From Food to Mood: Psychological and Psychiatric Impact of Diet in Bipolar Disorder
Abstract
1. Introduction
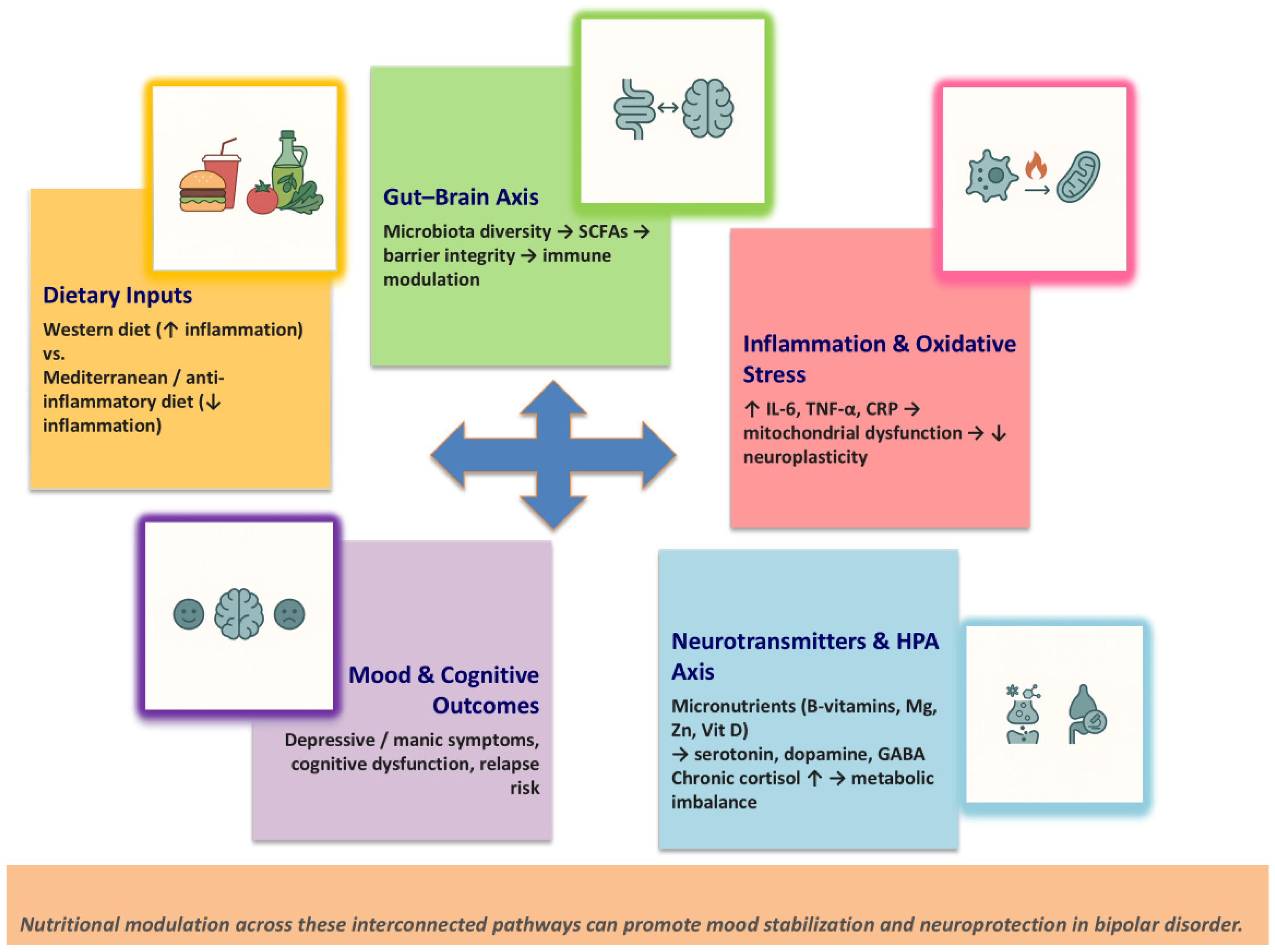
2. Nutritional Psychiatry: Mechanisms and Pathways
2.1. Gut–Brain Axis
2.2. Neuroinflammation and Oxidative Stress
2.3. Neurotransmitter Synthesis and Micronutrients
2.4. Hypothalamic–Pituitary–Adrenal Axis and Metabolic Dysregulation
3. Dietary Patterns and Bipolar Disorder
3.1. Western vs. Mediterranean Diet
3.2. Ketogenic and Low–Glycemic Index Diet
3.3. Plant-Based and Anti-Inflammatory Diets
4. Micronutrients and Mood Regulation
4.1. Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids (PUFAs)
4.2. B-Vitamins (Folate, B12, B6)
4.3. Magnesium, Zinc, Iron, and Selenium
4.4. Vitamin D
5. Eating Behaviors, Mood, and Identity in Bipolar Disorder
5.1. Emotional Eating and Mood Episodes
5.2. Disordered Eating Patterns
5.3. The Psychological Meaning of Food
5.4. Body Image and Self-Perception
5.5. Clinical Interventions
6. The Role of Nutrition in Psychological Therapy
6.1. Nutritional Psychoeducation
6.2. Integration into Psychotherapy
6.3. Motivation and Adherence
7. Comorbidities and Lifestyle Factors in Bipolar Disorder
7.1. Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity
7.2. Sleep and Circadian Rhythms
7.3. Physical Activity and Sedentary Behavior
7.4. Substance Use and Addictive Behaviors
8. Gaps in Research and Future Directions
8.1. Methodological Limitations
8.2. Need for Interdisciplinary and Personalized Approaches
8.3. Translational and Clinical Implications
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grande, I.; Berk, M.; Birmaher, B.; Vieta, E. Bipolar disorder. Lancet 2016, 387, 1561–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merikangas, K.R.; Jin, R.; He, J.-P.; Kessler, R.C.; Lee, S.; Sampson, N.A.; Viana, M.C.; Andrade, L.H.; Hu, C.; Karam, E.G.; et al. Prevalence and Correlates of Bipolar Spectrum Disorder in the World Mental Health Survey Initiative. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2011, 68, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, A.J.; Stockings, E.; Khoo, J.-P.; Erskine, H.E.; Degenhardt, L.; Vos, T.; Whiteford, H.A. The prevalence and burden of bipolar disorder: Findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Bipolar Disord. 2016, 18, 440–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leboyer, M.; Soreca, I.; Scott, J.; Frye, M.; Henry, C.; Tamouza, R.; Kupfer, D.J. Can bipolar disorder be viewed as a multi-system inflammatory disease? J. Affect. Disord. 2012, 141, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sylvia, L.G.; Ametrano, R.M.; Nierenberg, A.A. Exercise Treatment for Bipolar Disorder: Potential Mechanisms of Action Mediated through Increased Neurogenesis and Decreased Allostatic Load. Psychother. Psychosom. 2010, 79, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarris, J.; Logan, A.C.; Akbaraly, T.N.; Amminger, G.P.; Balanzá-Martínez, V.; Freeman, M.P.; Hibbeln, J.; Matsuoka, Y.; Mischoulon, D.; Mizoue, T.; et al. Nutritional medicine as mainstream in psychiatry. Lancet Psychiatry 2015, 2, 271–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marx, W.; Moseley, G.; Berk, M.; Jacka, F. Nutritional psychiatry: The present state of the evidence. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2017, 76, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbaraly, T.N.; Sabia, S.; Shipley, M.J.; Batty, G.D.; Kivimaki, M. Adherence to healthy dietary guidelines and future depressive symptoms: Evidence for sex differentials in the Whitehall II study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 97, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.S.; Hiles, S.; Bisquera, A.; Hure, A.J.; McEvoy, M.; Attia, J. A systematic review and meta-analysis of dietary patterns and depression in community-dwelling adults. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 99, 181–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parletta, N.; Milte, C.M.; Meyer, B.J. Nutritional modulation of cognitive function and mental health. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2013, 24, 725–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, C.R.; Osadchiy, V.; Kalani, A.; Mayer, E.A. The Brain-Gut-Microbiome Axis. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 6, 133–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Kong, L.; Huang, H.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, D.; Jiang, J.; Shen, Y.; Xi, C.; Lai, J.; Ng, C.H.; et al. Gut Microbiota—A Potential Contributor in the Pathogenesis of Bipolar Disorder. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 830748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berk, M.; Kapczinski, F.; Andreazza, A.; Dean, O.; Giorlando, F.; Maes, M.; Yücel, M.; Gama, C.; Dodd, S.; Dean, B.; et al. Pathways underlying neuroprogression in bipolar disorder: Focus on inflammation, oxidative stress and neurotrophic factors. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2011, 35, 804–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Pinilla, F. Brain foods: The effects of nutrients on brain function. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2008, 9, 568–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calder, P.C. Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Inflammatory Processes. Nutrients 2010, 2, 355–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, B.J.; Rucklidge, J.J.; Romijn, A.; McLeod, K. The emerging field of nutritional mental health: Inflammation, the microbiome, oxidative stress, and mitochondrial function. Clin. Psychol. Sci. 2015, 3, 964–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, S.N. Folate and depression—A neglected problem. J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 2007, 32, 80–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firth, J.; Teasdale, S.B.; Allott, K.; Siskind, D.; Marx, W.; Cotter, J.; Veronese, N.; Schuch, F.; Smith, L.; Solmi, M.; et al. The efficacy and safety of nutrient supplements in the treatment of mental disorders: A meta-review of meta-analyses of randomized controlled trials. World Psychiatry 2019, 18, 308–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoll, A.L.; Severus, W.E.; Freeman, M.P.; Rueter, S.; Zboyan, H.A.; Diamond, E.; Cress, K.K.; Marangell, L.B. Omega 3 fatty acids in bipolar disorder: A preliminary double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1999, 56, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appleton, J. The Gut-Brain Axis: Influence of Microbiota on Mood and Mental Health. Integr. Med. 2018, 17, 28–32. [Google Scholar]
- Obi-Azuike, C.; Ebiai, R.; Gibson, T.; Hernandez, A.; Khan, A.; Anugwom, G.; Urhi, A.; Prasad, S.; Souabni, S.A.; Oladunjoye, F. A systematic review on gut–brain axis aberrations in bipolar disorder and methods of balancing the gut microbiota. Brain Behav. 2023, 13, e3037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickerson, F.; Adamos, M.; Katsafanas, E.; Khushalani, S.; Origoni, A.; Savage, C.; Schweinfurth, L.; Stallings, C.; Sweeney, K.; Goga, J.; et al. Adjunctive probiotic microorganisms to prevent rehospitalization in patients with acute mania: A randomized controlled trial. Bipolar Disord. 2018, 20, 614–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reininghaus, E.Z.; Wetzlmair, L.-C.; Fellendorf, F.T.; Platzer, M.; Queissner, R.; Birner, A.; Pilz, R.; Hamm, C.; Maget, A.; Koidl, C.; et al. The Impact of Probiotic Supplements on Cognitive Parameters in Euthymic Individuals with Bipolar Disorder: A Pilot Study. Neuropsychobiology 2020, 79, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansur, R.B.; Santos, C.M.; Rizzo, L.B.; Cunha, G.R.; Asevedo, E.; Noto, M.N.; Pedrini, M.; Zeni, M.; Cordeiro, Q.; McIntyre, R.S.; et al. Inter-relation between brain-derived neurotrophic factor and antioxidant enzymes in bipolar disorder. Bipolar Disord. 2016, 18, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, M.E.; Teixeira, A.L. Neuroinflammation in Mood Disorders: Role of Regulatory Immune Cells. Neuroimmunomodulation 2021, 28, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yirmiya, R.; Rimmerman, N.; Reshef, R. Depression as a Microglial Disease. Trends Neurosci. 2015, 38, 637–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapczinski, N.S.; Mwangi, B.; Cassidy, R.M.; Librenza-Garcia, D.; Bermudez, M.B.; Kauer-Sant’anna, M.; Kapczinski, F.; Passos, I.C. Neuroprogression and illness trajectories in bipolar disorder. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2017, 17, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazza, M.; Pomponi, M.; Janiri, L.; Bria, P.; Mazza, S. Omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants in neurological and psychiatric diseases: An overview. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2007, 31, 12–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupczyk, D.; Bilski, R.; Szeleszczuk, Ł.; Mądra-Gackowska, K.; Studzińska, R. The Role of Diet in Modulating Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Rheumatoid Arthritis, Ankylosing Spondylitis, and Psoriatic Arthritis. Nutrients 2023, 17, 1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gigante, A.D.; Bond, D.J.; Lafer, B.; Lam, R.W.; Young, L.T.; Yatham, L.N. Brain glutamate levels measured by magnetic resonance spectroscopy in patients with bipolar disorder: A meta-analysis. Bipolar Disord. 2012, 14, 478–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges-Vieira, J.G.; Cardoso, C.K.S. Efficacy of B-vitamins and vitamin D therapy in improving depressive and anxiety disorders: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Nutr. Neurosci. 2023, 26, 187–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAulay, C.; Mond, J.; Outhred, T.; Malhi, G.S.; Touyz, S. Eating disorder features in bipolar disorder: Clinical implications. J. Ment. Health 2023, 32, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonsson, B.H.; Orhan, F.; Bruno, S.; Oliveira, A.O.; Sparding, T.; Landen, M.; Sellgren, C.M. Serum concentration of zinc is elevated in clinically stable bipolar disorder patients. Brain Behav. 2022, 12, e2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lombardo, G.; Enache, D.; Gianotti, L.; Schatzberg, A.F.; Young, A.H.; Pariante, C.M.; Mondelli, V. Baseline cortisol and the efficacy of antiglucocorticoid treatment in mood disorders: A meta-analysis. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2019, 110, 104420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galvez, J.F.; Bauer, I.E.; Sanches, M.; Wu, H.E.; Hamilton, J.E.; Mwangi, B.; Kapczinski, F.P.; Zunta-Soares, G.; Soares, J.C. Shared clinical associations between obesity and impulsivity in rapid cycling bipolar disorder: A systematic review. J. Affect. Disord. 2014, 168, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, F.C.; Oliveira, M.; Berk, M.; Brietzke, E.; Jacka, F.N.; Lafer, B. Nutrition and bipolar disorder: A systematic review. Nutr. Neurosci. 