Abstract
Volcanic eruptions pose a major natural hazard influencing the environment, climate and human beings at different temporal and spatial scales. Nevertheless, several volcanoes worldwide are poorly monitored and assessing the impact of their eruptions remains, in some cases, challenging. Nowadays, different numerical dispersion models are largely employed in order to evaluate the potential effects of volcanic plume dispersion due to the transport of ash and gases. On 28 August 2019, both Mt. Etna and Stromboli had eruptive activity; Mt. Etna was characterised by mild-Strombolian activity at summit craters, while at Stromboli volcano, a paroxysmal event occurred, which interrupted the ordinary typical-steady Strombolian activity. Here, we explore the spatial dispersion of volcanic sulphur dioxide (SO) gas plumes in the atmosphere, at both volcanoes, using the Weather Research and Forecasting model coupled with Chemistry (WRF-Chem) considering the ground-measured SO amounts and the plume-height as time-variable eruptive source parameters. The performance of WRF-Chem was assessed by cross-correlating the simulated SO dispersion maps with data retrieved by TROPOMI and OMI sensors. The results show a feasible agreement between the modelled dispersion maps and TROPOMI satellite for both volcanoes, with spatial pattern retrievals and a total mass of dispersed SO of the same order of magnitude. Predicted total SO mass for Stromboli might be underestimated due to the inhibition from ground to resolve the sin-eruptive SO emission due to the extreme ash-rich volcanic plume released during the paroxysm. This study demonstrates the feasibility of a WRF-Chem model with time-variable ESPs in simultaneously reproducing two eruptive plumes with different SO emission and their dispersion into the atmosphere. The operational implementation of this method could represent effective support for the assessment of local-to-regional air quality and flight security and, in case of particularly intense events, also on a global scale.
1. Introduction
Volcanic eruptions can have important impacts on society, representing a potential source of hazard (e.g., Loughlin et al. 2015 [1]). Explosive eruptions may cause the formation of ash-gas columns, which may rise to several kilometres above the vent and be transported over long distances. The transport and deposition of volcanic ash and gases could have a high impact on transportation, mainly air traffic, but also vehicles and trains. Additionally, agriculture, human health and the climate system would be impacted [2,3,4,5]. Among the volcanic gases, sulphur dioxide (SO) is responsible for acid rain, due to the reaction with atmospheric water, forming sulphuric acid [6].
Furthermore, when extremely strong explosive paroxysms occur, volcanic ash and SO may reach the stratosphere. Since this atmospheric layer is characterised by vertical stratification, ash and sulphate aerosol particles (resulting from the oxidation and nucleation of SO emission), which interact with solar and terrestrial radiation, can reside in the stratosphere for a longer time than in the case of tropospheric injections, thus modulating the radiative balance and impacting the climate system (e.g., Pinatubo 1991 [7,8] and Tambora 1815 [9], Raikoke 2019 [10], Hunga Tonga 2022 [11,12]).
Generally, extreme explosive eruptions are associated with a negative short-wave radiative forcing and a transient decrease in global surface temperatures (e.g., Oppenheimer 2011 [13] and Luterbacher and Pfister 2015 [14]), even if the recent Hunga Tonga eruption in 2022 challenged this paradigm due to the large injection of water vapour for this Phreatoplinian eruption [11].
Due to the importance of volcanism and its impacts, intense research activity is presently focused on the development and optimization of numerical models which can simulate the atmospheric transport and surface deposition of pollutants, including volcanic ash and gases, such as the so-called Volcanic Ash Transport and Deposition (VATD) models [15]. This whole class of dispersion models can be classified into two main groups based on the physical–mathematical approach adopted. The first class considers the Eulerian models, in which the variables are discretized on grids and the equations are solved with numerical methods, i.e., WRF-Chem [16] and FALL3D [17]. The second class considers the Lagrangian models, in which the trajectory of single particles is studied, i.e., FLEXPART [18], Hysplit [19,20] and NAME [21,22]. The Eulerian Weather Research and Forecasting–Chemistry (WRF-Chem) model has been recently utilised to study single paroxysmal events of Mt. Etna (e.g., 23 November 2013 [23], and two sequences of paroxysms of Mt. Etna [24]).
The other application of the WRF-Chem model concerns the impact on the Mediterranean basin of bromine [25,26] because volcanoes are considered a geochemically important source of halogen species into the troposphere. Volcanic gases and aerosols are also subject to numerous physical and chemical evolution processes such as sulphate aerosol production or cloud condensation nuclei activation [27]. Pianezze et al. 2019 [28] observed that degassing has a strong impact on cloud condensation nuclei (CCN) formation) investigating both Mt. Etna and Stromboli volcanic plumes during the stage of quiescent degassing for Mt. Etna and ordinary explosive activity at Stromboli. More recently, Arghavani et al. 2022 [29] implemented a novel parameterisation of nucleation in the WRF-Chem model regarding new particle formation of a passive degassing of the Mt. Etna plume observed on 15 June 2016 [29].
Mt. Etna and Stromboli are ideal target volcanoes for testing and developing numerical modelling on physical and chemical evolution processes of volcanic degassing. They are both persistently active and well monitored and, therefore, allow for detailed model inputs and correlative data to be gathered.
Mt. Etna is one of the most important emitters of natural pollution on Earth, accounting for about 10% of the global average volcanic emissions of carbon dioxide and SO (e.g., [30,31]. The total volatile flux from Mt. Etna is evaluated at ∼21,000 t/day, with a large fraction accounted for by water vapour (HO, ∼13,000 t/day). HO dominates (>70%) the volatile budget during syn-eruptive degassing, while CO and HO contribute equally to the total volatile flux during passive degassing. SO accounts for a relatively minor fraction of the total volatile flux both during passive and eruptive degassing (respectively, (∼8% and ∼17% [32]).
Stromboli is well known for its mild and continuous Strombolian activity, occasionally interrupted by effusive eruptions and more-violent-than-ordinary explosive events, named based on their intensity of major explosions and paroxysms (e.g., [33]). The persistent eruptive activity of Stromboli is fed by a volatile-rich high-potassium basalt whose continuous degassing through open conduits sustains a permanent volcanic plume degassing, which contributes 1–2% of the estimated global volcanic yield of sulphur, halogens, and trace metals to the atmosphere [34]. Chemical investigation of Stromboli’s plume degassing has revealed a large spread of plume compositions depending on bulk-quiescent and sin-explosive degassing. The quiescent degassing shows a well-defined time-averaged chemical composition dominated by HO (48–98 mol%; mean 80%), CO (2–50 mol%; mean 17%) and SO (0.2–14 mol%; mean 3% [35]). SO represents by far the main sulphur-containing species: SO/HS molar ratios range from 14 to 17 [36] and particulate sulphur accounts for <5% of total sulphur [34,37].
Compared with quiescent emissions, the bursting gas slugs associated with ordinary Strombolian explosive activity have a distinct chemical composition. The gas phase is richer in CO (11–50%; mean 26%) and poorer in HO (48–88%; mean, 73%) than the bulk plume passively released by the volcano, and moreover displays higher CO/SO, SO/HCl, and CO/CO molar ratios [35]. Larger variations have been observed before the occurrence of paroxysm with a 10-fold increase in CO flux and high value of CO/SO ratios and 5-fold SO flux growth recorded in the days and hours before 15 March 2007 paroxysms [38].
