Abstract
Cervical dystonia (CD) is a neurological movement disorder characterized by sustained involuntary muscle contractions. First-line therapy for CD is intramuscular injections of botulinum neurotoxin (e.g., abobotulinumtoxinA) into the affected muscles. The objective of this systematic literature review is to assess the clinical evidence regarding the effects of abobotulinumtoxinA for treatment of CD in studies of safety, efficacy, patient-reported outcomes, and economic outcomes. Using comprehensive electronic medical literature databases, a search strategy was developed using a combination of Medical Subject Heading terms and keywords. Results were reviewed by two independent reviewers who rated the level of evidence. The search yielded 263 publications, of which 232 were excluded for being duplicate publications, not meeting the selection criteria, or failing to meet predefined eligibility criteria, leaving a total of 31 articles. Clinical efficacy, patient-reported outcomes, and safety data were in 6 placebo-controlled trials (8 articles), 6 active-controlled trials, and 16 observational studies (17 articles). Data on health economic outcomes were provided in one of the clinical trials, in two of the observational studies, and in one specific cost-analysis publication. This review demonstrated that the routine use of abobotulinumtoxinA in CD is well-established, effective, and generally well-tolerated, with a relatively low cost of treatment.
Key Contribution:
This review not only adds to the ongoing body of clinical evidence related to the overall benefits of abobotulinumtoxinA, it may also be informative to the design of new clinical trial programs and provide an evidence-based resource for clinical practice.
1. Introduction
Cervical dystonia (CD) is a chronic neurological movement disorder characterized by sustained involuntary muscle contractions, which frequently leads to abnormal head movements and disabling, sometimes painful, postures of the head and cervical spine [1]. The pathophysiology of CD is not well understood. CD primarily occurs in individuals aged 40‒50 years and the majority of cases are idiopathic, although about 10% of patients have a positive family history. Acquired CD is rare and can arise after exposure to anti-dopaminergic drugs, brain injury, and other neurological disorders, including neurodegenerative diseases (e.g., Parkinson’s disease). Worldwide, the estimated prevalence of CD varies anywhere from 20 to 4100 cases per million [2]. Estimates may underrepresent the true prevalence because of underdiagnosis or misdiagnosis.
The first-line symptomatic treatment of CD is intramuscular injections of botulinum neurotoxin into the affected muscles, which inhibits the release of acetylcholine at the neuromuscular junction [3,4]. In Western countries, there are three commercially available formulations of botulinum neurotoxin type A—onabotulinumtoxinA (Botox, Allergan), abobotulinumtoxinA (Dysport, Ipsen), and incobotulinumtoxinA (Xeomin, Merz Pharmaceuticals)—and one commercially available formulation of botulinum neurotoxin type B—rimabotulinumtoxinB (MyoBloc, Solstice Neurosciences/NeuroBloc, Eisai Co., Ltd.)—that are indicated for CD. The US Food and Drug Administration approved Dysport for the treatment of adults with CD in 2009 and Health Canada approved Dysport Therapeutic (abobotulinumtoxinA) for the treatment of adults with CD in 2017.
The aim of the current systematic literature review is to assess the depth of clinical evidence regarding the effects of abobotulinumtoxinA for the treatment of adults with CD in studies of safety, efficacy, patient-reported outcomes, and economic outcomes. Results from this analysis may inform the design of new clinical trial programs and provide an evidence-based resource for clinical practice.
2. Methods
Studies reporting on the effects of abobotulinumtoxinA for the treatment of adults with CD in terms of safety, efficacy, patient-reported outcomes, and economic outcomes were identified by way of a comprehensive systematic literature review performed in accordance with PRISMA (Prevention and Recovery Information System for Monitoring and Analysis) guidelines [5]. No language, publication date, or publication status restrictions were imposed. Three comprehensive electronic medical literature databases were searched (PubMed, Cochrane Library, and Embase) through 9 April 2018. The literature search strategy was developed using a combination of Medical Subject Heading (MeSH) terms and keywords. Relevant keywords and search strings are presented in Supplementary Materials, Table S1.
Search results were screened using the following inclusion criteria: (i) the study was interventional or observational in design; (ii) study patients were adults (aged ≥ 18 years) with CD; (iii) the therapeutic intervention included treatment with abobotulinumtoxinA; and (iv) eligible clinical trials had a control intervention such as placebo, onabotulinumtoxinA, incobotulinumtoxinA, rimabotulinumtoxinB, or Lanzhou BTX-A.
Two reviewers independently extracted information from the articles, first by reviewing titles and abstracts and then by reviewing full texts. Relevant information regarding (i) study type, (ii) number of patients and type of interventions used in the study, and (iii) outcomes and parameters utilized or outcome assessment was recorded. The reviewers rated the level of evidence and assessed bias using the Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development and Evaluations (GRADE) approach (Supplementary Materials, Table S2) [6].
3. Results
3.1. Identified Studies and Quality Assessment
A flowchart of the systematic literature search is shown in Figure 1. The search yielded a total of 263 potentially relevant publications across the three databases. On initial review, 77 articles were excluded for being duplicate publications. On title and abstract screening, an additional 116 publications were excluded either for not meeting the selection criteria or for being duplicates (e.g., a conference abstract being published as a full text). Lastly, an additional 39 articles were excluded on full text review for failing to meet the predefined eligibility criteria. Thus, a total of 31 articles were included in the analysis. Clinical efficacy, patient-reported outcomes, and safety data were from 6 placebo-controlled trials (covered by 8 publications; Table 1) [7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14], 6 active-controlled trials (Table 2) [15,16,17,18,19,20], and 16 observational studies (covered by 17 publications; Table 3) [21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37]. Data on health economic outcomes was provided for one of the clinical trials (but in a separate publication), in two of the observational studies, and in one specific cost-analysis publication.
