Abstract
College students experience new pressures and choices as they transition to independent living and can easily develop unhealthy eating habits, resulting in obesity and obesity-related chronic diseases in later life. This study aimed to test the hypothesis that nutrition literacy (NL) mediated the relationship between multi-level factors influencing healthy eating behavior identified from the social-ecological model and healthy eating behavior of college students. A four-part questionnaire was completed by 412 participants recruited from six different four-year universities in Taiwan (effective response rate = 85.8%). Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics, an independent samples t-test, hierarchical multiple regression, and mediation analysis. The results indicated that the students’ mean nutrition literacy score was 4.32 (SD = 0.78, range = 1–6). In the social-ecological framework, nutrition literacy significantly predicted healthy eating behavior (β = 0.28, p < 0.001; ΔF = 32.54, p < 0.001; ΔR2 = 0.05) with control variables of background, intrapersonal, interpersonal, environmental, and macrosystem factors. Nutrition literacy mediated the effects of seven factors on healthy eating behavior across four levels. These findings suggested that strengthening influential multi-level factors associated with healthy eating behavior not only enhanced NL, but also improved individuals’ healthy eating behavior.
1. Introduction
Chronic diseases are a major cause of death in modern society, and some types of chronic diseases are related to overweight and obesity caused by unhealthy dietary patterns [1,2]. College students are in a period of transition to independent living [3,4], whereby they experience new environments and face new types of pressures [5]. Therefore, they may easily develop unhealthy eating habits and are more likely to develop obesity and obesity-related diseases in adulthood, which increases the risk of chronic diseases [4,6,7,8,9].
The social-ecological framework was based on the theory of ecosystems (i.e., ecological model) proposed by Bronfenbrenner [10,11] for the study of human development, which emphasized the interaction between humans and their environments. This theory posits that the entire ecological system in which growth occurs should be considered when understanding the process of human development. This perspective was subsequently applied to the exploration of health behavior, and researchers have suggested that changes in individuals’ health behavior were influenced by not only intrapersonal factors but also the interaction between individuals and their living contexts, including social, cultural, economic, and environmental factors. Therefore, when examining factors influencing health behavior, various features should be considered at different levels to provide a comprehensive explanation framework [12,13]. Regarding changing individuals’ dietary patterns or obesity problems, the theory of social ecology has been used by many scholars to explain, predict, and change the relationships between individuals’ eating behavior and sociocultural, policy-related, and physical environments [14,15,16,17,18,19]. Several qualitative studies have examined factors influencing the dietary behaviors of college students via interviews, including multi-level barriers and enablers. The results revealed that the factors influencing healthy eating in college students included individual factors (e.g., taste preferences, lack of discipline, time, improved food knowledge and education, meal planning, and involvement in food preparation), social networks (e.g., social support from parents and peers), physical environments (e.g., product prices, limited budgets, and the availability and accessibility of healthy and unhealthy foods), and macrosystems [20,21,22,23,24] (e.g., media and advertising).
From the social ecology perspective, college students’ unhealthy eating behavior is related to unfavorable factors at all levels. Therefore, it is necessary to cultivate students’ ability to adapt to the daily dilemma of dietary choices. In addition, the enhancement of nutrition literacy (NL) in undergraduates is a promising solution to the problem at hand [25,26,27,28]. NL, a type of health literacy [29], refers to the ability to obtain, process, and understand the nutritional information and skills required to make appropriate nutrition-related decisions [30,31,32]. Several studies have indicated that health literacy mediated the relationship between sociodemographic variables and health-promoting behaviors/health outcomes [33,34,35]. Since NL is associated with healthy eating behavior and derived from health literacy [28,36,37,38], and sociodemographic variables are also predictors of NL [38,39], we assume that NL may play a similar role to health literacy in mediating the effect of factors influencing healthy eating on healthy eating behavior.
To our knowledge, the pathways of association between multi-level factors related to healthy eating, NL, and healthy eating behavior in college students have not yet been examined. Therefore, in the present study, it was hypothesized that NL was a mediator of the relationship between multi-level factors influencing healthy eating behavior identified from the social-ecological model and healthy eating behavior of college students.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Selection
A convenience sample consisting of 480 college students was recruited from 6 4-year universities in northern, central, and southern Taiwan (i.e., one national and one private university in each region). To be eligible for this study, participants had to be currently enrolled college students and taking at least 1 course.
