Correlation between Olive Oil Intake and Gut Microbiota in Colorectal Cancer Prevention
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Quality of Olive Oils on the Market
3. Oil: Components and Features
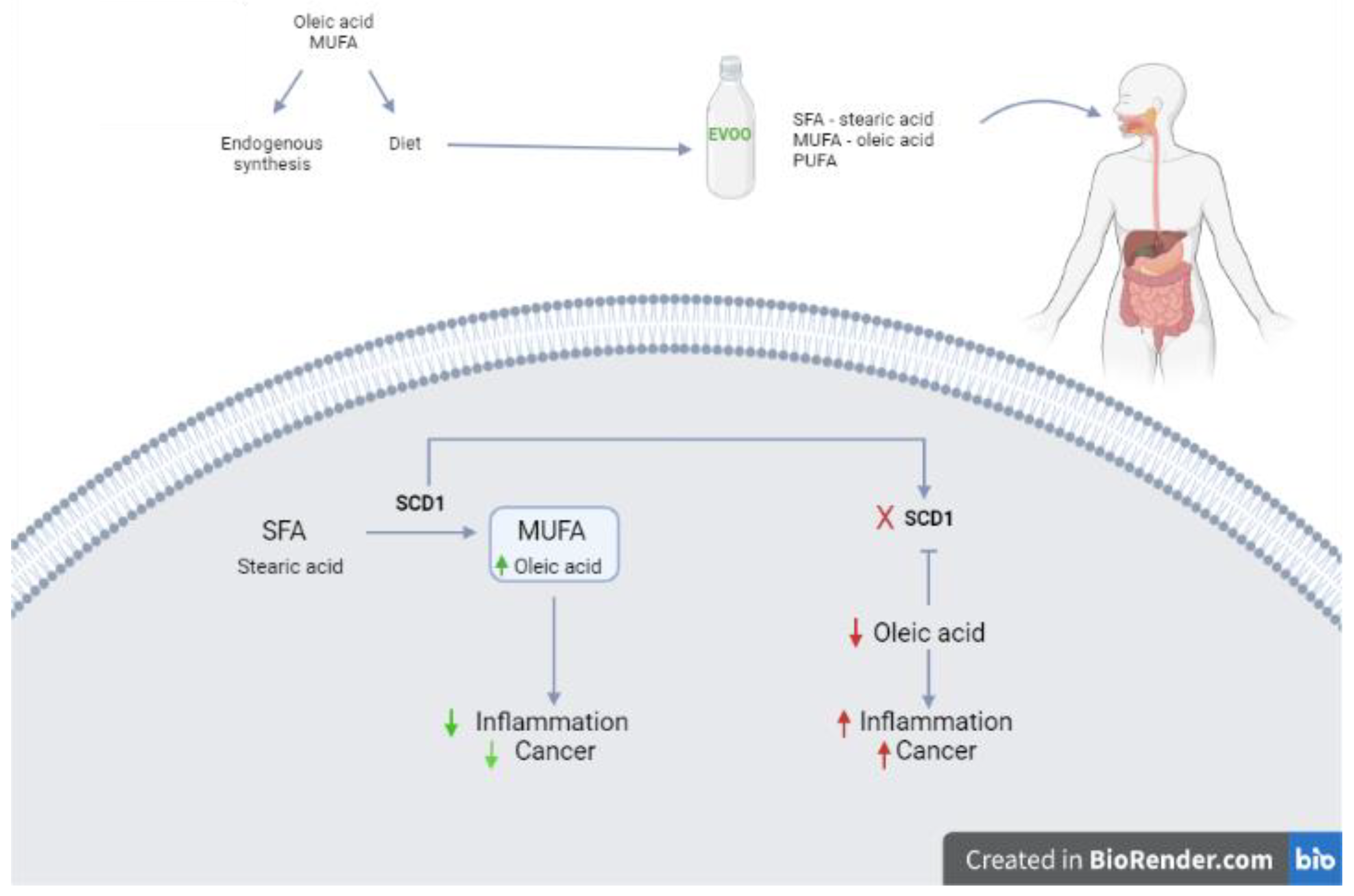
4. Role of Olive Oil in Colorectal Cancer Prevention
5. Gut Microbiota and CRC Development
6. Role of Olive Oil on Microbiota
7. Ongoing Clinical Trials
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gavahian, M.; Mousavi Khaneghah, A.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Munekata, P.E.S.; Garcia-Mantrana, I.; Collado, M.C.; Meléndez-Martínez, A.J.; Barba, F.J. Health benefits of olive oil and its components: Impacts on gut microbiota antioxidant activities, and prevention of noncommunicable diseases. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 88, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkels, R.M.; Heine-Bröring, R.C.; Van Zutphen, M.; van Harten-Gerritsen, S.; Kok, D.E.; Van Duijnhoven, F.J.; Kampman, E. The COLON study: Colorectal cancer: Longitudinal, Observational study on Nutritional and lifestyle factors that may influence colorectal tumour recurrence, survival and quality of life. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimenez-Lopez, C.; Carpena, M.; Lourenço-Lopes, C.; Gallardo-Gomez, M.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Barba, F.J.; Prieto, M.A.; Simal-Gandara, J. Bioactive Compounds and Quality of Extra Virgin Olive Oil. Foods 2020, 9, 1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- British Nutrition Foundation–Fat. Available online: https://www.nutrition.org.uk/healthy-sustainable-diets/fat/?level=Health%20professional (accessed on 9 September 2022).