2023, 26, 637–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacka, F.N. Nutritional Psychiatry: Where to Next? eBioMedicine 2017, 17, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordain, L.; Eaton, S.B.; Sebastian, A.; Mann, N.; Lindeberg, S.; Watkins, B.A.; O’Keefe, J.H.; Brand-Miller, J. Origins and evolution of the Western diet: Health implications for the 21st century. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 81, 341–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Donoso, C.; Sánchez-Villegas, A.; Martínez-González, M.A.; Gea, A.; de Deus Mendonça, R.; Lahortiga-Ramos, F.; Bes-Rastrollo, M. Ultra-Processed Food Consumption and the Incidence of Depression in a Mediterranean Cohort: The SUN Project. Eur. J. Nutr. 2020, 59, 1093–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbaraly, T.N.; Shipley, M.J.; Ferrie, J.E.; Virtanen, M.; Lowe, G.; Hamer, M.; Kivimaki, M. Long-term Adherence to Healthy Dietary Guidelines and Chronic Inflammation in the Prospective Whitehall II Study. Am. J. Med. 2015, 128, 152–160.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altomare, R.; Cacciabaudo, F.; Damiano, G.; Palumbo, V.D.; Gioviale, M.C.; Bellavia, M.; Tomasello, G.; Monte, A.I.L. The Mediterranean Diet: A History of Health. Iran. J. Public Health 2013, 42, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sofi, F.; Cesari, F.; Abbate, R.; Gensini, G.F.; Casini, A. Adherence to Mediterranean diet and health status: Meta-analysis. BMJ 2008, 337, a1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardea-Resendez, M.; Winham, S.J.; Romo-Nava, F.; Cuellar-Barboza, A.; Clark, M.M.; Andreazza, A.C.; Cabello-Arreola, A.; Veldic, M.; Bond, D.J.; Singh, B.; et al. Quantification of diet quality utilizing the rapid eating assessment for participants-shortened version in bipolar disorder: Implications for prospective depression and cardiometabolic studies. J. Affect. Disord. 2022, 310, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parletta, N.; Zarnowiecki, D.; Cho, J.; Wilson, A.; Bogomolova, S.; Villani, A.; Itsiopoulos, C.; Niyonsenga, T.; Blunden, S.; Meyer, B.; et al. A Mediterranean-style dietary intervention supplemented with fish oil improves diet quality and mental health in people with depression: A randomized controlled trial (HELFIMED). Nutr. Neurosci. 2019, 22, 474–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bostock, E.C.S.; Kirkby, K.C.; Taylor, B.V.M. The Current Status of the Ketogenic Diet in Psychiatry. Front. Psychiatry 2017, 8, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaini, G.; Andrews, T.; Lima, C.N.; Benevenuto, D.; Streck, E.L.; Quevedo, J. Mitochondrial dysfunction as a critical event in the pathophysiology of bipolar disorder. Mitochondrion 2021, 57, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Needham, N.; Campbell, I.H.; Grossi, H.; Kamenska, I.; Rigby, B.P.; Simpson, S.A.; McIntosh, E.; Bahuguna, P.; Meadowcroft, B.; Creasy, F.; et al. Pilot study of a ketogenic diet in bipolar disorder. BJPsych Open 2023, 9, e176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darand, M.; Amirinejad, A.; Salehi-Abargouei, A.; Davies, I.G.; Mirzaei, M.; Mazidi, M.; Khayyatzadeh, S.S. The association between dietary insulin index and load with mental health. BMC Psychol. 2022, 10, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breymeyer, K.L.; Lampe, J.W.; McGregor, B.A.; Neuhouser, M.L. Subjective mood and energy levels of healthy weight and overweight/obese healthy adults on high-and low-glycemic load experimental diets. Appetite 2016, 107, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheatham, R.A.; Roberts, S.B.; Das, S.K.; Gilhooly, C.H.; Golden, J.K.; Hyatt, R.; Lerner, D.; Saltzman, E.; Lieberman, H.R. Long-term effects of provided low and high glycemic load low energy diets on mood and cognition. Physiol. Behav. 2009, 98, 374–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Calkin, C.V.; Ruzickova, M.; Uher, R.; Hajek, T.; Slaney, C.M.; Garnham, J.S.; O’DOnovan, M.C.; Alda, M. Insulin resistance and outcome in bipolar disorder. Br. J. Psychiatry 2015, 206, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, M.S.; Calle, M.; Fernandez, M.L. Healthy plant-based diets improve dyslipidemias, insulin resistance, and inflammation in metabolic syndrome. A narrative review. Adv. Nutr. Int. Rev. J. 2023, 14, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calder, P.C. Omega-3 fatty acids and inflammatory processes: From molecules to man. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2017, 45, 1105–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kavyani, Z.; Musazadeh, V.; Fathi, S.; Faghfouri, A.H.; Dehghan, P.; Sarmadi, B. Efficacy of the omega-3 fatty acids supplementation on inflammatory biomarkers: An umbrella meta-analysis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 111, 109104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balanzá-Martínez, V.; Fries, G.R.; Colpo, G.D.; Silveira, P.P.; Portella, A.K.; Tabarés-Seisdedos, R.; Kapczinski, F. Therapeutic use of omega-3 fatty acids in bipolar disorder. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2011, 11, 1029–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes-Da-Costa, S.; Fernandéz-Pérez, I.; Borras, R.; Lopez, N.; Rivas, Y.; Ruiz, V.; Pons-Cabrera, M.T.; Giménez-Palomo, A.; Anmella, G.; Valentí, M.; et al. Is a vegetarian diet beneficial for bipolar disorder? Relationship between dietary patterns, exercise and pharmacological treatments with metabolic syndrome and course of disease in bipolar disorder. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2024, 150, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niklewicz, A.; Hannibal, L.; Warren, M.; Ahmadi, K.R. A systematic review and meta-analysis of functional vitamin B12 status among adult vegans. Nutr. Bull. 2024, 49, 463–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adan, R.A.; van der Beek, E.M.; Buitelaar, J.K.; Cryan, J.F.; Hebebrand, J.; Higgs, S.; Schellekens, H.; Dickson, S.L. Nutritional psychiatry: Towards improving mental health by what you eat. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2019, 29, 1321–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholipour, D.; Shahraki, M.; Shamsi-Goushki, A. Supplementation of Omega-3 Increases Serum Levels of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor and Decreases Depression Status in Patients with Bipolar Disorder: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2025, 38, e70076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholipour, D.; Shahraki, M.; Saravani, M.; Payandeh, A.; Eslahi, H. The Effect of Omega-3 Supplementation on Serum Levels of Antioxidant Status in Patients with Bipolar Disease: A Randomized Double-blind Controlled Clinical Trial. Basic Clin. Neurosci. J. 2024, 15, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppen, A.; Bolander-Gouaille, C. Treatment of depression: Time to consider folic acid and vitamin B12. J. Psychopharmacol. 2005, 19, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, Y.-C.; Chou, L.-S.; Lin, C.-H.; Wu, H.-C.; Li, D.-J.; Tseng, P.-T. Serum folate levels in bipolar disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Psychiatry 2019, 19, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Koning, E.J.; Van der Zwaluw, N.L.; Van Wijngaarden, J.P.; Sohl, E.; Brouwer-Brolsma, E.M.; Van Marwijk, H.W.J.; Enneman, A.W.; Swart, K.M.A.; Van Dijk, S.C.; Ham, A.C.; et al. Effects of Two-Year Vitamin B12 and Folic Acid Supplementation on Depressive Symptoms and Quality of Life in Older Adults with Elevated Homocysteine Concentrations: Additional Results from the B-PROOF Study, an RCT. Nutrients 2016, 8, 748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Sun, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Wen, H.; Chen, W.-J.; Zhu, S. Structural insights into the diverse actions of magnesium on NMDA receptors. Neuron 2025, 113, 1006–1018.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nechifor, M. Magnesium and Zinc in Bipolar Disorders. Biomed. Pharmacol. J. 2023, 16, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mlyniec, K. Interaction between Zinc, GPR39, BDNF and Neuropeptides in Depression. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2021, 19, 2012–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rog, J.; Łobejko, Ł.; Hordejuk, M.; Marciniak, W.; Derkacz, R.; Kiljańczyk, A.; Matuszczak, M.; Lubiński, J.; Nesterowicz, M.; Żendzian-Piotrowska, M.; et al. Pro/antioxidant status and selenium, zinc and arsenic concentration in patients with bipolar disorder treated with lithium and valproic acid. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2024, 17, 1441575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; You, L.; Zhang, J.; Chang, Y.-Z.; Yu, P. Brain Iron Metabolism, Redox Balance and Neurological Diseases. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyles, D.W. Vitamin D: Brain and Behavior. JBMR Plus 2021, 5, e10419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasoń, W.; Jantas, D.; Leśkiewicz, M.; Regulska, M.; Basta-Kaim, A. The Vitamin D Receptor as a Potential Target for the Treatment of Age-Related Neurodegenerative Diseases Such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Diseases: A Narrative Review. Cells 2023, 12, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cereda, G.; Enrico, P.; Ciappolino, V.; Delvecchio, G.; Brambilla, P. The role of vitamin D in bipolar disorder: Epidemiology and influence on disease activity. J. Affect. Disord. 2021, 278, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabi, A.; Nasrallah, D.; Mohsen, S.; Abugharbieh, L.; Al-Hashimi, D.; AlMass, S.; Albasti, S.; Al-Ajmi, S.A.; Khan, M.N.; Zughaier, S.M. Association between Serum Vitamin D Status and Circadian Syndrome: A Cross-Sectional Study. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patrick, R.P.; Ames, B.N. Vitamin D hormone regulates serotonin synthesis. Part 1: Relevance for autism. FASEB J. 2014, 28, 2398–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yakovleva, Y.V.; Kasyanov, E.D.; Mazo, G.E.; Виктoрoвна, Я.Я.; Дмитриевич, К.Е. Prevalence of eating disorders in patients with bipolar disorder: A scoping review of the literature. Consort. Psychiatr. 2023, 4, 91–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McElroy, S.L.; Crow, S.; Blom, T.J.; Cuellar-Barboza, A.B.; Prieto, M.L.; Veldic, M.; Winham, S.J.; Bobo, W.V.; Geske, J.; Seymour, L.R.; et al. Clinical features of bipolar spectrum with binge eating behaviour. J. Affect. Disord. 2016, 201, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujioka, Y.; Kawai, K.; Endo, K.; Ishibashi, M.; Iwade, N.; Tuerde, D.; Kaibuchi, K.; Yamashita, T.; Yamanaka, A.; Katsuno, M.; et al. Stress-impaired reward pathway promotes distinct feeding behavior patterns. Front. Neurosci. 