2.2. Recruitment and Procedures
A total of 80 undergraduate students were recruited from each school, with a maximum of 45 students in each academic discipline. In addition, the total number of students with medical-, public health-, and nutrition-related majors in each school were limited to 45, to prevent their majors from influencing the study results.
Trained research assistants approached students on campus, provided information regarding the study, and invited them to participate. Upon providing written informed consent, students were asked to complete a self-administered questionnaire that measured NL, factors influencing healthy eating behavior, healthy eating behavior, and demographic information, and took approximately 20 min to complete. Participants were informed that they could withdraw from the study at any stage without incurring adverse personal consequences. In addition, they received a small gift as compensation for participation. All study procedures were approved by the Human Research Ethics Committee. In total, 480 questionnaires were returned, and 412 were valid (valid response rate: 85.8%). Questionnaires that met the following criteria were considered completed: the total number of missing data did not exceed one-third of the length of the questionnaire, and the questionnaire passed the deception detection test.
2.3. Instruments
The instrument was divided into 4 parts: healthy eating behavior scale, NL scale, factors influencing healthy eating behavior scale, and demographic characteristics scale. The first draft of the questionnaire was reviewed by 6 experts in nutrition-related fields for the significance of each item and their relevance to the measurement. When an expert was invited to review, they would receive a description of the research plan and the scoring scheme for the review. A 4-point scale was adopted: 1 point meant “inappropriate,” 2 points meant “significant modification needed,” 3 points meant “minor modification needed,” and 4 points meant “appropriate.” The content validity index (CVI) was calculated based on the assessment results of the experts [40]. After the review was concluded, 207 college students were recruited to pretest the instrument. Cronbach’s α was calculated to demonstrate internal reliability, and intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) was calculated to reveal the test-retest reliability for a two-week interval.
Healthy eating behavior was assessed using a 13-item scale that measured the frequency with which the following types of healthy eating behaviors were practiced: a balanced diet (8 items), processed food consumption (1 item), nutrition label use (3 items), and healthy food choices (1 item). Responses were rated on a scale ranging from 1 (never) to 5 (always). Item scores were summed to provide a total score, and higher scores indicated higher levels of healthy eating behavior. This scale showed good reliability and content validity; Cronbach’s α was 0.86, ICC was 0.49 (p < 0.001), and the average content validity index (CVI) was 0.99.
NL was measured using an 8-item scale that measured capacity for processing nutritional information in the following five dimensions, based on the definition of NL [30,31,41]: obtain (i.e., the capacity to search for, locate, and acquire nutritional information; 2 items), understand (i.e., basic nutritional knowledge and the capacity to understand general nutritional information; 2 items), analyze (i.e., the capacity to discriminate between and analyze different types of nutritional information in a given situation; 1 item), appraise (i.e., the capacity to judge and assess nutritional information according to personal need; 2 items), and apply (i.e., the capacity to apply nutritional information to daily life, to maintain a healthy diet; 1 item). Responses were provided using a Likert scale ranging from 1 (very difficult) to 6 (very easy). Item scores were summed to provide a total score, and higher scores indicated higher levels of NL. This scale has undergone a rigorous development process [42], and the complete version of the scale is presented in the Supplementary Materials. It showed good reliability and content validity: Cronbach’s α was 0.93, ICC was 0.53 (p < 0.001), and the average CVI was 1.00.
Factors influencing healthy eating behavior were measured using a 34-item scale that measured the status of 13 factors on the following 4 levels of influences, based on the social-ecological framework: individual (intrapersonal), social (interpersonal), environmental (physical environmental or community settings), and macrosystem [43]. Furthermore, we included questions to identify deception to ensure high-quality questionnaire data. That is, the item “I prefer sugar-sweetened beverages to water” was modified as “I prefer water to sugar-sweetened beverages,” and both items were included in the questionnaire. Questionnaires returned with consistent responses for these 2 items were included in further analyses.
