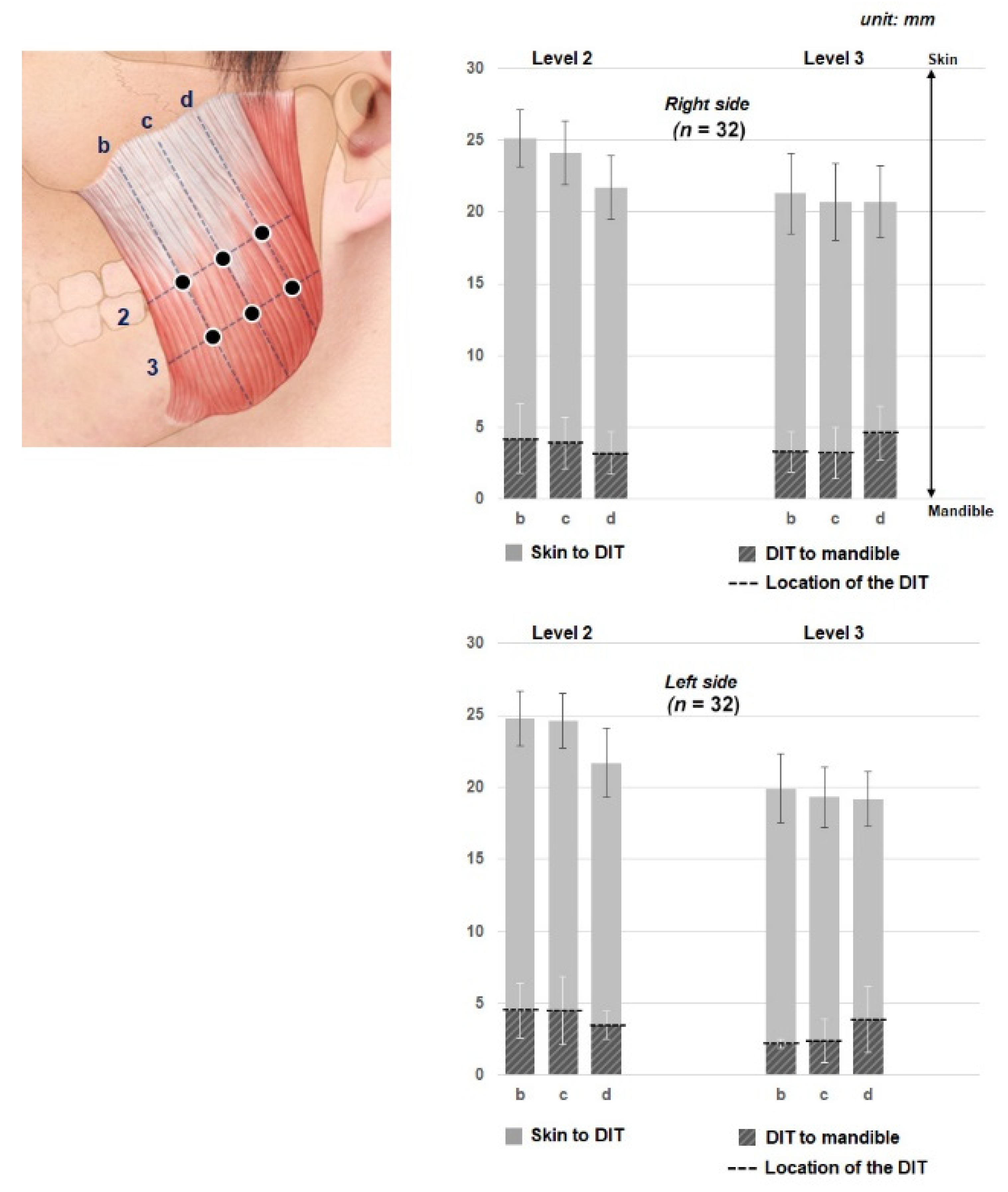
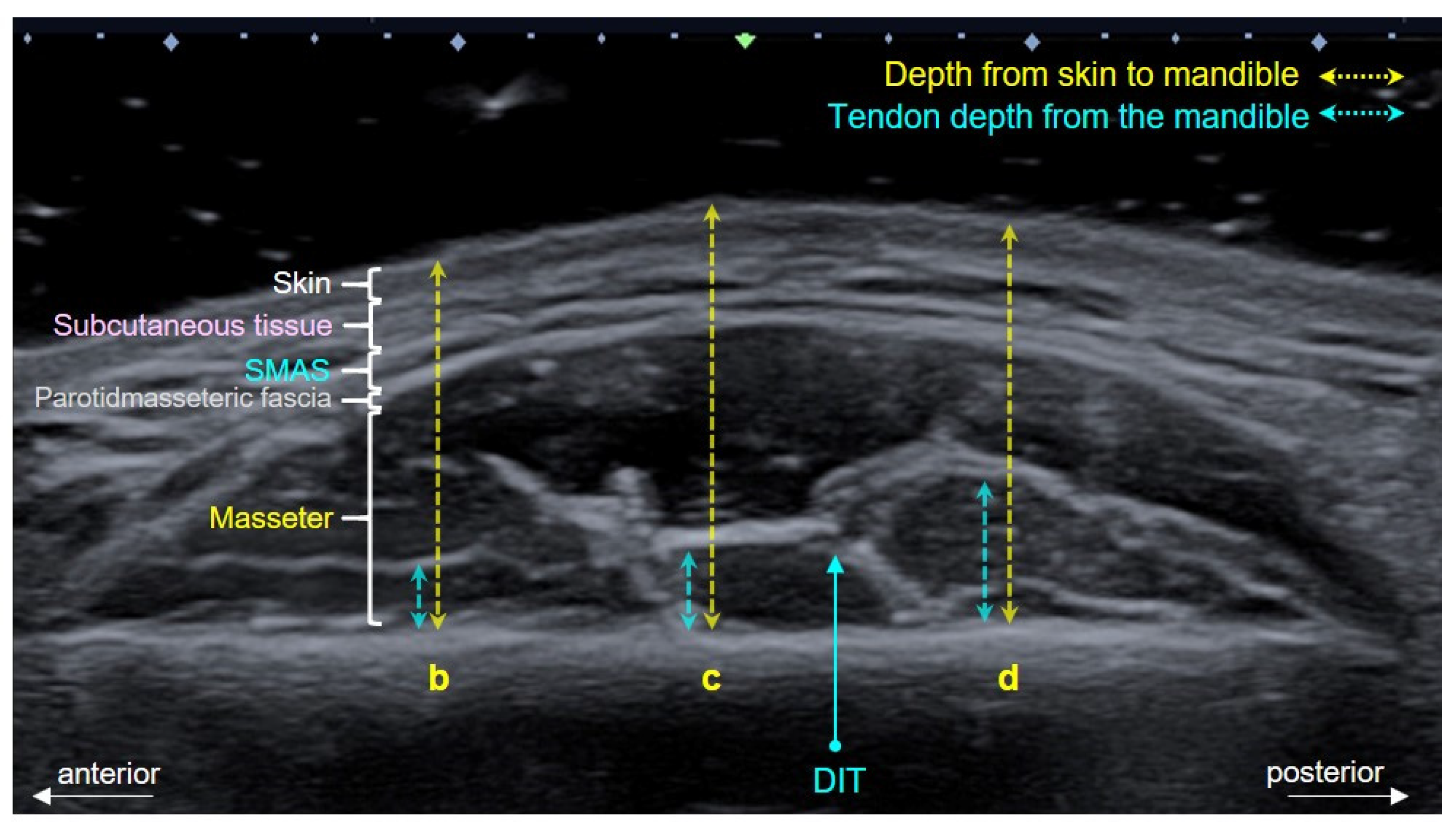
2.2. Depth at Each Reference Line
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
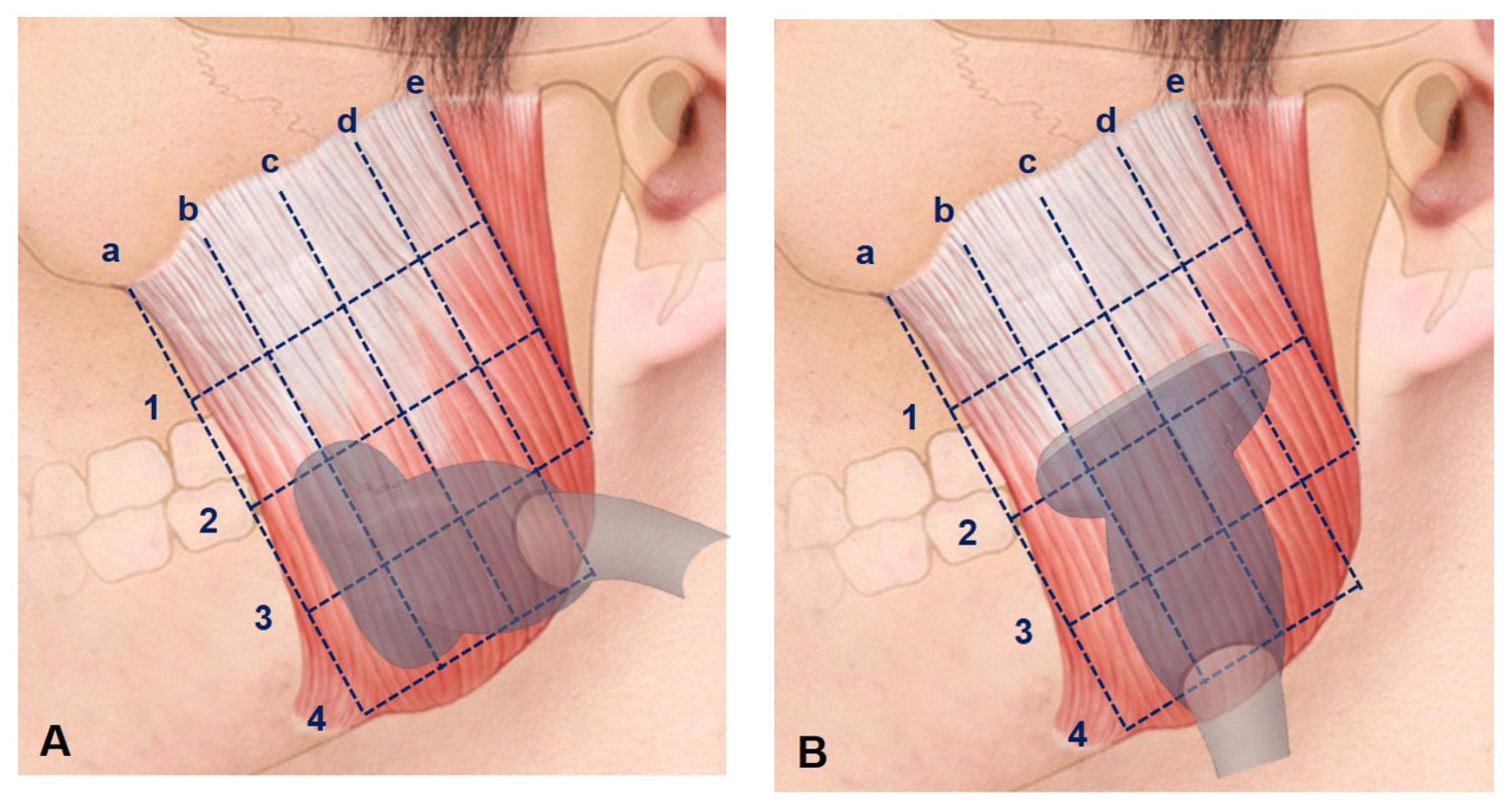
US Scanning of Healthy Young Subjects
- The anterior border of the masseter muscle.
- The line halfway between lines a and c.
- The line halfway between lines a and e.
- The line halfway between lines c and e.
- The posterior border of the masseter muscle.
- The line halfway between the inferior margin of the zygomatic arch and line 2.
- The line halfway between the inferior margin of the zygomatic arch and line 4.
- The line halfway between lines 2 and 4.
