Abstract
Satellite navigation spoofing is a major challenge in the field of satellite/inertial integrated navigation security. To effectively enhance the anti-spoofing capability of a low-cost GNSS/MEMS-SINS integrated navigation system, this paper proposes a method integrating a dual-antenna global navigation satellite system (GNSS) and a micro-inertial measurement unit (MIMU) to determine the two-dimensional directions of spoofing signal sources. The proposed method evaluates whether the single-difference carrier-phase measurements conform to the corresponding directions given in ephemeris files and employs micro-inertial navigation technology to determine the two-dimensional directions of the signal source. Based on a set of short-baseline dual-station measurements, the accuracy of the proposed method in determining the two-dimensional azimuths of satellites in synchronous orbits is verified, and the deviation from the real value is evaluated. The experimental results show that the proposed method can effectively identify the spoofed satellite signals while providing high-precision direction information at three different distances: 100 m, 10 km, and 36,000 km. The two-dimensional angle errors do not exceed 0.2 rad, 0.05 rad, and 0.01 rad, respectively.
1. Introduction
Due to the rapid development of unmanned intelligent carriers, the utilisation of autonomous navigation systems has increased. Among them, GNSS/MIMU integrated navigation is most widely utilised because of its low cost and high accuracy. As a result of the open structure of satellite navigation signals with low ground signal power, easy interference could occur. Therefore, its security and reliability have become key research topics. With the development of global navigation satellite system (GNSS) interference technology, the means of interference have gradually evolved into more complex forms, including jamming and spoofing [1]. Spoofing can be subdivided into generative spoofing and forwarding spoofing. The rapid development of traction spoofing in recent years poses a significant risk to the normal operation of GNSS systems, which not only affects the execution of military missions but also threatens the security of various fields such as civil aviation equipment and intelligent driving [2,3].
Although emerging technologies such as zeroing antennas have effectively mitigated the effects of traditional interference techniques [4,5], GNSS spoofing attacks remain a major challenge to navigation security. Spoofing attacks mimic the strength and coding of real satellite signals, making it difficult to accurately distinguish real signals from spoofed signals via traditional signal differentiation methods [6]. To address this challenge, researchers have proposed a series of anti-spoofing techniques. Among them, navigation information encryption techniques integrate specific code sequences into extended code sequences and employ dedicated hardware and software modules for decoding and verification, significantly enhancing the authenticity check of satellite navigation signals [7,8]. However, the effectiveness of these countermeasures remains limited because the nature of forwarding spoofing does not alter the navigation information.
In signal quality monitoring (SQM) techniques, the interaction between spoofed signals and real satellite signals affects correlator outputs. By tracking and calculating correlator outputs, usually researchers can identify distortions in the correlation peaks, which typically manifest as asymmetry, unusual sharpness, or unusual flatness. Some researchers have proposed the method to detect spoofing through multi-correlator measurements of shape distortion [9,10,11,12,13]. This method compares measurements of its autocorrelation function with typical values and makes judgements based on noise variance thresholds. Unfortunately, this technique is limited by its use of a scalar tracking structure, which is ineffective in the absence of overlapping correlation peaks. Zhang et al. [14] addressed this limitation by introducing an SQM detection method based on a vector tracking structure. In this method, the received signals are jointly analysed even in the absence of overlapping correlation peaks, thereby facilitating spoofing detection. Nonetheless, accurate determination of the positions of spoofing signal sources remains challenging.
Additionally, machine learning-based spoofing detection techniques have been increasingly applied for identifying spoofed signals. Junzhi et al. explored the feasibility of applying generative adversarial networks (GANs) to spoofing detection and utilising their powerful generative and generalisation capabilities [15,16]. Their experiments showed that the detection rate attains 98% when the pseudo-range code-phase difference between the spoofed and real signals exceeds 0.5 code slices [16]. Xu et al. [17] proposed a multi-channel one-dimensional fully convolutional neural network (CNN) for spoofing detection. This method utilises the residual sequences of the system measurements to extract features at various scales, generating point-by-point decision-making results and yielding good detection and false alarm rates. However, this technique requires massive computational resources and remains incapable of determining the exact positions of spoofing signal sources.
Existing spatial information processing techniques can be categorised mainly into three types: mobile single-antenna, dual-antenna array, and multi-antenna array. The mobile single-antenna technique detects spoofing in basic static scenarios based on Doppler information and single-differenced carrier-phase information; however, there are limitations in identifying the directions of the signal sources. Chen et al. employed two fixed antennas to form a baseline vector and ascertain the similarity of carrier-phase data to achieve spoofing detection [18]. However, this model is unable to effectively determine the direction of arrival (DOA) of a signal source and cannot provide direction indication for countermeasures such as zeroing antennas.
This study aims to independently determine the DOA of a navigation signal from a single satellite through integrated navigation based on the inter-station single-difference carrier-phase information received by the common-clock dual antennas and the information provided by a micro-inertial measurement unit (MIMU). The direction of the signal source is determined by constructing a dual-antenna inter-station single-difference carrier-phase observation model and utilising the multi-epoch data of the carrier in the dynamic motion state. The proposed method effectively addresses the challenges faced by small vehicles equipped with dual GNSS antennas in identifying spoofed signals and determining the directions of signal sources.