The items measuring factors influencing healthy eating behavior, such as preference for healthy food, healthy eating attitude and self-efficacy, emotional eating, mindless eating, social eating, and the availability of healthy and unhealthy food, were taken from the Multidimensional Home Environment Scale (MHES) [44]. Furthermore, factors influencing eating behavior in college students, as described in the literature, were also adopted [21,22,23,24]. The item selection and measurement of the scale were compiled by the research team, which included nutrition and health professionals, to meet the 4-level concept of the social-ecological model and echo the actual diet situation of Taiwanese college students. The items were adopted only when the experts reached a consensus, and the college students participating in the pre-test confirmed that none of the items had cultural adaption issues.
Responses were provided using a Likert scale ranging from 1 (strongly disagree) to 6 (strongly agree). Item scores were summed to provide a total score for each factor, and higher scores indicated stronger tendencies toward each factor. Table 1 shows the scale items and reliability and validity of the scale in measuring factors influencing healthy eating behavior. This scale showed good reliability and content validity: Cronbach’s α, ICC, and CVI for each factor are shown in Table 1. Moreover, Table 2 shows that the square root of average variance extracted (AVE) of each level in this scale was greater than its correlations with any other level in the model assessed, which indicates that the discriminant validity in this scale was acceptable [45].

Table 1.
Reliability and validity of the scale measuring factors influencing healthy eating behavior.

Table 2.
Discriminant validity of the scale measuring factors influencing healthy eating behavior.
Demographic characteristics, including sex, years at college, residence (on or off campus during the semester), and daily dietary expenses (average daily cost of food), were measured to control for alternative explanations regarding the relationships between NL and factors influencing healthy eating behavior.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analyses were performed using SPSS 18.0. Descriptive statistics were calculated to provide information regarding participants’ characteristics. Hierarchical multiple regression, which included 6 steps (control variables, intrapersonal variables, interpersonal variables, environmental variables, macrosystem variables, and NL), was performed to estimate the prediction of healthy eating behavior. Mediation analysis was conducted to determine whether NL mediated the effects of factors influencing healthy eating behavior on healthy eating behavior. We adopted Baron and Kenny’s [46] procedure to assess the mediating variable. The variables were regarded as mediators if the following 3 criteria were fulfilled: (1) the independent variable affected the dependent variable (M1), indicating that the total effect was significant; (2) the independent variable affected the mediating variable (M2); and (3) the independent and mediating variables both affected the dependent variable, and the effect of the mediating variable was significant (M3). If 3 regression models were firmly established, the mediation effect existed. Subsequently, the Bootstrap method was used to verify the significance of this indirect effect. Through 5000 repeated samples, a bias-corrected (BC) confidence interval was constructed for the indirect effect. If the 95% confidence interval does not exceed 0, it signifies an indirect effect (or that the hypothesis of the intermediary effect has been verified) [47], and that the ratio of indirect to total effects has been calculated. The mediating effects of NL on the influence of various independent variables on healthy eating behavior were examined in accordance with the above procedure. All analyses included demographic characteristics (i.e., sex, years at college, residence, and daily dietary expenses) as covariates.
3. Results
3.1. Participant Characteristics
In total, 412 college students were included in the study (218 women, 53.6%; 189 men, 46.4%). The participants’ mean age was 20.12 (SD = 1.8) years. Almost 33% of participants were aged 19 years, and 22.3% were aged 20 years. Regarding living conditions during the semester, most students (66.3%) lived in dormitories (without kitchens), while 20.0% lived with their families, and 13.8% rented houses outside the school. Regarding daily dietary expenses, 206 and 145 students spent NTD$ 100–199 and 200–299 on food per day, respectively.
3.2. Nutrition Literacy and Healthy Eating Behavior
The mean score for NL was 4.32 (SD = 0.78), which was between “somewhat easy” and “easy” on the six-point scale. The mean score for healthy eating behavior was 3.13 (SD = 0.57), which was close to the midpoint on the five-point scale. This indicated that the mean frequency with which students practiced healthy eating behavior was close to “sometimes” (i.e., 3–4 days per week).
3.3. Predictive Effect of Nutrition Literacy on Healthy Eating Behavior
As shown in Model 6 in Table 3, NL predicted healthy eating behavior with all the influencing factors controlled for (β = 0.28, p < 0.001; ΔF = 32.54, p < 0.001; ΔR2 = 0.05). This result indicated that with background, intrapersonal, interpersonal, environmental, and macrosystem factors controlled for, NL still significantly predicted healthy eating behavior.

