Abstract
Urban farming, practiced by about 800 million people globally, has contributed significantly to food security and food safety. The practice has sustained livelihood of the urban and peri-urban low income dwellers in developing countries for many years. Its popularity among the urban low income is largely due to lack of formal jobs and as a means of adding up to household income. There is increasing need to sustainably manage urban farming in developing nations in recent times. Population increase due to rural-urban migration and natural, coupled with infrastructure developments are competing with urban farming for available space and scarce resources such as water for irrigation. Lack of reliable data on the extent of urban/peri-urban areas being used for farming has affected developing sustainable policies to manage urban farming in Accra. Using ground based survey methods to map the urban farmlands are inherently problematic and prohibitively expensive. This has influenced accurate assessment of the future role of urban farming in enhancing food security. Remote sensing, however, allows areas being used as urban farmlands to be rapidly established at relatively low cost. This paper will review advances in the use of remote sensing technology to develop an integrated monitoring technique for urban farmlands in Accra.
1. Introduction
Urban farming, a phenomenon that can be observed worldwide, is a widely practiced industry that has existed for a long time. In considering the broad development and sustainability of urban farming practices, many assumptions are often made. This is with regard, particularly, to the likely risks and public health hazards of the practice to urban farmers, market workers and the consumers of the products. The benefits that accrue from urban farming, such as increased availability of fresh crops, especially vegetables, and contributions to food security and sustainable livelihoods, are often underestimated and undervalued. However, in times of harsh economic situations and periods of food insecurity, urban farming is often adopted as an important livelihood strategy for survival. Urban farming has assumed global concern and become a topic of scientific research in recent years. This is because the increasing growth of hunger in most parts of the world, especially in developing nations, has presented a huge challenge to governments. Currently about 65 million people are affected by hunger, which is expected to increase by 20 percent in about 30 years [1]. The World Bank [2] reported that by the year 2025 the urban population of sub-Sahara Africa would be growing at 6.9 percent per annum as compared to 3.1 percent of total population of the region. This will require producing enough food to meet the expected demand and sustaining the practice under the increasing effect of global climate change.
Urban farming can be defined as an agricultural enterprise located within or on the fringes of a town, a city or a metropolis, which grows or raises, processes and distributes a diversity of food and non-food products, (re-)using largely human and material resources, products and services found in and around that urban area, and in turn supplying human and material resources, products and services largely to that same urban area [31]. The practice has become an extremely visible economic activity in urban and peri-urban areas of cities all over the world. It engages about 800 million people globally [1] and utilises available urban/peri-urban empty spaces. Of the estimated number, about 200 million are considered to be market producers employing approximately 150 million people on a full-time basis. Thus it contributes significantly to food security and safety for the approximately 50% of the world's population, who are city dwellers [3]. Urban farming has also sustained livelihood of the urban and peri-urban low income dwellers in developing countries for many years.
Practicing urban farming in the developing nations is significant since a substantial and growing proportion of the population lives in or around metropolitan areas and large cities including the peri-urban zone, where their livelihoods depend to some extent on natural resources such as land for food, water, fuel and space for living [4]. Motivation for city farming among the urban low income is largely due to lack of formal jobs and as a means of adding up to household income practices. Many urban farmers, especially women, use income earned from farming on food provision for the family [5]. Rapid growth at the peri-urban fringe has resulted in increased commercial development along arterial roads connecting cities and the countryside [6]. This development threatens the sustainability of urban farming since the practice is largely influenced considerably by changing land use and land cover patterns. Significant proportions of agricultural lands have thus been changed with built-up or urban land use. Uncontrolled momentum of urban sprawl and land use change raises many issues [7] which might have considerable impact on urban farming practices. Vegetable production in urban and peri-urban areas may face difficulties to survive in the long run due to the scarcity of land resources, unless pragmatic and sustainable management strategies are adopted. Rapidly increasing population in cities and limited cultivated areas require higher farming productivity without polluting soil, air and water [8].
Urban/peri-urban farming practice offer substantial advantages to the urban areas. It provides a solution to ecologically unhealthy development of large urban agglomerations [9]. It also offers substantial opportunities for environmental enhancement and protection through organic waste recycling and natural resource conservation [10]. The practice is thus accepted as an integral part of the urban ecosystem. According to local ecological conditions and habitat, urban farming can contribute to preserve natural areas despite the increase of the price of land [11] to favour intensive production of perishable foods like fruits and vegetables. The demand for perishable products can be expected to remain high in urban areas because people living in those areas mainly depend on market supplies for their food consumption as compared to rural people [12]. In addition to supplying perishable products to the urban dwellers, urban farming also generates formal and informal employment for food processors and distributors. Thus the practice has been a significant source of job creation for the urban unemployed, improved livelihood and sustained the urban ecology. It is estimated that about a fifth to a third of families in some cities are engaged in urban farming, with some not having any other source of sustenance or income [13].
This development is significantly high in developing nations, where interest in urban farming is increasing due to the prevailing relatively harsh economic conditions. In Maputo about 30 percent of the land is being used for urban farming, while in Dar es Salam urban farming practice provided work for approximately 67 percent of the city’s adult population in 1991, thus making it the second largest source of employment in Dar es Salam [14]. Urban farming in Kathmandu, Nepal, enables about 37 percent of food producers to meet all their household vegetable needs and about 90 percent of Havana's fresh produce come from local urban farms [15]. Urban farming practice has thus sustained the physical and economic survival of the urban poor in most developing nations.
The ability of urban farming to continuously supply food for the urban poor, especially in developing nations, will depend on better planning based on accurate geospatial information to enable sustainable management of the practice. Reliable data on the extent of urban/peri-urban areas being used for farming, spatial distribution of such areas, types of crops and proximity to market places are lacking in most developing nations. In recent years, increasing attention is being paid to urban land use/land cover change because ecosystems in urban areas are affected immensely by human activities. Using ground-based surveys method for data capturing to detect and measure change are relatively expensive and time consuming [16]. For this reason, the actual extent of areas being used for urban farming in most developing nations has not been properly quantified. Little is also known of the spatial distribution of urban farming in cities [14]. Remote sensing, however, provides spatially consistent data sets that cover large areas with both high spatial detail and high temporal frequency. Thus the technique allows the current size of city farmlands to be rapidly determined at relatively low cost. Remote sensing can also provide consistent historical time series data. Future repeated observations will, over time, allow detailed quantification of changes in the farmland sizes and types of crops produced. Thus remote sensing provides a detailed insight into the spatial and temporal dynamics of the processes in urban growth and land use change. Satellite remote sensing techniques have, therefore, been widely used in detecting and monitoring land cover change, including urban farming, at various scales with useful results [17]. Recently, remote sensing has been used in combination with Geographical Information Systems (GIS) and Global Positioning Systems to assess land cover change more effectively than by remote sensing data only [18]. It has already proved useful in mapping urban areas, and as data source for the analysis and modeling of urban growth and land use/land cover change [19]. In the meantime changes in urban farming in developing nations can be quantified by coupling remote sensed data with available historic information from archival area photography and other sources in a GIS environment.
2. Objectives
This paper presents an overview of the advances in the use of remote sensing technology to develop an integrated monitoring technique for urban farmlands in Accra and how the information derived can be used to develop sustainable policies for urban farming in developing countries. Different methods are compared and the advantages or strengths of remote sensing is highlighted to underscore the need for developing nations to adopt remote sensing techniques in monitoring spatial changes in urban and peri-urban farmlands.