Here, we report on the evolution of the spatial distribution of SO in the Mt. Etna and Stromboli volcanic plumes during a case study on 28 August 2019. At that time, the signatures of the activities of both volcanoes are visible simultaneously. Mt. Etna was in passive degassing and moderate erupting phase, whereas Stromboli was experiencing a paroxysmal event. With the WRF-Chem model, simulations were carried out using in situ ESPs (SO emitted burden and injection height).
The main objectives of this paper are (i) to reproduce the observed spatial and temporal evolution of the volcanic plumes produced by Mt Etna and Stromboli volcanoes using the WRF-Chem model, (ii) to test an innovative method, which allows us to take into account the transient and fluctuating nature of the volcanic emissions, and (iii) to model, for the first time, the transport of the eruptive column-produced transport by a paroxysmal event of Stromboli with the interaction of the Etna summit crater plume.
This manuscript is structured into five sections. In Section 2, the volcanology framework of Mt. Etna and Stromboli is introduced. The data and methodology used in this work are described in Section 3. Section 4 presents the results of the simulations and their evaluation with the available observational data; ageing of the volcanic plumes; and their effects. Conclusions are drawn in Section 5.
2. Volcanology Framework
Sicily is part of the western central Mediterranean and its segment constitutes a link between the African Maghrebides with Southern Apennines across the Calabrian accretionary wedge (e.g., Lentini et al. 2014 [39]).
Active volcanism is located in the eastern and northern part of the island. Mt. Etna and Stromboli share the common feature of most active volcanoes in the world with an almost continuous eruptive activity [40,41], characterized by a wide range and intense voluminous eruptive phenomena, ranging from lava effusion to explosive paroxysms, causing columns of ash up to different km above the vent.
Specifically, in the period of study, Mt. Etna was characterised by explosive activity variables in both intensity and style, mainly from the South-East crater (SEC, see Figure 1). The activity consisted of mild explosions coupled with episodic summit effusive events between late May and July [42]. Throughout the month of August, and specifically on 28 August, eruptive activity gradually declined in intensity, consisting of mild Strombolian activity mainly from SEC and secondary from the North-East crater and Bocca Nuova (respectively, NEC and BN, see Figure 1).
At Stromboli volcano, during summer 2019, two paroxysms occurred on 3 July and 28 August. Specifically, the August episodes consisted mainly of three explosions followed by a pyroclastic flow along the Sciara del Fuoco sector that travelled about 1 km on the sea surface and caused a tsunami with waves about 60 cm high. The eruptive column reached up to ∼6.4 km [43] with a fall-out dispersion of ash and volcanic gas towards NNE (between P.ta Labronzo and Stromboli village [44]).
The Toulouse Volcanic Ash Advisory Centre (VAAC), operated by Météo-France (https://vaac.meteo.fr/, accessed on 17 March 2023), has the responsibility of the now-casting of volcanic emission dispersal in the Mediterranean basin, which hosts very active volcanoes like Etna and Stromboli. It released three Volcanic Ash Advisories (VAA) for Stromboli, following the eruptions analysed in this paper and reported in the Appendix A (see Table A1). The first two advisories (at 10:56 and 12:00 UTC) were classified as red indicating a warning alert, while the third one at 15:00 UTC (orange alert) denoted a reduction in ash emission.
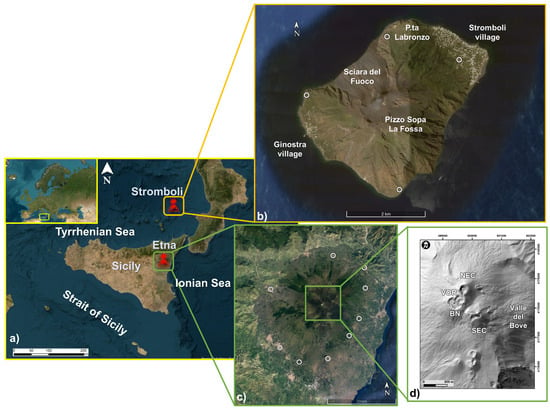

Figure 1.
(a) Map showing the position of both (b) Stromboli (top right panel, modified from Google Earth) and (c) Mt. Etna (bottom right panel, modified from Google Earth) volcanoes in southern Italy. The white dots in the panels (b,c) represent the Flame DOAS network. The gray map (d) shows the summit craters with their respective names: Voragine (VOR); Bocca Nuova (BN); North-East Crater (NEC); and South-East Crater (SEC) [45].
3. Data and Methods
In this chapter, we describe the experimental ESP data that are used to initialise the volcanic package of the WRF-Chem model and the satellite data that are used to validate the model output.
3.1. Ground-Based SO Flux Emission
The bulk plume SO flux released by the summit craters of Mt. Etna and Stromboli was measured during daylight hours using the FLAME (FLux Automatic MEasurement) ultraviolet DOAS (differential optical absorption spectroscopy) scanning spectrometer network (e.g., Salerno et al. 2018 [46]).
At Stromboli, the network consists of four ultraviolet scanning spectrometers placed near the coast of the island and intercepting the plume from a distance of ∼2 km from the summit craters of Stromboli.
At Mt. Etna, automatic FLAME stations are placed in the flank of the volcano at a mean altitude of 800 m a.s.l. and intercepting the volcanic plume at a mean distance of ∼14 km from the summit craters.
At both volcanoes, each instrument scans the sky over 156 from horizon to horizon every 5 min during daylight. Open-path ultraviolet spectra were reduced on-site applying the DOAS method (e.g., Platt and Stutz 2008 [47]) and using a modelled clear sky spectrum [48]. SO mass emission rates are automatically computed by inverting the SO volcanic column amounts’ plume profiles, and the uncertainty in SO flux ranges between −22 and +36% (e.g., [46,48]). The details and configuration of the network are given in [46,48].
3.2. WRF-Chem Setup
For this study, we have utilised the WRF-Chem model version 4.3.1 in a numerical domain covering the southern Mediterranean, with 310 × 320 grid points and a horizontal grid spacing of 6 km.
Initial and boundary conditions are available at the WRF input system (https://www2.mmm.ucar.edu/wrf/users/download/free_data.html accessed on 17 March 2023) and provided by the NCAR/NCEP Final Analysis from Global Forecast System (FNL from GFS at 1-degree resolution, ds083.2, available at this link: https://rda.ucar.edu/datasets/ds083.2/ accessed on 17 March 2023).
Both simulations started on 28 August 2019 00:00 UTC and finished on 30 August 2019 00:00 UTC. The parameterisations of the physics and chemistry components of the WRF-Chem model are reported in Table 1.

Table 1.
Physical and chemical options of the WRF-Chem model.
Based on the WRF setup recommended by [24], the physics parameterisations that are utilised consist in the Mellor–Yamada–Janjic Scheme parameterisation (MYJ; [49]) to define the planetary boundary layer (bl_pbl_physics = 2) and the surface layer (sf_sfclay_phy-sics = 2) Eta similarity scheme ([50]).
The land surface exchange processes and the associated fluxes are represented by the Noah-MP Land Surface Model (sf_surface_physics = 4; [51]). The radiative schemes are parameterised using the Goddard radiation model [52] for both shortwave and longwave (ra_sw/lw_physics = 5) components. The microphysics parameterisation considers the one-moment Goddard four-class ice (4ICE) scheme developed by [53]. This scheme considers prognostic variables for cloud ice, snow, graupel and hail.