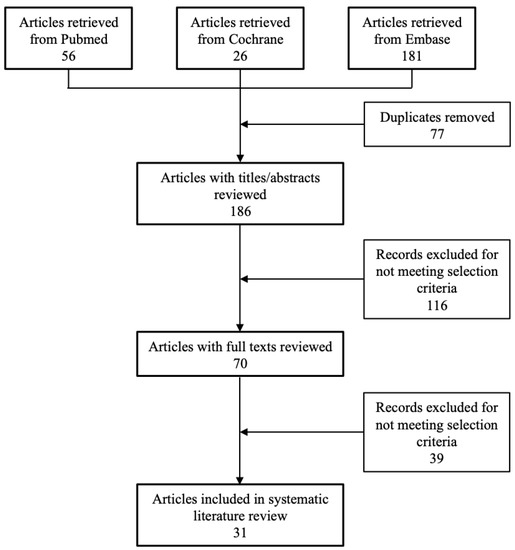
Figure 1.
Flow chart of study selection.

Table 1.
Placebo-controlled studies.

Table 2.
Active-controlled studies.

Table 3.
Other studies.
3.2. Efficacy
Of 31 identified articles, a total of 26 publications published in the 1995–2018 period described clinical efficacy. Six studies were placebo-controlled, six active-controlled, two open-label, two prospective observational, one retrospective observational, two retrospective cohort, one longitudinal cohort, one database study, four miscellaneous prospective, and one retrospective chart review. Objective efficacy measures included the Toronto Western Spasmodic Torticollis Rating Scale (TWSTRS) [38,39] and Tsui scores [38]. Data from placebo-controlled studies are summarized in Table 1, active-controlled studies in Table 2, and observational studies in Table 3.
3.2.1. Placebo-Controlled Studies
Dosing and injection pattern varied across the six placebo-controlled studies. Most studies used an average abobotulinumtoxinA dose of 500 U; a few studies used lower or higher doses (range, 125 to 1000 U; Table 1).
Poewe et al. (1998) demonstrated significantly greater reductions in Tsui score from baseline to week 4 with abobotulinumtoxinA 500 U and 1000 U relative to placebo (p < 0.05) in a placebo-controlled study of three doses of abobotulinumtoxinA (250 U, 500 U, and 1000 U) conducted in 73 adults with CD [7]. Wissel et al. (2001) described significant reductions in TWSTRS score from baseline to weeks 4 and 8 (p = 0.001 and p = 0.002, respectively) with abobotulinumtoxinA 500 U versus placebo in another small study (N = 68) [8]. A similar result to Wissel et al. (2001) was observed by Truong et al. (2005; Table 1) [9]. Lew et al. (2018) assessed abobotulinumtoxinA at a mean dose of 452 U (median dose of 500 U) in 134 patients, which showed change from baseline in mean TWSTRS total score at week 4 compared with placebo [10]. A statistically significant difference from placebo was observed at week 2. Again, abobotulinumtoxinA was shown to be effective both in botulinum toxin-naïve and in previously botulinum toxin-treated patients. The efficacy was maintained during the open-label extension phase, in which patients were treated with abobotulinumtoxinA for up to four treatment cycles (mean dose, cycle 1, 502 U; cycle 2, 643 U; cycle 3, 716 U; and cycle 4, 776 U). The relative dose adjustment from onabotulinumtoxinA to abobotulinumtoxinA used in the study was 1:2.5.
In the largest randomized, placebo-controlled trial to date, 648 patients were assigned to abobotulinumtoxinA solution (500 U), abobotulinumtoxinA dry formulation (500 U), or placebo for the double-blind phase [11]. Both formulations of abobotulinumtoxinA demonstrated a statistically significant difference versus placebo in change from baseline to week 4 and observed up to week 12 in TWSTRS total score and subscale scores. A further post hoc analysis indicated that abobotulinumtoxinA solution was non-inferior to dry formulation [11].
3.2.2. Active-Controlled Studies
Our search identified six active-controlled studies. Odergren et al. (1998) enrolled 73 patients and used a 3:1 bioequivalence ratio to evaluate the dose equivalence and efficacy of abobotulinumtoxinA (mean dose of 477 U) and onabotulinumtoxinA (mean dose of 152 U) [15]. Both groups showed improvements in Tsui score up to week 12. The difference between treatment groups in mean post-treatment Tsui scores was not statistically significant. Laubis-Herrmann et al. (2002) compared the efficacy of abobotulinumtoxinA at the recommended dose (500 U) and at a low dose (125 U) in 31 patients; both dose groups experienced statistically significant improvements in TWSTRS total score and two subscale scores from baseline to week 4 [16]. The difference between groups was not statistically significant for the TWSTRS total or subscales scores. In a crossover study by Ranoux et al. (2002), 54 enrolled patients were randomly assigned to receive onabotulinumtoxinA at the usually effective dose (defined as the dose at which a satisfactory response was achieved in the previous two treatments), abobotulinumtoxinA at a dose ratios of 1:3 and 1:4 (onabotulinumtoxinA:abobotulinumtoxinA) [17]. At week 4, statistically significant improvements from baseline in Tsui score and TWSTRS pain score were observed with the abobotulinumtoxinA treatment compared to the onabotulinumtoxinA treatment. The mean duration of action was 7 days longer with abobotulinumtoxinA 1:3 and 25 days longer with abobotulinumtoxinA 1:4 than with onabotulinumtoxinA (p = 0.58 and p = 0.02, respectively). Yun et al. (2015) compared onabotulinumtoxinA (mean dose, 144 U) and abobotulinumtoxinA (mean dose, 361 U) at a 1:2.5 treatment ratio in 94 patients, with a 4-week washout period between 16-week treatment cycles [18]. There were no statistically significant differences between groups in Tsui score or TWSTRS total and subscale scores from baseline to week 4. The results demonstrated that onabotulinumtoxinA was non-inferior to abobotulinumtoxinA at the 1:2.5 treatment ratio. Barbosa et al. (2015) compared Lanzhou BTX-A with abobotulinumtoxinA at an equivalency ratio of 1:3 U (actual doses are not reported) [19]. Both treatments also demonstrated statistically significant decreases from baseline in all TWSTRS subscale scores at week 4 after the initial injection, again with no statistically significant difference between the two treatments.