- The inferior margin of the mandible.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liew, S.; Wu, W.T.L.; Chan, H.H.; Ho, W.W.S.; Kim, H.-J.; Goodman, G.J.; Peng, P.H.L.; Rogers, J.D. Consensus on Changing Trends, Attitudes, and Concepts of Asian Beauty. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2016, 40, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, A.; Wood, G. The medical management of masseteric hypertrophy with botulinum toxin type A. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 1994, 32, 26–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhee, S.C.; Lee, S.H. Attractive Composite Faces of Different Races. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2010, 34, 800–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, K.K. Botulinum Toxin for Asians; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.; Zhou, J.; Li, H.; Cheng, C.; Herrler, T.; Li, Q. Classification of Masseter Hypertrophy for Tailored Botulinum Toxin Type A Treatment. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2014, 134, 209e–218e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, N.-H.; Chung, J.-H.; Park, R.-H.; Park, J.-B. The Use of Botulinum Toxin Type A in Aesthetic Mandibular Contouring. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2005, 115, 919–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, J.-S.; Kim, S.; Jeon, Y.; Choi, J.-H. Effect of botulinum toxin type A injection into human masseter muscle on stimulated parotid saliva flow rate. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2009, 38, 316–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, W.H.; Yoon, S.H.; Park, J.H.; Choi, Y.-C.; Kim, S.T. Effect of Botulinum Toxin Type A Injection on Lower Facial Contouring Evaluated Using a Three-Dimensional Laser Scan. Dermatol. Surg. 2010, 36, 2161–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carruthers, J.; Carruthers, A. Aesthetic botulinum A toxin in the mid and lower face and neck. Dermatol. Surg. 2003, 29, 468–476. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.-J.; Seo, K.K.; Lee, H.-K.; Kim, J. Clinical Anatomy for Botulinum Toxin Injection. Clinical Anatomy of the Face for Filler and Botulinum Toxin Injection; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 55–92. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.-J.; Kim, J.-S.; Youn, K.-H.; Lee, J.; Kim, D.H.-J. Ultrasound-Guided Botulinum Neurotoxin Type A Injection for Correcting Asymmetrical Smiles. Aesthetic Surg. J. 2018, 38, NP130–NP134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Lee, K.W.; Tansatit, T.; Kim, H.J. Three-Dimensional Territory and Depth of the Corrugator Supercilii: Application to Botulinum Neurotoxin Injection. Clin. Anat. 2020, 33, 795–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-S.; Kang, G.C.-W. Achieving Ideal Lower Face Aesthetic Contours: Combination of Tridimensional Fat Grafting to the Chin with Masseter Botulinum Toxin Injection. Aesthetic Surg. J. 2016, 36, 1093–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Muharraqi, M.A.; Fedorowicz, Z.; Al Bareeq, J.; Al Bareeq, R.; Nasser, M. Botulinum toxin for masseter hypertrophy. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaofeng, L.; Jun, T.; Bo, P.; Bosheng, Z.; Qian, Z.; Dongping, L. Evaluation and selecting indications for the treatment of improving facial morphology by masseteric injection of botulinum toxin type A. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2010, 63, 2026–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.-H.; Shin, J.H.; Kim, S.T.; Kim, C.-Y. Effects of Two Different Units of Botulinum Toxin Type A Evaluated by Computed Tomography and Electromyographic Measurements of Human Masseter Muscle. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2007, 119, 711–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Xu, H.; Dong, J.; Li, Q.; Dai, C. Prolonging the Duration of Masseter Muscle Reduction by Adjusting the Masticatory Movements After the Treatment of Masseter Muscle Hypertrophy With Botulinum Toxin Type A Injection. Dermatol. Surg. 2015, 41, S101–S109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, Y.-T.; Peng, J.-H.; Peng, H.-L.P. Literature review of the adverse events associated with botulinum toxin injection for the masseter muscle hypertrophy. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2018, 17, 675–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-J.; Kang, I.-W.; Seo, K.K.; Choi, Y.-J.; Kim, S.-T.; Hu, K.-S.; Kim, H.