In WRF-Chem, the “chem_volc package” (option 402) is utilised and it transports sulphur dioxide (SO) and volcanic ash bins (not utilised in this study) in the numerical domain. The FLAME-DOAS data were pre-processed and elaborated to be compatible with the WRF-Chem input system. In particular, since the SO ground FLAME-DOAS time series are not stationary, depending on the spread direction of the volcanic plume with respect to the spatial distribution of the stations in the volcano, it was necessary to apply RAW-data processing techniques, including both time-regularization and interpolation algorithms. Subsequently, they were filtered on a 30 s time lag to be ingested in the numerical model at each time step. The corresponding time series of SO mass eruption rate and injection height are depicted in Figure 2 and Figure 3, respectively, for both eruptive time series.
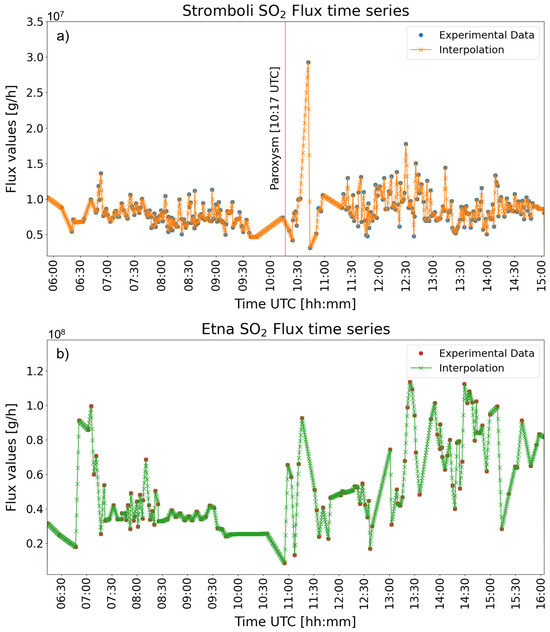
Figure 2.
The SO flux time series provided to model WRF-Chem related to Stromboli (orange line in panel (a)) and Etna (green line in panel (b)) volcanoes, respectively. Units are 10 g/h (a) and 10 g/h (b).
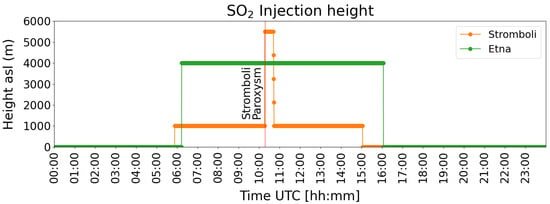
Figure 3.
Injection height (asl) related to both Stromboli (orange line) and Mt. Etna (green line) SO flux time series during 28 August 2019, obtained via INGV instrumentation. The red line refers to the start of the Stromboli paroxysm.
For Stromboli volcano, during the ordinary “Strombolian” activity, the value of SO injection height considered in the simulation, obtained using the INGV realtime camera observations, was about 1000 m asl (about 100 m above the Pizzo Sopra La Fossa), according to the plume height values recorded during the typical Strombolian activity [33,41]. Instead, during the paroxysmal event of 28 August 2019, the height of the ash-gas column injected in the model was computed using a calibrated picture of the paroxysm taken from Panarea island (about 18 km from Stromboli), with respect to the altitude of Stromboli island. Using qualitative inversion, we estimate a height of 5500 m ejected for about 15 min between 10:17 (start of the paroxysm) and 10:42 UTC, which is consistent with that estimated by [44].
The injection height parameter was ingested in the model simulation at each time step as indicated by Figure 3. A linear interpolation technique has been over-imposed in order to take into account decreasing plume height values at the end of the paroxysm.
Concerning the Mt. Etna simulation, a constant SO injection was taken into account at around 4000 m asl (about 700 m above the summit craters, which are at altitude of about 3300 m), obtained from the real time monitoring cameras of INGV. Table 2 reports the ESPs for both eruptive events of Stromboli and Mt. Etna, respectively, STR1 and ETN1. The duration of almost 10 h for both STR1 and ETN1 events and the Total Emitted Mass (TEM) from ETN1 being almost six times more powerful in terms of total SO mass emitted in the atmosphere can be noted.

Table 2.
The Eruption Source Parameters (ESPs) for the eruptions of 28 August 2019.
3.3. Tropomi Data
The TROPOspheric Monitoring Instrument (TROPOMI) is a passive-sensing hyperspectral nadir-viewing imager onboard the Sentinel-5 Precursor satellite of the European Space Agency (ESA). It operates with four separate spectrometers measuring the ultraviolet (UV), UV–visible (UV-VIS), near-infrared (NIR) and short-wavelength infrared (SWIR) spectral bands [54]. It was launched on 13 October 2017, and its swath width is approximately 2600 km, with an along-track resolution of 7 km and daily global coverage [55].
The Global Sulfur Dioxide Monitoring Home Page of the Goddard Space Flight Center (https://www.nasa.gov/goddard accessed on 17 March 2023) provides in its web-portal (https://so2.gsfc.nasa.gov accessed on 17 March 2023) the “archived daily OMI/OMPS/TR0POMI images”. Selecting the region and the date of interest, SO maps may be downloaded all over the globe; in particular, we have downloaded the TROPOMI image of Mt. Etna and Stromboli relative to the eruptive activities of 28 August 2019 (available at this link: https://so2.gsfc.nasa.gov/pix/daily/ixxxza/troploop5pca.php?yr=19&mo=08&dy=28&bn=etna accessed on 17 March 2023).
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Synoptic Analysis
To analyse the synoptic conditions, the maps of geopotential height and winds obtained from the simulations performed using the WRF-Chem model are shown in Figure 4. In particular, Figure 4a–c represent the mid-troposphere (at an altitude equal to 500 hPa, about 5500 m above sea level). The geopotential height and wind at 700 hPa (about 3000 m above sea level) are shown in Figure 4d–f.
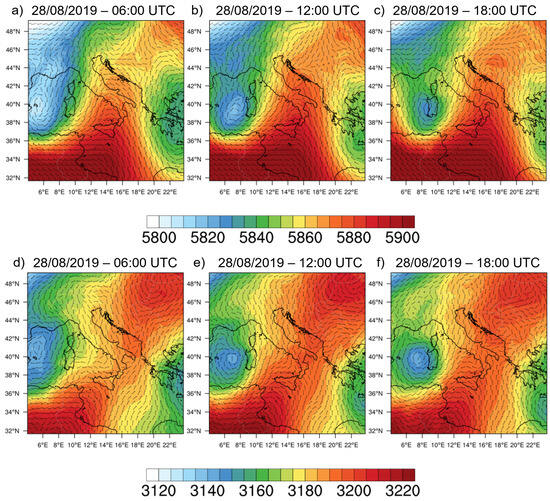
Figure 4.
Geopotential height (m) and wind barbs (m/s) at 500 hPa at 06:00 (a), 12:00 (b) and 18:00 (c) UTC on 28 August 2019 and at 700 hPa at 06:00 (d), 12:00 (e) and 18:00 (f) UTC on 28 August 2019.
The day of 28 August 2019 was characterized by a sequence of ridges and troughs. In particular, the presence of a high pressure pattern (ridge) of the north-African matrix, has affected areas in southern Italy, especially Sicily (see Figure 4). During the day, the anticyclonic system tended to weaken, favouring the zonal translation (from West to East) of a cyclonic vortex. The trough, initially close to the Balearic Islands (Figure 4a), reached Sardinia and, during the evening, the northwestern coast of Sicily (Figure 4b,c). This synoptic framework, at first, favoured the presence of winds at 500 hPa coming from the southwest to the western sector of Sicily, while the eastern one was affected by northwestern winds (Figure 4a). In the following hours, the winds at 500 hPa gradually tended to align from the southwestern quadrants across the entire Sicilian territory (Figure 4c).