Table 3.
Predictive effect of nutrition literacy on healthy eating behavior.
3.4. The Mediating Effect of Nutrition Literacy
Table 4 illustrates the results regarding the mediating effect of NL on the influences of various independent variables on healthy eating behavior. The analysis of total effects indicated that only four (emotional eating, social eating, availability of unhealthy food, and exposure to food-related advertising) of 13 influential factors were not significantly associated with healthy eating behavior. With regard to the analysis of mediating effects, the factors that were mediated by NL on an intrapersonal level included a preference for healthy food, healthy eating attitude, and healthy eating self-efficacy. The proportions of the total effects of preference for healthy food, healthy eating attitude, and healthy eating self-efficacy explained by mediation were 27.3%, 41.4%, and 25.9%, respectively. A graphical example of the mediating effect of NL is presented in Figure 1. On an interpersonal level, the factors that were mediated by NL included peer social support and family social support. The proportions of the total effects of peer social support and family social support explained by mediation were 31.0% and 48.3%, respectively. On an environmental level, only the availability of healthy foods was mediated by NL, and the proportion of the total effect of the availability of healthy foods explained by mediation was 43.1%. On a macrosystem level, only exposure to healthy eating campaigns was mediated by NL, and the proportion of the total effect of exposure to healthy eating campaigns explained by mediation was 42.4%.

Table 4.
Summary of the Mediating Effects of Nutrition Literacy.
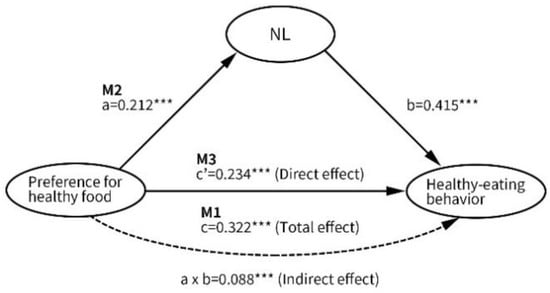
Figure 1.
A graphical example of the mediating effect of NL, (*** p < 0.001).
4. Discussion
Existing literature indicates that NL is significantly related to sociodemographic variables and healthy eating behavior [28,36,37,38,39]. Many scholars have used the social-ecological model to identify multi-level factors that affect healthy eating behavior [14,15,16,17,18,19]. To our knowledge, this is the first study to explore the mediating effect of NL on the relationship between healthy eating behavior and its influencing factors, incorporating the social-ecological model. The present study provides further evidence that NL is not only an independent predictor of healthy eating behavior but also a mediator of the effect of multi-level factors influencing the healthy eating behavior identified from the social-ecological model on healthy eating behaviors of college students.
Our hypothesis that NL was a mediator of the relationship between multi-level factors influencing healthy eating behavior identified from the social-ecological model and healthy eating behavior of college students was partly supported. According to the definition of the mediating effect in this study, these constructs should both satisfy the criterion of M1, M2, and M3 were all statistically significant in the hierarchical regression analysis, and in the Sobel test, the indirect effects of mediation variables should also be statistically significant. Seven out of the 13 factors influencing college students’ healthy eating behavior in four levels of the social-ecological model met the conditions mentioned above for determining the existence of the mediating effect. Thus, NL mediated the effects of seven factors on healthy eating behavior, and the ratio of indirect to total effects was calculated in the Sobel test to indicate the proportions of the total effects explained by the mediating effect of NL. The proportions of the seven factors mediated by NL were listed in descending order: 48.3% for family social support, 43.1% for availability of healthy foods, 42.4% for exposure to healthy eating campaigns, 41.4% for healthy eating attitude, 31.0% for peer social support, 27.3% for preference for healthy food, and 25.9% for healthy eating self-efficacy.