Based on the background mentioned earlier, this paper proposes a method for determining the directions of the deceptive signal source in the dynamic carrier coordinate system based on the dual-antenna carrier phase observations and inertial measurements with multiple epochs. A new method is proposed to determine the single-differenced integer ambiguity between two GNSS antenna with short baseline which is combined with the dual-GNSS antenna/MIMU integration information to determine the two-dimensional directions of the spoofing interference source. This method utilises the broadcasted satellite ephemeris and MEMS-based inertial navigation to forecast the direction of satellite navigation signals. By analysing the anomalies between the direction of the spoofing signal source and the forecasted direction from the ephemeris information, effective identification of the spoofing signals can be achieved. Due to insufficient observation information from a single epoch, this paper proposes a trajectory planning strategy that involves significant manoeuvring in at least one direction over multiple epochs. A multi-epoch observation model is established based on the changes in the attitude and carrier-phase observations along the trajectory, thereby providing high-accuracy two-dimensional direction information for the spoofing signal source. Furthermore, this paper establishes a real-time two-dimensional direction determination model for extended Kalman Filter (EKF) filtering. This study assesses the effectiveness and accuracy of the proposed method through both simulation and experimental tests.
The structure of the paper is presented as follows. Section 2 briefly introduces the system models of the proposed method, including the integrated system model, the satellite signal observation model, and two-dimensional direction model for spoofer. Section 3 derives a new method for single-frequency single-epoch dual-frequency station single-difference ambiguity resolution, and establishes the two-dimensional direction determination method for spoofing signal sources. Section 4 verifies the effectiveness of the proposed method through a comprehensive simulation analysis and a land vehicular test. Section 5 concludes this paper.
2. System Model and Signal Processing Methods
To meet the demand for precise and reliable autonomous navigation of carriers under GNSS-denied conditions, this paper focuses on the research of anti-jamming technology for BeiDou deceptive interference modes using airborne dual-antenna BeiDou/MIMU integrated navigation systems. It proposes a method for determining the direction of deceptive signal sources based on dual-antenna BeiDou/MIMU integration to endow carriers with credible navigation capabilities under BeiDou-denied conditions and counteracting abilities to determine the position of interference sources.
This study proposes a direction-finding method for GNSS spoofing signal sources, utilising a MEMS-based dual antenna GNSS/INS integrated navigation system and a short-baseline common-clock GNSS receiver. The proposed method is usually applied to the scenario depicted in Figure 1. By carrying a dual-antenna GNSS/MIMU system and a common-clock receiver, the vehicles, which travel normally in this scenario, can process the real satellite signals as well as the spoofed signals using the proposed method, making it possible to effectively identify and locate GNSS spoofing signal sources. Additionally, the proposed method is applicable to the localisation for GNSS spoofing signal sources in airborne or shipborne scenarios.
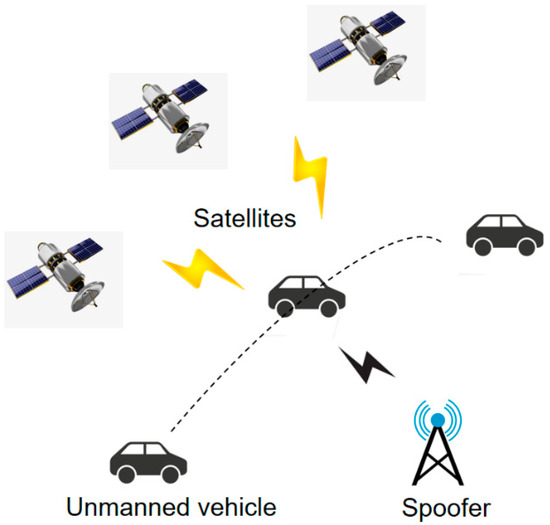
Figure 1.
Typical application scenario for the proposed method. The dotted line represents the trajectory of the unmanned vehicle during satellite signal deception.
2.1. Integrated Navigation Model
Liu et al. [19] proposes a direction-finding model for satellite navigation signal sources identified by a 6 + 1 antenna array; however, it is expensive, and the inertial measurement unit (IMU) carried by common carriers remains underutilised. Effective identification and correction of deceptive interference can be realized with the aid of auxiliary information from IMU or wheel sensor [20]. However, the classic pseudorange consistency detection makes it difficult to support high-accuracy signal source identification and localization. Therefore, this study utilises an integrated navigation model as illustrated in Figure 2, wherein two antennas are arranged along the X-axis of the MIMU body coordinate system. The proposed method is applicable to any antenna and common-clock receiver that can simultaneously receive at least two navigation frequency bands of the same navigation satellite. The model can be widely applied in vehicles and other carriers that require MIMU/satellite integrated navigation because of its length demand for a single direction only. Additionally, this research proposes a short-baseline integer ambiguity determination method based on an improved ambiguity function method (AFM); therefore, there is no spatial ambiguity between the two antennas. Consequently, the baseline length between the units is extended, providing higher direction-finding accuracy.
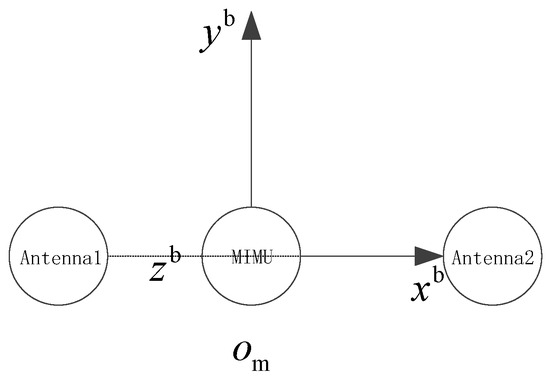
Figure 2.
Integrated navigation model.