3. Study Area
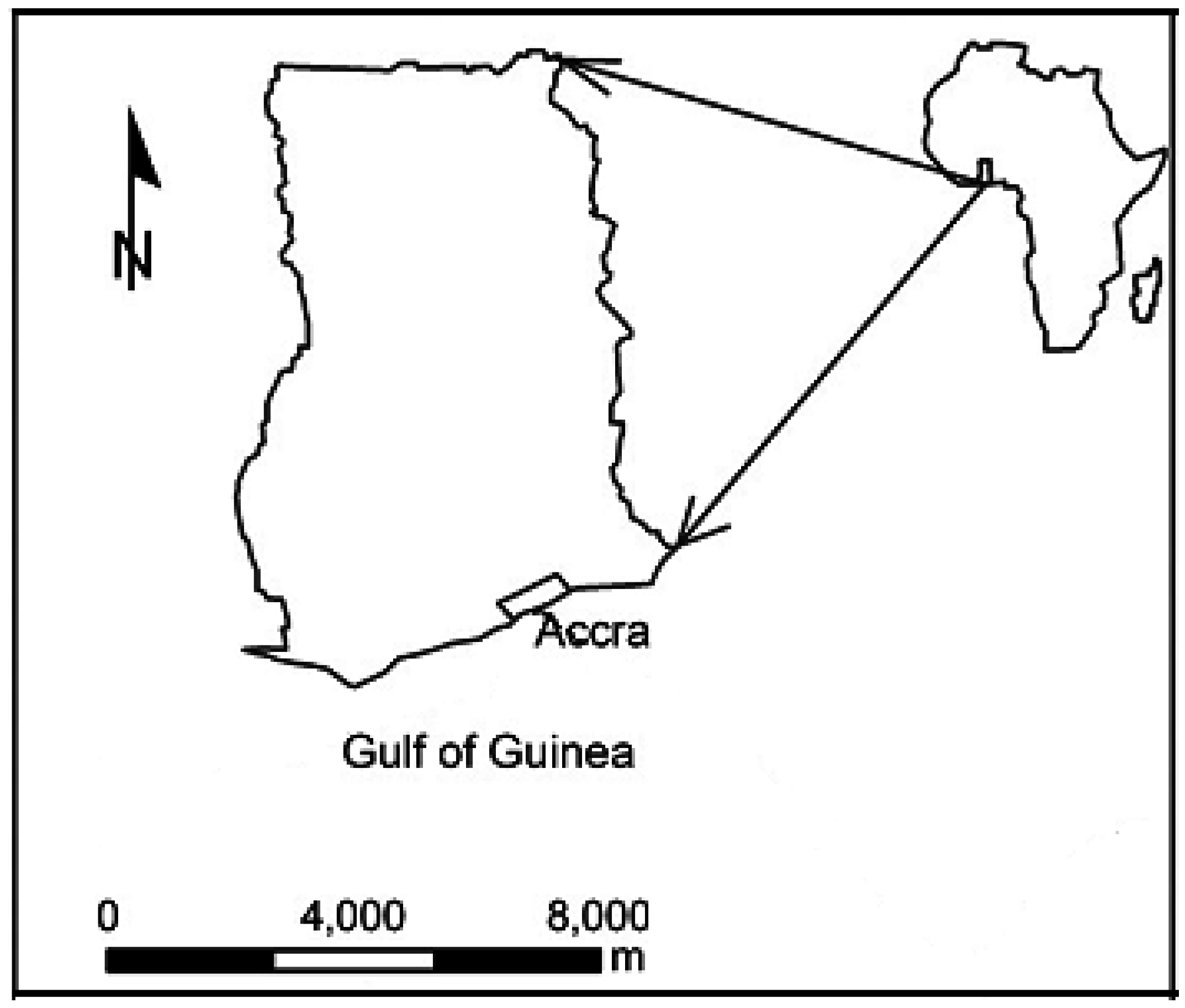
Accra, the capital city of Ghana, covers an area of about 170 km². The city lies along the Gulf of Guinea at latitude 5.626°N and longitude 0.1014°W (Figure 1). It has an estimated population of about 2 million [21] and a functional population of between 3.0–3.4 million. The population growth rate of Accra is about 3.4 percent per annum, however only about 10 percent of this population resides in its peri-urban districts [21]. The opportunity for employment in Accra continues to attract an average of about 25,000 migrants per year and according to Duedall and Maul [22], this is expected to increase by 82% in 2025.
Urban farming in Ghana, a developing country, contributes to city food supply, employment creation and achievement of sustainable livelihoods, and poverty reduction. Although these benefits are well known, this knowledge has not positively influenced the recognition of urban farming as an important component of urban development and land use planning. This is mainly because of the high demand for land for other more profitable land use sectors and the fact that farming within the city is often associated with health risks by the municipal authorities. Approximately 44 percent of the estimated population of 20 million Ghanaians currently resides in urban areas and in some cities the annual urban population growth rate is estimated at about 4.4 percent [20]. This rate of urbanization is rapid and exceeds the current levels of urban infrastructural development, consequently existing limited public services, such as sanitation facilities, are woefully over-stretched and remain inadequate. Waste collection systems are inefficient and solid and liquid wastes are consistently dumped and discharged into urban spaces and open drains. Furthermore, continuous migration of people from rural areas to the cities in search of ‘greener pastures’ creates high pressures on and demands for food and municipal services, while the percentage of urban poor who cannot afford the basic amenities of life also continues to increase. Increase in the urban demand for food is challenged by low agricultural productivity in rural areas. In response to this situation, an increasing number of city dwellers have resorted to various kinds of income generating activities in the urban informal sector. These activities include intensive urban and peri-urban farming, which takes advantage of urban runoff/wastewater and vacant open spaces in the city for food production. The practice of urban and peri-urban food production has continued to increase during the last decade in efforts to address the problems of urban poverty reduction and environmental management. A critical assessment of the development of urban farming in Accra reveals vital issues that need to be addressed by the policy makers to maximize the benefits and ensure its sustainability. The most essential issue is the need to recognize the importance of urban farming and institutionalise it through integration into overall urban development plans.
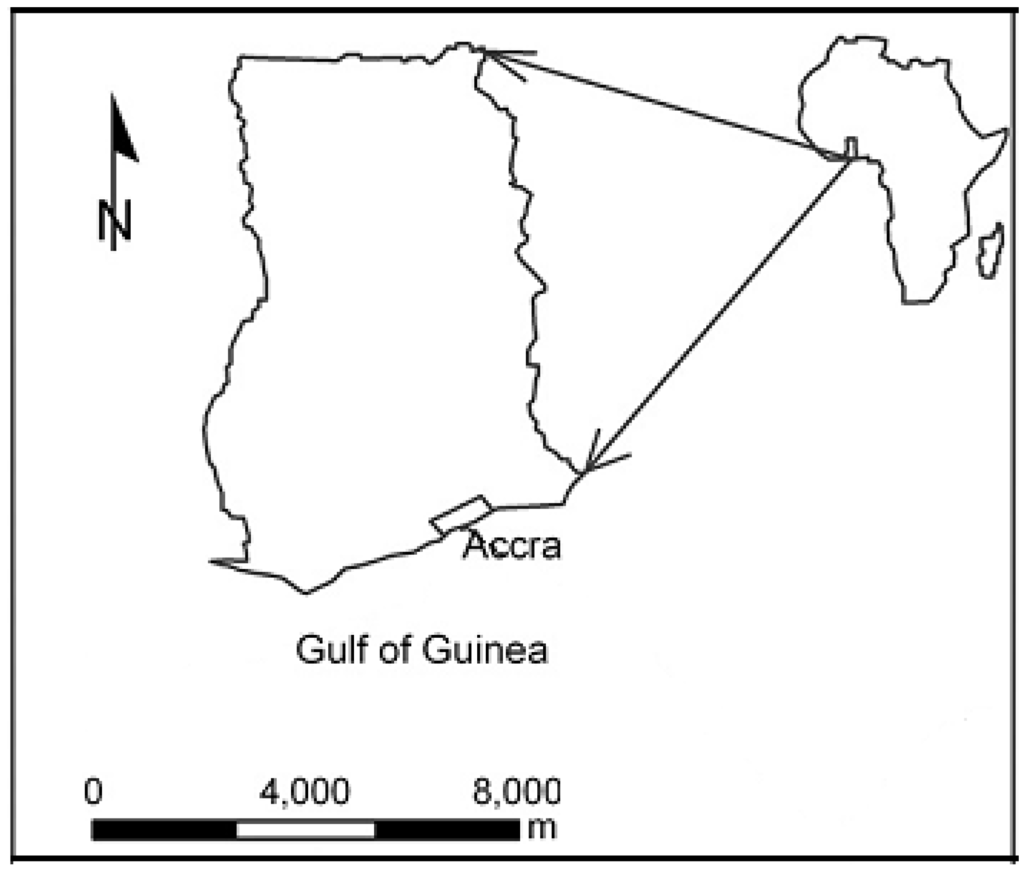
Figure 1.