In Figure 4d, it is possible to notice that, close to Stromboli volcano, the winds at 700 hPa are directed eastward; in the following hours (Figure 4e,f), they turn southward.
Finally, to show the direction and velocity of winds at different altitudes, close to both Mt. Etna and Stromboli volcanoes, the Skew-T diagrams obtained from the WRF-Chem simulation are reported in Figure 5 and Figure 6.
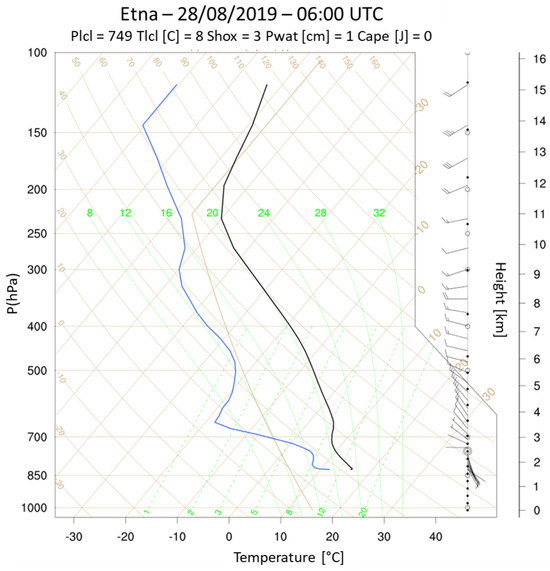
Figure 5.
Skew-T diagram obtained in the proximity of Etna volcano. The blue line represents the Dewpoint plot. The black line represents environmental sounding.
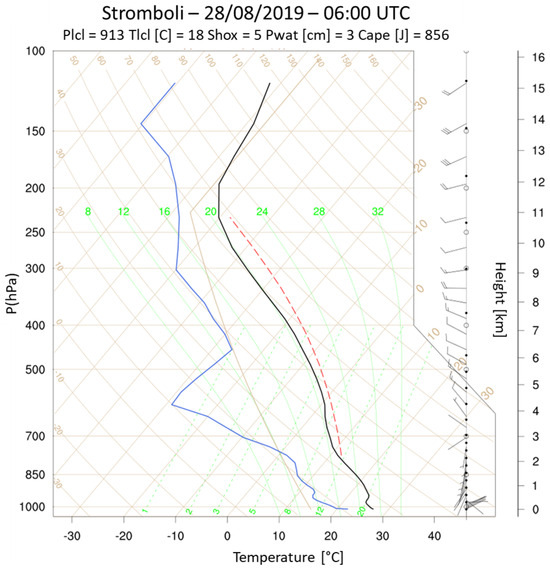
Figure 6.
Skew-T diagram obtained in the proximity of Stromboli volcano. The blue line represents the Dewpoint plot. The black line represents the environmental sounding. The red line represents the parcel lapse rate.
In particular, it is possible to note that at 06:00 UTC, time corresponding to the beginning of the SO flux data series recorded by the FLAME network, winds on the Etna volcano (see Figure 5), at an altitude of 700 hPa (about 3000 m), were oriented from the northwestern quadrants.
Instead, on Stromboli volcano, the phenomenon of wind shear (see Figure 6) was observed, consisting of an abrupt variation in both wind intensity and direction with altitude. Indeed, at up to 700 hPa, the winds came from the southwestern quadrants, while at higher altitudes they tended to start from the northwestern sector.
4.2. Results from the WRF-Chem Model and Comparison with TROPOMI
As mentioned in the Introduction, the main purpose of this work is to analyse two simultaneous eruptions from the Mt. Etna and Stromboli volcanoes in Sicily (Italy). These two volcanoes are 120 km apart, and in the case of simultaneous eruptions, the volcanic plumes may overlap in a complex pattern. The numerical modelling of such events and the analysis of satellite data may be helpful in the interpretation of the spatial pattern and the relative consequences on the territory.
On the Tropomi image, reported in Figure 7a, it is evident that there are two distinct SO plumes at granule time 11:13–13:14 UTC on 28 August. The WRF-Chem simulation (Figure 7b) reproduces, with high fidelity, the spatial pattern retrievals from the Tropomi sensor. To obtain Dobson Units (DU) from the WRF-Chem output SO variable, which is expressed in ppmv (part per million by volume), it must be first transformed in g m, then integrated vertically over each grid-point column to give g m and finally converted in DU; the corresponding converted variable will be denoted in the following text as SO_du.
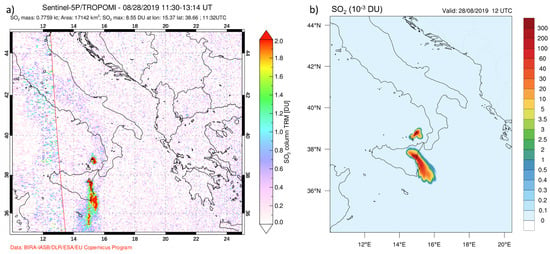
Figure 7.
(a) TROPOMI retrievals for 28 August 2019 at 11:30–13:14; (b) WRF-Chem output SO_du at 13:00 UTC of 28 August 2019. Units for Tropomi (a) are DU and 10 DU for WRF-Chem (b).
In particular, according to the synoptic analysis and considering the Skew-T diagrams reported in Figure 5 and Figure 6, the plume from Mt. Etna being oriented from the northwestern quadrant is directed south-east, while the plume from Stromboli is oriented north/north-east. The intensity of SO_du predicted by WRF-Chem is in some way under-estimated, even if the maximum SO_du values on the map are close to 2 DU.
Considering the fair agreement between the observed and the modelled columnar SO_du at 13:00 UTC, it may be interesting to show the time evolution of the two different plumes also because the two eruptive sequences stopped at 15:00 (Stromboli) and 16:00 UTC (Mt. Etna) on August 2018, as reported in Table 2. On the six panels of Figure 8, we have reported the time sequence of the two SO_du plumes at different times, namely at 11:00 (a), 14:00 (b), 17:00 (c), 20:00 (d) and 23:00 (e) UTC on 28 August and 04:00 UTC on 29 August (f).
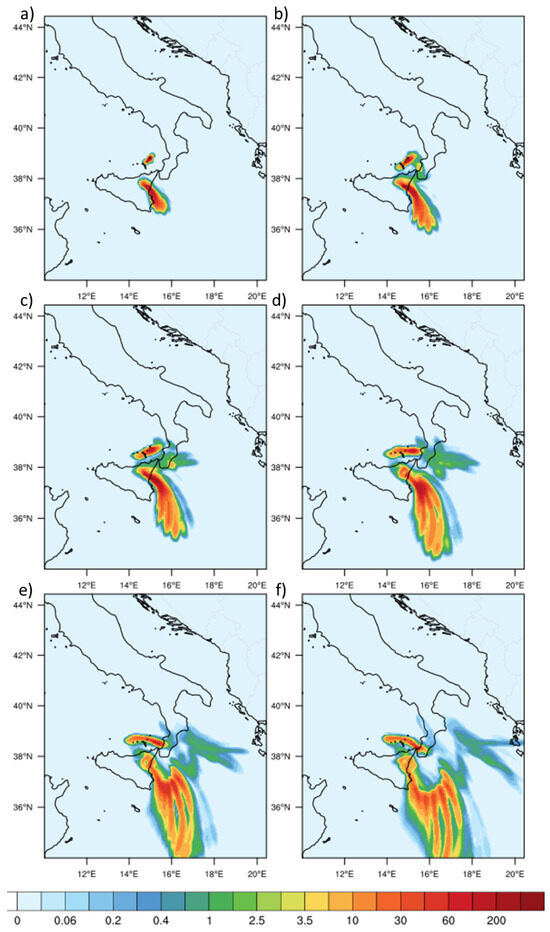
Figure 8.