As illustrated in Figure 2, two antennas and an MIMU are solidly connected to the carrier. Antenna 1 serves as the origin of the body coordinate system. The baseline vector between the two antennas aligns with the X-axis of the carrier coordinate system. The X-axis of the MIMU body coordinate system is parallel to the X-axis defined for the carrier coordinate system. The plane of the MIMU body coordinate system coincides with the plane of the carrier body coordinate system. The Y-axis of the MIMU body coordinate system is parallel to the Y-axis defined for the carrier coordinate system.
2.2. Observation Model for Real Signals
After data acquisition via the integrated navigation model discussed in Section 2.1, all the real and spoofed GNSS signals received by each antenna are efficiently processed, and MIMU measurements are recorded. This ensures accurate acquisition, tracking, and carrier-phase measurements of all signal sources.
The carrier-phase observation equation is given as follows:
where is the wavelength of the carrier phase, is the real value of the carrier phase, and is the integer ambiguity of the carrier phase; is the frequency of the carrier phase; is the real position of Satellite i, is the real position of Antenna 1, and is the clock difference between Antenna 1 and the receiver; and are ionospheric and tropospheric errors, respectively. When the distance between the two stations is short, the ionospheric and tropospheric errors experienced by the two stations are approximately identical. Therefore, errors can be eliminated in the differences. The single-difference carrier-phase ambiguity observation equations are constructed for the two frequency points of the two stations as follows:
where and denote the real values of the single-difference carrier phases between the two stations at two frequency points, and , respectively; and denote the positions of the satellite corresponding to the signals received by Antennas 1 and 2, respectively; and represent the real positions of Antennas 1 and 2, respectively; and are the frequencies of the two frequency points, and , respectively; and are the inter-station clock difference between Antennas 1 and 2 at the two frequency points, and , respectively; and indicate the single-difference integer ambiguities of Antennas 1 and 2 relative to satellite at the two frequency points, and , respectively.
As depicted in Figure 3, θ (i.e., the angle between the DOA and the baseline vector formed by Antennas 1 and 2) can be expressed as follows:
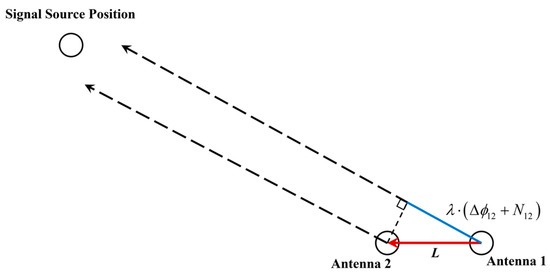
Figure 3.
Single-differenced carrier phase between two antennas on the baseline vector-source plane.
As illustrated in Figure 4, θ in Equation (3) can be decomposed into the pitch angle (β) and yaw angle (α) from the carrier to the signal source.
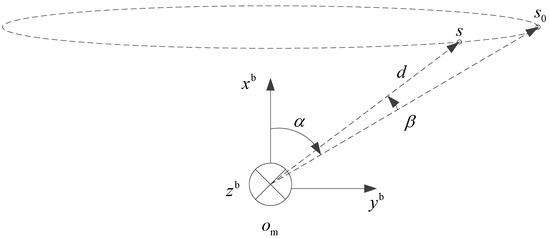
Figure 4.
Signal source position in the body coordinate system.
The yaw angle α and pitch angle β in the figure are the objectives to be solved in this study. When the signal source is a real satellite signal, the geometric configuration of the cosine function is given by
Then Equation (3) can be reduced to
2.3. Two-Dimensional Direction Observation Model for Spoofing Signal Sources
The vector of the carrier’s Antenna 1 pointing to the signal source at the same moment can be expressed as in the system, and , , and are the axial components of , as follows:
Equation (5) can be reduced to a two-dimensional direction observation equation for signal sources:
As the scenario defined in this study is that there exists a spoofing risk in satellite navigation, satellite navigation and positioning pose a risk of unreliability. In Equation (5), is obtained by extrapolating the data in ephemeris files, is obtained by independently extrapolating the data provided by the MIMU, and is to be solved.
Conventional methods for solving inter-station single-difference carrier phases in satellite navigation include multi-epoch filtering techniques such as the least-squares ambiguity decorrelation adjustment (LAMBDA) algorithm and objective function solving techniques such as the AFM algorithm [21,22,23,24,25]. The former requires multi-epoch filtering of possibly unreliable pseudo-range information, and the latter is disadvantaged by large computational amounts and insufficient reliability. Therefore, this study constructs a novel AFM objective function to rapidly resolve the integer ambiguities of carrier phases in the environment of this study via a single channel. Additionally, in the two-dimensional observation equation for spoofing signal sources, that is, Equation (7), the observed value has one dimension, and the value to be observed has two dimensions. There is a rank loss in single-epoch direction finding for spoofing signal sources. However, due to the non-linearity of the two-dimensional direction observation model, it is more complicated to calculate the matrix of state transfer between two consecutive epochs. Therefore, it is necessary to propound a new multi-epoch observation model and construct a least squares observation equation and an Extended Kalman Filter (EKF) model to determine high-precision directions of spoofing signal sources.
