Abstract
Patients with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) are increasingly presenting with a wide range of neuropsychiatric symptoms, such as deterioration in gastroenteric physiology, including visceral hypersensitivity, altered intestinal membrane permeability, and gastrointestinal motor dysfunction. Functional imaging of IBS patients has revealed several abnormalities in various brain regions, such as significant activation of amygdala, thinning of insular and anterior cingulate cortex, and increase in hypothalamic gray matter, which results in poor psychiatric and cognitive outcomes. Interrelations between the enteric and central events in IBS-related gastrointestinal, neurological, and psychiatric pathologies have compelled researchers to study the gut-brain axis—a bidirectional communication that maintains the homeostasis of the gastrointestinal and central nervous system with gut microbiota as the protagonist. Thus, it can be disrupted by any alteration owing to the gut dysbiosis or loss of diversity in microbial composition. Available evidence indicates that the use of probiotics as a part of a balanced diet is effective in the management of IBS and IBS-associated neurodegenerative and psychiatric comorbidities. In this review, we delineate the pathogenesis and complications of IBS from gastrointestinal and neuropsychiatric standpoints while also discussing the neurodegenerative events in enteric and central nervous systems of IBS patients and the therapeutic potential of gut microbiota-based therapy established on clinical and preclinical data.
1. Introduction
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a gastrointestinal-related disorder that manifests as persistent abdominal pain or discomfort, which is commonly correlated with altered bowel habits as well as defecation frequency and form [,]. Its global prevalence is estimated at 3−11% [,,]. The risk of being diagnosed with IBS is marginally higher in women compared to men and in individuals aged ≤50 years [,]. Although IBS was once assumed to primarily affect the Western population, it is becoming increasingly prevalent in developing Asian countries, such as Malaysia (affecting 10.9−15.8% of the population), owing to the more widespread adoption of the Western lifestyle and diet [,,]. The ethnic distribution in the incidence of IBS is estimated at 16.2−17.5%, 15.2−16.8%, and 10.9−15.8% among Chinese, Indians, and Malays, respectively [,,].
IBS is frequently associated with pathophysiology, such as dietary sensitivity, inflammation, genetics, infection, visceral hypersensitivity, psychosocial distress, gut dysbiosis, and intestinal barrier deterioration (Table 1) [,]. These complex causative factors typically result in persistent abdominal discomfort and pain in IBS patients, which is severe enough to warrant a hospital visit. Based on Rome IV criteria and the Bristol Stool Form Scale (BSFS), IBS can be divided into several predominant subtypes, namely IBS-C (constipation), IBS-D (diarrhea), IBS-M (mixed type), and IBS-U (unclassified) [,]. This IBS classification process aids clinicians in determining the most optimal treatment strategies that are specifically tailored to the diagnosed predominant subtype [,].

Table 1.
Brief summary of pathophysiology that are known to cause irritable bowel syndrome.
Healthcare costs associated with IBS management including investigation, treatment, medication, and delivery are estimated at US $2 billion yearly in China, £45.6 to £200 million per year in the UK, and US $1562 to US $7547 per person yearly in the US [,,]. The aforementioned figures signify the financial burden incurred by IBS, and some patients also lose their source of income due to the severity of IBS symptoms []. Such challenges can cause significant psychosocial distress, affecting social interactions, spontaneity, and freedom []. Occasionally, IBS patients also face stigma from physicians, family members, and colleagues, which further undermines their quality of life [,].
2. Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Gut Dysbiosis
The human gastrointestinal tract harbors a hundred trillion diverse and complex microbial communities, including bacteria, fungi, viruses, and archaea [,]. The gut microbiota plays an essential role in maintaining the host physiology, specifically related to metabolism, neuronal development, and immune response []. Human gut microbiota is divided into four major phyla, mainly the Firmicutes, Actinobacteria, Bacteroidetes, and Proteobacteria []. The Firmicutes phylum consists of hundreds of genera, including Lactobacillus, Enterococcus, Bacillus, Ruminicoccus, and Clostridium []. On the other hand, Actinobacteria phylum comprises of Bifidobacterium genus, and Bacteroidetes phylum is composed of Prevotella and Bacteroides genera []. Lastly, the Proteobacteria phylum comprises of few predominant genera, such as Escherichia, Shigella, and Helicobacter []. This highly heterogeneous microbial community is capable of rapidly adapting to environmental changes as well as host-derived stimuli such as diet, chemical exposure, and immunological response [,]. Disruptions to gut microbial composition, also known as gut dysbiosis, have been observed in several diseases, such as the functional gastrointestinal-related disorders [].
Gut dysbiosis is considered as a one of the focal determinants in IBS etiopathogenesis []. Microbial populations, such as Lactobacillus, Bifidobacterium, and Faecalibacterium, are significantly depleted in IBS patients, with a profound influence on their health []. Lactobacillus is essential for elevating the mucin production in the intestinal lining, which in turn prevents the adherence of pathogenic microbes, such as bacteria (Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Helicobacter pylori), parasites (Entamoeba histolytica), and fungi (Candida albicans) []. Similarly, Bifidobacterium provides a mucosal barrier that is necessary in the overall maintenance of gut homeostasis []. Faecalibacterium prausnitzii, which serves as a major butyrate producer in the human intestine that is crucial for the maintenance of gut homeostasis, is often low in IBS patients []. The production of butyrate reduces the intestinal inflammation and releases other essential metabolites to enhance the mucosal barrier function [].
In IBS patients, pathogenic microbial populations such as Campylobacter jejuni, Campylobacter concisus, Clostridium difficile, Helicobacter pylori, Escherichia coli, Shigella spp., and Salmonella spp. are also often enriched; thus, they can be considered as the risk factor for developing functional gastrointestinal disorders such as IBS []. For instance, Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter concisus are capable of disrupting the intestinal barrier by promoting cell death and increasing gut permeability []. The deterioration of this intestinal barrier following Campylobacter infection can be notably observed in the urinary lactose and mannitol (L:M) excretion ratio, with a significant increase even after 6 to 12 weeks of Campylobacter gastroenteritis []. However, the urinary L:M excretion ratio among post-infective IBS (PI-IBS) patients continued to increase, up to 4 years after initial infection []. Reportedly, during infection, also numerous immune-related cells particularly mast cells, macrophages, T lymphocytes, and several pro-inflammatory cytokines including TNF-α, IFN-γ, IL-3, IL-4, IL-5, and IL-6 were elevated. The elevation of these immune-related cells were normally associated with prominent effects on vascular permeability, motility, secretion, and pain signaling [,].
According to Dayananda and Wilcox, Clostridium difficile infection is more common in post-infectious IBS patients []. As Clostridium difficile releases toxins that are detrimental to the enteric glial cells, neurons, colonocytes, and enterocytes, it disrupts the gut homeostasis []. Helicobacter pylori is a Gram-negative bacterium normally found in the mucous epithelium of the gut []. This pathogenic microbial was recently reported to cause systemic inflammation, visceral hypersensitivity at the upper GI tract, and increased gut permeability [,].
Another pathogenic organism that is closely associated with IBS development is Escherichia coli virulent pathotype (diarrheagenic and adherent-invasive) []. The pathogenic Escherichia coli invades the intestinal barrier and causes gut hypersensitivity as well as inflammation []. Other pathogenic organisms frequently observed in IBS development are Shigella spp. and Salmonella spp., which recruit inflammation-related cells (lymphocytes, cytokines, macrophages, and mast cells), causing a severe immunological response, thereby increasing the intestinal permeability and gut hypersensitivity in IBS patients []. The relationship between gut dysbiosis and mental disorder such as depression has been intriguingly discussed in multiple studies for the past few years. Suggestively, gut microbials interact with the host via several routes, including neural, neuroimmune, and neuroendocrine pathways [,]. Few studies also indicated that a compromised intestinal barrier allows pathogenic microbial products to be translocated, thus modulating the central nervous system (CNS) function by heightening the immune response and through the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal (HPA) axis []. For instance, Jiang et al., 2015 reported that there was a significant abundance of Proteobacteria (Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Pseudomonas putida, and Klebsielle pneumonia), Bacteroidetes (Alistipes) populations, and markedly reduced Firmicutes population in patients with major depressive disorder, as compared to healthy individuals []. Purportedly, a notable increase of Alistipes can cause severe abdominal pain as well as gut inflammation among IBS patients. Alistipes is also capable of impeding the tryptophan availability and consequently disrupting the intestinal serotonergic process [].
3. Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Depression
Clinical unipolar depression or major depression disorder is a common mental illness, affecting more than 300 million people worldwide []. Depression is a form of behavioral dysregulation caused by an interplay of many factors, such as the environment, gender, age, and comorbidity with other pre-existing illnesses, including IBS [,]. Patients with IBS often suffer from significantly higher levels of depression compared to healthy subjects [,,,] as well as individuals affected by inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) []. For example, according to the univariate analyses conducted by Midenfjord et al. (2019), IBS patients that suffer from psychological distress also report more severe gastrointestinal symptoms []. Lee et al. (2017) similarly found that severe depressive symptoms were associated with a high odds ratio for IBS []. Empirical evidence also indicates that psychosomatic symptoms, such as depression, result in a two-fold increase in the onset of gastrointestinal symptoms in IBS [,].
4. Cognition and Neurology in Irritable Bowel Syndrome
The association between IBS and cognitive function is rather inconclusive. However, as depression is strongly linked to cognitive deficit, and IBS patients are often depressed, they are hypothesized to suffer from some form of cognitive impairment. In line with this argument, some researchers have noted a reduction in verbal IQ (but no significant decline in performance on incidental memory assessment, troop color word test, or Wechsler Abbreviated Scale of Intelligence) in patients with IBS relative to their own performance IQ and compared with healthy controls []. Yet, other authors have failed to find a meaningful association between cognitive function (based on the Mini mental state examination, Trail-making tests, Grooved Pegboard test, Hopkins verbal learning test, brief visual memory test, Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale 3rd Edition, Stroop test, or Controlled oral word association test) and IBS []. According to a more recent systematic literature review, there was insufficient evidence to show a relationship between IBS and cognitive deteriorations [].
Nonetheless, the ample body of brain imaging findings points to the presence of differences between IBS patients and healthy controls, primarily in brain regions associated to stress [], visceral stimulation [], sensory integration [,], affective processing [], cognitive/executive functions [], and somatic pain []. Most of these findings indicate a greater engagement of regions associated with emotional processing, such as hypothalamus, amygdala, pregenual anterior cingulate cortex, and anterior insula [,,,,,,], owing to the emotional component of pain and other associated symptoms of IBS, including anxiety and depression. Significant reductions in activity in the prefrontal cortex (dorsolateral prefrontal cortex and orbitofrontal cortex) and limbic areas, such as amygdala, hippocampus, and anterior cingulate cortex, have been identified in brains of depressed individuals [,,]. The volumetric changes in the hippocampus are closely associated with the duration of depression and its episodes [,]. A meta-analysis of prior studies investigating the changes in brain activity in clinical depression during emotionally valanced tasks, cognitively demanding tasks, and resting conditions revealed altered common brain regions during the resting state and when engaged in cognitively undemanding tasks. According to Schmaal et al. (2017), patients suffering from major depressive disorder (MDD) also had thinner cortical gray matter in the orbitofrontal cortex, insula, anterior, and posterior cingulate, and temporal lobe, which were most pronounced during the first episode and in adult-onset MDD []. The authors also found evidence of regional reductions and a lower surface area of medial orbitofrontal cortex, superior frontal gyrus, somatosensory, motor areas, and higher-order visual areas in MDD patients [].
5. Neurodegeneration in Irritable Bowel Syndrome: Roles of Enteric Nervous System
Neurodegenerative events in IBS are due to immune injuries in the submucosal and myenteric plexuses []. Neuronal injury affects the activation profile of enteric neurons, thus resulting in altered responses of submucous neurons []; secretory neurons of submucous plexus; and musculomotor neurons of myenteric plexus []. In a chronic and acute stress (CAS)-induced IBS rat model adopted by Li et al. (2016) in their study, accelerated transit of small intestine was accompanied by an increase in the secretory motor neurons in the submucosal plexus, along with an increase in the secretion of excitatory neurotransmitters of enteric nervous system, such as acetylcholine and vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) []. These findings are consistent with those previously reported by Palsson et al. (2004), who noted markedly escalated VIP levels in the intestinal plasma of IBS patients []. Apart from increased excitatory transmission, Li et al. (2016) also reported a reduced number of nitric oxide synthase (NOS)-positive inhibitory interneurons (nitrergic neurons), with no notable changes in total and cholinergic neurons in the myenteric plexus, suggesting that the loss of inhibitory and heightened excitatory enteric neurotransmission enhanced small intestinal motility in the CAS-induced IBS in rats [].
Several authors also found that nitrergic neurons were also sensitive to the type of diet consumed. For example, in the study conducted by Ye et al. (2020), mice fed a Western diet exhibited delayed colonic transit and impaired electric field stimulation-induced colonic relaxation response due to an increase in myenteric neuronal pyroptosis, which is a novel form of programmed cell death []. The Western diet increased the expression of TLR4 and cleaved caspase-1 (marker of pyroptosis), which was accompanied by loss of myenteric nitrergic neurons, without affecting the population of cholinergic neurons, hence indicating the vulnerability of nitrergic neurons toward a high-fat diet. The same researchers also reported increased neuronal pyroptosis of myenteric neurons (mainly nitrergic neurons, but not cholinergic neurons) in colons of obese and overweight patients, corroborating the findings reported in animal studies []. According to Fan et al. (2018), the anti-enteric neuronal antibodies (AENA)-positive rate was higher in IBS patients than in patients with slow transit functional constipation and those with IBD, as well as healthy controls []. On the other hand, Pittock et al. (2011) failed to identify a significant difference in the AENA-positive rate between healthy subjects and individuals suffering from functional gastrointestinal diseases []. Fan et al. (2018) also reported that the exposure of moderately and highly AENA-positive sera from IBS patients to cultured myenteric neurons of Guinea pigs and human SH-Sy5Y cells led to neuronal apoptosis with a significant increase in the expression of anti-active caspase 3, TUNEL-positive cells, cleaved caspase 3, and pro-apoptotic factor Bax, and a decrease in inhibitor of apoptosis Bcl-2 [].
6. Neurodegeneration in IBS: Roles of Central Nervous System
Patients with IBS are at a greater risk of developing neurodegenerative diseases, including Parkinson’s disease [,], and dementia []. Brain imaging studies have uncovered various abnormalities in brain regions of IBS patients, especially decreased functional connectivity density (FCD) in brain regions pertaining to emotional arousal, cognitive regulation, and afferent network, and increased FCD in regions associated with sensorimotor modulation []. Neurodegenerative features, such as white matter integrity loss, are increasingly being reported. For example, Fang et al. (2017) found a significant decrease in fractional anisotropy (FA; a measure of white matter integrity) and axial diffusivity (AD; density and diameter of axon) []. In their subsequent investigation, Fang et al. (2017) also observed increased mean diffusivity (MD; changes in myelin integrity or cell membrane) in the right retrolenticular area of the internal capsule, splenium of the corpus callosum (CC), right superior corona radiata, and right posterior of internal capsule of IBS patients []. Decreases in FA and AD values indicate that white matter integrity has been compromised due to axonal injury or loss, as detected by diffusion tensor imaging []. In addition to IBS, white matter damage in CC was also reported in other chronic pain-related studies, indicating the important role of CC in abnormal somatosensory or nociceptive processing in IBS [].