The location of Accra in Ghana (source: [9]).
Figure 1.
The location of Accra in Ghana (source: [9]).
Urban farming in Accra assumed prominence between 1972 and 1976 when the then government, through the Operation Feed Yourself (OFY) programme, encouraged farming in the cities due to the harsh economic conditions and related acute shortage of food. These conditions resulted in the devaluation of the Ghanaian currency, huge external debts and unfavourable climatic conditions (severe drought). Supplying food for the country's population became a national issue as prices of food items became exorbitant, especially in the cities [23]. The OFY programme was described as the most ambitious programme to respond to Ghana's food problem [23]. It was a crash programme aimed at increasing both food production and promoting national self-reliance by encouraging Ghanaians in rural as well as urban areas to grow their own food. Urban farming activities were tolerated and stringent regulations and by-laws that curtailed the practice were relaxed.
Despite the high interest in urban farming in Accra [24] after the OFY programme, primary agricultural production remains the smallest economic sector of Accra. It contributes to local economic development in many ways. For example, it provides a reliable and alternative source of livelihood for many unemployed youth and retirees as well as improves the family budgets of the farmers. Urban farming also contributes significantly to food security in Accra by making food available in the households, and making food more accessible and affordable. Urban farming practices enhance price stability and helps to lower the cost of similar agricultural produce imported from elsewhere. In that way, it contributes towards poverty reduction. Urban farming in Accra provides gainful employment and reliable income generating activity to many urban resource poor farmers, who otherwise would have been without any source of gainful livelihood to survive the harsh economic conditions. Most of the urban farmers in Accra derive sufficient income that enable them to live above the national poverty line with an average monthly income of US$40–50, especially for irrigated vegetable farmers [25]. Thus the aggregate benefits of urban farming to local economic development are significant. Although the contribution of urban farming to the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) may be small [11], its importance for certain commodities, such as vegetables production, might be substantial [26]. Two forms of urban farming are practiced in Accra. They include those that are practiced in open spaces and those around dwellings, commonly known as ‘backyard’ gardens. Produce from the open space farmlands are usually sold to the public, while the ‘backyard’ produce is consumed in the homes of the farmers. For the purpose of this paper, urban farming is referring to practices in the open spaces.
Urban farming in Accra is typically done along water bodies and drains and backyards that ensure year-round production [27]. Produce include basically varieties of vegetables including okro, garden eggs, tomatoes, carrots, cucumber, cabbage, cauliflower and lettuce (Figure 2). The increasing land value in Accra is resulting in changes in the use of land for urban farming to use for commercial and economic purposes. Urban and peri-urban agriculture activities take place on residential areas, open spaces reserved for future development, as well as along riverbanks, dams and catchments areas, along roadsides, railway reserves and hills. Urban farming production systems identified in Accra include irrigated vegetable production, backyard gardening and seasonal crop farming [28,29,30].
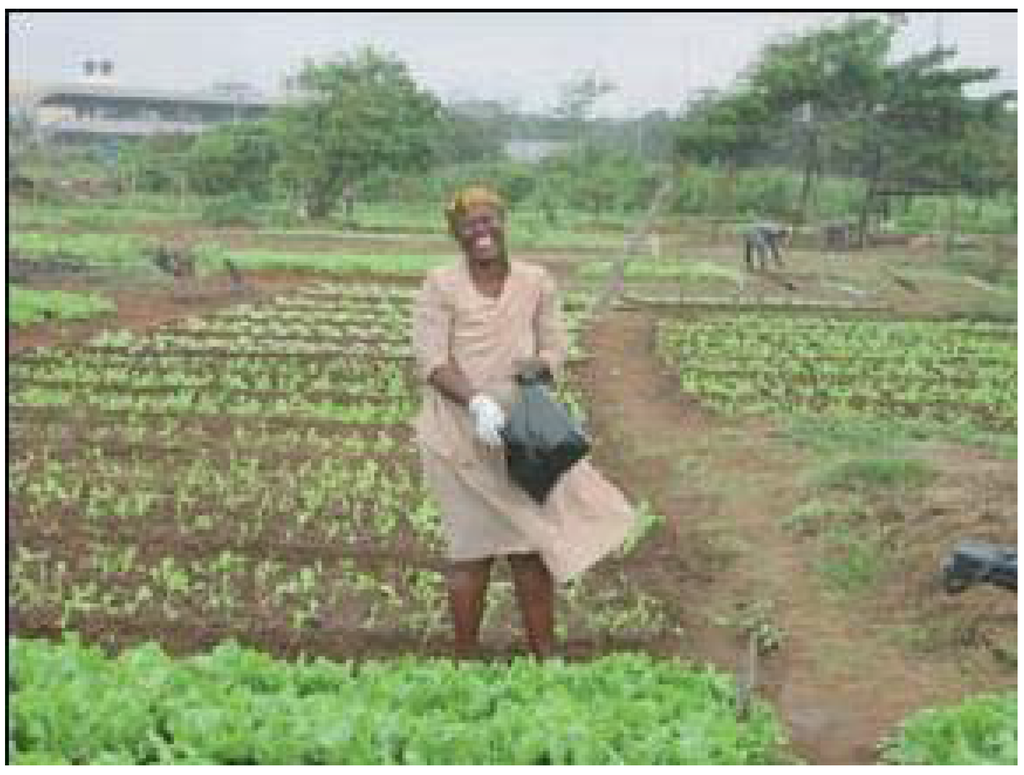

Figure 2.
Urban farming in Accra, Ghana (source: [33]).
Figure 2.
Urban farming in Accra, Ghana (source: [33]).

Most urban farmers in Accra have rural backgrounds and have some level of experience in farming before migrating to the urban areas [31,24]. Many of them principally come to the city to seek employment opportunities, to trade or to attend school for higher education. Such migrants take up urban agriculture to earn enough money to meet these main needs. However, if they fail, they end up depending on urban vegetable production as a reliable source of livelihood. Later, their children and relatives participate in urban farming. Urban farming in Accra seems to be a reliable and sustainable source of income especially as people with better income levels still continues to practice it. A study has revealed that about 66 percent of urban farmers have no intention to stop farming even if they were offered regular paid employment, while the remaining percentage mentioned sickness and loss of farm land as issues that could compel them to stop farming [24]. This is because urban agriculture could bring in significantly high earnings in spite of the risks of crop loss due to pests, diseases and other environmental factors. Apart from the practice being the significant source of food supply, revenue generation, employment creation, livelihood support, poverty reduction and urban waste management in the city [32], it is also an avenue for promoting a greener city with its ecological benefits. It is estimated that about 90 percent of fresh perishable intake of the population in Accra is being met by urban production [27]. The practice, if properly managed, could address future food security issues in Accra in the light of the global climate change phenomenon.
Managing urban and peri-urban farming activities within the city of Accra has been on adhoc basis due to lack of reliable information. Unplanned siting of farmlands and indiscriminate usage of available spaces has resulted in problems to the urban dwellers and the farmers. The quest for Accra attaining modern city status has resulted in an urbanisation drive with new structures being constructed daily. Available spaces that were formally used for urban farming are now being converted for construction activities. This situation has compelled the urban low income dwellers, who are mostly engaged in farming practices to encroach waterways for their activities. The situation has led to the creation of pools of stagnant waters (Figure 3), which serve as breeding grounds for mosquitoes, and thus increasing cases of malaria [34]. Unplanned and ineffective management of Accra's urban farming practices has also resulted in the pollution of urban rivers [35]. Encroachment of available empty spaces among development has also resulted in protracted land disputes in Accra. Significant proportions of the farms are also sited along motorways, especially within earmarked road reservations, which compromise the safety of the farmers.