A further review of the factors that were most strongly mediated by NL at each level is provided below. On an interpersonal level, the proportion of the total effect of family social support explained by NL was the highest at 48.3%. Although only 20% of participants lived with their families during university study, the results implied that if students’ families valued the importance of a healthy diet during their childhoods, it could lead to the development of good NL [48,49]. Moreover, even if students left their families and lived independently, these values could exert a positive effect on their healthy eating behavior. On an environmental level, the proportion of the total effect of the availability of healthy foods explained by NL was the highest at 43.1%, while on a macrosystem level, the proportion of the total effect of exposure to healthy eating campaigns is explained by NL was the highest at 42.4%. These results indicated that a university campus with a good eating environment and adequate healthy eating campaigns could enhance the NL of students and thus effectively improve healthy eating behavior in college students. From this perspective, health-promoting strategies in schools [50], that actively improve environmental support regarding college students’ eating behavior via the setting approach, and have been promoted in Taiwan in recent years constitute an appropriate direction for interventions to enhance college students’ NL. On an intrapersonal level, the proportion of the total effect of healthy eating attitudes explained by NL was the highest at 41.4%. The impact of personal attitudes on behavior was explored in the traditional knowledge-attitude-practice model in previous research [51,52]. However, the impact of healthy eating attitudes on behavior occurred largely via the enhancement of NL. That is, college students’ NL should be strengthened by their positive attitudes toward a healthy diet, such as those involving enhancement of their belief in a healthy diet or the use of value clarification. Healthy eating behavior could ultimately be enhanced via this process.
Contrarily, two factors on the intrapersonal level (i.e., preference for healthy food and healthy eating self-efficacy) were less affected by the mediation of NL, suggesting that these two factors had a relatively stronger power to directly affect healthy eating behavior than the other five factors in the present study, or that there were other influences from unknown factors that needed to be further studied. Food preferences are malleable. If the goal is to improve people’s acceptance of healthier foods, then promoting the development of healthy food preferences early in life may be an important direction for future research [53]. Additionally, healthy eating self-efficacy gives people the necessary confidence in their ability to engage in healthy eating behavior, and it is gained through knowledge, understanding, and skill development [54]. Previous studies suggested a complex role of self-efficacy in affecting healthy eating behavior [55,56]. More research is needed in the future to confirm whether there are factors that affect the relationship between healthy eating self-efficacy and healthy eating behavior.
The findings of this study suggested that strengthening influential multi-level factors associated with healthy eating behavior not only enhanced NL, but also improved individuals’ healthy eating behavior. This study found that college students’ healthy eating behavior was not ideal, which was also reported in previous studies [3,4,57]. In the future, the use of the social-ecological model to develop nutrition intervention, whether to directly improve healthy eating behavior or indirectly improve healthy eating behavior through enhancing NL, is a feasible way to improve the health status of college students. Evidence provided by this research can help to prioritize contributing factors when developing interventions with a focus on improving healthy eating behavior.
The study was subject to the following limitations: convenience sampling and discrepancies in self-reported data. The results are not generalizable to all college students in Taiwan because we used convenience sampling, and the sample size was rather small. In addition, because this study used self-reported data, there may have been discrepancies in the participants’ subjective perceptions and actual practice, which may have led to errors in the interpretation of the results. Future studies can use objective measures to evaluate NL or subjective assessments supplemented by NL objective testing to avoid this shortcoming. Despite these limitations, this study adopted a rigorous research design, including valid and reliable measures, more than 400 participants from six universities in Taiwan, and strict statistical procedures, to reduce possible research biases.
5. Conclusions
This was the first study to examine the mediating effect of NL on the relationship between college students’ healthy eating behavior and related influential factors. This finding could be used as the empirical basis of the application of NL to the design of nutrition-based educational interventions. Future studies trying to adopt the social-ecological model to develop nutrition intervention to promote healthy eating behavior in college students should focus on constructs that may enhance students NL, such as family social support, availability of healthy foods, exposure to healthy eating campaigns, healthy eating attitude, and peer social support. While strengthening constructs, such as preference for healthy food and healthy eating self-efficacy, may directly affect healthy eating behavior, it will not be as heavily affected by NL.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/nu13103451/s1, Table S1: Items of the Nutrition Literacy (NL) Scale.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization and Methodology, I.-J.L. and L.-L.L.; Software, Validation and Formal Analysis, L.-C.C.; Investigation, Resources and Data Curation, C.-K.L.; Writing—Original Draft Preparation, I.-J.L.; Writing—Review & Editing, L.-L.L.; Project Administration, I.-J.L.; Funding Acquisition, I.-J.L. and L.-L.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Taiwan Ministry of Science and Technology in 2016 [grant number MOST 105-2511-S-214-001].