An open-label study of 28 patients by Van den Bergh et al. (1995) demonstrated improvement in the mean composite score (comprising subjective rating Tsui score and video score) in patients treated with abobotulinumtoxinA 384 U (mean composite score was 18.9 at baseline and improved to 5.2 at peak improvement) [21]. Mean composite scores dropped significantly from first treatment to last (mean: five cycles). In a study by Kessler et al. (1999) involving 303 patients who received at least six treatments with abobotulinumtoxinA, statistically significant reductions in modified Tsui score over the first six injections were observed and remained generally consistent up to the 15th treatment [22]. The greatest reduction in modified Tsui score was seen after the first treatment. Similar improvement in Tsui scores was noted with abobotulinumtoxinA in three other studies (Table 3) [23,24,26].
An expert group of neurologists observed 404 patients for treatment response following a single injection of botulinum toxin A: approximately 33% of patients treated with abobotulinumtoxinA (median dose, 500 U) and 23% of patients treated with onabotulinumtoxinA (median dose, 160 U) were considered treatment responders [27]. The ANCHOR-CD prospective registry study analyzed 304 patients and showed the TWSTRS total score decreased by 27.4% from baseline to week 4 after treatment with abobotulinumtoxinA (mean dose, 504 U), with a 31.7%, 18.5%, and 25.3% decrease in the TWSTRS severity, disability, and pain subscale scores, respectively [28].
Bentivoglio et al. (2017) assessed long-term efficacy and safety of abobotulinumtoxinA (mean dose, 702 U) in 39 patients who cumulatively received more than 750 total treatments [29]. Mean Tsui score was 5.7 before treatment and 3.5 at maximum efficacy. A ≥2-point reduction (improvement) in Tsui score was observed in 70.9% of the treatments. The mean overall duration of clinical improvement was 93 days and the median inter-treatment interval was 131 days. Hefter et al. (2014) analyzed 568 patients and reported that 5.8% of patients had developed partial secondary treatment failure (PSTF; determined using ≥4 Tsui scores collected during treatment with ≥3 consecutive abobotulinumtoxinA injections) [30]. Incidence of PSTF was estimated to be 1.6% per year. The time of onset of PSTF varied, with one patient experiencing PSTF after 4 injections and another after 38 injections.
3.2.3. Patient-Reported Outcomes
Eighteen abobotulinumtoxinA studies conducted from 1995 to 2018 described patient-reported outcomes. Seven of these were placebo-controlled studies (covered by eight publications), two were active-controlled studies, two were pharmacoeconomic studies, two were prospective open-label studies, and two were longitudinal studies; one long-term and one real-world registry described patient-related outcomes. In total, five different tools were used to assess quality of life (QoL) in CD patients: the 36-Item Short Form Health Survey (SF-36) [12], the Patient Global Impression of Change (PGIC) [10,23], the Cervical Dystonia Impact Profile-58 (CDIP-58) [10,11], the Craniocervical Dystonia Questionnaire-24 (CDQ-24) [24,25], and the Visual Analog Scale (VAS) [9,11,12,24,25,29], as well as study-specific subjective measures of change and duration of effect.
Poewe et al. (1998) demonstrated a subjective global improvement in modified Tsui scale rating of >50% for the 1000 U-treated group at weeks 4 and 8 and for the 500 U-treated group at week 8 [11]. Wissel et al. (2001) observed that patients treated with abobotulinumtoxinA were 3.3 times more likely than those randomly assigned to placebo to experience a reduction in CD-associated pain at week 4, and were 8.5 times more likely than those receiving placebo to indicate a global improvement of disease at week 4 and 6.8 times more likely to do so at week 8 [8]. Truong et al. (2005) demonstrated a statistically significant improvement in patient-assessed change in CD signs and symptoms with abobotulinumtoxinA versus placebo at weeks 4 and 8 [9].
Laubis-Herrmann et al. (2002) observed 77% of patients who had received the recommended dose of abobotulinumtoxinA indicated “marked improvement” and 23% indicated “mild improvement,” compared with 50% and 29%, respectively, in the low-dose group [16]. In another study, 14% of patients with abobotulinumtoxinA and 25% of patients with Lanzhou BTX-A reported the improvement persisted for more than three months after the first injection. After the fifth treatment, 55% with abobotulinumtoxinA and 50% with Lanzhou BTX-A reported more than three months’ duration of improvement [19].