Columnar density of SO_du expressed in 10 Dobson Units (DU), estimated from the simulation carried out by the WRF-Chem model, for 28 August 2019 at 11:00 UTC (a), 14:00 UTC (b), 17:00 UTC (c), 20:00 UTC (d), 23:00 UTC (e) and 04:00 UTC on 29 August 2019 (f).
When analysing this figure in detail, it can be seen that a portion of the Stromboli plume, starting at 14:00 UTC (Figure 8b), is being deviated in he south-east direction; this allows the merging of the two plumes at a later time, as shown by Figure 8c (17:00 UTC) and subsequent times (Figure 8d–f). An important feature highlighted by Figure 8 concerns the spatial extension of the two volcanic plumes that in the case of Mt. Etna occupy a much larger region; this is not surprising if we consider the total emitted mass (TEM) that is reported in Table 2.
To further verify this concept (merging), it is necessary to show the SO patterns at given times and at a pressure level of 500 hPa (about 5500 m). For this purpose, we have provided Figure 9 in which we reported the sequence of a SO snapshot from 11:00 UTC on 28 August 2019 (Figure 9a) to 04:00 UTC on 29 August 2019 (Figure 9f). In particular, Figure 9c shows that the merging of the two plumes starts just after 17:00 UTC, but it becomes more evident at 20:00 UTC (red circle in Figure 9d). At later times, the two merged plumes are directed south-east according to the synoptic circulation at this pressure level. In addition, in the Appendix, SO pattern sequences are also shown at a pressure level of 600 (Figure A6) and 700 hPa (Figure A7). This allows us to investigate the region between 3 and 5 km asl where the largest portion of SO mass is transported. The analysis of the two supplementary maps confirms the considerations reported above at 500 hPa.
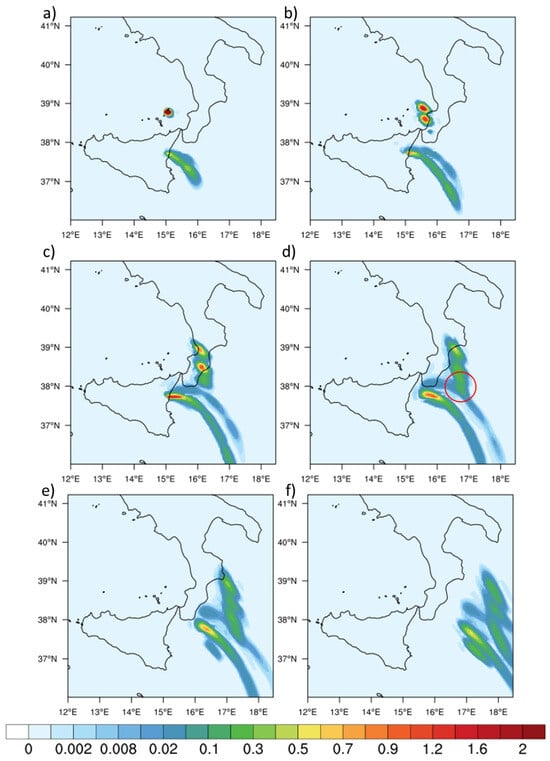
Figure 9.
Sequence of images illustrating the distribution of sulphur dioxide (in g m) at 500 hPa, obtained from the WRF-Chem simulation, for 28 August 2019 at 11:00 UTC (a), 14:00 UTC (b), 17:00 UTC (c), 20:00 UTC (d), 23:00 UTC (e) and 04:00 UTC on 29 August 2019 (f).
The SO spatial pattern displayed by Figure 8 and Figure 9 (and Figure A6 and Figure A7 in Appendix A) reveals a complex structure of both volcanic plumes. In this context, the necessity of coupling a meteorological model with an aerosol dispersion module and with time-varying ESPs is mandatory.
5. Conclusions
In this work, we studied the transport of volcanic SO eruptive plumes from Mt. Etna and Stromboli using the Weather Research and Forecasting model coupled with Chemistry (WRF-Chem). The two volcanoes emitted different SO-burdens and plume heights as a consequence of their different eruptive styles. The former featured mild-Strombolian activity while the second a paroxysmal event.
Modelling was configured by considering the time-variable Eruptive Source Parameters (ESPs) related to the SO flux released by the summit craters, obtained by the ground scanning spectrometer FLAME DOAS network and plume height inverted by the literature and calibrated images. The total erupted mass of Stromboli and Mt. Etna covered almost one order of magnitude (0.077–0.5 Tg) with durations of almost 10 h for both events. The synoptic conditions at 500 hPa were characterised by the presence of an African high-pressure field that during the day was weakening, favouring the zonal translation (from west to east) of the low-pressure system.
The comparison between the SO dispersion maps simulated by the model, and data observed by TROPOMI for both Mt. Etna and Stromboli show good agreement with the simulated total mass of SO of the same order of magnitude as the satellite data. However, in the case of Stromboli, the total mass of SO predicted by the WRF-Chem simulation is underestimated. This is probably due to the inhibition of the actual detection of syn-eruptive SO by the FLAME system, caused by the extremely ash-rich volcanic plume released during the paroxysm.
The additional analysis of SO transport at 500 hPa shows a complex pattern characterised by two distinctive plumes merging a few hours after the main eruptive events. In conclusion, here, we demonstrate the feasibility of the WRF–Chem model with time-variable ESPs in reproducing different levels of volcanic SO and their dispersion into the atmosphere. This approach could represent effective and operational support for the assessment of flight security in the Mediterranean area.
Future developments of the volcanic package of the WRF-Chem model will consider an improved definition of injection heights and columnar ash distribution in the early stage of a paroxysm. An online chemistry package will also be considered to describe the proper transformation of sulphur dioxide and sulphur trioxide into sulphate aerosols and its negative radiative forcing on the stratosphere.
Author Contributions
All authors contributed to the conceptualization, methodology, investigation, writing, reviewing, and editing of the present work. Supervision, G.C.; software, U.R.; funding acquisition, G.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Project IMPACT—a multidisciplinary Insight on the kinematics and dynamics of Magmatic Processes at Mt. Etna Aimed at identifying preCursor phenomena and developing early warning sysTems, INGV–Progetto Strategico Dipartimento Vulcani 2019.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
G.S. acknowledge Filippo Murè, Paolo Principato and Roberto Maugeri for technical assistance in the FLAME networks of Mt Etna and Stromboli. The IMPACT project is acknowledged for supporting scientific activities of FLAME networks.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A

Table A1.
VAA issued by the Toulouse VAAC MeteoFrance for Stromboli on 28 August 2019; NIL = no ash cloud is produced; green = normal; yellow = advisory; orange = watch; red = warning.
Table A1.