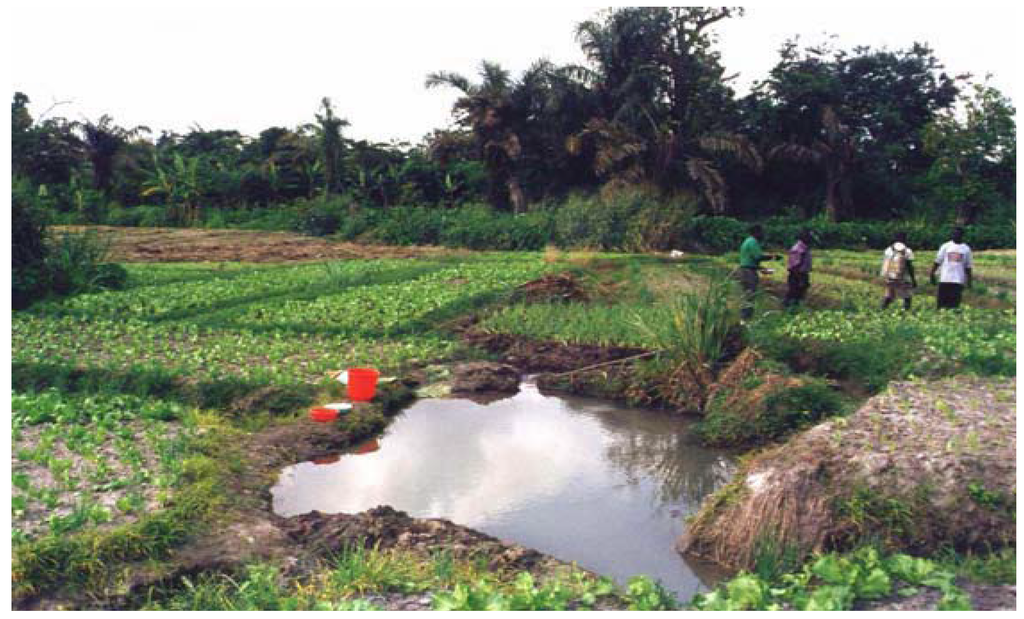

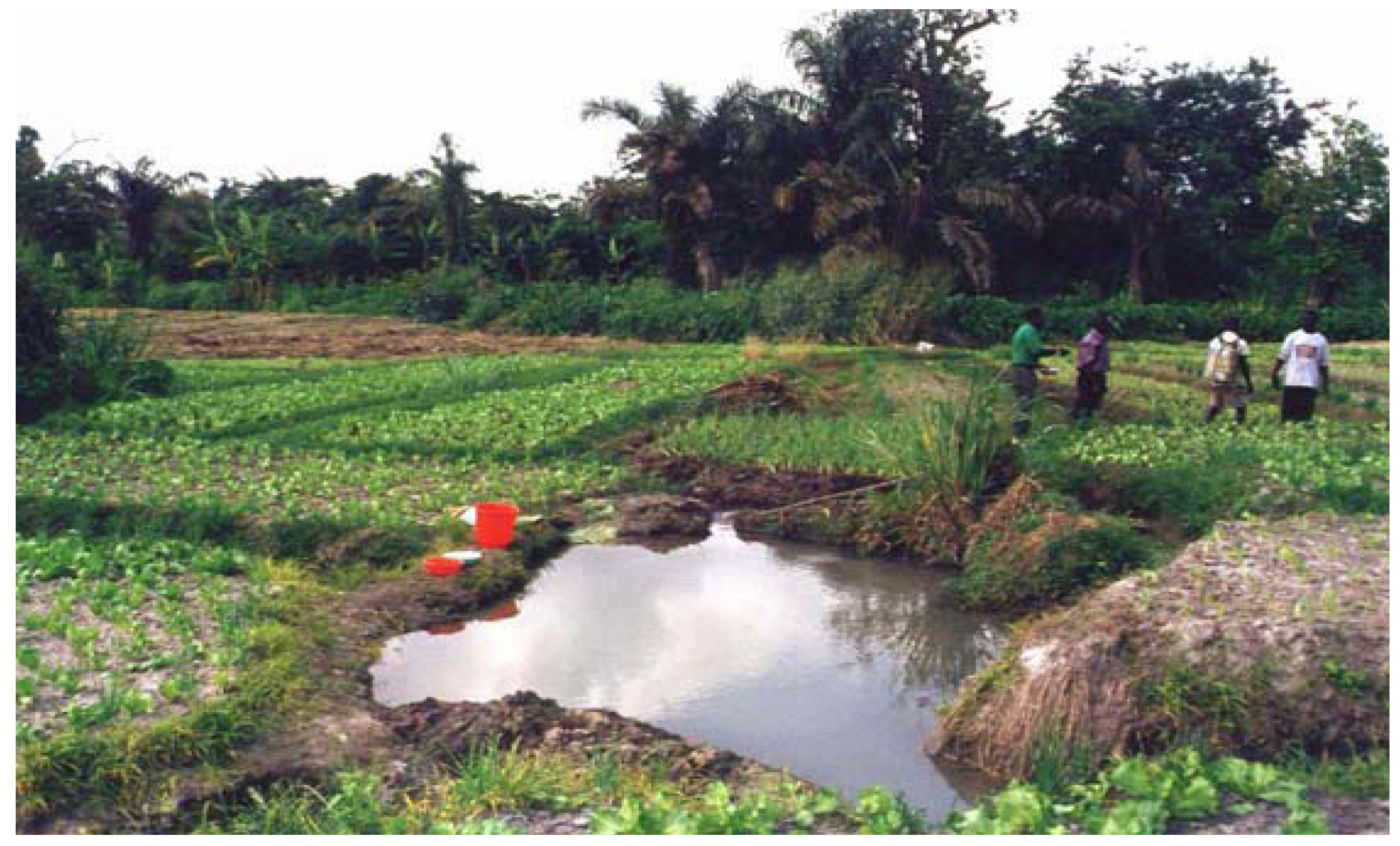
Figure 3.
Stagnant water as a result of urban farming (source [32]).
Figure 3.
Stagnant water as a result of urban farming (source [32]).

Sustaining urban farming practices in Accra in the long term under the present harsh climatic conditions remains a major challenge to the Ghana government. Lack of reliable geospatial data has prevented developing effective and pragmatic land use management strategies. The growth of the city, in terms of habitability and competitiveness, has undermined the sustainability of urban farming as a channel of addressing food security in Accra. Having recognised the dynamism of the urban environment of Accra, an innovative approach to address the challenges associated with urban farming is to develop effective data capturing methods. This will facilitate generating baseline information to monitor the changing trends in Accra's urban farming activities that will promote pragmatic management policies.
4. Methods
A number of methods that differ in approach, accuracy, cost and duration have been developed to meet the demand for higher accuracy in urban farmlands mapping. The techniques have evolved over the years and progressed from manual to semi automated that is consistent with advances in technology. This has resulted in improvement in farmland data processing and storage capabilities, increased accuracy and reduction in uncertainty. The frequent change in technology has prevented the emergence of a standard method of farmland mapping since none of the methods address the entire range of cartographic and photogrammetric techniques required for accurate mapping. The mapping methods adopt techniques that extract the farmland boundaries on historical maps and aerial photographs. Selecting a particular method for mapping is influenced by factors such as the level of accuracy required, type of output desired, method of ground control point collection, availability of funding and /or equipment, and the method to be adopted to analyse change.