- Borzì, A.M.; Biondi, A.; Basile, F.; Luca, S.; Vicari, E.S.D.; Vacante, M. Olive Oil Effects on Colorectal Cancer. Nutrients 2019, 11, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccinin, E.; Cariello, M.; De Santis, S.; Ducheix, S.; Sabbà, C.; Ntambi, J.M.; Moschetta, A. Role of Oleic Acid in the Gut-Liver Axis: From Diet to the Regulation of Its Synthesis via Stearoyl-CoA Desaturase 1 (SCD1). Nutrients 2019, 11, 2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trichopoulou, A.; Lagiou, P.; Kuper, H.; Trichopoulos, D. Cancer and Mediterranean Dietary Traditions. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2000, 9, 869–873. [Google Scholar]
- Van den Brandt, P.A.; Schulpen, M. Mediterranean diet adherence and risk of postmenopausal breast cancer: Results of a cohort study and meta-analysis. Int. J. Cancer 2017, 140, 2220–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psaltopoulou, T.; Kosti, R.I.; Haidopoulos, D.; Dimopoulos, M.; Panagiotakos, D.B. Olive oil intake is inversely related to cancer prevalence: A systematic review and a meta-analysis of 13,800 patients and 23,340 controls in 19 observational studies. Lipids Health Dis. 2011, 10, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwingshackl, L.; Schwedhelm, C.; Galbete, C.; Hoffmann, G. Adherence to Mediterranean Diet and Risk of Cancer: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Biedma, A.; Sánchez-Quesada, C.; Delgado-Rodríguez, M.; Gaforio, J.J. The biological activities of natural lignans from olives and virgin olive oils: A review. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 26, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, C.I.; Boyd, A.; McDermott, E.; McCann, M.; Servili, M.; Selvaggini, R.; Taticchi, A.; Esposto, S.; Montedoro, G.; McGlynn, H.; et al. Potential anti-cancer effects of virgin olive oil phenols on colorectal carcinogenesis models in vitro. Int. J. Cancer 2005, 117, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartolí, R.; Fernández-Bañares, F.; Navarro, E.; Castellà, E.; Mañé, J.; Alvarez, M.; Pastor, C.; Cabre, E.; Gassull, M.A. Effect of olive oil on early and late events of colon carcinogenesis in rats: Modulation of arachidonic acid metabolism and local prostaglandin E(2) synthesis. Gut 2000, 46, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Francesco, A.; Falconi, A.; Di Germanio, C.; Micioni Di Bonaventura, M.V.; Costa, A.; Caramuta, S.; Del Carlo, M.; Compagnone, D.; Dainese, E.; Cifani, C.; et al. Extravirgin olive oil up-regulates CB₁ tumor suppressor gene in human colon cancer cells and in rat colon via epigenetic mechanisms. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2015, 26, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Wang, H.; Ning, W.; Backlund, M.G.; Dey, S.K.; DuBois, R.N. Loss of Cannabinoid Receptor 1 Accelerates Intestinal Tumor Growth. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 6468–6476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Yan, C.; Zhao, Q.; Xu, J.; Liu, Z.; Gao, J.; Zhu, H.; Dai, Z.; Wang, D.; Tang, D. The roles of microbial products in the development of colorectal cancer: A review. Bioengineered 2021, 12, 720–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Ling, Z.; Li, L. The Intestinal Microbiota and Colorectal Cancer. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 615056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-García, C.; Sánchez-Quesada, C.; Algarra, I.; Gaforio, J.J. The High-Fat Diet Based on Extra-Virgin Olive Oil Causes Dysbiosis Linked to Colorectal Cancer Prevention. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasello, G.; Mazzola, M.; Leone, A.; Sinagra, E.; Zummo, G.; Farina, F.; Damiani, P.; Cappello, F.; Geagea, A.G.; Jurjus, A.; et al. Nutrition, oxidative stress and intestinal dysbiosis: Influence of diet on gut microbiota in inflammatory bowel diseases. Biomed. Pap. Med. Fac. Univ. Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2016, 160, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cueva, C.; Silva, M.; Pinillos, I.; Bartolomé, B.; Moreno-Arribas, M.V. Interplay between Dietary Polyphenols and Oral and Gut Microbiota in the Development of Colorectal Cancer. Nutrients 2020, 12, 625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Madani, R.; Mukhtar, H. Streptococcus bovis endocarditis, a silent sign for colonic tumour. Colorectal Dis. 2010, 12, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boleij, A.; van Gelder, M.M.; Swinkels, D.W.; Tjalsma, H. Clinical Importance of Streptococcus gallolyticus infection among colorectal cancer patients: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2011, 53, 870–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, X.; Wong, C.C.; Tong, L.; Chu, E.S.H.; Ho Szeto, C.; Go, M.Y.Y.; Coker, O.O.; Chan, A.W.; Chan, F.K.; Sung, J.J.Y.; et al. Peptostreptococcus anaerobius promotes colorectal carcinogenesis and modulates tumour immunity. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 2319–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.F.; Cudhea, F.; Shan, Z.; Michaud, D.S.; Imamura, F.; Eom, H.; Ruan, M.; Rehm, C.D.; Liu, J.; Du, M.; et al. Preventable Cancer Burden Associated With Poor Diet in the United States. JNCI Cancer Spectrum. 2019, 3, pkz034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grobbee, E.J.; Lam, S.Y.; Fuhler, G.M.; Blakaj, B.; Konstantinov, S.R.; Bruno, M.J.; Peppelenbosch, M.P.; Kuipers, E.J.; Spaander, M.C. First steps towards combining faecal immunochemical testing with the gut microbiome in colorectal cancer screening. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2020, 8, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvie, M. Nutritional supplements and cancer: Potential benefits and proven harms. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. Book 2014, e478–e486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djuric, Z.; Bassis, C.M.; Plegue, M.A.; Ren, J.; Chan, R.; Sidahmed, E.; Turgeon, D.K.; Ruffin, M.T.; Kato, I.; Sen, A. Colonic Mucosal Bacteria Are Associated with Inter-Individual Variability in Serum Carotenoid Concentrations. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2018, 118, 606–616.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cockbain, A.J.; Volpato, M.; Race, A.D.; Munarini, A.; Fazio, C.; Belluzzi, A.; Loadman, P.; Toogood, G.; Hull, M.A. Anticolorectal cancer activity of the omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid eicosapentaenoic acid. Gut 2014, 63, 1760–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appunni, S.; Rubens, M.; Ramamoorthy, V.; Tonse, R.; Saxena, A.; McGranaghan, P.; Kaiser, A.; Kotecha, R. Emerging Evidence on the Effects of Dietary Factors on the Gut Microbiome in Colorectal Cancer. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 718389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Microorganisms Associated with CRC Increased Risk | Microorganisms Associated with CRC Prevention |
|---|---|
| Streptococcus bovis Bacteroides fragilis Fusobacterium nucleatum Enterococcus faecalis Escherichia coli Peptostreptococcus anaerobius Staphylococcus spp. Pseudomonas spp. Neisseria spp. Sphingomonas spp. Prevotella spp. | Akkermansia muciniphila Bifidobacterium spp. Firmicutes spp. Lactococcus lactis |
| Name of Study and NCT Number | Phase | Study Arms | N° of Patients | Study Type | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phase 3 Study of Enteral Nutrition Rich in Eicosapentaenoic Acid (EPA) in Patients Receiving Chemotherapy for Gastric Cancer or Colorectal Cancer NCT01048463 [27] | Phase 3 | Placebo Comparator: EN vs. Experimental: ENLDEPA (Nutriall+LDEPA+ Xelox) vs. Experimental: ENHDEPA (nutriall+HDEPA+ Xelox) | 90 | Interventional | Unknown status |
| A Mediterranean Diet in Colon Cancer Prevention NCT00475722 [28] | Not Applicable | Active Comparator: 1 Healthy Eating vs. Experimental: 2 Mediterranean | 120 | Interventional | Completed |
| The Effects of EPA on Biomarkers of Growth and Vascularity in Human Colorectal Cancer Liver Metastases (The EPA for Metastasis Trial) NCT01070355 [29] | Phase 2 | Placebo Comparator: Placebo vs Active. Comparator: EPA free fatty acid | 88 | Interventional | Completed |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Memmola, R.; Petrillo, A.; Di Lorenzo, S.; Altuna, S.C.; Habeeb, B.S.; Soggiu, A.; Bonizzi, L.; Garrone, O.; Ghidini, M. Correlation between Olive Oil Intake and Gut Microbiota in Colorectal Cancer Prevention. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3749. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14183749
Memmola R, Petrillo A, Di Lorenzo S, Altuna SC, Habeeb BS, Soggiu A, Bonizzi L, Garrone O, Ghidini M. Correlation between Olive Oil Intake and Gut Microbiota in Colorectal Cancer Prevention. Nutrients. 2022; 14(18):3749. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14183749
Chicago/Turabian StyleMemmola, Raffaella, Angelica Petrillo, Sara Di Lorenzo, Sara C. Altuna, Baker Shalal Habeeb, Alessio Soggiu, Luigi Bonizzi, Ornella Garrone, and Michele Ghidini. 2022. "Correlation between Olive Oil Intake and Gut Microbiota in Colorectal Cancer Prevention" Nutrients 14, no. 18: 3749. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14183749
APA StyleMemmola, R., Petrillo, A., Di Lorenzo, S., Altuna, S. C., Habeeb, B. S., Soggiu, A., Bonizzi, L., Garrone, O., & Ghidini, M. (2022). Correlation between Olive Oil Intake and Gut Microbiota in Colorectal Cancer Prevention. Nutrients, 14(18), 3749. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14183749