3. Proposed Methods
As it is challenging to effectively identify spoofing in terms of signal strength, angle estimation based on the antenna array can barely achieve effective direction finding for spoofing. Considering the DOA stability of spoofing, we apply the system and signal processing model discussed in Section 2 to determine the inter-station single-difference directions of all the GNSS signals received by the dual-antenna GNSS/MIMU system so as to obtain the DOA angles of the single sources for each epoch. We propose a mobile dual-antenna GNSS/MIMU-based method for direction finding of signal sources. The proposed method first utilises the inter-station single-difference carrier-phase measurements after integer ambiguity compensation to distinguish real GNSS signals from spoofed signals to confirm and extract false and spoofed satellite signals. Subsequently, we select the most favourable computational coordinate system based on multiple simplified assumptions. Finally, based on multi-epoch DOA angle measurements of spoofing signal sources, we establish a multi-epoch least squares observation equation and an EKF filtering model to determine high-precision directions of spoofing signal sources. The proposed method is described in this section.
3.1. Method for Determining the AFM Carrier-Phase Ambiguity at Dual Frequencies
In this method, the short-baseline inter-station single-difference integer ambiguity is effectively determined after real and spoofed GNSS signals are successfully received, thus realising subsequent positioning of spoofed signals. This method utilises the inter-frequency information difference to fuse the inter-station single-difference carrier-phase information at dual frequencies so as to obtain a strong correlation constraint between dual-frequency carrier phases and their ambiguities. Additionally, a new method for resolving the ambiguities of short-baseline inter-station carrier phases is proposed.
As the effect of the inter-station clock difference between the two antennas still exists in Equation (2) given in Section 2, we can obtain the following equation by subtracting the upper and lower equations of Equation (2):
where and are the inter-station single-difference carrier-phase measurements for satellite i at two frequency points, and , respectively; and are the inter-station single-difference carrier-phase measurement errors for satellite i at two frequency points, and , respectively.
By analysing the clock difference part in Equation (8), we obtain
The clock difference between two frequency points, and , of the same receiver can be ignored because it is considerably smaller than the noise (random error).
Moreover, the inter-station single-difference carrier phase at and represents the same distance, and this distance does not exceed the baseline length. Therefore, we obtain
As depicted in Figure 5, the points in the range of Equation (10) represent the integer ambiguity group at and .
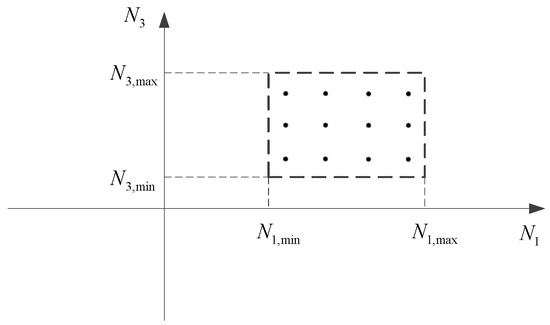
Figure 5.
Domains and standardised points of inter-station single-difference integer ambiguities on B1 and B3. The square area represents the range of values for carrier phase ambiguities N1 and N3. Due to the integer constraints for N1 and N3, the feasible candidates for (N1, N3) can be illustrated as the dots in the square area.
Considering the stochastic measurement errors and with the same standard deviation , Equations (10) and (11) can be transformed as follows:
The optimal solution to Equation (12) can be obtained using the AFM-based objective function as follows:
It is indicated in Equation (13) that the integer ambiguity can be approximately obtained with the smallest error at and .
3.2. Method for Determining Spoofed Signals
The method described in Section 3.1 can quickly determine carrier-phase integer ambiguities from received GNSS signals using two short-baseline common-clock antennas. On this basis, we directly determine spoofed signals by using the inter-station single-difference carrier-phase measurements after integer ambiguity compensation and the information provided by the MIMU of the carrier. Due to the dynamic nature of the observation scenario in this paper, there are certain carrier-phase measurement errors, as well as extrapolation errors from the MIMU of the carrier.
Therefore, the attitude transformation matrix from the system (CGCS2000) to the b system (carrier body coordinate system) provided by the MIMU in the trusted environment of satellite navigation before spoofing is and . If there is no spoofing, we can derive the following equation from Equation (5):
The information on the right side of the above equation is obtained based on the MIMU measurements and ephemeris files, while the information on the left side of the equation is solved based on the satellite navigation signal measurements. Therefore, we define as follows:
where is known; can complete the calibration work in advance; and vary not much in two consecutive epochs; is the measured value; is the carrier-phase integer ambiguity revolved in Section 3.1.
By defining the threshold at , we can determine that the measured signals of the satellite are spoofed signals. The value of is defined by the maximum error of satellite two-dimensional direction determination in the following paper.
3.3. Multi-Epoch Method for Determining the Two-Dimensional Directions of Spoofing Signal Source
After determining spoofed signals (Section 3.2), we track the same signal source in multiple epochs. First, an appropriate computational coordinate system is selected. Then, the dynamic multi-epoch inter-station single-difference carrier-phase measurements after integer ambiguity compensation and MIMU observation information are used to perform multi-epoch least-squares operation for the target spoofing signal source to obtain the initial position of the spoofing signal source. Finally, the two-dimensional direction information of the spoofing signal source is obtained through filtering in real-time.
To determine the two-dimensional direction of the signal source, it is first necessary to select a suitable observation coordinate system. Because the direction of the signal source changes in real-time under the real-time body coordinate system for the carrier, the model constructed is characterised by high complexity. Additionally, geoid systems, especially CSCG2000, have larger value representations for positions, which is not beneficial to computation. Therefore, we choose the body coordinate system created for the epoch where the signal source points approximately to the X-axis in the motion as the observation coordinate system. In this coordinate system, the direction of the carrier-pointing signal source in this epoch is the value to be solved by the model.