4.1. Physical Survey
Physical surveying of the farmland involves determining the boundaries with reference to an established control point. Ground measurements using planetable techniques that combine fieldwork with office work has enabled production of sufficiently accurate farmlands maps for many decades. Although the method is time consuming and, expensive, it provides the most accurate form of information [43] since the plotted farmland boundary is continually under the surveillance of the surveyor. Potential sources of uncertainty with this method include precise setting over the reference point, drawing rays and imprecision in projection. Through time, triangulation techniques improved the accuracy of field survey methods and new instruments improved the speed at which a survey could be conducted. Notable among the new techniques is the Kinematic Global Position System, which enables three-dimensional coordinates to be obtained by receiving and processing signals from GPS satellites. Data can be collected by moving a monocycle equipped with a GPS unit directly along the farmland boundary at a constant speed and continuously tracking a roving antenna relative to a static base station (Figure 4). Coordinates are collected at specified time intervals, allowing real-time digitisation of the boundary, and each epoch of data collected is processed to create a string of point coordinates representing the farmland boundary. The method is relatively rapid, low cost and highly accurate [44] and errors are minimal on flat surfaces as compared to difficult terrain [45]. However, the labour-intensive method of sending survey teams out into the field to obtain data makes ground based survey technique unattractive for farmland mapping. The varied locations of the farmlands limit the parcels of farmlands that can be surveyed within a period. The technique also prevents obtaining different date data over short periods for monitoring changes.
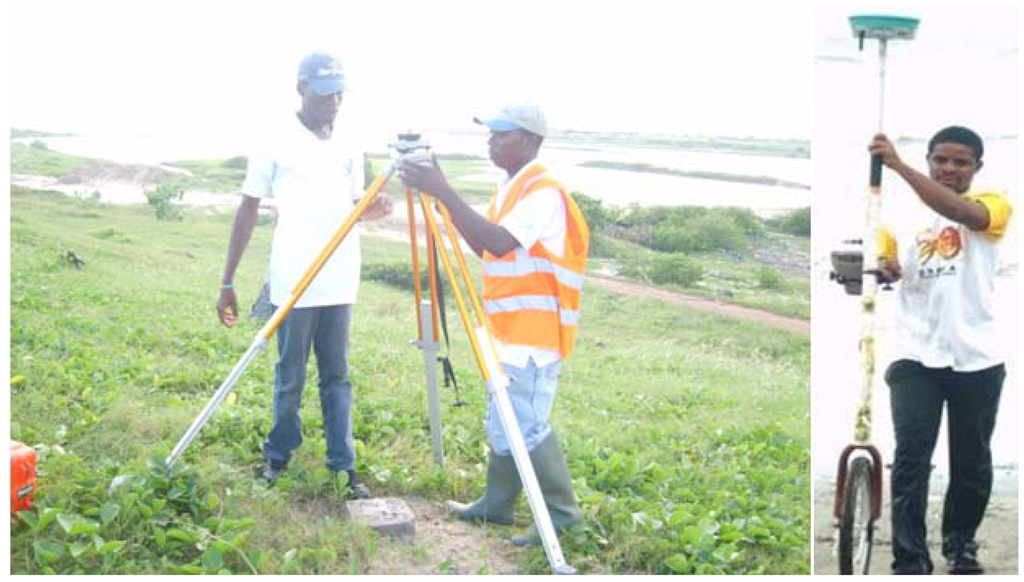

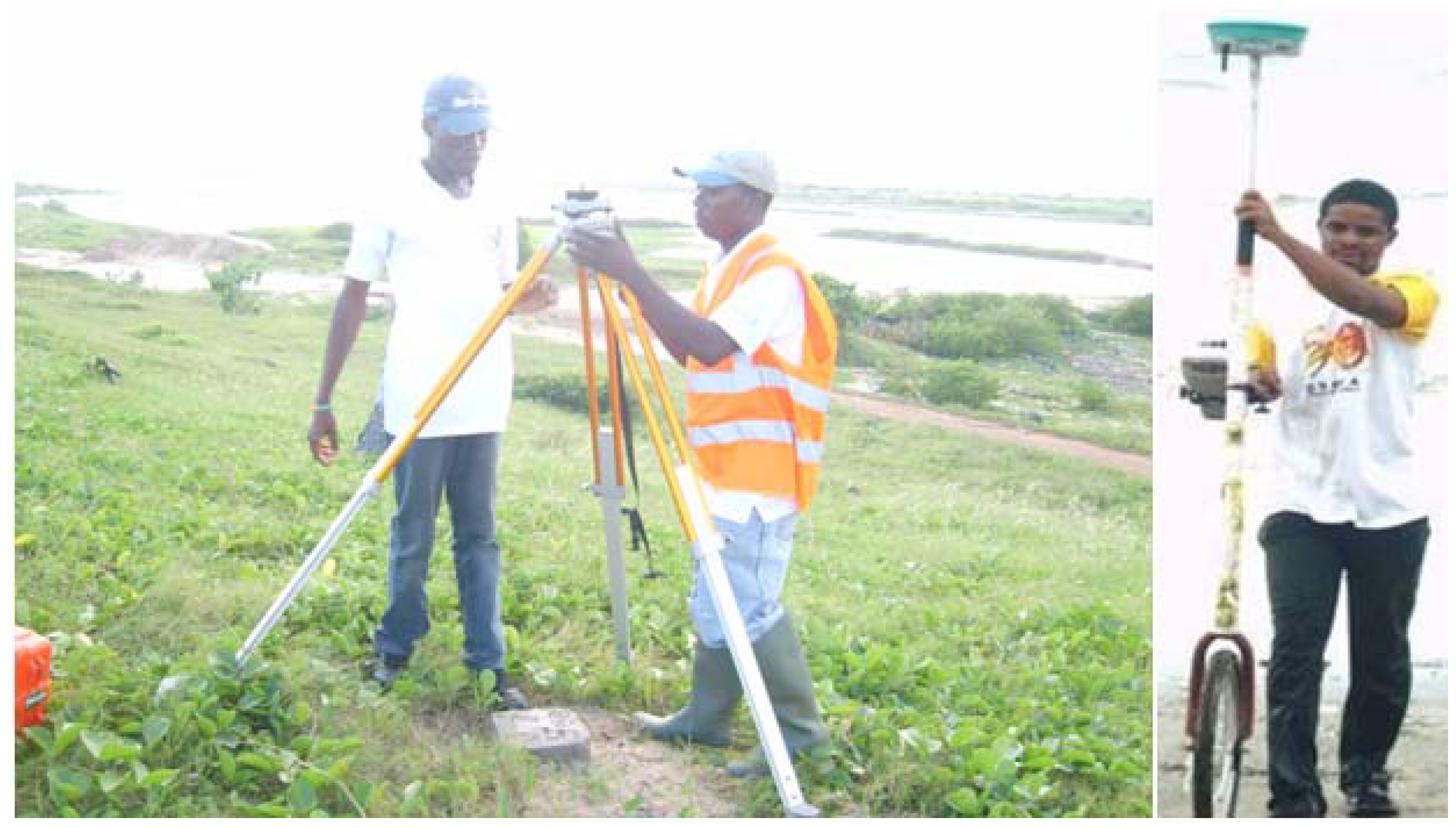
Figure 4.
Kinematic GPS survey using a monocycle mounted with GPS receiver.
Figure 4.
Kinematic GPS survey using a monocycle mounted with GPS receiver.