White matter abnormalities in the retrolenticular area of internal capsule and corona radiata indicate disrupted ascending somatosensory and descending motor inputs []. Ellingson et al. (2013) also reported reduced FA values in the regions associated with sensory perception/integration and motor association/integration, such as thalamus and basal ganglia, and higher FA values in the CC and frontal lobe of IBS patients compared to healthy controls []. The discrepancies in the findings yielded by the aforementioned studies could be due to differences in sample size or the imaging methods used. It is worth noting that Hubbard et al. (2018) reported decreased FA in the right (but not left) dorsal cingulum in female adolescent IBS patients (n = 12; 11.96–18.5 years old) compared to controls (n = 12; 16.24 ± 1.89 years old), especially in the retrosplenial portion of the cingulum bundle []. On the other hand, they found no significant correlation between the changes in white matter abnormalities and disease duration, pain intensity, or psychometric measures. Using voxel-wise analysis of the diffusion parameters, Nan et al. (2018) found reduced FA and increased RD values in the genu of corpus callosum of female patients suffering from IBS-C (n = 20; 21.9 ± 1.41 years old) compared to healthy controls (n = 19; 22.74 ± 1.19 years old) []. The authors also reported greater white matter abnormalities in female patients with functional constipation (n = 18; 21.11 ± 1.28 years old) compared to those diagnosed with IBS-C. According to their analyses, the observed changes in FA values were negatively correlated with abdominal discomfort or pain intensity, whereas the RD values of CC were positively associated with abdominal discomfort or pain intensity, linking CC disorder with perception of pain []. Corpus callosum white matter abnormalities have also been reported in anxiety disorders [], depression [], bipolar disorder [], mild cognitive impairment [], and early course of cognitive decline in Alzheimer’s disease []. Corpus callosum is the largest tract connecting the left and right brain hemispheres, supplying the neural inputs for various regions involved in sensory and motor integration, cognition, and emotion [,]. Corpus callosum white matter abnormalities are the most consistently associated central degenerative feature in IBS, which appears to be due to altered pain perception in pediatric patients. However, whether these abnormalities are early signs of central nervous system (CNS) changes in IBS or a compensatory change in CNS due to altered bowel movement over time remains to be established.
7. Therapeutic Interventions in IBS: The Role of Antidepressants
The effectiveness of several antidepressant agents in IBS patients has been studied, including the tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs), selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), and serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs). The exact mechanism of action of antidepressants in IBS is presently not fully understood. Anxiolytic and antidepressant drugs may directly act on the enteric nervous system involving pain perception, visceral hypersensitivity, and gastrointestinal motility. Almost 90% of serotonin is produced by the enterochromaffin cells of the intestinal mucosa and has been shown to cause bloating, nausea, and vomiting []. According to Creed (2006), apart from their antidepressant effect in IBS patients with concomitant mood disorders, SSRIs might alter psychological processes, causing reduced somatization []. In line with this view, Kreiter et al. (2021) associated escitalopram treatment with changes in the symptom networks in IBS patients with panic disorder based on their electronic momentary assessments []. They also purported that an alleviation of physical symptoms was possibly due to healthier emotion regulation [].
There are growing evidence of anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative effects of antidepressant agents [,]. In the animal model of seizure by Sitges et al. (2014), the authors found that the administration of repeated dose of sertraline (SSRI) decreased the expression of IL-1β mRNA and TNF-αN in the hippocampus []. Another animal study by Rafiee et al. (2016) concluded the anti-inflammatory effect of fluvoxamine (SSRI). They had shown that the administration of fluvoxamine was able to significantly decrease the expression of inflammatory genes such as intercellular adhesion molecule (ICAM1), vascular cell adhesion molecule (VCAM1), cyclooxygenases2 (COX2), and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) []. Moreover, Venlafaxine (SNRI) was shown to have an inhibitory effect on superoxide generation by the microglia, albeit it had only a marginal effect on major pro-inflammatory parameters []. As the inflammation process has been postulated to play a role in the pathogenesis of IBS [], it is wise to hypothesize that these antidepressant agents possibly alleviate the IBS symptoms through its anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative effects.
TCAs are one of the oldest classes of antidepressants, and they have been used in IBS patients for more than four decades []. The most comprehensively studied TCAs include desipramine, trimipramine, imipramine, and amitriptyline. Evidence yielded by these investigations indicates that the dose employed in treating IBS is much lower (e.g., amitriptyline: 10−25 mg/day) compared to the therapeutic dose for depression (e.g., amitriptyline: 25−150 mg/day). SSRIs are among the newer classes of antidepressants, which include paroxetine, fluoxetine, escitalopram, and citalopram. As the name implies, SSRIs selectively inhibit serotonin reuptake into presynaptic cells by blocking the serotonin transporter. This leads to an abrupt increase in serotonin levels in the brain and eventually contributes to their therapeutic actions.
Ford et al. (2019) recently conducted a meta-analysis of 18 randomized controlled trials (RCTs) consisting of 11 TCA trials, 6 SSRI trials, and 1 trial involving both drug classes []. The pooled sample comprised of 1127 patients, 612 of whom received active therapy and 515 of whom received placebos. The proportion of patients with no IBS symptom improvement was much lower in subjects receiving TCAs compared to placebo groups (42.7%, 186/436 vs. 63.8%, 224/351, respectively) with the relative risk (RR) of 0.65 and number needed to treat (NNT) of 4.5. SSRIs also showed similar efficacy with the RR of 0.68 and NNT of 5 (seven trials, as a part of which 176 patients took SSRIs and 180 were given placebo) []. However, given the significant heterogeneity among studies and a broad range of 95% confidence intervals employed in analyses, the findings related to SSRIs have to be interpreted with caution. The authors of two small pilot non-randomized studies (n ≤ 15) examined the role of duloxetine (SNRI) in IBS patients. Their findings indicated a significant improvement in quality of life, abdominal pain, and anxiety; however, most participants experienced side effects such as fatigue, constipation, nausea, and insomnia [,].
For their more recent 6-week-long RCT of vortioxetine (SSRI), Seddighnia et al. (2020) recruited 72 patients and randomly assigned them to the vortioxetine (n = 36) and placebo (n = 36) groups []. The vortioxetine group demonstrated a greater increase in quality of life as compared to placebo (p < 0.01), irrespective of depression or anxiety score changes []. Vortioxetine is a potent 5-HT3 receptor antagonist, and suppression of the 5-HT3 receptor improves IBS symptoms such as abdominal pain, stool consistency, and gastrointestinal motility, as shown by studies involving 5-HT3 blockers (alosetron and ramosetron) [,]. In another recent RCT, Khalilian et al. (2018) examined the role of mirtazapine in the treatment of diarrhea-predominant IBS []. Mirtazapine is an atypical antidepressant agent with 5-HT3 receptor antagonist property. This 8-week trial involved 67 patients and showed promising results, including significant improvement in the severity of IBS symptoms (p = 0.002), quality of life (p = 0.04), and anxiety symptoms (p = 0.005). Most patients’ gastrointestinal symptoms (abdominal pain, urgency, and diarrhea) significantly improved, with the exception of bloating [].
One of the major drawbacks of prescribing antidepressants to IBS patients is considerable side or adverse effects. According to Ford et al. (2019), the incidence of adverse effects was significantly higher among those taking antidepressants (RR = 1.56, NNT = 8.5) []. However, none of these adverse events was serious. Due to TCAs’ effect on muscarinic, alpha1 adrenergic, and histaminic receptors, side effects (such as drowsiness and dry mouth) are more common in patients taking TCAs as compared to SSRIs [,]. Given the shortcomings of extant studies, such as inadequate sample size, and inclusion of IBS patients with concomitant psychological disorders, as well as different subtypes of IBS [], further investigations into the use of antidepressants in the management of IBS are warranted.