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by National Cheng Kung University Human Research Ethics Committee (NCKU-HREC No. 105-216-2, date of approval: 09/14/2016).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained by all subjects involved in this study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to privacy and ethical concerns, neither the data nor the source of the data can be made available.
Acknowledgments
All study procedures were approved by the National Cheng Kung University Human Research Ethics Committee (NCKU-HREC No. 105-216-2). This work was supported by the Taiwan Ministry of Science and Technology in 2016 [grant number MOST 105-2511-S-214-001]. The sponsor was not involved in any stages of the study. The purpose of the grant was purely for scientific discoveries.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declared no potential conflict of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
References
- Kearns, K.; Dee, A.; Fitzgerald, A.P.; Doherty, E.; Perry, I.J. Chronic disease burden associated with overweight and obesity in Ireland: The effects of a small BMI reduction at population level. BMC Public Health 2014, 14, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, P.; Saxena, N.; Zhu, Z. Effect of Asian BMI on risk of chronic disease progression: A Singapore perspective. Proc. Singap. Heal. 2018, 27, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, S.; Noriega, B.R.; Shin, J.Y. College students eating habits and knowledge of nutritional requirements. J. Nutr. Hum. Health 2018, 2, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stok, F.M.; Renner, B.; Clarys, P.; Lien, N.; Lakerveld, J.; Deliens, T. Understanding Eating Behavior during the Transition from Adolescence to Young Adulthood: A Literature Review and Perspective on Future Research Directions. Nutrients 2018, 10, 667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyson, R.; Renk, K. Freshmen adaptation to university life: Depressive symptoms, stress, and coping. J. Clin. Psychol. 2006, 62, 1231–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arts, J.; Fernandez, M.L.; Lofgren, I.E. Coronary Heart Disease Risk Factors in College Students. Adv. Nutr. 2014, 5, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Hang, J.-M.; Wang, R.-L.; Lai, I.-J.; Yang, H.-C. Investigation of Dietary Environment of Universities and Eating Patterns of College Students; Chinese Culture University: Taipei, Taiwan, 2011; pp. 1–205. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Deliens, T.; Clarys, P.; Van Hecke, L.; De Bourdeaudhuij, I.; Deforche, B. Changes in weight and body composition during the first semester at university. A prospective explanatory study. Appetite 2013, 65, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vella-Zarb, R.A.; Elgar, F.J. The ‘freshman 5’: A meta-analysis of weight gain in the freshman year of college. J. Am. Coll. Health 2009, 58, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronfenbrenner, U. Ecological Systems Theory; Jessica Kingsley Publishers: London, UK, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Bronfenbrenner, U. The Ecology of Human Development: Experiments by Nature and Design; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Stokols, D. Translating Social Ecological Theory into Guidelines for Community Health Promotion. Am. J. Health Promot. 1996, 10, 282–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallis, J.F.; Cervero, R.B.; Ascher, W.; Henderson, K.A.; Kraft, M.K.; Kerr, J. An ecological approach to creating active living communities. Annu. Rev. Public Health 2006, 27, 297–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, J.; Kaur, M.; Chakrapani, V.; Kumar, R. Multilevel Influences on Fat, Sugar, Salt, Fruit, and Vegetable Consumption Behaviors among Urban Indians: Application of the Social Ecological Model. SAGE Open 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- e Pereira, M.M.C.; Padez, C.M.P.; Nogueira, H.G.D.S.M. Describing studies on childhood obesity determinants by Socio-Ecological Model level: A scoping review to identify gaps and provide guidance for future research. Int. J. Obes. 2019, 43, 1883–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, C.M.; Devine, C.M.; Dollahite, J.S. Characteristics associated with the application of an ecological approach to preventing childhood obesity. Public Health Nutr. 2017, 20, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohri-Vachaspati, P.; Delia, D.; Deweese, R.S.; Crespo, N.C.; Todd, M.; Yedidia, M.J. The relative contribution of layers of the Social Ecological Model to childhood obesity. Public Health Nutr. 2015, 18, 2055–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buro, B.; Gold, A.; Contreras, D.; Keim, A.L.; Mobley, A.R.; Oscarson, R.; Peters, P.; Procter, S.; Smathers, C. An Ecological Approach to Exploring Rural Food Access and Active Living for Families with Preschoolers. J. Nutr. Educ. Behav. 