2024, 18, 1349366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, M.; Prakash, B.A.; Zhao, L.; Ni, G.; Ru, Y.; Vasudevan, S.R. Circadian rhythms in metabolism and mental health: A reciprocal regulatory network with implications for metabolic and neuropsychiatric disorders. Curr. Opin. Physiol. 2025, 45, 100836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frigerio, S.; Strawbridge, R.; Young, A.H. The impact of caffeine consumption on clinical symptoms in patients with bipolar disorder: A systematic review. Bipolar Disord. 2021, 23, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berghorst, L.H.; Kumar, P.; Greve, D.N.; Deckersbach, T.; Ongur, D.; Dutra, S.J.; Pizzagalli, D.A. Stress and reward processing in bipolar disorder: A functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Bipolar Disord. 2016, 18, 602–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, K.A.; Al-Mugaddam, F.; Sugathan, S.; Saseedharan, P.; Jouini, T.; Elamin, M.E.; Moselhy, H.; El-Gabry, D.A.; Arnone, D.; Karam, S.M. Decreased acylated and total ghrelin levels in bipolar disorder patients recovering from a manic episode. BMC Psychiatry 2022, 22, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McElroy, S.L.; Crow, S.; Blom, T.J.; Biernacka, J.M.; Winham, S.J.; Geske, J.; Cuellar-Barboza, A.B.; Bobo, W.V.; Prieto, M.L.; Veldic, M.; et al. Prevalence and correlates of DSM-5 eating disorders in patients with bipolar disorder. J. Affect. Disord. 2016, 191, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fornaro, M.; Daray, F.M.; Hunter, F.; Anastasia, A.; Stubbs, B.; De Berardis, D.; Shin, J.I.; Husain, M.I.; Dragioti, E.; Fusar-Poli, P.; et al. The prevalence, odds and predictors of lifespan comorbid eating disorder among people with a primary diagnosis of bipolar disorders, and vice-versa: Systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Affect. Disord. 2021, 280, 409–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdulkadir, M.; Hübel, C.; Herle, M.; Loos, R.J.F.; Breen, G.; Bulik, C.M.; Micali, N. Eating disorder symptoms and their associations with anthropometric and psychiatric polygenic scores. Eur. Eat. Disord. Rev. 2022, 30, 221–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, K.; Woo, J.; Timmins, V.; Collins, J.; Islam, A.; Newton, D.; Goldstein, B.I. Binge eating and emotional eating behaviors among adolescents and young adults with bipolar disorder. J. Affect. Disord. 2016, 195, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koning, E.; Vorstman, J.; McIntyre, R.S.; Brietzke, E. Characterizing eating behavioral phenotypes in mood disorders: A narrative review. Psychol. Med. 2022, 52, 2885–2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.; Kauffman, B.Y.; Rosenfield, D.; Smits, J.A.J.; Zvolensky, M.J. Emotion dysregulation and body mass index: The explanatory role of emotional eating among adult smokers. Eat. Behav. 2019, 33, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, M.; Siddiqi, N.; Ahmad, B.; Afsheen, N.; Aslam, F.; Ali, A.; Ayesha, R.; Bryant, M.; Holt, R.; Khalid, H.; et al. Prevalence of Overweight and Obesity in People With Severe Mental Illness: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 769309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepúlveda-Lizcano, L.; Arenas-Villamizar, V.V.; Jaimes-Duarte, E.B.; García-Pacheco, H.; Paredes, C.S.; Bermúdez, V.; Rivera-Porras, D. Metabolic Adverse Effects of Psychotropic Drug Therapy: A Systematic Review. Eur. J. Investig. Health Psychol. Educ. 2023, 13, 1505–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Kan, L.; Zhang, X.; Li, M.; Wang, M.; Cao, Y. Association between body mass index and cognitive impairment in Chinese older adults. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1255101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lengvenyte, A.; Aouizerate, B.; Aubin, V.; Loftus, J.; Marlinge, E.; Belzeaux, R.; Dubertret, C.; Gard, S.; Haffen, E.; Schwan, R.; et al. Violent suicide attempt history in elderly patients with bipolar disorder: The role of sex, abdominal obesity, and verbal memory: Results from the FACE-BD cohort (FondaMental Advanced center of Expertise for Bipolar Disorders). J. Affect. Disord. 2022, 296, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdez-Aguilar, M.; Vazquez-Arevalo, R.; López-Aguilar, X.; Martínez, A.O.R.; Rosinska, M.; Mancilla-Díaz, J.M. Online multidisciplinary treatment of binge eating disorder in people with high weight: A case series study. J. Eat. Disord. 2023, 11, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liquori, S.; Faidutti, G.; Garzitto, M.; Saetti, L.; Bendotti, M.; Balestrieri, M. Efficacy of a Group Psychoeducation Treatment in Binge Eating Disorder: An Open-Label Study. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 822282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.-Y.; Patterson, J.S.; Tang, R.; Chi, J.; Ho, N.B.P.; Sears, D.D.; Gu, H. Metabolomic profiles impacted by brief mindfulness intervention with contributions to improved health. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 27022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller-Stierlin, A.S.; Cornet, S.; Peisser, A.; Jaeckle, S.; Lehle, J.; Moerkl, S.; Teasdale, S.B. Implications of Dietary Intake and Eating Behaviors for People with Serious Mental Illness: A Qualitative Study. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocks, T.; Teasdale, S.B.; Fehily, C.; Young, C.; Howland, G.; Kelly, B.; Dawson, S.; Jacka, F.; Dunbar, J.A.; O’nEil, A. Effectiveness of nutrition and dietary interventions for people with serious mental illness: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Med. J. Aust. 2022, 217, S7–S21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simjanoski, M.; Patel, S.; De Boni, R.; Balanzá-Martínez, V.; Frey, B.N.; Minuzzi, L.; Kapczinski, F.; Cardoso, T.d.A. Lifestyle interventions for bipolar disorders: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2023, 152, 105257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, V.; Cooper, C.C. The Role of Food and Nutrition in Treating Bipolar Disorder: A Narrative Review for The Allied Health Professions. Med. Res. Arch. 2024, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walburg, F.S.; van Meijel, B.; Hoekstra, T.; Kol, J.; Pape, L.M.; de Joode, J.W.; van Tulder, M.; Adriaanse, M. Effectiveness of a Lifestyle Intervention for People With a Severe Mental Illness in Dutch Outpatient Mental Health Care. JAMA Psychiatry 2023, 80, 886–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zauszniewski, J.A.; Burant, C.J.; Almutairi, R.; Juratovac, E.; Sweetko, J.S.; Jeanblanc, A.; Larsen, C.; Colon-Zimmerman, K.; Sajatovic, M. Family Caregivers of Persons with Bipolar Disorder: Caregiver Demographics and Need and Preference for Intervention. Issues Ment. Health Nurs. 2024, 45, 1132–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urhan, M.; Cengisiz, C.; Türk, M.; Akanalçı, C. Can mindful eating be a psycho-marker of obesity in bipolar disorder? Nutr. Hosp. 2024, 41, 1082–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, H.; Aouad, P.; Le, A.; Marks, P.; Maloney, D.; Touyz, S.; Maguire, S. Psychotherapies for eating disorders: Findings from a rapid review. J. Eat. Disord. 2023, 11, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sylvia, L.G.; Pegg, S.L.; Dufour, S.C.; Janos, J.A.; Bernstein, E.E.; Chang, W.C.; Hall, N.E.; Ellard, K.K.; Nierenberg, A.A.; Deckersbach, T. Pilot study of a lifestyle intervention for bipolar disorder: Nutrition exercise wellness treatment (NEW Tx). J. Affect. Disord. 2019, 250, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saunders, E.F.H.; Mukherjee, D.; Myers, T.; Wasserman, E.; Hameed, A.; Krishnamurthy, V.B.; MacIntosh, B.; Domenichiello, A.; Ramsden, C.E.; Wang, M. Adjunctive dietary intervention for bipolar disorder: A randomized, controlled, parallel-group, modified double-blinded trial of a high n-3 plus low n-6 diet. Bipolar Disord. 2022, 24, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teasdale, S.B.; Tripodi, E.; Harman, A.; Plain, J.; Burrows, T.L. Exploring the role of dietitians in mental health services and the perceived barriers and enablers to service delivery: A cross-sectional study. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2023, 36, 1771–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crump, C.; Sundquist, K.; Winkleby, M.A.; Sundquist, J. Comorbidities and Mortality in Bipolar Disorder. JAMA Psychiatry 2013, 70, 931–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vancampfort, D.; Vansteelandt, K.; Correll, C.U.; Mitchell, A.J.; De Herdt, A.; Sienaert, P.; Probst, M.; De Hert, M. Metabolic Syndrome and Metabolic Abnormalities in Bipolar Disorder: A Meta-Analysis of Prevalence Rates and Moderators. Am. J. Psychiatry 2013, 170, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boccara, E.; Golan, S.; Beeri, M.S. The association between regional adiposity, cognitive function, and dementia-related brain changes: A systematic review. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1160426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.M.; Lin, C.-C.; Chen, J.-Y.; Chen, T.T.; Su, T.-P.; Chou, P. Association of Weight Gain and Metabolic Syndrome in Patients Taking Clozapine. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2010, 72, 751–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psara, E.; Papadopoulou, S.K.; Mentzelou, M.; Voulgaridou, G.; Vorvolakos, T.; Apostolou, T.; Giaginis, C. Omega-3 Fatty Acids for the Treatment of Bipolar Disorder Symptoms: A Narrative Review of the Current Clinical Evidence. Mar. Drugs 2025, 23, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonon, A.C.; Nexha, A.; da Silva, M.M.; Gomes, F.A.; Hidalgo, M.P.; Frey, B.N. Sleep and circadian disruption in bipolar disorders: From psychopathology to digital phenotyping in clinical practice. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2024, 78, 654–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottlieb, J.F.; Benedetti, F.; Geoffroy, P.A.; Henriksen, T.E.G.; Lam, R.W.; Murray, G.; Phelps, J.; Sit, D.; Swartz, H.A.; Crowe, M.; et al. The chronotherapeutic treatment of bipolar disorders: A systematic review and practice recommendations from the ISBD task force on chronotherapy and chronobiology. Bipolar Disord. 2019, 21, 741–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wada, K.; Yata, S.; Akimitsu, O.; Krejci, M.; Noji, T.; Nakade, M.; Takeuchi, H.; Harada, T. A tryptophan-rich breakfast and exposure to light with low color temperature at night improve sleep and salivary melatonin level in Japanese students. J. Circadian Rhythm. 