In another study of 362 patients, 64.4% of patients receiving abobotulinumtoxinA had improvement with a mean duration of effect of 12.1 weeks and 73.9% of onabotulinumtoxinA patients had improvement with a mean duration of effect of 11.3 weeks [31]. Electromyography-guided abobotulinumtoxinA injections in 13 patients with CD demonstrated a positive moderate correlation between patient-reported and objective improvement in CD symptoms [32]. Similarly, after four consecutive injections, 163 CD patients with a mean dose of 389 U of abobotulinumtoxinA and 44 patients with 145 U of onabotulinumtoxinA reported the duration of treatment effect was 11 ± 1.6 weeks and 10 ± 2.4 weeks, respectively [33]. No statistically significant difference was found between the two treatments.
Mordin et al. (2014) observed significant improvements in SF-36 domain scores with abobotulinumtoxinA compared with placebo for physical functioning, role-physical, bodily pain, general health, and role-emotional domains [14]. In addition, patients treated with abobotulinumtoxinA demonstrated statistically significant improvements versus placebo-treated patients on the VAS for pain severity at weeks 4 and 8. Similarly, another study reported patients treated with abobotulinumtoxinA had statistically significant improvements versus placebo on the VAS for pain severity at weeks 4, 8, and 12 [12]. Poewe et al. (2016) observed significant improvements in health-related quality of life (HRQoL) using the CDIP-58 and VAS scores for pain total score from baseline to week 4 in the abobotulinumtoxinA solution for injection and dry formulation groups compared with placebo [11]. In another study, Lew et al. (2018) observed 23.6% and 38.4% of abobotulinumtoxinA-treated patients rated their CD “much improved” or “very much improved” at weeks 2 and 4, respectively, on the PGIC compared with 6.8% of placebo-treated patients (Table 1) [10]. Although there was no statistically significant difference between abobotulinumtoxinA and placebo in the change from baseline in CDIP-58 total score at week 4, abobotulinumtoxinA demonstrated a statistically significant change from baseline in the CDIP-58 head and neck domain compared with placebo. Van den Bergh et al. (1995) reported 67% of patients had complete pain relief and 25% of patients had >50% pain relief after botulinum toxin injections [21].
Brefel-Courbon et al. (2000) evaluated patients’ global assessments of treatment effect, as well as patients’ HRQoL via the French version of the Nottingham Health Profile (NHP) [26]. More than 60% of patients indicated “moderate” or “marked” improvement for each injection. There was a significant improvement in the pain domain and a numerical improvement in the domains of social isolation and emotional behavior. However, Hefter et al. (2013) observed statistically significant improvement in CDQ-24 total score and five subscales of the CDQ-24 (stigma, emotional well-being, pain, activities of daily living, and social/family life), as well as statistically significant reductions in patient diary item scores (activities of daily living, pain, pain duration) at weeks 4 and 12 [24]. Correspondingly, patient diaries demonstrated statistically significant patient-reported improvements in day-to-day capacities and activities, pain, and duration of pain.
Haussermann et al. (2004) observed that 57 patients (63%) were still being treated with abobotulinumtoxinA after 10‒12 years of follow-up [34]. The primary reasons for discontinuation were inconvenience due to travel and costs, and side effects of therapy (Table 3). In the ANCHOR-CD real-world registry study, 43.6% of patients treated with abobotulinumtoxinA 500 U rated global improvement of change via PGIC at week 4 after cycle 1 injection [28].
3.3. Safety
A total of 21 of the 31 identified studies provided safety findings. These are summarized in Table 1, Table 2 and Table 3. The common treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) reported in abobotulinumtoxinA-treated patients in randomized controlled trials (RCTs) were dysphagia, muscular weakness, nasopharyngitis, injection site pain, neck pain, back/shoulder pain, neck muscle weakness, tiredness/fatigue, dry mouth, cold/upper respiratory tract infection, pharyngitis, and headache. A higher rate of TEAEs was observed in patients treated with onabotulinumtoxinA (69%) than with abobotulinumtoxinA (58%), though the difference was not statistically significant (p = 0.35) [15]. Dysphagia occurred more frequently with abobotulinumtoxinA than with onabotulinumtoxinA; dysphagia was reported in 16% of patients treated with abobotulinumtoxinA at a 1:3 ratio compared to onabotulinumtoxinA and 17% of patients treated with abobotulinumtoxinA at a 1:4 ratio, compared to 3% of patients treated with onabotulinumtoxinA [17]. Dysphagia did not appear to be a dose- or treatment-cycle-related adverse event [12]. Headache, fatigue, and upper respiratory tract infection occurred less frequently in patients treated with abobotulinumtoxinA [15]. Dysphonia occurred with high-dose (550 U + SD 233) treatment with abobotulinumtoxinA [20].
There were no statistically significant differences between abobotulinumtoxinA and Lanzhou BTX-A regarding occurrence of TEAEs, with dysphagia being the most common TEAE experienced across all treatment sessions in both treatment groups [19]. Botulinum toxin-naïve patients reported more TEAEs (7 of 11 patients; 64%) than did those in the non-naïve group (8 of 24 patients; 33%) [8]. Common TEAEs in observational studies generally mirrored those reported in RCTs.