As shown in Figure 4, if the carrier has a hovering motion on a horizontal plane, then is approximately stable, and the value of is directly affected by . From the geometric relationship, we can obtain
As shown in Equation (16), when the carrier phase reaches its maximum value, approximates to 0, and . This moment is recorded as Moment 0, at which the body coordinate system is the system.
For a brief period, the body system error in the process of MIMU-assisted rotation does not significantly vary with time. The value of the signal source in the b system at different moments can be expressed as . The distance from the carrier to the signal source is much larger than the change in the position of the signal source, i.e., .
As the MIMU can obtain the rotation matrix from the system (i.e., the body coordinate system for the current epoch) to the system, we use the system for the transfer. and are defined as the representations of the vector from the carrier to the signal source in the and systems, respectively; is the rotation matrix from the system to the system; is the rotation matrix from the system to the system.
A Taylor expansion is performed for Equation (17) at to obtain
where is a unit vector for ; and are the yaw and pitch angle errors, respectively.
By establishing a least-squares observation equation set, then Equation (7) can be transformed as follows:
in which,
The two-dimensional direction of the spoofing signal source is obtained after least-squares compensation as follows:
To obtain the real-time source position information, we construct an EKF model for the carrier-phase measurement information that is updated in real-time.
We define the state parameters as the yaw angle () and pitch angle () of the two-dimensional direction vector of the signal source in the system, and denote them in the following equation:
Given that the signal source is static, then
The measurement equation at epoch (t+1) can be established as
The error states and their variances can be estimated for epoch (t+1):
To reduce the linearisation error of the measurement equation, we calculate the initial state value and the estimated error state for epoch (t+1) as follows:
4. Test Validation
4.1. Setup of Experimental Scenarios
To verify the proposed method (i.e., the dynamic dual-antenna method for determining the directions of spoofing signal sources), we performed real-time data acquisition and analysis. Additionally, we utilised a spoofing signal source to simulate satellite navigation signals and conducted satellite navigation spoofing on the vehicle-mounted antennas. To ensure the reliability of the reference system, only the signals on B1 and B3 frequency points of BeiDou were spoofed. GPS observation data are reserved for reliability. The latitude, longitude, and elevation of the observation site are approximately written as (112.99 deg, 28.23 deg, 60 m).
As depicted in Figure 6, two antennas and an MIMU were firmly connected to the carrier; the X-axis of the MIMU body coordinate system coincided with the X-axis defined for the carrier coordinate system; the plane of the MIMU body coordinate system coincided with the plane of the carrier body coordinate system; the Y-axis of the MIMU body coordinate system was parallel to the Y-axis defined for the carrier coordinate system. To obtain the high-precision position and attitude information of the carrier, we installed a high-precision INS in the vehicle body, where the plane of the MIMU body coordinate system coincided with the plane of the carrier body coordinate system and the Y-axis of the MIMU body coordinate system was parallel to the Y-axis defined for the carrier coordinate system.
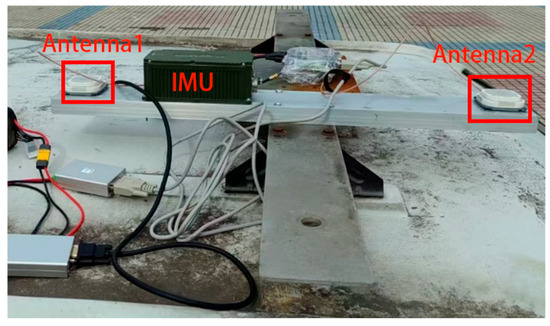
Figure 6.
Experimental device.
Real-time observation data were collected with the Sinan dual-antenna board. The high-precision attitude information associated with the reference position was obtained via the integration of high-precision inertial navigation and satellite navigation. The vehicle hovered in a nearly horizontal field with the circle-shaped trajectory.
In the experiments, the carrier-phase error of the Sinan dual-antenna board was less than 0.05 rad; signals on BeiDou B1 and B3 frequency points were observed; the MIMU error was less than 10 deg/h; POS620 was applied for high-precision inertial navigation, with an error being less than 0.012 deg/h. Detailed information is shown in Table 1, Table 2 and Table 3.

Table 1.
MP-POS620 performance parameters.

Table 2.
EIMU630 performance parameters.

Table 3.
K825 performance parameters.
In this study, experiments 1 and 2 were conducted to determine the two-dimensional direction of long-distance BeiDou satellite signal sources in synchronous orbits and a spoofing signal source in the short distance, respectively, to verify the accuracy of the system in determining the two-dimensional directions of signal sources at different distances. Experiment 3 was conducted to simulate the accuracy of determining the two-dimensional direction of a 10 km spoofing signal source in the background environment so as to illustrate the working accuracy of the model in the real-world environment.
The position of the spoofing device in the system was calculated using the method proposed in this study (i.e., the dual-antenna GNSS/MIMU-based method for determining the two-dimensional directions of satellite navigation signal sources). The high-precision attitude position information of the carrier was obtained based on the vehicle-mounted high-precision INS combined with the inter-station differential method. Using such information, we calculated the DOA of the satellite navigation signal source to determine its position. The computational accuracy of the proposed method was obtained by calculating the error between the real and calculated values.
4.2. Test for BeiDou Satellites in Synchronous Orbits
In order to evaluate the capability of the method model for simultaneous multi-signal source direction finding and to determine the deceptive signal recognition threshold by establishing the two-dimensional orientation accuracy towards on-orbit satellites, multiple BeiDou on-orbit satellites are used as targets for two-dimensional orientation.