4.2. Digitising
Farmland boundaries on historic maps must be converted into digital format before they can be used for change analysis in Geographic Information System (GIS). The digitising process is either done manually or automated by scanning. Manual digitising is performed by placing the historic map on a digitising board and digitising two or more calibration points. The farmland boundary, as it appears on the historic map, is then digitised by collecting a series of points along the boundary using the sensitive digitising puck. The resulting Cartesian coordinates (x,y) are converted to geographic coordinates (u,v). Simple Cartesian conversion from digitising table’s coordinates system to another rectangular coordinate system produces farmland boundary coordinates, which are in the same projection (e.g., Universal Transverse Mercator) and reflect the same ellipsoid constants (e.g., Clarke 1866 ellipsoid) and datum as the digitised historic map. The manual digitising process, which is capable of providing a high degree of accuracy, is labour intensive and slow. The accuracy of the output depends on the accuracy of the historic map and the skills of the operator. This process however has some advantages. These include the ability to correct errors or distortions of the original map at the time of data capture, highly reliable recognition of map objects and the ability to interpret ambiguous or incomplete information and select the relevant information during the time of data capture. Digital scanners convert analogue information of documents into digital format. They store a file of raw coordinate data for all the lines and symbols contained in the original document [36]. According to [37], scanning is far more efficient than manual digitising of lines. The general features affecting the performance of a scanner are its speed, resolution and the type of interface. The raster image obtained after the scanning process are converted to vector image by either automatic vectorisation or heads-up digitising by setting an appropriate scanning resolution.
The automated vectorisation method uses software to trace the farmland boundary on the historic map. This method is useful if the historic map is in a very good condition, i.e. all lines are clear and there is no annotation [37]. Although automated vectorisation is the quickest method of farmland boundary data conversion, historic maps are usually adequate. Vectorisation software cannot identify features and most type of vectorisation software cannot distinguish between text and lines. Thus maps with a lot of features will require a lot of editing to delete extra features and annotation. However, the advantages in using this method include the fact that it is very fast, inexpensive and provides a very accurate digitisation of the farmland boundaries. Heads-up digitising method is usually used when the historic map is in bad condition and when a digitising board is not available. It involves manually tracing the farmland boundary on a computer screen of the scanned raster image. Like manual digitising, the quality of the results depends on the operator skills. An advantage of this method is that several people can work simultaneously because the work can be distributed between several computers.
4.3. Photogrammetry
Aerial photographs have increasingly been used to provide topographic information, and thereby creating a good database for compilation of historic farmland change maps. Farmland boundaries mapped from vertical aerial photographs can be accurate and cost effective as a result of their extensive coverage and the greater details they provide. Photographs, unlike maps, contain a number of distortions and displacements introduced during the photographic processes that are perturbations of the geometric relationship between image space and object space. Image space coordinate system has perturbations as a result of lens distortion that is either radial or tangential, and film deformation that affect the representation of image points on the film. At a photo scale of 1:20,000, shrinkage and expansion of 1–2 mm are equivalent to 20–40 m on the ground [39]. The magnitude of lens distortions, especially in old photographs, is highly variable [39]. Lens with a radial distortion of up to 0.110 mm translates to a ground displacement of over 2 m in the position of image points for a 1:20,000 scale photograph. However, in modern precision cameras, lens distortions are typically less than 5 µm [40] and are therefore negligible [41]. Objects on a photo image are displaced from their true ground positions through ground relief displacement, aerial camera tilt and atmospheric refraction. On a 1:20,000 scale aerial photographs, a 1° tilt can result in approximately 20 m of displacement between a point on an air photo and its actual ground location, while a 3° tilt may yield a horizontal displacement that exceeds 60 m [42]. In [39] it is estimated that at a photographic scale of 1:20,000 the displacement due to atmospheric refraction is approximately 10 cm, which is very small and negligible. A number of photogrammetric methods have been employed to remove these distortions and obtain useful measurement of farmland boundaries from aerial photographs.
Methods for farmland mapping from aerial photographs are composed of three steps that include inner orientation, relative orientation and absolute orientation. Inner orientation is the process of recreating the geometry of the camera centre at the time of photograph exposure [40] and is heavily reliant on camera calibration. It applies a coordinate system to each photograph that exists in a photogrammetric project, incorporating the various distortions that affect the camera lens system. Relative orientation determines the relationship between the exterior orientation parameters of different camera stations, recreating the relative tilts at the time of exposure, so that stereomodels can be formed [40]. It is a completely computational procedure, based on the measurement of conjugate points between images. The final stage of photogrammetric orientation is the transformation of the stereomodel to the required object space coordinate system, in the process known as absolute orientation. By means of aerial triangulation, multiple stereomodels are adjusted simultaneously that minimises the amount of control points fixed in the field. Individual stereomodels are relatively oriented, tie points are recorded between connected models and a simultaneous adjustment is then carried out to relate the block to the ground control points.
Traditionally, farmland boundaries have been mapped from aerial photographs using photogrammetric techniques that have evolved as advances in technology and the need for accurate results increases. Originally, mechanical evaluation methods were used in which the imaging geometry was reconstructed through optical or mechanical devices. Two images of the farmland area are oriented that enable a three-dimensional model to be formed. An operator moves a floating mark and controls the movement under stereoscopic vision. This enables the boundary to be mapped directly as well as contour lines of the farmland. The physical properties of the analogue plotter are a limitation on its operation in terms of the type and size of the photography used and the amount of adjustment that can be made as a result of the mechanical processes involved. Evolution of computers has resulted in development of analytical methods to replace the analogue method. Analytical methods enable the relationships between image points and object points to be described through numerical calculations based on the collinearity equations (the condition in which the image space, object space and the focal point lie in a straight line). This allows greater flexibility in terms of application through the plotter’s ability to handle different formats, scales of photography and a much greater range of distortion and obliqueness of the image. It also offers relatively high accuracy since the systems support the operator during the orientation processes. The plot information is stored and displayed on screen with the possibility of editing.
Over the past few years, digital methods have been introduced, first with the scanning of analogue images and increasingly through the use of digital cameras [43]. Digital methods have many advantages. Unlike physical photographic prints, digital images stay geometrically constant under varied environmental conditions and software can be used to pre-process images to improve subsequent precision and efficiency.
4.4. Remote Sensing
Recent developments in remote sensing technologies coupled with GIS have significantly increased the capability to conduct farmland mapping. GIS have emerged in the last decade as an essential tool for urban and resource planning and management. Many landuse mapping projects, including urban farmlands, have benefited from the advantage of using GIS [46]. Remote sensing techniques can be used to distinguish between farmlands and farmlands use. Satellite imageries facilitate the estimation over a wide area the impact of farmlands change on nearby facilities. Future repeated observations will, over time, allow detailed quantification of factors militating against sustainability of urban farmlands. Archival data with available historic information, such as aerial photographs and other sources, coupled with recent remote sensing data facilitate quantification and analysis of change in a GIS environment. GIS applications are of vital importance in this regard for a number of reasons. It allows for quick visualisation of spatial data, facilitates the distribution and estimation of sizes of open spaces being used for urban and peri-urban farming, and enables data overlay to detect changes in the farmlands extent. It also enables the influence of rapid urban development to be critically assessed on urban farmlands.

Table 1.
Summary of farmlands mapping methods.