2013, 11, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vancampfort, D.; Firth, J.; Schuch, F.B.; Rosenbaum, S.; Mugisha, J.; Hallgren, M.; Probst, M.; Ward, P.B.; Gaughran, F.; De Hert, M.; et al. Sedentary behavior and physical activity levels in people with schizophrenia, bipolar disorder and major depressive disorder: A global systematic review and meta-analysis. World Psychiatry 2017, 16, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Liu, F.; Ding, F.; Ma, X.; Zhu, Y. Exercise interventions for depressive, manic, and anxiety symptoms in bipolar disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Psychiatry 2025, 16, 1648008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhoury, M.; Eid, F.; El Ahmad, P.; Khoury, R.; Mezher, A.; El Masri, D.; Haddad, Z.; Zoghbi, Y.; Ghayad, L.M.; Sleiman, S.F.; et al. Exercise and Dietary Factors Mediate Neural Plasticity Through Modulation of BDNF Signaling. Brain Plast. 2022, 8, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCartan, C.J.; Yap, J.; Best, P.; Breedvelt, J.; Breslin, G.; Firth, J.; Tully, M.A.; Webb, P.; White, C.; Gilbody, S.; et al. Factors that influence participation in physical activity for people with bipolar disorder: A synthesis of qualitative evidence. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2024, 2024, CD013557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preuss, U.W.; Schaefer, M.; Born, C.; Grunze, H. Bipolar Disorder and Comorbid Use of Illicit Substances. Medicina 2021, 57, 1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperry, S.H.; Stromberg, A.R.; Murphy, V.A.; Lasagna, C.A.; McInnis, M.G.; Menkes, M.W.; Yocum, A.K.; Tso, I.F. Longitudinal Interplay Between Alcohol Use, Mood, and Functioning in Bipolar Spectrum Disorders. JAMA Netw. Open 2024, 7, e2415295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zare, M.; Shateri, Z.; Shakeri, M.; Nouri, M.; Zare, S.; Sarbakhsh, P.; Eftekhari, M.H.; Gargari, B.P. The association between diet quality indices and oxidative stress biomarkers in male footballers and healthy active controls. BMC Res. Notes 2024, 17, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balmori, A.; de la Puente, M.P. Importance of Nutrition Care During the Addiction Recovery Process. Psychoactives 2025, 4, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudd, M.K.; Angelotta, C. Nutrition Education in Psychiatry Residency Programs: A Call to Action. J. Nutr. 2024, 154, 2431–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtenstein, A.H.; Petersen, K.; Barger, K.; Hansen, K.E.; Anderson, C.A.M.; Baer, D.J.; Lampe, J.W.; Rasmussen, H.; Matthan, N.R. Perspective: Design and Conduct of Human Nutrition Randomized Controlled Trials. Adv. Nutr. Int. Rev. J. 2020, 12, 4–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marx, W.; Visser, M.; Wallace, C.; Jacka, F.N.; Bayes, J.; Francis, H.; Opie, R.; Hockey, M.; Teasdale, S.B.; Villegas, A.S.; et al. Methodological and reporting recommendations for clinical trials in Nutritional Psychiatry: Guidelines from the International Society for Nutritional Psychiatry Research. Br. J. Nutr. 2024, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatoum, A.H.; Burton, A.L.; Berry, S.L.; Abbott, M.J. Psychometric properties of self-report measures of eating disorder cognitions: A systematic review. J. Eat. Disord. 2023, 11, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansour, S.; Alkhaaldi, S.M.I.; Sammanasunathan, A.F.; Ibrahim, S.; Farhat, J.; Al-Omari, B. Precision Nutrition Unveiled: Gene–Nutrient Interactions, Microbiota Dynamics, and Lifestyle Factors in Obesity Management. Nutrients 2024, 16, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansari, F.; Neshat, M.; Pourjafar, H.; Jafari, S.M.; Samakkhah, S.A.; Mirzakhani, E. The role of probiotics and prebiotics in modulating of the gut-brain axis. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1173660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ee, C.; Lake, J.; Firth, J.; Hargraves, F.; de Manincor, M.; Meade, T.; Marx, W.; Sarris, J. An integrative collaborative care model for people with mental illness and physical comorbidities. Int. J. Ment. Health Syst. 2020, 14, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mentzelou, M.; Voulgaridou, G.; Papadimitriou, K.; Alexatou, O.; Deligiannidou, E.-G.; Serdari, A.; Papadopoulou, S.K.; Psara, E.; Tsourouflis, G.; Giaginis, C. An Interventional Study Exploring the Effects of Nutritional Psychoeducation on Emotional Eating After 3 Months. Med. Sci. 2025, 13, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrows, T.; Teasdale, S.; Rocks, T.; Whatnall, M.; Schindlmayr, J.; Plain, J.; Roberton, M.; Latimer, G.; Harris, D.; Forsyth, A. Cost effectiveness of dietary interventions for individuals with mental disorders: A scoping review of experimental studies. Nutr. Diet. 2022, 79, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, C.-H.; Lee, T.; Lee, J.-B.; Seo, J.Y.; Jee, H.-J.; Son, S.; An, H.; Kim, L.; Lee, H.-J. Effectiveness of a Smartphone App With a Wearable Activity Tracker in Preventing the Recurrence of Mood Disorders: Prospective Case-Control Study. JMIR Ment. Health 2020, 7, e21283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Dietary Pattern | Core Characteristics | Primary Biological Mechanisms | Observed or Proposed Effects in BD | BD-Specific vs. Extrapolated Evidence | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Western diet | High in ultra-processed foods, refined carbohydrates, saturated and trans fats; low in fiber and antioxidants. | ↑ Systemic inflammation, ↑ oxidative stress, gut dysbiosis, insulin resistance. | Associated with higher CRP, IL-6, TNF-α; greater mood instability, metabolic comorbidities, and poorer cognitive outcomes. | Extrapolated (general population, MDD, metabolic studies) | [38,39,40] |