Figure 7 illustrates that the two-dimensional direction of the signal source has an error of less than 0.1 rad, which aligned with the positioning error expected for the signal source.
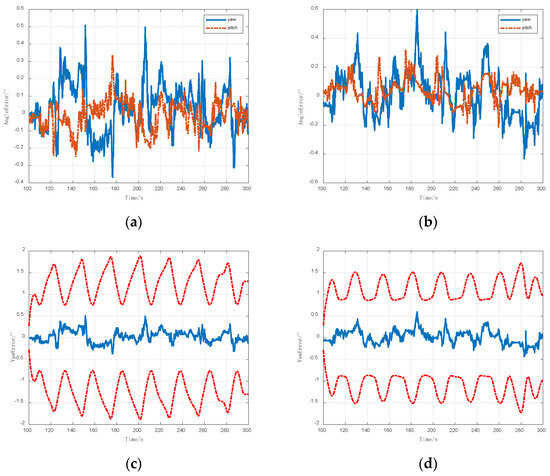
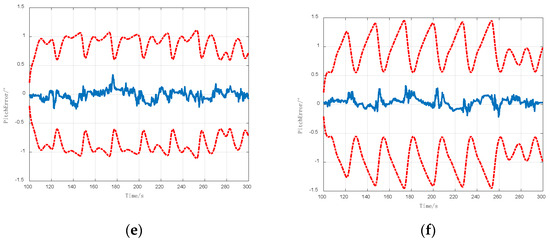
Figure 7.
BDS real signal two-dimensional signal source determining errors. (a) Two-dimensional direction-finding error of BeiDou-2 in this experiment; (b) two-dimensional direction-finding error of BeiDou-3 in this experiment; (c) yaw angle error and line of BeiDou-2 in this experiment; (d) yaw angle error and line of BeiDou-3 in this experiment; (e) pitch angle error and line of BeiDou-2 in this experiment; and (f) pitch angle error and line of BeiDou-3 in this experiment.
4.3. Test for a Short-Distance Spoofing Signal Source
Due to the simplification of the carrier motion in the computational model of this method, the increased influence of positional changes on the single-difference carrier phase between satellite navigation signal stations during close-range movements may affect the accuracy and reliability of the model. To analyse how the simplification of the position changes of the carrier affected the two-dimensional direction measurements for short-distance signal sources, we utilised a spoofing signal source to deceive the carrier. The position of the target carrier relative to the spoofing signal source is illustrated in Figure 8.
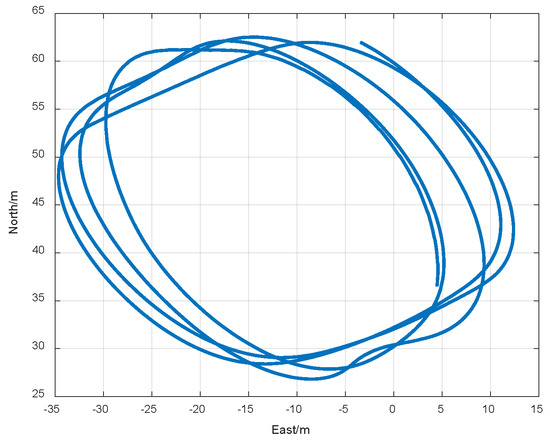
Figure 8.
Horizontal reference trajectories of the carrier.
Figure 9a depicts that the error in the two-dimensional heading angle of the signal source was basically less than 0.1 rad, which was in line with the expected positioning error for the signal source. When the difference between the distance of the signal source distance and the motion amplitude of the carrier was not obvious, the pitch angle error of the signal source rapidly increased, but the heading angle maintained high accuracy. When the system was applied to signal-source position search or fused with the zeroing antenna technology, it retained high reliability and effectiveness.
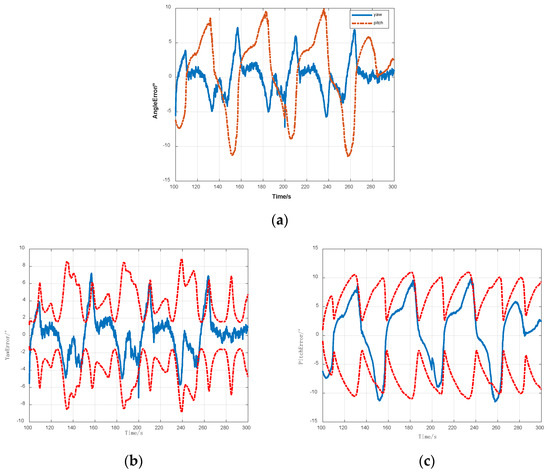
Figure 9.
Near-range spoofing signal two-dimensional signal source determining errors. (a) Two-dimensional direction-finding error for the short-distance spoofing signal source; (b) yaw angle error and line for the short-distance spoofing signal source; and (c) pitch angle error and line for the short-distance spoofing signal source.
Moreover, Figure 9b,c illustrates that the two-dimensional direction error of the signal source basically conformed to the envelope of the line, and the error gradually converged to approximately zero.
Essentially, the sudden change of this error reflected the direction-finding error of the least squares model.
A sudden change occurred in the computational error, carrier-phase compensation noise (error), and micro-inertial navigation error. The computational error was on the order of 10−4 rad, which was not obvious under the influence of the carrier-phase compensation error. The carrier-phase compensation error was approximated as a normally distributed error with a mean value of 0, which was kept on the order of 10−3 rad after the error was smoothed in the multi-epoch least squares algorithm. The micro-inertial navigation error could not be smoothed in the least squares algorithm because of the existence of the error dispersion, and the error experienced a sudden change on the order of 10−2 rad. This implies that the micro-inertial navigation error in the experimental environment as depicted in Figure 10 was the main factor causing sudden changes in navigation errors.
