Error in Figure
In the original publication [1], there were mistakes in the published version of Figure 7A (LPS group), 7D (control group), 7F (LPS group), 7G (LPS group); the authors uploaded the wrong images during final proofreading. In the correction, they have been replaced. The corrected version of Figure 7 appears below.
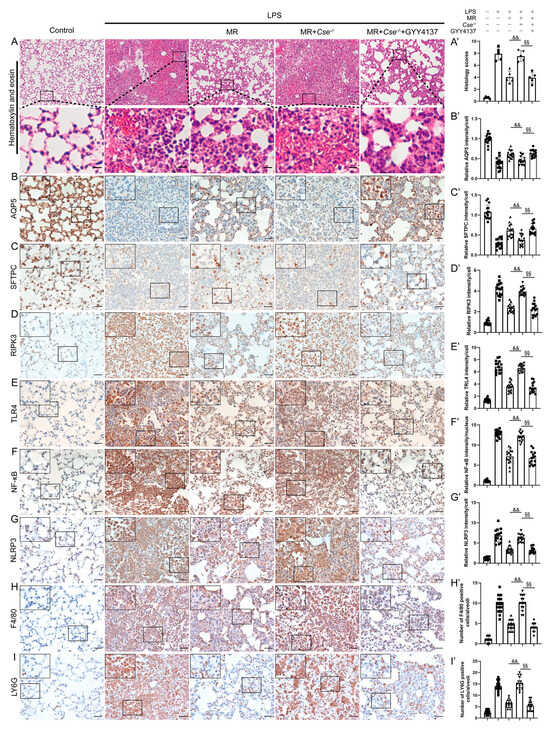
Figure 7.
Exogenous H2S administration mimicked the protective effects of MR in Cse−/− mice after LPS administration. (A,A’) Lung tissues were stained with hematoxylin and eosin and correlated histology scores were counted at day 3 after LPS administration. Immunohistochemical staining and quantification of relative intensity of AQP5 (B,B’), SFTPC (C,C’), RIPK3 (D,D’), TLR4 (E,E’), NF-κB (F,F’), NLRP3 (G,G’), F4/80 (H,H’), LY6G (I,I’) at day 3 after LPS administration. Values are expressed as the means ± SE; n = 5 in each group (A’); n = 15 alveoli from 5 mice (B’–I’). && p < 0.01 compared with LPS + MR group. §§ p < 0.01 compared with LPS + MR + Cse−/− group. Scale bars: 100 μm (original micrograph), 15 μm (enlarged) (A); 20 μm (original micrograph), 5 μm (enlarged) (B–I).
The authors apologize for any inconvenience caused and state that the scientific conclusions are unaffected. This correction was approved by the Academic Editor.
Reference
- Duan, J.; Xiang, L.; Yang, Z.; Chen, L.; Gu, J.; Lu, K.; Ma, D.; Zhao, H.; Yi, B.; Zhao, H.; et al. Methionine Restriction Prevents Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Lung Injury via Modulating CSE/H2S Pathway. Nutrients 2022, 14, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).