3.4. Health Economic Outcomes
Four studies reported health economic outcomes. In a study by Brefel-Courbon et al. (2000; N = 21; Table 3), pharmacoeconomic data were collected from eight months before the first injection of abobotulinumtoxinA through the eight months following the first injection [26]. The mean direct medical cost of CD increased from $97 ± $29 USD per patient/month before treatment (1997 French Franc converted to 1997 USD) to $228 ± $30 USD per patient/month after treatment (p < 0.01). The increase in cost after initiating treatment was largely attributed to the cost of abobotulinumtoxinA itself ($157 ± $27 USD per patient/month), because hospital inpatient care costs were null (p < 0.01), diagnostic procedure costs were significantly decreased (p < 0.05), and other direct medical costs remained relatively similar. Taken together, investigators estimated the annual cost of abobotulinumtoxinA treatment for CD as $2752 ± $360 USD. The investigators concluded that although the cost of treatment may be considered substantial, it may only represent the first year of treatment because the clinical benefits and duration of improvement appear to increase with multiple injections.
In another study of 362 patients seen at four movement disorder clinics in Germany and the United States (Table 3), the annual cost of abobotulinumtoxinA and onabotulinumtoxinA for an individual with CD (converted from 1997 Deutschmarks to 1997 USD) was similar ($2419 ± $1038 and $2790 ± $1161 USD, respectively) [31]. However, results were inconsistent in providing sub-analyses of efficacy, safety, and specific medical costs for abobotulinumtoxinA vs. onabotulinumtoxinA in CD, precluding conclusions regarding the cost-benefit differences between the two preparations.
In a retrospective single-center cost analysis comparing patients who switched from onabotulinumtoxinA to abobotulinumtoxinA, the latter was associated with reduced median toxin reimbursement costs ($1710 vs. $988 USD, p < 0.0001), patient out-of-pocket toxin costs in case of copays or coinsurance ($285 vs. $181 USD, p < 0.0001), and the cost of unavoidable toxin waste ($165 vs. $148 USD, p < 0.0001). The data projected that treating CD with abobotulinumtoxinA approximately every 13 weeks could provide median savings of US $2844 over a period of 1 year [40].
In a cost-effectiveness analysis modeled on data from the RCT by Truong et al. (2010; Table 1) [41], abobotulinumtoxinA was compared with best supportive care (BSC) for the treatment of CD in the United Kingdom. In the base-case scenario, total incremental quality-adjusted life years (QALYs) gained from abobotulinumtoxinA compared with BSC was 0.235 per patient and the total incremental cost was UK £7160 in direct medical costs, corresponding to an incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER) of UK £30,468 per QALY gained. Several alternative scenarios were also presented, with the scenario considering indirect costs due to productivity loss implying cost-savings with abobotulinumtoxinA versus BSC. Compared with the base-case scenario, ICER per QALY gained was lower (>UK £3000) for the scenario considering a 16-week re-injection interval for abobotulinumtoxinA and the scenario considering vial sharing. Interestingly, ICER versus BSC for onabotulinumtoxinA and incobotulinumtoxinA were UK £48,978 and UK £58,554, respectively, per QALY gained in the base-case scenario.
4. Discussion
This systematic literature review identified 31 studies reporting on the safety, efficacy, patient-reported outcomes, and economic outcomes of abobotulinumtoxinA for the treatment of adults with CD.
All six of the double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trials identified demonstrated the efficacy of abobotulinumtoxinA versus placebo in patients with CD [7,8,9,10,11,12]. Relative to placebo, abobotulinumtoxinA demonstrated efficacy in both botulinum toxin-naïve patients and patients previously treated with botulinum toxin. AbobotulinumtoxinA produced significant decreases from baseline in mean TWSTRS (range, −6.0 to −15.6 ± 2.0) and mean post-treatment Tsui (range, 4.0 to 6.5) scores compared with placebo at week 4, with significant improvement sustained to week 12 (TWSTRS range −9.1 ± 1.7; Tsui mean post-treatment score 4.8). The onset of improvement with abobotulinumtoxinA versus placebo was seen as early as week 2 (TWSTRS score −5.4). Repeated administration of abobotulinumtoxinA was associated with symptomatic improvements in short- and long-term TWSTRS total and subscale scores. The recommended dosing of abobotulinumtoxinA for routine treatments is 250–1000 U; however, it was effective across a range of doses, with dose-dependent improvement observed across doses of 500 to 1000 U, but inconsistent dose-response relationships were noted for lower doses (125 U) [16].
AbobotulinumtoxinA was also shown to be effective in patients with CD in all six active-controlled clinical trials. Studies comparing abobotulinumtoxinA and onabotulinumtoxinA showed no statistically significant differences in efficacy supporting non-inferiority of abobotulinumtoxinA (onabotulinumtoxinA vs. abobotulinumtoxinA 1:3 ratio, p = 0.02; onabotulinumtoxinA vs. abobotulinumtoxinA 1:4 ratio, p = 0.01) [15,17,33]. Whereas Ranoux et al. (2002) [17] proposed that abobotulinumtoxinA (7 days longer with abobotulinumtoxinA 1:3 ratio (p = 0.58), 25 days longer with abobotulinumtoxinA 1:4 ratio (p = 0.02)) has a longer duration of action than onabotulinumtoxinA, this finding was not substantiated by other studies. Challenges around defining the bioequivalence ratio complicate interpretation of abobotulinumtoxinA and onabotulinumtoxinA comparisons [10,15,17,18]. Recent publications recommend using a conversion of 1:3 U of onabotulinumtoxinA to abobotulinumtoxinA, although conversion ratios of 1:2.5 might be equally safe and effective [15,17,18].