-J. The Anatomical Basis of Paradoxical Masseteric Bulging after Botulinum Neurotoxin Type A Injection. Toxins 2016, 9, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Choi, Y.; Bs, K.L.; Hu, K.; Kim, S.-T.; Kim, H.-J. Ultrasonography of the internal architecture of the superficial part of the masseter muscle in vivo. Clin. Anat. 2019, 32, 446–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, J.-H.; Choi, D.-Y.; Lee, J.-G.; Seo, K.K.; Tansatit, T.; Kim, H.-J. The risorius muscle: Anatomic considerations with reference to botulinum neurotoxin injection for masseteric hypertrophy. Dermatol. Surg. 2014, 40, 1334–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinnett, D. Botulinum toxin A injections in children: Technique and dosing issues. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2004, 83, S59–S64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepage, D.; Parratte, B.; Tatu, L.; Vuiller, F.; Monnier, G. Extra- and intramuscular nerve supply of the muscles of the anterior antebrachial compartment: Applications for selective neurotomy and for botulinum toxin injection. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 2005, 27, 420–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, T.S.J.; Dover, J.S.; Arndt, K.A. Effect of Volume and Concentration on the Diffusion of Botulinum Exotoxin A. Arch. Dermatol. 2004, 140, 1351–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, Y.H.; Park, J.K.; Yang, H.M.; Kim, S.H. Ultrasound-guided versus blind temporomandibular joint injections: A pilot cadaveric evaluation. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2019, 48, 540–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, S.N.; Grushka, M.; Beituni, H.K.; Rehman, M.; Bressler, H.B.; Friedman, L. Advanced Ultrasound Screening for Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) Internal Derangement. Radiol. Res. Pr. 2020, 2020, 1809690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.-H.; Hong, H.-S.; Won, S.-Y.; Kim, H.-J.; Hu, K.-S.; Choi, J.-H.; Kim, H.-J. Intramuscular Nerve Distribution of the Masseter Muscle as a Basis for Botulinum Toxin Injection. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2010, 21, 588–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.-S.; Kim, S.-T.; Hur, M.-S.; Park, J.-H.; Song, W.-C.; Koh, K.-S.; Kim, H.-J. Topography of the masseter muscle in relation to treatment with botulinum toxin type A. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endodontol. 2010, 110, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cioffi, I.; Gallo, L.M.; Palla, S.; Erni, S.; Farella, M. Macroscopic Analysis of Human Masseter Compartments Assessed by Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Cells Tissues Organs 2011, 195, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayil, M.; Keser, G.; Demir, A.; Pekiner, F.N. Assessment of Masseter Muscle Appearance and Thickness in Edentulous and Dentate Patients by Ultrasonography. Open Dent. J. 2018, 12, 723–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| 2 (n = 32) | 3 ( n = 32) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Skin to DIT | DIT to Mandible | Skin to DIT | DIT to Mandible | |||||
| Right | Left | Right | Left | Right | Left | Right | Left | |
| b | 20.9 ± 2.0 | 20.3 ± 1.9 | 4.2 ± 2.4 | 4.5 ± 1.9 | 18.0 ± 2.8 | 17.7 ± 2.4 | 3.3 ± 1.4 | 2.2 ± 0.3 |
| c | 20.2 ± 2.2 | 20.1 ± 1.9 | 3.9 ± 1.8 | 4.5 ± 2.4 | 17.5 ± 2.7 | 16.9 ± 2.1 | 3.2 ± 1.8 | 2.4 ± 1.5 |
| d | 18.5 ± 2.2 | 18.2 ± 2.4 | 3.2 ± 1.5 | 3.5 ± 1.0 | 16.1 ± 2.5 | 15.3 ± 1.9 | 4.6 ± 1.9 | 3.9 ± 2.3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, H.-J.; Jung, S.-J.; Kim, S.-T.; Kim, H.-J. Ultrasonographic Considerations for Safe and Efficient Botulinum Neurotoxin Injection in Masseteric Hypertrophy. Toxins 2021, 13, 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13010028
Lee H-J, Jung S-J, Kim S-T, Kim H-J. Ultrasonographic Considerations for Safe and Efficient Botulinum Neurotoxin Injection in Masseteric Hypertrophy. Toxins. 2021; 13(1):28. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13010028
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Hyung-Jin, Su-Jin Jung, Seong-Taek Kim, and Hee-Jin Kim. 2021. "Ultrasonographic Considerations for Safe and Efficient Botulinum Neurotoxin Injection in Masseteric Hypertrophy" Toxins 13, no. 1: 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13010028
APA StyleLee, H.-J., Jung, S.-J., Kim, S.-T., & Kim, H.-J. (2021). Ultrasonographic Considerations for Safe and Efficient Botulinum Neurotoxin Injection in Masseteric Hypertrophy. Toxins, 13(1), 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13010028