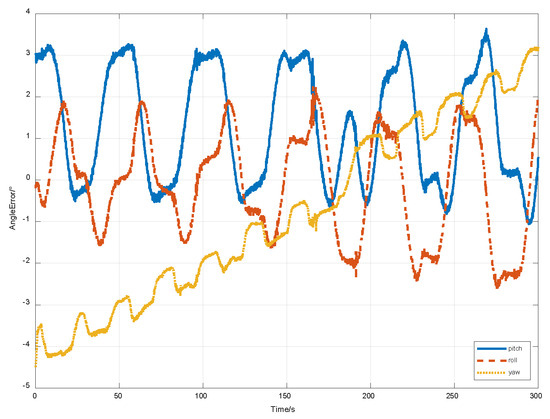
Figure 10.
MIMU attitude error curves.
4.4. Test for the Spoofing Signal Source in the General Environment
This section discusses a simulation scenario wherein a spoofing signal source approximately 10 km away from the carrier is set up. The motion trajectory of the carrier remained the same trajectory as depicted in Figure 7; that is, the position of the simulated signal source is at the position [7000, 7000, −100] in the front-right-lower body coordinate system at 500 s in the carrier motion. Using the high-precision inertial navigation as the reference value, the carrier-phase observation from the spoofing signal source to the deceived carrier is generated, introducing the normal distribution noises with for the simulated carrier phase observations.
Figure 11a illustrates that the error in the two-dimensional heading angle of the signal source was basically less than 0.03 rad, which aligned with the expected positioning error for the signal source. When there was a difference between the distance of the signal source distance and the motion amplitude of the carrier, both the pitch and heading angles of the signal source retained high accuracy, and the accuracy of the former was higher than that of the latter. When the system was applied to signal-source position search or fused with the zeroing antenna technology, it retained high reliability and effectiveness. This also provided high-precision angle information for multiple systems to determine the position of the spoofing signal source via multi-position orientation.
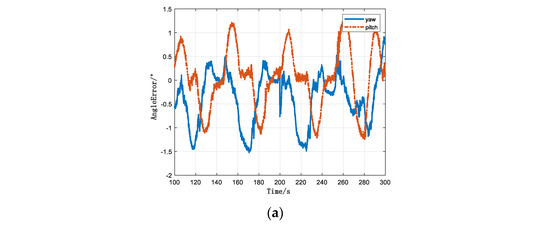
Figure 11.
Simulation of spoofing signal two-dimensional signal source determining errors. (a) Simulation of two-dimensional direction-finding errors for the spoofing signal source; (b) simulation of the yaw angle error and line for the spoofing signal source; and (c) simulation of the pitch angle error and line for the spoofing signal source.
Additionally, it can be observed from Figure 11 that the two-dimensional direction error of the signal source roughly conformed to the envelope of the line, demonstrating the filtering stability of the proposed algorithm. Table 4 lists all the maximum errors for two-dimensional directions in corresponding tests, paving the way for the quantitative analysis of the proposed algorithm.

Table 4.
The result of test validation.
As indicated in Table 4, the experimental results indicate that distance has a significant impact on the directional accuracy of the method, and when the distance is too close, the pitch angle error is greater than the yaw angle error. However, the errors are within an acceptable range at all distances, suggesting that the method has good adaptability in practical applications. Combining the attitude angle error curve of inertial navigation in Figure 10, it can be observed that the fluctuation peaks of the orientation error curve in Figure 9 and Figure 11 are related to the changes in inertial navigation errors.
5. Conclusions
This study proposes a dynamic dual-antenna positioning method for spoofed signals. This technique utilises the carrier body coordinate system information provided by the MIMU to identify the difference between the signal source DOA measured using the short-baseline common-clock dual-antenna method and the actual DOA of the signal source obtained from the ephemeris files, enabling the determination of signal authenticity and source direction. When the baseline length is less than 1 m, the computational error in the yaw and pitch angles of the signal source can remain less than 0.1 rad. In the short-distance case, the yaw angle error is maintained within 0.1 rad so that the direction of the signal source could be effectively determined to satisfy the zeroing angle requirement of the zeroing antenna. In the middle- and long-distance cases, the two-dimensional direction error is maintained within 0.03 rad, which basically meets the demand of multi-position orientation and thus the demand of signal source positioning. With the assistance of an MIMU, the novel common-clock short-baseline dual-antenna method for determining the DOA of the signal source can rapidly and accurately determine the DOA of the measured source under a minor increase in the size, weight, and arithmetic cost, thereby showing superiority.
Compared with the conventional methods of spoofed signal suppression, the proposed method effectively suppresses the jamming and spoofing signals by determining the two-dimensional direction of the signal source and incorporating the rapidly evolving zero-tuning antenna technology, thus showing higher application potential. In summary, the proposed method not only improves the measurement accuracy of the DOA of the signal source but also helps to improve the performance of the existing signal spoofing suppression techniques, laying a foundation for future research and application in related fields.
Author Contributions
Conceptualisation, C.Z.; methodology, J.W. and C.Z.; software, D.W. and C.Z.; validation, J.W. and D.W.; formal analysis, D.W.; investigation, all; resources, J.W. and D.W.; data curation, C.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, C.Z.; writing—review and editing, D.W. and C.Z.; visualisation, J.W. and D.W.; supervision, J.W. and D.W.; project administration, J.W. and D.W.; funding acquisition, J.W. and D.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 61903367).