8. Therapeutic Intervention in IBS: Roles of Prebiotics, Probiotics, and Psychobiotics
Over more than a decade, studies in the literature have testified the alteration in the gut microbiota composition following diet modification for a long time []. Recently, the roles of pre- and probiotics are widened to include ecosystem regulation by modulating the immune system and exerting positive physiological effects as well as affecting the metabolic health of the host [,]. A prebiotic is a substrate that provides an optimal environment with minimal side effects for boosting the growth of beneficial gut microbiota. Normally, prebiotics are broken down by the anaerobic gut microbiota to produce fermentation products, including short-chain fatty acids (acetic acid, butyric acid, and propionate) and gases (carbon dioxide and hydrogen) []. Prebiotics are carbohydrate-based fibers that remain undigested in the human gut to support microbial survival. The most widely studied prebiotics are fructo-oligosaccharides and inulin []. The majority of prebiotics are taken orally at a daily dose of three to five grams. Natural sources of fructo-oligosaccharides are asparagus, wheat, garlic, and artichokes [].
Low doses of functional food products containing prebiotics have a tendency to relieve IBS symptoms, including anxiety and depression []. Out of the four randomized controlled trials (RCTs) reported, only a single study involving 50 IBS patients showed improvement in global symptoms and bloating []. Following their meta-analysis involving 27 studies with a total of 2293 IBS patients of all subtypes, Lee et al. (2017) reported significantly higher levels of depression and anxiety in IBS patients as compared to healthy controls []. Further sub-analysis in which IBS subtypes were considered separately showed the highest depression among IBS-C patients []. More recently, our research team demonstrated that about 32.1% of the IBS-C patient population in Malaysia has sub-threshold or subclinical depression, which can be easily missed in clinical practice []. According to Bahrudin et al. (2020), the consumption of cultured drinks (probiotics) containing prebiotics in the form of polydextrose can significantly improve bowel function in IBS-C patients []. Polydextrose is a type of fermented soluble fiber, which is a low-calorie carbohydrate that can be added to dairy products and baked goods []. More RCTs involve the intake of either a single or a combination of prebiotics (inulin, galactooligosaccharides, and fructooligosaccharides) by patients suffering from a variety of acute and chronic diseases [].
The acceptable definition of probiotics is “live microorganisms that give health benefits to the host when administered in adequate amount” (page 507) []. Probiotics were initially consumed by healthy individuals for maintaining health and reducing the risk of developing a disease, based on the belief that the consumption of probiotics would displace or replace harmful gut bacteria with beneficial microbiota []. However, over time, their use expanded to medicine, whereby they are now prescribed as a treatment modality or alternative therapy in multiple gastrointestinal disorders, including IBS []. Probiotics are administered in either a single or a combination of multiple strains of bacteria or fungi []. Commercially, probiotics are sold as foods (e.g., yogurt) and supplements (sachets). Lactobacilli and Bifidobacterium species are the most common ingredients of probiotics. The health benefits of probiotics were documented on the defined strain of gut microbiota. Among their actions include the production of antimicrobial agents, reduction of luminal pH, and displacement of pathobionts through competitive exclusion [].
McCarthy et al. (2003) studied the effect of a probiotics murine model of colitis, whereby colitis was induced in an interleukin-10 (IL-10) knockout mouse model []. Lactobacillus salivarius UCC118 and Bifidobacterium infantis (B. infantis) 35,624 were chosen for their specific properties, including non-pathogenicity, ability to adhere to human epithelial cells, tolerance to intestinal acid and bile, and ability to survive in the human gastrointestinal tract []. The authors found that the administration of probiotics reduced mucosal inflammation, as indicated by declines in the levels of TNF-α, IFN-δ, and IL-12 in isolated splenocytes obtained from the knock-out mice, suggesting that probiotics ameliorate colitis through their actions on multiple pro-inflammatory mediators. The role of probiotics is likely to be effective in IBS, too, as there is increasing evidence of low-grade inflammation especially in post-infectious gastroenteritis [].
The safety and efficacy of probiotics in IBS were tested in 16 double-blind placebo controlled RCTs as early as 1996, using the Manning criteria []. However, based on this systematic review, there was no single study that reported adverse events following probiotics consumption. It was difficult to come out with the final consensus on the use of probiotics in IBS because of the variability in the types and dosages of probiotics, the criteria used to define IBS subgroups, and small sample sizes []. Despite these limitations, findings yielded by the meta-analysis of single-center and multi-center studies with variable treatment durations (4−8 weeks) conducted by Yuan et al. (2017) indicated that a mixture of probiotics containing B. infantis 35,624 relieves IBS-related symptoms, including abdominal pain, distension, and change in bowel habits []. Therefore, the benefit of probiotics in IBS has a tendency to be symptom and strain-specific [].
Synbiotic is a combination of prebiotics and probiotics []. As an example of the use of synbiotics in IBS, a meta-analysis conducted by Ford et al. (2014) found two RCTs that were based in Italy and South Korea []. The single-blinded study in Italy used L. acidophilus and L. helveticus, with Bifidobacterium species, combined with phytoextract medium for 12-week duration. Meanwhile, the double-blinded RCT in South Korea utilized B. lactis with acacia fiber for 8-week. Both studies failed to demonstrate statistical significance in alleviating IBS symptoms. The authors attributed these results to the heterogeneity in dosage, duration, and combinations of prebiotics and probiotics used. Thus, they concluded that while probiotics provide good outcome for IBS patients, available evidence is insufficient to support the beneficial effects of either prebiotics or synbiotics. Intestinal microbiota is capable of producing neurochemicals that influence physiological processes in the brain and psychological symptoms via the microbiota–gut–immune–glia axis. Dinan et al. (2013) has introduced the term “psychobiotics”, referring to living microorganisms capable of producing neuroactive substances and providing benefits to the nervous system []. Their effectiveness was examined in a double-blind RCT using multiple bacterial species of Lactobacillus acidophilus, L. plantarum, L. rhamnosus, Bifidobacterium breve, B. lactis, B. longum, and Streptococcus thermophilus performed by Han et al. (2017) in 50 IBS-D patients based on Rome III criteria []. According to the authors, the supplementation of probiotics for four weeks was found to significantly improve depression symptoms, which were probably modulated by the gut−brain axis. The human gut microbiota promotes the biosynthesis of serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5-HT) in the enterochromaffin cells that secrete into lumen and modulate circulating serotonin []. In their analyses, the authors examined the effects of specific subsets of spore-forming bacteria, including Bacteroides fragilis and B. uniformis. They showed a schematic of prebiotics’ and probiotics’ roles in modulating neuroendocrine system in the enteric nervous system. Figure 1 shows the link of the enteric nervous system with the brain through the bidirectional gut−brain axis.
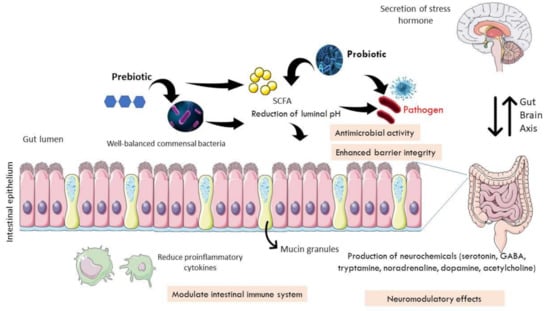
Figure 1.