2015, 47, 548–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, N.; Foster, C. Developing and applying a socio-ecological model to the promotion of healthy eating in the school. Public Health Nutr. 2013, 16, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sogari, G.; Velez-Argumedo, C.; Gómez, M.I.; Mora, C. College Students and Eating Habits: A Study Using an Ecological Model for Healthy Behavior. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deliens, T.; Clarys, P.; De Bourdeaudhuij, I.; Deforche, B. Determinants of eating behaviour in university students: A qualitative study using focus group discussions. BMC Public Health 2014, 14, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacaille, L.J.; Dauner, K.N.; Bas, R.J.K.; Pedersen, J. Psychosocial and Environmental Determinants of Eating Behaviors, Physical Activity, and Weight Change Among College Students: A Qualitative Analysis. J. Am. Coll. Health 2011, 59, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greaney, M.L.; Less, F.D.; White, A.A.; Dayton, S.F.; Riebe, D.; Blissmer, B.; Shoff, S.; Walsh, J.R.; Greene, G.W. College Students’ Barriers and Enablers for Healthful Weight Management: A Qualitative Study. J. Nutr. Educ. Behav. 2009, 41, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, M.C.; Kocos, R.; Lytle, L.A.; Perry, C.L. Understanding the Perceived Determinants of Weight-related Behaviors in Late Adolescence: A Qualitative Analysis among College Youth. J. Nutr. Educ. Behav. 2009, 41, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doustmohammadian, A.; Omidvar, N.; Shakibazadeh, E. School-based interventions for promoting food and nutrition literacy (FNLIT) in elementary school children: A systematic review protocol. Syst. Rev. 2020, 9, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joulaei, H.; Keshani, P.; Kaveh, M.H. Nutrition literacy as a determinant for diet quality amongst young adolescents: A cross sectional study. Prog. Nutr. 2018, 20, 455–464. [Google Scholar]
- Kalkan, I. The impact of nutrition literacy on the food habits among young adults in Turkey. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2019, 13, 352–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, L.-L.; Lai, I.-J.; Chang, L.-C. Nutrition literacy is associated with healthy-eating behaviour among college students in Taiwan. Health Educ. J. 2019, 78, 756–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuen, E.; Thomson, M.; Gardiner, H. Measuring Nutrition and Food Literacy in Adults: A Systematic Review and Appraisal of Existing Measurement Tools. HLRP Health Lit. Res. Pract. 2018, 2, e134–e160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silk, K.J.; Sherry, J.; Winn, B.; Keesecker, N.; Horodynski, M.A.; Sayir, A. Increasing Nutrition Literacy: Testing the Effectiveness of Print, Web site, and Game Modalities. J. Nutr. Educ. Behav. 2008, 40, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aihara, Y.; Minai, J. Barriers and catalysts of nutrition literacy among elderly Japanese people. Health Promot. Int. 2011, 26, 421–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoellner, J.; Connell, C.; Bounds, W.; Crook, L.; Yadrick, K. Nutrition Literacy Status and Preferred Nutrition Communication Channels among Adults in the Lower Mississippi Delta. Prev. Chronic Dis. 2009, 6, A128. [Google Scholar]
- Noroozi, A.; Khademolhosseini, F.; Lari, H.; Tahmasebi, R. The Mediator Role of Mental Health Literacy in the Relationship between Demographic Variables and Health-Promoting Behaviours. Iran. J. Psychiatry Behav. Sci. 2018, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Oh, J. The Relationship between E-Health Literacy and Health-Promoting Behaviors in Nursing Students: A Multiple Mediation Model. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lastrucci, V.; Lorini, C.; Caini, S.; Bonaccorsi, G.; Florence Health Literacy Research Group. Health literacy as a mediator of the relationship between socioeconomic status and health: A cross-sectional study in a population-based sample in Florence. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0227007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, M.K.; Sullivan, D.K.; Ellerbeck, E.F.; Gajewski, B.J.; Gibbs, H.D. Nutrition literacy predicts adherence to healthy/unhealthy diet patterns in adults with a nutrition-related chronic condition. Public Health Nutr. 2019, 22, 2157–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taleb, S.; Itani, L. Nutrition Literacy among Adolescents and Its Association with Eating Habits and BMI in Tripoli, Lebanon. Diseases 2021, 9, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koca, B.; Arkan, G. The relationship between adolescents’ nutrition literacy and food habits, and affecting factors. Public Health Nutr. 2021, 24, 717–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doustmohammadian, A.; Mohammadi, N.K.; Omidvar, N.; Amini, M.; Abdollahi, M.; Eini-Zinab, H.; Amirhamidi, Z.; Esfandiari, S.; Nutbeam, D. Food and nutrition literacy (FNLIT) and its predictors in primary schoolchildren in Iran. Health Promot. Int. 2019, 34, 1002–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynn, M.R. Determination and quantification of content validity. Nurs. Res. 1986, 35, 382–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen-Bohlman, L.; Panzer, A.; Kindig, D. Health Literacy: A Prescription to End Confusion; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, L.-L.; Lai, I.-J.; Shih, S.-F.; Chang, L.-C. Development and validation of the nutrition literacy measure for Taiwanese college students. Taiwan J. Public Health 2018, 37, 582–597. [Google Scholar]
- Story, M.; Neumark-Sztainer, D.; French, S. Individual and Environmental Influences on Adolescent Eating Behaviors. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2002, 102, S40–S51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabbakh, T.; Freeland-Graves, J. Development and validation of the Multidimensional Home Environment Scale (MHES) for adolescents and their mothers. Eat. Behav. 2016, 22, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornell, C.; Larcker, D.F. Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error. J. Mark. Res. 1981, 18, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, R.M.; Kenny, D.A. The moderator–mediator variable distinction in social psychological research: Conceptual, strategic, and statistical considerations. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 1986, 51, 1173–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrout, P.E.; Bolger, N. Mediation in experimental and nonexperimental studies: New procedures and recommendations. Psychol. Methods 2002, 7, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodruff, S.J.; Hanning, R.M. A Review of Family Meal Influence on Adolescents’ Dietary Intake. Can. J. Diet. Pract. Res. 2008, 69, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dallacker, M.; Hertwig, R.; Mata, J. The frequency of family meals and nutritional health in children: A meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. 2018, 19, 638–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, L.-L.; Liu, C.-H.; Chang, F.-C.; Cheng, C.-C.J.; Niu, Y.-Z.; Chang, T.-C. Evaluation of the Health-Promoting School Supporting Network in Taiwan. J. Sch. Health 2015, 85, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettinghaus, E.P. Health promotion and the knowledge-attitude-behavior continuum. Prev. Med. 1986, 15, 475–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooke, R.; Papadaki, A. Nutrition label use mediates the positive relationship between nutrition knowledge and attitudes towards healthy eating with dietary quality among university students in the UK. Appetite 2014, 83, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anzman-Frasca, S.; Ventura, A.K.; Ehrenberg, S.; Myers, K.P. Promoting healthy food preferences from the start: A narrative review of food preference learning from the prenatal period through early childhood. Obes. Rev. 2018, 19, 576–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandura, A. Health promotion from the perspective of social cognitive theory. Psychol. Health 1998, 13, 623–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muturi, N.W.; Kidd, T.; Khan, T.; Kattelmann, K.; Zies, S.; Lindshield, E.; Adhikari, K. An Examination of Factors Associated with Self-Efficacy for Food Choice and Healthy Eating among Low-Income Adolescents in Three U.S. States. Front. Commun. 2016, 1, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulik, N.L.; Moore, E.W.G.; Centeio, E.E.; Garn, A.C.; Martin, J.J.; Shen, B.; Somers, C.L.; McCaughtry, N. Knowledge, Attitudes, Self-Efficacy, and Healthy Eating Behavior Among Children: Results from the Building Healthy Communities Trial. Health Educ. Behav. 2019, 46, 602–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M. Investigation and analysis on outdoor sports and dietary nutrition of college students. Carpathian J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 8, 160–167. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).