| Methods | Types | Data sources | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Photogrammetric | Analog/ Analytical | Aerial photos | Relatively fast | Expensive |
| Digital | Aerial photos/ | Accurate | Photo distortions | |
| Multispectral imagery | Wide coverage | |||
| Digitising | Manual/Scanning | Historic maps | Ability to correct errors | Labour intensive |
| Correct distortions | Slow | |||
| Reliable | Depend on map accuracy | |||
| Physical survey | Planetable | Field measurement | Higher accuracy | Very tedious |
| Time consuming | ||||
| Expensive |
5. Discussion
Several studies have discussed land cover and land use changes in arid, semi-arid and agricultural productive land at both local and regional scales. Satellite imagery in addition to other sources of data was used to monitor farmland change in Shanxi, China [47]. The study categorised farmlands into high, medium and low yield using Landsat TM data, colour infrared aerial photographs and special maps at various scales. The maps provided a hierarchical inquiry of agricultural information at different scales. A farm monitoring system was established that is supported by remote sensing, GIS and multi-media technology. It was established that the accuracy of farmland monitoring in high-medium-low-yield reaches as high as 95 percent using remote sensing. A recent project by [48] in Dar es Salam, Tanzania used remote sensing and GIS to map out vegetable production in open spaces. The aim of this study was to elaborate an inventory of all open spaces used for vegetable production in Dar es Salaam. The exact locations and sizes were mapped and integrated into the GIS database of the Dar es Salaam City Council. The sources of data for the study included 1992 aerial photographs, cadastral maps and physical ground survey method using GPS. GIS environment was adopted because of advantages it offers such as visualisation of spatial data, simple analytical functions, data overlays, etc. The results of this study gave indications about the importance of this type of urban land use, mainly in terms of its viability in view of competing land uses such as new constructions. High resolution IKONOS satellite imagery was used to map the urban and peri-urban agricultural areas in Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso [49]. The study surveyed the agricultural activities in the cities by using time-series of images to determine the spatial dynamics of these activities. In [50] the authors used 10 years of NOAA-AVHRR data to assess and analyze land cover changes in the African continent between 1982 and 1991. The study showed that continuous unidirectional change process affected less than 4 percent of Sub-Saharan regions during the study period. [51] studied land cover changes in lake regions of central/south Ethiopia using aerial photographs dated 1972 and 1994 Landsat TM image. [52] combined black and white aerial photographs with fieldwork and GIS to monitor land cover changes covering 56 years (1940–1996) in parts of Bogota, Colombia. [53] used Landsat TM data to explore the impacts of land management policies on vegetation structure in two study areas in southern Kalahari Desert in South Africa in the period 1989–1994. [54] studied land use changes in arid areas in India by visual comparison of satellite imagery, maps and aerial photographs. In Egypt, [55] used satellite imagery to highlight agricultural boundaries and monitor reclamation process. [56] used field calibrated, multi-temporal NDVI features derived from ten Landsat TM images dating from 1984 to 1993 to assess land cover changes in Egypt. The study showed a high rate of reclamation in the period 1986–1993 and low rate of conversion from agricultural productive land to new urban areas between 1984 and 1990. Remote sensing provides an efficient tool to monitor long term farmland changes in urban/ peri-urban areas, while GIS environment provides a framework for spatial analysis and modeling based on geographic principles and seeks to integrate the analytical capabilities to broaden the understanding of the real world system [57].
6. Conclusions
Ground based survey methods are unattractive due to the cost involved and the duration for data capturing. Although technological advances has significantly improved the accuracies associated with using this method for urban and peri-urban farmland mapping, the varied locations of the farmlands make this labour intensive and time consuming technique unattractive. The accuracy of digitised farmlands from historic maps depend on the accuracy of the historic map and the competence of the operator. This influence the reliability of the end product. Though digitising enables distortions in the original maps to be corrected, the method is slow and labour intensive, and thus unattractive for farmland mapping. Phototgrammetric method of farmland mapping enables the boundary to be mapped directly and also facilitate generating contour lines of the farmland, which can provide additional information on the topography. However, the cost involved in obtaining repeated photographs of an area over a period and the distortions in the photographs make the method unattractive. Remote sensing technique provides spatially consistent data sets and allow farmlands to be mapped at relatively low cost. It also provides reliable historical time series data, which when combined with future repeated observations facilitate in-depth quantification of changes in farmland sizes. Combining remote sensing and GIS for urban peri-urban farmland mapping enable data overlay, which is significant for effective management.
Ghana's Accra region, similar to most developing nations, has paucity of data that has deterred systematic monitoring and managing urban farmlands. The plausible method of assessing farmland change in Accra is to use an integrated approach. This method involves mapping farmland boundaries from archival data sources (aerial photographs), recent data sources (satellite imageries) and future data sources (satellite imageries) in digital format ready for use in GIS environment. Archival data, in the form of near vertical aerial photographs provide rich information about the state of urban farmlands in Accra. Extracting this information from the photographs will enable historic farmland maps to be generated for the period the photographs were taken. Recent satellite imagery will enable the current state of the farmlands in Accra to be mapped. Future repeated satellite data capture will enable the future state of the farmlands to be assessed through overlay of the farmland boundaries in a GIS environment. This information will facilitate the development of a farmland monitoring scheme for Accra and form the basis for developing sustainable policies to effectively manage urban farming practices in Accra.
References
- Smit, J.; Ratta, A.; Asr, J. Urban Agriculture, Food, Jobs and Sustainable Cities; UNDP Habitat II Series; UNDP: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Sub-Saharan Africa: From Crisis to Sustainable Growth; The World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 1989.
- Fournier, F. The city: so human an ecosystem. Nat. Res. 1996, 32, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, A. Environmental planning and management of the peri-urban interface. In Proceedings of the Conference on Rural-Urban Encounters: Managing the Environment of the Peri-urban Interface, London, UK, November 2001.
- McGee, T.G.; Robinson, I.M. The Mega-Urban Regions of Southeast Asia; UBC Press: Vancouver, Canada, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan, W.C.; Lovell, S.T. Improving the visual quality of commercial development at the rural-urban fringe. Landscape Urban Plan. 2006, 77, 152–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brook, R.M.; Davila, J.D. The Peri-Urban Interface: A Tale of Two Cities; School of Agricultural and Forest Sciences, University of Wales and Development Planning Unit, University College London: London, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- De Bon, H. Safe and year round vegetable production in peri-urban areas. In Proceedings of the National Workshop, RIFAV and CIRAD, Hanoi, Vietnam, December 1999.
- Neuppenau, E.A. Agro-ecologically oriented land use and the creation of viable rural urban interfaces. In 2nd Newsletter Peri-Urban Development in South East Asia; RAUF: Leusden, The Netherlands, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Etuah-Jackson, I.; Klaassen, W.P.; Awuye, J.A. Turning Municipal Waste into Compost: the Case of Accra. In Waste Composting for Urban and Peri-urban Agriculture: Closing the Rural-Urban Nutrient Cycle in Sub-Saharan Africa; Drechsel, P., Kunze, D., Eds.; CABI Publishing: Wallingford, UK, 2001; pp. 84–95. [Google Scholar]
- Borne, F.; Satornkich, J.P.; Anwar, S.M. Plant modeling for landscape changes visualization: application to a peri-urban agricultural area. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Plant Growth Modeling, Simulation, Visualization and Their Applications PMA03 Conference, Beijing, China, October 2003.
- Midmore, D.J.; Jansen, H.G.P.; Dumsday, R.G. Soil erosion and environmental impact of vegetable production in the Cameron Highlands, Malaysis. Agr. Ecosyst. Environ. 1996, 60, 29–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rees, W.E. Why Urban Agriculture? Notes for the IDRC Development Forum on Cities Feeding People: A Growth Industry. Vancouver, BC. City Farmer: Canada's Office of Urban Agriculture, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 1997. Available online: http://www.cityfarmer.org/rees.html (assessed on 19 August 2009).
- Bryld, E. Potentials, problems, and policy implications for urban agriculture in developing countries. J. Agr. Human Values 2003, 20, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koont, S. The Urban Agriculture of Havana. 2009. Available online: http://www.monthlyreview.org/090119koont.php (accessed on 17/11/2009).
- Appeaning Addo, K. Detection, Measurement and Prediction of Shoreline Change in Accra, Ghana; Lambert Academic Publishing: Saarbrücken, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Stefanov, W.L.; Ramsey, M.S.; Christensen, P.R. Monitoring urban land cover change: an expert system approach to land cover classification of semiarid to arid urban centers. Remote Sens. Environ. 2001, 77, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Q. Landuse change analysis in the Zhujiang delta of China using satellite remote sensing, GIS and stochastic modeling. J. Environ. Manag. 2002, 64, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herold, M.; Goldstein, N.; Clarke, K. The spatiotemporal form of urban growth: measurement, analysis and modeling. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 86, 286–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cofie, O.; Veenhuizen, R.; Drechsel, P. Contribution of urban and peri-urban agriculture to food security in sub-Saharan Africa. In Africa session of 3rd World Water Forum, Kyoto, Japan, March 2003.
- GSS (Ghana Statistical Services). 2000 Population and Housing Census: Summary Report of Final Results, Accra, Ghana, 2002.