| Mediterranean Diet | Rich in fruits, vegetables, legumes, nuts, olive oil, and fish; low in red and processed meat. | ↓ Neuroinflammation and oxidative stress; improved mitochondrial and endothelial function; modulation of gut microbiota. | Linked to lower depressive symptoms, improved cognition, reduced relapse risk, and better metabolic profile. | Partially BD-specific (some BD data) + extrapolated evidence | [41,42,43,44] |
| Ketogenic Diet | High-fat, moderate-protein, low-carbohydrate; induces nutritional ketosis. | ↑ Mitochondrial efficiency; ↓ oxidative stress; modulation of GABA/glutamate balance and HPA axis. | Improved mood stability, cognition, and weight control in small open-label studies; long-term safety yet to be established. | BD-specific (small open-label trials) | [45,46,47] |
| Low-Glycemic Index Diet | Focuses on complex carbohydrates, low refined sugars, and stable postprandial glucose. | Stabilization of insulin and glucose metabolism; reduced oxidative and inflammatory load. | Associated with fewer mood fluctuations, improved fatigue and energy levels, particularly in insulin-resistant patients. | Extrapolated (metabolic/overweight samples) | [48,49,50] |
| Plant-Based/Anti-Inflammatory Diets | Emphasis on fruits, vegetables, legumes, whole grains, polyphenol-rich and omega-3-rich foods. | Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory action; modulation of gut microbiota; ↑ BDNF expression. | Linked to lower depressive symptoms, improved metabolic indicators (BMI, lipids), and enhanced psychosocial functioning. | Partially BD-specific (few studies) + extrapolated evidence | [52,53,54,55,56] |
| Micronutrient | Primary Biological Mechanisms | Key Findings/Evidence in BD | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Omega-3 fatty acids (EPA, DHA) | Anti-inflammatory effects; modulation of serotonergic and dopaminergic transmission; stabilization of neuronal membranes; reduction in oxidative stress | Lower omega-3 levels associated with greater depressive symptoms; supplementation (1–2 g/day) improves residual depressive symptoms and reduces inflammatory cytokines; beneficial as adjunct to medication | [6,10,15,18,19,28,29,59,60] |
| B-vitamins (Folate, B12, B6) | One-carbon metabolism; synthesis of SAM; monoamine neurotransmitter production; methylation processes | BD patients frequently show lower folate/B12 levels; deficiencies linked to cognitive symptoms, emotional instability, elevated homocysteine, and poorer antidepressant response; supplementation normalizes homocysteine | [17,31,61,62,63] |
| Magnesium | NMDA receptor regulation; modulation of excitatory/inhibitory balance; anti-inflammatory and antioxidant roles | Low serum magnesium during manic/depressive episodes; deficiency associated with increased severity and impaired stress regulation; supplementation shows mild antidepressant effects | [64,65,66] |
| Zinc | Regulation of GABA and glutamate transmission; antioxidant activity; involvement in neuroplasticity | Lower zinc levels associated with worse mood symptoms and cognitive impairment; some BD patients show elevated zinc under stable conditions; supplementation may exert antidepressant-like effects | [33,65,66,67] |
| Iron | Neurotransmitter synthesis; mitochondrial respiration; oxygen transport | Both deficiency and iron overload impact oxidative stress and neuroprogression; abnormalities may contribute to fatigue, cognitive dysfunction, and mood instability | [67,68] |
| Selenium | Cofactor for glutathione peroxidase; modulation of thyroid metabolism; antioxidant and anti-inflammatory pathways | Lower selenium associated with impaired antioxidant defense in BD; abnormalities linked to treatment with lithium or valproate; possible contribution to cognitive and emotional dysregulation | [67] |
| Vitamin D | Neurosteroid activity; immune regulation; serotonin synthesis; calcium homeostasis; circadian rhythm modulation | Low vitamin D linked to depressive symptoms, cognitive impairment, and sleep disturbances; supplementation beneficial mainly in deficiency states; abnormalities reported across mood phases | [69,70,71,72,73] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marano, G.; Boggio, G.; Abate, F.; Caroppo, E.; Traversi, G.; Mazza, O.; Capristo, E.; Gaetani, E.; Mazza, M. From Food to Mood: Psychological and Psychiatric Impact of Diet in Bipolar Disorder. Nutrients 2025, 17, 3728. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17233728
Marano G, Boggio G, Abate F, Caroppo E, Traversi G, Mazza O, Capristo E, Gaetani E, Mazza M. From Food to Mood: Psychological and Psychiatric Impact of Diet in Bipolar Disorder. Nutrients. 2025; 17(23):3728. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17233728
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarano, Giuseppe, Gianluca Boggio, Francesca Abate, Emanuele Caroppo, Gianandrea Traversi, Osvaldo Mazza, Esmeralda Capristo, Eleonora Gaetani, and Marianna Mazza. 2025. "From Food to Mood: Psychological and Psychiatric Impact of Diet in Bipolar Disorder" Nutrients 17, no. 23: 3728. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17233728
APA StyleMarano, G., Boggio, G., Abate, F., Caroppo, E., Traversi, G., Mazza, O., Capristo, E., Gaetani, E., & Mazza, M. (2025). From Food to Mood: Psychological and Psychiatric Impact of Diet in Bipolar Disorder. Nutrients, 17(23), 3728. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17233728