Patient-reported outcome data generally reflected abobotulinumtoxinA-associated improvements in disease severity. AbobotulinumtoxinA treatment was associated with statistically significant and clinically meaningful improvements across several patient-reported outcome measures, including HRQoL, pain severity, symptom severity, and impression of global change in disease (Table 1).
AbobotulinumtoxinA for the treatment of CD was generally safe and well-tolerated, with few reported severe TEAEs. The most commonly reported adverse effects of abobotulinumtoxinA across studies were dysphagia, injection site pain, muscle weakness, fatigue, and dysphonia. These events were usually mild or moderate, transient, and dose-related, and resolved spontaneously without further interventions. The frequency of TEAEs did not change substantially over time.
The cost of treatment of CD is relatively low when other cost factors, such as non-medical costs or intangible costs, are taken into account. The effect of abobotulinumtoxinA on reducing impairment and improving functional health seems to increase in magnitude and duration after the first year of treatment, suggesting a cumulative clinical effect, which could lower the total cost of treatment after the first year. The cost of treatment may be outweighed by the clinical effects and the impact of abobotulinumtoxinA on QoL. Importantly, treatment may lead to overall cost savings by reducing indirect costs due to productivity loss.
Although this systematic literature review used a robust method of identifying, grading, and summarizing evidence of the safety, efficacy, patient-reported outcomes, and economic outcomes of abobotulinumtoxinA in patients with CD, there are some limitations. The heterogeneity of the identified studies precluded meta-analysis, thus limiting the overall interpretability of the findings. In addition, some studies did not report relevant data (such as specific time points); therefore, it was not possible to compare some outcomes across studies. The limited number of patients in some studies also made it difficult to draw firm conclusions. Lastly, there were no studies comparing newer formulations of toxin A (i.e., rimabotulinumtoxinB, daxibotulinum toxin, incobotulinumtoxinA) to abobotulinumtoxinA in CD, leaving a gap in clinical knowledge. Further research is needed in large placebo- and active-controlled trials with robust reporting of study outcomes in order to provide more empirical evidence of comparative efficacy, cost-effectiveness, and dose conversion in patients with CD treated with botulinum toxin A.
5. Conclusions
Our systematic review of abobotulinumtoxinA demonstrated that routine use of abobotulinumtoxinA in CD is well-established and effective. At recommended doses, benefits were sustained for up to 8‒12 weeks, with significant improvements in TWSTRS and Tsui scores as well as pain and QoL. However, in extension studies, re-treatment was determined by a clinical need after a minimum of 12 weeks and the median time to re-treatment was 14 weeks (18 weeks for the 75th percentile). Future studies are needed to compare the beneficial effects of other botulinum toxin formulations relative to abobotulinumtoxinA in CD.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6651/12/8/470/s1, Table S1. Database search strategy, Table S2. GRADE approach on interpreting methodological quality.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.F., V.P. and M.J.; methodology, A.F., V.P. and M.J.; formal analysis, A.F., V.P. and M.J.; investigation, A.F., V.P. and M.J.; writing—original draft preparation, A.F., V.P. and M.J.; writing—review and editing, A.F., V.P. and M.J.; visualization, A.F., V.P., and M.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Funding for this systematic literature review was provided by Ipsen Biopharmaceuticals Canada, Inc., Mississauga, ON, Canada, which also paid the publication fee. The company was not involved in the concept, execution, writing and decision to publish this manuscript.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Julie O’Grady and Philip Sjostedt, BPharm, MPH (The Medicine Group, New Hope, PA, US) for providing medical writing support, which was funded by Ipsen Biopharmaceuticals Canada, Inc., Mississauga, ON, Canada in accordance with Good Publication Practice guidelines.
Conflicts of Interest
A.F. received consultancy fees from Abbott, Medtronic, Boston Scientific, Ipsen, Sunovion, and AbbVie; research support from Medtronic, Boston Scientific, University of Toronto, Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinson’s Research, and Dystonia Medical Research Foundation; speaker for Abbott, Brainlab, UCB pharma, Medtronic, Novartis, Chiesi, Boston Scientific, AbbVie, Ipsen, and Sunovion. V.P. received a scholarship from Ipsen. M.J. has no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Standards
The authors confirm that the approval of an institutional review board and patient consent were not required for this work.
Data Availability
Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no new data were created or analyzed in this study.
References
- Jinnah, H.A.; Berardelli, A.; Comella, C.; Defazio, G.; Delong, M.R.; Factor, S.; Galpern, W.R.; Hallett, M.; Ludlow, C.L.; Perlmutter, J.S.; et al. The focal dystonias: Current views and challenges for future research. Mov. Disord. 2013, 28, 926–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Defazio, G.; Jankovic, J.; Giel, J.L.; Papapetropoulos, S. Descriptive epidemiology of cervical dystonia. Tremor Other Hyperkinet. Mov. 2013, 3, tre-03-193-4374-4372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, D.M.; Blitzer, A.; Brashear, A.; Comella, C.; Dubinsky, R.; Hallett, M.; Jankovic, J.; Karp, B.; Ludlow, C.L.; Miyasaki, J.M.; et al. Assessment: Botulinum neurotoxin for the treatment of movement disorders (an evidence-based review): Report of the Therapeutics and Technology Assessment Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology 2008, 70, 1699–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albanese, A.; Abbruzzese, G.; Dressler, D.; Duzynski, W.; Khatkova, S.; Marti, M.J.; Mir, P.; Montecucco, C.; Moro, E.; Pinter, M.; et al. Practical guidance for CD management involving treatment of botulinum toxin: A consensus statement. J. Neurol. 2015, 262, 2201–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberati, A.; Altman, D.G.; Tetzlaff, J.; Mulrow, C.; Gotzsche, P.C.; Ioannidis, J.P.; Clarke, M.; Devereaux, P.J.; Kleijnen, J.; Moher, D. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: Explanation and elaboration. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schünemann, H.; Oxman, A.; Vist, G.; Higgins, J.; Deeks, J.; Glasziou, G. Interpreting Results and Drawing Conclusions. In Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Version 5.1.0. 2011. Available online: https://handbook-5-1.cochrane.org/index.htm#chapter_12/12_interpreting_results_and_drawing_conclusions.htm (accessed on 11 July 2020).