VAA issued by the Toulouse VAAC MeteoFrance for Stromboli on 28 August 2019; NIL = no ash cloud is produced; green = normal; yellow = advisory; orange = watch; red = warning.
| Advisory | Aviation Colour Code | Eruption Details | TEM (Rmk) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2019-08-28 10:56 UTC | Red | Explosion at summit | Significant ash emission |
| 2019-08-28 12:00 UTC | Red | Strong Eruption with ash emission occurred at 10:17 UTC. Eruption has decreased now | Ash emission now seems negligible |
| 2019-08-28 15:00 UTC | Orange | Negligible ash emission | VA not identifiable on sat imagery in spite of good visibility. Some volcanic ash possible in the direct vicinity of the volcano. |
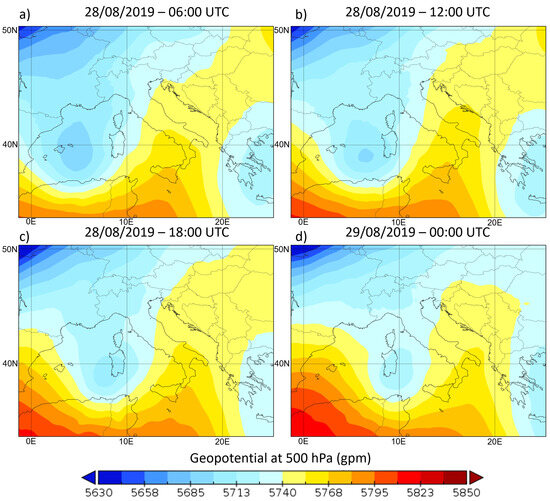
Figure A1.
Geopotential height (m) at 500 hPa at 06:00 (a), 12:00 (b) and 18:00 (c) UTC on 28 August 2019 and 00:00 UTC (d) on 29 August 2019. Data have been downloaded from the ERA5 reanalysis [56].
Figure A2.
Wind (m/s) at 500 hPa at 06:00 (a), 12:00 (b) and 18:00 (c) UTC on 28 August 2019 and 00:00 UTC (d) on 29 August 2019. Data have been downloaded from the ERA5 reanalysis [56].
Figure A3.
Geopotential height (m) at 700 hPa at 06:00 (a), 12:00 (b) and 18:00 (c) UTC on 28 August 2019 and 00:00 UTC (d) on 29 August 2019. Data have been downloaded from the ERA5 reanalysis [56].
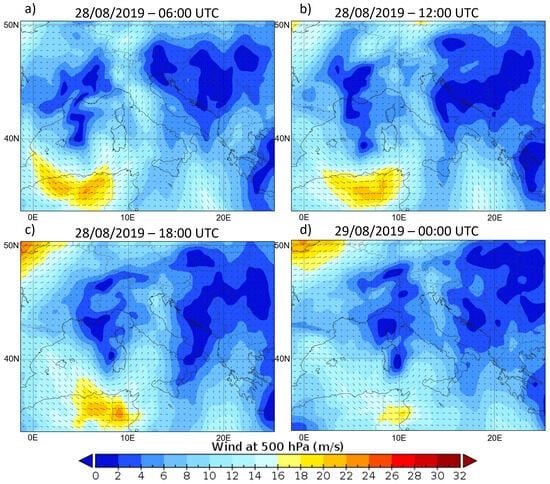
Figure A4.
Wind (m/s) at 700 hPa at 06:00 (a), 12:00 (b) and 18:00 (c) UTC on 28 August 2019 and 00:00 UTC (d) on 29 August 2019. Data have been downloaded from the ERA5 reanalysis [56].
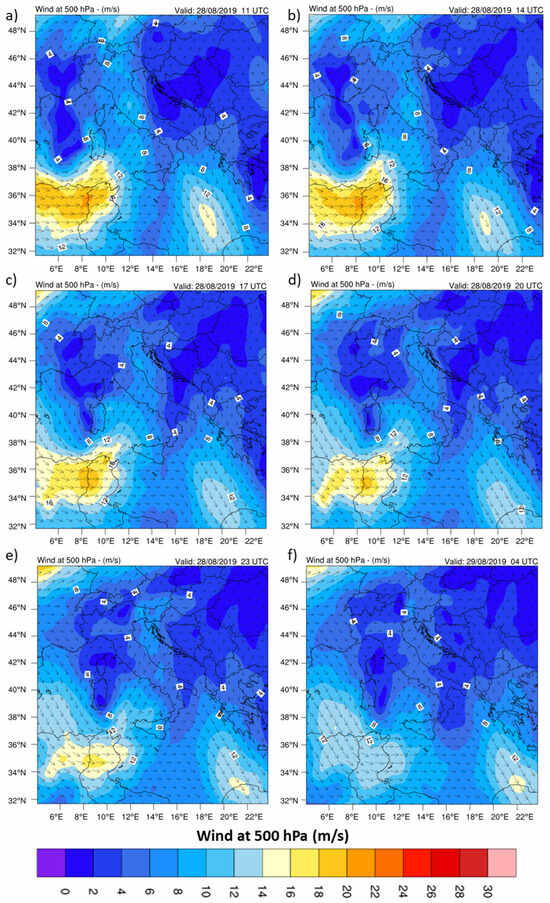
Figure A5.
Wind (m/s) at 500 hPa for 28 August at 11:00 UTC (a), 14:00 (b), 17:00 UTC (c), 20:00 UTC (d) and 23:00 UTC (e), and 04:00 on 29 August (f).
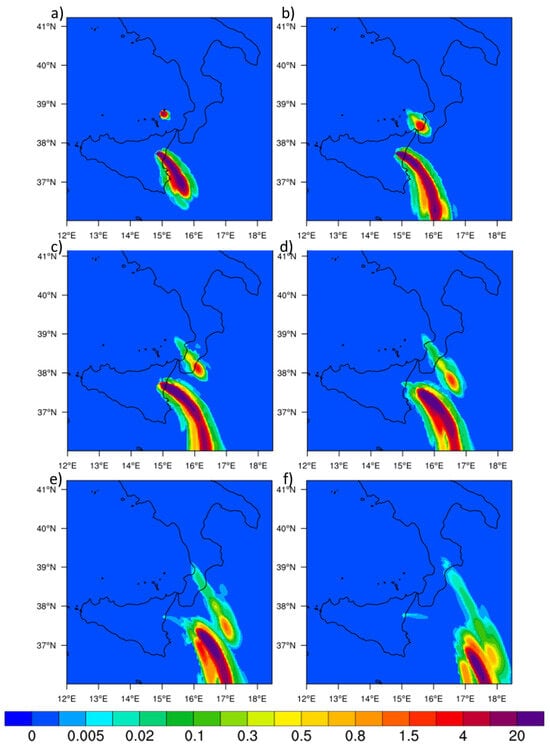
Figure A6.
WRF-Chem snapshots for 28 August at 600 hPa at 11:00 UTC (a), 14:00 (b), 17:00 UTC (c), 20:00 UTC (d) and 23:00 UTC (e), and 04:00 on 29 August (f).
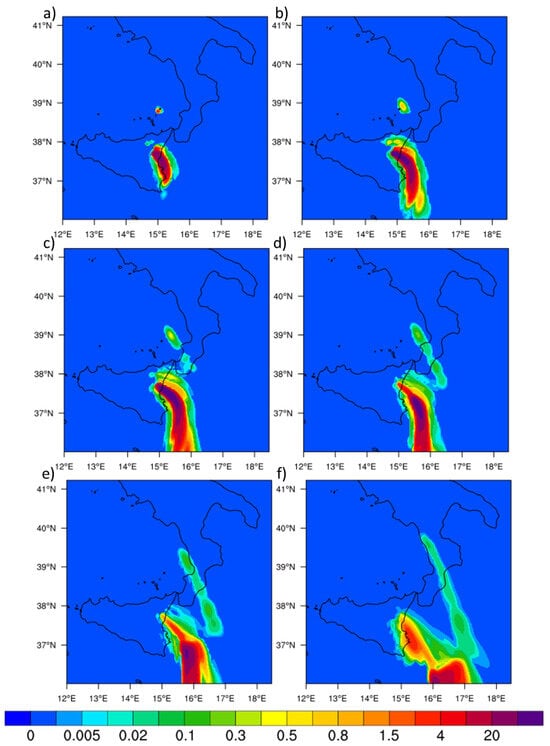
Figure A7.