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors on request. The data are not publicly available due to their integration within the team’s internal database, which is structured for internal access and use. Direct public access to this database is not feasible due to operational, privacy, and security protocols.
Acknowledgments
Thanks to Li Caihua of Hunan Boshang Electronic Technology Ltd. and Gao Zhijian of ComNav Technology Ltd. for providing experimental components.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Meng, L.; Yang, L.; Yang, W.; Zhang, L. A survey of GNSS spoofing and anti-spoofing technology. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Wengen, G.; Yunfei, L.; XinXin, G.; Pengfei, H. Joint detection and state estimation based on GPS spoofing attack in smart grids. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2024, 161, 110151. [Google Scholar]
- Salman, L.; Muhammad, F.; Jawwad, N.C.; Faran, A.B.; Nor, M.M.; Ijaz, H.N. A framework for preventing unauthorized drone intrusions through radar detection and GPS spoofing. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2024, 15, 102707. [Google Scholar]
- Omid, S.-T.; Mohamad, F.S.; Danaee, M.R. Null broadened-deepened array antenna beamforming for GNSS jamming mitigation in moving platforms. ICT Express 2022, 8, 161–165. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, M.; Xia, W.; Wei, S.; Li, H.; Li, P. A Robust GNSS Interference Suppression Method Based on Null Broadening of Dual-polarized Antenna Arrays. In Proceedings of the 14th IEEE International Conference on Signal Processing (ICSP), Beijing, China, 12–16 August 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, J.; Huang, F.; Zhang, L.; Xu, D.; Hsu, L.T. Selection of Areas for Effective GNSS Spoofing Attacks to a Vehicle-Mounted MSF System Based on Scenario Classification Models. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2023, 72, 14645–14655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhijun, W.; Cheng, L.; Yun, Z.; Rusen, L.; Meng, Y. Anti-spoofing: Integrated information authentication of BeiDou-II civil navigation message. China Commun. 2024, 21, 242–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, P.; Yue, M. BDSec: Security authentication protocol for BeiDou-II civil navigation message. China Commun. 2024, 21, 206–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, M.; Lyu, X.; Meng, Z.; You, Z. GNSS spoofing detection for single antenna receivers via CNR variation monitoring. J. Syst. Eng. Electron. 2024, 35, 1276–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, S.H.; Xiao, X.; Fu, Q.W. INS-aided GNSS spoofing detection based on two antenna raw measurements. Gyroscopy Navig. 2016, 7, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, X.; Sun, F.; Wang, D.; Xiao, K.; Dou, S.; Lu, X.; Sun, J. GNSS spoofing detection based on multicorrelator distortion monitoring. GPS Solut. 2023, 27, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Kou, Y.; Huang, Z.; Zhao, Y. GNSS spoofing maximum-likelihood estimation switching between MEDLL and CADLL. GPS Solut. 2023, 27, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Yue, J.; Xu, B.; Hsu, L.-T. A post-correlation graphical way for continuous GNSS spoofing detection. Measurement 2023, 216, 112974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, H.; Yang, C.; Lu, M. Signal quality monitoring-based spoofing detection method for Global Navigation Satellite System vector tracking structure. IET Radar SonarNavig. 2020, 14, 944–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, W.; Fu, Q.; Liu, B. Research Progress of GNSS Spoofing and Spoofing Detection Technology; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: Xi’an, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Zhu, X.; Ouyang, M.; Li, W.; Chen, Z.; Fu, Q. GNSS spoofing jamming detection based on generative adversarial network. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 22823–22832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Lian, B. Fault Detection for Multi-Source Integrated Navigation System Using Fully Convolutional Neural Network. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2018, 12, 774–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Ni, S.; Cheng, L.; Lei, T.; Song, X. GNSS spoofing detection method based on the intersection angle between two directions of arrival (IA-DOA) for single-antenna receivers. GPS Solut. 2024, 28, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui, L.; Zhiwei, Y.; Qidong, C.; Guisheng, L.; Qinglin, Z. Localization of GNSS spoofing interference source based on a moving array antenna. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, W.; Yuwei, Y. Vehicle mounted single-antenna GNSS spoofing detection method based on motion trajectory. GPS Solut. 2024, 28, 155. [Google Scholar]
- Cellmer, S.; Wielgosz, P.; Rzepecka, Z. Modified ambiguity function approach for GPS carrier phase positioning. J. Geod. 2010, 84, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.; Zhao, L.; Li, L.; Gao, Y.; Gao, Y.T. Pivot single-difference ambiguity resolution for multi-GNSS positioning with non-overlapping frequencies. GPS Solut. 2019, 23, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Si, C.Z.; Ye, X.; Zhang, B.; Qin, G.; Bai, Y. A TCAR method for common clock source single difference carrier phase observation ambiguity fixing. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2022, 2253, 012008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forssell, B.; Martin-Neira, M.; Harris, R.A. Carrier phase ambiguity resolution in GNSS-2. In Proceedings of the 1997 10th International Technical Proceedings of the 1997 10th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation, ION GPS-97, Kansas City, MO, USA, 16–19 September 1997. Part 2 (of 2). [Google Scholar]
- Enge, P.; Jung, J.; Pervan, B. High integrity carrier phase navigation for future LAAS using multiple civilian GPS signals. In Proceedings of the 1999 American Control Conference (Cat. No. 99CH36251), San Diego, CA, USA, 2–4 June 1999. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).