- Duedall, I.W.; Maul, G.A. Demography of coastal populations. encyclopaedia of coastal science. In Encyclopedia of Coastal Science; Encyclopedia of Earth Sciences Series; Schwartz, M.L., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, the Netherlands, 2005; pp. 368–374. [Google Scholar]
- Asomani-Boateng, R. Urban cultivation in Accra: an examination of the nature, practices, problems, potentials and urban planning implications. Habitat Int. 2002, 26, 591–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obosu-Mensah, K. Food Production in Urban Areas. A Study of Urban Agriculture in Accra, Ghana; Ashgate Publishing: Aldershot, England, UK, 1999; p. 227. [Google Scholar]
- Danso, G.; Drechsel, P.; Fialor, S.; Giordano, M. Estimating the demand for municipal waste compost via farmers’ willingness to pay in three Ghanaian cities. Waste Manag. 2006, 10, 1400–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nugent, R.A. Using economic analysis to measure the sustainability of urban and peri urban agriculture: a comparison of cost-benefit and contingent valuation analyses. In Proceedings of the CIP-SUIPA and ETC-RUAF Workshop on Appropriate Methodology in Urban Agriculture Research, Planning, Implementation and Evaluation, Nairobi, Kenya, October 2001.
- Cofie, O.; Drechsel, P.; Obuobie, E.; Danso, G.; Keraita, B. Environmental sanitation and urban agriculture in Ghana. In Proceedings of 29th WEDC International Conference Ghana: Towards the Millennium Development Goals, Abuja, Nigeria, September 2003.
- Danso, G.; Keraita, B.; Afrane, A. Farming Systems in (Peri) Urban Accra, Ghana: Special Focus on Its Profitability, Wastewater Use and Added Malaria Risks; IWMI Internal Report, Ghana Office: Ghana, 2002; p. 73. [Google Scholar]
- Zakaria, S.; Lamptey, M.G.; Maxwell, D. Urban agriculture in accra: a descriptive analysis. In Urban Agriculture in the Greater Metropolitan Area; Klemesu-Armar, M., Maxwell, D., Eds.; Noguchi Memorial Institute for Medical Research: University of Ghana, Legon, Ghana, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Armar-Klemesu, M.; Maxwell, D. Urban agriculture as an assist strategy, supplementing income and diets. A case study of Accra. In Growing Cities, Growing Food; Bakker, N., Dubelling, M., Gündel, S., Sabel-Koschella, U., Zeeuw, H., Eds.; DSE: Feldafing, Germany, 2000; pp. 183–205. [Google Scholar]
- Mougeot, L.J.A. Urban agriculture: definition, presence, potentials and risks, main policy challenges. In Proceedings of International Workshop on Growing Cities Growing Food: Urban Agriculture on the Policy Agenda, La Habana, Cuba, October 1999.
- Cofie, O. Emerging Issues in Urban and Peri-Urban Agriculture (UPA) in West Africa. Available online: http://ruaf.iwmi.org/Data/Sites/4/PDFs/UPA%20Briefing%20note.pdf (accessed on 10 September 2009).
- RAUF Foundation, Accra-Ghana, 2005. Available online: http://www.ruaf.org/node/498 (Accessed on 9 September 2009).
- Klinkenberg, E.; McCall, P.J.; Wilson, M.D.; Amerasinghe, F.P.; Donnelly, M.J. Impact of urban agriculture on malaria vectors in Accra, Ghana. Malaria J. 2008, 7, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chimhowu, A.; Gumbo, D. Urban agriculture: southern and eastern Africa. In Urban Environment; Mougeot, L., Masse, D., Eds.; IDRC: Ottawa, Canada, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Petrie, G.; Kennie, T.J.M. Terrain Modelling in Surveying and Civil Engineering; Whittles Publishing: London, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Pequet, D.J.; Boyle, A.R. Raster scanning, processing and plotting of cartographic documents. In Proceedings of Cartography, Williamsville, NY, USA, 1984.
- Moore, L.J. Shoreline mapping techniques. J. Coastal Res. 2000, 16, 111–124. [Google Scholar]
- Thieler, E.R.; Danforth, W.W. Historical shoreline mapping 1. Improving techniques and reducing positioning errors. J. Coastal Res. 1994, 10, 549–563. [Google Scholar]
- Wolf, P.R.; Dewitt, B.A. Elements of Photogrammetry (with Applications in GIS), 3rd ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Thieler, E.R.; Hapke, C.J. Photgrammetry. In Encyclopedia of Coastal Science; Encyclopedia of Earth Sciences Series; Schwartz, M.L., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, the Netherlands, 2005; pp. 323–327. [Google Scholar]
- Leatherman, S.P. Historical and projected shoreline mapping. In Proceedings of the Coastal Zone ’83, San Diego, CA, USA, June 1983; pp. 2902–2910.
- Graham, D.; Sault, M.; Bailey, J.C. National ocean service shoreline: past, present, and future. J. Coastal Res. 2003, 38, 14–32. [Google Scholar]
- Morton, R.A.; Speed, F.M. Evaluation of shoreline and legal boundaries controlled by water levels on sandy beaches. J. Coastal Res. 1998, 14, 1373–1384. [Google Scholar]
- Buckley, S.J. Geomatics Data Fusion Technique for Change Monitoring. Ph.D. Dissertation, Newcastle University, Newcastle, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Seto, K.C.; Woodcock, C.E.; Song, C.; Huang, X.; Lu, J.; Kaufmann, R.K. Monitoring land-use change in the Pearl River Delta using Landsat TM. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2002, 23, 1985–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuliang, Q.; Buzhou, M.; Jiuiiang, F. Study on monitoring farmland by using remote sensing and GIS in Shanxi China. Adv. Smce Res. 2000, 26, 1059–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dongus, S.; Drescher, A.W. The use of GIS, GPS and aerial imagery for mapping urban agricultural activities on open space in cities. GIS Development Weekly 2006, 2. Available online: http://www.gisdevelopment.net/application/agriculture/overview/me05_108b.htm (accessed on 15 September 2009). [Google Scholar]
- Kemeling, I. Mapping Urban and Peri-Urban Agricultural Areas in Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso. Centre for Geo-Information, Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Lambin, E.F.; Ehrlich, D. Land-cover changes in Sub-Saharan Africa (1982–1991): application of a change index based on remotely sensed surface temperature and vegetation indices at a continental scale. Remote Sens. Environ. 1997, 61, 181–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rembold, F.; Carnicelli, S.; Nori, M.; Ferrari, A. Use of aerial photographs, Landsat TM imagery and multidisciplinary field survey for land-cover change analysis in the lakes region (Ethiopia). Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinform. 2000, 2, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, J.E.; Etter, R. Multitemporal analysis (1940–1996) of land cover changes in the southwestern Bogota highplain (Colombia). Landscape Urban Plan. 2002, 59, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, A.R.; Van Rooyen, A.F. Detecting vegetation change in the southern Kalahari using Landsat TM data. J. Arid Environ. 1998, 39, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ram, B.; Kolarkar, A.S. Remote sensing application in monitoring land-use changes in arid Rajasthan. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1993, 14, 3191–3220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadek, S.H.A. Use of landsat imagery for monitoring agricultural expansion of East and West Nile Delta, Egypt. Egypt. J. Soil Sci. 1993, 33, 23–24. [Google Scholar]
- Lenney, M.P.; Woodcock, C.E.; Collins, J.B.; Hamdi, H. The status of agricultural lands in Egypt: the use of multi temporal NDVI features derived from Landsat TM. Remote Sens. Environ. 1996, 56, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, H.G.P.; Bouman, B.A.M.; Schipper, R.A.; Hengsdijk, H.; Nieuwenhuyse, A. An interdisciplinary approach to regional land use analysis using GIS, with applications to the Atlantic Zone of Costa Rica. Agr. Econom. 2005, 32, 87–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2010 by the author; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