WRF-Chem snapshots for 28 August at 700 hPa at 11:00 UTC (a), 14:00 (b), 17:00 UTC (c), 20:00 UTC (d) and 23:00 UTC (e), and 04:00 on 29 August (f).
References
- Loughlin, S.; Sparks, S.; Brown, S.; Jenkins, S.; Vye-Brown, C. Global Volcanic Hazards and Risk; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, A.; Ostro, B.; Carslaw, K.S.; Wilson, M.; Thordarson, T.; Mann, G.W.; Simmons, A.J. Excess mortality in Europe following a future Laki-style Icelandic eruption. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 15710–15715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carn, S.A.; Krueger, A.J.; Krotkov, N.A.; Yang, K.; Evans, K. Tracking volcanic sulfur dioxide clouds for aviation hazard mitigation. Nat. Hazards 2009, 51, 325–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, S.M. Sulfidation: Turbine blade corrosion. In Aircraft Maintenance Technology; 2008; pp. 12–15. Available online: https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?hl=en&volume=May+2008&publication_year=2008&pages=12-15&journal=Aircraft+Maint.+Technol.&author=S.+M.+Fisher&title=Sulfidation%3A+Turbine+blade+corrosion (accessed on 17 March 2023).
- Millert, T.; Casadevall, T. Volcanic ash hazards to aviation. In Encyclopedia of Volcanoes; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Grainger, R.G.; Highwood, E.J. Changes in stratospheric composition, chemistry, radiation and climate caused by volcanic eruptions. Geol. Soc. Spec. Publ. 2003, 213, 329–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Self, S.; Zhao, J.X.; Holasek, R.E.; Torres, R.C.; King, A.J. The Atmospheric Impact of the 1991 Mount Pinatubo Eruption; No. NASA/CR-93-207274. 1993. Available online: https://ntrs.nasa.gov/citations/19990021520 (accessed on 17 March 2023).
- McCormick, M.P.; Thomason, L.W.; Trepte, C.R. Atmospheric effects of the Mt Pinatubo eruption. Nature 1995, 373, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oppenheimer, C. Climatic, environmental and human consequences of the largest known historic eruption: Tambora volcano (Indonesia) 1815. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2003, 27, 230–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloss, C.; Berthet, G.; Sellitto, P.; Ploeger, F.; Taha, G.; Tidiga, M.; Eremenko, M.; Bossolasco, A.; Jégou, F.; Renard, J.-B.; et al. Stratospheric aerosol layer perturbation caused by the 2019 Raikoke and Ulawun eruptions and their radiative forcing. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 535–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellitto, P.; Podglajen, A.; Belhadji, R.; Boichu, M.; Carboni, E.; Cuesta, J.; Duchamp, C.; Kloss, C.; Siddans, R.; Bègue, N.; et al. The unexpected radiative impact of the Hunga Tonga eruption of 15th January 2022. Commun. Earth Environ. 2022, 3, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, S.; Smith, C.; Allen, M.; Grainger, R. Tonga eruption increases chance of temporary surface temperature anomaly above 1.5 °C. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2023, 13, 127–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oppenheimer, C. Volcanoes and global climate change. In Eruptions that Shook the World; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2011; pp. 53–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luterbacher, J.; Pfister, C. The year without a summer. Nat. Geosci. 2015, 8, 246–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, R.A.; Dean, K. Coupling a Lagrangian Dispersion Model and Remote Sensing Data for Quantification of Volcanic Ash Transport and Deposition. In Proceedings of the American Geophysical Union, Fall Meeting 2003, San Francisco, CA, USA, 8–12 December 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Grell, G.A.; Peckham, S.E.; Schmitz, R.; McKeen, S.A.; Frost, G.; Skamarock, W.C.; Eder, B. Fully coupled online chemistry within the WRF model. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 6957–6975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folch, A.; Costa, A.; Macedonio, G. FALL3D: A computational model for transport and deposition of volcanic ash. Comput. Geosci. 2009, 35, 1334–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampouri, A.; Amiridis, V.; Georgiou, T.; Solomos, S.; Binietoglou, I.; Gialitaki, A.; Marinou, E.; Gkikas, A.; Proestakis, E.; Rennie, M.; et al. Inversion Techniques on Etna’s Volcanic Emissions and the Impact of Aeolus on Quantitative Dispersion Modeling. Environ. Sci. Proc. 2023, 26, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draxler, R.R.; Hess, G.D. An overview of the HYSPLIT_4 modeling system for trajectories, dispersion, and deposition. Aust. Meteorol. Mag. 1998, 47, 295–308. [Google Scholar]
- Hurst, T.; Davis, C. Forecasting volcanic ash deposition using HYSPLIT. J. Appl. Volcanol. 2017, 6, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, A.; Thomson, D.; Hort, M.; Devenish, B. The U.K. Met Office’s Next-Generation Atmospheric Dispersion Model, NAME III. In Air Pollution Modeling and Its Application XVII, Proceedings of the 27 NATO/CCMS International Technical Meeting on Air Pollution Modeling and Its Application, Banff, AB, Canada, 24–29 October 2004; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2007; pp. 580–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heard, I.P.C.; Manning, A.J.; Haywood, J.M.; Witham, C.; Redington, A.; Jones, A.; Clarisse, L.; Bourassa, A. A comparison of atmospheric dispersion model predictions with observations of SO2 and sulphate aerosol from volcanic eruptions. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117, D00U22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizza, U.; Donnadieu, F.; Magazu, S.; Passerini, G.; Castorina, G.; Semprebello, A.; Morichetti, M.; Virgili, S.; Mancinelli, E. Effects of Variable Eruption Source Parameters on Volcanic Plume Transport: Example of the 23 November 2013 Paroxysm of Etna. Remote. Sens. 2021, 13, 4037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizza, U.; Donnadieu, F.; Morichetti, M.; Avolio, M.; Castorina, G.; Semprebello, A.; Magazu, S.; Passerini, G.; Mancinelli, E.; Biensan, C. Airspace contamination by volcanic ash from sequences of Etna paroxysms: Coupling the WRF-Chem dispersion model with near-source L-band radar observations. Remote. Sens. 2023, 15, 3760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surl, L.; Donohoue, D.; von Glasow, R. Modelling the regional impact of volcanic bromine using WRF-Chem. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly 2014, Vienna, Austria, 27 April–2 May 2014; p. EGU2014-1509. [Google Scholar]