- Poewe, W.; Deuschl, G.; Nebe, A.; Feifel, E.; Wissel, J.; Benecke, R.; Kessler, K.R.; Ceballos-Baumann, A.O.; Ohly, A.; Oertel, W.; et al. What is the optimal dose of botulinum toxin A in the treatment of cervical dystonia? Results of a double blind, placebo controlled, dose ranging study using Dysport. German Dystonia Study Group. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1998, 64, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wissel, J.; Kanovsky, P.; Ruzicka, E.; Bares, M.; Hortova, H.; Streitova, H.; Jech, R.; Roth, J.; Brenneis, C.; Muller, J.; et al. Efficacy and safety of a standardised 500 unit dose of Dysport (clostridium botulinum toxin type A haemaglutinin complex) in a heterogeneous cervical dystonia population: Results of a prospective, multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel group study. J. Neurol. 2001, 248, 1073–1078. [Google Scholar]
- Truong, D.; Duane, D.D.; Jankovic, J.; Singer, C.; Seeberger, L.C.; Comella, C.L.; Lew, M.F.; Rodnitzky, R.L.; Danisi, F.O.; Sutton, J.P.; et al. Efficacy and safety of botulinum type A toxin (Dysport) in cervical dystonia: Results of the first US randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Mov. Disord. 2005, 20, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lew, M.F.; Brashear, A.; Dashtipour, K.; Isaacson, S.; Hauser, R.A.; Maisonobe, P.; Snyder, D.; Ondo, W. A 500 U/2 mL dilution of abobotulinumtoxinA vs. placebo: Randomized study in cervical dystonia. Int. J. Neurosci. 2018, 128, 619–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poewe, W.; Burbaud, P.; Castelnovo, G.; Jost, W.H.; Ceballos-Baumann, A.O.; Banach, M.; Potulska-Chromik, A.; Ferreira, J.J.; Bihari, K.; Ehler, E.; et al. Efficacy and safety of abobotulinumtoxinA liquid formulation in cervical dystonia: A randomized-controlled trial. Mov. Disord. 2016, 31, 1649–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, D.; Brodsky, M.; Lew, M.; Brashear, A.; Jankovic, J.; Molho, E.; Orlova, O.; Timerbaeva, S. Long-term efficacy and safety of botulinum toxin type A (Dysport) in cervical dystonia. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2010, 16, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jen, M.-H.; Kurth, H.; Iheanacho, I.; Dinet, J.; Gabriel, S.; Wasiak, R.; Jost, W. Improvement of SF-36 scores in cervical dystonia patients—Is there a treatment effect when evaluating subscales? Basal Ganglia 2014, 4, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mordin, M.; Masaquel, C.; Abbott, C.; Copley-Merriman, C. Factors affecting the health-related quality of life of patients with cervical dystonia and impact of treatment with abobotulinumtoxinA (Dysport): Results from a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. BMJ Open 2014, 4, e005150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odergren, T.; Hjaltason, H.; Kaakkola, S.; Solders, G.; Hanko, J.; Fehling, C.; Marttila, R.J.; Lundh, H.; Gedin, S.; Westergren, I.; et al. A double blind, randomised, parallel group study to investigate the dose equivalence of Dysport and Botox in the treatment of cervical dystonia. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1998, 64, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laubis-Herrmann, U.; Fries, K.; Topka, H. Low-dose botulinum toxin-a treatment of cervical dystonia—A double-blind, randomized pilot study. Eur. Neurol. 2002, 47, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranoux, D.; Gury, C.; Fondarai, J.; Mas, J.; Zuber, M. Respective potencies of Botox and Dysport: A double blind, randomised, crossover study in cervical dystonia. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2002, 72, 459–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, J.Y.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, H.T.; Chung, S.J.; Kim, J.M.; Cho, J.W.; Lee, J.Y.; Lee, H.N.; You, S.; Oh, E.; et al. Dysport and Botox at a ratio of 2.5:1 units in cervical dystonia: A double-blind, randomized study. Mov. Disord. 2015, 30, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, P.M.; Rodrigues, G.R.; de Oliveira, D.S.; de Souza, C.P.; Tumas, V. Comparison between Dysport and Prosigne in the treatment of cervical dystonia. Clin. Neuropharmacol. 2015, 38, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigalke, H.; Wohlfarth, K.; Irmer, A.; Dengler, R. Botulinum A toxin: Dysport improvement of biological availability. Exp. Neurol. 2001, 168, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Bergh, P.; Francart, J.; Mourin, S.; Kollmann, P.; Laterre, E.C. Five-year experience in the treatment of focal movement disorders with low-dose Dysport botulinum toxin. Muscle Nerve 1995, 18, 720–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessler, K.R.; Skutta, M.; Benecke, R. Long-term treatment of cervical dystonia with botulinum toxin A: Efficacy, safety, and antibody frequency. German Dystonia Study Group. J. Neurol. 