Mechanisms of prebiotic and probiotic action in modulating bidirectional gut−brain axis. A healthy human gut is unable to digest macronutrients, including plant-derived polysaccharides. Probiotics produce enzymes to digest the fibers and carbohydrates to produce short-chain fatty acids (SCFA) in the form of lactic acid and acetic acids. Prebiotics serve as a source of nutrition for the stimulation and propagation of commensal bacteria in the gut. The presence of SCFA reduces the pH of the intestinal lumen, preventing the growth of pathogen, or it has anti-microbial activity. Certain probiotic strains could restore the intestinal barrier function by increasing the expression of tight junction proteins as well as mucus-secretion genes. They also help modulate the intestinal immune system by reducing the amount of pro-inflammatory cytokines. In addition, probiotics exhibit neuromodulatory effects by enhancing neurochemical production in the gut, including serotonin, GABA, tryptamine, noradrenaline, dopamine, and acetylcholine. As cytokines and neurotransmitters will impair the integrity of the blood−brain barrier, this leads to potentially damaging effects of inflammatory or pathogenic elements that link to the central nervous system to secrete stress hormones.
9. Conclusions
Irritable bowel syndrome is a functional gastrointestinal disorder that manifests as physical and mental symptoms. Gut dysbiosis is one of the fundamental theories that could explain this condition. Patients with severe IBS often suffer from psychological distress and report more severe gastrointestinal symptoms. Even though affective disorders such as depression and anxiety have been associated with IBS, such correlation is yet to be established from an empirical standpoint. Brain imaging studies of IBS patients indicate changes primarily in the areas related to pain and emotional processing, whereas the alterations in the depressed brains were more pertaining to learning and emotional regions, which corroborates the stronger association between depression and poor cognitive outcomes than IBS. Preclinical studies have related altered bowel movement in IBS to decreased inhibitory (nitregenic) and increased excitatory neurotransmission. The nitregenic neurons are sensitive to dietary intake, and undergo cell death in the colons of obese and overweight patients. However, in IBS, this is yet to be proven. The complex interactions between gut microbiota and the host’s nervous, immune, and endocrine system point to the favorable role of probiotics in managing IBS. Probiotics’ ability to alleviate the depressive symptoms associated with irritable bowel syndrome has demonstrated their therapeutic effect beyond the gastrointestinal tract via the gut−brain axis, which is a fascinating bidirectional pathway in humans.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.M.M., R.A.R.A. and J.K.; methodology, M.N.M.A., N.M.M. and J.K.; investigation, M.N.M.A., N.M.M., J.K. and K.N.M.N.; resources, R.A.R.A. and N.M.M.; data curation M.N.M.A., N.M.M., J.K. and K.N.M.N.; writing—original draft preparation, M.N.M.A., N.M.M., J.K. and K.N.M.N.; writing—review and editing, M.N.M.A., N.M.M., J.K. and K.N.M.N.; visualization, N.M.M. and J.K.; supervision, R.A.R.A. and N.M.M.; project administration, R.A.R.A. and N.M.M.; funding acquisition, R.A.R.A. and N.M.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Cotra Enterprise Sdn. Bhd., grant number (FF-2019-064/1).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank all Department of Physiology staff to provide facilities to make it possible to prepare the review paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Black, C.J.; Ford, A.C. Global burden of irritable bowel syndrome: Trends, predictions and risk factors. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 17, 473–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvernale, C.; Kuo, B.; Staller, K. Racial disparity in healthcare utilization among patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome: Results from a multicenter cohort. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2020, 33, e14039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovell, R.M.; Ford, A.C. Global prevalence of and risk factors for irritable bowel syndrome: A meta-analysis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 10, 712–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oka, P.; Parr, H.; Barberio, B.; Black, C.J.; Savarino, E.V.; Ford, A.C. Global prevalence of irritable bowel syndrome according to Rome III or IV criteria: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 5, 908–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.-M.; Goh, K.L.; Muhidayah, R.; Ooi, C.L.; Salem, O. Prevalence of irritable bowel syndrome in young adult Malaysians: A survey among medical students. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2003, 18, 1412–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.Y.; Waid, A.; Tan, H.J.; Chua, A.S.B.; Whitehead, W.E. Rome III survey of irritable bowel syndrome among ethnic Malays. World J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 18, 6475–6480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendra, S.; Alahuddin, S. Prevalence of irritable bowel syndrome in a multi-ethnic Asian population. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2004, 19, 704–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oświęcimska, J.; Szymlak, A.; Roczniak, W.; Girczys-Połedniok, K.; Kwiecień, J. New insights into the pathogenesis and treatment of irritable bowel syndrome. Adv. Med. Sci. 2017, 62, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjivasilis, A.; Tsioutis, C.; Michalinos, A.; Ntourakis, D.; Christodoulou, D.K.; Agouridis, A.P. New insights into irritable bowel syndrome: From pathophysiology to treatment. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2019, 32, 554–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defrees, D.N.; Bailey, J. Irritable bowel syndrome. Prim. Care: Clin. Off. Pr. 2017, 44, 655–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grad, S.; Dumitrascu, D.L. Irritable bowel syndrome subtypes: New names for old medical conditions. Dig. Dis. 2019, 38, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holtmann, G.; Ford, A.; Talley, N.J. Pathophysiology of irritable bowel syndrome. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 1, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farzaei, M.H.; Bahramsoltani, R.; Abdollahi, M.; Rahimi, R. The Role of visceral hypersensitivity in irritable bowel syndrome: Pharmacological targets and novel treatments. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2016, 22, 558–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GonzálezCastro, A.M.; Martínez, C.; SalvoRomero, E.; Fortea, M.; PardoCamacho, C.; Perez, M.V.; AlonsoCotoner, C.; Santos, J.; Vicario, M. Mucosal pathobiology and molecular signature of epithelial barrier dysfunction in the small intestine in irritable bowel syndrome. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 32, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camilleri, M.; Madsen, K.; Spiller, R.; Meerveld, B.G.-V.; Verne, G.N. Intestinal barrier function in health and gastrointestinal disease. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2012, 24, 503–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canavan, C.; West, J.; Card, T. Review article: The economic impact of the irritable bowel syndrome. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 40, 1023–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Xiang, W.; Li, C.-Y.; Li, S.-C. Economic burden of irritable bowel syndrome in China. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 10450–10460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drossman, D.A.; Chang, L.; Schneck, S.; Blackman, C.; Norton, W.F.; Norton, N.J. A Focus Group Assessment of Patient Perspectives on Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Illness Severity. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2009, 54, 1532–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thursby, E.; Juge, N. Introduction to the human gut microbiota. Biochem. J. 2017, 474, 1823–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, P.P.; Chin, V.K.; Looi, C.Y.; Wong, W.F.; Madhavan, P.; Yong, V.C. The microbiome and irritable bowel syndrome—A review on the pathophysiology, current research and future therapy. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zmora, N.; Suez, J.; Elinav, E. You are what you eat: Diet, health and the gut microbiota. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 16, 35–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinninella, E.; Raoul, P.; Cintoni, M.; Franceschi, F.; Miggiano, G.A.D.; Gasbarrini, A.; Mele, M.C.; Rinninella, E.; Raoul, P.; Cintoni, M.; et al. What is the healthy gut microbiota composition? A changing ecosystem across age, environment, diet, and diseases. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Zhou, G.; Qin, X.; Huang, S.; Wang, B.; Cao, H. The potential role of gut mycobiome in irritable bowel syndrome. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herndon, C.C.; Wang, Y.; Lu, C. Targeting the gut microbiota for the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2019, 36, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, C.N.; Sidani, S.; Marshall, J.K. Clinical management of the microbiome in irritable bowel syndrome. J. Can. Assoc. Gastroenterol. 2020, 4, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carco, C.; Young, W.; Gearry, R.B.; Talley, N.J.; McNabb, W.C.; Roy, N.C. Increasing evidence that irritable bowel syndrome and functional gastrointestinal disorders have a microbial pathogenesis. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Siles, M.; Duncan, S.; Garcia-Gil, L.J.; Martinez-Medina, M. Faecalibacterium prausnitzii: From microbiology to diagnostics and prognostics. ISME J. 2017, 11, 841–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shariati, A.; Fallah, F.; Pormohammad, A.; Taghipour, A.; Safari, H.; Chirani, A.S.; Sabour, S.; AlizadehSani, M.; Azimi, T. The possible role of bacteria, viruses, and parasites in initiation and exacerbation of irritable bowel syndrome. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 234, 8550–8569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dayananda, P.; Wilcox, M.H. Irritable bowel syndrome following Clostridium difficile infection. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2019, 35, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-A.; Cho, Y.J.; Kwak, S.G. The association between Helicobacter pylori infection and irritable bowel syndrome: A meta-analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogan, B.; Belcher-Timme, H.F.; I Dogan, E.; Jiang, Z.-D.; Dupont, H.L.; Synder, N.; Yang, S.; Chandler, B.; Scherl, E.J.; Simpson, K.W. Evaluation of Escherichia coli pathotypes associated with Irritable Bowel Syndrome. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2018, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, J.R.; Borre, Y.; O’Brien, C.; Patterson, E.; El Aidy, S.; Deane, J.; Dinan, T.G.; Kennedy, P.J.; Beers, S.; Scott, K.; et al. Transferring the blues: Depres-sion-associated gut microbiota induces neurobehavioural changes in the rat. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2016, 82, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.; Li, A.; Huang, T.; Lai, J.; Li, J.; Sublette, M.E.; Lu, H.; Lu, Q.; Du, Y.; Hu, Z.; et al. Gut microbiota changes in patients with bipolar depression. Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1900752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Ling, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Mao, H.; Ma, Z.; Yin, Y.; Wang, W.; Tang, W.; Tan, Z.; Shi, J.; et al. Altered fecal mi-crobiota composition in patients with major depressive disorder. Brain Behav. Immun. 2015, 48, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Depression and Other Common Mental Disorders: Global Health Estimates; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Gardner, A.; Boles, R.G. Beyond the serotonin hypothesis: Mitochondria, inflammation and neurodegeneration in major depression and affective spectrum disorders. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2011, 35, 730–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtar, N.M.; Bahrudin, M.F.; Ghani, N.A.; Rani, R.A.; Ali, R.A.R. Prevalence of subthreshold depression among constipation-predominant irritable bowel syndrome patients. Front. Psychol. 2020, 11, 1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fond, G.; Loundou, A.; Hamdani, N.; Boukouaci, W.; Dargel, A.; Oliveira, J.; Roger, M.; Tamouza, R.; Leboyer, M.; Boyer, L. Anxiety and depression comorbidities in irritable bowel syndrome (IBS): A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2014, 264, 651–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roohafza, H.; Bidaki, E.Z.; Hasanzadeh-Keshteli, A.; Daghaghzade, H.; Afshar, H.; Adibi, P. Anxiety, depression and distress among irritable bowel syndrome and their subtypes: An epidemiological population based study. Adv. Biomed. Res. 2016, 5, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.; Doo, E.; Choi, J.M.; Jang, S.H.; Ryu, H.S.; Lee, J.Y.; Oh, J.H.; Park, J.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Brain-Gut Axis Research Group of Korean Society of, N.; et al. The increased level of depression and anxiety in irritable bowel syndrome patients compared with healthy controls: Systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2017, 23, 349–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamani, M.; Alizadeh-Tabari, S.; Zamani, V. Systematic review with meta-analysis: The prevalence of anxiety and depression in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 50, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, Q.; Zhang, Q.-E.; Wang, F.; Zheng, W.; Ng, C.H.; Ungvari, G.S.; Wang, G.; Xiang, Y.-T. Comparison of comorbid depression between irritable bowel syndrome and inflammatory bowel disease: A meta-analysis of comparative studies. J. Affect. Disord. 2018, 237, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midenfjord, I.; Polster, A.; Sjövall, H.; Törnblom, H.; Simrén, M. Anxiety and depression in irritable bowel syndrome: Exploring the interaction with other symptoms and pathophysiology using multivariate analyses. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2019, 31, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibelli, A.; Chalder, T.; Everitt, H.; Workman, P.; Windgassen, S.; Moss-Morris, R. A systematic review with meta-analysis of the role of anxiety and depression in irritable bowel syndrome onset. Psychol. Med. 2016, 46, 3065–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takajo, T.; Tomita, K.; Tsuchihashi, H.; Enomoto, S.; Tanichi, M.; Toda, H.; Okada, Y.; Furuhashi, H.; Sugihara, N.; Wada, A.; et al. Depression promotes the onset of irritable bowel syndrome through unique dysbiosis in rats. Gut Liver 2019, 13, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attree, E.A.; Dancey, C.P.; Keeling, D.; Wilson, C. Cognitive function in people with chronic illness: Inflammatory bowel disease and irritable bowel syndrome. Appl. Neuropsychol. 2003, 10, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farup, P.G.; Hestad, K. Cognitive functions and depression in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterol. Res. Pr. 2015, 2015, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Lam, N.C.-Y.; Yeung, H.-Y.; Li, W.-K.; Lo, H.-Y.; Yuen, C.-F.; Chang, R.C.-C.; Ho, Y.-S. Cognitive impairment in irritable bowel syndrome (IBS): A systematic review. Brain Res. 2019, 1719, 274–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blankstein, U.; Chen, J.; Diamant, N.E.; Davis, K.D. Altered brain structure in irritable bowel syndrome: Potential contributions of pre-existing and disease-driven factors. Gastroenterology 2010, 138, 1783–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nan, J.; Yang, W.; Meng, P.; Huang, W.; Zheng, Q.; Xia, Y.; Liu, F. Changes of the postcentral cortex in irritable bowel syndrome patients. Brain Imaging Behav. 2019, 14, 1566–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seminowicz, D.A.; Labus, J.S.; Bueller, J.A.; Tillisch, K.; Naliboff, B.D.; Bushnell, M.C.; Mayer, E.A. Regional gray matter density changes in brains of patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology 2010, 139, 48–57.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Li, S.; Tian, J.; Jiang, G.; Wen, H.; Wang, T.; Fang, J.; Zhan, W.; Xu, Y. Altered brain spontaneous activity and connectivity network in irritable bowel syndrome patients: A resting-state fMRI study. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2015, 126, 1190–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, R.; Liu, C.; Ke, J.; Xu, Q.; Ye, Y.; Jia, L.; Wang, F.; Zhang, L.; Lu, G. Abnormal amygdala resting-state functional connectivity in irritable bowel syndrome. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2016, 37, 1139–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.-Y.; Naliboff, B.; Labus, J.S.; Gupta, A.; Kilpatrick, L.A.; Ashe-McNalley, C.; Stains, J.; Heendeniya, N.; Smith, S.R.; Tillisch, K.; et al. Altered brain responses in subjects with irritable bowel syndrome during cued and uncued pain expectation. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2015, 28, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tillisch, K.; Mayer, E.A.; Labus, J.S. Quantitative meta-analysis identifies brain regions activated during rectal distension in irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology 2011, 140, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellingson, B.M.; Mayer, E.; Harris, R.J.; Ashe-McNally, C.; Naliboff, B.D.; Labus, J.S.; Tillisch, K. Diffusion tensor imaging detects microstructural reorganization in the brain associated with chronic irritable bowel syndrome. Pain 2013, 154, 1528–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubbard, C.S.; Becerra, L.; Heinz, N.; Ludwick, A.; Rasooly, T.; Yendiki, A.; Wu, R.; Schechter, N.L.; Nurko, S.; Borsook, D. Microstructural white matter abnormalities in the dorsal cingulum of adolescents with IBS. eNeuro 2018, 5, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempton, M.J.; Salvador, Z.; Munafo, M.; Geddes, J.R.; Simmons, A.; Frangou, S.; Williams, S. Structural neuroimaging studies in major depressive disorder. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2011, 68, 675–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.-H. Gray matter volume in major depressive disorder: A meta-analysis of voxel-based morphometry studies. Psychiatry Res. Neuroimaging 2013, 211, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lener, M.S.; Iosifescu, D.V. In pursuit of neuroimaging biomarkers to guide treatment selection in major depressive disorder: A review of the literature. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2015, 1344, 50–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bremner, J.D.; Narayan, M.; Anderson, E.R.; Staib, L.; Miller, H.L.; Charney, D.S. Hippocampal volume reduction in major depression. Am. J. Psychiatry 2000, 157, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKinnon, M.C.; Yucel, K.; Nazarov, A.; MacQueen, G.M. A meta-analysis examining clinical predictors of hippocampal volume in patients with major depressive disorder. J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 2009, 34, 41–54. [Google Scholar]
- Schmaal, L.; for the ENIGMA-Major Depressive Disorder Working Group; Hibar, D.; Sämann, P.; Hall, G.; Baune, B.; Jahanshad, N.; Cheung, J.; Van Erp, T.; Bos, D.; et al. Cortical abnormalities in adults and adolescents with major depression based on brain scans from 20 cohorts worldwide in the ENIGMA major depressive disorder working group. Mol. Psychiatry 2016, 22, 900–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Giorgio, R.; Volta, U.; Stanghellini, V.; Cogliandro, R.F.; Barbara, G.; Corinaldesi, R.; Towns, R.; Guo, C.; Hong, S.; Wiley, J.W. Neurogenic chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction: Antineuronal antibody-mediated activation of autophagy via fas. Gastroenterology 2008, 135, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostertag, D.; Buhner, S.; Michel, K.; Pehl, C.; Kurjak, M.; Gotzberger, M.; Schulte-Frohlinde, E.; Frieling, T.; Enck, P.; Phillip, J.; et al. Reduced responses of submucous neurons from irritable bowel syndrome patients to a cocktail containing histamine, serotonin, TNFalpha, and Tryptase (IBS-Cocktail). Front. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Fei, G.; Fang, X.; Yang, X.; Sun, X.; Qian, J.; Wood, J.D.; Ke, M. Changes in enteric neurons of small intestine in a rat model of irritable bowel syndrome with diarrhea. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2016, 22, 310–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palsson, O.S.; Morteau, O.; Bozymski, E.M.; Woosley, J.T.; Sartor, R.B.; Davies, M.J.; Johnson, D.A.; Turner, M.J.; Whitehead, W.E. Elevated vasoactive intestinal peptide concentrations in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2004, 49, 1236–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Li, G.; Goebel, A.; Raju, A.V.; Kong, F.; Lv, Y.; Li, K.; Zhu, Y.; Raja, S.; He, P.; et al. Caspase-11–mediated enteric neuronal pyroptosis underlies Western diet–induced colonic dysmotility. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 3621–3636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Fei, G.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Hu, C.; Xin, H.; Sun, X.; Li, Y.; Wood, J.D.; Fang, X. Sera with anti-enteric neuronal antibodies from patients with irritable bowel syndrome promote apoptosis in myenteric neurons of guinea pigs and human SH-Sy5Y cells. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2018, 30, e13457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pittock, S.J.; Lennon, V.A.; Dege, C.L.; Talley, N.J.; Locke, G.R. Neural autoantibody evaluation in functional gastrointestinal disorders: A population-based case–control study. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2010, 56, 1452–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, S.-W.; Liao, K.-F.; Lin, C.-L.; Sung, F.-C. Irritable bowel syndrome correlates with increased risk of Parkinson’s disease in Taiwan. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2014, 29, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Sjolander, A.; Pedersen, N.L.; Ludvigsson, J.F.; Chen, H.; Fang, F.; Wirdefeldt, K. Irritable bowel syndrome and Parkinson’s disease risk: Register-based studies. NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2021, 7, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-H.; Lin, C.-L.; Kao, C.-H. Irritable bowel syndrome is associated with an increased risk of dementia: A nationwide population-based study. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0144589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, Y.; Qi, R.; Liu, C.; Ke, J.; Xu, Q.; Wang, F.; Zhang, L.J.; Lu, G.M. Disrupted functional connectivity density in irritable bowel syndrome patients. Brain Imaging Behav. 2016, 11, 1812–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Li, S.; Li, M.; Chan, Q.; Ma, X.; Su, H.; Wang, T.; Zhan, W.; Yan, J.; Xu, M.; et al. Altered white matter microstructure identified with tract-based spatial statistics in irritable bowel syndrome: A diffusion tensor imaging study. Brain Imaging Behav. 2016, 11, 1110–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edlow, B.L.; Copen, W.A.; Izzy, S.; van der Kouwe, A.; Glenn, M.B.; Greenberg, S.M.; Greer, D.M.; Wu, O. Longitudinal Diffusion Tensor Imaging Detects Recovery of Fractional Anisotropy Within Traumatic Axonal Injury Lesions. Neurocrit. Care 2016, 24, 342–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moayedi, M.; Weissman-Fogel, I.; Salomons, T.V.; Crawley, A.P.; Goldberg, M.B.; Freeman, B.V.; Tenenbaum, H.C.; Davis, K.D. White matter brain and trigeminal nerve abnormalities in temporomandibular disorder. Pain 2012, 153, 1467–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarman, J.; Fernandez, M.; Davies, P.T.; Glover, V.; Steiner, T.J.; Thompson, C.; Rose, F.C.; Sandler, M. High incidence of endogenous depression in migraine: Confirmation by tyramine test. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1990, 53, 573–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nan, J.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Q.; Zong, N.; Zhang, P.; Ji, X.; Ma, S.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, W.; Du, Z.; et al. White matter microstructural similarity and diversity of functional constipation and constipation-predominant irritable bowel syndrome. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2018, 24, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Qian, S.; Liu, K.; Li, B.; Li, M.; Xin, K.; Sun, G. Reduced white matter integrity and its correlation with clinical symptom in first-episode, treatment-naive generalized anxiety disorder. Behav. Brain Res. 2016, 314, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Won, E.; Choi, S.; Kang, J.; Kim, A.; Han, K.M.; Chang, H.S.; Tae, W.S.; Son, K.R.; Joe, S.H.; Lee, M.S.; et al. Association between reduced white matter integrity in the corpus callosum and serotonin transporter gene DNA methylation in medication-naive patients with major depressive disorder. Transl. Psychiatry 2016, 6, e866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetti, F.; Yeh, P.H.; Bellani, M.; Radaelli, D.; Nicoletti, M.A.; Poletti, S.; Falini, A.; Dallaspezia, S.; Colombo, C.; Scotti, G.; et al. Disruption of white matter integrity in bipolar depression as a possible structural marker of illness. Biol. Psychiatry 2011, 69, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elahi, S.; Bachman, A.H.; Lee, S.H.; Sidtis, J.J.; Ardekani, B.A.; Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging, I. Corpus callosum atrophy rate in mild cognitive impairment and prodromal Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2015, 45, 921–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Paola, M.; Phillips, O.; Orfei, M.D.; Piras, F.; Cacciari, C.; Caltagirone, C.; Spalletta, G. Corpus callosum structure is topographically correlated with the early course of cognition and depression in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2015, 45, 1097–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabri, M.; Pierpaoli, C.; Barbaresi, P.; Polonara, G. Functional topography of the corpus callosum investigated by DTI and fMRI. World J. Radiol. 2014, 6, 895–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenlon, L.; Richards, L.J. Contralateral targeting of the corpus callosum in normal and pathological brain function. Trends Neurosci. 2015, 38, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gershon, M.D. Plasticity in serotonin control mechanisms in the gut. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2003, 3, 600–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creed, F. How do SSRIs help patients with irritable bowel syndrome? Gut 2006, 55, 1065–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreiter, D.; Drukker, M.; Mujagic, Z.; Vork, L.; Rutten, B.P.F.; van Os, J.; Masclee, A.A.M.; Kruimel, J.W.; Leue, C. Symptom-network dynamics in irritable bowel syndrome with comorbid panic disorder using electronic momentary assessment: A randomized controlled trial of escitalopram vs. placebo. J. Psychosom Res. 2021, 141, 110351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonard, B.E. The immune system, depression and the action of antidepressants. Prof. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2001, 25, 767–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galecki, P.; Mossakowska-Wojcik, J.; Talarowska, M. The anti-inflammatory mechanism of antidepressants—SSRIs, SNRIs. Prof. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2018, 80, 291–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitges, M.; Gomez, C.D.; Aldana, B.I. Sertraline reduce IL-1β and TNF-α mRNA expression and overcomes their rise induced by seizures in the rat hippocampus. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rafiee, L.; Hajhashemi, V.; Javanmard, S.H. Fluvoxaminne inhibits some inflammatory gene expression in LPS/stimulated human endothelial cells, U937 macrophages, and carrageenan-induced paw edema in rat. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2016, 19, 977–984. [Google Scholar]
- Dubovicky, M.; Csaszar, E.; Melichercikova, K.; Rackova, L. Modulation of microglial function by the antidepressant drug venlafaxine. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 2014, 7, 201–207. [Google Scholar]
- Vara, E.J.; Brokstad, K.A.; Hausken, T.; Lied, G.A. Altered levels of cytokines in patients with irritable bowel syndrome are not correlated with fatigue. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2018, 11, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heefner, J.D.; Wilder, R.M.; Wilson, I.D. Irritable colon and depression. Psychosomatics 1978, 19, 540–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, A.C.; Lacy, B.E.; Harris, L.A.; Quigley, E.M.M.; Moayyedi, P. Effect of antidepressants and psychological therapies in irritable bowel syndrome: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 114, 21–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brennan, B.P.; Fogarty, K.V.; Roberts, J.L.; Reynolds, K.A.; Pope, H.G., Jr.; Hudson, J.I. Duloxetine in the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome: An open-label pilot study. Hum. Psychopharmacol. Clin. Exp. 2009, 24, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, A.; Franzen, M.D.; Nickell, P.V.; Ransom, D.; Lebovitz, P.J. An open-label trial of duloxetine in patients with irritable bowel syndrome and comorbid generalized anxiety disorder. Int. J. Psychiatry Clin. Pr. 2014, 18, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seddighnia, A.; Tadayon Najafabadi, B.; Ghamari, K.; Noorbala, A.A.; Ebrahimi Daryani, N.; Kashani, L.; Akhondzadeh, S. Vortioxetine effects on quality of life of irritable bowel syndrome patients: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2020, 45, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, E.A.; Bradesi, S. Alosetron and irritable bowel syndrome. Expert Opin. Pharm. 2003, 4, 2089–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsueda, K.; Harasawa, S.; Hongo, M.; Hiwatashi, N.; Sasaki, D. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial of the effectiveness of the novel serotonin type 3 receptor antagonist ramosetron in both male and female Japanese patients with diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 43, 1202–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalilian, A.; Ahmadimoghaddam, D.; Saki, S.; Mohammadi, Y.; Mehrpooya, M. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study to assess efficacy of mirtazapine for the treatment of diarrhea predominant irritable bowel syndrome. Biopsychosoc. Med. 2021, 15, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.D.; Chen, J.; Hoffmann, C.; Bittinger, K.; Chen, Y.Y.; Keilbaugh, S.A.; Bewtra, M.; Knights, D.; Walters, W.A.; Knight, R.; et al. Linking long-term dietary patterns with gut microbial enterotypes. Science 2011, 334, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Propst, E.L.; Flickinger, E.A.; Bauer, L.L.; Merchen, N.R.; Fahey, G.C., Jr. A dose-response experiment evaluating the effects of oligofructose and inulin on nutrient digestibility, stool quality, and fecal protein catabolites in healthy adult dogs. J. Anim. Sci. 2003, 81, 3057–3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, M.E.; Merenstein, D.J.; Reid, G.; Gibson, G.R.; Rastall, R.A. Probiotics and prebiotics in intestinal health and disease: From biology to the clinic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 605–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, A.C.; Quigley, E.M.; Lacy, B.E.; Lembo, A.J.; Saito, Y.A.; Schiller, L.R.; Soffer, E.E.; Spiegel, B.M.; Moayyedi, P. Efficacy of prebiotics, probiotics, and synbiotics in irritable bowel syndrome and chronic idiopathic constipation: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 109, 1547–1561; quiz 1546, 1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarino, M.P.L.; Altomare, A.; Emerenziani, S.; Di Rosa, C.; Ribolsi, M.; Balestrieri, P.; Iovino, P.; Rocchi, G.; Cicala, M. Mechanisms of action of prebiotics and their effects on gastro-intestinal disorders in adults. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, S.; Reid, G. Distant site effects of ingested prebiotics. Nutrients 2016, 8, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whelan, K. Probiotics and prebiotics in the management of irritable bowel syndrome: A review of recent clinical trials and systematic reviews. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2011, 14, 581–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahrudin, M.F.; Abdul Rani, R.; Tamil, A.M.; Mokhtar, N.M.; Raja Ali, R.A. Effectiveness of sterilized symbiotic drink containing lactobacillus helveticus comparable to probiotic alone in patients with constipation-predominant irritable bowel syndrome. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2020, 65, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, C.; Guarner, F.; Reid, G.; Gibson, G.R.; Merenstein, D.J.; Pot, B.; Morelli, L.; Canani, R.B.; Flint, H.J.; Salminen, S.; et al. Expert consensus document. The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics consensus statement on the scope and appropriate use of the term probiotic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 11, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Power, S.E.; O’Toole, P.W.; Stanton, C.; Ross, R.P.; Fitzgerald, G.F. Intestinal microbiota, diet and health. Br. J. Nutr. 2014, 111, 387–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapman, C.M.; Gibson, G.R.; Rowland, I. Health benefits of probiotics: Are mixtures more effective than single strains? Eur. J. Nutr. 2011, 50, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarthy, J.; O’Mahony, L.; O’Callaghan, L.; Sheil, B.; Vaughan, E.E.; Fitzsimons, N.; Fitzgibbon, J.; O’Sullivan, G.C.; Kiely, B.; Collins, J.K.; et al. Double blind, placebo controlled trial of two probiotic strains in interleukin 10 knockout mice and mechanistic link with cytokine balance. Gut 2003, 52, 975–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohman, L.; Simren, M. Pathogenesis of IBS: Role of inflammation, immunity and neuroimmune interactions. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 7, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, D.M.; Moeller, M.J.; Chey, W.D.; Schoenfeld, P.S. The utility of probiotics in the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome: A systematic review. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 104, 1033–1049; quiz 1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.; Ni, H.; Asche, C.V.; Kim, M.; Walayat, S.; Ren, J. Efficacy of Bifidobacterium infantis 35624 in patients with irritable bowel syndrome: A meta-analysis. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2017, 33, 1191–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinan, T.G.; Stanton, C.; Cryan, J.F. Psychobiotics: A novel class of psychotropic. Biol. Psychiatry 2013, 74, 720–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.; Wang, J.; Seo, J.G.; Kim, H. Efficacy of double-coated probiotics for irritable bowel syndrome: A randomized double-blind controlled trial. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 52, 432–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yano, J.M.; Yu, K.; Donaldson, G.P.; Shastri, G.G.; Ann, P.; Ma, L.; Nagler, C.R.; Ismagilov, R.F.; Mazmanian, S.K.; Hsiao, E.Y. Indigenous bacteria from the gut microbiota regulate host serotonin biosynthesis. Cell 2015, 161, 264–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).