- Surl, L.; Warnach, S.; Wagner, T.; Roberts, T.; Bekki, S. Using WRF-Chem Volcano to model the in-plume halogen chemistry of Etna’s 2018 eruption. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly 2020, Online, 4–8 May 2020; p. EGU2020-10892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pöschl, U. Gas–particle interactions of tropospheric aerosols: Kinetic and thermodynamic perspectives of multiphase chemical reactions, amorphous organic substances, and the activation of cloud condensation nuclei. Atmos. Res. 2011, 101, 562–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pianezze, J.; Tulet, P.; Foucart, B.; Leriche, M.; Liuzzo, M.; Salerno, G.; Colomb, A.; Freney, E.; Sellegri, K. Volcanic plume aging during passive degassing and low eruptive events of Etna and Stromboli volcanoes. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arghavani, S.; Rose, C.; Banson, S.; Lupascu, A.; Gouhier, M.; Sellegri, K.; Planche, C. The Effect of Using a New Parameterization of Nucleation in the WRF-Chem Model on New Particle Formation in a Passive Volcanic Plume. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allard, P.; Carbonnelle, J.; Dajlevic, D.; Le Bronec, J.; Morel, P.; Robe, M.C.; Maurenas, J.M.; Faivre-Pierret, R.; Martin, D.; Sabroux, J.C.; et al. Eruptive and diffuse emissions of CO2 from Mount Etna. Nature 1991, 351, 387–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, M.R.; Sawyer, G.M.; Granieri, D. Deep Carbon Emissions from Volcanoes. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2013, 75, 323–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiuppa, A.; Giudice, G.; Gurrieri, S.; Liuzzo, M.; Burton, M.; Caltabiano, T.; McGonigle, A.J.S.; Salerno, G.; Shinohara, H.; Valenza, M. Total volatile flux from Mount Etna. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L24302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barberi, F.; Rosi, M.; Sodi, A. Volcanic hazard assessment at Stromboli based on review of historical data. Acta Vulcanol. 1993, 3, 173–187. [Google Scholar]
- Allard, P.; Aiuppa, A.; Loyer, H.; Carrot, F.; Gaudry, A.; Pinte, G.; Michel, A.; Dongarrà, G. Acid gas and metal emission rates during long-lived basalt degassing at Stromboli Volcano. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2000, 27, 1207–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allard, P.; Aiuppa, A.; Burton, M.; Caltabiano, T.; Federico, C.; Salerno, G.; La Spina, A. Crater gas emissions and the magma feeding system of Stromboli volcano. In The Stromboli Volcano: An Integrated Study of the 2002–2003 Eruption; Calvari, S., Inguaggiato, S., Puglisi, G., Ripepe, M., Rosi, M., Eds.; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 2008; Volume 182, pp. 65–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiuppa, A.; Inguaggiato, S.; Mcgonigle, A.; O’Dwyer, M.; Oppenheimer, C.; Padgett, M.; Rouwet, D.; Valenza, M. H2S fluxes from Mt. Etna, Stromboli, and Vulcano (Italy) and implications for the sulfur budget at volcanoes. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2005, 69, 1861–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellitto, P.; Salerno, G.; Doussin, J.-F.; Triquet, S.; Dulac, F.; Desboeufs, K. Photometric Observations of Aerosol Optical Properties and Emission Flux Rates of Stromboli Volcano Plume during the PEACETIME Campaign. Remote. Sens. 2021, 13, 4016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiuppa, A.; Bertagnini, A.; Métrich, N.; Moretti, R.; Di Muro, A.; Liuzzo, M.; Tamburello, G. A model of degassing for Stromboli volcano. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2010, 295, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lentini, F.; Carbone, S. Geologia della Sicilia—Geology of Sicily. Memorie descrittive della Carta Geologica d’Italia 2014, 95, 7–414. [Google Scholar]
- Branca, S.; Del Carlo, P. Eruptions of Mt. Etna during the past 3,200 Years: A revised compilation integrating the historical and stratigraphic records. In Mt. Etna: Volcano Laboratory; Bonaccorso, A., Calvari, S., Coltelli, M., Negro, C.D., Falsaperla, S., Eds.; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 2004; Volume 143, pp. 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosi, M.; Bertagnini, A.; Landi, P. Onset of the persistent activity at Stromboli Volcano (Italy). Bull. Volcanol. 2000, 62, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollettino Settimanale sul Monitoraggio Multiparametrico del Vulcano Etna. Available online: https://www.ct.ingv.it/ (accessed on 17 March 2023).
- Giordano, G.; De Astis, G. The summer 2019 basaltic Vulcanian eruptions (paroxysms) of Stromboli. Bull. Volcanol. 2021, 83, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andronico, D.; Del Bello, E.; D’Oriano, C.; Landi, P.; Pardini, F.; Scarlato, P.; de’ Michieli Vitturi, M.; Taddeucci, J.; Cristaldi, A.; Ciancitto, F.; et al. Uncovering the eruptive patterns of the 2019 double paroxysm eruption crisis of Stromboli volcano. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sciotto, M.; Watson, L.M.; Cannata, A.; Cantarero, M.; De Beni, E.; Johnson, J.B. Infrasonic gliding reflects a rising magma column at Mount Etna (Italy). Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 16954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salerno, G.G.; Burton, M.R.; Di Grazia, G.; Caltabiano, T.; Oppenheimer, C. Coupling between Magmatic Degassing and Volcanic Tremor in Basaltic Volcanism. Front. Earth Sci. 2018, 6, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platt, U.; Stutz, J. Differential Optical Absorption Spectroscopy Principles and Applications. In Physics of Earth and Space Environments; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salerno, G.G.; Burton, M.R.; Oppenheimer, C.; Caltabiano, T.; Tsanev, V.I.; Bruno, N. Novel retrieval of volcanic SO2 abundance from ultraviolet spectra. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2009, 181, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janjić, Z.I. The Step-Mountain Eta Coordinate Model: Further Developments of the Convection, Viscous Sublayer, and Turbulence Closure Schemes. Mon. Weather. Rev. 1994, 122, 927–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janjić, Z.I. The surface layer in the NCEP Eta Model. In Proceedings of the Eleventh Conference on Numerical Weather Prediction, Norfolk, VA, USA, 19–23 August 1996; American Meteorological Society: Boston, MA, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, G.-Y.; Yang, Z.-L.; Mitchell, K.E.; Chen, F.; Ek, M.B.; Barlage, M.; Kumar, A.; Manning, K.; Niyogi, D.; Rosero, E.; et al. The community Noah land surface model with multiparameterization options (Noah-MP): 1. Model description and evaluation with local-scale measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Atmspheres 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, M.D.; Suarez, M.J. A solar radiation parameterization for atmospheric studies. NASA Tech. Memo. 1999, 15, 40. [Google Scholar]
- Lang, S.E.; Tao, W.K.; Chern, J.D.; Wu, D.; Li, X. Benefits of a fourth ice class in the simulated radar reflectivities of convective systems using a bulk microphysics scheme. J. Atmos. Sci. 2014, 71, 3583–3612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veefkind, J.P.; Aben, I.; McMullan, K.; Förster, H.; de Vries, J.; Otter, G.; Claas, J.; Eskes, H.J.; de Haan, J.F.; Kleipool, Q.; et al. TROPOMI on the ESA Sentinel-5 Precursor: A GMES mission for global observations of the atmospheric composition for climate, air quality and ozone layer applications. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2012, 120, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theys, N.; De Smedt, I.; Yu, H.; Danckaert, T.; van Gent, J.; Hörmann, C.; Wagner, T.; Hedelt, P.; Bauer, H.; Romahn, F.; et al. Sulfur dioxide retrievals from TROPOMI onboard Sentinel-5 Precursor: Algorithm theoretical basis. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2017, 10, 119–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D.; Simmons, A.; Soci, C.; et al. Global reanalysis: Goodbye ERA-Interim, hello ERA5. ECMWF Newsl. 2019, 159, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).