1999, 246, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamieson, D.R.S.; Mann, A.C. Long-term follow-up by video of cervical dystonia treated with botulinum toxin. Eur. J. Neurol. 1997, 4, 443–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hefter, H.; Benecke, R.; Erbguth, F.; Jost, W.; Reichel, G.; Wissel, J. An open-label cohort study of the improvement of quality of life and pain in de novo cervical dystonia patients after injections with 500 U botulinum toxin A (Dysport). BMJ Open 2013, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hefter, H.; Kupsch, A.; Mungersdorf, M.; Paus, S.; Stenner, A.; Jost, W. A botulinum toxin A treatment algorithm for de novo management of torticollis and laterocollis. BMJ Open 2011, 1, e000196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brefel-Courbon, C.; Simonetta-Moreau, M.; More, C.; Rascol, O.; Clanet, M.; Montastruc, J.L.; Lapeyre-Mestre, M. A pharmacoeconomic evaluation of botulinum toxin in the treatment of spasmodic torticollis. Clin. Neuropharmacol. 2000, 23, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misra, V.P.; Ehler, E.; Zakine, B.; Maisonobe, P.; Simonetta-Moreau, M. Factors influencing response to Botulinum toxin type A in patients with idiopathic cervical dystonia: Results from an international observational study. BMJ Open 2012, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trosch, R.M.; Espay, A.J.; Truong, D.; Gil, R.; Singer, C.; LeWitt, P.A.; Lew, M.F.; Tagliati, M.; Adler, C.H.; Chen, J.J.; et al. Multicenter observational study of abobotulinumtoxinA neurotoxin in cervical dystonia: The ANCHOR-CD registry. J. Neurol. Sci. 2017, 376, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bentivoglio, A.R.; Di Stasio, E.; Mulas, D.; Cerbarano, M.L.; Ialongo, T.; Laurienzo, A.; Petracca, M. Long-Term Abobotulinumtoxin a treatment of cervical dystonia. Neurotox. Res. 2017, 32, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hefter, H.; Spiess, C.; Rosenthal, D. Very early reduction in efficacy of botulinum toxin therapy for cervical dystonia in patients with subsequent secondary treatment failure: A retrospective analysis. J. Neural Transm. 2014, 121, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodel, R.C.; Kirchner, A.; Koehne-Volland, R.; Kunig, G.; Ceballos-Baumann, A.; Naumann, M.; Brashear, A.; Richter, H.P.; Szucs, T.D.; Oertel, W.H. Costs of treating dystonias and hemifacial spasm with botulinum toxin A. Pharmacoeconomics 1997, 12, 695–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finsterer, J.; Fuchs, I.; Mamoli, B. Quantitative electromyography-guided botulinum toxin treatment of cervical dystonia. Clin. Neuropharmacol. 1997, 20, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi, B.; Buhr, N.; Bigalke, H.; Krampfl, K.; Dengler, R.; Kollewe, K. A long-term follow-up of botulinum toxin A in cervical dystonia. Neurol. Res. 2009, 31, 463–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haussermann, P.; Marczoch, S.; Klinger, C.; Landgrebe, M.; Conrad, B.; Ceballos-Baumann, A. Long-term follow-up of cervical dystonia patients treated with botulinum toxin A. Mov. Disord. 2004, 19, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchetti, A.; Magar, R.; Findley, L.; Larsen, J.P.; Pirtosek, Z.; Ruzicka, E.; Jech, R.; Slawek, J.; Ahmed, F. Retrospective evaluation of the dose of Dysport and BOTOX in the management of cervical dystonia and blepharospasm: The REAL DOSE study. Mov. Disord. 2005, 20, 937–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rystedt, A.; Nyholm, D.; Naver, H. Clinical experience of dose conversion ratios between 2 botulinum toxin products in the treatment of cervical dystonia. Clin. Neuropharmacol. 2012, 35, 278–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vivancos-Matellano, F.; Ybot-Gorrin, I.; Diez-Tejedor, E. A 17-year experience of abobotulinumtoxina in cervical dystonia. Int. J. Neurosci. 2012, 122, 354–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jost, W.H.; Hefter, H.; Stenner, A.; Reichel, G. Rating scales for cervical dystonia: A critical evaluation of tools for outcome assessment of botulinum toxin therapy. J. Neural Transm. (Vienna) 2013, 120, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consky, E.; Basinski, A.; Belle, L.; Ranawaya, R.; Lang, A. The Toronto Western Spasmodic Torticollis Rating Scale (TWSTRS): Assessment of validity and inter-rater reliability (abstract). Neurology 1990, 40, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trosch, R.M.; Shillington, A.C.; English, M.L.; Marchese, D. A retrospective, single-center comparative cost analysis of OnabotulinumtoxinA and AbobotulinumtoxinA for cervical dystonia treatment. J. Manag. Care Spec. Pharm. 2015, 21, 854–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthukumar, M.; Desai, K.; Abogunrin, S.; Harrower, T.; Gabriel, S.; Dinet, J. Cost-effectiveness analysis of abobotulinumtoxinA for the treatment of cervical dystonia in the United Kingdom. Clinicoecon. Outcomes Res. 2017, 9, 211–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).